Improvement of Statistical Models by Considering Correlations among Parameters: Local Anesthetic Agent Simulator for Pharmacological Education
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. Computer Simulation
2.2.1. Software and Programs Used
2.2.2. Drug Parameters
2.2.3. Probability Prediction Curve, Score Value, and Duration
2.2.4. Comparison of Local Anesthetic Agent Duration between Animal and Simulation Data
2.2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Correlation of Parameter Values of Each Drug in Animal Experiments
3.2. Correlation of Parameter Values among Drugs in Animal Experiments
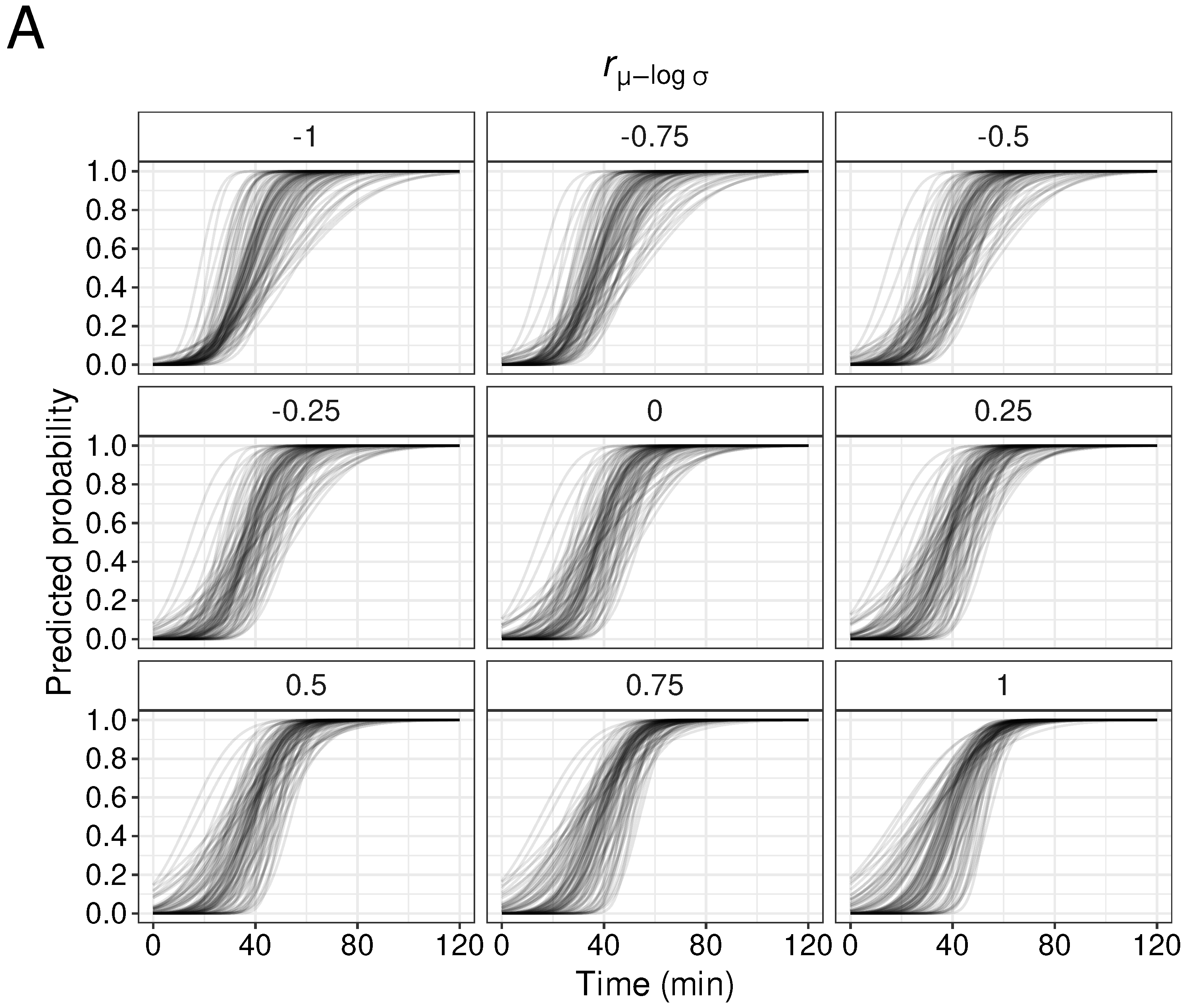
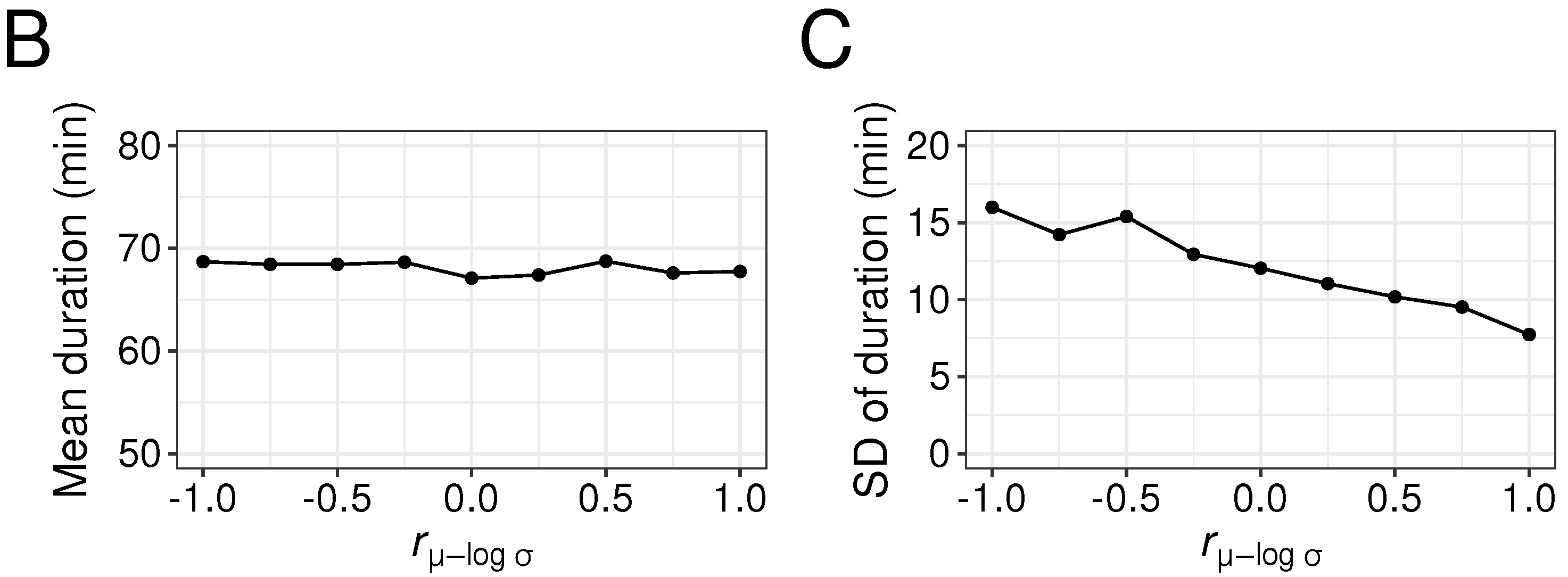
3.3. Effects of Correlation of Drug Parameter Values () in Simulation Experiments
3.4. Effects of Correlations between Drug Parameter Values ( and ) on Generated Parameters
3.5. Effects of Correlation Between Drug Parameter Values (, and ) on Duration
4. Discussion
4.1. The Model Used in This Study
4.2. Drug Parameters
4.2.1. Relationship between Duration and
4.2.2. Relationship between Duration and Parameters ( and )
4.2.3. Significance of Setting the Correlation Coefficient between Parameters
4.3. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Pro | Procaine |
| Lid | Lidocaine |
| Mep | Mepivacaine |
| Bup | Bupivacaine |
| Adr | Adrenaline |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Brunton, L.; Knollman, B.C. Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 14th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ritteri, J.; Flower, R.; Henderson, G.; Loke, Y.K.; MacEwan, D.; Rang, H. Rang & Dale’s Pharmacology, 9th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Council, N.R. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; Voinov, A. Modeling ecological and economic systems with STELLA: Part III. Ecol. Model. 2001, 143, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghardt, J.M.; Weber, B.; Staab, A.; Kloft, C. Pharmacometric Models for Characterizing the Pharmacokinetics of Orally Inhaled Drugs. AAPS J. 2015, 14, 853–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempster, J. Strathclyde Pharmacology Simulations. 2022. Available online: http://spider.science.strath.ac.uk/sipbs/page.php?page=software_sims (accessed on 24 August 2024).
