Minimal Hip Joint Space Width Measured on X-rays by an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm—A Study of Reliability and Agreement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics and Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. AI Algorithm and Processing of Study Data
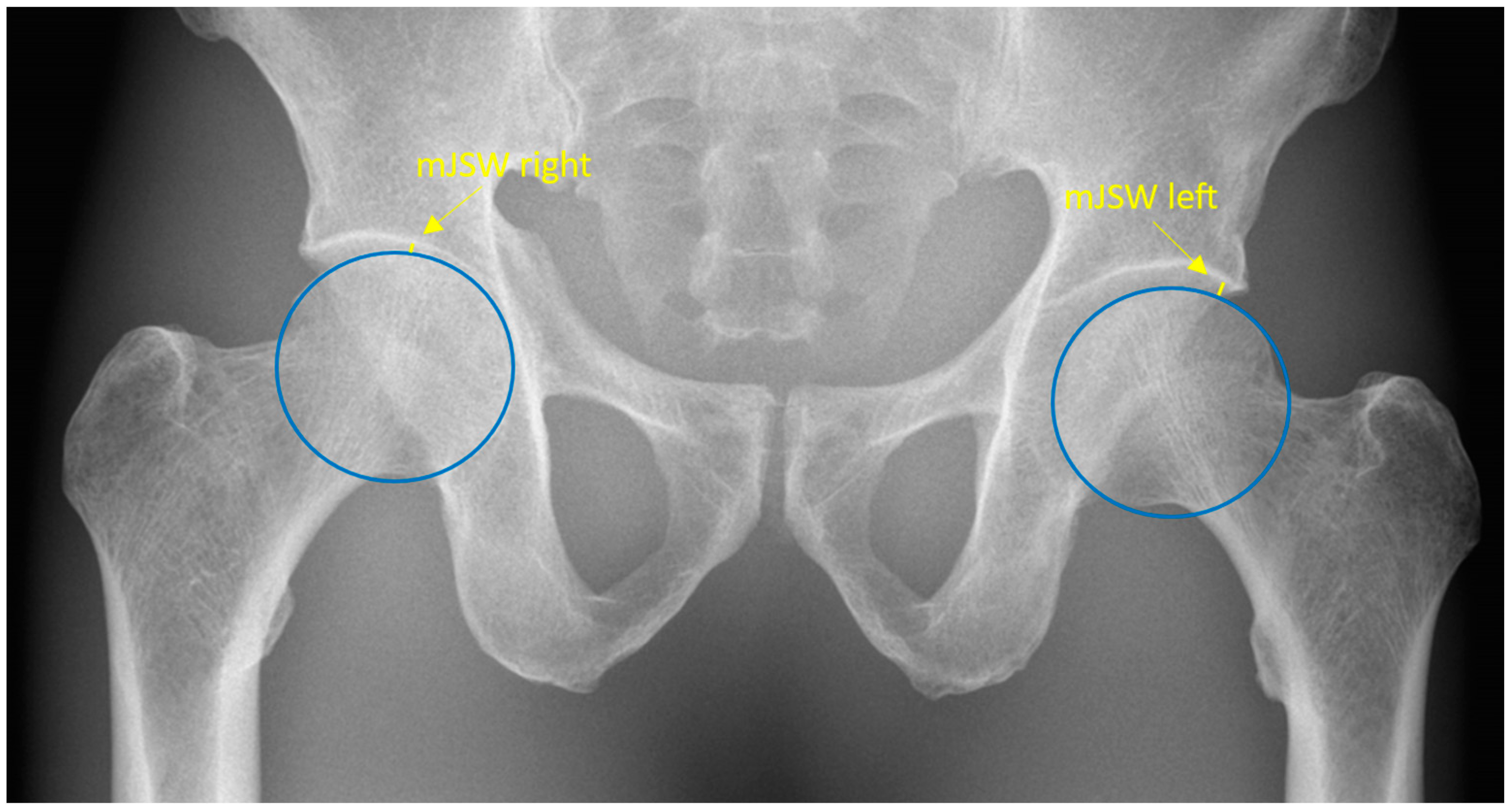
2.4. Anatomical Definition
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Statistical Analyses
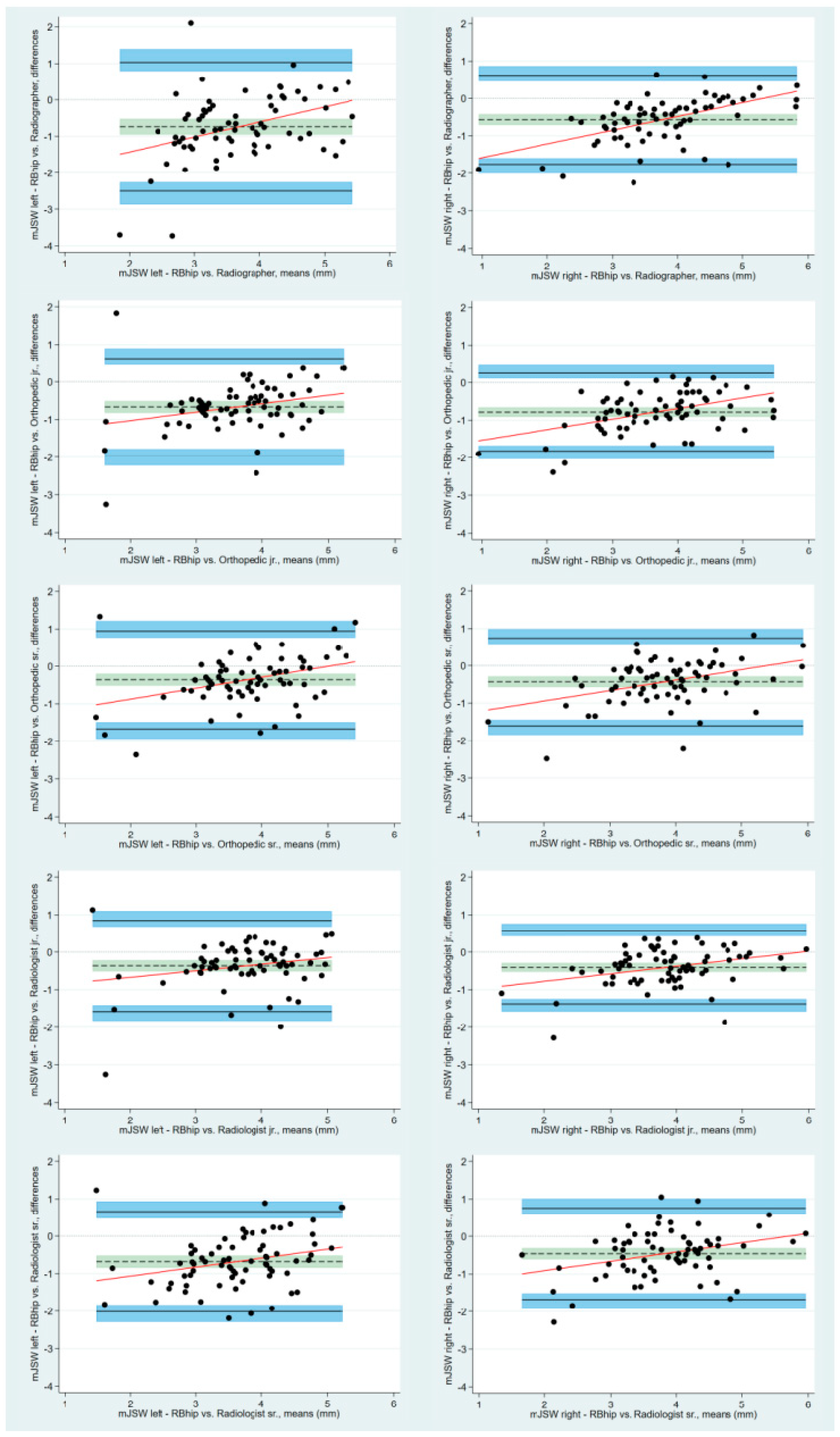
3. Results
4. Discussion
Clinical Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, R.; Deng, Y.; Chen, K.; Jiang, T. A preliminary examination of the diagnostic value of deep learning in hip osteoarthritis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebre, R.K.; Hirvasniemi, J.; van der Heijden, R.A.; Lantto, I.; Saarakkala, S.; Leppilahti, J.; Jämsä, T. Detecting hip osteoarthritis on clinical CT: A deep learning application based on 2-D summation images derived from CT. Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, S.S.; Rajasekaran, M.P. Automatic detection and classification of knee osteoarthritis using deep learning approach. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, N.J.; Eyles, J.P.; Hunter, D.J. Hip Osteoarthritis: Etiopathogenesis and Implications for Management. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 1921–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troelsen, A. Assessment of adult hip dysplasia and the outcome of surgical treatment. Dan. Med. J. 2012, 59, B4450. [Google Scholar]
- Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1545–1602. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakellariou, G.; Conaghan, P.G.; Zhang, W.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Boyesen, P.; D’Agostino, M.A.; Doherty, M.; Fodor, D.; Kloppenburg, M.; Miese, F.