The Expression of Fibrogenic Cytokines by Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Response to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Samples and Reagents
2.2. Blood Cell Separation and Culture of PBMC
2.3. Proliferation Assays
2.4. Measuring Cytokine Gene Expression at mRNA and Protein Level
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Proliferation Assay
3.2. RT-qPCR
3.2.1. RT-qPCR: Profibrotic Cytokines
3.2.2. RT-qPCR: Antifibrotic Cytokines
3.2.3. RT-qPCR: Antiviral Cytokines
3.2.4. RT-qPCR: Unclassified Cytokines/Chemokines
3.3. ELISA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- George, P.M.; Wells, A.U.; Jenkins, R.G. Pulmonary fibrosis and COVID-19: The potential role for antifibrotic therapy. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Balan, I.; Yadav, S.; Matos, W.F.; Kharawala, A.; Gaddam, M.; Sarabia, N.; Koneru, S.C.; Suddapalli, S.K.; Marzban, S. Post-COVID-19 Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cureus 2022, 14, e22770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oronsky, B.; Larson, C.; Hammond, T.C.; Oronsky, A.; Kesari, S.; Lybeck, M.; Reid, T.R. A Review of Persistent Post-COVID Syndrome (PPCS). Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruaro, B.; Confalonieri, P.; Pozzan, R.; Tavano, S.; Mondini, L.; Baratella, E.; Pagnin, A.; Lerda, S.; Geri, P.; Biolo, M.; et al. Severe COVID-19 ARDS treated by bronchoalveolar lavage with diluted exogenous pulmonary surfactant as salvage therapy: In pursuit of the Holy Grail. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maione, F.; Casillo, G.M.; Raucci, F.; Salvatore, C.; Ambrosini, G.; Costa, L.; Scarpa, R.; Caso, F.; Bucci, M. Interleukin-17A (IL-17A): A silent amplifier of COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Chiovato, L.; Croce, L.; Magri, F.; Rotondi, M. The cytokine storm in COVID-19: An overview of the involvement of the chemokine/chemokine-receptor system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 53, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-J.; Dong, X.; Liu, G.-H.; Gao, Y.-D. Risk and protective factors for COVID-19 morbidity, severity, and mortality. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, S.M.; Saleh, R.; Sasidharan Nair, V.; Taha, R.Z.; Elkord, E. T-cell responses and therapies against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Immunology 2021, 162, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhao, Y.-D.Z.; Wang, X.-M. CXCL10 an important chemokine associated with cytokine storm in COVID-19 infected patients. Europ. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 7497–7505. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.K.; Lichtman, A.H.; Pillai, S. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 10th ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Philadephia, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Cao, Z.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.Y.-C.; Wang, H.; Menachery, V.D.; Rajsbaum, R.; Shi, P.-Y. Evasion of Type I Interferon by SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Subramanian, S.; Wu, L.; Bu, H.F.; Wang, X.; Du, C.; De Plaen, I.G.; Tan, X.-D. SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Forms Intracellular Aggregates and Inhibits IFNgamma-Induced Antiviral Gene Expression in Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 679482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Moore Vofel, J.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID: Major findings, mechanisms and recommendation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.; Xiong, F.; Al Hasani, L.; Shi, Y.; Simpson, E.N.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Y.-T.; Shivshankar, P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 restructures host chromatin architecture. