Abstract
In the past two decades, a growing body of research regarding the utilization of natural bacterial pigments or dyes for textile dyeing has emerged. Bacterial pigments are bacterial secondary metabolites that usually have bright colors and some special properties (e.g., antimicrobial, antioxidative, UV protective etc.). In addition to their high production yield, these special properties led scientists to research and develop methods for utilizing bacterial pigments in textile dyeing. This study presents the current state this field of research, with a focus on the dyeing potential of bacterial pigments for different types of textile material. The potential future directions of research in this area are also highlighted. In addition to the durable dyeing of textiles, bacterial pigments with special properties, such as antimicrobial activity, can add multifunctionality to dyed materials, thus increasing the value of the final product. This emerging field of research will also have a great impact on sustainability and the environment, contributing to the decreased usage of synthetic dyes in the textile industry.
1. Introduction
The coloration of textile materials has been performed since ancient times [1,2]. The textile dyeing industry has long been environmentally challenging in several respects. First, there is very high water consumption during all stages of dyeing, which consequently generates a significant amount of contaminated water waste. Second, the use of very harsh chemicals is also a significant threat to the environment, especially given that residue from these chemicals can come into contact with consumers during their use of textile products. Third, the energy consumption during dyeing through the heating and drying stages is also very high. Finally, the dyes that are currently used are mostly of synthetic origin. One of the ways to reduce these issues is to use natural dyes. Natural dyes were in use before synthetic ones [1,3]; however, their extraction and use are technologically time-consuming and very expensive. In the past decade, research has focused on emerging, novel and exciting sources of natural dyes: bacteria [3,4,5]. Bacterial, or, as they are sometimes called, microbial dyes are byproducts of bacteria that represent a relatively novel and scarcely investigated source of natural dyes, with tremendous potential for dyeing various textile materials in very intense, durable and esthetically beautiful colors, which are nontoxic and safe for human skin, thus producing environmentally sustainable textile products.
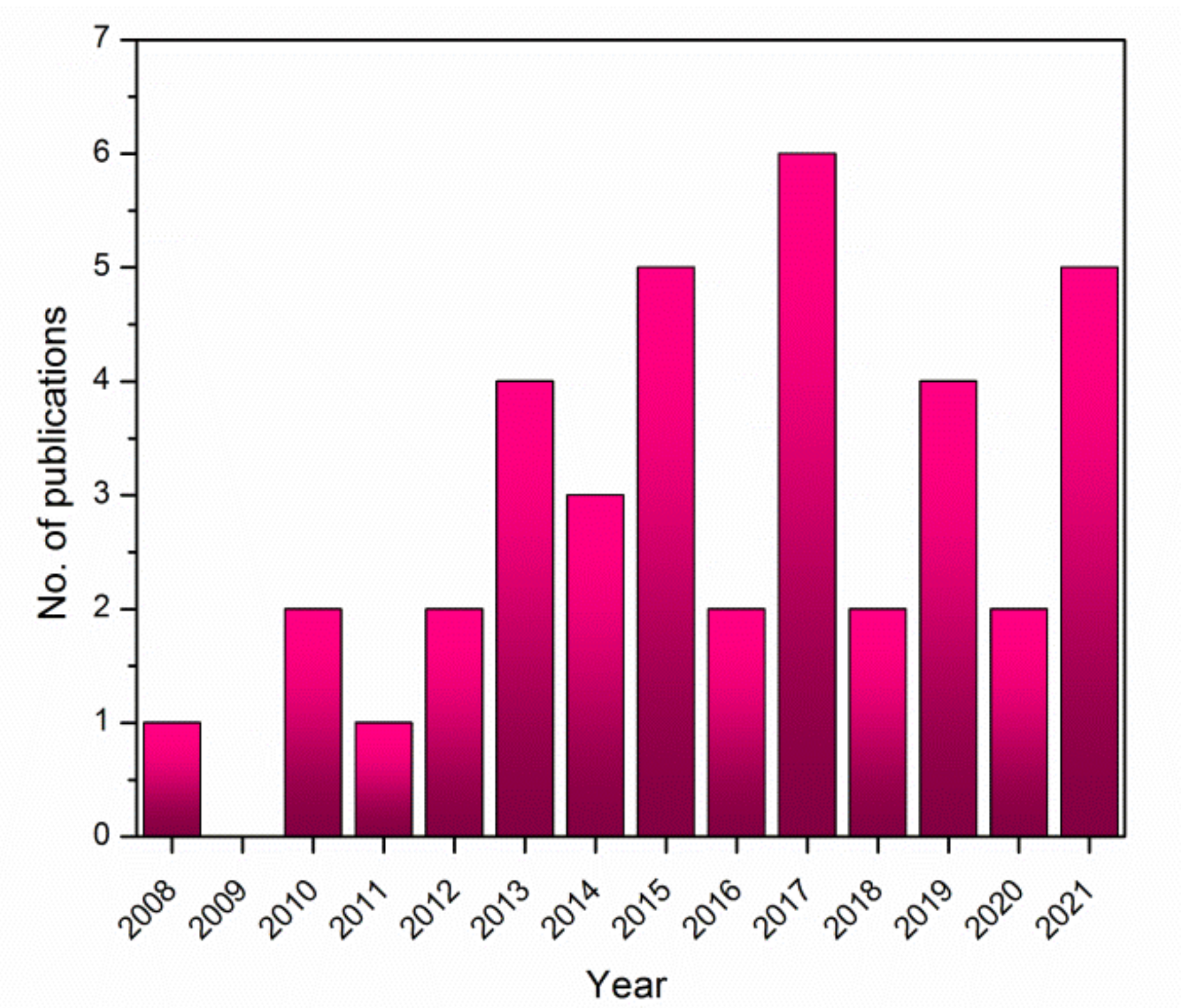
Research into the possibility of using bacterial pigments as natural sources of dyes for the textile industry has grown. For this study, the Scopus and ScienceDirect databases were used with several research keywords, including “bacterial pigments dyes microbial textile fibers fabrics dyeing.” After refining the search results by excluding all articles related to processes involving the decolorization of textile dyes from wastewater using bacteria or the dyeing of textiles using plant extracts, there was only a small number of publications in the field relevant to the dyeing of textiles with bacterial pigments, and a slight increase in publication numbers occurring with time (Figure 1).
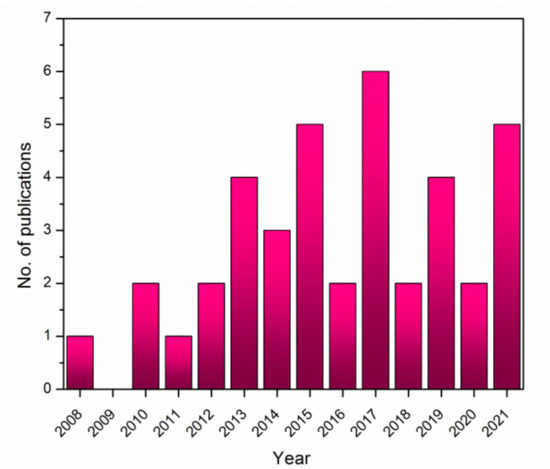
Figure 1.
Number of publications per year (for years between 2008 and 2021) regarding textile dyeing using bacterial pigments, according to Scopus database.
In the search for representative articles, the term “microbial pigments” was used, even though microbial pigments cover pigments and dyes derived from both bacteria and fungi [5]. Fungal pigments are also important sources of natural dyes and have potential for the dyeing of textiles [6], but the use of fungal pigments as dye sources is beyond the scope of this study.
One of the first suggestions in the literature, which is not presented in Figure 1, is the possibility of using color pigment, published in 2000 by Shirata et al. [7]. This publication was followed by a study by Alihosseini et al. [8] in 2008; therefore, there was a gap of several years before the interest in bacterial pigments as textile dyes was revived. Together, the authors of these two studies can be considered pioneers in this field, since they produced the first results about the possibility of using a naturally occurring pigment derived from bacteria to dye various fabrics. The following years marked the growth of research groups studying this field, while in 2017, there was even a first mention of the use of biopigment for ink formulation in printing [9].
Their high production yield, non-toxicity and good safety profile make bacterial pigments or dyes novel, sustainable and promising alternatives to synthetic dyes. In this article, important studies regarding the utilization of bacterial pigments on different textile materials and fibers are presented, with a focus on the necessary step of the preparation of pigment solutions, the use of mordants, and other pre- or post-textile treatments to improve dye fixation on specific fibers and increase the exhaustion of the dyebath, as well as the possibility of imparting additional properties to colored materials, in order to obtain high-added-value textile products.