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in the clinical management of peripheral joint osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.; Sonne-Holm, S.; Søballe, K.; Gebuhr, P.; Lund, B. Radiographic case definitions and prevalence of osteoarthrosis of the hip: A survey of 4 151 subjects in the Osteoarthritis Substudy of the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Acta Orthop. Scand. 2004, 75, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Schacky, C.E.; Sohn, J.H.; Liu, F.; Ozhinsky, E.; Jungmann, P.M.; Nardo, L.; Posadzy, M.; Foreman, S.C.; Nevitt, M.C.; Link, T.M.; et al. Development and Validation of a Multitask Deep Learning Model for Severity Grading of Hip Osteoarthritis Features on Radiographs. Radiology 2020, 295, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeta, J.; Aditi, J.; Sabina, A.; Harshit, G.; Mukund, B. FDA approved Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)-Enabled Medical Devices: An updated 2022 landscape. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottner, J.; Audigé, L.; Brorson, S.; Donner, A.; Gajewski, B.J.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Roberts, C.; Shoukri, M.; Streiner, D.L. Guidelines for Reporting Reliability and Agreement Studies (GRRAS) were proposed. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.; Lijmer, J.G.; Moher, D.; Rennie, D.; de Vet, H.C.; et al. STARD 2015: An Updated List of Essential Items for Reporting Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.; Graumann, O.; Overgaard, S.; Gerke, O.; Lundemann, M.; Haubro, M.H.; Varnum, C.; Bak, L.; Rasmussen, J.; Olsen, L.B.; et al. A Deep Learning Algorithm for Radiographic Measurements of the Hip in Adults-A Reliability and Agreement Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1999, 8, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carkeet, A. Exact parametric confidence intervals for Bland-Altman limits of agreement. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2015, 92, e71–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornetti, P.; Maillefert, J.F.; Paternotte, S.; Dougados, M.; Gossec, L. Influence of the experience of the reader on reliability of joint space width measurement. A cross-sectional multiple reading study in hip osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine 2011, 78, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lequesne, M.; Malghem, J.; Dion, E. The normal hip joint space: Variations in width, shape, and architecture on 223 pelvic radiographs. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehrer, S.; Ljuhar, R.; Steindl, P.; Simon, R.; Maurer, D.; Ljuhar, D.; Bertalan, Z.; Dimai, H.P.; Goetz, C.; Paixao, T. Automated Knee Osteoarthritis Assessment Increases Physicians’ Agreement Rate and Accuracy: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Cartilage 2021, 13, 957s–965s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratzlaff, C.; Van Wyngaarden, C.; Duryea, J. Location-specific hip joint space width for progression of hip osteoarthritis--data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs-Winkelmann, S.; Peterlein, C.D.; Tibesku, C.O.; Weinstein, S.L. Comparison of pelvic radiographs in weightbearing and supine positions. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzyoud, K.; Hogg, P.; Snaith, B.; Flintham, K.; England, A. Optimum Positioning for Anteroposterior Pelvis Radiography: A Literature Review. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2018, 49, 316–324.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terjesen, T.; Gunderson, R.B. Reliability of radiographic parameters in adults with hip dysplasia. Skeletal Radiol. 2012, 41, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, F.S.; Williams, B.T.; Polce, E.M.; Maheshwer, B.; Williams, J.C.; Nho, S.J.; Chahla, J. No Differences in Hip Joint Space Measurements Between Weightbearing or Supine Anteroposterior Pelvic Radiographs. Arthroscopy 2020, 36, 2843–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
