Antibody Response against the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Subdomains—Identification of Pre-Immunization Status by Human Coronaviruses with Multipanel Nucleocapsid Fragment Immunoblotting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Sampling
2.2. Nucleocapsid ELISA Screening Test
2.3. Molecular Cloning
2.4. Immunoblotting
2.5. Bioinformatics and In Silico Analysis
2.6. Ethics Approval
3. Results
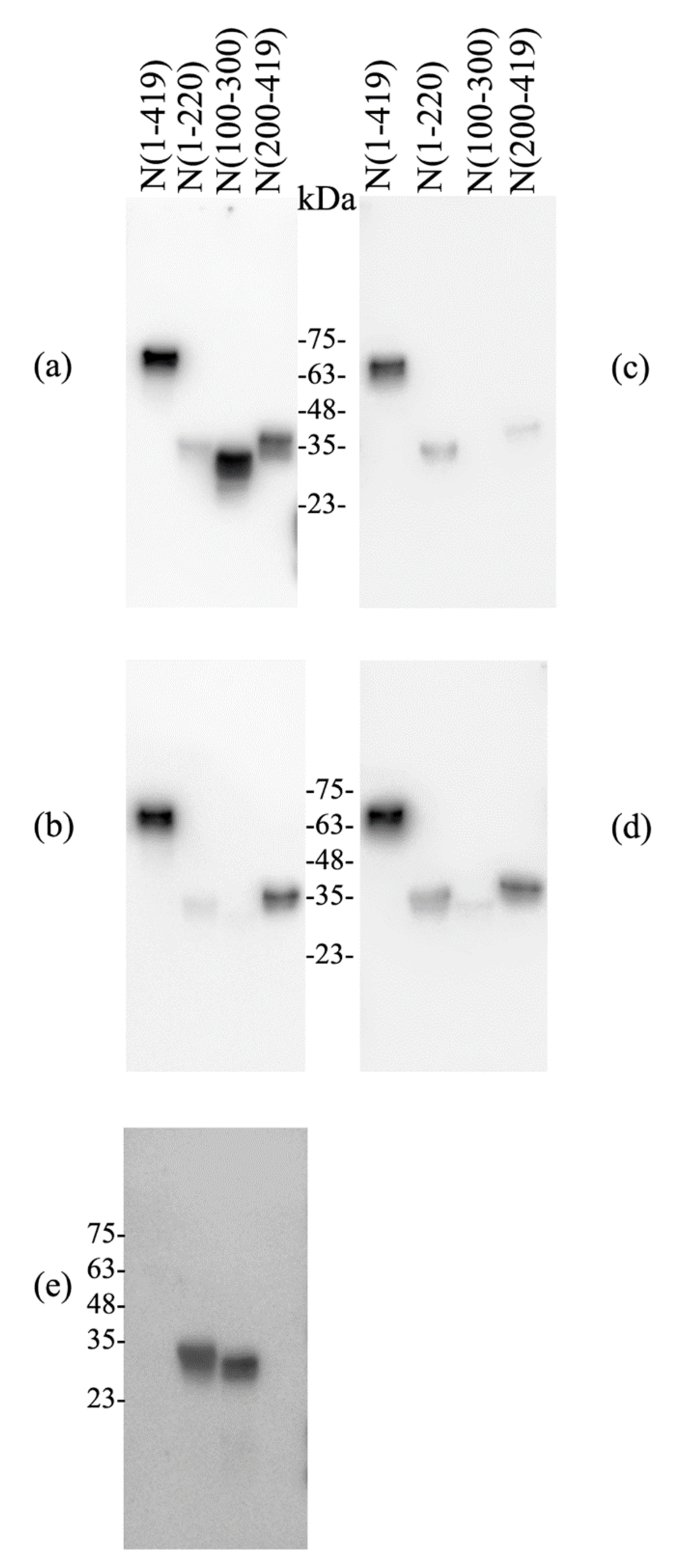
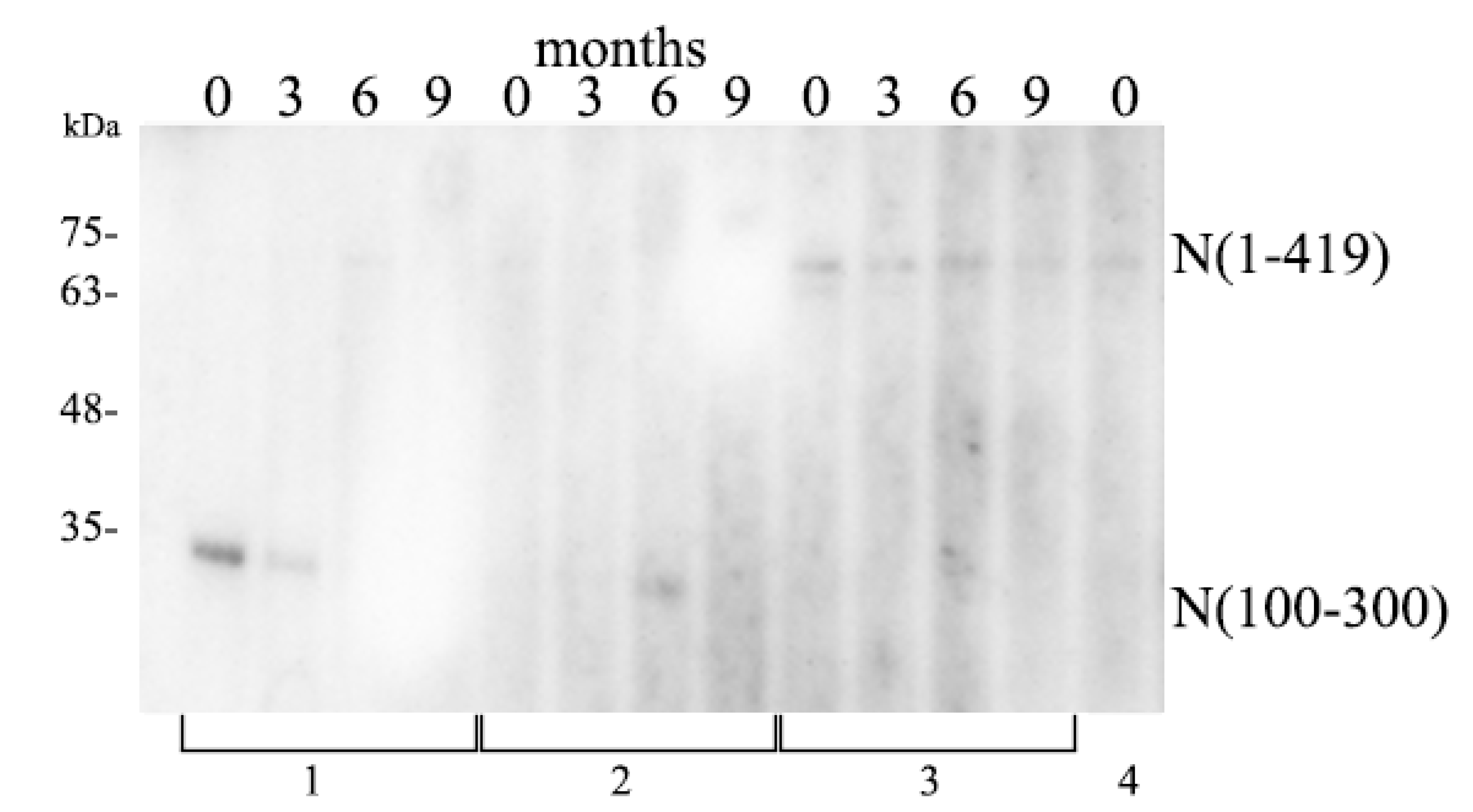
3.1. Individual Fragment Per Lane Immunoblotting of Donor IgG Phenotype
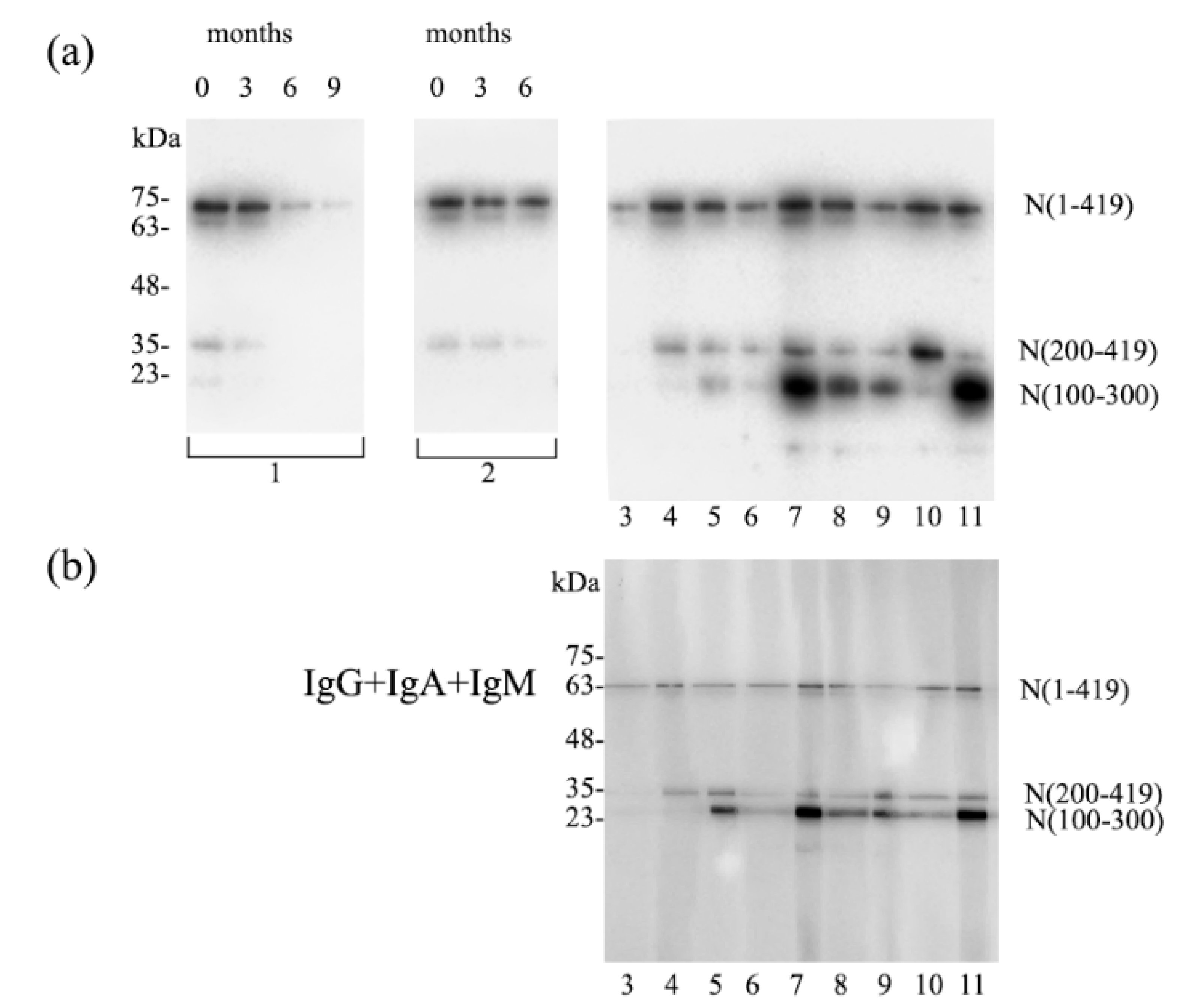
3.2. Individual Donor Per Lane Testing for the Immunodominant Region with a Multislot Immunoblotting Device
3.3. Participants with Borderline IgG ELISA Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smits, V.A.J.; Hernández-Carralero, E.; Paz-Cabrera, M.C.; Cabrera, E.; Hernández-Reyes, Y.; Hernández-Fernaud, J.R.; Gillespie, D.A.; Salido, E.; Hernández-Porto, M.; Freire, R. The Nucleocapsid protein triggers the main humoral immune response in COVID-19 patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 543, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrock, E.; Fujimura, E.; Kula, T.; Timms, R.T.; Lee, I.H.; Leng, Y.; Robinson, M.L.; Sie, B.M.; Li, M.Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. Viral epitope profiling of COVID-19 patients reveals cross-reactivity and correlates of severity. Science 2020, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Ren, L.; Yang, S.; Xiao, M.; Chang, D.; Yang, F.; Dela Cruz, C.S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Profiling Early Humoral Response to Diagnose Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, S.; Tworowski, D.; Detroja, R.; Mukherjee, S.B.; Frenkel-Morgenstern, M. Immunoinformatics and Structural Analysis for Identification of Immunodominant Epitopes in SARS-CoV-2 as Potential Vaccine Targets. Vaccines 