A Preliminary Evaluation of “GenDAI”, an AI-Assisted Laboratory Diagnostics Solution for Genomic Applications †
Abstract
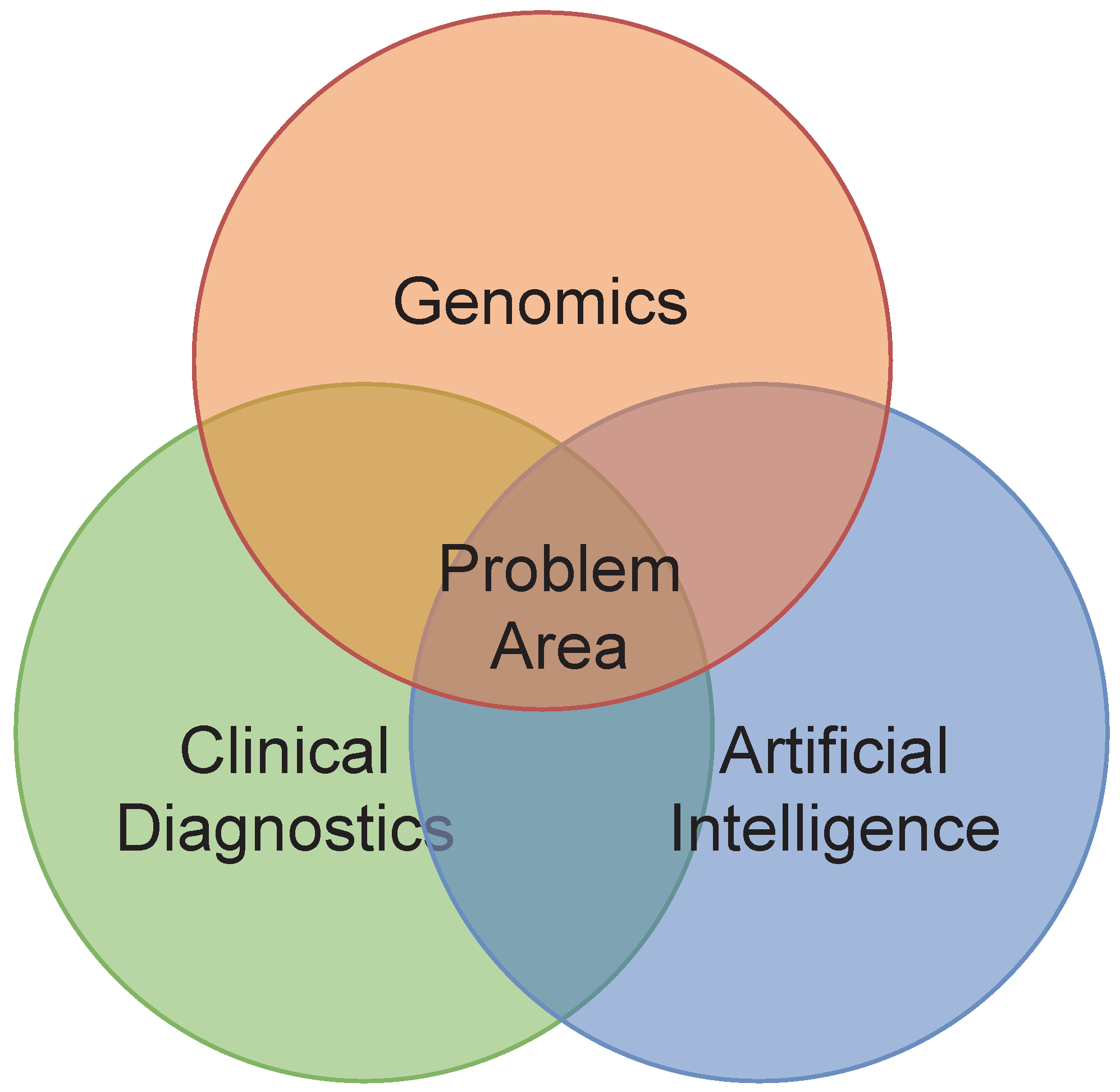
:1. Introduction
2. State of the Art
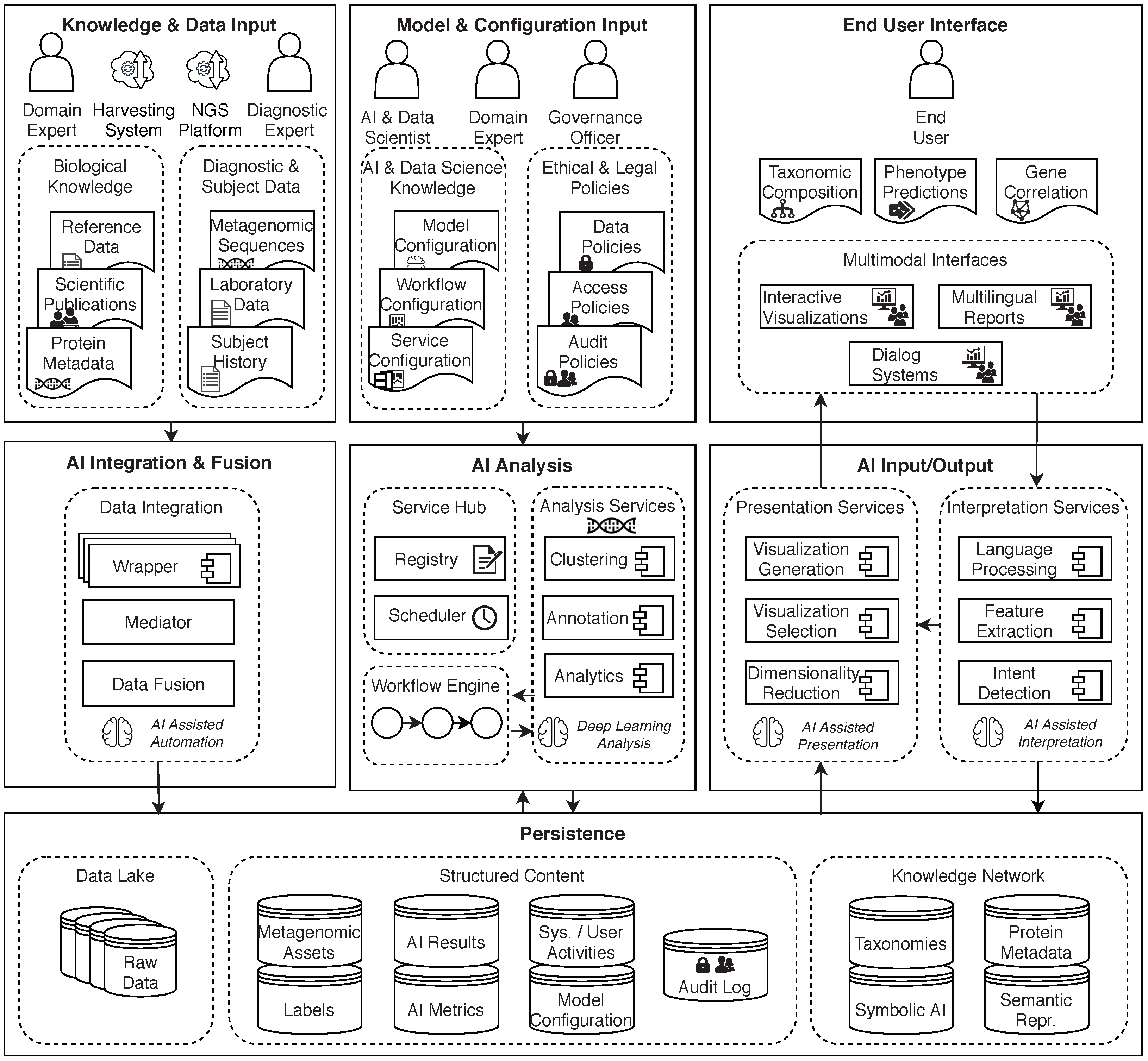
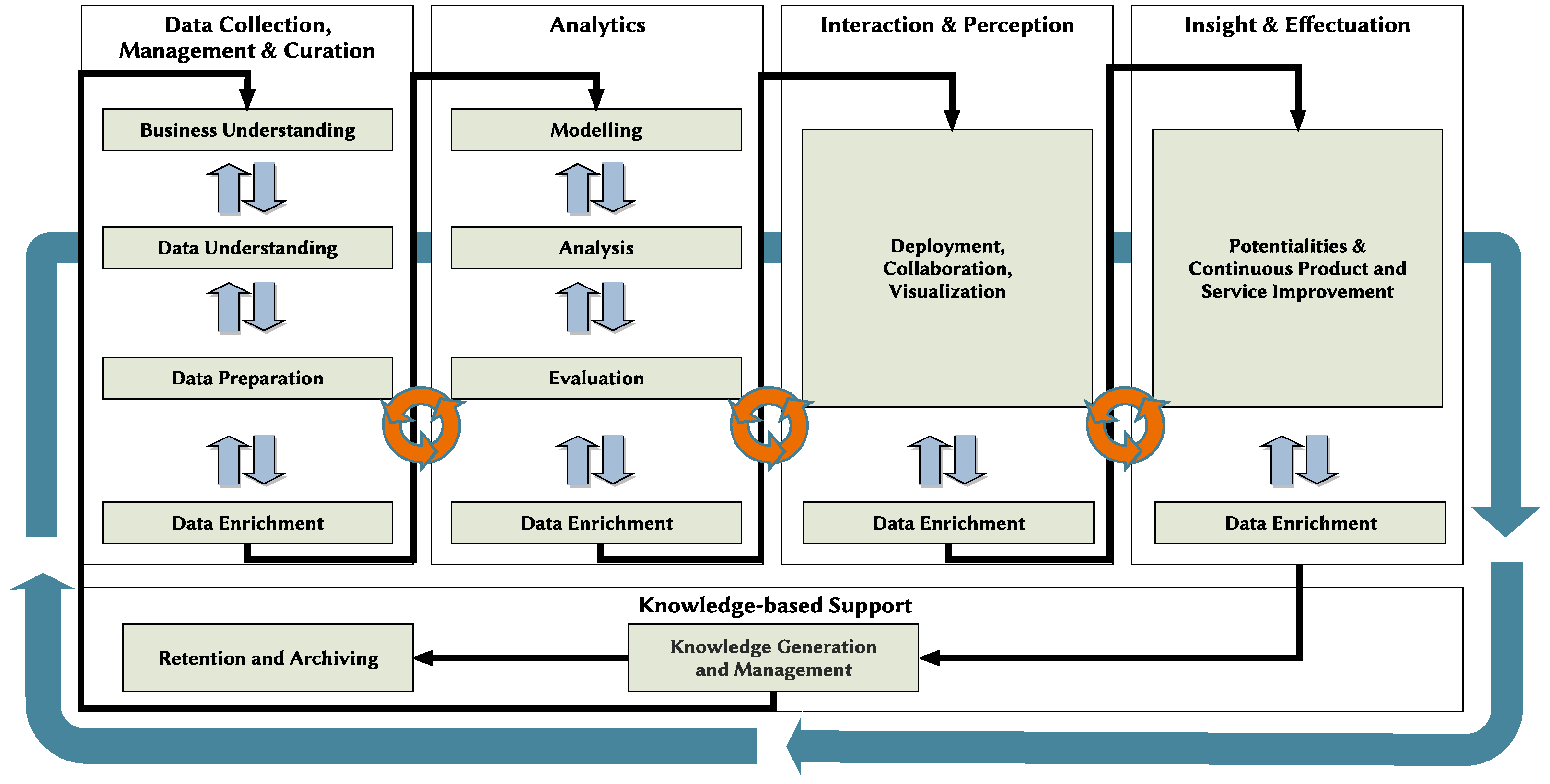
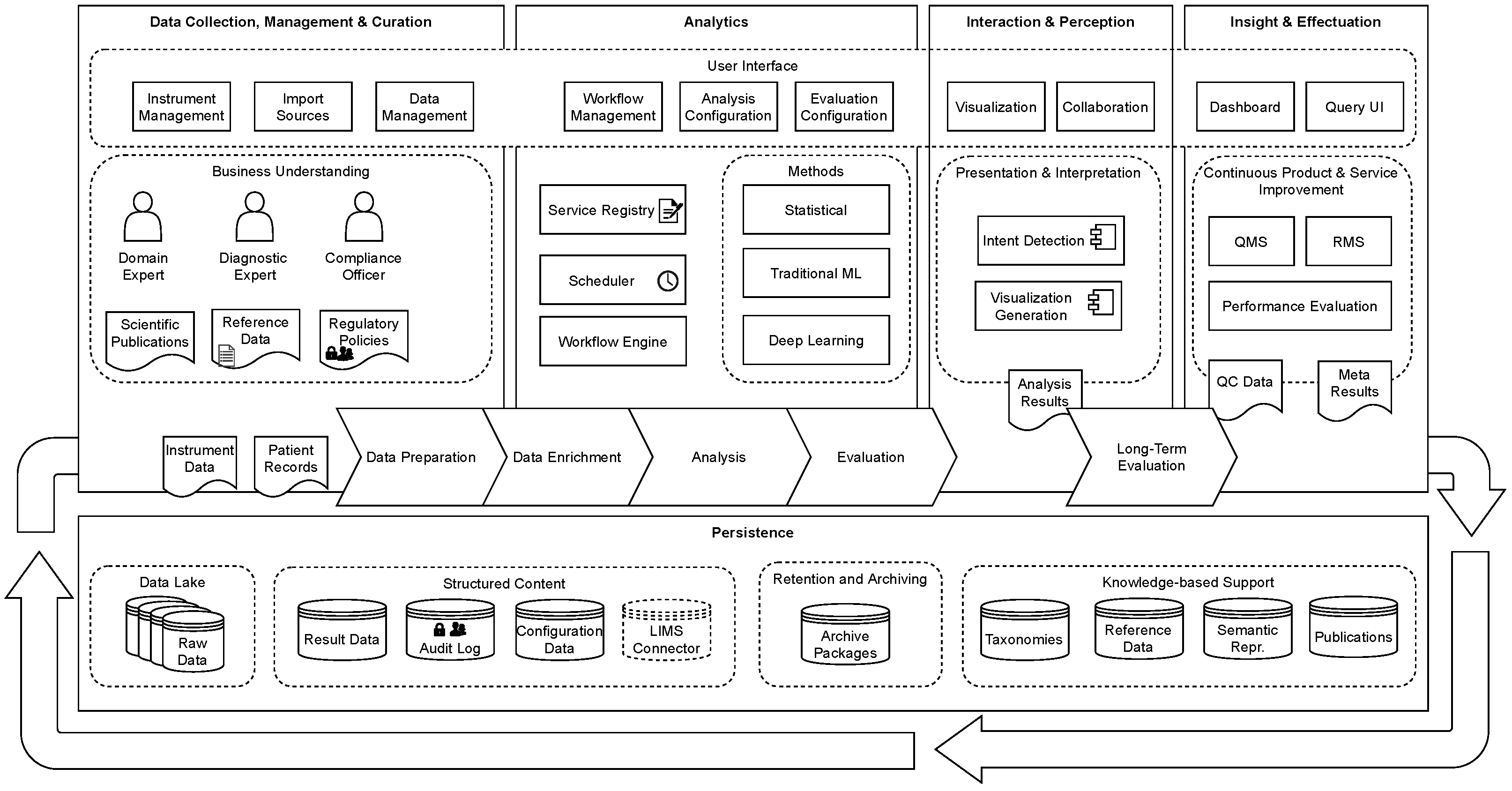
3. Conceptual Model
4. Evaluation and Requirement Engineering
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stephens, Z.D.; Lee, S.Y.; Faghri, F.; Campbell, R.H.; Zhai, C.; Efron, M.J.; Iyer, R.; Schatz, M.C.; Sinha, S.; Robinson, G.E. Big Data: Astronomical or Genomical? PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abawajy, J. Comprehensive analysis of big data variety landscape. Int. J. Parallel Emergent Distrib. Syst. 2015, 30, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Huss, M.; Abid, A.; Mohammadi, P.; Torkamani, A.; Telenti, A. A primer on deep learning in genomics. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, T.; Wassan, J.T.; Mc Kevitt, P.; Wang, H.; Zheng, H.; Hemmje, M.L. Analyzing Large Microbiome Datasets Using Machine Learning and Big Data. BioMedInformatics 2021, 1, 138–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, T.; Krause, T.; Bornschlegl, M.X.; Hemmje, M.L. A Conceptual Architecture for AI-based Big Data Analysis and Visualization Supporting Metagenomics Research. In Proceedings of the