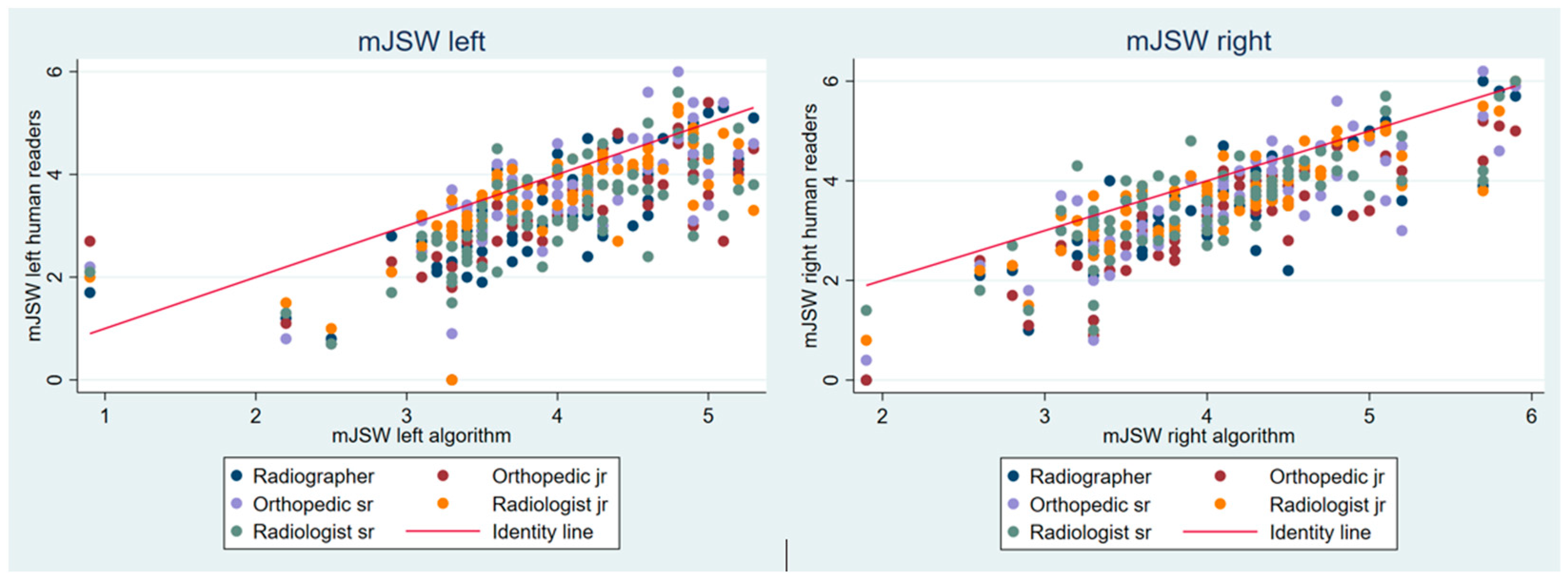
| mJSW (SD) [Range] Left | Right | |
|---|---|---|
| Radiographer | 3.32 (1.08) [0.0 to 5.6] | 3.48 (1.09) [0.0 to 6.0] |
| Orthopedic jr. | 3.29 (0.93) [0.0 to 5.4] | 3.27 (1.01) [0.0 to 5.2] |
| Orthopedic sr. | 3.59 (0.99) [0.0 to 7.6] | 3.62 (1.00) [0.4 to 6.2] |
| Radiologist jr. | 3.59 (0.89) [0.0 to 5.3] | 3.65 (0.94) [0.8 to 6.0] |
| Radiologist sr. | 3.27 (0.94) [0.7 to 5.6] | 3.59 (0.97) [1.0 to 6.0] |
| Algorithm | 3.96 (0.76) [0.9 to 5.3] | 4.05 (0.78) [1.9 to 5.9] |
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) diff | Range [min;max] | Range diff [min;max] | Q1 | Q1 diff | Q3 | Q3 diff | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mJSW right | 4.05 (0.78) | 0.00 (0.00) | [1.89;5.93] | [0.00;0.00] | 3.44 | 0.00 | 4.53 | 0.00 |
| mJSW left | 3.95 (0.77) | 0.00 (0.00) | [0.90;5.29] | [0.00;0.00] | 3.48 | 0.00 | 4.47 | 0.00 |
| Bias | Bias | LoA | Lower LoA | Upper LoA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | 95% CI | 95% CI | 95% CI | |||
| mJSW right | Radiographer | −0.57 (0.61) | −0.71 to −0.42 | −1.76 to 0.63 | −2.01 to −1.59 | 0.47 to 0.88 |
| Orthopedic jr. | −0.78 (0.52) | −0.91 to −0.66 | −1.81 to 0.25 | −2.02 to −1.67 | 0.11 to 0.46 | |
| Orthopedic sr. | −0.43 (0.60) | −0.57 to −0.29 | −1.60 to 0.74 | −1.84 to −1.44 | 0.58 to 0.99 | |
| Radiologist jr. | −0.40 (0.50) | −0.52 to −0.29 | −1.39 to 0.58 | −1.59 to −1.25 | 0.44 to 0.78 | |
| Radiologist sr. | −0.46 (0.62) | −0.61 to −0.31 | −1.68 to 0.76 | −1.93 to −1.51 | 0.60 to 1.02 | |
| mJSW left | Radiographer | −0.64 (0.69) | −0.80 to −0.48 | −1.99 to 0.71 | −2.27 to −1.81 | 0.53 to 0.99 |
| Orthopedic jr. | −0.67 (0.66) | −0.83 to −0.51 | −1.97 to 0.63 | −2.24 to −1.79 | 0.45 to 0.90 | |