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basheer, M.; Saad, E.; Kananeh, M.; Asad, L.; Khayat, O.; Badarne, A.; Abdo, Z.; Arraf, N.; Milhem, F.; Bassal, T.; et al. Cytokine Patterns in COVID-19 Patients: Which Cytokines Predict Mortality and Which Protect Against? Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 4735–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasarmidi, E.; Tsitoura, E.; Spandidos, D.A.; Tzanakis, N.; Antoniou, K.M. Pulmonary fibrosis in the aftermath of the COVID-19 era (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 2557–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, D.R.; Kazakoff, M.A.; Patel, A.; Jaynes, J.; Willis, M.S.; Yates, C.C. Chemokine-Based Therapeutics for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Fibrotic Convergent Pathways in COVID-19. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2021, 9, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colarusso, C.; Terlizzi, M.; Maglio, A.; Molino, A.; Candia, C.; Vitale, C.; Hansbro, P.M.; Vatrella, A.; Pinto, A.; Sorrentino, R. Activation of the AIM2 Receptor in Circulating Cells of Post-COVID-19 Patients With Signs of Lung Fibrosis Is Associated With the Release of IL-1alpha, IFN-alpha and TGF-beta. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 934264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colarusso, C.; Maglio, A.; Terlizzi, M.; Vitale, C.; Molino, A.; Pinto, A.; Vatrella, A.; Sorrentino, R. Post-COVID-19 Patients Who Develop Lung Fibrotic-like Changes Have Lower Circulating Levels of IFN-beta but Higher Levels of IL-1alpha and TGF-beta. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpino, M.V.; Quarleri, J. SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis: Imbalance in the Renin-Angiotensin System Favors Lung Fibrosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A. Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehal, W.Z.; Iredale, J.; Friedman, S.L. Scraping fibrosis: Expressway to the core of fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 552–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, K.; Biswas, P.S. Interleukin-17: Friend or foe in organ fibrosis. Cytokine 2019, 120, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leask, A. COVID-19: Is fibrosis the killer? J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 14, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Flores, D.; Zepeda-Cervantes, J.; Cruz-Resendiz, A.; Aguirre-Sampieri, S.; Sampieri, A.; Vaca, L. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Based on the Spike Glycoprotein and Implications of New Viral Variants. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 701501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sziksz, E.; Pap, D.; Lippai, R.; Beres, N.J.; Fekete, A.; Szabo, A.J.; Vannay, A. Fibrosis Related Inflammatory Mediators: Role of the IL-10 Cytokine Family. Mediators Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 764641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peter, H.H.; Pichler, W.; Müller-Ladner, U. Klinische Immunologie, 3rd ed.; Urban&Fischer: Munich, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tager, A.M.; Kradin, R.L.; LaCamera, P.; Bercury, S.D.; Campanella, G.S.V.; Leary, C.P.; Polosukhin, V.; Zhao, L.-H.; Sakamoto, H.; Blackwell, T.S.; et al. Inhibition of pulmonary fibrosis by the chemokine IP-10/CXCL10. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacreas, A.; Yang, J.Y.C.