2. Bacterial Dyes
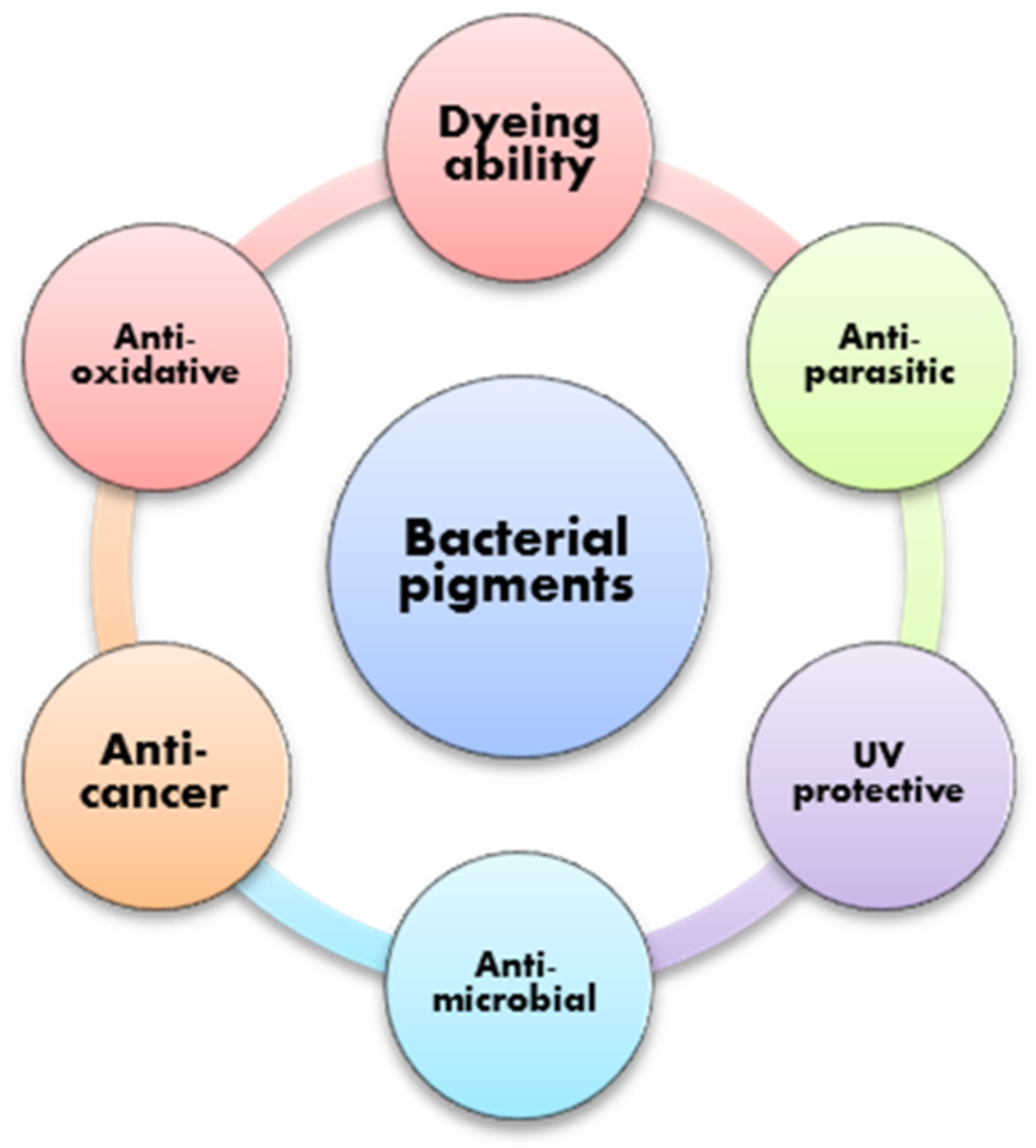
Bacterial metabolites/secondary metabolites are by-products of bacterial growth [5]. Usually, these byproducts are bacterial responses to external stimuli [10]. Besides color, these metabolites can possess important additional properties, such as potent antimicrobial activity against different pathogens, anticancer activity, antioxidative activity, UV properties, etc. [3,11,12,13]. These properties suggest that these pigments could be used as functional dyes for different textile materials, since they offer a range of potential applications in addition to their esthetic, qualities (Figure 2). Bacterial pigments, or biopigments, are terms that are used to describe these types of colorant or dyestuff, but from a textile-science point of view, these bacterial metabolites behave more as dyes than as pigments. Even though they are not soluble in water, they can be considered dyes rather than pigments because it has been shown that they are chemically bound to textile materials, forming bonds with functional groups on fibers and, therefore, behaving as dyes. However, in current research, the term pigment is frequently used, since these bacterial products are usually insoluble in water, they are in powder form after isolation and drying and, in some cases, they are used as suspensions and not solutions.
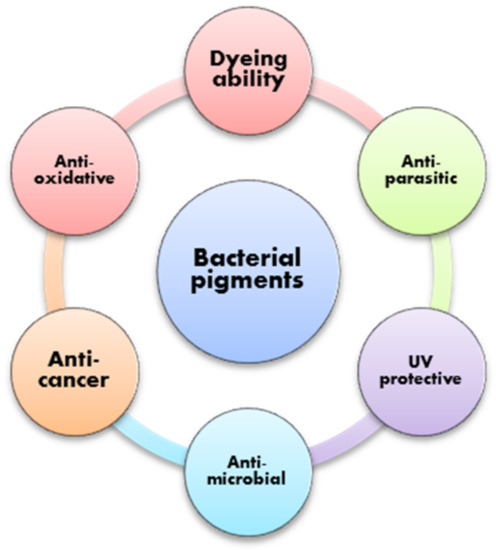
Figure 2.
Some of the properties of bacterial pigments that have potential to be transferred to textile materials during dyeing.
If dyes can offer additional properties to textile materials, by binding to textiles in a way that it does not disturb their antimicrobial or anticancer function, for example, then certain functions can be transferred to textile materials after dyeing. The vast range of special properties of bacterial pigments presented in Figure 2 opens up the possibility that dyed textiles possess the same properties. This is one of the most important aspects that should be explored in the future, i.e., whether certain properties of bacterial pigments are retained on textile materials after dyeing.
Several bacterial strains are able to produce pigments or dyes capable of imparting color to textile materials [11]. These bacteria are isolated from various sources, such as soil, water, plants, insects, etc. [11,12]. Among many, the most important are Serratia, Streptomyces and Pseudomonas [4,13]. The range of colors that these bacteria produce is wide, including pink, red-orange, yellow, blue, green, etc. [14,15]. However, it is important to note that the color of the extracted pigment does not always match the resulting color of the dyed fiber/fabric. As discussed later in this article, the resulting color depends on the nature of the substrate, meaning that various shades can be obtained by the same pigment on different fabrics; the shade also depends on the dyeing conditions (the temperature, pH, and use of mordants).
Pigment production using certain bacteria can be altered by using different conditions during growth. For example, Alihoseini et al. investigated the possibility of mutating Vibrio gazogenes to selectively develop the best pigment-producing strain capable of imparting, in addition to color, durable antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus to textile materials [16]. On the other hand, Kanelli et al. optimized the culture conditions of Janthinobacterium lividum for pigment (violacein) production and the simultaneous dyeing of fabrics, which resulted in dyed fabrics with significant antifungal activity against several Candida pathogens, C. albicans, C. parapsilosis and C. krusei, as well as antibacterial properties against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and the methicillin-resistant S. aureus, MRSA [17].
3. Dyeing of Textile Materials with Biopigments
3.1. Type of Bacteria Used for Textile Dyeing and Resulting Color
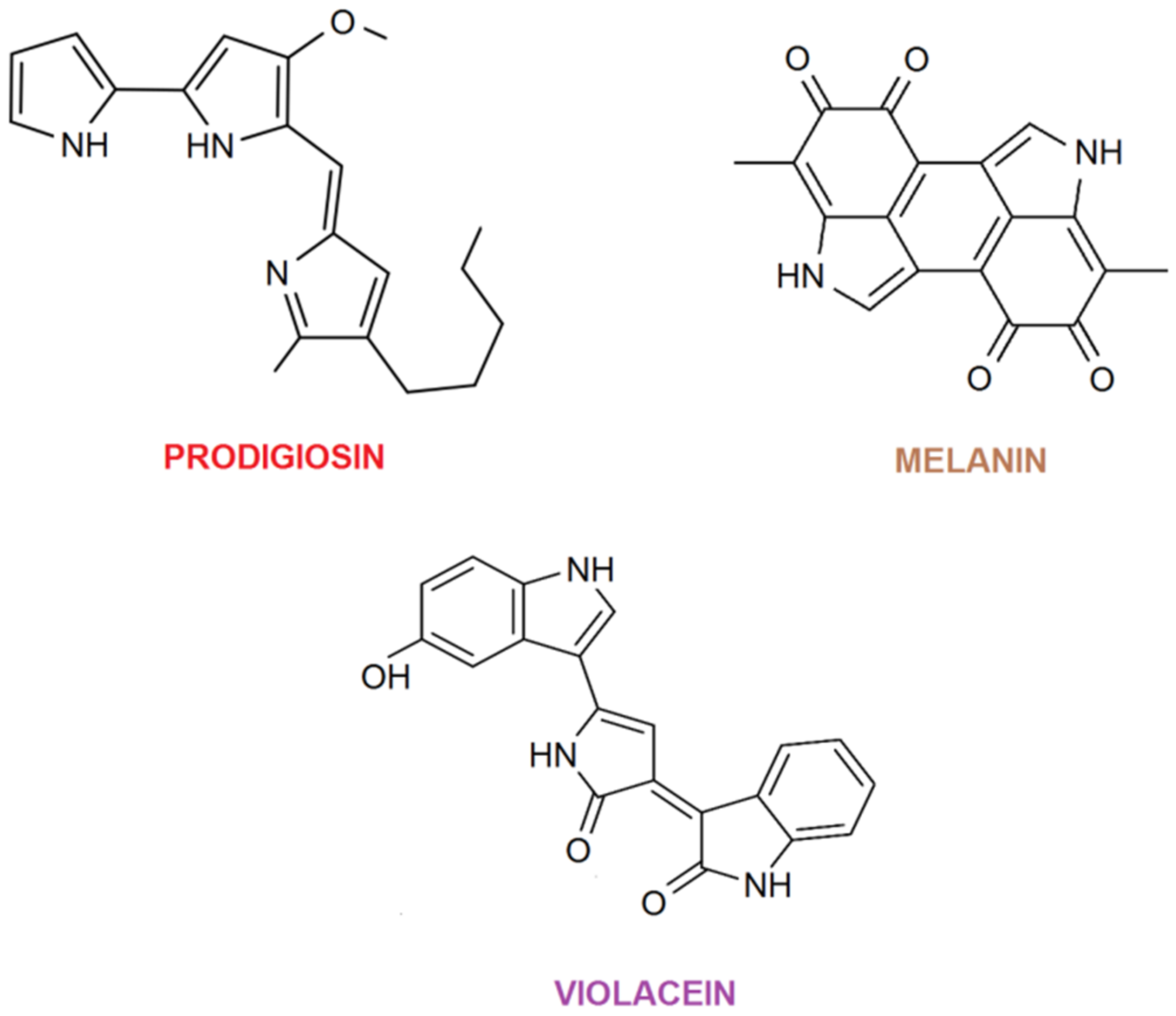
Bacterial pigments have a wide range of colors that can be utilized in textile dyeing, as mentioned above. However, not all pigments can impart color to different textile materials. This is mostly related to the structures of the pigments and how they bond to fibers during dyeing. In Table 1, an overview of various pigments and their current use in the dyeing of different textile materials is given. As can be seen from the table, the most commonly used bacterial extracts frequently have prodigiosin, violacein, and melanin as major components. Their molecular structure is given in Figure 3.