- Ara, T.; Kitamura, H. Development of a Predictive Statistical Pharmacological Model for Local Anesthetic Agent Effects with Bayesian Hierarchical Model Parameter Estimation. Medicines 2023, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, H.C.; Tam, V.H. Optimizing Clinical Outcomes through Rational Dosing Strategies: Roles of Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Modeling Tools. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. PK/PD Modeling to Assess Rifaximin Clinical Dosage in a Mouse Model of Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Mastitis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 651369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumoto, S.; Ohbayashi, M.; Okada, A.; Kohyama, N.; Tamatsukuri, T.; Inoue, H.; Kato, A.; Kotani, T.; Sagara, H.; Dohi, K.; et al. Population Pharmacokinetic Model and Dosing Simulation of Meropenem Using Measured Creatinine Clearance for Patients with Sepsis. Ther. Drug Monit. 2023, 45, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumoto, M.; Motegi, T.; Uno, H.; Yokono, M.; Harada, K. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis of cefmetazole against extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in dogs using Monte Carlo Simulation. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1270137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drusano, G.L.; D’Argenio, D.Z.; Preston, S.L.; Barone, C.; Symonds, W.; LaFon, S.; Rogers, M.; Prince, W.; Bye, A.; Bilello, J.A. Use of Drug Effect Interaction Modeling with Monte Carlo Simulation to Examine the Impact of Dosing Interval on the Projected Antiviral Activity of the Combination of Abacavir and Amprenavir. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1655–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sale, M.; Sadler, B.M.; Stein, D.S. Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulations of Interaction of Amprenavir and Ritonavir. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, J.; Barnes, K.I.; Workman, L.; Kredo, T.; Vestergaard, L.S.; Hoglund, R.M.; Byakika-Kibwika, P.; Lamorde, M.; Walimbwa, S.I.; Chijioke-Nwauche, I.; et al. An Individual Participant Data Population Pharmacokinetic Meta-analysis of Drug-Drug Interactions between Lumefantrine and Commonly Used Antiretroviral Treatment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e02394-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, J.M.; Vicini, P.; Orlansky, A.; Li, S.; Zhou, F.; Ma, J.; Pulfer, S.; Bookman, M.A.; Guo, P. Pharmacokinetic Model-Predicted Anticancer Drug Concentrations in Human Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8048–8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chetty, M.; Kenworthy, J.J.; Langham, S.; Walker, A.; Dunlop, W.C.N. A systematic review of health economic models of opioid agonist therapies in maintenance treatment of non-prescription opioid dependence. Addict. Sci. Clin. Pract. 