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Sigdel, T.K.; Liberto, J.M.; Damm, I.; Verleden, G.M.; Vos, R.; Verleden, S.E.; Sarwal, M.M. The common rejection module in chronic rejection post lung transplantation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zawawi, A.; Naser, A.Y.; Alwafi, H.; Minshawi, F. Profile of Circulatory Cytokines and Chemokines in Human Coronaviruses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 666223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurczynski, S.J.; Moore, B.B. IL-17 in the lung: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2018, 314, L6–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramshaw, I.A.; Ramsay, A.J.; Karupiah, G.; Rolph, M.S.; Mahalingam, S.; Ruby, J.C. Cytokines and immunity to viral infections. Immunol. Rev. 1997, 159, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyel, P.A. How is inflammation initiated? Individual influences of IL-1, IL-18 and HMGB1. Cytokine 2014, 69, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, F.; Corry, D.B. Chemokines, CXC / CXCL10. In Encyclopedia of Respiratory Medicine, 1st ed.; Laurent, G.J., Shapiro, S.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 402–407. [Google Scholar]
- Coperchini, F.; Chiovato, L.; Rotondi, M. Interleukin-6, CXCL10 and Infiltrating Macrophages in COVID-19-Related Cytokine Storm: Not One for All But All for One! Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 668507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, J.; De Leeuw, E.; Lambrecht, B.N. Inflammasomes and IL-1 family cytokines in SARS-CoV-2 infection: From prognostic marker to therapeutic agent. Cytokine 2022, 157, 155934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Caraffa, A.; Gallenga, C.E.; Ross, R.; Kritas, S.K.; Frydas, I.; Younas, A.; Ronconi, G. Coronavirus-19 (SARS-CoV-2) induces acute severe lung inflammation via IL-1 causing cytokine storm in COVID-19: A promising inhibitory strategy. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karina, K.; Christoffel, L.M.; Novariani, R.; Rosadi, I.; Rosliana, I.; Rosidah, S.; Sobariah, S.; Fatkhurohman, N.; Puspitaningrum, N.; Hertati, Y.; et al. The Effect of Intravenous Autologous Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy on “Profibrotic Cytokine” IL-1beta Levels in Severe and Critical COVID-19 Patients: A Preliminary Study. Scientifica 2021, 2021, 9427978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huet, T.; Beaussier, H.; Voisin, O.; Jouveshomme, S.; Dauriat, G.; Lazareth, I.; Sacco, E.; Naccache, J.-M.; Bezie, Y.; Laplanche, S.; et al. Anakinra for severe forms of COVID-19: A cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e393–e400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.A.; Stewart, I.; Fabbri, L.; Moss, S.; Robinson, K.; Smyth, A.R.; Jenkins, G. Systematic review and meta-analysis of anakinra, sarilumab, siltuximab and tocilizumab for COVID-19. Thorax 2021, 76, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudowska-Sawczuk, M.; Mroczko, B. What Is Currently Known about the Role of CXCL10 in SARS-CoV-2 Infection? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardicurti, O.; Ruscitti, P.; Ursini, F.; D’Andrea, S.; Ciaffi, J.; Meliconi, R.; Iagnocco, A.; Cipriani, P.; Giacomelli, R. Mortality in tocilizumab-treated patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- REMAP-GAP Investigators. Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Tanaka, K.; Fujita, T.; Umezawa, H.; Amano, H.; Yoshioka, K.; Naito, Y.; Hatano, M.; Kimura, S.; Tatsumi, K.; et al. Bidirectional role of IL-6 signal in pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Yu, X.; Lan, H.-Y. Signaling mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in viral infection, cell death and inflammation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 4704–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, A.; Kuba, K.; Morita, M.; Chida, S.; Tezuka, H.; Hara, H.; Sasaki, T.; Ohteki, T.; Ranieri, V.M.; dos Santos, C.C.; et al. CXCL10-CXCR3 enhances the development of neutrophil-mediated fulminant lung injury of viral and nonviral origin. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Welch, J.L.; Xiang, J.; Chang, Q.; Houtman, J.C.D.; Stapleton, J.T. T-Cell Expression of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and Binding of Severe Acute Respiratory Coronavirus 2. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipoor, S.D.; Mirsaeidi, M. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry beyond the ACE2 receptor. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 10715–10727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oettgen, H.C.J. Mast cells in food allergy: Inducing immediate reactons and shaping long-term immunity. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Moy, V.T. Cross-linking of cell surface receptors enhances cooperiativity of moleuclar adhesion. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 2814–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moody, P.R.; Syers, E.J.; Magnusson, J.P.; Alexander, C.; Borri, P.; Watson, P.; Jones, A.T. Receptor crosslinking: A general method to trigger internalization and lysosomal targeting of therapeutic receptor-ligand comples. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mkaddem, S.B.; Benhamou, M.; Monteiro, R.C. Understanding Fc receptor involvement in inflammatory diseases: From mechanisms to new therapeutic tools. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, V.E.; Chluyan, H.E. SLAM and CD31: Signaling molecules involved in cytokine secretion druing the development of innate and adaptive immune responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007, 18, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.J.; Nikolaienko, S.I.; Dibrova, V.A.; Dibrova, Y.V.; Vasylyk, V.M.; Novikov, M.Y.; Shults, N.V.; Gychka, S.G. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein mediated cell signaling in lung vasular cells. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2021, 137, 106923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palakkott, A.R.; Alneyadi, A.; Muhammad, K.; Eid, A.H.; Amiri, K.M.A.; Ayoub, M.A.; Iratni, R. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein activates epidermal growth ractor receptor-mediated signaling. Vaccines 2023, 11, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos Alves, V.; Silva Santos, S.A.C.; Leite-Aguiar, R.; Rapiva-Pereira, E.; Rodrigues dos Reis, R.; Calazans, M.L.; Gripp Fernandes, G.; Silva Antonio, L.; de Lima, E.V.; Kurtenbach, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alters microglial purinergic signaling. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1158460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cytokine | Forward Primer | Cytokine | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β F | GGGCCTCAAGGAAAAGAATC | IL-1β R | TTCTGCTTGAGAGGTGCTGA |
| IL-2 F | AGAATCCCAAACTCACCAGGA | IL-2 R | TGCTGATTAAGTCCCTGGGT |
| IL-4 F | GCAGTTCTACAGCCACCATG | IL-4 R | ACTCTGGTTGGCTTCCTTCA |
| IL-6 F | CCTTCCAAAGATGGCTGAAA | IL-6 R | CAGGGGTGGTTATTGCATCT |
| IL-10 F | GATCCAGTTTTACCTGGAGG | IL-10 R | CTCATGGCTTTGTAGATGCC |
| IL-12 F | AAGGAGGCGAGGTTCTAAGC | IL-12 R | AAGAGCCTCTGCTGCTTTTG |
| IL 13 F | GGTCAACATCACCCAGAACC | IL 13 R | CAGCATCCTCTGGGTCTTCT |
| IL-17A F | GGTTTGACTGAGTACCAATTTGC | IL17A R | AAATTCCCAAGCCCAGAATC |
| IL-18 F | ATGGCTGCTGAACCAGTAGA | IL-18 R | CTCTACAGTCAGAATCAGTCAT |
| IL-22 F | AGTCACCAGTTGCTCGAGTT | IL-22 R | CTAGCCTCCTTAGCCAGCAT |
| IL-23 F | GTTCCCCATATCCAGTGTGG | IL-23 R | GAGGCTTGGAATCTGCTGAG |
| IFN-γ F | TGACCAGAGCATCCAAAAGA | IFN-γ R | CTCTTCGACCTCGAAACAGC |
| TGF-β 1 F | CACGTGGAGCTGTACCAGAA | TGF-β 1 R | GAACCCGTTGATGTCCACTT |
| TNF-α F | TGGCATGGAGCTGAGAGA | TNF-α R | GCAATGATCCCAAAGTAGACCT |
| CXCL-10 F | AGGAACCTCCAGTCTCAGCA | CXCL-10 R | CAAAATTGGCTTGCAGGAAT |
| Actin F | CATCCGCAAAGACCTGTACG | Actin R | CCTGCTTGCTGATCCACATC |
| GAPDH F | AGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTT | GAPDH R | TGACAAGCTTCCCGTTCTCA |
| Blood Donor Number | Conditions with Significant Proliferation | Blood Donor Number | Conditions with Significant Proliferation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PHA | 7 | PHA |