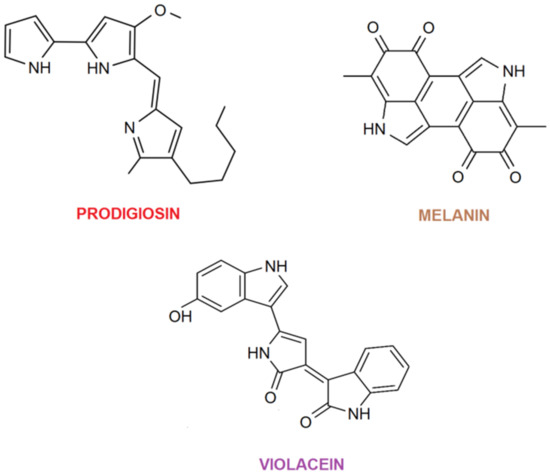
Figure 3.
Molecular structure of prodigiosin, melanin and violacein.
By observing their molecular structure, it can be concluded that these compounds have the ability to produce ionic interactions with textile fibers, depending on the pH of the used dyebath, which is also proven to be important during dyeing [18]. Prodigiosin is mostly known as an antibacterial, antioxidative pigment, even exhibiting UV-protective properties [5,13,19]. Violacein is known as an antifungal, antibacterial, antiparasitic and antitumoral pigment, while melanin has anticancer properties [5,17].

Table 1.
Overview of different pigment-producing bacteria, use of pigments for different textile materials, colors of the pigments and resulting colors of textiles, as well as auxiliaries in the dyeing process.
Table 1.
Overview of different pigment-producing bacteria, use of pigments for different textile materials, colors of the pigments and resulting colors of textiles, as well as auxiliaries in the dyeing process.
| Pigment/Active Substance | Textile Material | Color of Pigment/Color of Dyed Material | Use of Mordants | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromobacterium violaceum UTM5/violacein | cotton, silk, rayon, polyester | violet/dark blue | alum, Fe2(SO4)3, CuSO4, Ca(OH)2 | [20] |
| Janthinobacterium lividu/violacein | polyamide 6.6 | deep purple/purple | / | [17] |
| Serratia marcescens SB08/prodigiosin | cotton, silk | dark red/pink | Na2SO4 | [21,22] |
| Serratia marcescens /prodigiosin | cotton, nylon, polyester, muslin, rubber | red/pink | / | [10] |
| Serratia rubidaea/prodigiosin | cotton, wool, polyester | dark pink/pink | FeSO4, CuSO4, NaHCO3, lemon | [23,24] |
| Serratia sakuensis/prodigiosin | cotton, silk, wool | red/red-pink | Na2SO4·10H2O | [25] |
| Rhodonellum psychrophylium GL8/prodigiosin | cotton, silk, rayon | dark red/red | NaCl | [26] |
| Serathia plymuthica/prodigiosin | bacterial cellulose, polyvinyl alchohol chitosan nanofibers | red/pink | / | [27] |
| Streptomyces virginiae/melanin | wool (dyeing and printing) | yellow, light brown, dark brown | / | [28] |
| Pseudomonas aureginosa/pyocyanin | polyester | blue-green/yellow | / | [29] |
| Serratia sp. KH-1/prodigiosin | cotton and wool | red/pink | tannic acid, FeSO4, CuSO4, NaCl, ammonium alum ((NH4)Al(SO4)2) | [30] |
| Pseudomonas sp. HOB1/indigo | cotton | blue/blue | aluminum, NaOH | [31] |
| Streptomyces sp. NP2 and NP4/prodigiosin | multifiber fabric | dark red/red-pink | / | [18] |
| Streptomyces sp. NP4/prodigiosin | viscose | dark red/red-blue | / | [32] |
According to Table 1, it is obvious that there is a limitation on the possible colors that can be imparted to textile materials. Currently successful dyeing procedures make it possible to obtain materials in pink, red, violet, blue and brown color. Furthermore, the authors of some studies have used mordants to improve dyeing ability, while in other studies, it was possible to dye textiles without mordants. This is further explored in next section.
3.2. Dyeing Procedure Using Biopigments
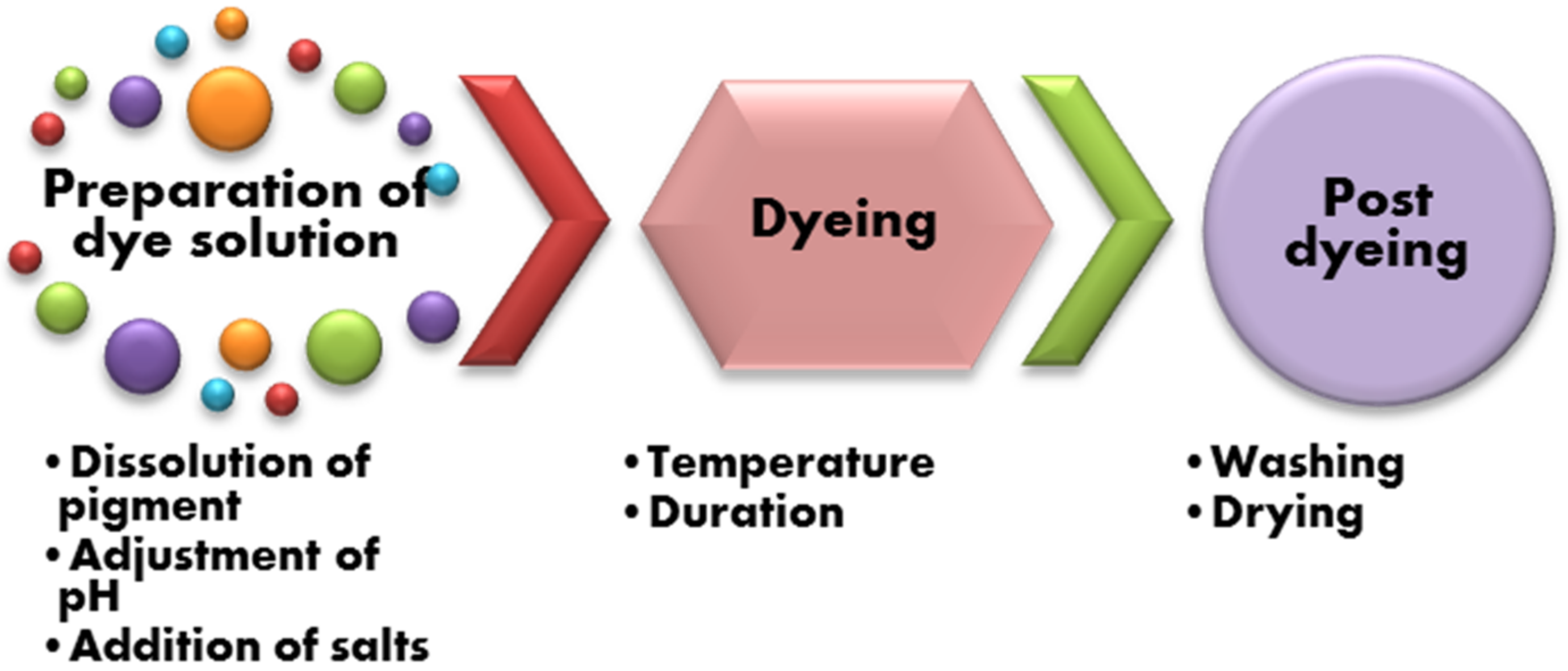
Bacterial pigments or dyes are usually prepared for dyeing as a solution of extract in a liquid [4]. The extract is cultured and purified and can be utilized further for dyeing through the dissolution/suspension of the pigmented extract to a suitable solvent. Other dyeing parameters include pH, temperature and the use of auxiliaries; the conditions are chosen according to the pigment and fabric/fiber type.
The usual procedure for the dyeing of textiles with bacterial pigments follows the scheme given in Figure 4.
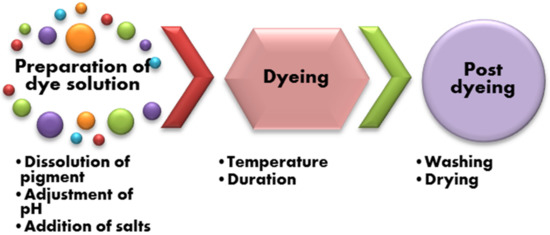
Figure 4.
Scheme of phases for preparation and dyeing of textile material using microbial pigment.
The first step, the preparation of the solution, is important to ensure the proper dissolution of the pigment. Dissolution depends on the nature of the pigment; bacterial pigments are usually soluble in ethanol [24,33,34], methanol [8,18,35,36] or acetone [32]. Kramar et al. [32] used a pigment that was previously presented as soluble in a methanol/water system [18], but their new work showed that the same pigment can be dissolved in an acetone/water (1:99) system, thus obtaining a highly ecofriendly dyebath with a high exhaustion rate [32]. In this case, the bacterial extract was dissolved in acetone, rendering a highly concentrated solution that was later diluted with water to produce a dyebath with a desirable concentration.
In fact, the preparation of dyebaths using acetone, ethanol or water is considered highly ecofriendly and can lead to the production of sustainable dyebaths. In the future, researchers should aim to investigate the possible recycling and reuse of the excess dye from dyebaths or the decolorization of unused dye from liquid waste, thus closing the loop of the dyeing procedure with bacterial colorants.
3.3. The pH and Temperature Used for Dyeing Textiles with Biopigments
In textile dyeing, the pH should always be optimized and chosen according to the type of textile material used. For cellulose and other plant-based materials, a higher pH is desirable, while for protein-based fibers (wool, silk) acidic dyebaths are acceptable.
