Effect of Functionalized CdSSe Quantum Dots in the CYP450 Activity of HEPG2 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of CdSSe QDs
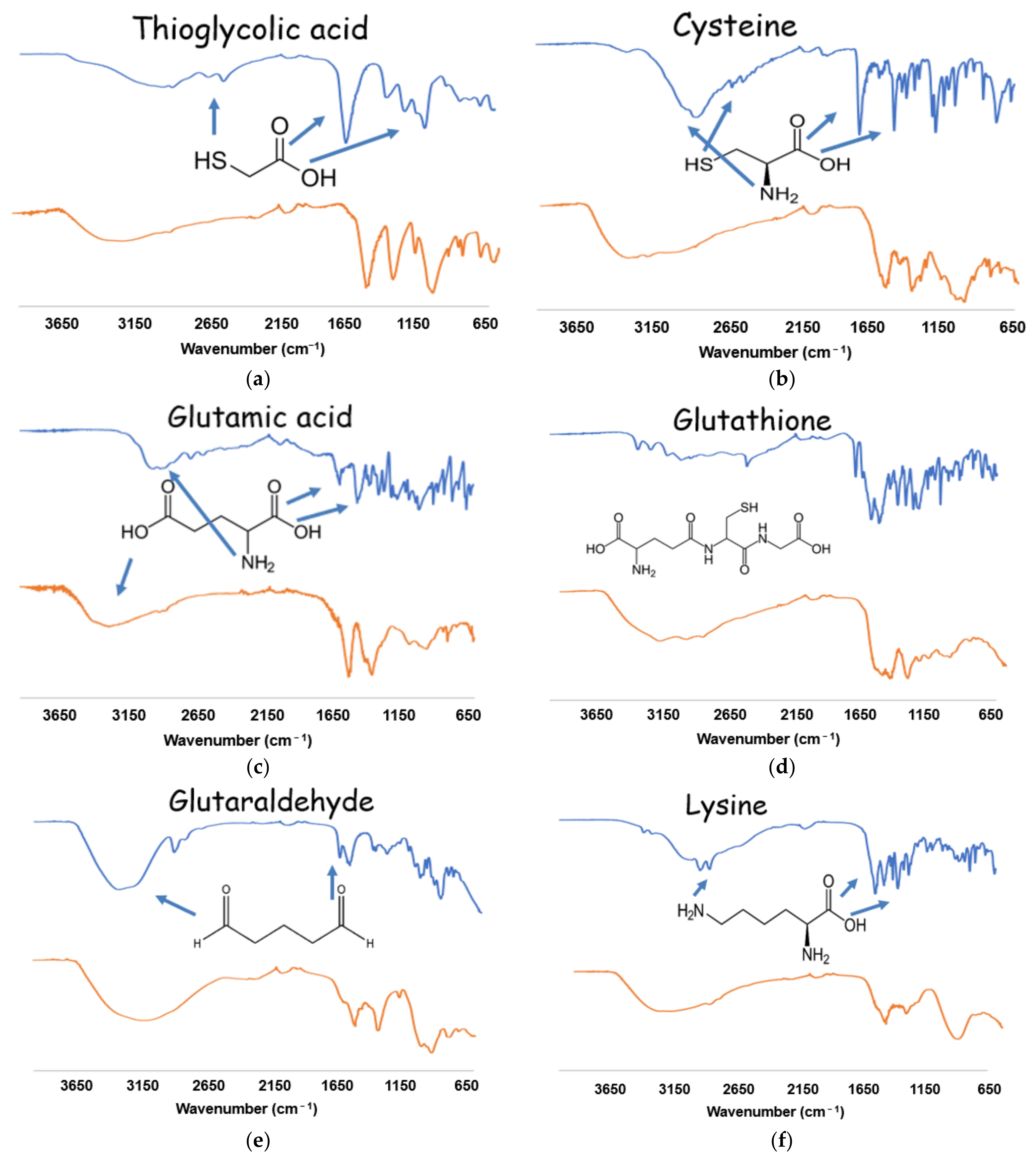
2.2. Functionalization of CdSSe QDs
2.3. Characterization of QDs
2.4. HEP-G2 Cells Culture
2.5. Cell Viability
2.6. Activity of Cytochrome P450 Isoenzymes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
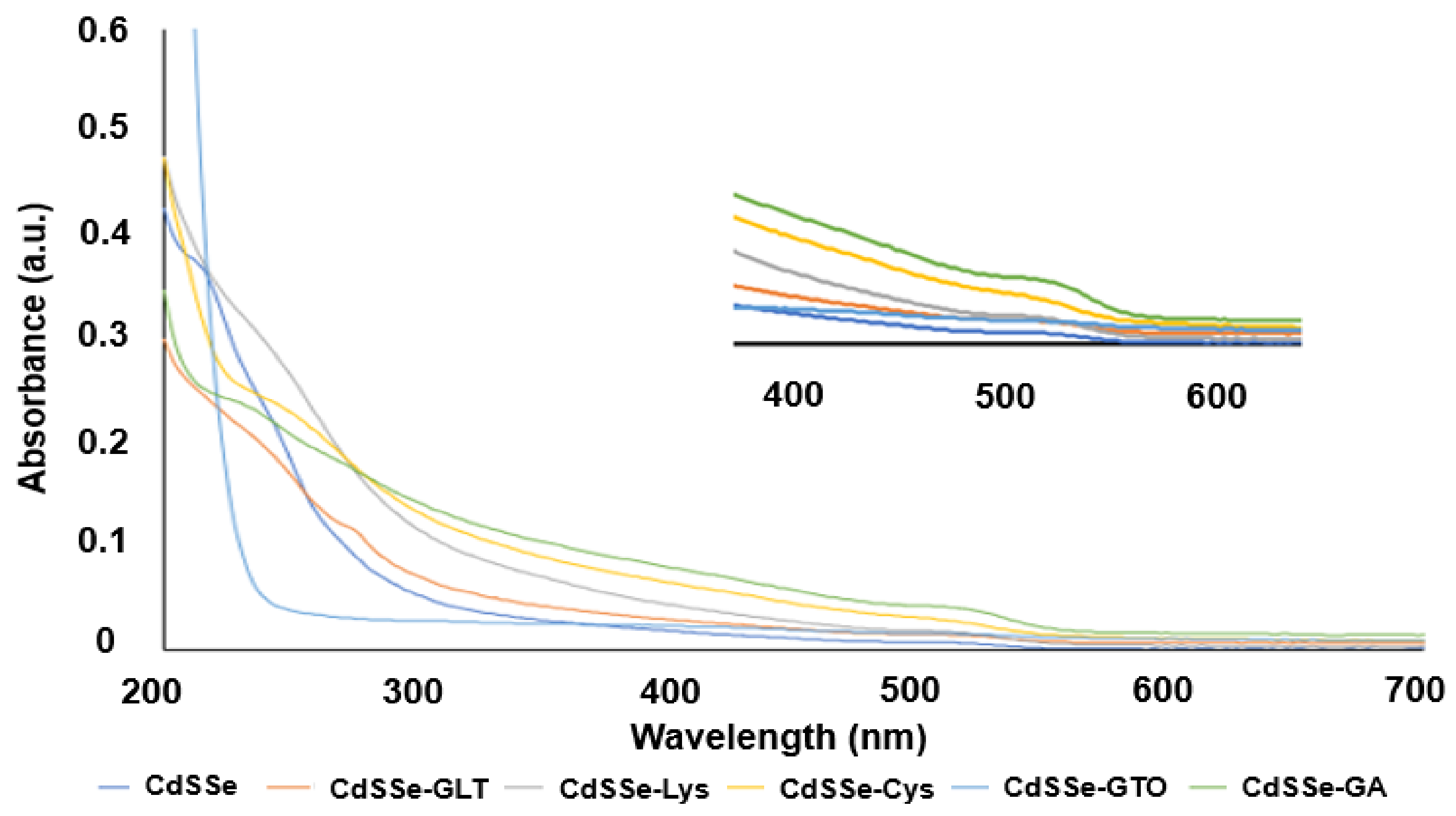
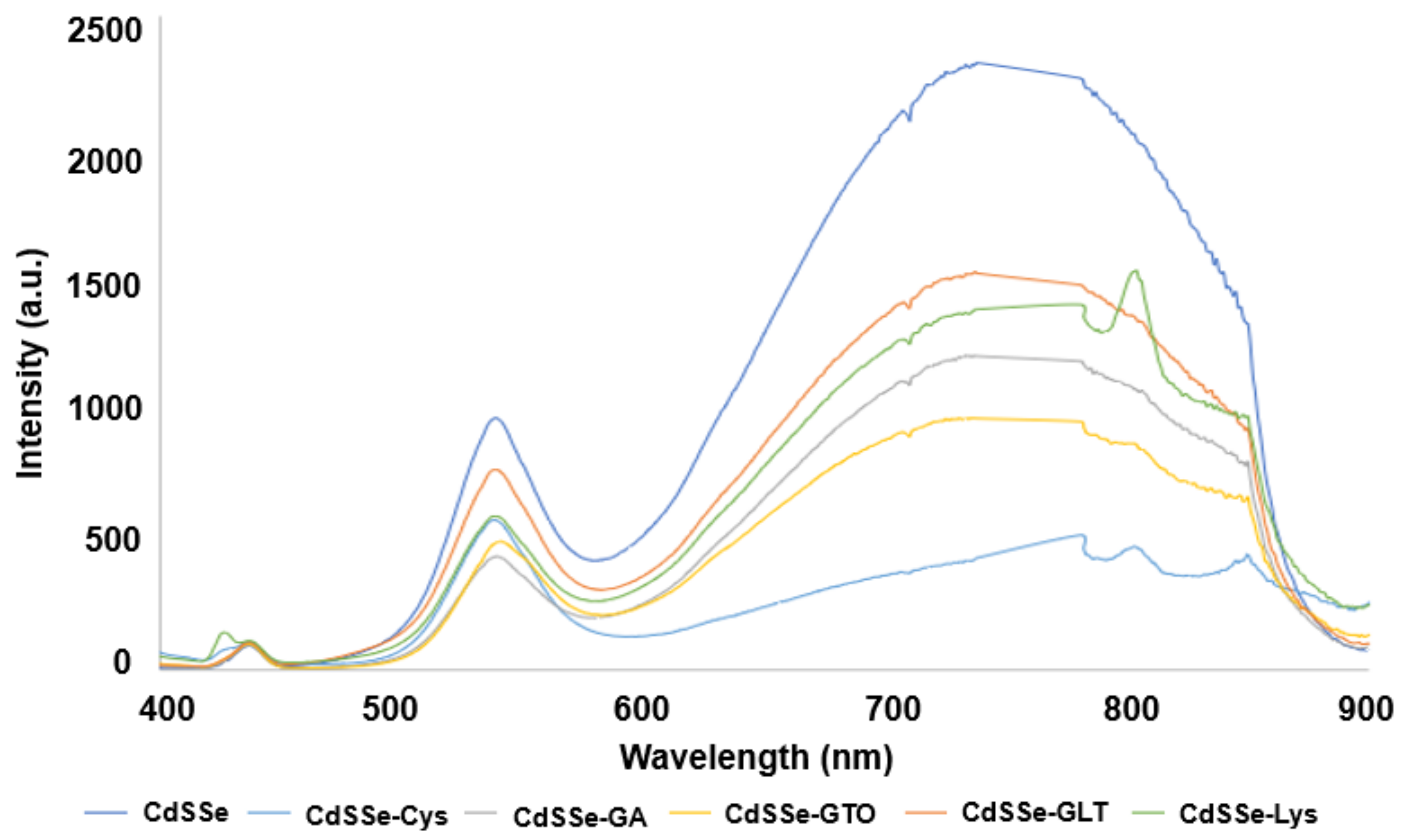
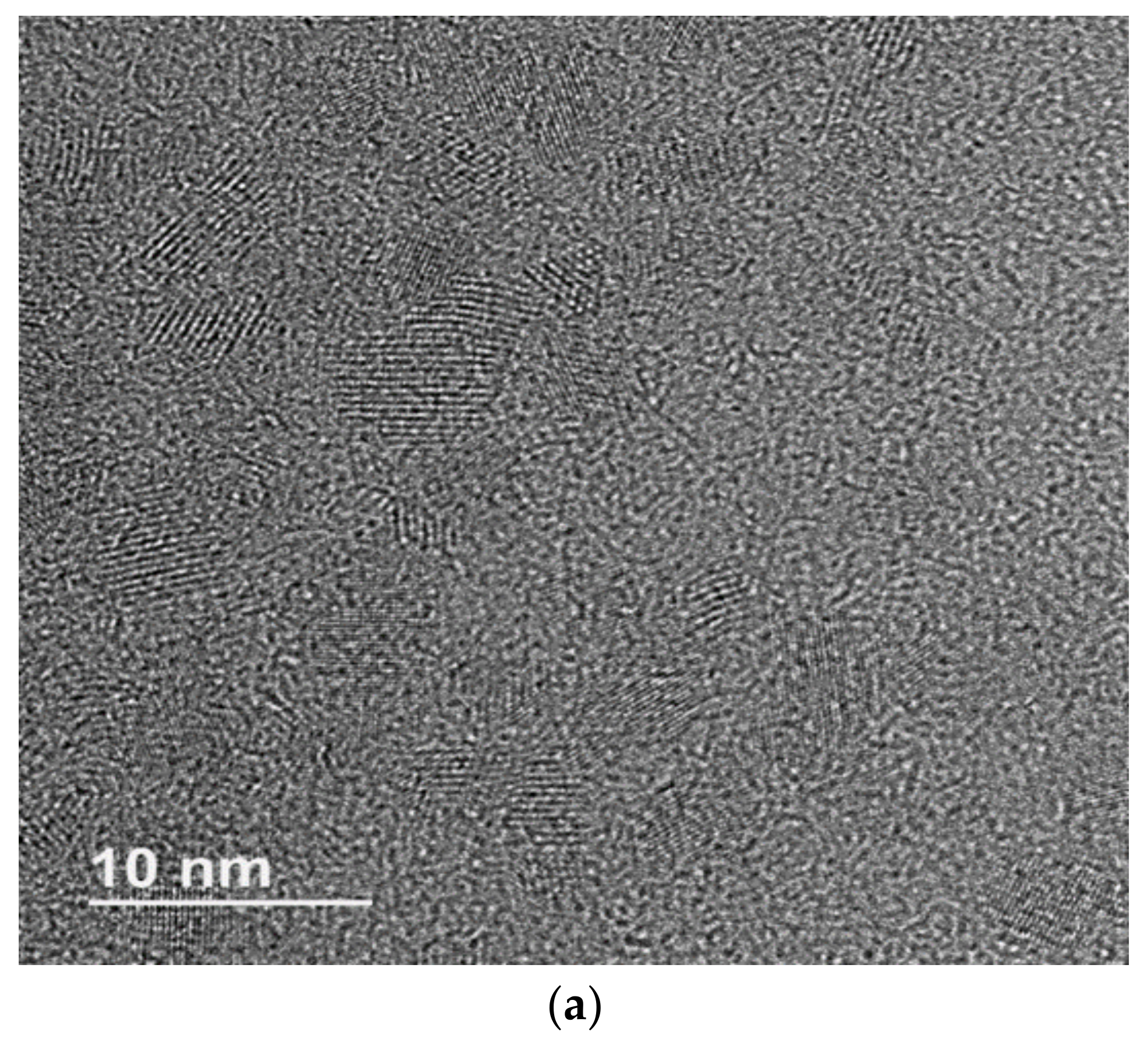
3.1. Characterization of Functionalized and Non-Functionalized CdSSe QDs
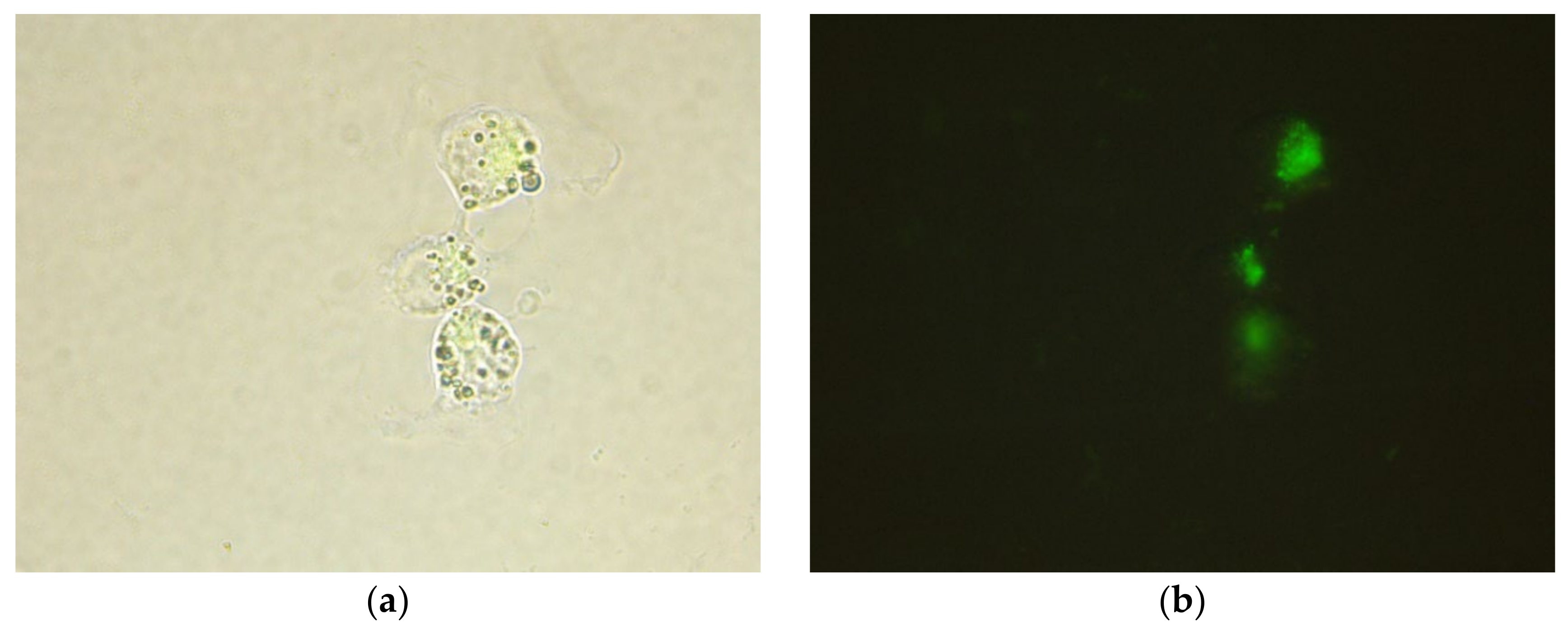
3.2. Microscopic Analysis of the HEP-G2 Cells
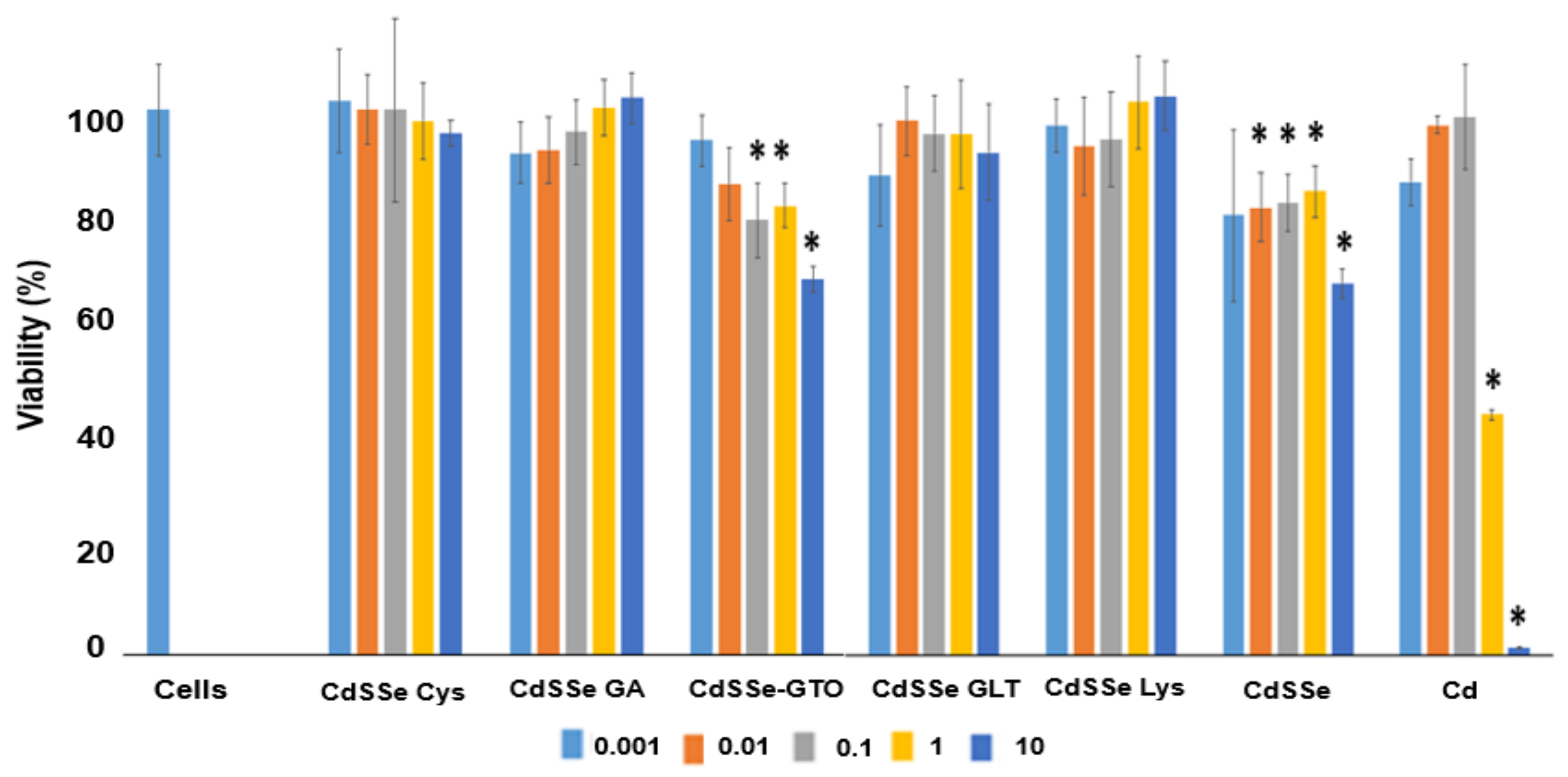
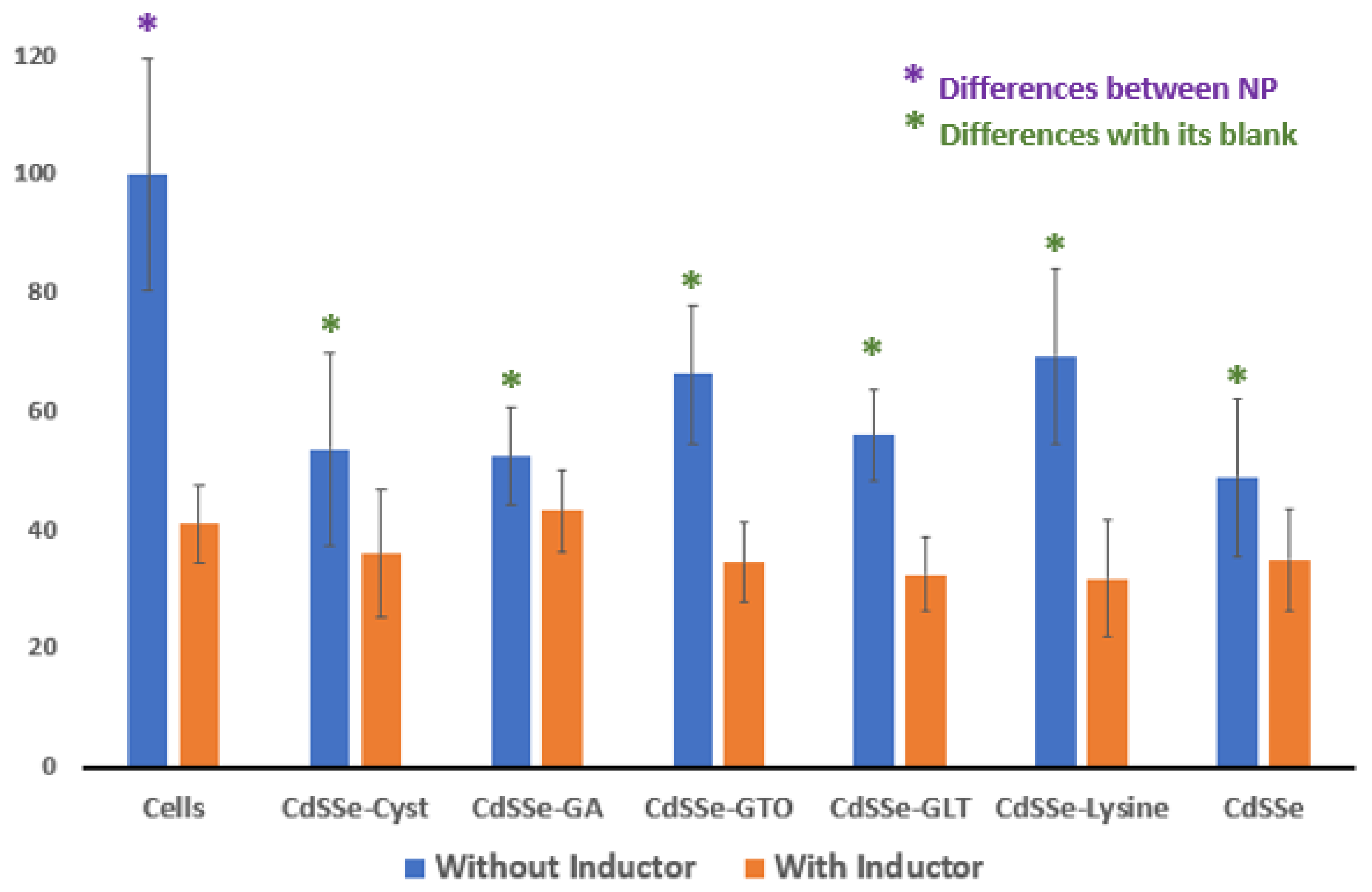
3.3. HEPG2 Cell Viability
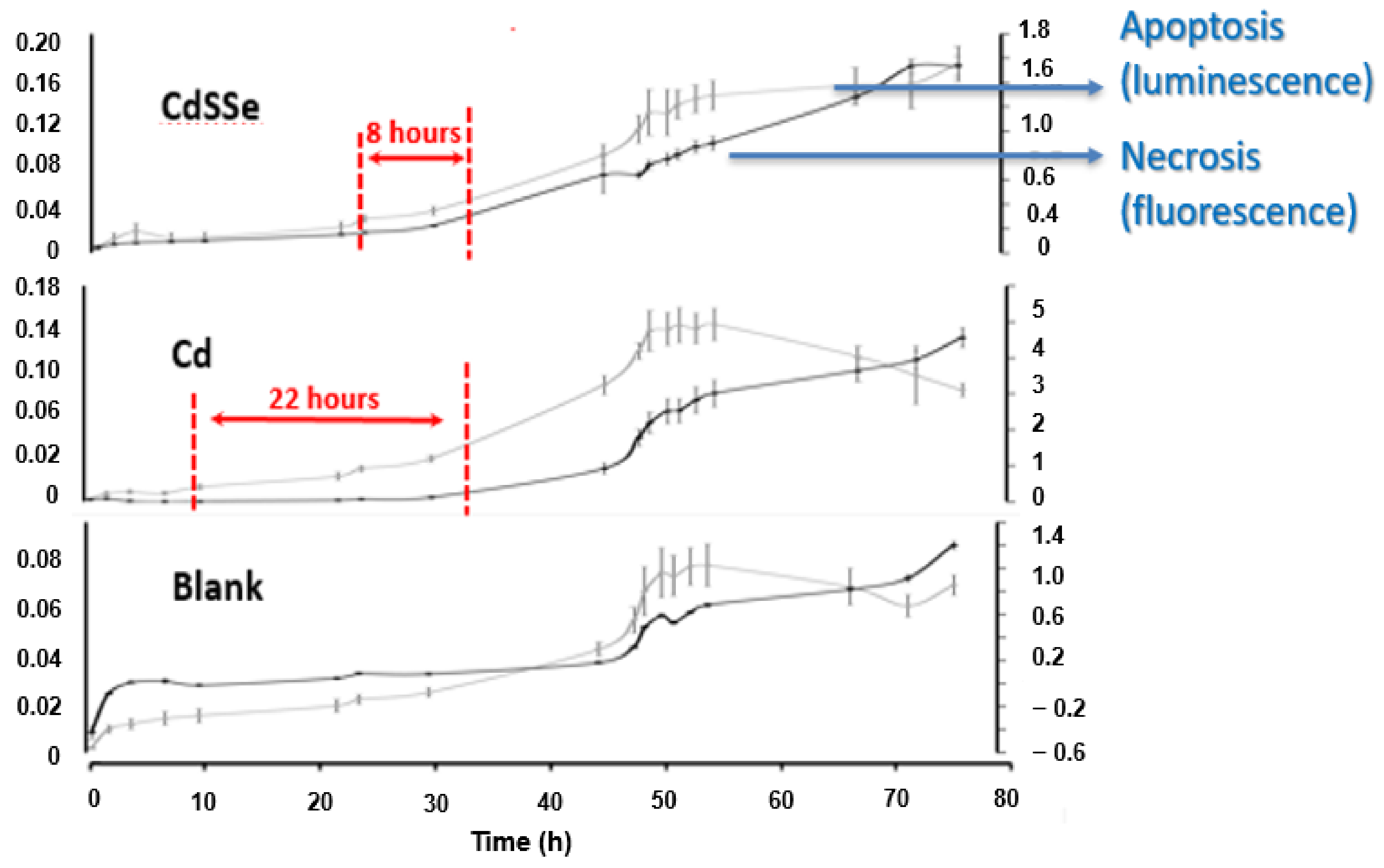
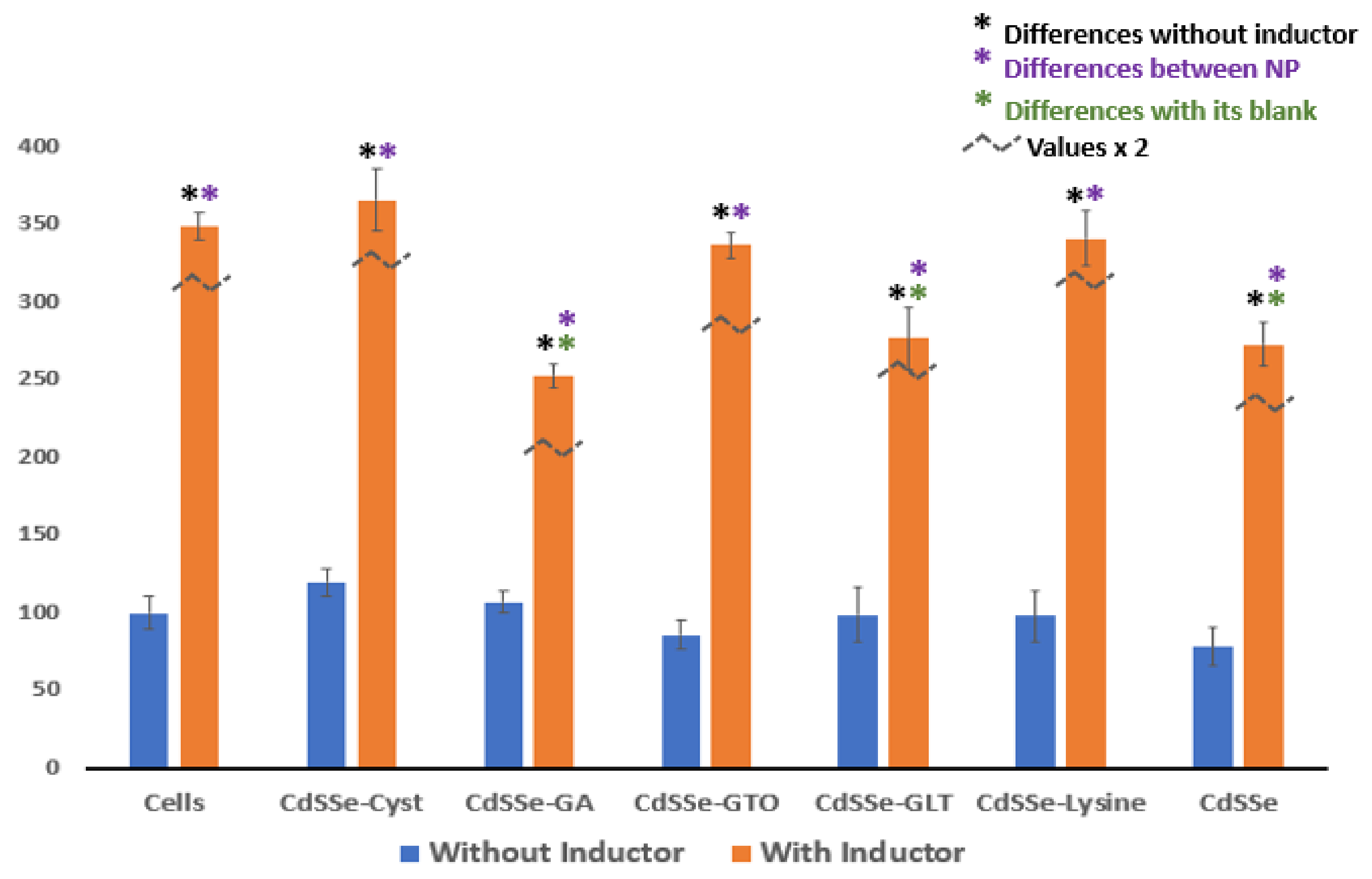
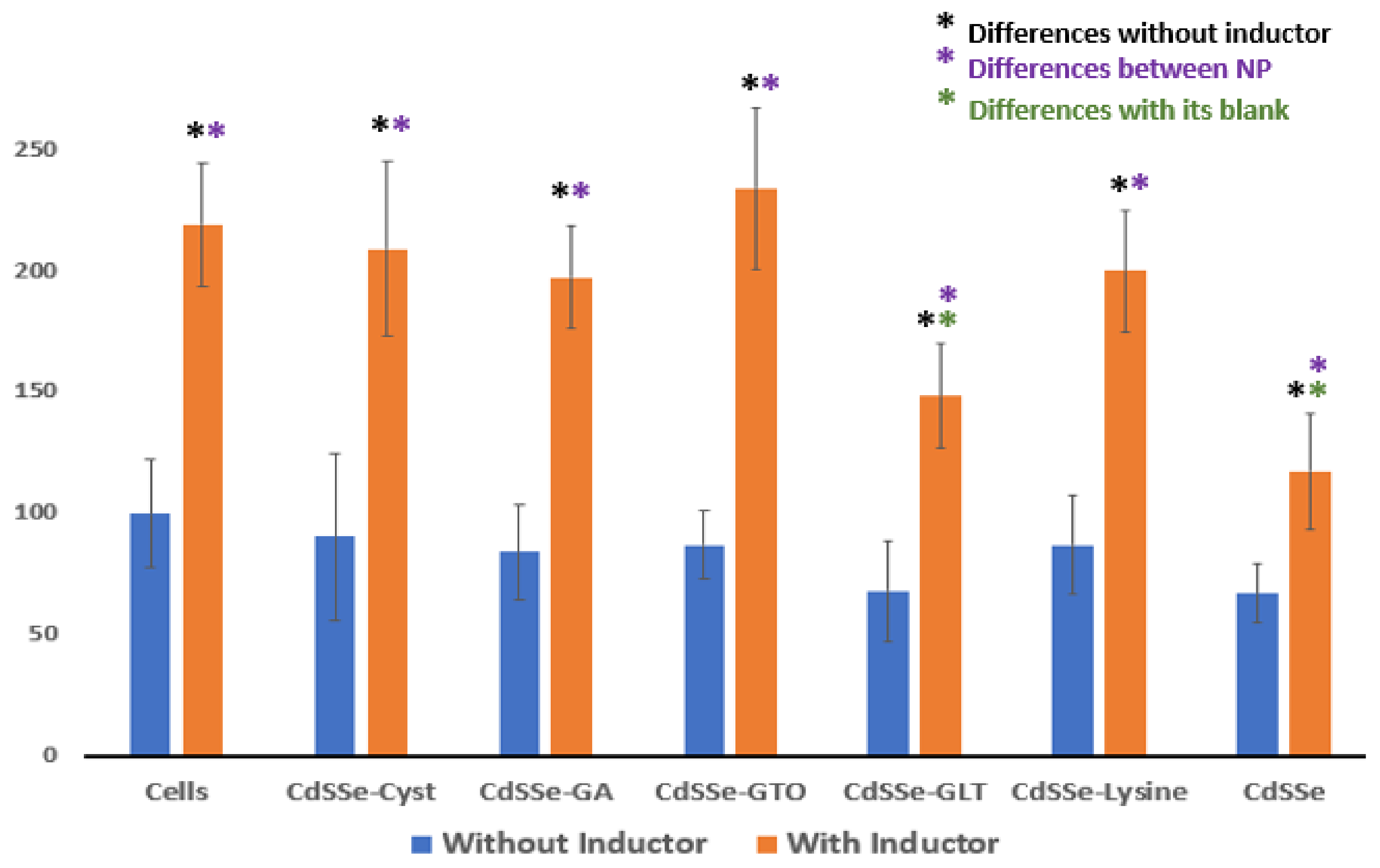
3.4. Response of the CYP-450 Isoenzymes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, C.; Cao, Z.; Wu, M.; Lu, C. Intracellular Tracking of Single Native Molecules with Electroporation-Delivered Quantum Dots. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11403–11409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.C.; Willmore, W.G.; Tayabali, A.F. Cadmium telluride quantum dots cause oxidative stress leading to extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Toxicology 2013, 306, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goharshadi, E.K.; Goharshadi, K.; Moghayedi, M. The use of nanotechnology in the fight against viruses: A critical review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 464, 214559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Nagesha, D.K.; Selvarasah, S.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Carrier, R.L. Toxicity of CdSe Nanoparticles in Caco-2 Cell Cultures. J. Nanobiotechnology 2008, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.-H.; Wu, S.-B.; Wei, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Ho, C.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Yang, C.-S.; Lin, P. Cadmium-Based Quantum Dot Induced Autophagy Formation for Cell Survival via Oxidative Stress. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Xu, Y.-M.; Wu, D.-D.; Yao, Y.; Liang, Z.-L.; Tan, H.W.; Lau, A.T.Y. Acute and chronic cadmium telluride quantum dots-exposed human bronchial epithelial cells: The effects of particle sizes on their cytotoxicity and carcinogenicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semashko, V.V.; Pudovkin, M.S.; Cefalas, A.-C.; Zelenikhin, P.V.; Gavriil, V.E.; Nizamutdinov, A.S.; Kollia, Z.; Ferraro, A.; Sarantopoulou, E. Tiny Rare-Earth Fluoride Nanoparticles Activate Tumour Cell Growth via Electrical Polar Interactions. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, S.; Behzadi, S.; Laurent, S.; Forrest, M.L.; Stroeve, P.; Mahmoudi, M. Toxicity of nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2323–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; He, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Tai, R.; Fan, C. The cytotoxicity of cadmium-based quantum dots. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yi, D.; Sun, H.; Zhang, H. Cadmium-based quantum dots: Preparation, surface modification, and applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 1409–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.