Advancing Bladder Cancer Biomarker Discovery: Integrating Mass Spectrometry and Molecular Imaging
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
Cancer Metabolism and Metabolites
2. Literature Search Strategy
2.1. Serum Metabolic Analysis in Bladder Cancer
2.2. Urine Metabolic Analysis in Bladder Cancer
2.3. Tissue Metabolic Analysis in Bladder Cancer
3. Targeted Molecular Imaging of Bladder Cancer
4. Integration of Mass Spectrometry and Molecular Imaging for Bladder Cancer Biomarker Detection as Advancing Precision Oncology
5. Future Directions in the Integration of Mass Spectrometry and Molecular Imaging for Bladder Cancer Biomarker Detection
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Dai, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wei, D. Molecular-electromechanical system for unamplified detection of trace analytes in biofluids. Nat. Protoc. 2023, 18, 2313–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, P.M.; Leehans, A.; Ravishankar, P.; Daily, A. Multiomic Approaches for Cancer Biomarker Discovery in Liquid Biopsies: Advances and Challenges. Biomark. Insights 2023, 18, 11772719231204508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.W.; Qiu, S.Q.; Zhang, G.J. Molecular and functional imaging in cancer-targeted therapy: Current applications and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, S.P.; Pomper, M.G. Molecular imaging in oncology: Current impact and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Shay, C.; Saba, N.F.; Teng, Y. Cancer metabolism and carcinogenesis. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 13, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Zhu, J.; Thompson, C.B. The hallmarks of cancer metabolism: Still emerging. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Jin, D.; Huang, M.; Ji, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhou, L.; Bao, B.; Jiang, F.; Xu, W.; et al. Glycolysis in the tumor microenvironment: A driver of cancer progression and a promising therapeutic target. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1416472. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.; He, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhao, S.; Wei, P.; Li, D. Warburg effect in colorectal cancer: The emerging roles in tumor microenvironment and therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lai, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Cao, X.; Li, Y.; Nie, Z. Urine Metabolic Profiling for Rapid Lung Cancer Screening: A Strategy Combining Rh-Doped SrTiO3-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry and Machine Learning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 12302–12309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmelevskaya, E.A.P.E.S.; Buiko, E.E.; Ufandeev, A.A.; Kaydash, O.A.; Ivanov, V.V.; Baykov, A.N.; Parochkina, E.V.; Udut, E.V. Precision Medicine in Oncology: The Role and Prospects of Mass Spectrometry. Bull. Sib. Med. 2024, 23, 162–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, W.; Ji, Z.; Liu, X.; Qiao, Y. Serum metabolites as early detection markers of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer in Chinese patients. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1061083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira de Sousa, T.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Pinto, J. Metabolomic Signatures of Treatment Response in Bladder Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantaku, V.; Donepudi, S.R.; Piyarathna, D.W.B.; Amara, C.S.; Ambati, C.R.; Tang, W.; Putluri, V.; Chandrashekar, D.S.; Varambally, S.; Terris, M.K.; et al. Large-scale profiling of serum metabolites in African American and European American patients with bladder cancer reveals metabolic pathways associated with patient survival. Cancer 2019, 125, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, C.S.; Ambati, C.R.; Vantaku, V.; Badrajee Piyarathna, D.W.; Donepudi, S.R.; Ravi, S.S.; Arnold, J.M.; Putluri, V.; Chatta, G.; Guru, K.A.; et al. Serum Metabolic Profiling Identified a Distinct Metabolic Signature in Bladder Cancer Smokers: A Key Metabolic Enzyme Associated with Patient Survival. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akand, M.; Jatsenko, T.; Muilwijk, T.; Gevaert, T.; Joniau, S.; Van der Aa, F. Deciphering the molecular heterogeneity of intermediate- and (very-)high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer using multi-layered -omics studies. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1424293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G.; Xiang, Y.; Jing, Z.; Zeng, J.; Yu, F.; Pan, X.; Zhou, W.; Zeng, X. Metabolomics assisted by transcriptomics analysis to reveal metabolic characteristics and potential biomarkers associated with treatment response of neoadjuvant therapy with TCbHP regimen in HER2 + breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2024, 26, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Zhao, L.; Chen, H.; Xue, W.; Lin, D. NMR-based Metabolomic Analysis of Human Bladder Cancer. Anal. Sci. Int. J. Jpn. Soc. Anal. Chem. 2012, 28, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, N.; Gupta, A.; Mitash, N.; Shakya, P.S.; Mandhani, A.; Mahdi, A.A.; Sankhwar, S.N.; Mandal, S.K. Low- and high-grade bladder cancer determination via human serum-based metabolomics approach. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 5839–5850. [Google Scholar]
- Lodewijk, I.; Dueñas, M.; Rubio, C.; Munera-Maravilla, E.; Segovia, C.; Bernardini, A.; Teijeira, A.; Paramio, J.M.; Suárez-Cabrera, C. Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers in Bladder Cancer: A Current Need for Patient Diagnosis and Monitoring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Kang, H.; Zhang, X.; Nie, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhou, S. Urinary metabolomics for discovering metabolic biomarkers of bladder cancer by UPLC-MS. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; McKinney, K.Q.; Pavlopoulos, A.J.; Niu, M.; Kang, J.W.; Oh, J.W.; Kim, K.P.; Hwang, S. Altered Proteome of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Bladder Cancer Patients Urine. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Lai, Y.F.; Tang, P.; Chien, K.Y.; Yu, J.S.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, H.W.; Wu, C.C.; Chung, T.; Hsu, C.W.; et al. Comparative and targeted proteomic analyses of urinary microparticles from bladder cancer and hernia patients. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 5611–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiyama, E.; Matsuzaki, K.; Fujita, K.; Shiromizu, T.; Narumi, R.; Jingushi, K.; Koh, Y.; Matsushita, M.; Nakano, K.; Hayashi, Y.; et al. Proteomic analysis of urinary and tissue-exudative extracellular vesicles to discover novel bladder cancer biomarkers. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 2033–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Juo, B.R.; Yeh, Y.H.; Fu, S.H.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, C.L.; Wu, K.P. Putative markers for the detection of early-stage bladder cancer selected by urine metabolomics. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loras, A.; Suárez-Cabrera, C.; Martínez-Bisbal, M.C.; Quintás, G.; Paramio, J.M.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Gil, S.; Ruiz-Cerdá, J.L. Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis for the Study of Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putluri, N.; Shojaie, A.; Vasu, V.T.; Vareed, S.K.; Nalluri, S.; Putluri, V.; Thangjam, G.S.; Panzitt, K.; Tallman, C.T.; Butler, C.; et al. Metabolomic profiling reveals potential markers and bioprocesses altered in bladder cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7376–7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Sun, Z.; Chen, D.; Su, X.; Jiang, J.; Li, G.; Lin, B.; Yan, J. Developing urinary metabolomic signatures as early bladder cancer diagnostic markers. Omics 2015, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, L.S.; Fioole-Bruining, A.; Vegt, E.; Vogel, W.V.; van Rhijn, B.W.; Horenblas, S. Impact of (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-positron-emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) on management of patients with carcinoma invading bladder muscle. BJU Int. 2013, 112, 729–734. [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld, C.S.; Sanchez-Quiles, V.; Dufour, F.; Shi, M.; Dingli, F.; Nicolle, R.; Chapeaublanc, E.; Poullet, P.; Jeffery, D.; Krucker, C.; et al. Proteogenomic Characterization of Bladder Cancer Reveals Sensitivity to Apoptosis Induced by Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand in FGFR3-mutated Tumors. Eur. Urol. 2024, 85, 483–494. [Google Scholar]
- Nizioł, J.; Ossoliński, K.; Płaza-Altamer, A.; Kołodziej, A.; Ossolińska, A.; Ossoliński, T.; Krupa, Z.; Ruman, T. Untargeted metabolomics of bladder tissue using liquid chromatography and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry for cancer biomarker detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 240, 115966. [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann, B.M.; Stirdivant, S.M.; Mitchell, M.W.; Wulff, J.E.; McDunn, J.E.; Li, Z.; Dennis-Barrie, A.; Neri, B.P.; Milburn, M.V.; Lotan, Y.; et al. Bladder cancer biomarker discovery using global metabolomic profiling of urine. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Khonsari, M.M. Numerical optimization of texture shape for parallel surfaces under unidirectional and bidirectional sliding. Tribol. Int. 2015, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeb, D.S.; Wollensak, C.; Kretschmer, S.; González-Cerdas, G.; Ataman, C.; Kayser, G.; Dressler, F.F.; Gratzke, C.; Zappe, H.; Miernik, A. Ex-vivo evaluation of miniaturized probes for endoscopic optical coherence tomography in urothelial cancer diagnostics. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 77, 103597. [Google Scholar]
- Valdés, A.; Bitzios, A.; Kassa, E.; Shevchenko, G.; Falk, A.; Malmström, P.U.; Dragomir, A.; Segersten, U.; Lind, S.B. Proteomic comparison between different tissue preservation methods for identification of promising biomarkers of urothelial bladder cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7595. [Google Scholar]
- Tenori, L.; Oakman, C.; Claudino, W.M.; Bernini, P.; Cappadona, S.; Nepi, S.; Biganzoli, L.; Arbushites, M.C.; Luchinat, C.; Bertini, I.; et al. Exploration of serum metabolomic profiles and outcomes in women with metastatic breast cancer: A pilot study. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee, E.E.; Zeleznik, O.A.; Balasubramanian, R.; Hu, J.; Rosner, B.A.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Clish, C.B.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Willett, W.C.; Rexrode, K.M.; et al. Differences in metabolomic profiles between Black and White women in the U.S.: Analyses from two prospective cohorts. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2024, 39, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacyna, J.; Kordalewska, M.; Artymowicz, M.; Markuszewski, M.; Matuszewski, M.; Markuszewski, M.J. Pre- and Post-Resection Urine Metabolic Profiles of Bladder Cancer Patients: Results of Preliminary Studies on Time Series Metabolomics Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Amaro, F.; Lima, A.R.; Carvalho-Maia, C.; Jerónimo, C.; Henrique, R.; Bastos, M.L.; Carvalho, M.; Guedes de Pinho, P. Urinary Volatilomics Unveils a Candidate Biomarker Panel for Noninvasive Detection of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 3068–3077. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Yu, Y.; Ding, G.; Wu, J. Ultrasensitive and High Reproducible Detection of Urinary Metabolites Using the Tip-Contact Extraction Method Coupled with Negative LDI-MS. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 4022–4030. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Corsetti, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Huang, Z.; Nabi, G. Optical sensory arrays for the detection of urinary bladder cancer-related volatile organic compounds. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, Z.; Nabi, G. Fluorometric optical sensor arrays for the detection of urinary bladder cancer specific volatile organic compounds in the urine of patients with frank hematuria: A prospective case-control study. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einerhand, S.M.H.; van Gennep, E.J.; Mertens, L.S.; Hendricksen, K.; Donswijk, M.L.; van der Poel, H.G.; van Rhijn, B.W.G. 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2020, 30, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondergem, M.; van der Zant, F.M.; Rafimanesh-Sadr, L.; Knol, R.J.J. Effect of forced diuresis during 18F-DCFPyL PET/CT in patients with prostate cancer: Activity in ureters, kidneys and bladder and occurrence of halo artefacts around kidneys and bladder. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2019, 40, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitoussi, O.; Roche, J.B.; Riviere, J.; Wallerand, H.; Poulain, J.E.; Gordien, P.; Galland, S.; Henriques, B.; Dupin, C.; Vincent, M.; et al. Accuracy of FDG-PET/CT for Response Evaluation of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer following Neoadjuvant or Induction Chemotherapy. Urol. Int. 2023, 107, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchelouche, K. PET/CT in Bladder Cancer: An Update. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 52, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; You, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Xie, S.; Li, D.; Ai, S.; Yang, R.; Guo, H. Performance of (18)F-FDG PET/MRI and its parameters in staging and neoadjuvant therapy response evaluation in bladder cancer. iScience 2024, 27, 109657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahait, M.; Abu-Hijlih, R.; Farkouh, A.; Obeidat, S.; Salah, S.; Abdlkadir, A.S.; Al-Ibraheem, A. Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG PET)-computed tomography (CT) in the initial staging of bladder cancer: A single institution experience. J. Egypt. Natl. Canc Inst. 2023, 35, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodler, S.; Solyanik, O.; Ingenerf, M.; Fabritius, M.; Schulz, G.B.; Jokisch, F.; Volz, Y.; Westhofen, T.; Ebner, B.; Casuscelli, J.; et al. Accuracy and prognostic value of radiological lymph node features in variant histologies of bladder cancer. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, A.H.; Abdel Maksoud, T.A.S.; El-Noueam, K.I.; Ataa, M.A.; Abdallah, D.M. Multiparametric-MRI as a comprehensive study in evaluation, characterization & local staging of urinary bladder carcinomas. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2017, 48, 493–507. [Google Scholar]
- Sherif, A.; Garske, U.; Torre, M.d.L.; Thörn, M. Hybrid SPECT-CT: An Additional Technique for Sentinel Node Detection of Patients with Invasive Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, J.; Han, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Shi, G.; Yan, Z.; Yang, L.; Han, R.; Huang, F.; Ban, X.; et al. CT and MRI features of sarcomatoid urothelial carcinoma of the bladder and its differential diagnosis with conventional urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Imaging 2024, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Koo, P.J.; Pak, K.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, K. Diagnostic accuracy of C-11 choline and C-11 acetate for lymph node staging in patients with bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöder, H.; Ong, S.C.; Reuter, V.E.; Cai, S.; Burnazi, E.; Dalbagni, G.; Larson, S.M.; Bochner, B.H. Initial results with (11)C-acetate positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) in the staging of urinary bladder cancer. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2012, 14, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novruzov, E.; Dendl, K.; Ndlovu, H.; Choyke, P.L.; Dabir, M.; Beu, M.; Novruzov, F.; Mehdi, E.; Guliyev, F.; Koerber, S.A.; et al. Head-to-head Intra-individual Comparison of [(68)Ga]-FAPI and [(18)F]-FDG PET/CT in Patients with Bladder Cancer. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2022, 24, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshkin, V.S.; Kumar, V.; Kline, B.; Escobar, D.; Aslam, M.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Aggarwal, R.R.; de Kouchkovsky, I.; Chou, J.; Meng, M.V.; et al. Initial Experience with (68)Ga-FAP-2286 PET Imaging in Patients with Urothelial Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duijnhoven, S.M.; Robillard, M.S.; Nicolay, K.; Grüll, H. Tumor targeting of MMP-2/9 activatable cell-penetrating imaging probes is caused by tumor-independent activation. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Fels, C.A.M.; Leliveld, A.; Buikema, H.; van den Heuvel, M.C.; de Jong, I.J. VEGF, EGFR and PSMA as possible imaging targets of lymph node metastases of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. BMC Urol. 2022, 22, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourebrahimi, E.; Moradi Tabriz, H.; Miratashi Yazdi, S.A.; Nazar, E.; Batmani, S. The value of BCL2 and CK20 expression in predicting behavioral patterns of bladder cancer, a cross sectional study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 81, 104372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, Y.; Konishi, H.; Makino, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kawashima, H.; Iovanna, J.L.; Nakatani, T.; Kiyama, H. Urinary levels of hepatocarcinoma-intestine-pancreas/pancreatitis-associated protein as a diagnostic biomarker in patients with bladder cancer. BMC Urol. 2012, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruch, P.G.; Plage, H.; Hofbauer, S.; Kornienko, K.; Weinberger, S.; Roßner, F.; Schallenberg, S.; Kluth, M.; Lennartz, M.; Blessin, N.C.; et al. Cytokeratin 20 expression is linked to stage progression and to poor prognosis in advanced (pT4) urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2023, 131, 104860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejrananda, T.; Kanjanapradit, K.; Saetang, J.; Sangkhathat, S. Impact of immunohistochemistry-based subtyping of GATA3, CK20, CK5/6, and CK14 expression on survival after radical cystectomy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21186. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, S.; Dug Lim, S.; Jimenez, R.E.; Chun, T.; Keane, T.E.; McKenney, J.K.; Zavala-Pompa, A.; Cohen, C.; Young, R.H.; Amin, M.B. Relationship of Cytokeratin 20 and CD44 Protein Expression with WHO/ISUP Grade in pTa and pT1 Papillary Urothelial Neoplasia. Mod. Pathol. 2000, 13, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Dum, D.; Menz, A.; Völkel, C.; De Wispelaere, N.; Hinsch, A.; Gorbokon, N.; Lennartz, M.; Luebke, A.M.; Hube-Magg, C.; Kluth, M.; et al. Cytokeratin 7 and cytokeratin 20 expression in cancer: A tissue microarray study on 15,424 cancers. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2022, 126, 104762. [Google Scholar]
- Jangir, H.; Nambirajan, A.; Seth, A.; Sahoo, R.K.; Dinda, A.K.; Nayak, B.; Kaushal, S. Prognostic stratification of muscle invasive urothelial carcinomas using limited immunohistochemical panel of Gata3 and cytokeratins 5/6, 14 and 20. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 43, 151397. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.; Kim, B.; Moon, K.C. Immunohistochemistry of cytokeratin (CK) 5/6, CD44 and CK20 as prognostic biomarkers of non-muscle-invasive papillary upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Histopathology 2019, 74, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Carbayo, M.; Urrutia, M.; González de Buitrago, J.M.; Navajo, J.A. Evaluation of two new urinary tumor markers: Bladder tumor fibronectin and cytokeratin 18 for the diagnosis of bladder cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 3585–3594. [Google Scholar]