In a study by Gong et al. [37], the authors used a suspension of prodigiosin nanomicelle for dyeing and obtaining antimicrobial cotton at a very low pH of 3. In this study, particularly interesting was the step involving the extraction of the nanomicelles that were used for the dyeing. Surfactant Tween 80 was added to the culture media and the pigment from the bacteria cells of Serratia marcescens migrated from the bacteria cells to the surfactant micelle under continuous oscillation. Upon preparation for dyeing, the pH of the suspension was adjusted to pH 1–5 and under acidic conditions and a higher dyeing temperature (90 °C), the nanomicelle of the surfactant-containing pigment broke down, releasing prodigiosin into the solution and penetrating the cotton fiber. The highest color intensity was obtained when the dyebath had a pH of 3. However, dyebaths with low pH are not desirable if used with cellulose-based materials, since this can lead to the degradation of cellulose under acidic conditions.
In addition to assessing the pH of the dyebath according to fiber type, it is important to determine whether a chosen bacterial extract is sensitive to pH.
Prodigiosin is known to possess pH sensitivity [18,22,25]. For example, an increase in the pH of the ethanol solution of prodigiosin obtained from Serratia marscences changed the color of the solution from pink, in a pH range of 2–8, to yellow, for a pH of 10–12 [22]. Pigment from Serratia sakuensis exhibits pH sensitivity, producing different-colored solutions at pH 4 (pink), pH 5 (red), pH 7 (orange) and pH 9 (yellow) [25].
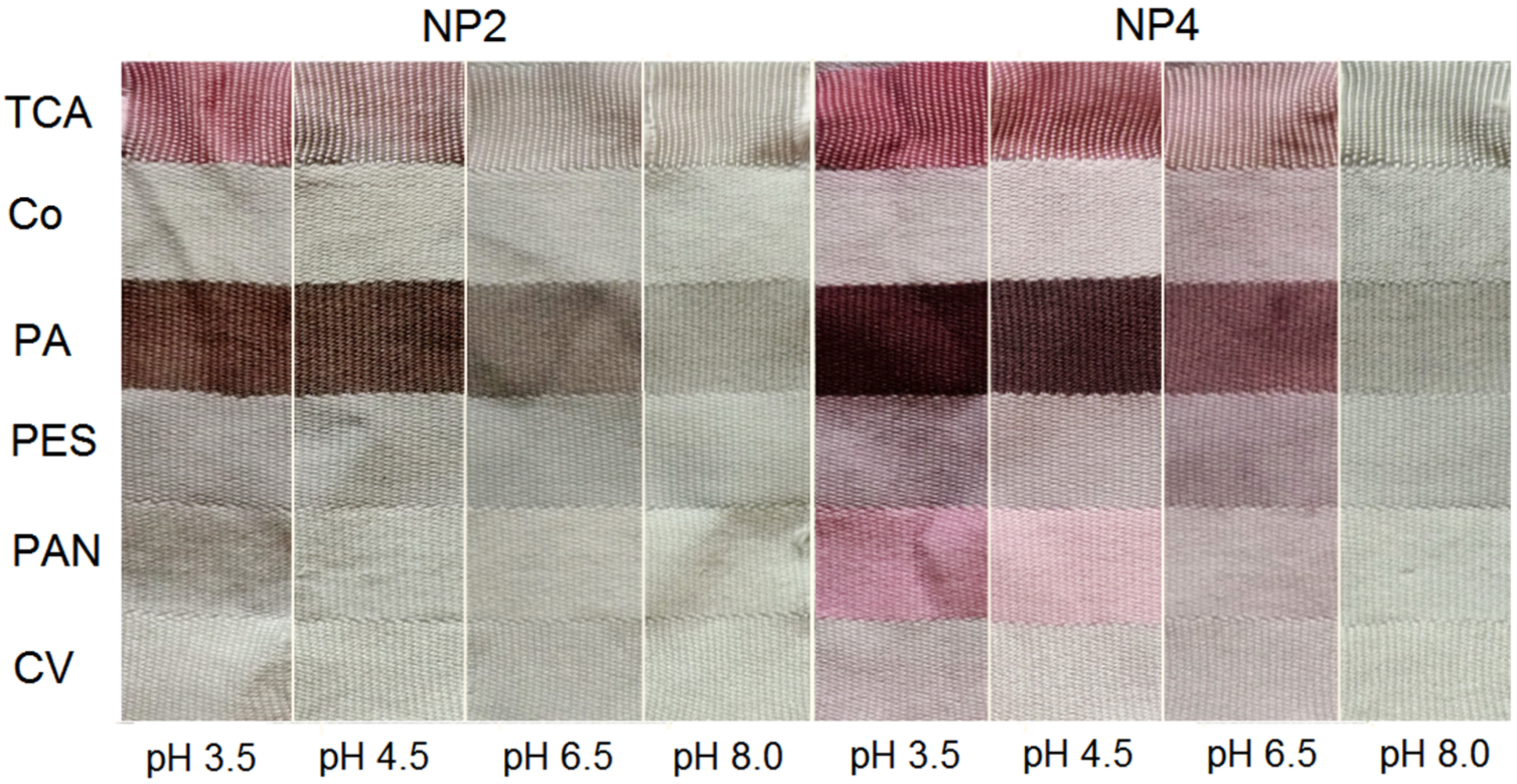
Another study, using prodigiosin from the strains Streptomyces sp. NP2 and NP4, showed that an extracted pigment and its solution in water–methanol exhibited a brownish-to-red color at low pH values of 3.5 and 4.5 and gray-to-blue at a pH of 8 [18]. Additionally, the strongest color was obtained in polyamide and triacetate fabrics (Figure 5), and a fair color intensity was achieved on polyester PES and polyacrylonitrile PAN. Dyeing in solutions of different pH induced different shades and colors in the multifiber fabric, as seen in Figure 5.
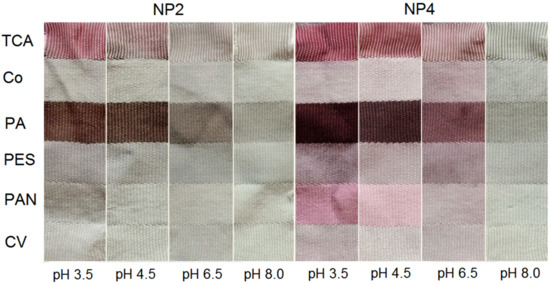
Figure 5.
Multifiber fabric (TCA-cellulose triacetate, co-cotton, PA-polyamide, PES-polyester, PAN-polyacrylonitrile, CV-viscose) dyed with prodigiosin isolated from Streptomyces sp. strains NP2 and NP4 in dyebaths with different pH (reprinted with permission from reference [18]. Copyright 2014 Springer).
The temperature of the dyebath significantly affects the dyeing performance of bacterial dyes, i.e., dyeing rate and color depth. Furthermore, the extent of the dyeing differs according to the duration of the immersion in the dye bath. For example, Shirata et al. [7] used the methanol solution of a pigment isolated from Janthinobacterium lividum to dye silk fabric and achieve color variation in the dyed silk fabric by changing the dipping time and temperature of the dye bath. To achieve the color depth obtained after 15 min of dyeing at 20 °C, the immersion time at 40 °C was decreased down to 5 min, at 60 °C to 1 min and at 70 °C to only 30 s. The immersion times required for the color depth obtained after 6 h at 20 °C were one day at 10 °C and three days at 0 °C.
The influences of various dyeing conditions, including the pigment concentration (2–14% owl), pH (4–9), retention time (20–120 min) and temperature (20–90 °C), on the dyeing of pure silk, China silk and cotton yarns with pigment from Serratia marcescens SB08 was studied by Venil et al. [21]. The optimized conditions for effective dyeing, namely a pigment concentration of 5% owl, a pH of 6, a retention time of 100 min and temperatures of 70 °C for pure silk and 60 °C for China silk and cotton, resulted in maximum pigment exhaustions of 96.0%, 90.0% and 81.6% for pure silk, China silk and cotton, respectively.
In addition to the color depth and dye exhaustion, the dyeing parameters, such as the pH values and temperatures, can affect the results of dyeing, which cannot be easily predicted. For example, the pigment isolated from Pseudomonas Aeruginosa was blue under alkali pH, but the color of dyed polyester was yellow [29], which was explained by the pyrolisis of the pigment pyocynanin when the dyeing was performed at 130 °C, since PES dyeing requires high temperatures. This also shows that it is important to determine the sensitivity of pigments that are intended to be used for dyeing at both different pH values and different temperatures.