2020, 8, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamecnik, C.R.; Rajan, J.V.; Yamauchi, K.A.; Mann, S.A.; Loudermilk, R.P.; Sowa, G.M.; Zorn, K.C.; Alvarenga, B.D.; Gaebler, C.; Caskey, M.; et al. ReScan, a Multiplex Diagnostic Pipeline, Pans Human Sera for SARS-CoV-2 Antigens. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hou, X.; Wu, X.; Liang, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Teng, F.; Dai, J.; Duan, H.; Guo, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 proteome microarray for mapping COVID-19 antibody interactions at amino acid resolution. bioRxiv 2020, 6, 2238–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folegatti, P.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Becker, S.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Bellamy, D.; Bibi, S.; Bittaye, M.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A preliminary report of a phase 1/2, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, M.J.; Lyke, K.E.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Raabe, V.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K.A.; et al. Phase I/II study of COVID-19 RNA vaccine BNT162b1 in adults. Nature 2020, 586, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, R.; van Zyl, M.; Fielding, B.C. The coronavirus nucleocapsid is a multifunctional protein. Viruses 2014, 6, 2991–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cong, Y.; Ulasli, M.; Schepers, H.; Mauthe, M.; V’kovski, P.; Kriegenburg, F.; Thiel, V.; de Haan, C.A.M.; Reggiori, F. Nucleocapsid Protein Recruitment to Replication-Transcription Complexes Plays a Crucial Role in Coronaviral Life Cycle. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01925-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, W.; Liu, G.; Ma, H.; Zhao, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Mohammed, A.