Collaborative European Research Conference (CERC 2020), Belfast, UK, 10–11 September 2020; Afli, H., Bleimann, U., Burkhardt, D., Loew, R., Regier, S., Stengel, I., Wang, H., Zheng, H., Eds.; CEUR Workshop Proceedings. CERC: New Delhi, India, 2020; pp. 264–272. [Google Scholar]
- Soueidan, H.; Nikolski, M. Machine learning for metagenomics: Methods and tools. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.06621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, R.; Junklewitz, H.; Sanchez, I. Robustness and Explainability of Artificial Intelligence; EUR, Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020; Volume 30040. [Google Scholar]
- Standard ISO 13485:2016; Medical Devices—Quality Management Systems—Requirements for Regulatory Purposes. ISO International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Standard ISO 15189:2012; Medical Laboratories—Requirements for Quality and Competence. ISO International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Standard IEC 62304:2006; Medical Device Software—Software Life Cycle Processes. IEC International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- The European Parliament; The Council of the European Union. In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Spitzenberger, F.; Patel, J.; Gebuhr, I.; Kruttwig, K.; Safi, A.; Meisel, C. Laboratory-Developed Tests: Design of a Regulatory Strategy in Compliance with the International State-of-the-Art and the Regulation (EU) 2017/746 (EU IVDR In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Device Regulation). Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2021, 56, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, T.; Jolkver, E.; Bruchhaus, S.; Kramer, M.; Hemmje, M.L. GenDAI—AI-Assisted Laboratory Diagnostics for Genomic Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Houston, TX, USA, 9–12 December 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afgan, E.; Baker, D.; Batut, B.; van den Beek, M.; Bouvier, D.; Čech, M.; Chilton, J.; Clements, D.; Coraor, N.; Grüning, B.A.; et al. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W537–W544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, F.; Paarmann, D.; D’Souza, M.; Olson, R.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; Paczian, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Stevens, R.; Wilke, A.; et al. The metagenomics RAST server—A public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Almeida, A.; Beracochea, M.; Boland, M.; Burgin, J.; Cochrane, G.; Crusoe, M.R.; Kale, V.; Potter, S.C.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. MGnify: The microbiome analysis resource in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D570–D578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- What Makes qbase+ Unique? Available online: https://www.qbaseplus.com/features (accessed on 7 June 2021).
- Hellemans, J.; Mortier, G.; de Paepe, A.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. qBase relative quantification framework and software for management and automated analysis of real-time quantitative PCR data. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reis, T.; Bornschlegl, M.X.; Hemmje, M.L. Toward a Reference Model for Artificial Intelligence Supporting Big Data Analysis. In Advances in Data Science and Information Engineering; Stahlbock, R., Weiss, G.M., Abou-Nasr, M., Yang, C.Y., Arabnia, H.R., Deligiannidis, L., Eds.; Transactions on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
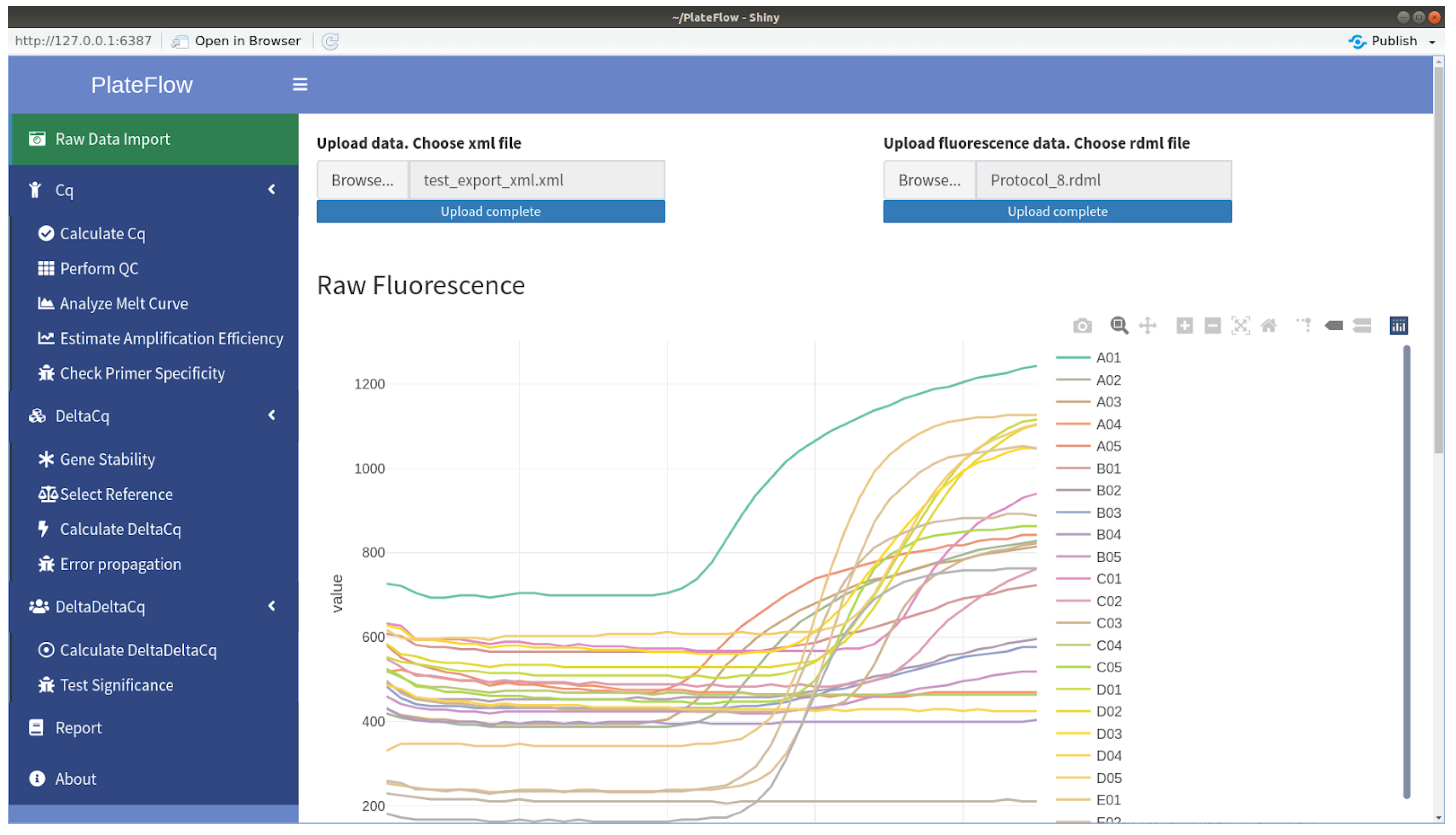
- Krause, T.; Jolkver, E.; Bruchhaus, S.; Kramer, M.; Hemmje, M.L. An RT-qPCR Data Analysis Platform. In Proceedings of the Collaborative European Research Conference (CERC 2021), Cork, Ireland, 9–10 September 2021; Afli, H., Bleimann, U., Burkhardt, D., Hasanuzzaman, M., Loew, R., Reichel, D., Wang, H., Zheng, H., Eds.; CEUR Workshop Proceedings. CERC: New Delhi, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Berwind, K.; Bornschlegl, M.X.; Kaufmann, M.A.; Hemmje, M.L. Towards a Cross Industry Standard Process to support Big Data Applications in Virtual Research Environments. In Proceedings of the