Spatial Correlation Network Characteristics of Comprehensive Transportation Green Efficiency in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
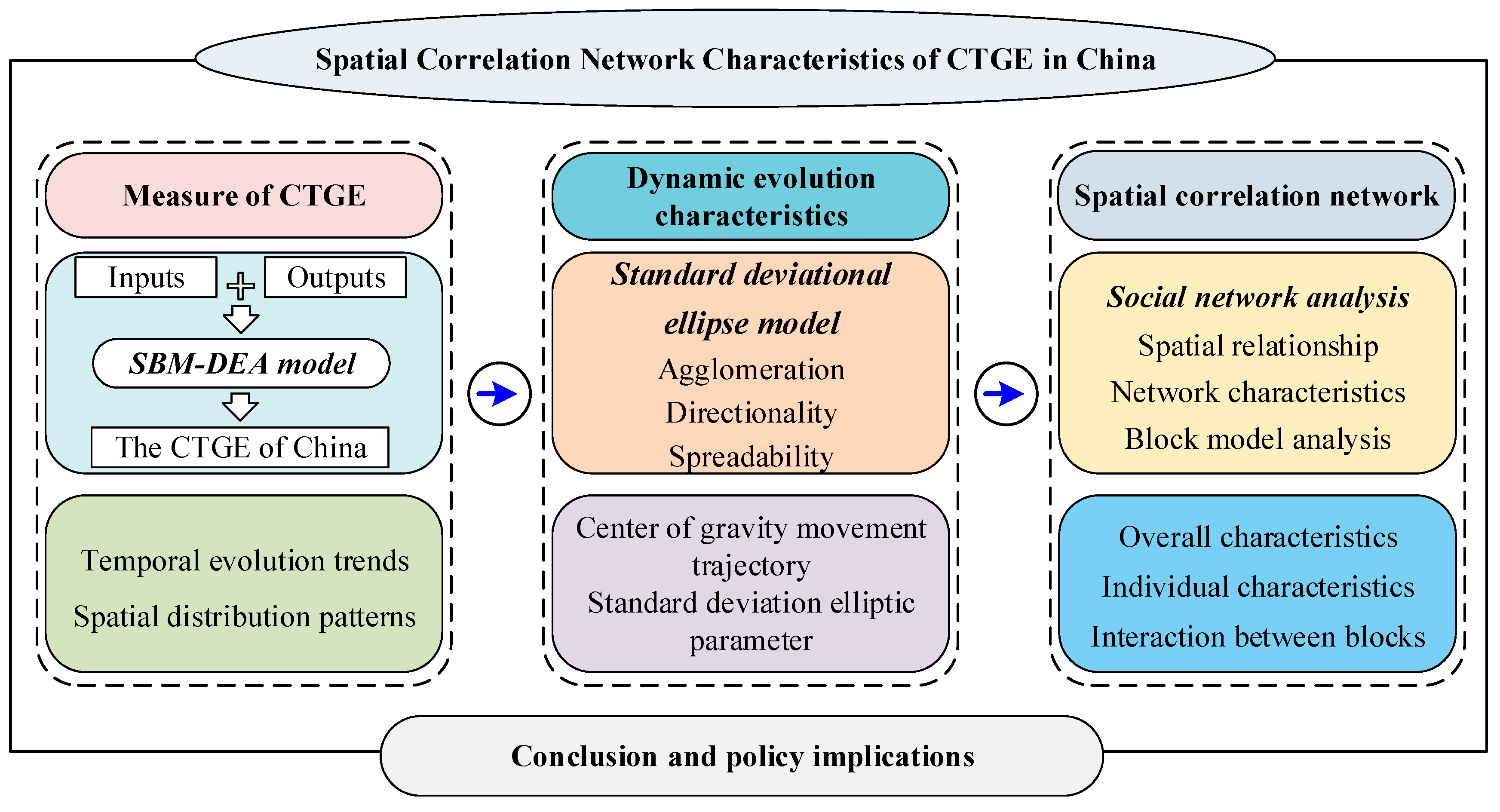
3.1. Research Framework
3.2. Model
3.2.1. SBM-DEA Model
3.2.2. Standard Deviation Elliptic Model
3.2.3. Social Network Analysis Method
3.3. Indicator Selection and Data Source
4. Results and Discussion
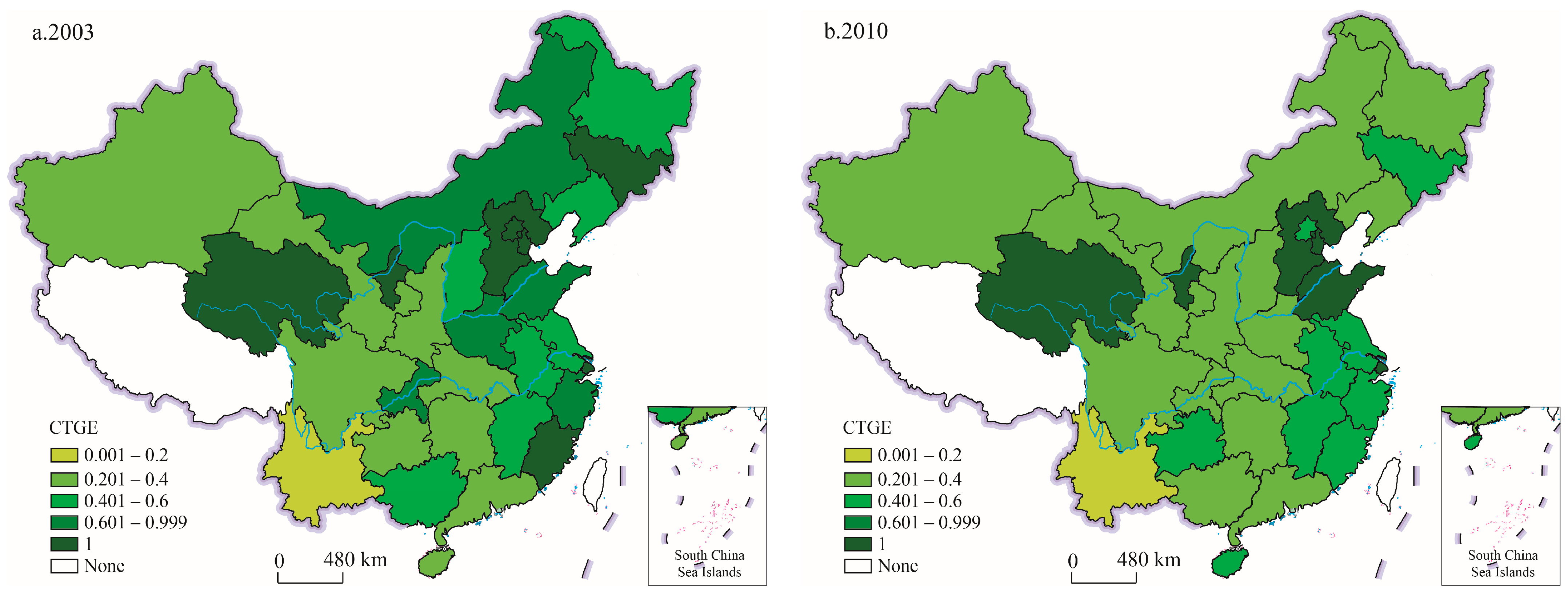
4.1. Analysis of China’s CTGE Measurement Results Based on the SBM-DEA Model
4.2. Spatiotemporal Evolution of China’s CTGE Using the SDE Model
4.2.1. Analysis of CTGE Gravity Center Transfer Route
4.2.2. Standard Deviation Ellipse Analysis of CTGE
4.3. Network Correlation Characteristics of China’s CTGE via the SNA Model
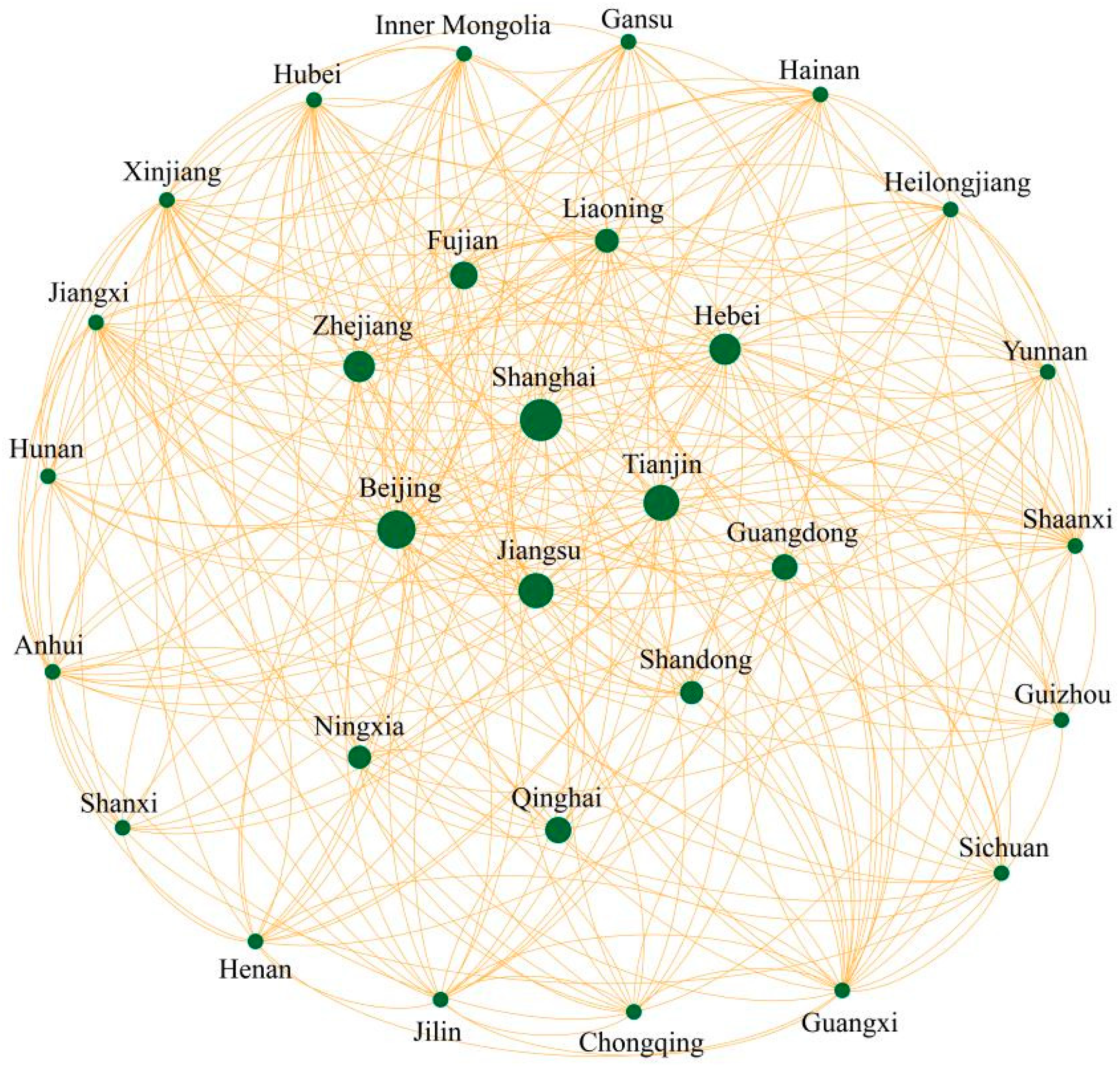
4.3.1. The Overall Features of the Network Structure
4.3.2. The Individual Features of the Network Structure
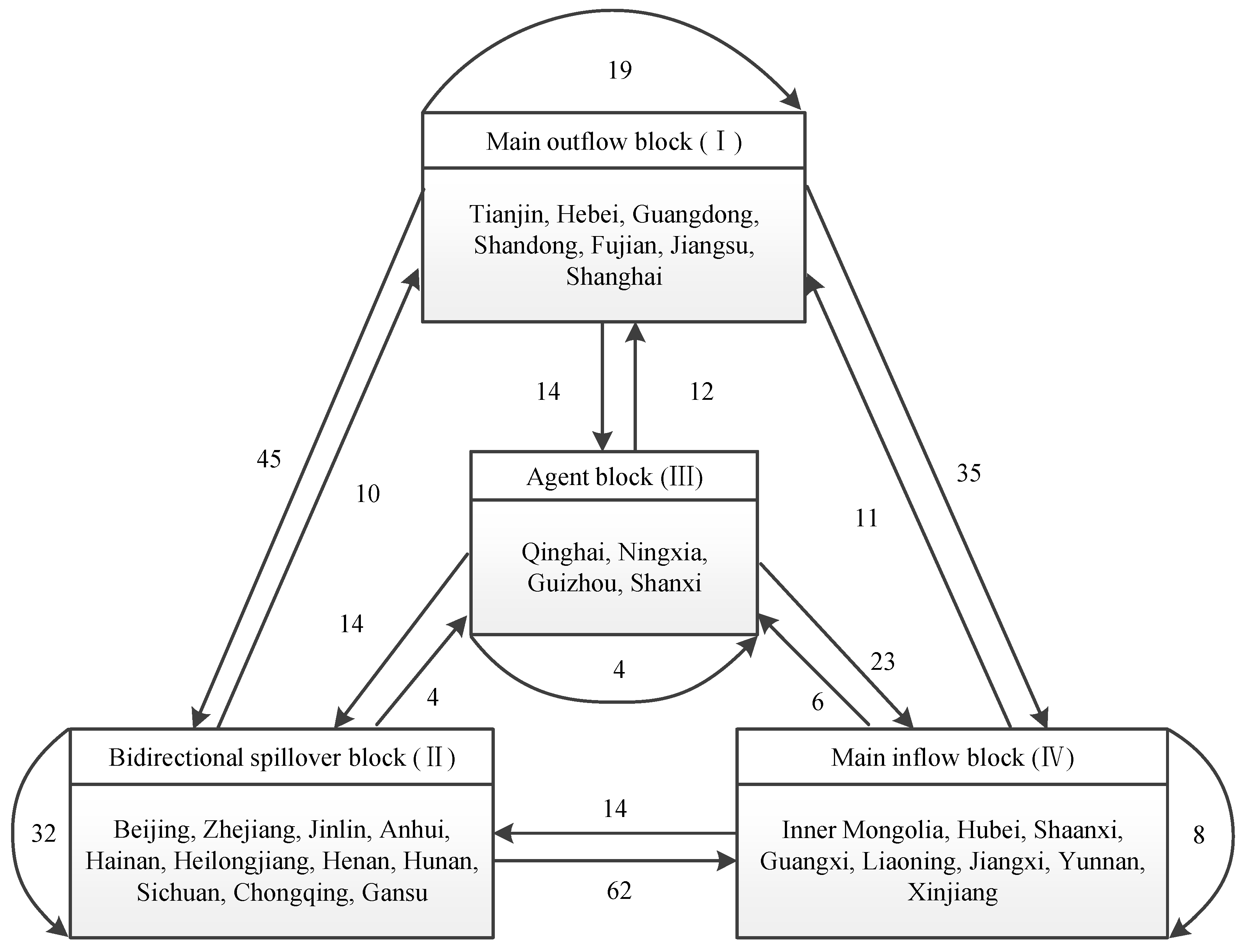
4.3.3. Block Model Analysis
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Policy Implications
5.3. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Q.F.; Jia, P.; Kuang, H.B. Green efficiency changes of comprehensive transportation in China: Technological change or technical efficiency change? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 304, 127115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Song, J.N. Research on the Improvement Path of Green Total Factor Productivity in Transportation from the Perspective of Configuration. Soft Sci. 2024, 38, 22–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Lu, X.R.; Wu, J.; Han, X. Relationship between the development and CO2 emissions of transport sector in China. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2019, 74, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandalinas, S.I.; Fritschi, F.B.; Mittler, R. Global warming, climate change, and environmental pollution: Recipe for a multifactorial stress combination disaster. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Ecological network analysis of China’s energy-related input from the supply side. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.F.; Jia, P.; Kuang, H.B. Spatial Characteristics of Comprehensive Transportation Green Efficiency in China. J. Transp. Syst. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2022, 22, 300–308. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.Y.; Shi, Z.W.; Chi, B.; Wang, J. Evaluating the Development Levels of Green Urban Transportation Systems. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.W.; Gao, B.; Zhang, J.W.; Chen, C. Measuring the Energy and Carbon Emission Efficiency of Regional Transportation Systems in China: Chance-Constrained DEA Models. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 9740704. [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar, K.K.P. Novel sustainable green transportation: A neutrosophic multi-objective model considering various factors in logistics. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2025, 46, 101096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, G.J.; Babitsky, T.T.; Brenner, M.E. Performance evaluation for bus transit. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 1985, 19, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.C.; Fielding, G.L. Comparative Analysis of Transit Performance; Final Report for the US Department of Transportation; US Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Karlaftis, M.G.; Tsamboulas, D. Efficiency measurement in public transport: Are findings specification sensitive? Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2012, 46, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H. eXplainable DEA approach for evaluating performance of public transport origin-destination pairs. Res. Transp. Econ. 2024, 108, 101491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Nakamura, F.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y. Efficiency Assessment of Transit-Oriented Development by Data Envelopment Analysis: Case Study on the Den-en Toshi Line in Japan. J. Adv. Transp. 2018, 2018, 6701484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraio, C.; Diana, M.; Costa, F.D.; Leporelli, C.; Matteucci, G.; Nastasi, A. Efficiency and effectiveness in the urban public transport sector: A critical review with directions for future research. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 248, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, W.W.; Seiford, L.M.; Tone, K. Data Envelopment Analysis, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Omrani, H.; Shafaat, K.; Alizadeh, A. Integrated data envelopment analysis and cooperative game for evaluating energy efficiency of transportation sector: A case of Iran. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 274, 471–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Lim, S.H.; Egilmez, G.; Szmerekovsky, J. Environmental Efficiency Assessment of U.S. Transport Sector: A Slack-based Data Envelopment Analysis Approach. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2016, 61, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Yang, R.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhu, Q. Measuring performance of road transportation industry in China in terms of integrated environmental efficiency in view of Streaming Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Cheng, S.Y.; Zhu, Z.T. Measuring environmental-adjusted dynamic energy efficiency of China’s transportation sector: A four-stage NDDF-DEA approach. Energy Effic. 