Evaluating Serum RBP4 as an Auxiliary Biomarker for CKDu Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Information and Study Design
2.2. Clinical Sample Collection
2.3. Luminex X-MAP Screening
2.4. ELISA Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
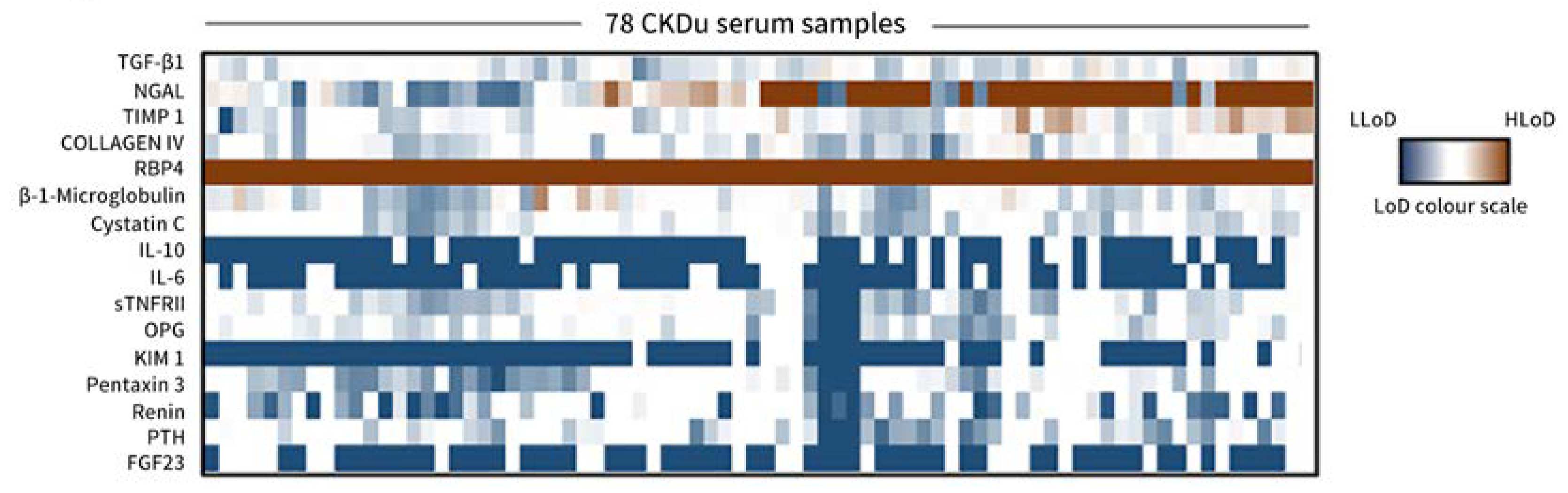
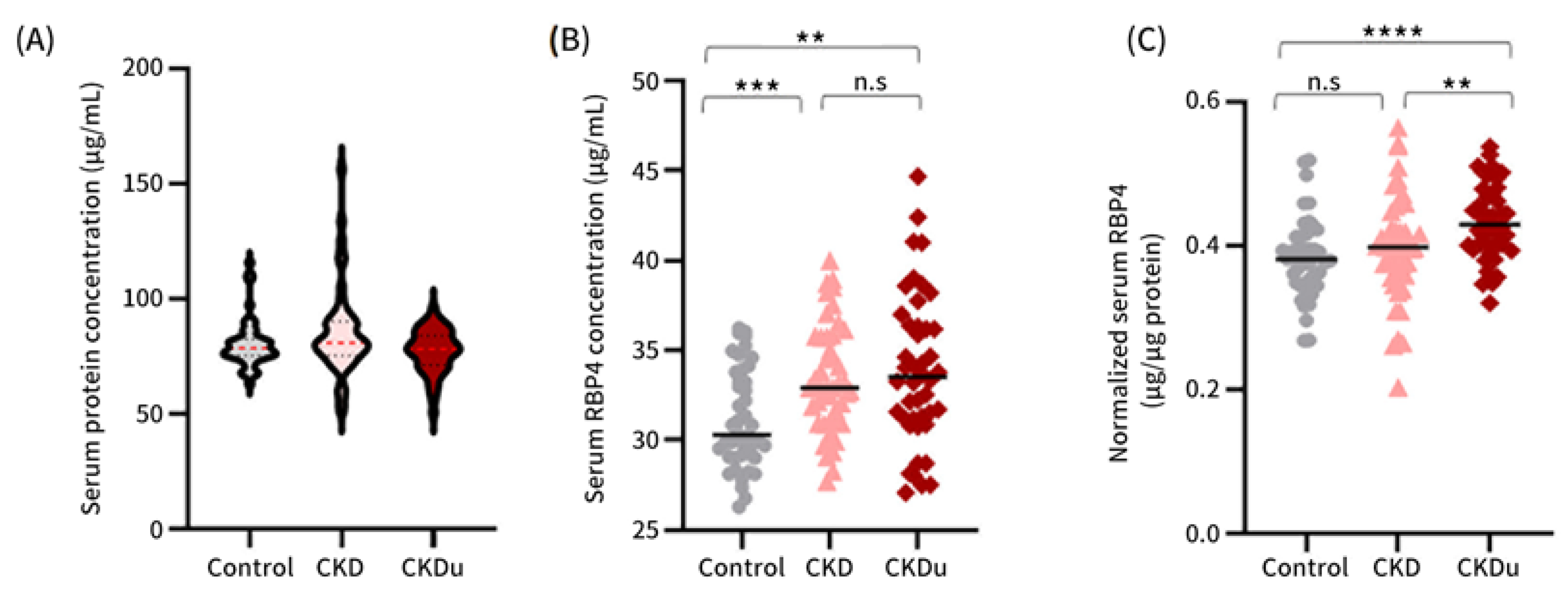
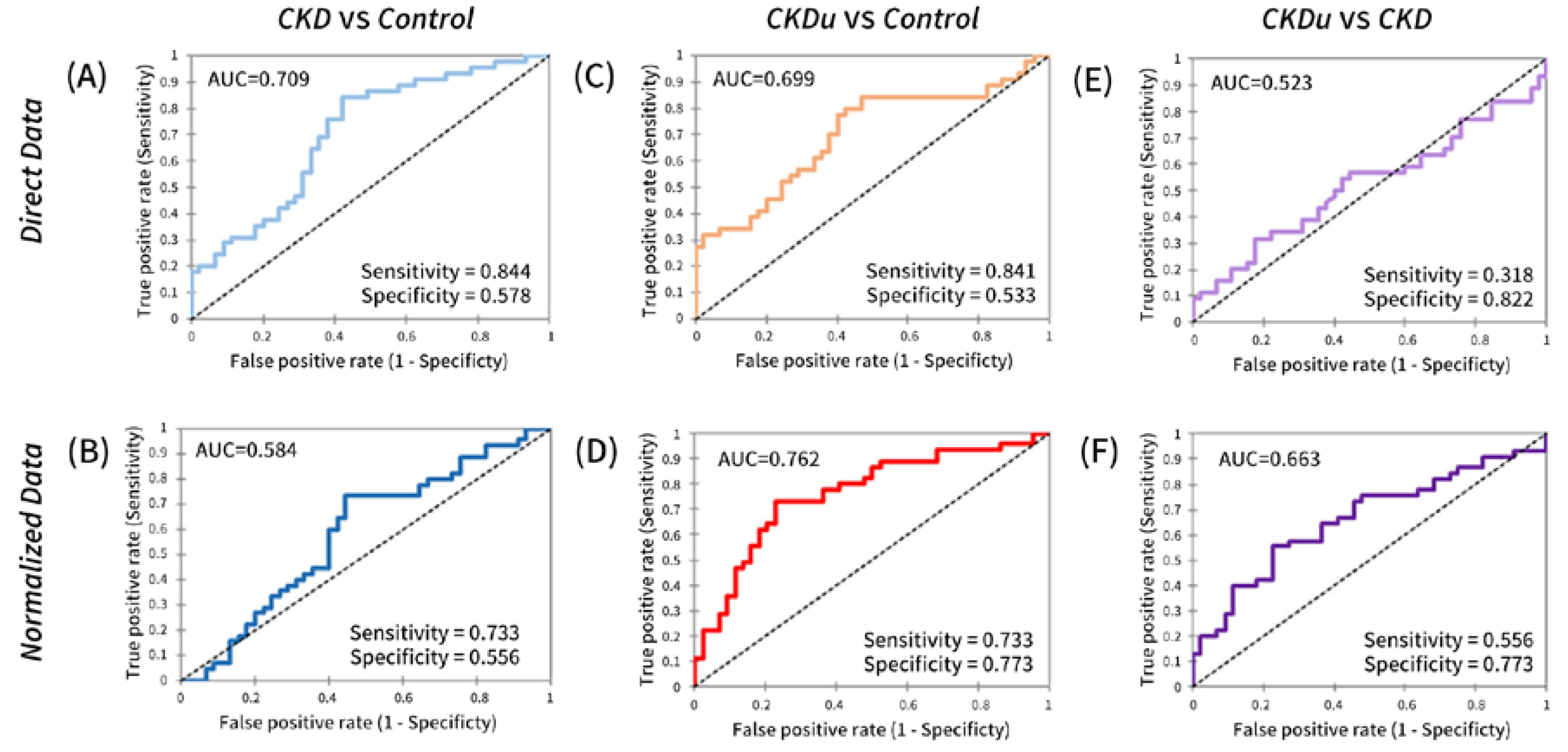
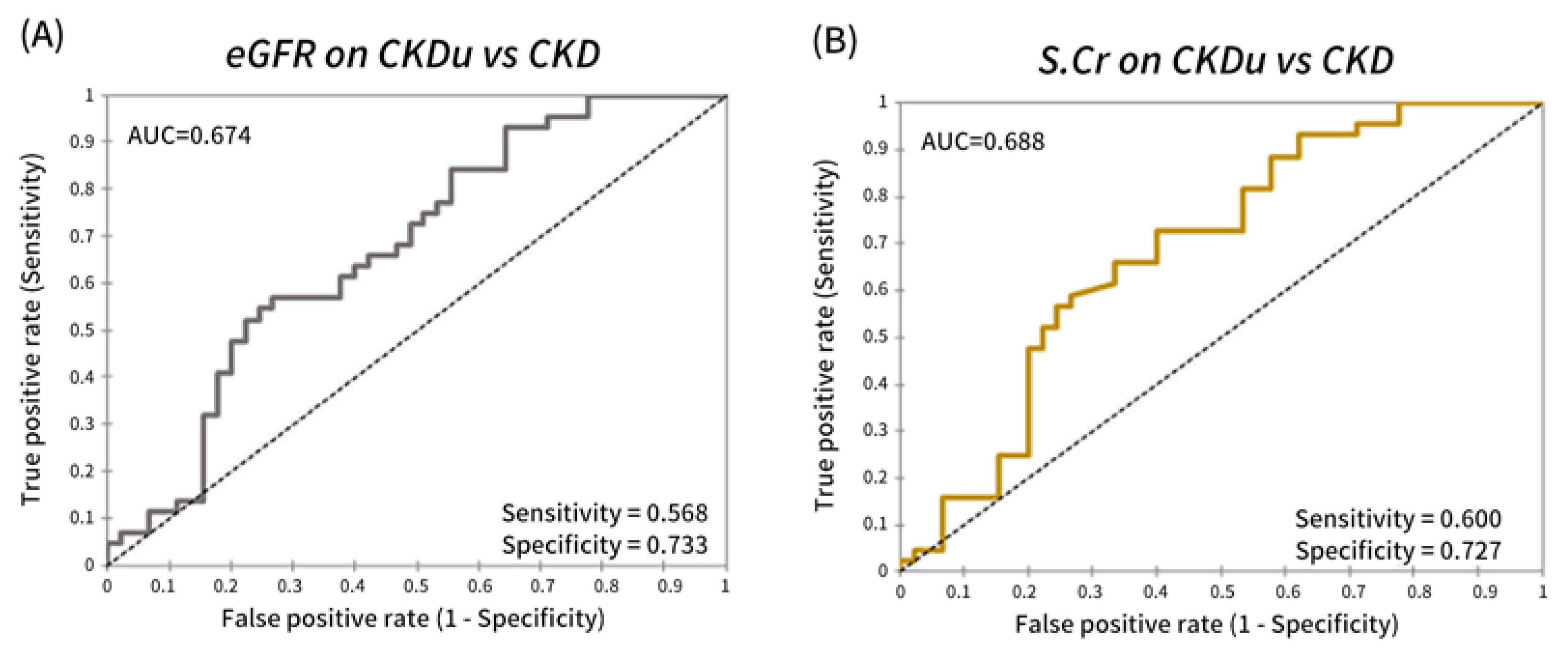
3.2. Serum RBP4 as a Potential Marker for Distinguishing between CKD and CKDu
3.3. Circulating RBP4 Levels and Significance in Study Cohorts