Collaborative European Research Conference (CERC 2016), Cork, Ireland, 23–24 September 2016; Bleimann, U., Humm, B., Loew, R., Stengel, I., Walsh, P., Eds.; CERC: New Delhi, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barrat, F.J.; Crow, M.K.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Interferon target-gene expression and epigenomic signatures in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunamaker, J.F.; Chen, M.; Purdin, T.D. Systems Development in Information Systems Research. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 1990, 7, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, T.; Jolkver, E.; Mc Kevitt, P.; Kramer, M.; Hemmje, M. A Systematic Approach to Diagnostic Laboratory Software Requirements Analysis. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabinger, S.; Rödiger, S.; Kriegner, A.; Vierlinger, K.; Weinhäusel, A. A survey of tools for the analysis of quantitative PCR (qPCR) data. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2014, 1, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

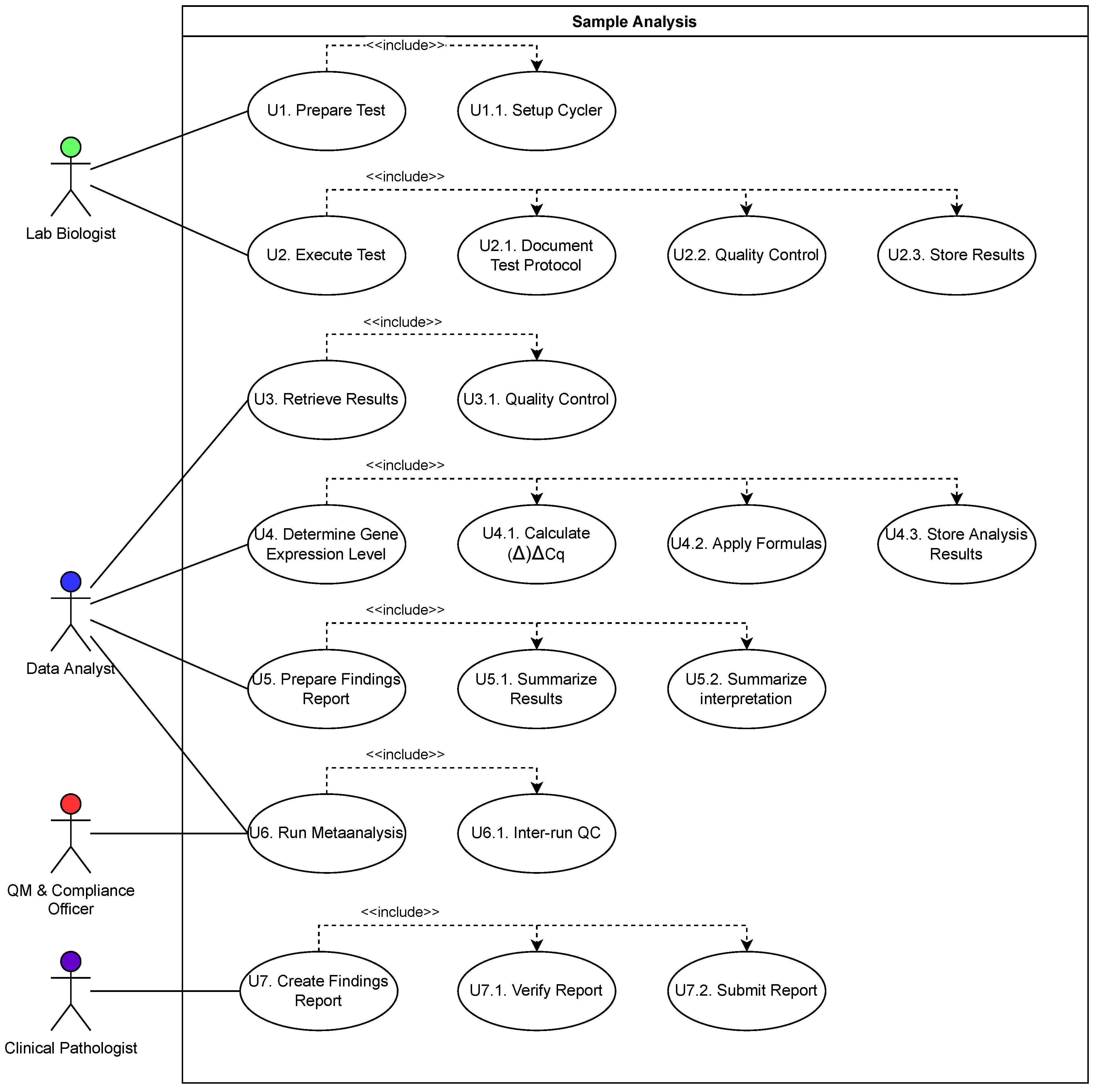
| Use Case | Potential | Limitations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Med. | High | ||
| U1. Prepare Test | x | |||
| U1.1. Program Cycler | x | Cycler Capabilities | ||
| U2. Execute Test | x | x | ||
| U2.1. Document Test Protocol | x | User Input | ||