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; et al. Biochemical characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, N.; Xu, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Weng, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; et al. Molecular Architecture of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Cell 2020, 183, 730–738 e713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanaga, K.; Yamanouchi, K.; Fujiwara, K. Protective effect of monoclonal antibodies on lethal mouse hepatitis virus infection in mice. J. Virol. 1986, 59, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutta, N.K.; Mazumdar, K.; Gordy, J.T. The Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2: A Target for Vaccine Development. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00647-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlen, G.; Frelin, L.; Nikouyan, N.; Weber, F.; Hoglund, U.; Larsson, O.; Westman, M.; Tuvesson, O.; Gidlund, E.K.; Cadossi, M.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Is a Good Component in a Vaccine. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01279-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, T.; Pajenda, S.; Wagner, L.; Gaggl, M.; Atamaniuk, J.; Holzer, B.; Zimpernik, I.; Gerges, D.; Mayer, K.; Aigner, C.; et al. Covid-19 serology in nephrology health care workers. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasisekharan, V.; Pentakota, N.; Jayaraman, A.; Tharakaraman, K.; Wogan, G.N.; Narayanasami, U. Orthogonal immunoassays for IgG antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 antigens reveal that immune response lasts beyond 4 mo post illness onset. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Tsoi, H.W.; Chan, K.H.; Wong, B.H.; Che, X.Y.; Tam, V.K.; Tam, S.C.; Cheng, V.C.; Hung, I.F.; et al. Relative rates of non-pneumonic SARS coronavirus infection and SARS coronavirus pneumonia. Lancet 2004, 363, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Le, M.Q.; Inoue, S.; Thai, H.T.; Hasebe, F.; Del