2021, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, D.T.; Mcneil, S.; Hart, J. Comparing the Efficiency of Public Transportation Subunits Using Data Envelopment Analysis. J. Public Transp. 2007, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.W.; Xu, H.Y.; Lv, H.X. Two-Sided Matching on Comprehensive Transportation Network Emergency Vehicles’ Allocation. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 5, 6817013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.Y.; Chen, Y.Y. Identification of Key Nodes in Comprehensive Transportation Network: A Case Study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration, China. Transp. Res. Rec. 2024, 2678, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greening, L.A.; Ting, M.; Davis, W.B. Decomposition of aggregate carbon intensity for freight: Trends from 10 OECD countries for the period 1971–1993. Energy Econ. 1999, 21, 331–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Syguiy, T.; Silva, D.N.E. Efficiency and Effectiveness Analysis of Public Transport of Brazilian Cities. J. Transp. Lit. 2015, 9, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Li, Y. The Evaluation of Transportation Energy Efficiency: An Application of Three-stage Virtual Frontier DEA. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Chu, J.F.; Liu, H.; Liang, L. Measuring energy and environmental efficiency of transportation systems in China based on a parallel DEA approach. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2016, 48, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.Q.; Zhang, X.Q.; Chu, J.F.; Yang, F.; Yuan, Z. Energy and environmental efficiency of China’s transportation sectors considering CO2 emission uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 97, 102955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, W.B.; Yu, H.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.C. Spatial effect of urban morphology on land surface tempature from the perspective of local climate zone. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 36, 101324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, M.Y. Realization of high-quality development of transportation in the New Ear. China J. Highw. Transp. 2021, 34, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.F.; Jia, P.; Sun, C.Z.; Kuang, H. Dynamic evolution trend of comprehensive transportation green efficiency in China: From a spatio-temporal interaction perspective. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 477–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, R.X.; Chen, M.H.; Su, C.H.J.; Zhi, Y.; Xi, J. Effects of rural revitalization on rural tourism. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 47, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.; Roodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. Dealing with Undesirable Outputs in DEA: A Slacks-Based Measure (SBM) Approach; GRIPS Research Report Series; GRIPS: Tokyo, Japan, 2004; pp. 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lefever, D.W. Measuring Geographic Concentration by Means of the Standard Deviational Ellipse. Am. J. Sociol. 1926, 32, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, Z.; Mao, X.Q.; Cai, B.F.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Guo, Z. Exploring the spatiotemporal pattern evolution of carbon emissions and air pollution In Chinese cities. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.X.; Jiang, Z.L.; Chu, X.; Ying, J. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Evolution Characteristics of Water Traffic Accidents in Asia since the 21st Century. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Bai, S.; Li, X.; Xian, K.; Liu, E.; Ding, W.; Ma, X. A universal geography neural network for mobility flow prediction in planning scenarios. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2025, 13398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, L.M.; Fox, A.M. Using social network analysis to examine gun violence. J. Forensic Sci. 2022, 67, 2230–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-adaway, I.H.; Abotaleb, I.S.; Vechan, E. Social Network Analysis Approach for Improved Transportation Planning. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2017, 23, 05016004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, U.; Alatas, B. A new direction in social network analysis: Online social network analysis problems and applications. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 535, 122372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.H.; Qin, C.L.; Ye, X.Y. Environmental Regulation and Industrial Structure Change in China: Integrating Spatial and Social Network Analysis. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Y. Urban Signalized Intersection Traffic State Prediction: A Spatial—Temporal Graph Model Integrating the Cell Transmission Model and Transformer. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, Y. Research on Spatial Correlation Evolution of Marine Ecological Efficiency Based on Social Network and Spatial Correlation Matrix Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; He, L.W. The spatial network structure of China’s provincial economic growth: Re-examination based on nonlinear Granger causality test. J. Financ. Econ. 2016, 42, 97–107. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Huang, X.X.; Zhang, W.X.; Li, Z. Examining the characteristics and influencing factors of China’s carbon emission spatial correlation network structure. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.Q.; Zhou, L.; Xia, M.L.; Feng, C. Analysis of the spatial association network structure of China’s transportation carbon emissions and its driving factors. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Liu, P.L. Spatial correlation network of renewable energy consumption and its influencing factors: Evidence from 31 Chinese provinces. Renew. Energy 2023, 217, 119173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Zhang, G.Q. Estimation of Capital Stock and Capital Return Rate of China’s Transportation Infrastructure. Contemp. Financ. Econ. 2016, 6, 3–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Li, S.J.; JI, Q. Regional differences and driving factors analysis of carbon emission intensity from transport sector in China. Energy 2021, 224, 120178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Ma, Q.F. Carbon quota allocation and emission reduction responsibility sharing at provincial level in China from transport industry. Sustain. Futures 2025, 9, 100535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.T. Urbanization under globalization: How does the Belt and Road Initiative affect urbanization levels in participating countries. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 2170–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.W.; Zhang, R.R.; Zhang, D.H.; Zhou, C. Urban Agglomerations in China: Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Population Agglomeration. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Kumar, V. Introduction to Intelligent Transportation System and Advanced Technology. In Energy, Environment, and Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Perspective | Primary Index | Secondary Index | Units | Obs | Mean | Std.Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inputs | Infrastructure | Total mileage of transportation network | 10,000 km | 540 | 13.586 | 8.028 | 0.9 | 41.056 |
| Capital | Capital stock of transportation industry | 100 million | 540 | 4488.417 | 4520.664 | 169.387 | 26,590.23 | |
| Labor force | Transportation industry employees | person | 540 | 244,801.8 | 14,604.5 | 32,225 | 83,1000 | |
| Energy consumption | Energy consumption of transportation industry | 10,000 tons of standard coal | 540 | 919.1 | 646.937 | 27.054 | 3720.54 | |
| Outputs | Expect outputs | Added value of transportation industry | 100 million | 540 | 865.613 | 757.154 | 27.64 | 4189.02 |
| Social development index | -- | 540 | 0.438 | 0.101 | 0.227 | 0.715 | ||
| Undesired output | CO2 emission from transportation industry | 10,000 tons | 540 | 1850.498 | 1304.055 | 60.910 | 6974.148 |