2017, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazaubon, Y.; Mauprivez, C.; Feliu, C.; Binet, L.; Oget, O.; Gozalo, C.; Djerada, Z. Population pharmacokinetics of articaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine during third molar surgery and simulation of high-dose regimens. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 114, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeberg, H.; Nilsson, J.; Århem, P. The Importance of the Dissociation Rate in Ion Channel Blocking. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karoly, R.; Lenkey, N.; Juhasz, A.O.; Vizi, E.S.; Mike, A. Fast- or Slow-inactivated State Preference of Na+ Channel Inhibitors: A Simulation and Experimental Study. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Genz, A.; Bretz, F. Computation of Multivariate Normal and t Probabilities; Lecture Notes in Statistics; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Therneau, T.M. A Package for Survival Analysis in R; R Package Version 3.7-0; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

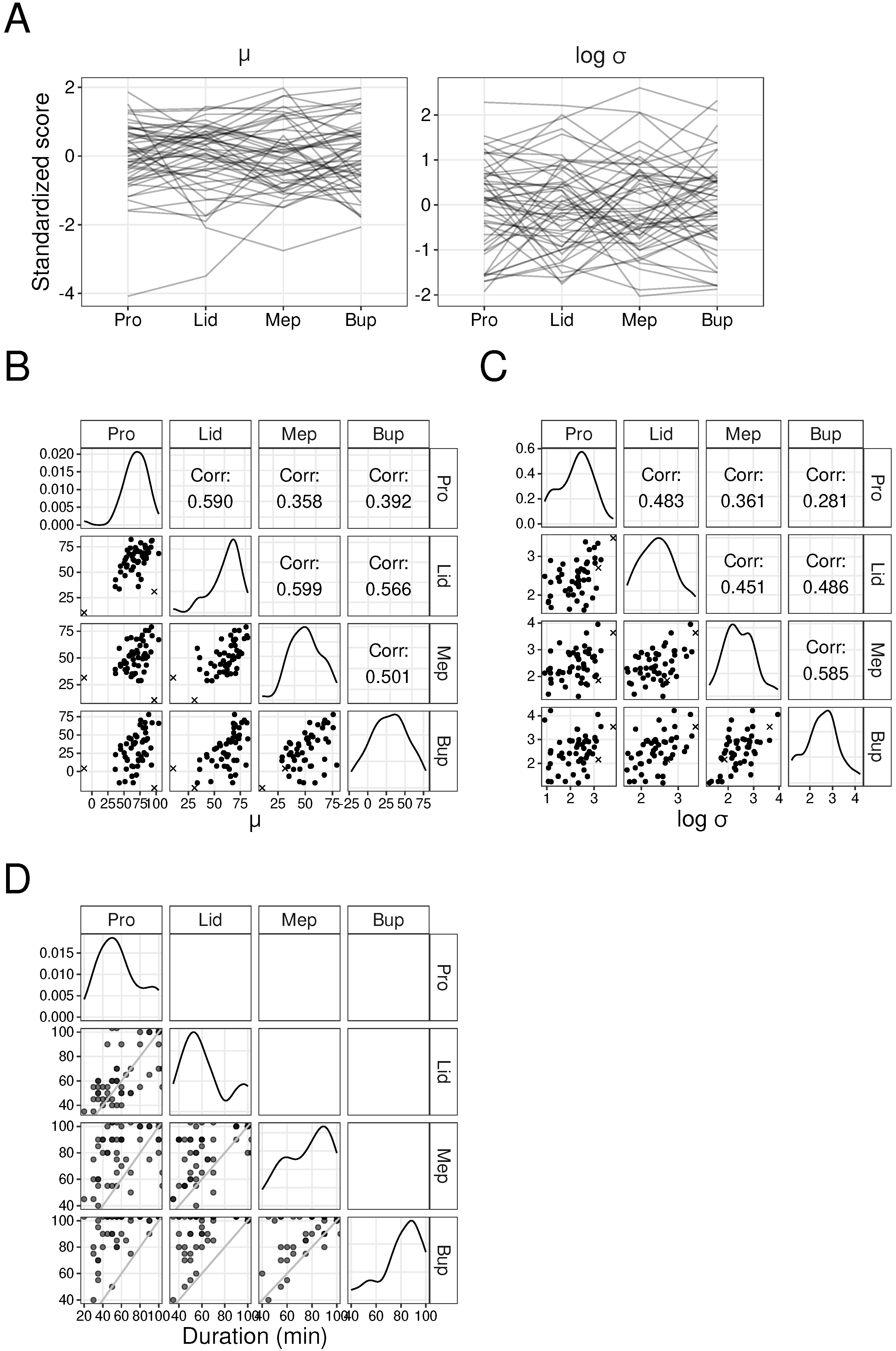


| Drug | All Data () | Without Outliers () |
|---|---|---|
| Pro | −0.308 | −0.219 |
| Lid | −0.415 | −0.301 |
| Mep | 0.012 | 0.014 |
| Bup | −0.154 | −0.160 |
| All Data () | Without Outliers () | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combination | ||||
| Pro–Lid | 0.590 | 0.483 | 0.568 | 0.416 |
| Pro–Mep | 0.358 | 0.361 | 0.467 | 0.336 |
| Pro–Bup | 0.392 | 0.281 | 0.498 | 0.257 |
| Lid–Mep | 0.599 | 0.451 | 0.526 | 0.414 |
| Lid–Bup | 0.566 | 0.486 | 0.527 | 0.466 |
| Mep–Bup | 0.501 | 0.585 | 0.420 | 0.559 |
| Drug | Combination | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro | 68 | 10 | 2.2 | 0.4 | −0.22 | Pro–Lid | 0.57 | 0.42 |
| Lid | 61 | 7 | 2.4 | 0.4 | −0.30 | Pro–Mep | 0.47 | 0.34 |
| Mep | 50 | 7 | 2.4 | 0.4 | −0.01 | Pro–Bup | 0.50 | 0.26 |
| Bup | 30 | 13 | 2.5 | 0.5 | −0.16 | Lid–Mep | 0.53 | 0.41 |
| Lid–Bup | 0.53 | 0.47 | ||||||
| Mep–Bup | 0.42 | 0.56 |
| Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Condition 3 | Condition 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | * | 0 | * | |
| and | 0 | 0 | * | * |
| Pro–Lid | 0.223 | 0.257 | 0.583 | 0.470 |
| Pro–Mep | −0.009 | −0.034 | 0.226 | 0.310 |
| Pro–Bup | 0.092 | 0.088 | 0.460 | 0.384 |
| Lid–Mep | −0.046 | 0.009 | 0.273 | 0.216 |
| Lid–Bup | −0.042 | 0.039 | 0.462 | 0.407 |
| Mep–Bup | −0.013 | −0.122 | 0.370 | 0.327 |
| Drug | Condition | n | Events | Median [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro | Raw data | 51 | 48 | 55.0 [50.0, 65.0] |
| Condition 1 | 100 | 100 | 57.5 [55.0, 60.0] | |
| Condition 2 | 100 | 100 | 55.0 [55.0, 60.0] | |