| Orthopedic sr. | −0.36 (0.67) | −0.52 to −0.21 | −1.67 to 0.94 | −1.94 to −1.67 | 0.77 to 1.22 | |
| Radiologist jr. | −0.37 (0.62) | −0.52 to −0.22 | −1.58 to 0.85 | −1.84 to −1.42 | 0.68 to 1.10 | |
| Radiologist sr. | −0.68 (0.68) | −0.85 to −0.52 | −2.02 to 0.65 | −2.29 to −1.84 | 0.47 to 0.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andersen, A.M.; Rasmussen, B.S.B.; Graumann, O.; Overgaard, S.; Lundemann, M.; Haubro, M.H.; Varnum, C.; Rasmussen, J.; Jensen, J. Minimal Hip Joint Space Width Measured on X-rays by an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm—A Study of Reliability and Agreement. BioMedInformatics 2023, 3, 714-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics3030046
Andersen AM, Rasmussen BSB, Graumann O, Overgaard S, Lundemann M, Haubro MH, Varnum C, Rasmussen J, Jensen J. Minimal Hip Joint Space Width Measured on X-rays by an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm—A Study of Reliability and Agreement. BioMedInformatics. 2023; 3(3):714-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics3030046
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndersen, Anne Mathilde, Benjamin S. B. Rasmussen, Ole Graumann, Søren Overgaard, Michael Lundemann, Martin Haagen Haubro, Claus Varnum, Janne Rasmussen, and Janni Jensen. 2023. "Minimal Hip Joint Space Width Measured on X-rays by an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm—A Study of Reliability and Agreement" BioMedInformatics 3, no. 3: 714-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics3030046
APA StyleAndersen, A. M., Rasmussen, B. S. B., Graumann, O., Overgaard, S., Lundemann, M., Haubro, M. H., Varnum, C., Rasmussen, J., & Jensen, J. (2023). Minimal Hip Joint Space Width Measured on X-rays by an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm—A Study of Reliability and Agreement. BioMedInformatics, 3(3), 714-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics3030046