3.4. Mordants Used for Dyeing Textile with Biopigments
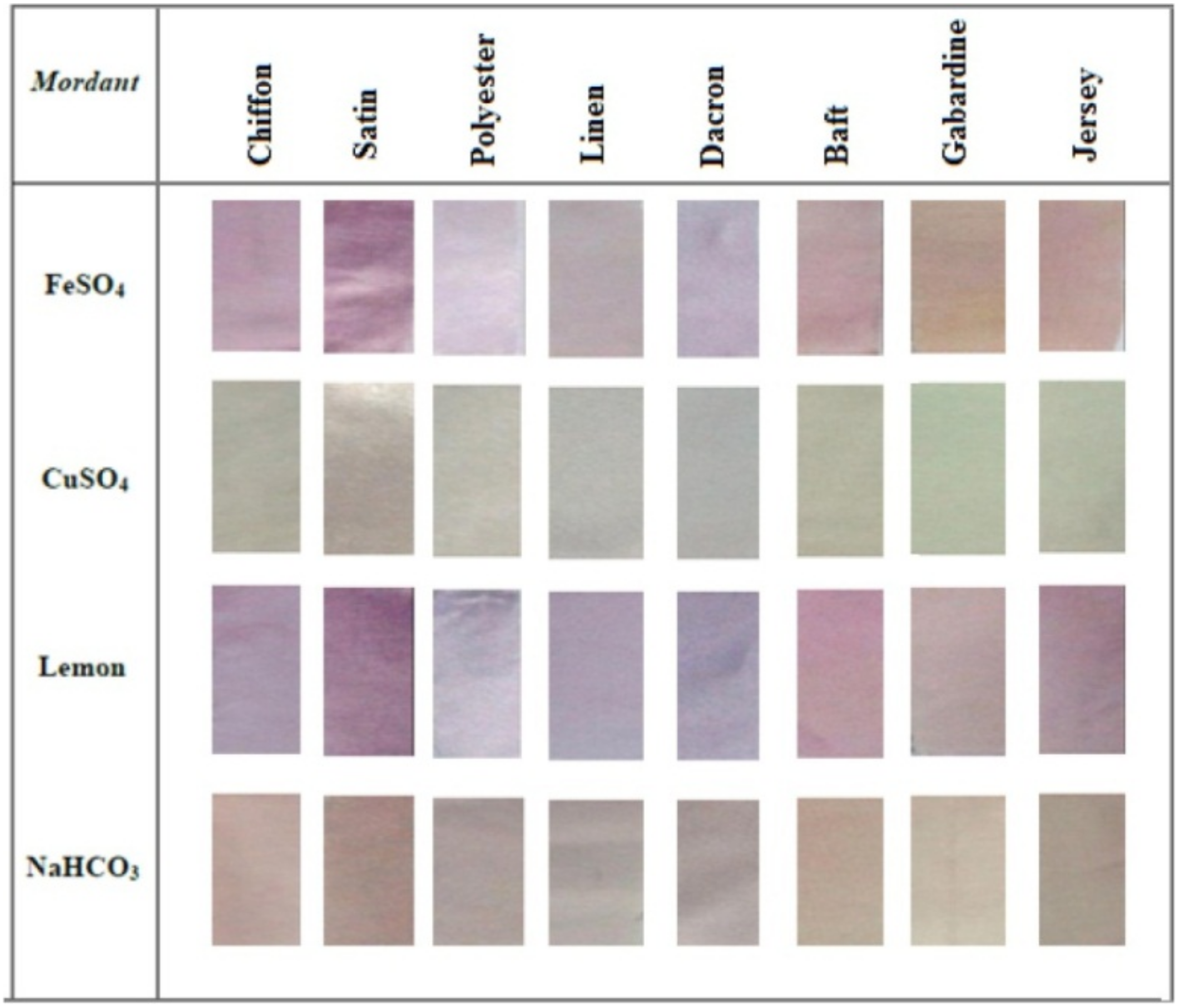
Mordants are salts that are frequently used as additives in dyebaths to improve the fixation of natural dyes to fibers [1,38]. Mordants form complexes with dyes and are additionally able to attach to the surfaces of fibers, thus increasing the exhaustion of dyebaths and improving the washing fastness of dyed fabrics. Frequently used conventional mordants are aluminum, iron and copper salts, among others [38]. Furthermore, mordants influence the resulting shade on the material; this was demonstrated in [24], where the uses of various mordants were tested during dyeing with prodigiosin pigment extracted from marine Serratia rubidaea RAM_Alex bacteria. The fabrics exhibited different shades and hues, as shown in Figure 6. The lowest color depth in all the samples was obtained using CuSO4 salt, while for other types of mordants, the color intensity was satisfying; the color hue strongly depended on the type of mordant.
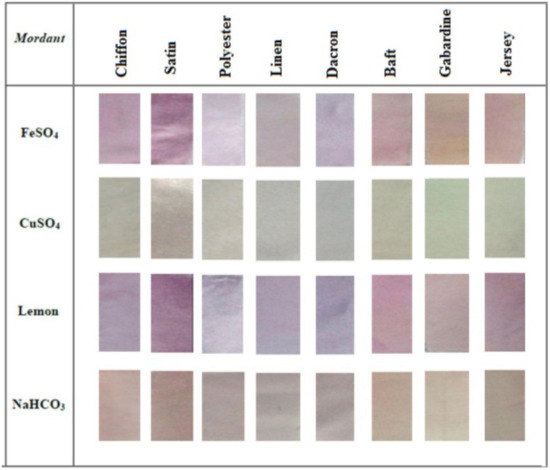
Figure 6.
Different color hues obtained after applying different mordants (Reprinted with permission from reference [24]. Copyright 2021 Elsevier).
Kim and Choi [34] studied the addition of Al, Fe, Cu and Ti mordants for the dyeing of silk using prodiginin extracted from Zooshikella rubidus. They concluded that Al and Ti mordants have a significant positive impact on dye uptake during dyeing with this pigment. The washing fastness, rubbing, perspiration and dry-cleaning of the dyed fabrics were good, except the light fastness, which was poor even with the use of mordants.
Another pigment from actinobacteria [39] can be used, for example, as a textile colorant and lip-balm colorant. When used with wool and cotton, dyeing with the addition of 5% FeSO4 and CuSO4 salt improved washing fastness. Additionally, the pigment exhibited antioxidant and hemolytic activity; however, the authors studied these properties only on pigment and not on samples dyed with this pigment.
From these results, it can be concluded that the type of mordant used in dyeing is dependent on the bacteria strain rather than the major component of the pigment, since for the same type (e.g., prodigiosin), different mordants were proven to be effective for the resulting colors.
As shown in Table 1, there are various successful investigations of dyeing without using any kind of mordant. For example, prodigiosin pigment can be used without purification and without the addition of mordant when isolated from Vibrio sp. [8] or Streptomyces sp. [18].
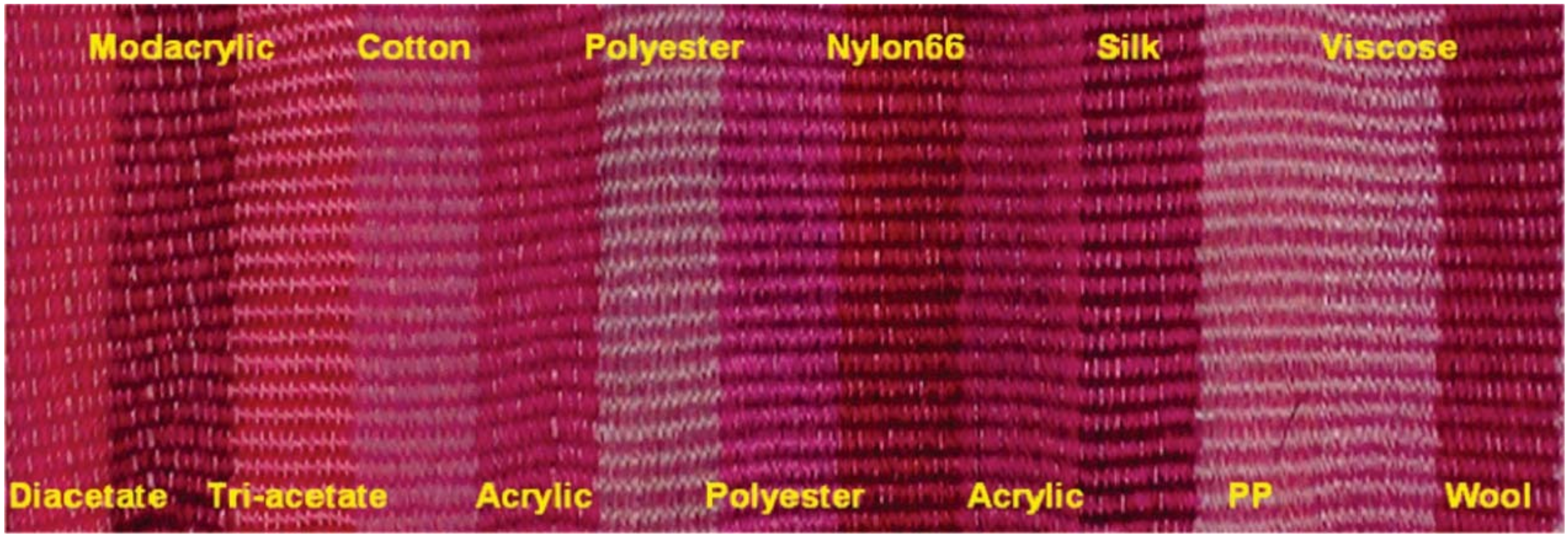
Prodigiosin from Vibrio sp. has the ability to impart colors to a wide range of fabrics without mordant (Figure 7), providing the highest color intensity on modacrylic, polyamide PA 6.6, silk and wool.
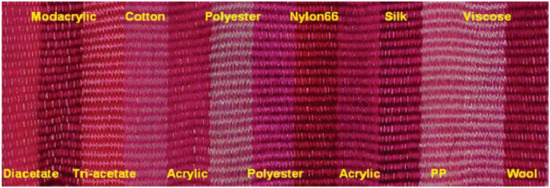
Figure 7.
Multifiber fabrics dyed with prodigiosin isolated from Vibrio sp. KSJ45 (reprinted with permission from reference [8]. Copyright 2008 Wiley).
4. Other Properties of Biopigments for Obtaining Functional Textile Materials
Since bacterial dyes show various additional properties, including antimicrobial, anticancer and antioxidative activity, among others, in the future, researchers should aim to study whether these properties could be imparted to textiles to obtain materials for special applications. Among many, the most important properties are antimicrobial, antioxidative and antitumoral activity [5]. In several studies, it has been shown that some of those properties can be transferred to dyed textile materials.
Venil et al. [21] used pigment from Serracia marscensc SB08 to dye silk and cotton. Additionally, these fabrics and yarns exhibited a good level of antibacterial activity and zone of inhibition against pathogenic bacteria, namely B. subtillis, E. coli and P. aeruginosa.
Ren et al. [22] studied the utilization of prodigiosin from Serratia marscences to dye silk. In addition to its good coloration, the dyed fabric showed an excellent bacteriostatic rate against S. aureus, while a cytotoxicity test indicated that the dyed fabric was not cytotoxic.