| Regions | 2003 | 2005 | 2007 | 2009 | 2011 | 2013 | 2015 | 2017 | 2020 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.562 | 0.494 | 0.547 | 0.558 | 0.814 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.774 |
| Tianjin | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Hebei | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Shanxi | 0.590 | 0.618 | 0.704 | 0.401 | 0.362 | 0.373 | 0.415 | 0.464 | 1.000 | 0.565 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.643 | 0.399 | 0.394 | 0.425 | 0.361 | 0.430 | 0.453 | 0.394 | 0.466 | 0.444 |
| Liaoning | 0.447 | 0.372 | 0.331 | 0.344 | 0.368 | 0.424 | 0.505 | 0.537 | 0.541 | 0.439 |
| Jilin | 1.000 | 0.559 | 0.458 | 0.448 | 0.423 | 0.447 | 0.439 | 0.448 | 0.453 | 0.514 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.447 | 0.444 | 0.411 | 0.388 | 0.306 | 0.307 | 0.357 | 0.362 | 0.354 | 0.379 |
| Shanghai | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Jiangsu | 0.429 | 0.442 | 0.445 | 0.486 | 0.530 | 0.665 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.693 |
| Zhejiang | 0.729 | 0.456 | 0.458 | 0.410 | 0.412 | 0.435 | 0.457 | 0.477 | 0.492 | 0.476 |
| Anhui | 0.551 | 0.658 | 0.443 | 0.461 | 0.380 | 0.356 | 0.373 | 0.352 | 0.356 | 0.433 |
| Fujian | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.556 | 0.475 | 0.547 | 0.560 | 0.643 | 0.659 | 0.698 |
| Jiangxi | 0.436 | 0.527 | 0.494 | 0.459 | 0.419 | 0.484 | 0.466 | 0.527 | 0.638 | 0.508 |
| Shandong | 0.636 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.527 | 0.577 | 0.558 | 0.457 | 0.782 |
| Henan | 0.677 | 0.681 | 0.522 | 0.381 | 0.300 | 0.351 | 0.442 | 0.501 | 0.392 | 0.466 |
| Hubei | 0.299 | 0.245 | 0.241 | 0.253 | 0.254 | 0.284 | 0.294 | 0.277 | 0.268 | 0.269 |
| Hunan | 0.371 | 0.352 | 0.372 | 0.365 | 0.296 | 0.329 | 0.329 | 0.355 | 0.338 | 0.349 |
| Guangdong | 0.368 | 0.300 | 0.308 | 0.301 | 0.289 | 0.303 | 0.389 | 0.551 | 0.355 | 0.358 |
| Guangxi | 0.403 | 0.343 | 0.310 | 0.342 | 0.353 | 0.403 | 0.399 | 0.398 | 0.421 | 0.376 |
| Hainan | 0.686 | 1.000 | 0.764 | 1.000 | 0.587 | 0.637 | 0.594 | 0.591 | 0.570 | 0.687 |
| Chongqing | 0.650 | 0.474 | 0.392 | 0.405 | 0.344 | 0.349 | 0.351 | 0.358 | 0.357 | 0.399 |
| Sichuan | 0.289 | 0.326 | 0.299 | 0.227 | 0.228 | 0.260 | 0.275 | 0.238 | 0.251 | 0.266 |
| Guizhou | 0.341 | 0.434 | 0.521 | 0.502 | 0.456 | 0.553 | 0.581 | 0.572 | 1.000 | 0.560 |
| Yunnan | 0.186 | 0.185 | 0.199 | 0.159 | 0.140 | 0.160 | 0.164 | 0.165 | 0.158 | 0.177 |
| Shaanxi | 0.373 | 0.360 | 0.337 | 0.308 | 0.291 | 0.336 | 0.366 | 0.402 | 0.392 | 0.357 |
| Gansu | 0.398 | 0.412 | 0.425 | 0.424 | 0.426 | 0.329 | 0.322 | 0.303 | 0.294 | 0.374 |
| Qinghai | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.498 | 0.448 | 0.882 |
| Ningxia | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Xinjiang | 0.346 | 0.313 | 0.307 | 0.307 | 0.269 | 0.293 | 0.351 | 0.385 | 0.369 | 0.336 |