-Q.; Yung, L.-Y.L. Ethylenediamine-Assisted Ligand Exchange and Phase Transfer of Oleophilic Quantum Dots: Stripping of Original Ligands and Preservation of Photoluminescence. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 2193–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, A.M.; Chandler, C.; Garling, M.; Chai, D.; Popovich, V.; Lystrom, L.; Kilina, S. Phenyldithiocarbamate Ligands Decompose During Nanocrystal Ligand Exchange. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 29455–29462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauf, R.R.; Lennox, J.C.; Dempsey, J.L. Quantifying Ligand Exchange Reactions at CdSe Nanocrystal Surfaces. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 4762–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Willmore, W.G.; Tayabali, A.F. Cadmium Telluride Quantum Dots Cause Oxidative Stress Leading to Extrinsic and Intrinsic Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Tan, L.; Wang, J. Toxicity of Co nanoparticles on three species of marine microalgae. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Zhang, H.; Du, N.; Chen, B.; Huang, H.; Wu, Y.; Yang, D. One-Pot Synthesis of Biocompatible CdSe/CdS Quantum Dots and Their Applications as Fluorescent Biological Labels. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kodriano, Y.; Schmidgall, E.R.; Benny, Y.; Gershoni, D. Optical control of single excitons in semiconductor quantum dots. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2014, 29, 53001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrad, R.; Poggi, M.; Ben Chaâbane, R.; Negrerie, M. Role of surface defects in colloidal cadmium selenide (CdSe) nanocrystals in the specificity of fluorescence quenching by metal cations. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 571, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migneault, I.; Dartiguenave, C.; Bertrand, M.J.; Waldron, K.C. Glutaraldehyde: Behavior in aqueous solution, reaction with proteins, and application to enzyme crosslinking. Biotechniques 2004, 37, 790–796, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomayor, C.G.; Groothof, D.; Vodegel, J.J.; Eisenga, M.F.; Knobbe, T.J.; IJmker, J.; Lammerts, R.G.M.; de