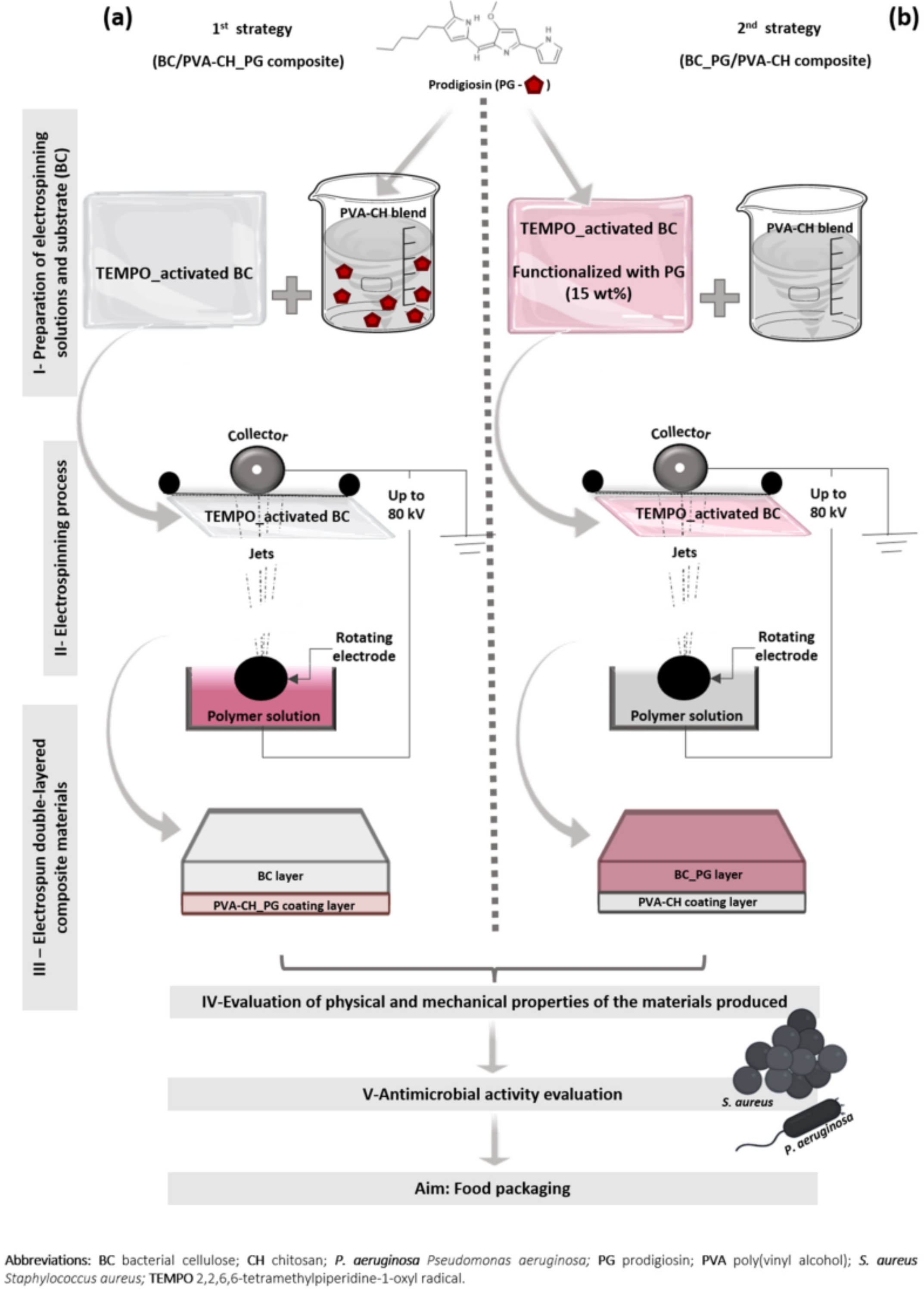
A very interesting study explored the addition of prodigiosin isolated from Serratia plymuthica to composite nanofibers prepared from PVA/chitosan/bacterial cellulose [27] to obtain antimicrobial food packaging films. Prior to the addition of prodigiosin, the bacterial cellulose was TEMPO-oxidized. Furthermore, the authors investigated different routes to the production of an antibacterial layer by adding prodigiosin in PVA/CH solution prior to electrospinning and adding the whole layer to the bacterial cellulose (Figure 8).
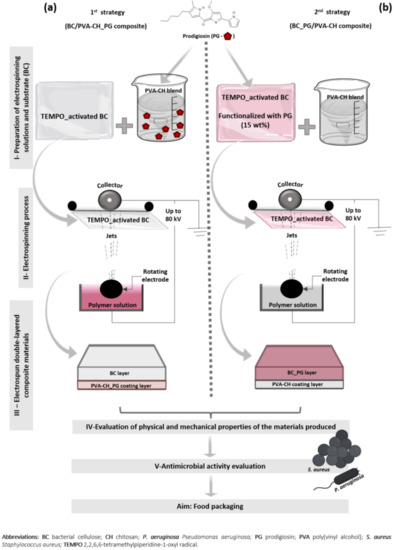
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of the production strategies used in composite preparation: (a) BC/PVA-CH_PG composite, with TEMPO-activated BC, used as a substrate for PVA-CH_PG nanofiber deposition; (b) BC_PG/PVA-CH composite, with PVA-CH nanofiber deposition in TEMPO-activated BC, previously functionalized with PG (reprinted with permission from reference [27]. Copyright 2022 MDPI).
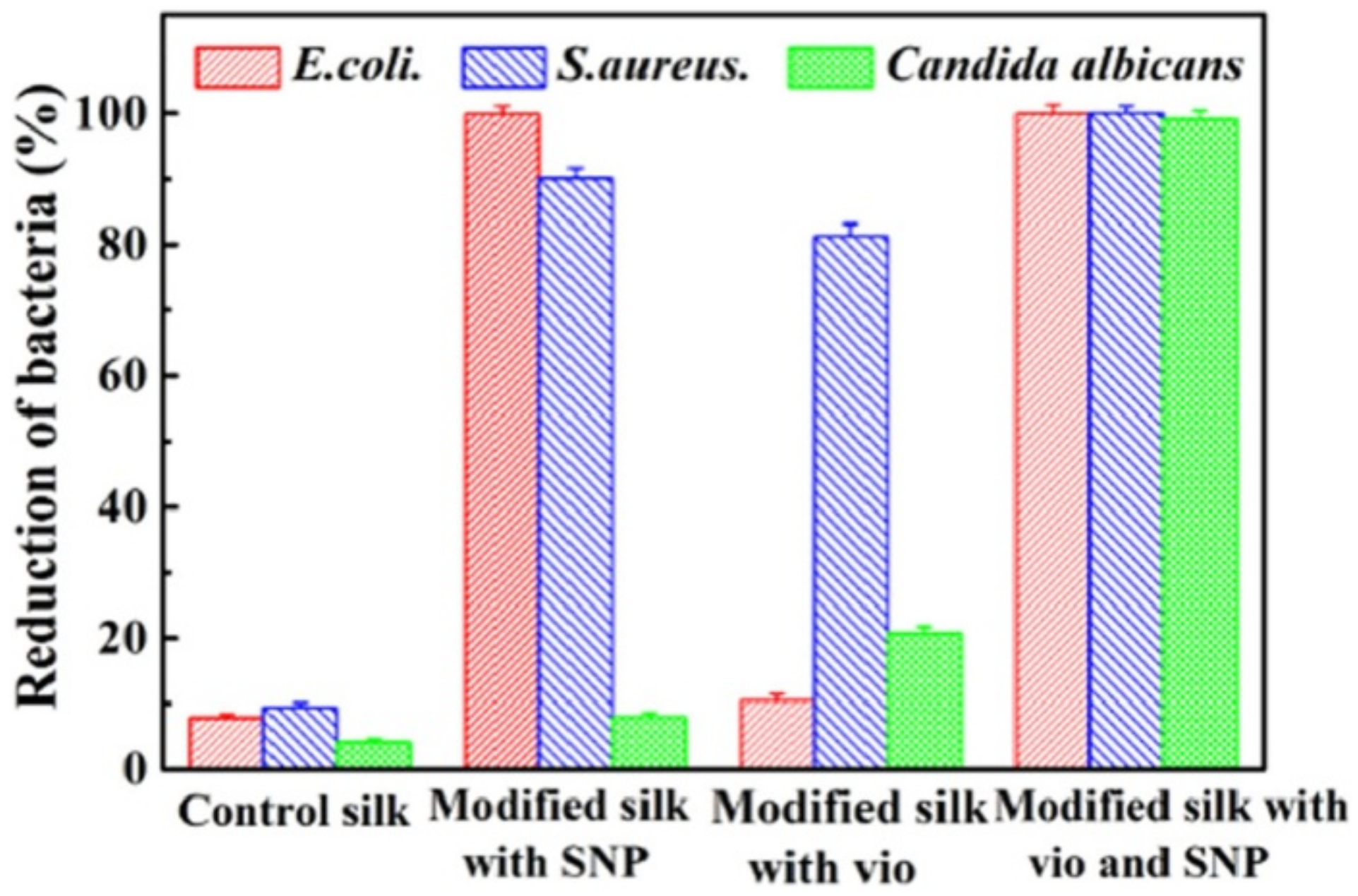
Gao et al. [34] studied the synergistic effect of the bacterial pigment, violacein, and silver nanoparticles for imparting antimicrobial activity to silk. Finishing the silk with only violacein produced a good antimicrobial effect on S. aureus (81.25% reduction); however, the synergistic effect of the pigment and AgNP provided excellent antimicrobial activity against all the tested pathogens, S. aureus, E. coli and C. albicans, producing a reduction of over 99.9% (Figure 9).
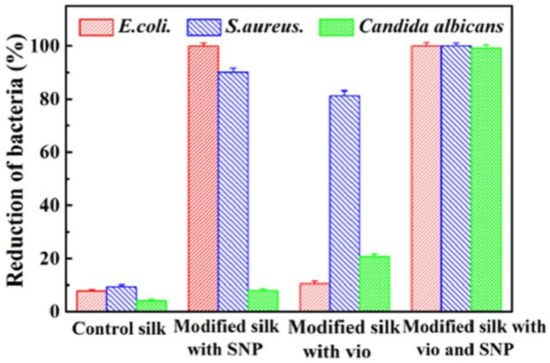
Figure 9.
Differences in antimicrobial activity against S. aureus, E. coli and C. albicans of silk modified with only silver nanoparticles (SNP), only violacein pigment (vio) and with combined treatment (reprinted with permission from reference [34]. Copyright 2019. Elsevier).
Similarly, pigment violacein produced by Janthinobacterium lividum, when combined with silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles, was shown to impart excellent antimicrobial properties [40]. The authors coated a viscose fabric, after pigment dyeing, with silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles and concluded that the violacein created a hybrid with the nanoparticles, causing greater antimicrobial activity against E. coli than only dyed fabric.