| Eastern | 0.754 | 0.779 | 0.715 | 0.670 | 0.655 | 0.685 | 0.718 | 0.760 | 0.754 | 0.722 |
| Central | 0.546 | 0.510 | 0.456 | 0.394 | 0.342 | 0.366 | 0.389 | 0.411 | 0.475 | 0.434 |
| Western | 0.512 | 0.477 | 0.471 | 0.464 | 0.442 | 0.465 | 0.478 | 0.489 | 0.489 | 0.478 |
| National | 0.610 | 0.597 | 0.557 | 0.528 | 0.494 | 0.505 | 0.542 | 0.565 | 0.568 | 0.555 |
| Year | Barycentric Coordinates | Moving Direction | Moving Distance (km) | East–West Distance (km) | North–South Distance (km) | Moving Speed (km/a) | East–West Speed (km/a) | North–South Speed (km/a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 113.27° E, 34.62° N | |||||||
| 2010 | 112.71° E, 34.45° N | S-W 16.842° | 64.87 | 62.09 | 18.80 | 12.97 | 12.42 | 3.76 |
| 2015 | 112.59° E, 34.25° N | S-W 59.602° | 25.82 | 13.07 | 22.27 | 5.16 | 2.61 | 4.45 |
| 2020 | 113.47° E, 34.31° N | N-E 4.123° | 97.82 | 97.57 | 7.03 | 19.56 | 19.51 | 1.41 |
| Year | Rotation θ/° | Area/10,000 km2 | XStdDist/km | YStdDist/km | Oblateness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 21.54 | 347.930 | 988.112 | 1120.876 | 0.882 |
| 2010 | 24.05 | 334.411 | 993.280 | 1074.925 | 0.924 |
| 2015 | 24.56 | 351.987 | 1016.878 | 1101.871 | 0.923 |
| 2020 | 13.38 | 308.151 | 928.858 | 1056.056 | 0.880 |
| Regions | Degree Centrality | Closeness Centrality | Betweenness Centrality | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Out-Degree | In-Degree | Degree | Ranking | Closeness | Ranking | Betweenness | Ranking | |
| Beijing | 20 | 18 | 68.966 | 2 | 74.359 | 2 | 17.891 | 1 |
| Tianjin | 19 | 3 | 65.517 | 4 | 70.732 | 4 | 1.156 | 20 |
| Hebei | 20 | 3 | 68.966 | 3 | 74.359 | 3 | 1.616 | 15 |
| Shanxi | 6 | 7 | 20.690 | 24 | 47.541 | 25 | 0.556 | 26 |
| Inner Mongolia | 6 | 15 | 20.690 | 25 | 50.000 | 23 | 2.983 | 14 |
| Liaoning | 8 | 22 | 27.586 | 17 | 52.727 | 18 | 3.482 | 10 |
| Jilin | 10 | 8 | 34.483 | 12 | 54.717 | 16 | 0.896 | 23 |
| Heilongjiang | 9 | 7 | 31.034 | 15 | 54.717 | 14 | 0.319 | 30 |
| Shanghai | 21 | 1 | 72.414 | 1 | 76.316 | 1 | 3.473 | 11 |
| Jiangsu | 17 | 2 | 58.621 | 5 | 67.442 | 5 | 4.394 | 6 |
| Zhejiang | 15 | 10 | 51.724 | 6 | 61.702 | 7 | 5.865 | 4 |
| Anhui | 10 | 12 | 34.483 | 13 | 54.717 | 15 | 1.553 | 16 |
| Fujian | 14 | 3 | 48.276 | 7 | 59.184 | 9 | 0.935 | 22 |
| Jiangxi | 5 | 20 | 17.241 | 27 | 43.284 | 29 | 4.205 | 7 |
| Shandong | 13 | 2 | 44.828 | 8 | 63.043 | 6 | 0.621 | 25 |
| Henan | 8 | 10 | 27.586 | 18 | 51.786 | 20 | 8.157 | 2 |
| Hubei | 7 | 20 | 24.138 | 20 | 50.877 | 21 | 6.572 | 3 |
| Hunan | 6 | 8 | 20.690 | 23 | 48.333 | 24 | 3.742 | 8 |
| Guangdong | 12 | 6 | 41.379 | 9 | 56.769 | 12 | 2.998 | 13 |
| Guangxi | 8 | 21 | 27.586 | 19 | 53.704 | 17 | 0.320 | 29 |