| U2.2. Quality Control | x | |||
| U2.3. Store Results | x | |||
| U3. Retrieve Results | x | |||
| U3.1. Quality Control | x | |||
| U4. Determine Gene Expression Level | x | |||
| U4.1. Calculate ()Cq | x | |||
| U4.2. Apply Formulas | x | |||
| U4.3. Store Analysis Results | x | |||
| U5. Prepare Findings Report | x | x | ||
| U5.1. Summarize Results | x | |||
| U5.2. Summarize interpretation | x | Plausibility Checks | ||
| U6. Run Metaanalysis | x | |||
| U6.1. Inter-Run QC | x | Not Formalized | ||
| U7. Create Findings Report | x | x | ||
| U7.1. Verify Report | x | Legal Responsibility | ||
| U7.2. Submit Report | x | |||
| Tool | PCR Efficiency Estimation | Melt Curve Analysis | Reference Gene Selection | Cq Calculation | Error Propagation | Normalization | Absolute Quantifcation | Relative Quantification | Outlier Detection | NA Handling | Statistics | Graphs | MIQE Compliant | Last Update |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAmpER | + | nd | nd | + | − | − | − | + | nd | − | − | + | − | 2009 |
| Cy0 Method | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | 2010 |
| DART-PCR | − | − | − | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | − | + | − | 2002 |
| Deconvolution | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | + | 2010 |
| ExpressionSuite Software | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | 2019 |