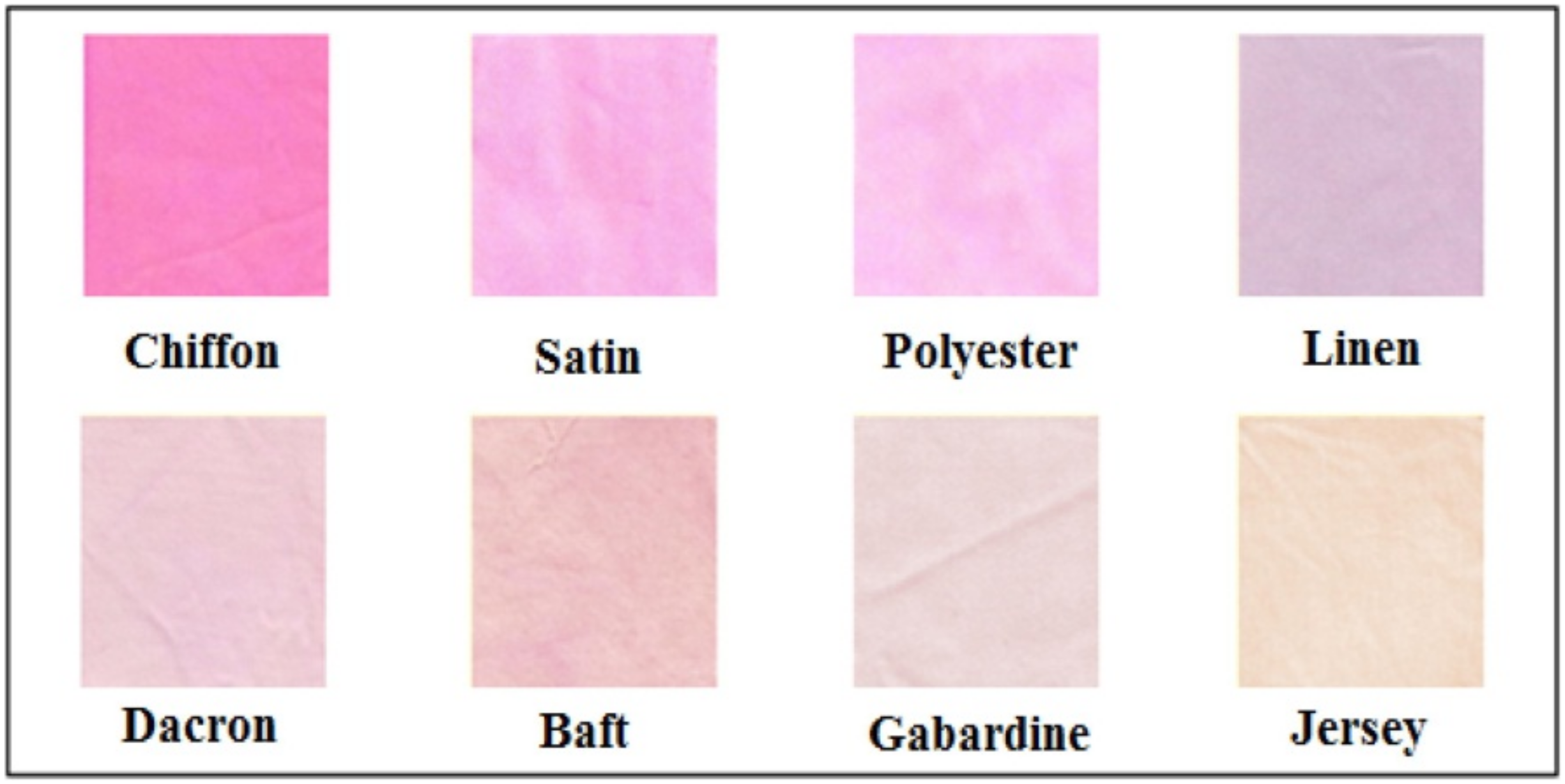
The antimicrobial activity imparted by bacterial pigments can be also influenced by the type of knitted textile that is used for dyeing, as shown in [24]. Serratia rubidaea RAM_Alex produces a prodigiosin-type pigment [24]. This pigment can dye a wide range of different fabrics and it was interesting to study the influence of the type of fabric on coloration (Figure 10). Cotton fabrics (baft, gabardine and jersey), linen and synthetic fabrics (chiffon, satin, Dacron and polyester) were used. The authors did not give the detailed fiber composition of the synthetic fabrics used in this work. The antimicrobial activity against S. aureus and E. coli was exceptionally high for all the fabrics, except for gabardine. This type of fabric also exhibited low color intensity, which may have been related to the fact that this type of fabric is very tight and densely woven.
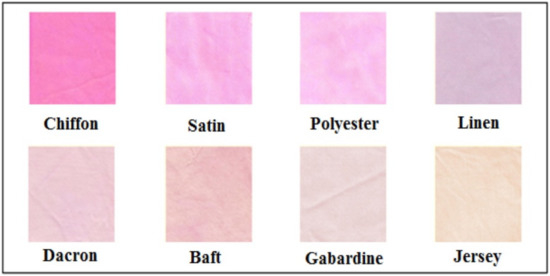
Figure 10.
Fabrics of different weaving patterns dyed with Serratia rubidaea RAM_Alex prodigiosin (Reprinted with permission from reference [24]. Copyright 2021 Elsevier).
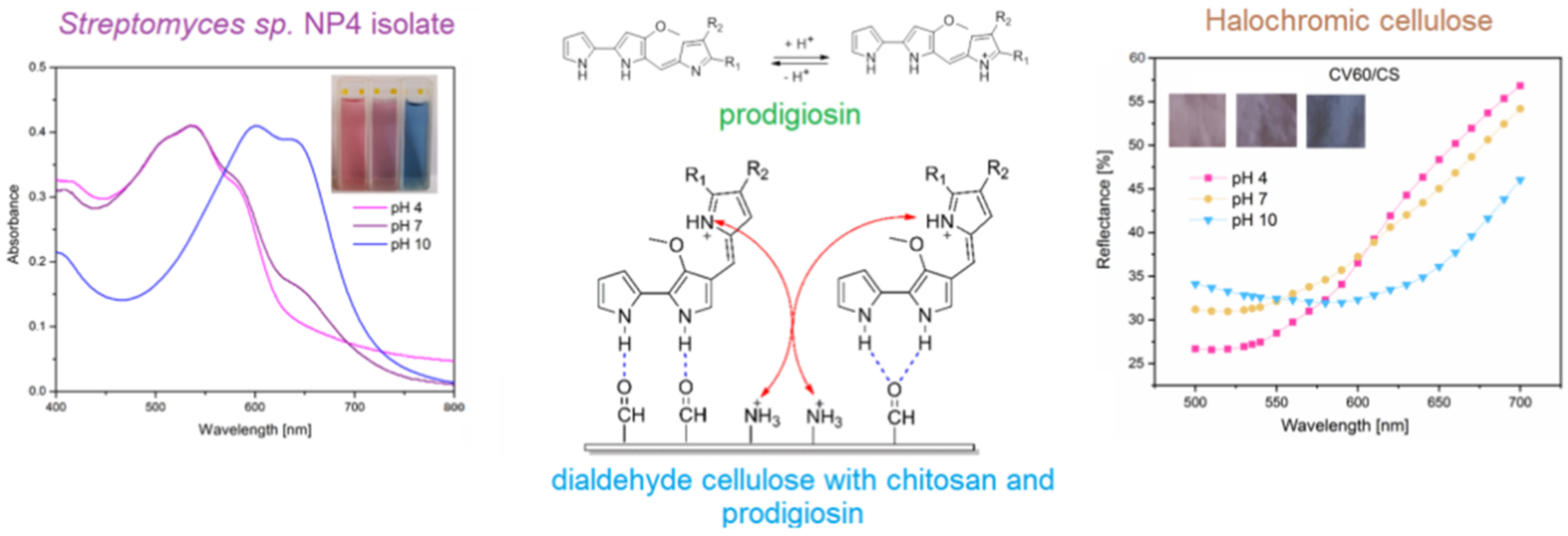
Kramar et al. successfully developed a pH-sensitive viscose fabric using prodigiosin pigment isolated from Streptomyces sp. NP4 [32]. The fabric was functionalized prior to dyeing following an oxidation procedure and the deposition of chitosan to make it susceptible to dyeing with this pigment. As can be seen (Figure 11, left), the bacterial isolate possessed pH sensitivity, which was preserved and imparted to the dyed viscose cellulose fabric after dyeing (Figure 11, right). The functionalized and dyed fabric showed pH responsiveness in a wide range of pH, from 4 to 10 (Figure 11); the fabrics showed no cytotoxicity and the authors proposed that the material can be used as a burn-dressing indicator, since severe burns cause an increases in the pH of wounds, while healing lowers the pH.
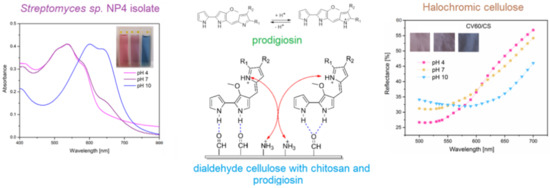
Figure 11.
Schematic representation of interaction between oxidized viscose (dialdehyde cellulose) and deposited chitosan and color-changing prodigiosin isolate to obtain pH-sensitive color-changing fabric (reprinted with permission from reference [32] Copyright 2021 Springer).
This represents a novel approach to obtaining color-changing textiles dyed with prodigiosin, a color changing-pigment. Future research could also focus on this aspect of investigating the pH sensitivity of natural bacterial dyes and the possibility of obtaining pH-sensitive textile materials, thereby obtaining high-value products.
5. Conclusions
The new and emerging field of the application of bacterial dyes in the textile industry has received a significant amount of research interest in recent years. Bacterial pigments or dyes are natural, sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives to the synthetic dyes that have been used in the textile industry for decades. Further research is encouraged, especially towards exploring new pigments and investigating their potential use as textile colorants. No less important is the fact that besides color, these dyes possess additional functionalities, such as antimicrobial, antioxidative and anticancer properties, among many others, which could be used to prepare special textile materials with ecofriendly, sustainable and nontoxic compounds. There are already several successful procedures for obtaining durable colors on textile materials and, additionally, imparting antimicrobial or color-changing properties. There are, however, almost endless possibilities and combinations of different bacterial pigments to investigate with different types of fibers; moreover, it is possible to investigate their combinations with other antimicrobial compounds, such as metallic nanoparticles, which can be used to produce materials with exceptionally high antibacterial activity.