| Hainan | 11 | 14 | 37.931 | 10 | 59.184 | 10 | 3.687 | 9 |
| Chongqing | 10 | 7 | 34.483 | 14 | 52.727 | 19 | 3.334 | 12 |
| Sichuan | 11 | 6 | 37.931 | 11 | 58.000 | 11 | 1.343 | 17 |
| Guizhou | 7 | 7 | 24.138 | 21 | 46.774 | 26 | 0.951 | 21 |
| Yunnan | 5 | 13 | 17.241 | 28 | 56.769 | 13 | 1.331 | 18 |
| Shaanxi | 7 | 22 | 24.138 | 22 | 50.877 | 22 | 4.742 | 5 |
| Gansu | 9 | 8 | 31.034 | 16 | 60.417 | 8 | 1.241 | 19 |
| Qinghai | 6 | 5 | 20.690 | 26 | 46.032 | 27 | 0.385 | 27 |
| Ningxia | 5 | 6 | 17.241 | 29 | 43.284 | 30 | 0.876 | 24 |
| Xinjiang | 4 | 23 | 13.793 | 30 | 44.615 | 28 | 0.364 | 28 |
| Average value | 10.3 | 10.3 | 35.517 | - | 56.099 | - | 2.951 | - |
| Block | Accept Relationship Matrix | Receive Relationship | Spillover Relationship | Expected Internal Relationship Ratio/% | Actual Internal Relationship Ration/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) | Inside the Block | Outside the Block | Inside the Block | Outside the Block | |||
| (I) | 19 | 45 | 14 | 35 | 19 | 33 | 19 | 94 | 20.68 | 16.81 |
| (II) | 10 | 32 | 4 | 62 | 32 | 73 | 32 | 76 | 34.48 | 29.63 |
| (III) | 12 | 14 | 4 | 23 | 4 | 24 | 4 | 49 | 10.34 | 7.55 |
| (IV) | 11 | 14 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 120 | 8 | 31 | 24.13 | 20.51 |
| Block | Density Matrix | Image Matrix | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) | (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) | |
| (I) | 0.392 | 0.228 | 0.593 | 0.852 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| (II) | 0.393 | 0.435 | 0.311 | 0.861 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| (III) | 0.222 | 0.056 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| (IV) | 0.204 | 0.194 | 0.333 | 0.267 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z. Spatial Correlation Network Characteristics of Comprehensive Transportation Green Efficiency in China. Future Transp. 2025, 5, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp5020040
Ma Q, Li S, Zhang Z. Spatial Correlation Network Characteristics of Comprehensive Transportation Green Efficiency in China. Future Transportation. 2025; 5(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp5020040
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Qifei, Sujuan Li, and Zhenchao Zhang. 2025. "Spatial Correlation Network Characteristics of Comprehensive Transportation Green Efficiency in China" Future Transportation 5, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp5020040
APA StyleMa, Q., Li, S., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Spatial Correlation Network Characteristics of Comprehensive Transportation Green Efficiency in China. Future Transportation, 5(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp5020040





