Spatial Variation of Tetracycline-Resistant E. coli and Relationships with Water Quality Variables in Irrigation Water: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
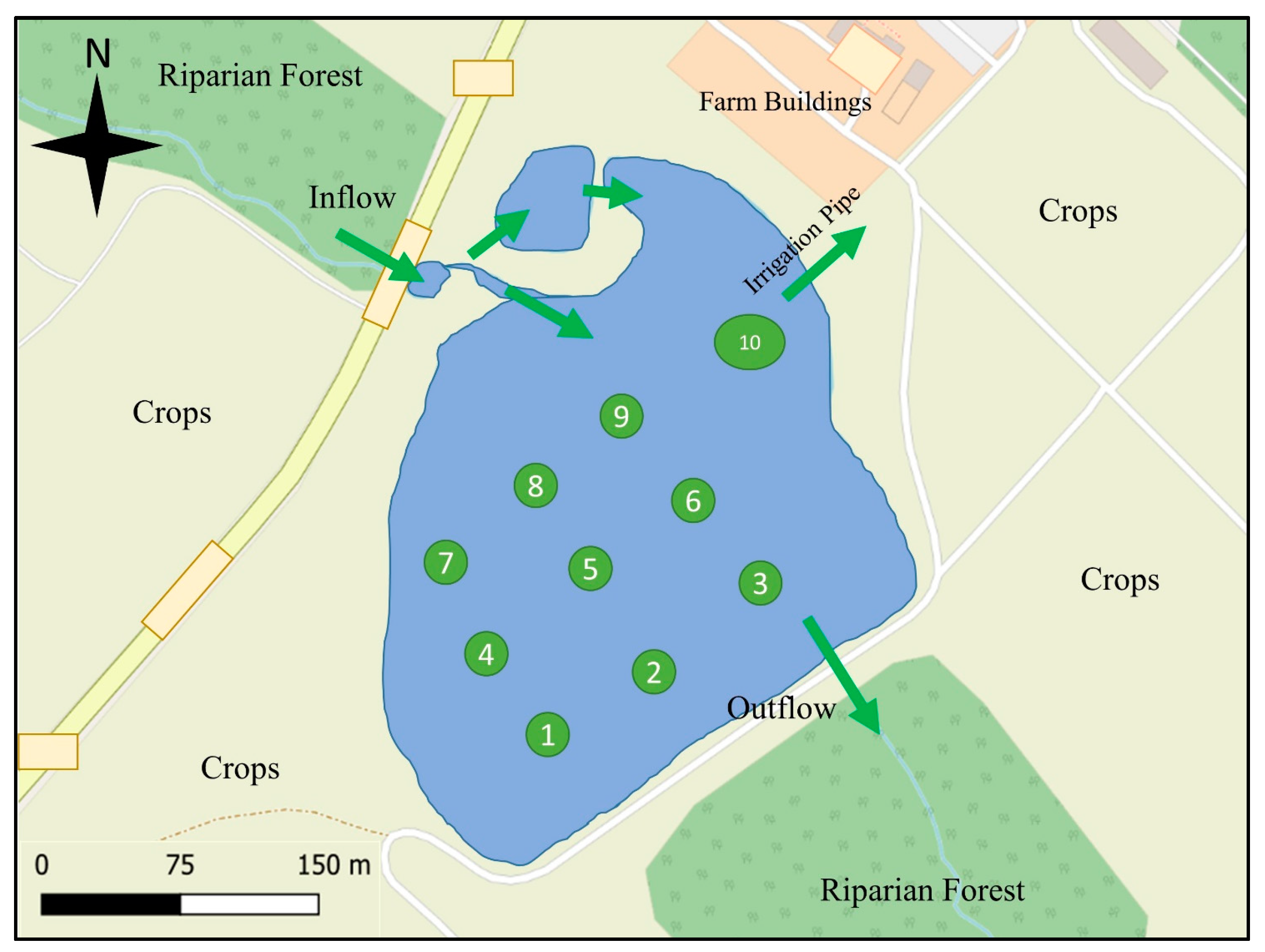
2. Materials and Methods
Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Variation of E. coli Concentrations across the Observation Period
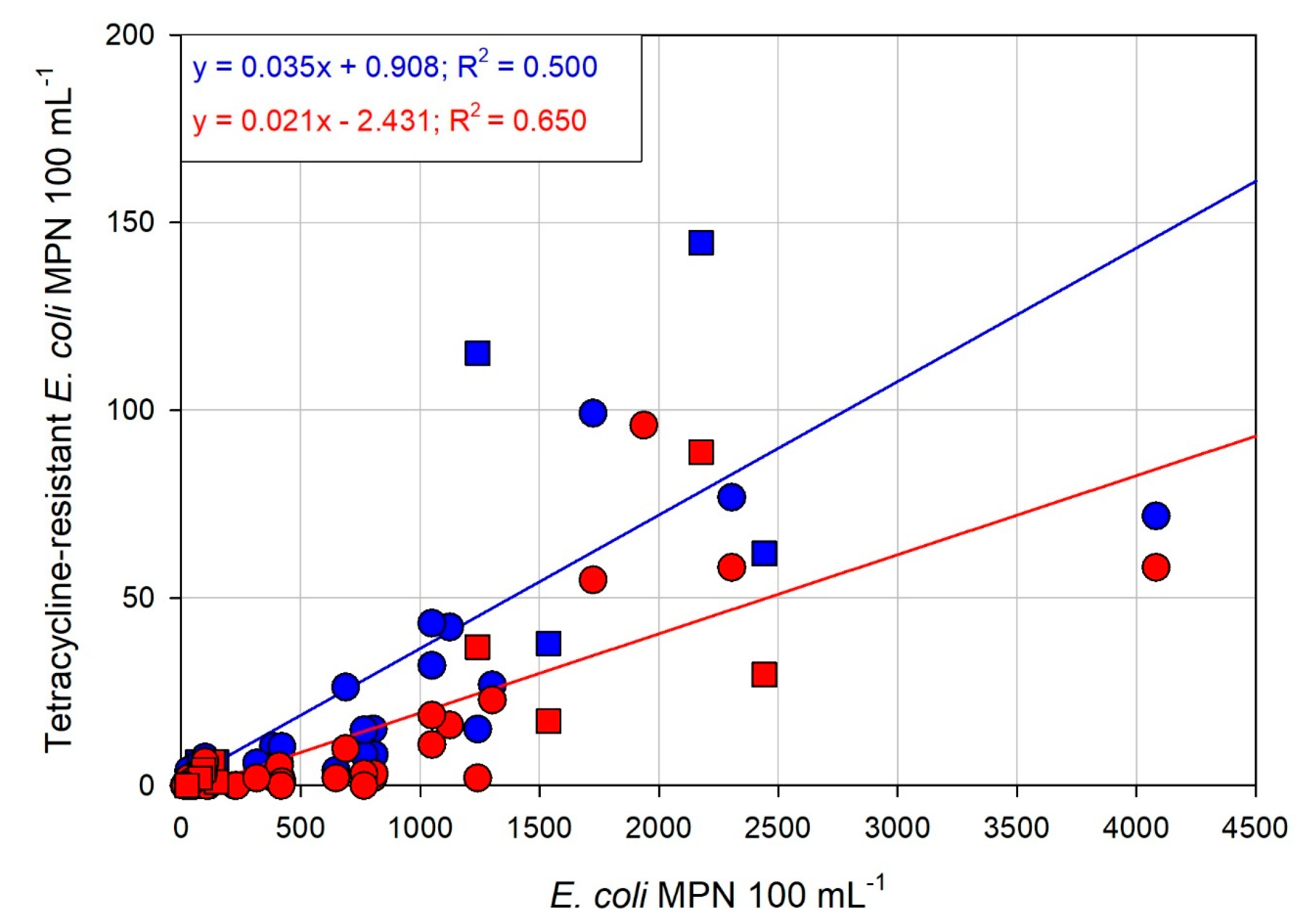
3.2. Dynamics of Tetracycline-Resistant E. coli
3.3. Relationships between Water Quality Variables and Percentage of Tetracycline-Resistant E. coli
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larsson, D.J.; Flach, C.F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gekenidis, M.T.; Qi, W.; Hummerjohann, J.; Zbinden, R.; Walsh, F.; Drissner, D. Antibiotic-resistant indicator bacteria in irrigation water: High prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Integrated Global Surveillance on ESBL-Producing E. coli Using a “One Health” Approach: Implementation and Opportunities. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240021402 (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Liguori, K.; Keenum, I.; Davis, B.C.; Calarco, J.; Milligan, E.; Harwood, V.J.; Pruden, A. Antimicrobial resistance monitoring of water environments: A framework for standardized methods and quality control. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9149–9160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachepsky, Y.A.; Allende, A.; Boithias, L.; Cho, K.; Jamieson, R.; Hofstra, N.; Molina, M. Microbial water quality: Monitoring and modeling. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaker, M.; Spanogiannopoulos, P.; Wright, G.D. The tetracycline resistome. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC); European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Medicines Agency (EMA). ECDC/EFSA/EMA second joint report on the integrated analysis of the consumption of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from humans and food-producing animals: Joint Interagency Antimicrobial Consumption and Resistance Analysis (JIACRA) Report. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04872. [Google Scholar]
- Berglund, F.; Böhm, M.E.; Martinsson, A.; Ebmeyer, S.; Österlund, T.; Johnning, A.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Kristiansson, E. Comprehensive screening of genomic and metagenomic data reveals a large diversity of tetracycline resistance genes. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, e000455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, I.; Rozanah, U.N.; Nishiyama, M.; Mith, H.; Watanabe, T. Detection and genetic analysis of Escherichia coli from Tonle Sap Lake and its tributaries in Cambodia: Spatial distribution, seasonal variation, pathogenicity, and antimicrobial resistance. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.; Mao, D.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Y. Conjugative multi-resistant plasmids in Haihe River and their impacts on the abundance and spatial distribution of antibiotic resistance genes. Water Res. 2017, 111, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Hashimoto, R.; Xie, H.; Nishimura, E.; Nishiyama, M.; Nukazawa, K.; Ishii, S. Growth and antibiotic resistance acquisition of Escherichia coli in a river that receives treated sewage effluent. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, J.A.; Aslan, A.; Cohen, R.A. Land Use and Environmental Variables Influence Tetracycline-Resistant Bacteria Occurrence in Southeastern Coastal Plain Streams. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungan, R.S.; Bjorneberg, D.L. Antimicrobial resistance in escherichia coli and enterococcal isolates from irrigation return flows in a high-desert watershed. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 660697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H.; Nagahashi, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Hirano, R. Screening Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli in Wastewater and River Water Using a Novel Simple Phenotypic Antibiotic-Susceptibility Testing Method. ACS EST Water 2022, 2, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Guo, C.; Gu, J.; Hou, J. Characterization of Antibiotic-Resistance Genes in Antibiotic Resistance Escherichia coli Isolates From a Lake. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 65, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.C.; Xi, J.Y.; Li, G.Q.; Shi, X.J.; Hu, H.Y. Prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in a lake for the storage of reclaimed water before and after usage as cooling water. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Vellidis, G.; Liu, H.; Jay-Russell, M.; Zhao, S.; Hu, Z.; Wright, A.; Elkins, C.A. Diversity and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica isolates from surface water in southeastern United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6355–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, D.E.; Miranda, O.A.; McCarley, A.; Eshaghian, M.; Carlson, N.; Ruiz, C. Prevalence and characterization of carbapenem-resistant bacteria in water bodies in the Los Angeles–Southern California area. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, C.X.; Hübner, U.; Fajnorova, S.; Schwartz, T.; Drewes, J.E. Antibiotic microbial resistance (AMR) removal efficiencies by conventional and advanced wastewater treatment processes: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craddock, H.A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Rjoub, Y.; Rosen, D.; Greif, J.; Lipchin, C.; Mongodin, E.F.; Sapkota, A.R. Antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. in greywater reuse systems and pond water used for agricultural irrigation in the West Bank, Palestinian Territories. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nnadozie, C.F.; Odume, O.N. Freshwater environments as reservoirs of antibiotic resistant bacteria and their role in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Agüera, A.; Bayona, J.M.; Cytryn, E.; Fotopoulos, V.; Lambropoulou, D.; Manaia, C.M.; Michael, C.; Revitt, M.; Schröder, P.; et al. The potential implications of reclaimed wastewater reuse for irrigation on the agricultural environment: The knowns and unknowns of the fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistant bacteria and resistance genes—A review. Water Res. 2017, 123, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.; Dasí, D.; González, A.; Ferrús, M.A.; Castillo, M.Á. Occurrence of antibiotic resistant bacteria and resistance genes in agricultural irrigation waters from Valencia city (Spain). Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, S.; Boyle, F.; Hickey, P.; Vellinga, A.; Morris, D.; Cormican, M. Enumeration and characterization of antimicrobial-resistant Escherichia coli bacteria in effluent from municipal, hospital, and secondary treatment facility sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4772–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, M.P.; Lewis, J.S.; Bobenchik, A.M.; Campeau, S.; Cullen, S.K.; Galas, M.F.; Gold, H.; Humphries, R.M.; Kirn, T.J.; Limbago, B.; et al. M100 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing A CLSI Supplement for Global Application. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Sci. Rep. 2020. Available online: https://www.nih.org.pk/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/CLSI-2020.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Hothorn, T.; Hornik, K.; Zeileis, A. Unbiased recursive partitioning: A conditional inference framework. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2006, 15, 651–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Hothorn, T.; Seibold, H.; Zeileis, A. Package ‘Partykit’ a Toolkit for Recursive Partitioning v1.2-20. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/partykit/index.html (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Steele, M.; Mahdi, A.; Odumeru, J. Microbial assessment of irrigation water used for production of fruit and vegetables in Ontario, Canada. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, C.S.; Tertuliano, M.; Rajeev, S.; Vellidis, G.; Levy, K. Impact of storm runoff on Salmonella and Escherichia coli prevalence in irrigation ponds of fresh produce farms in southern Georgia. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.D.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Smith, J.; Morgan, B.; Hill, R.L.; Kim, M.S. Persistent Patterns of E. coli Concentrations in Two Irrigation Ponds from 3 Years of Monitoring. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeki, S. A preliminary evaluation of microbial water quality in the irrigation pond. Water Environ. Res. 2022, 94, e10757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, C.M.; Coote, B.G.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Stevenson, I.M. Relationships between indicators, pathogens and water quality in an estuarine system. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2045–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.H.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Kim, J.H.; Guber, A.K.; Shelton, D.R.; Rowland, R. Release of Escherichia coli from the bottom sediment in a first-order creek: Experiment and reach-specific modeling. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Rodriguez, T.M.; Tremblay, R.L.; Toledo-Hernandez, C.; Gonzalez-Nieves, J.E.; Ryu, H.; Santo Domingo, J.W.; Toranzos, G.A. 2012. Microbial quality of tropical inland waters and effects of rainfall events. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5160–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEgan, R.; Mootian, G.; Goodridge, L.D.; Schaffner, D.W.; Danyluk, M.D. Predicting Salmonella populations from biological, chemical, and physical indicators in Florida surface waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4094–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, B.W.; Porter, L.; Webb, A.; Thomas, J. Seasonal influence of environmental variables and artificial aeration on Escherichia coli in small urban lakes. J. Water Health 2016, 14, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antaki, E.M.; Vellidis, G.; Harris, C.; Aminabadi, P.; Levy, K.; Jay-Russell, M.T. Low concentration of Salmonella enterica and generic Escherichia coli in farm ponds and irrigation distribution systems used for mixed produce production in southern Georgia. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalcengiz, Z.; Strawn, L.K.; Danyluk, M.D. Microbial quality of agricultural water in Central Florida. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, A.D.; Doores, S.; Gourama, H.; Laborde, L.F. Microbial Survey of Pennsylvania Surface Water Used for Irrigating Produce Crops. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Tertuliano, M.; Vellidis, G.; Harris, C.; Grossman, M.K.; Rajeev, S.; Levy, K. Evaluation of grower-friendly, science-based sampling approaches for the detection of Salmonella in ponds used for irrigation of fresh produce. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.D.; Smith, J.E.; Pachepsky, Y.A. Depth-Dependent Concentrations of E. coli in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds. Water 2022, 14, 2276. [Google Scholar]
- Brissaud, F.; Tournoud, M.G.; Drakides, C.; Lazarova, V. Mixing and its impact on faecal coliform removal in a stabilisation pond. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Valeo, C.; Chu, A. Variation in water quality of a stormwater pond from diurnal thermal stratification. J. Water Resour. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 4, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Luo, Z.; Cevallos-Cevallos, J.M.; Adams, P.; Vellidis, G.; Wright, A.; van Bruggen, A.H. Occurrence and population density of Campylobacter jejuni in irrigation ponds on produce farms in the Suwannee River Watershed. Can. J. Microbiol. 2013, 59, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, M.B.; Endale, D.M.; Fisher, D.S.; Adams, M.P.; Lowrance, R.; Newton, G.L.; Vellidis, G. Survival dynamics of fecal bacteria in ponds in agricultural watersheds of the Piedmont and Coastal Plain of Georgia. Water Res. 2012, 46, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenca, R.; Garcia, L.; Espinosa, C.; Flor, D.; Mohanty, S.K. Can water composition and weather factors predict fecal indicator bacteria removal in retention ponds in variable weather conditions? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarbøvik, E.; Perović, A.; Shumka, S.; Nagothu, U.S. Nutrient inputs, trophic status and water management challenges in the transboundary Lake Skadar/Shkodra, Western Balkans. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2014, 66, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallin, M.A.; McIver, M.R.; Wambach, E.J.; Robuck, A.R. Algal blooms, circulators, waterfowl, and eutrophic Greenfield Lake, North Carolina. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2016, 32, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aura, C.M.; Odoli, C.O.; Musa, S. Microbial dynamics within Lake Victoria Basin in relation to human activities. In Lakes of Africa; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 455–473. [Google Scholar]