Currently, for successful textile dyeing, most biopigments contain prodigiosin, melanin, and violacein. As was shown, different strains of bacteria produce the same compound, such as, for example, prodigiosin, but these bacterial metabolites have different abilities to dye certain types of textile fiber. This leads to the conclusion that there is a need for future research regarding dye–fiber interactions in the coloration of textiles using bacterial dyes, in order to elucidate the exact mechanism behind the successful dyeing of textiles and, moreover, to establish exact and predictive protocols for the possible future use of these dyes on an industrial scale. The current limitations of these studies lie in the fact that the majority of the presented research is focused more on the isolation and general application of bacterial dyes for textile dyeing, rather than on in-depth studies of dye–fiber interactions. Moreover, there is still a need to expand research in two directions: the first should focus on exploring more metabolites with dyeing potential and widening the range of colors that can be extracted from bacteria in order to compete with synthetic dyes and consumer demands. Current research covers only limited shades of pink, red, violet and blue. Another direction that should be strengthened the repeatability and durability of achieved colors on materials, the impact of dyes on the physicomechanical properties of textiles and their influence on consumers in terms of potential cytotoxicity and safety of use.
Nevertheless, research regarding bacterial pigments and dyes can bring sustainability to the textile industry and improve its environmental impact and safety.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization A.K. and M.M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.; writing—review and editing M.M.K.; supervision M.M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (contract no. 451-03-68/2022-14/200135).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable. All data are available in the review and references herein.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jasmina Nikodinović-Runić and Tatjana Ilić-Tomić from the Institute of Molecular Genetics and Genetic Engineering, University of Belgrade for introducing us to the world of bacterial pigments and our fruitful collaboration over many years.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AgNP | silver nanoparticles |
| BC | bacterial cellulose |
| CH | chitosan |
| PA 6.6 | polyamide 6.6 |
| PAN | polyacrylonitrile |
| PES | polyester |
| PVA | poly (vinyl alcohol) |
| TEMPO | (2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl) oxyl |
| UV | ultraviolet |
References
- Bechtold, T.; Turcanu, A.; Ganglberger, E.; Geissler, S. Natural dyes in modern textile dyehouses-How to combine experiences of two centuries to meet the demands of the future? J. Clean. Prod. 2003, 11, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.J. Is there a future for natural dyes? Rev. Prog. Color. Relat. Top. 1997, 27, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venil, C.K.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Ahmad, W.A. Bacterial pigments and their applications. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman Mohammadi, M.; Ahangari, H.; Mousazadeh, S.; Hosseini, S.M.; Dufossé, L. Microbial pigments as an alternative to synthetic dyes and food additives: A brief review of recent studies. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsing Rao, M.P.; Xiao, M.; Li, W.J. Fungal and bacterial pigments: Secondary metabolites with wide applications. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A.; Hernández, F.G.; Thibaut, R.; Müller, A. Fungal dyes for textile applications: Testing of industrial conditions for wool fabrics dyeing. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shirata, A.; Tsukamoto, T.; Yasui, H.; Hata, T.; Hayasaka, S.; Kojima, A.; Kato, H. Isolation of bacteria producing bluish-purple pigment and use for dyeing. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2000, 34, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Alihosseini, F.; Ju, K.S.; Lango, J.; Hammock, B.D.; Sun, G. Antibacterial colorants: Characterization of prodiginines and their applications on textile materials. Biotechnol. Prog. 2008, 24, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venil, C.K.; Wahidin, M.A.B.; Aruldass, C.A.; Ahmad, W.A. Production of bacterial pigments in low cost medium and formulation of biodegradable ink. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 55, 441–447. [Google Scholar]
- El-Bialy, H.A.; Abou El-Nour, S.A. Physical and chemical stress on Serratia marcescens and studies on prodigiosin pigment production. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazotto, A.M.; De Ramos Silva, J.; De Brito, L.A.A.; Rocha, N.U.; De Souza Soares, A. How can microbiology help to improve sustainability in the fashion industry? Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, R.; Bashir, S.; Numan, M.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Ali, M. Pigments from Soil Bacteria and Their Therapeutic Properties: A Mini Review. Curr. Microbiol. 2019, 76, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, N.; Senerovic, L.; Ilic-Tomic, T.; Vasiljevic, B.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Properties and applications of undecylprodigiosin and other bacterial prodigiosins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 3841–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.; Tokkas, J.; Goyal, S. Microbial Pigments: A review. Int. J. Microb. Resour. Technol. 2012, 1, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, H.M.; Abdulkadir, N.; Gani, M.; Maiturare, H.M. Bacterial Pigments and its Significance. MOJ Bioequivalence Bioavailab. 2017, 4, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alihosseini, F.; Lango, J.; Ju, K.S.; Hammock, B.D.; Sun, G. Mutation of bacterium Vibrio gazogenes for selective preparation of colorants. Biotechnol. Prog. 2010, 26, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanelli, M.; Mandic, M.; Kalakona, M.; Vasilakos, S.; Kekos, D.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.; Topakas, E. Microbial production of violacein and process optimization for dyeing polyamide fabrics with acquired antimicrobial properties. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramar, A.; Ilic-Tomic, T.; Petkovic, M.; Radulović, N.; Kostic, M.; Jocic, D.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Crude bacterial extracts of two new Streptomyces sp. isolates as bio-colorants for textile dyeing. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, N.; Radulovic, V.; Petkovic, M.; Vuckovic, I.; Jadranin, M.; Vasiljevic, B.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Streptomyces sp. JS520 produces exceptionally high quantities of undecylprodigiosin with antibacterial, antioxidative, and UV-protective properties. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1217–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venil, C.K.; Yusof, N.Z.; Aruldass, C.A.; Ahmad, W.A. Application of violet pigment from Chromobacterium violaceum UTM5 in textile dyeing. Biologia 2016, 71, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venil, C.K.; Dufossé, L.; Velmurugan, P.; Malathi, M.; Lakshmanaperumalsamy, P. Extraction and Application of Pigment from Serratia marcescens SB08, an Insect Enteric Gut Bacterium, for Textile Dyeing. Textiles 2021, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Gong, J.; Fu, R.; Zhang, J.; Fang, K.; Liu, X. Antibacterial dyeing of silk with prodigiosins suspention produced by liquid fermentation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, R.; Subha, K.; Bhakta, D.; Ghosh, A.R.; Babu, S. Characterization and enhanced production of prodigiosin from the spoiled coconut. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, R.A.; El Sikaily, A.; El-Sersy, N.A.; Ghozlan, H.A.; Sabry, S.A. Antimicrobial activity of textile fabrics dyed with prodigiosin pigment extracted from marine Serratia rubidaea RAM_Alex bacteria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2021, 47, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, J.; Bhathena-Langdana, Z.; Adivarekar, R.V.; Nerurkar, M. Production, partial characterization, and use of a red biochrome produced by Serratia sakuensis subsp. nov strain KRED for dyeing natural fibers. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, G.; Srivastava, S.; Kulshreshtha, R.; Sourirajan, A.; Baumler, D.J.; Dev, K. Applications of red pigments from psychrophilic Rhodonellum psychrophilum GL8 in health, food and antimicrobial finishes on textiles. Process Biochem. 2020, 94, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, L.F.A.; Mouro, C.; Riool, M.; Gouveia, I.C. Antimicrobial Food Packaging Based on Prodigiosin-Incorporated Double-Layered Bacterial Cellulose and Chitosan Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amal, A.M.; Abeer, K.A.; Samia, H.M.; Nadia, A.E.-N.H.; Ahmed, K.A.; El-Hennawi, H.M. Selection of pigment (melanin) production in Streptomyces and their application in printing and dyeing of wool fabrics. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2011, 1, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Govindaraj, C.; Ugamoorthi, R.; Ramarethinam, S. Isolation of pseudomonas aeruginosa for bacterial pigment production and its application on synthetic knitted fabric. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2021, 46, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, K.; Dalsaniya, P.; Pathak, H. Optimization of prodigiosin-type biochrome production and effect of mordants on textile dyeing to improve dye fastness. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, H.; Madamwar, D. Biosynthesis of indigo dye by newly isolated naphthalene-degrading strain pseudomonas sp. HOB1 and its application in dyeing cotton fabric. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramar, A.D.; Ilic-Tomic, T.R.; Lađarević, J.M.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.B.; Kostic, M.M. Halochromic cellulose textile obtained via dyeing with biocolorant isolated from Streptomyces sp. strain NP4. Cellulose 2021, 28, 8771–8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Choi, J. Dyeing properties of microbial prodiginine from Zooshikella rubidus for silk fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Chen, H.; Hou, A.; Xie, K. Efficient antimicrobial silk composites using synergistic effects of violacein and silver nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.J.; Luti, K.J.K. A kinetic model for prodigiosin production by Serratia marcescens as a bio-colorant in bioreactor. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2213, 020027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Choudhuri, A.; Abraham, J. Evaluation of antimicrobial, cytotoxicity, and dyeing properties of prodigiosin produced by Serratia marcescens strain JAR8. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, J.; Ren, Y.; Fu, R.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. pH-mediated antibacterial dyeing of cotton with prodigiosins nanomicelles produced by microbial fermentation. Polymers 2017, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahid, M.; Shahid-Ul-Islam; Mohammad, F. Recent advancements in natural dye applications: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 53, 310–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, I.; Redkar, P.; Munjal, M.; Sathish Kumar, S.R.; Bhaskara Rao, K.V. Isolation and characterization of pigment producing marine actinobacteria from mangrove soil and applications of bio-pigments. Der Pharm. Lett. 2015, 7, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Khaksar, F.; Rigi, G.; Mirdamadian, S.H. Creation of a violacein pigment hybrid with silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles to produce multifunctional textiles with antimicrobial properties. Nanomed. Res. J. 2021, 6, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).