- Fouad, H.; Salem, H.; Ellakwa, D.E.; Abdel-Hamid, M. MMP-2 and MMP-9 as prognostic markers for the early detection of urinary bladder cancer. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2019, 33, e22275. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, A.; Loloi, J.; Pina Martina, L.; Sankin, A. The Development of Non-Invasive Diagnostic Tools in Bladder Cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2022, 15, 497–507. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, K.; Stenzl, A.; Sharma, A.; Vasdev, N. Urinary biomarkers in bladder cancer: A review of the current landscape and future directions. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Alavi, A.; Izadpanahi, M.H.; Haghshenas, L.; Faridizad, R.; Eslami, M.J.; Ghadimi, K. Comparing urine levels of BLCA-4 nuclear matrix protein in patients with bladder cancer and non-bladder cancer. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 11, 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, X. Diagnostic accuracy of urine cytokeratin 20 for bladder cancer: A meta-analysis. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 15, e11–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roupret, M.; Gontero, P.; McCracken, S.R.C.; Dudderidge, T.; Stockley, J.; Kennedy, A.; Rodriguez, O.; Sieverink, C.; Vanié, F.; Allasia, M.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of MCM5 for the Detection of Recurrence in Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Followup: A Blinded, Prospective Cohort, Multicenter European Study. J. Urol. 2020, 204, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, H.; Pagano, I.; Chee, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Wong, R.S.; Lee, R.; Rosser, C.J. Comparison of Commercial ELISA Kits, a Prototype Multiplex Electrochemoluminescent Assay, and a Multiplex Bead-Based Immunoassay for Detecting a Urine-Based Bladder-Cancer-Associated Diagnostic Signature. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-J.; Liu, T.; Xiong, Y. Anti-cancer effect of LINC00478 in bladder cancer correlates with KDM1A-dependent MMP9 demethylation. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirasawa, Y.; Pagano, I.; Chen, R.; Sun, Y.; Dai, Y.; Gupta, A.; Tikhonenkov, S.; Goodison, S.; Rosser, C.J.; Furuya, H. Diagnostic performance of Oncuria™, a urinalysis test for bladder cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karashima, T.; Umemoto, S.; Kishida, T.; Osaka, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Yoshida, E.; Yoshimura, T.; Sakaguchi, M.; Nishimoto, H.; Tai, M.; et al. Clinical evaluation of urine laminin-γ2 monomer as a potent biomarker for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, P.; Ye, J.; Xie, G.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. Serum EZH2 is a novel biomarker for bladder cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1303918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouprêt, M.; Gontero, P.; McCracken, S.R.C.; Dudderidge, T.; Stockley, J.; Kennedy, A.; Rodriguez, O.; Sieverink, C.; Vanié, F.; Allasia, M.; et al. Reducing the Frequency of Follow-up Cystoscopy in Low-grade pTa Non–muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Using the ADXBLADDER Biomarker. Eur. Urol. Focus 2022, 8, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecke, T.H.; Meisl, C.J.; Schlomm, T.; Rabien, A.; Labonté, F.; Rong, D.; Hofbauer, S.; Friedersdorff, F.; Sommerfeldt, L.; Gagel, N.; et al. BTA stat®, NMP22® BladderChek®, UBC® Rapid Test, and CancerCheck® UBC® rapid VISUAL as urinary marker for bladder cancer: Final results of a German multicenter study. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2023, 41, 484.e417–484.e426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plage, H.; Furlano, K.; Neymeyer, J.; Weinberger, S.; Gerdes, B.; Hubatsch, M.; Ralla, B.; Franz, A.; Fendler, A.; de Martino, M.; et al. CEA (CEACAM5) expression is common in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder but unrelated to the disease course. BJUI Compass 2024, 5, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VandenBussche, C.J.; Heaney, C.D.; Kates, M.; Hooks, J.J.; Baloga, K.; Sokoll, L.; Rosenthal, D.; Detrick, B. Urinary IL-6 and IL-8 as predictive markers in bladder urothelial carcinoma: A pilot study. Cancer Cytopathol. 2024, 132, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boström, P.J.; Aaltonen, V.; Söderström, K.-O.; Uotila, P.; Laato, M. Expression of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in urinary bladder carcinomas in vivo and in vitro and prostaglandin E2 synthesis in cultured bladder cancer cells. Pathology 2001, 33, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kong, T.; Qu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Niu, Z.; Lv, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Wei, P.; Fu, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Identification of novel protein biomarkers from the blood and urine for the early diagnosis of bladder cancer via proximity extension analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuya, H.; Tabula, L.; Lee, R.; Kralovec, P.; Ramsden, M.; Wong, R.; Rosser, C.J. Analytical validation of ONCURIA™ a multiplex bead-based immunoassay for the non-invasive bladder cancer detection. Pract. Lab. Med. 2020, 22, e00189. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, B.B.; López-Cortés, R.; Casas-Nebra, F.J.; Vázquez-Estévez, S.; Pérez-Fentes, D.; Chantada-Vázquez, M.D.P.; Bravo, S.B.; Núñez, C. Detection of Circulating Serum Protein Biomarkers of Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer after Protein Corona-Silver Nanoparticles Analysis by SWATH-MS. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Du, P. The diagnostic and prognostic value of nuclear matrix protein 22 in bladder cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 7174–7182. [Google Scholar]
- Nerli, R.B.; Ghagane, S.C.; Rangrez, S.; Chandra, S.; Thakur, M.L.; Gomella, L. Detection of bladder cancer using voided urine sample and by targeting genomic VPAC receptors. Indian. J. Urol. 2021, 37, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghagane, S.C.; Shadab, R.; Nerli, R.B.; Rai, S.; Thakur, M.; Gomella, L. Voided Urine Sample in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer in Patients with Serum PSA Ranging between 2.6 to 10 ng/mL. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Biol. 2023, 8, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, M.L.; Tripathi, S.K.; Gomella, L.G.; Salmanoglu, E.; Kim, S.; Kelly, W.K.; Keith, S.W.; Intenzo, C.; McCue, P.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; et al. Imaging urothelial bladder cancer: A VPAC PET targeted approach. Can. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 10596–10602. [Google Scholar]
- Muilwijk, T.; Baekelandt, L.; Akand, M.; Daelemans, S.; Marien, K.; Waumans, Y.; van Dam, P.-J.; Kockx, M.; Van den Broeck, T.; Van Cleynenbreugel, B.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein-α and the Immune Landscape: Unraveling T1 Non–muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Progression. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2024, 66, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
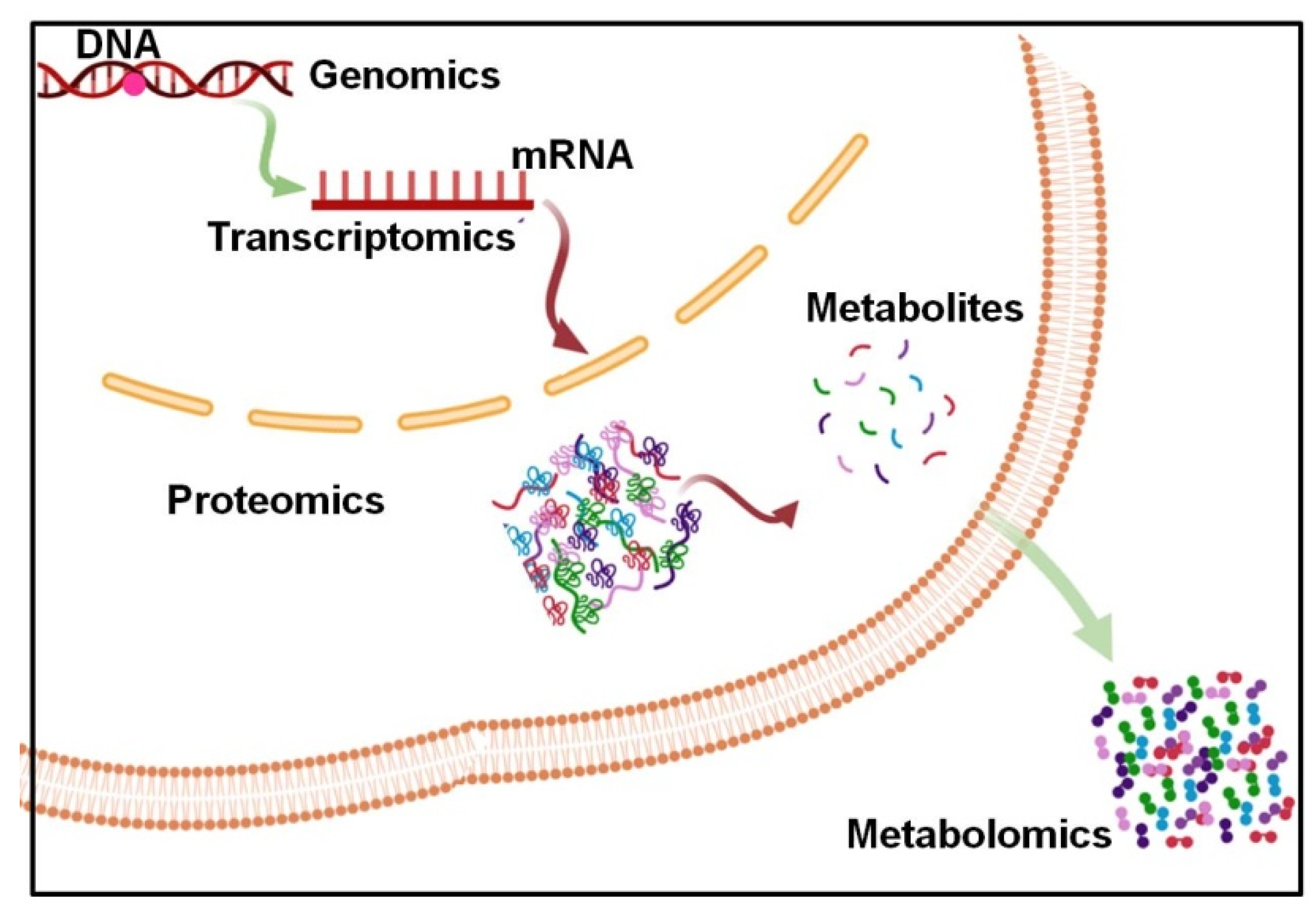
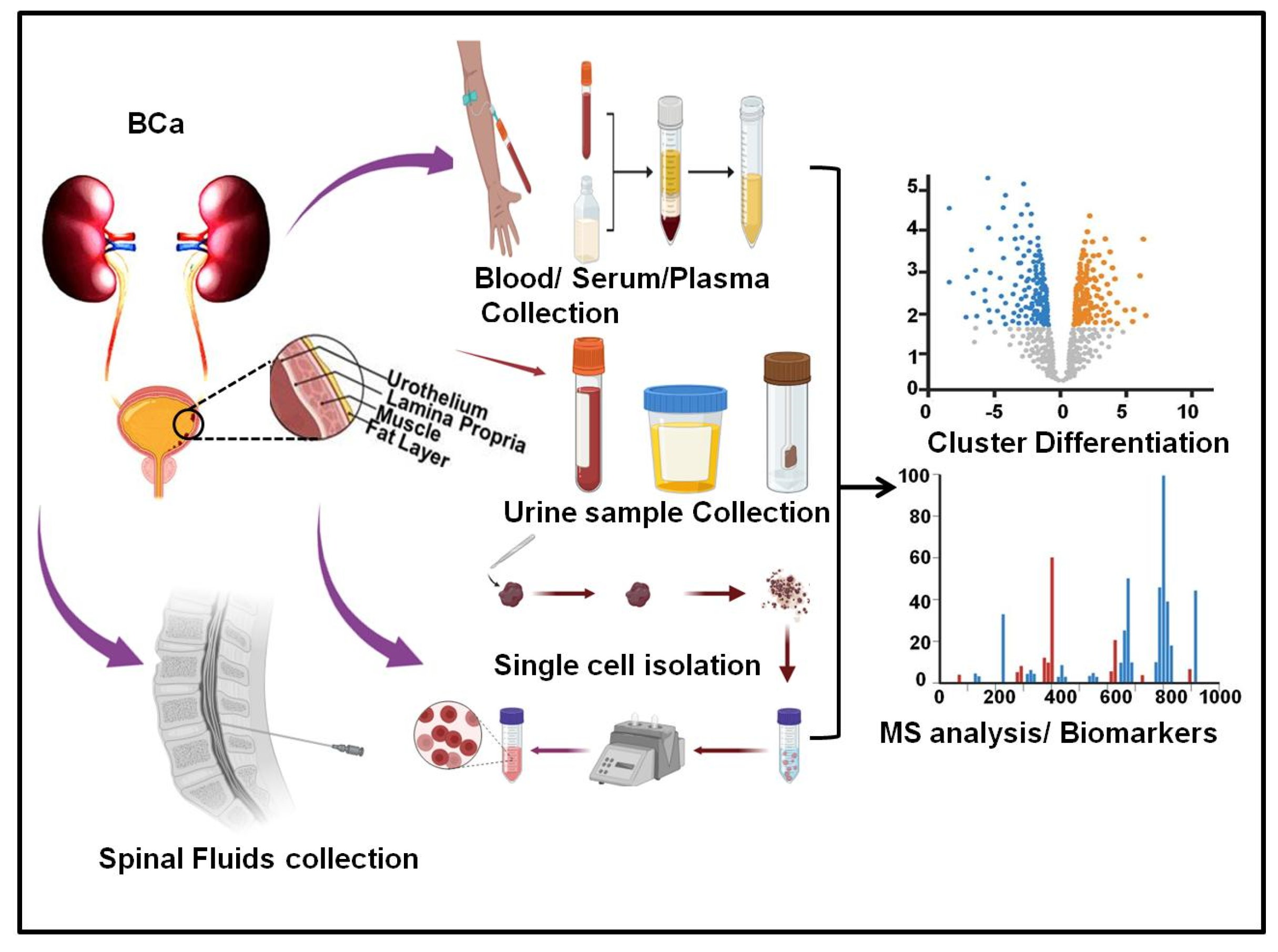
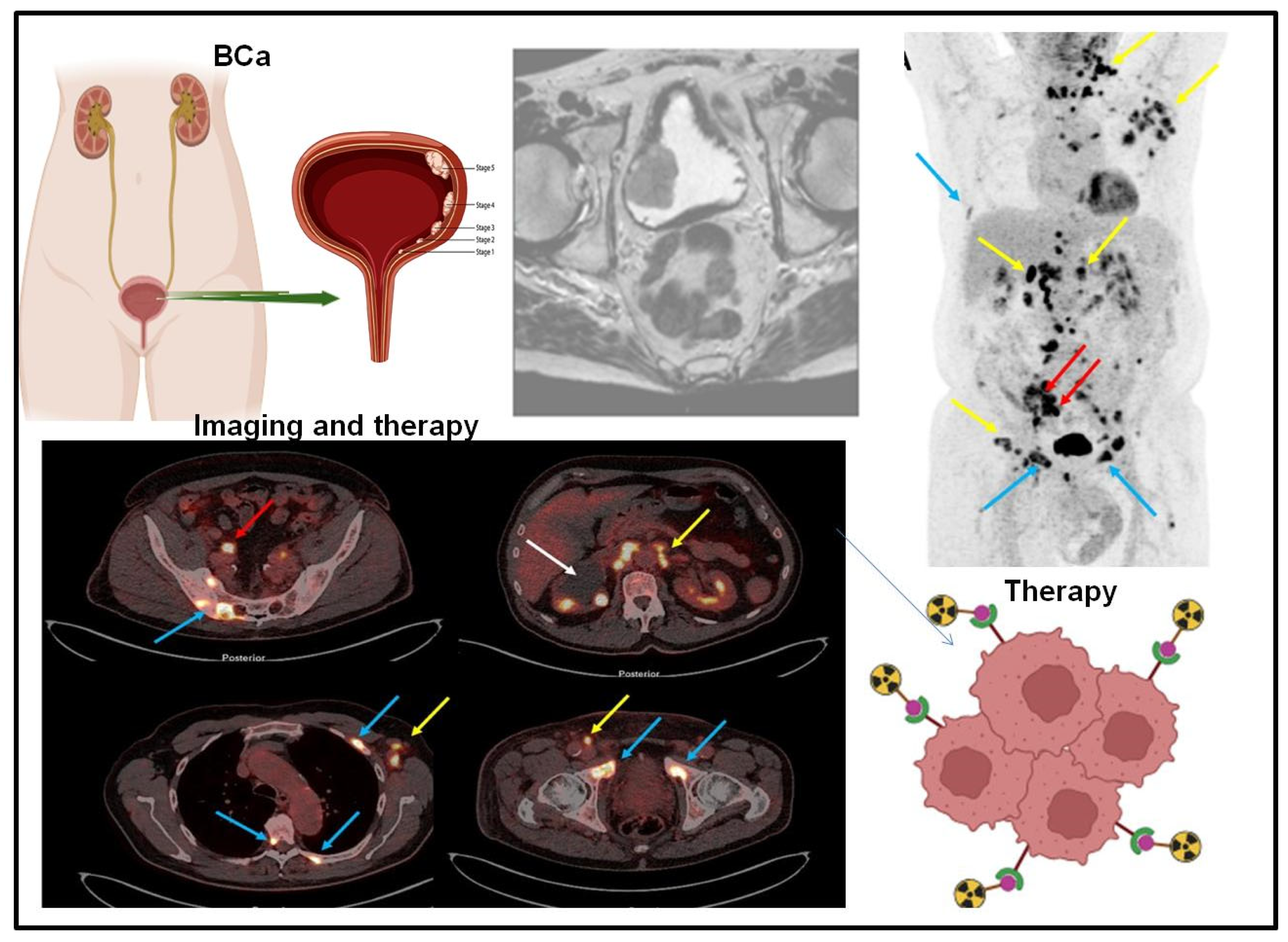
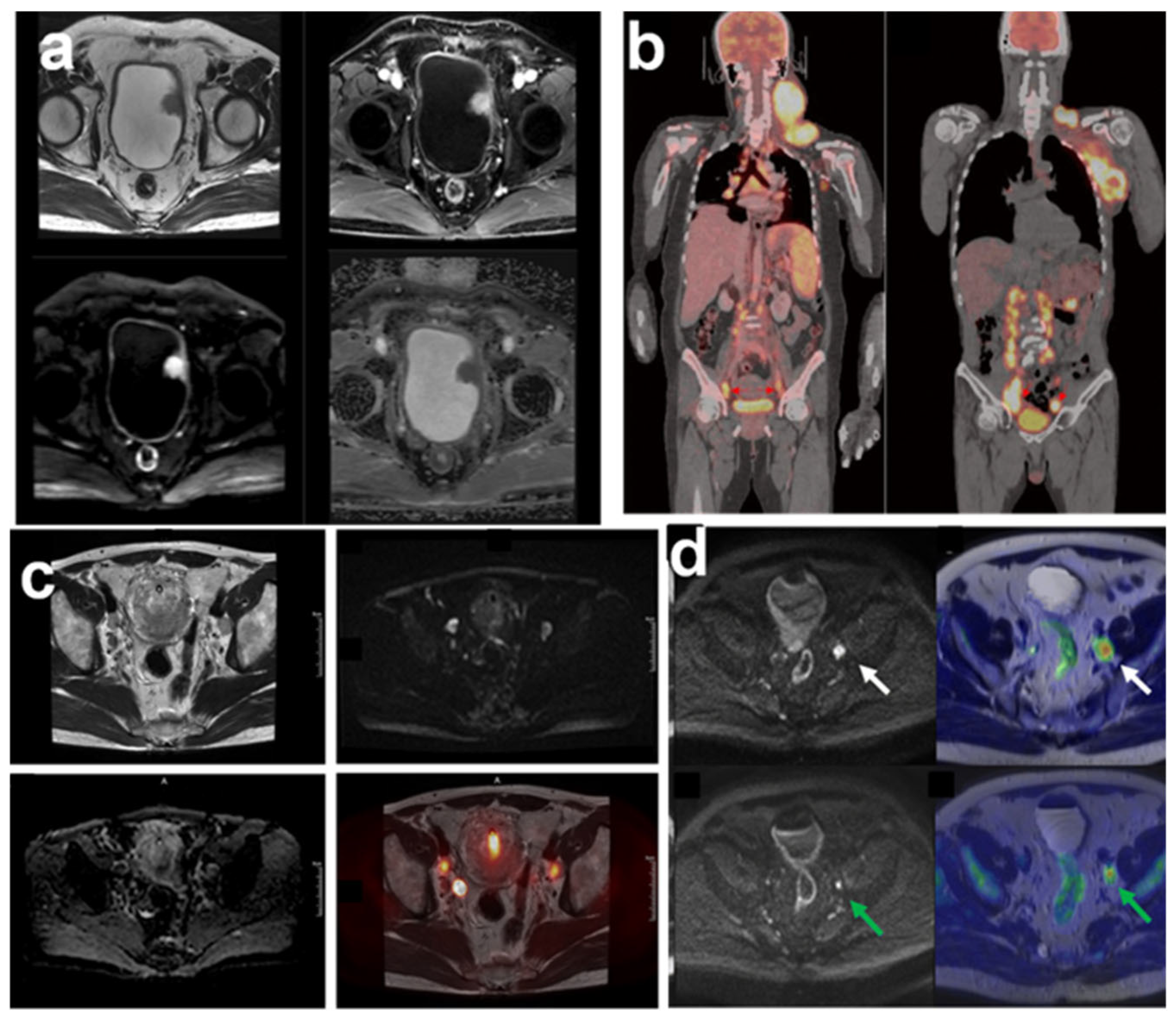