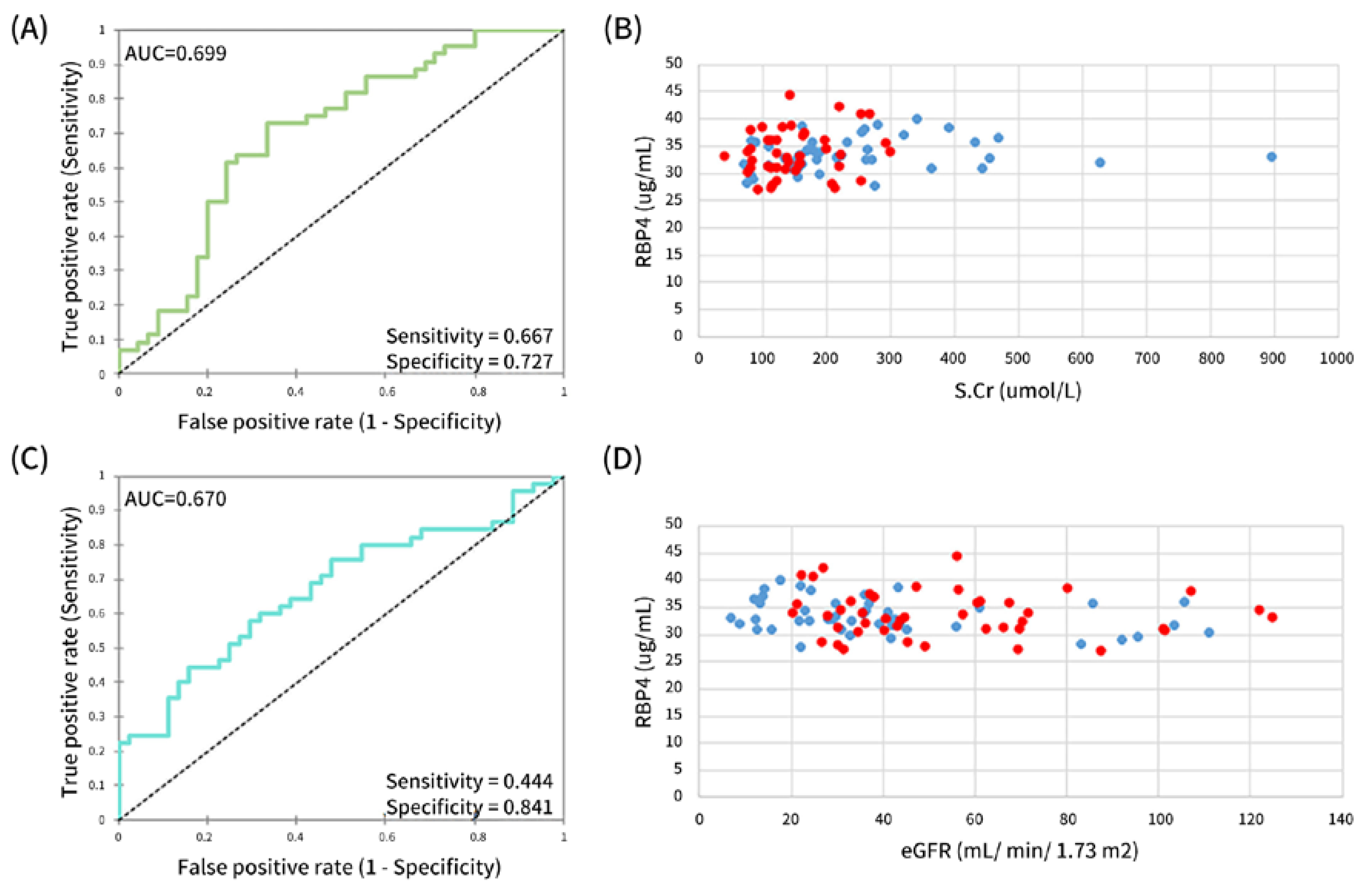
3.4. Performance of Serum RBP4 in Identifying Proximal Tubular Disease
3.5. Synergy in Glomerular and Tubular Markers for Distinguishing between CKD and CKDu
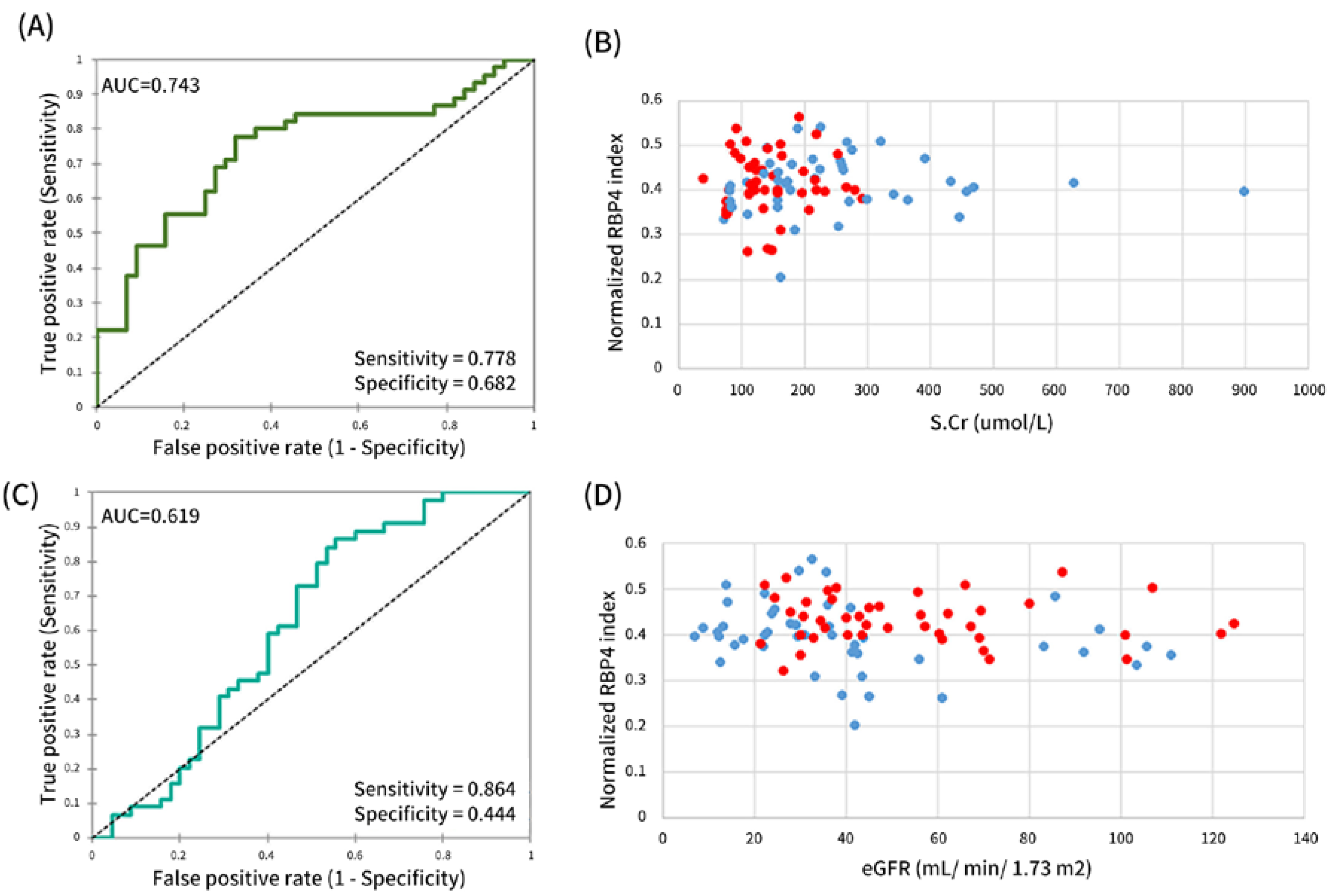
3.6. A Robust Putative Discriminatory Marker—Normalized RBP4:S.Cr Index
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weaver, V.M.; Fadrowski, J.J.; Jaar, B.G. Global dimensions of chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu): A modern era environmental and/or occupational