- Chudoba, E.A.; Mallin, M.A.; Cahoon, L.B.; Skrabal, S.A. Stimulation of fecal bacteria in ambient waters by experimental inputs of organic and inorganic phosphorus. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3455–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, K. Impact of nutrient addition on diversity and fate of fecal bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korajkic, A.; Wanjugi, P.; Brooks, L.; Cao, Y.; Harwood, V.J. Persistence and decay of fecal microbiota in aquatic habitats. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2019, 83, e00005-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.J.; Kampbell, D.H.; Breidenbach, G.P. Escherichia coli and total coliforms in water and sediments at lake marinas. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowski, W.S.; Aguiar, T.A.; Jolly, E.C.; Hunter, J.; Stockwell, R.D.; Albright, M.S.; Godbey, S.E.; West, B.E. Characteristics and environmental problems of a eutrophic, seasonally-stratified lake, Wilgreen Lake, Madison County, Kentucky. J. Ky. Acad. Sci. 2012, 73, 41–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, D.F.C.; Passos, R.G.; von Sperling, M. A review of bacterial indicator disinfection mechanisms in waste stabilisation ponds. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2017, 16, 517–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, T.O. The Emergence and Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance in Aquatic Environments: Effects of Plankton Interactions. Ph.D. Thesis, Ulster University, Coleraine, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, T.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Gillings, M.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Penuelas, J.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Zhou, N.-Y.; et al. Cyanobacterial blooms contribute to the diversity of antibiotic-resistance genes in aquatic ecosystems. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.H.; Wolny, J.; Kase, J.A.; Unno, T.; Pachepsky, Y. Interactions of E. coli with algae and aquatic vegetation in natural waters. Water Res. 2022, 209, 117952. [Google Scholar]
- Beattie, R.E.; Walsh, M.; Cruz, M.C.; McAliley, L.R.; Dodgen, L.; Zheng, W.; Hristova, K.R. Agricultural contamination impacts antibiotic resistance gene abundances in river bed sediment temporally. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.C.; Zheng, J.; Wei, Y.Y.; Chen, T.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Shang, X.; Chen, H. Antibiotic resistance genes in an urban river as impacted by bacterial community and physicochemical parameters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 23753–23762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Qin, L.; Guan, C.; Wilson, M.E.; Li, X.; Cheng, D.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Gong, F. Antibiotic resistance gene profiling in response to antibiotic usage and environmental factors in the surface water and groundwater of Honghu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 31995–32005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somerville, C.C.; Sweeney, A.P.; Chadwick, S.L.; Dotson, T. Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in the Ohio River are not a Subset of Fecal Indicator Bacteria. In Proceedings of the 107th General Meeting of the American Society for Microbiological, Toronto, ON, Canada, 21 May 2007; pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Devarajan, N.; Laffite, A.; Graham, N.D.; Meijer, M.; Prabakar, K.; Mubedi, J.I.; Elongo, V.; Mpiana, P.T.; Ibelings, B.W.; Wildi, W.; et al. Accumulation of clinically relevant antibiotic-resistance genes, bacterial load, and metals in freshwater lake sediments in Central Europe. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6528–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 13.0, 2023. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 4 April 2023).