| Condition 3 | 100 | 100 | 55.0 [55.0, 60.0] | |
| Condition 4 | 100 | 100 | 55.0 [55.0, 60.0] | |
| Lid | Raw data | 51 | 47 | 60.0 [55.0, 70.0] |
| Condition 1 | 100 | 100 | 65.0 [65.0, 70.0] | |
| Condition 2 | 100 | 100 | 65.0 [65.0, 70.0] | |
| Condition 3 | 100 | 100 | 70.0 [65.0, 70.0] | |
| Condition 4 | 100 | 100 | 65.0 [65.0, 70.0] | |
| Mep | Raw data | 51 | 45 | 85.0 [75.0, 90.0] |
| Condition 1 | 100 | 100 | 80.0 [80.0, 80.0] | |
| Condition 2 | 100 | 100 | 80.0 [75.0, 85.0] | |
| Condition 3 | 100 | 100 | 80.0 [80.0, 85.0] | |
| Condition 4 | 100 | 100 | 80.0 [75.0, 85.0] | |
| Bup | Raw data | 51 | 25 | – [90.0, –] |
| Condition 1 | 100 | 100 | 105.0 [100.0, 105.0] | |
| Condition 2 | 100 | 100 | 100.0 [100.0, 105.0] | |
| Condition 3 | 100 | 100 | 100.0 [100.0, 110.0] | |
| Condition 4 | 100 | 100 | 102.5 [100.0, 105.0] | |
| Lid + Adr | Raw data | 51 | 8 | – [–, –] |
| Condition 1 | 100 | 35 | – [–, –] | |
| Condition 2 | 100 | 38 | – [–, –] | |
| Condition 3 | 100 | 38 | – [–, –] | |
| Condition 4 | 100 | 42 | – [180.0, –] |
| Comparison | Raw Data | Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Condition 3 | Condition 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Pro > Lid | 31 (60.8%) | 69 (69.0%) | 73 (73.0%) | 79 (79.0%) | 80 (80.0%) |
| Pro < Lid | 20 (39.2%) | 31 (31.0%) | 27 (27.0%) | 21 (21.0%) | 20 (20.0%) | |
| Duration | Pro < Lid | 29 (56.9%) | 68 (68.0%) | 67 (67.0%) | 75 (75.0%) | 70 (70.0%) |
| Pro = Lid | 6 (11.8%) | 5 (5.0%) | 4 (4.0%) | 9 (9.0%) | 11 (11.0%) | |
| Pro > Lid | 15 (29.4%) | 27 (27.0%) | 29 (29.0%) | 16 (16.0%) | 19 (19.0%) | |
| both censored | 1 (2.0%) | — | — | — | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ara, T.; Kitamura, H. Improvement of Statistical Models by Considering Correlations among Parameters: Local Anesthetic Agent Simulator for Pharmacological Education. BioMedInformatics 2024, 4, 2133-2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4040114
Ara T, Kitamura H. Improvement of Statistical Models by Considering Correlations among Parameters: Local Anesthetic Agent Simulator for Pharmacological Education. BioMedInformatics. 2024; 4(4):2133-2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4040114
Chicago/Turabian StyleAra, Toshiaki, and Hiroyuki Kitamura. 2024. "Improvement of Statistical Models by Considering Correlations among Parameters: Local Anesthetic Agent Simulator for Pharmacological Education" BioMedInformatics 4, no. 4: 2133-2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4040114
APA StyleAra, T., & Kitamura, H. (2024). Improvement of Statistical Models by Considering Correlations among Parameters: Local Anesthetic Agent Simulator for Pharmacological Education. BioMedInformatics, 4(4), 2133-2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4040114