Carmen Parquet, M.; Morita, K. Evaluation of inapparent nosocomial severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection in Vietnam by use of highly specific recombinant truncated nucleocapsid protein-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, L.; Cao, H.; Xie, T.; Long, R.; Li, H.; Yang, T.; Yan, M.; Xie, Z. N-terminally truncated nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 as a better serological marker than whole nucleocapsid protein in evaluating the immunogenicity of inactivated SARS-CoV-2. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbelo, P.D.; Riedo, F.X.; Morishima, C.; Rawlings, S.; Smith, D.; Das, S.; Strich, J.R.; Chertow, D.S.; Davey, R.T., Jr.; Cohen, J.I. Detection of Nucleocapsid Antibody to SARS-CoV-2 is More Sensitive than Antibody to Spike Protein in COVID-19 Patients. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; West, A.M.V.; Silletti, S.; Corbett, K.D. Architecture and self-assembly of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 1890–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; O’Meara, M.J.; Guo, J.Z.; Swaney, D.L.; Tummino, T.A.; Huttenhain, R.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2-Human Protein-Protein Interaction Map Reveals Drug Targets and Potential Drug-Repurposing. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terry, J.S.; Anderson, L.B.R.; Scherman, M.S.; McAlister, C.E.; Perera, R.; Schountz, T.; Geiss, B.J. Development of a SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid specific monoclonal antibody. Virology 2021, 558, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, B.; Wen, K.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Han, C.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, L.; Dan, Y.; et al. Diagnosis of Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection by Detection of Nucleocapsid Protein. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, J.; Fan, Z. Nuclear war: The granzyme A-bomb. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pajenda, S.; Kapps, S.; Reiter, T.; Freire, R.; Smits, V.A.J.; Wagner, L.; Gerges, D.; Winnicki, W.; Sunder-Plassmann, G.; Schmidt, A. Antibody Response against the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Subdomains—Identification of Pre-Immunization Status by Human Coronaviruses with Multipanel Nucleocapsid Fragment Immunoblotting. COVID 2021, 1, 105-114. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid1010009
Pajenda S, Kapps S, Reiter T, Freire R, Smits VAJ, Wagner L, Gerges D, Winnicki W, Sunder-Plassmann G, Schmidt A. Antibody Response against the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Subdomains—Identification of Pre-Immunization Status by Human Coronaviruses with Multipanel Nucleocapsid Fragment Immunoblotting. COVID. 2021; 1(1):105-114. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid1010009
Chicago/Turabian StylePajenda, Sahra, Sebastian Kapps, Thomas Reiter, Raimundo Freire, Veronique A. J. Smits, Ludwig Wagner, Daniela Gerges, Wolfgang Winnicki, Gere Sunder-Plassmann, and Alice Schmidt. 2021. "Antibody Response against the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Subdomains—Identification of Pre-Immunization Status by Human Coronaviruses with Multipanel Nucleocapsid Fragment Immunoblotting" COVID 1, no. 1: 105-114. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid1010009
APA StylePajenda, S., Kapps, S., Reiter, T., Freire, R., Smits, V. A. J., Wagner, L., Gerges, D., Winnicki, W., Sunder-Plassmann, G., & Schmidt, A. (2021). Antibody Response against the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Subdomains—Identification of Pre-Immunization Status by Human Coronaviruses with Multipanel Nucleocapsid Fragment Immunoblotting. COVID, 1(1), 105-114. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid1010009