| 2 | PHA, SSP, SST, SNP, SNP | 8 | PHA, SNP |
| 3 | PHA | 9 | no significance |
| 4 | PHA, SNP | 10 | no significance |
| 5 | PHA, SST | 11 | PHA SSP |
| 6 | PHA, VLPD | 12 | PHA SSP |
| Cytokine | CTL | VLPD | VLPS | SST | SNP | PHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
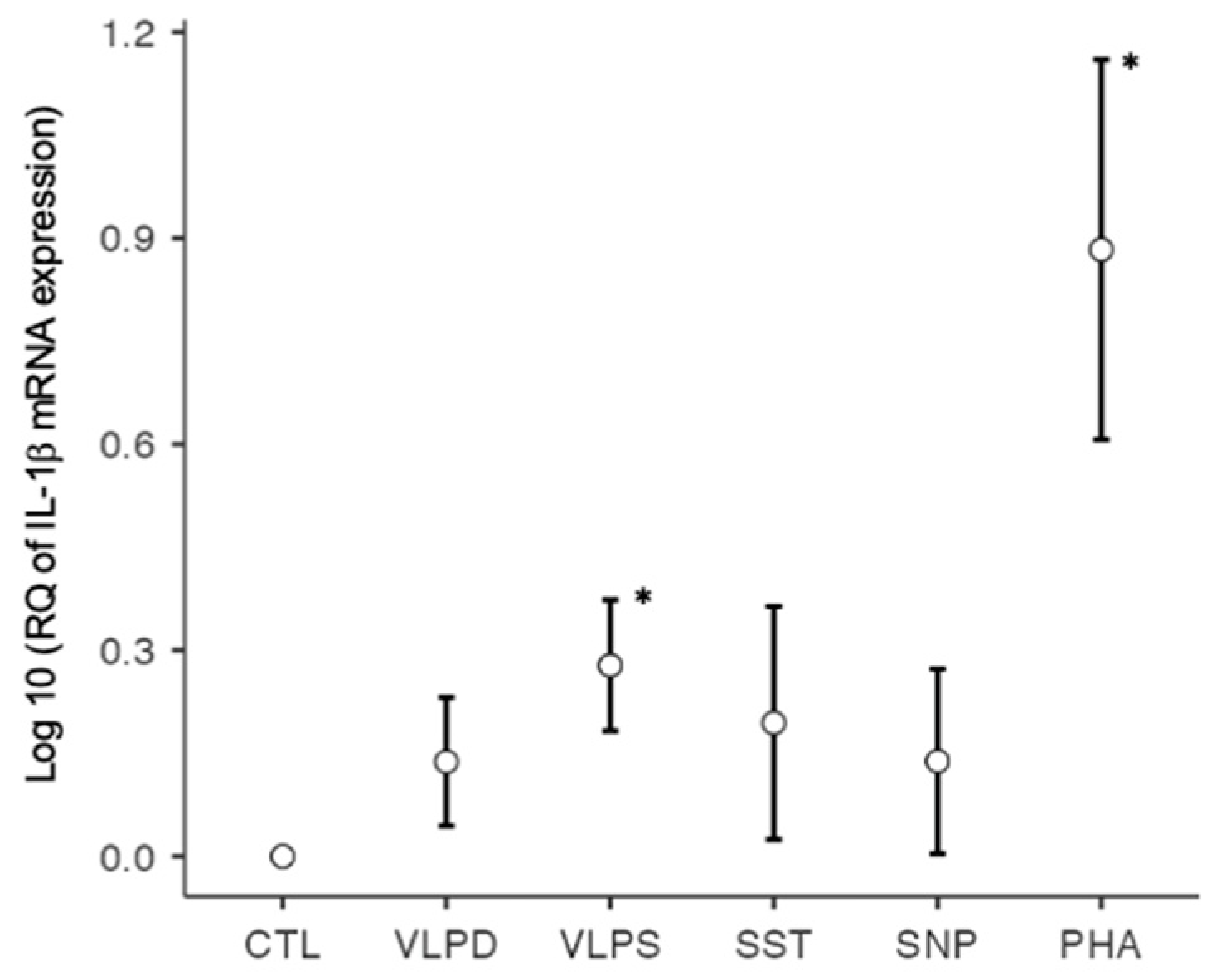
| IL-1β | 1.0000 | 1.4543 | 2.0037 * | 2.0417 | 1.5503 | 12.3211 * |
| IL-6 | 0.9992 | 1.7258 | 2.9330 * | 4.6835 | 1.7476 | 38.5463 * |
| IL-13 | 1.0007 | 3.3645 | 5.7906 | 2.8958 | 2.9978 | 277.2940 * |
| IL-17 | 0.9999 | 10.9838 * | 13.0255 | 18.0707 | 23.2681 | 13.7146 |
| TGF-β | 1.0003 | 1.0548 | 1.0202 | 1.1250 | 1.0458 | 0.5895 * |
| TNF-α | 0.9994 | 1.7852 | 2.2973 | 1.8613 | 1.8452 | 2.7390 * |
| Cytokine | CTL | VLPD | VLPS | SST | SNP | PHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ | 1.0008 | 1.3252 | 1.2621 | 2.3304 | 1.2954 | 28.8799 * |
| IL-10 | 1.0004 | 1.0184 | 1.1791 | 1.1932 | 1.0573 | 1.5886 |
| IL-12 | 1.0004 | 9.3729 | 22.7191 | 8.0548 | 16.6519 | 20.5071 |
| IL-22 | 0.9998 | 2.6487 | 4.4910 | 3.7454 | 27.5370 | 3.3154 |
| Cytokine | CTL | VLPD | VLPS | SST | SNP | PHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-2 | 1.0001 | 1.0835 | 1.0374 | 1.4260 | 1.2244 | 11.4364 * |
| IL-18 | 1.0001 | 1.0251 | 1.0267 | 0.9239 | 0.9422 | 0.3335 * |
| Cytokine | CTL | VLPD | VLPS | SST | SNP | PHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-23 | 0.9998 | 1.5099 | 2.4363 | 1.3674 | 1.9487 | 1.2240 |
| CXCL10 | 0.9999 | 1.6430 | 3.6965 | 41.4720 | 10.8317 * | 108.3192 * |
| Cytokine | Control | VLP Dengue | VLP SARS | Spike Trimer | Nucleo- Protein | PHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | 40.34 | 56.70 | 84.76 | 89.12 | 78.73 | 727.72 |
| IL-2 | 2.84 | 0.33 | 0.54 | 4.63 | 0.93 | 185.69 |
| IL-6 | 395.50 | 447.31 | 562.64 | 515.65 | 488.089 | 1333.86 |
| IL-10 | 6.18 | 7.71 | 8.49 | 7.68 | 9.19 | 118.37 |
| IL-12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| IL-13 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| IL-17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 56.43 |
| IL-18 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| IL-22 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| IL-23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| IFN-γ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CXCL-10 | 54.90 | 43.06 | 41.29 | 43.38 | 50.20 | 815.04 |
| TGF-β | 161.56 | 0 | 69.52 | 0 | 57.022 | 85.98 |
| TNF-α | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aeby, M.; Blanc, P.; Fellay, I.; Oberson, A.; Filgueira, L. The Expression of Fibrogenic Cytokines by Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Response to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. COVID 2023, 3, 897-913. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid3060065
Aeby M, Blanc P, Fellay I, Oberson A, Filgueira L. The Expression of Fibrogenic Cytokines by Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Response to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. COVID. 2023; 3(6):897-913. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid3060065
Chicago/Turabian StyleAeby, Michael, Pauline Blanc, Isabelle Fellay, Anne Oberson, and Luis Filgueira. 2023. "The Expression of Fibrogenic Cytokines by Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Response to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein" COVID 3, no. 6: 897-913. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid3060065
APA StyleAeby, M., Blanc, P., Fellay, I., Oberson, A., & Filgueira, L. (2023). The Expression of Fibrogenic Cytokines by Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Response to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. COVID, 3(6), 897-913. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid3060065