| Factor-qPCR | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | 2020 |
| GenEx | + | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 2019 |
| geNorm | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | 2018 |
| LinRegPCR | + | − | − | + | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | + | + | 2021 |
| LRE Analysis | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | + | 2012 |
| LRE Analyzer | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | + | + | 2014 |
| MAKERGAUL | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | + | 2013 |
| PCR-Miner | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | 2011 |
| PIPE-T | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | 2019 |
| pyQPCR | + | − | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | + | 2012 |
| Q-Gene | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | − | + | − | 2002 |
| qBase | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | 2007 |
| qbase+ | + | − | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | 2017 |
| qCalculator | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | 2004 |
| QPCR | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | + | + | 2013 |
| qPCR-DAMS | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | + | 2006 |
| RealTime StatMiner | − | − | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | 2014 |
| REST | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | 2009 |
| SARS | − | nd | nd | − | − | + | − | + | nd | − | + | − | + | 2011 |
| SoFAR | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | 2003 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krause, T.; Jolkver, E.; Bruchhaus, S.; Mc Kevitt, P.; Kramer, M.; Hemmje, M. A Preliminary Evaluation of “GenDAI”, an AI-Assisted Laboratory Diagnostics Solution for Genomic Applications. BioMedInformatics 2022, 2, 332-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2020021
Krause T, Jolkver E, Bruchhaus S, Mc Kevitt P, Kramer M, Hemmje M. A Preliminary Evaluation of “GenDAI”, an AI-Assisted Laboratory Diagnostics Solution for Genomic Applications. BioMedInformatics. 2022; 2(2):332-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrause, Thomas, Elena Jolkver, Sebastian Bruchhaus, Paul Mc Kevitt, Michael Kramer, and Matthias Hemmje. 2022. "A Preliminary Evaluation of “GenDAI”, an AI-Assisted Laboratory Diagnostics Solution for Genomic Applications" BioMedInformatics 2, no. 2: 332-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2020021
APA StyleKrause, T., Jolkver, E., Bruchhaus, S., Mc Kevitt, P., Kramer, M., & Hemmje, M. (2022). A Preliminary Evaluation of “GenDAI”, an AI-Assisted Laboratory Diagnostics Solution for Genomic Applications. BioMedInformatics, 2(2), 332-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2020021