| Sample Type | Analytical Platform | Tool of Analysis | Specified Biomarkers | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum | LC MS | PCA | 16-hydroxy-10-oxohexadecanoic acid, PGF2a ethanolamide, sulfoglycolithocholate, and threoninyl-alanine | [11] |
| Serum | LC MS | MetaboAnalyst 3.0 | Taurine, glutamine, glutamate, aspartate, and serine | [13] |
| Plasma | LC MS | PCA | N6, N6-dimethlylysine, riglycerides, phosphatidylcholines, lysophosphatidylethanolamines, phosphatidylethanolamines, and organoheterocyclic compounds, but higher levels of phosphatidylethanolamine plasmalogens, phosphatidylcholine plasmalogens, cholesteryl esters, and carnitines | [36] |
| Urine | HPLC-TOF/MS and GC-QqQ/MS | Data Acquisition Reprocessor(DA Reprocessor) | Propanoic acid, creatinine l, 2-deoxy-ribonic acid, and benzenediol | [37] |
| Serum | HPLC and LC-MS/MS | TCGA and KEGG/HMDB | Urea, glycine, Aminobutyraldehyde, pyruvate, Putrescine, sarcosine, alanine, lactic acid, and 2-Hydroxypyridine betaine aldehyde. | [14] |
| Plasma | LC-MS | PCA and OPLS-DA | 3-Hydroxynonanoic acid, DOPA sulfate, Glutamyl-Threonine, and N-lactoyl-Leucine | |
| Urine | HS–SPME-GC-MS | VOC and VCC PLS-DA models b | 3-methylbutanal, benzaldehyde, 2-furaldehyde, 4-heptanone, and p-cresol | [38] |
| Urine | LDI-MS | PCA and OPLS-DA | Melamine, cyromazine and imazalil, serine, creatinine, proline, valine, Cysteine, Nicotinic acid, taurine, Citraconic acid, Allysine, N-acetylvaline (L) N-acetylthreonine, and Lauric acid | [39] |
| Urine | LC-MS | PCA and OPLS-DA | Ethylbenzene, Hexanal, Laurie aldehyde, and Nonanoyl chloride | [40] |
| Urine | LC-MS and GC MS | PLSDA | Other organic compounds | [41] |
| Type of Cancer | Sample Type | Biomarkers | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCa | Urine | Hepatocarcinoma-intestine-pancreas/pancreatitis-associated protein | [59] |
| Urine | Cytokeratin 20 | [60] | |
| Urine | CK20 | [61] | |
| Tissue | CK 8 | [62] | |
| Tissue | CK7 and CK20 | [63] | |
| Tissue | CK 5/6 | [64] | |
| Tissue | CK 5/6 &20 | [65] | |
| Bladder tumor fibronectin and CK 20 | [66] | ||
| Urine | Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and Metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) | [67] | |
| Urine | Bladder tumor antigen | [68] | |
| NMP22 | [69] | ||
| Urine | BLCA-4 nuclear matrix protein | [70] | |
| Urine | Cytokeratin 20 | [71] | |
| Urine | MCM5 | [72] | |
| Urine | MMP-9 | [73] | |
| Tissue | MMP-9 | [74] | |
| Urine | VEGFA | [75] | |
| Urine | Laminin-γ2 monomer | [76] | |
| Blood | EZH2 | [77] | |
| Urine | MCM5 protein | [78] | |
| Urine | Bladder tumor antigen | [79] | |
| Tissue | Carcinoembryonic antigen | [80] | |
| Urine | Interleukin-8 | [81] | |
| Tissue | Cyclooxygenase-2 | [82] | |
| Serum | AREG, RET, WFDC2, FGFBP1, ESM-1, and PVRL4 | [83] | |
| Urine | IL8, MMP10, MMP9, SDC1, VEGF, and CA9 | [84] | |
| Serum | Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 | [85] | |
| Urine | NMP22 | [86] | |
| Tissue | VPAC | [87] | |
| Serum | NMP22 | [88] | |
| Blood | VPAC receptor | [89] | |
| Tissue | FAP | [90] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vedarethinam, V. Advancing Bladder Cancer Biomarker Discovery: Integrating Mass Spectrometry and Molecular Imaging. Onco 2025, 5, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020013
Vedarethinam V. Advancing Bladder Cancer Biomarker Discovery: Integrating Mass Spectrometry and Molecular Imaging. Onco. 2025; 5(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleVedarethinam, Vadanasundari. 2025. "Advancing Bladder Cancer Biomarker Discovery: Integrating Mass Spectrometry and Molecular Imaging" Onco 5, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020013
APA StyleVedarethinam, V. (2025). Advancing Bladder Cancer Biomarker Discovery: Integrating Mass Spectrometry and Molecular Imaging. Onco, 5(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020013