| 24 August 2022 | 1 September 2022 | 8 September 2022 | 29 September 2022 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Low | High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | High |
| 1-1 | N.M. | 0.0 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 3.8 | 1.4 | 9.0 | 3.0 |
| 1-2 | N.M. | 0.9 | N.M. | N.M. | 2.5 | 1.1 | 8.9 | 1.4 |
| 2-1 | N.M. | 0.0 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 0.0 |
| 2-2 | N.M. | 4.8 | N.M. | N.M. | 2.5 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 0.8 |
| 3-1 | N.M. | 0.0 | 2.7 | 0.5 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 3-2 | N.M. | 0.0 | N.M. | N.M. | 6.6 | 4.1 | 1.9 | 0.9 |
| 4-1 | N.M. | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 10.6 | 5.0 | 1.9 | 0.9 |
| 4-2 | N.M. | 0.0 | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. |
| 5-1 | N.M. | 0.0 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 4.1 | 1.8 | 12.7 | 6.3 |
| 5-2 | N.M. | 4.1 | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | 4.7 | 2.3 |
| 6-1 | N.M. | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 3.8 | 0.0 |
| 6-2 | N.M. | 0.0 | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. |
| 7-1 | N.M. | 0.0 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 3.1 | 1.0 | 7.5 | 6.3 |
| 7-2 | N.M. | 0.0 | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | 4.2 | 0.7 |
| 8-1 | N.M. | 0.0 | 2.5 | 0.2 | 3.8 | 1.4 | 6.4 | 3.3 |
| 8-2 | N.M. | 0.0 | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | 5.6 | 4.4 |
| 9-1 | N.M. | 0.0 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 5.8 | 3.2 | 4.8 | 2.4 |
| 9-2 | N.M. | 0.0 | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | N.M. | 6.5 | 2.5 |
| 10-1 | N.M. | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 1.9 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 10-2 | N.M. | 0.0 | N.M. | N.M. | 9.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| x surface | N.M. | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 4.8 | 2.2 |
| x sub-surface | N.M. | 1.0 | N.M | N.M. | 5.2 | 1.6 | 4.2 | 1.6 |
| x combined | N.M. | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 4.4 | 1.9 | 4.5 | 2.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stocker, M.; Smith, J.; Pachepsky, Y. Spatial Variation of Tetracycline-Resistant E. coli and Relationships with Water Quality Variables in Irrigation Water: A Pilot Study. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 504-518. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3020036
Stocker M, Smith J, Pachepsky Y. Spatial Variation of Tetracycline-Resistant E. coli and Relationships with Water Quality Variables in Irrigation Water: A Pilot Study. Applied Microbiology. 2023; 3(2):504-518. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3020036
Chicago/Turabian StyleStocker, Matthew, Jaclyn Smith, and Yakov Pachepsky. 2023. "Spatial Variation of Tetracycline-Resistant E. coli and Relationships with Water Quality Variables in Irrigation Water: A Pilot Study" Applied Microbiology 3, no. 2: 504-518. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3020036
APA StyleStocker, M., Smith, J., & Pachepsky, Y. (2023). Spatial Variation of Tetracycline-Resistant E. coli and Relationships with Water Quality Variables in Irrigation Water: A Pilot Study. Applied Microbiology, 3(2), 504-518. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3020036