Borst, M.H.; Berger, S.P.; Nolte, I.M.; et al. Plasma cadmium is associated with increased risk of long-term kidney graft failure. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derfus, A.M.; Chan, W.C.W.; Bhatia, S.N. Probing the Cytotoxicity of Semiconductor Quantum Dots. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Li, H.L.; Zeng, X.J.; Lu, C.; Fu, J.Y.; Guo, L.J.; Kimani, W.M.; Yan, H.L.; He, Z.Y.; Hao, H.Q.; et al. Coupling phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soil with safe crop production based on a sorghum farming system. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ock, K.; Jeon, W.I.; Ganbold, E.O.; Kim, M.; Park, J.; Seo, J.H.; Cho, K.; Joo, S.-W.; Lee, S.Y. Real-time monitoring of glutathione-triggered thiopurine anticancer drug release in live cells investigated by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2172–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messner, B.; Türkcan, A.; Ploner, C.; Laufer, G.; Bernhard, D. Cadmium overkill: Autophagy, apoptosis and necrosis signalling in endothelial cells exposed to cadmium. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1699–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, G.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Sang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Ge, W.; Sun, Z.; et al. Silica nanoparticles inducing the apoptosis via microRNA-450b-3p targeting MTCH2 in mice and spermatocyte cell. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-J.; Shin, S.; Chun, Y.-J. Biological roles of cytochrome P450 1A1, 1A2, and 1B1 enzymes. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2021, 44, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gan, J.; Ke, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; You, L.; Yu, J.; Wu, H. Identification and expression profile of a new cytochrome P450 isoform (CYP414A1) in the hepatopancreas of Venerupis (Ruditapes) philippinarum exposed to benzo[a]pyrene, cadmium and copper. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 33, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonprasert, K.; Satarug, S.; Morais, C.; Gobe, G.C.; Johnson, D.W.; Na-Bangchang, K.; Vesey, D.A. The stress response of human proximal tubule cells to cadmium involves up-regulation of haemoxygenase 1 and metallothionein but not cytochrome P450 enzymes. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 249, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alamo-Nole, L.; Cruz-Hernandez, J. Effect of Functionalized CdSSe Quantum Dots in the CYP450 Activity of HEPG2 Cells. Micro 2023, 3, 391-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3020027
Alamo-Nole L, Cruz-Hernandez J. Effect of Functionalized CdSSe Quantum Dots in the CYP450 Activity of HEPG2 Cells. Micro. 2023; 3(2):391-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlamo-Nole, Luis, and Jury Cruz-Hernandez. 2023. "Effect of Functionalized CdSSe Quantum Dots in the CYP450 Activity of HEPG2 Cells" Micro 3, no. 2: 391-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3020027
APA StyleAlamo-Nole, L., & Cruz-Hernandez, J. (2023). Effect of Functionalized CdSSe Quantum Dots in the CYP450 Activity of HEPG2 Cells. Micro, 3(2), 391-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3020027