nephropathy? BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gooneratne, I.; Ranaweera, A.; Liyanarachchi, N.; Gunawardane, N.; Lanerolle, R. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease in a Sri Lankan population. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries 2008, 28, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin-Cleary, C.; Ortiz, A. CKD hotspots around the world: Where, why and what the lessonsare. A CKJ review series. Clin. Kidney J. 2014, 7, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tatapudi, R.R.; Rentala, S.; Gullipalli, P.; Komarraju, A.L.; Singh, A.K.; Tatapudi, V.; Goru, K.B.; Bhimarasetty, D.M.; Narni, H. High Prevalence of CKD of Unknown Etiology in Uddanam, India. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, D.R.; Ramirez-Rubio, O.; Amador, J.J. CKD in Central America: A hot issue. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 59, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.V.; Gunasekar, A. Chronic kidney disease in two coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh, India: Role of drinking water. Environ. Geochem. Health 2013, 35, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minshawy, E.I. End-stage renal disease in the El-Minia Governorate, upper Egypt: An epidemiological study. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2011, 22, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Jayatilake, N.; Mendis, S.; Maheepala, P.; Mehta, F.R. Chronic kidney disease of uncertain aetiology: Prevalence and causative factors in a developing country. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wanigasuriya, K.P.; Peiris-John, R.J.; Wickremasinghe, R.; Hittarage, A. Chronic renal failure in North Central Province of Sri Lanka: An environmentally induced disease. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 101, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, J.M.R.S.; Senevirathna, D.M.A.N.; Dasanayake, D.M.R.S.B.; Herath, V.; Abeysekara, T.; Rajapaksha, K.H. Chronic renal failure among farm families in cascade irrigation systems in Sri Lanka associated with elevated dietary cadmium levels in rice and freshwater fish (Tilapia). Environ. Geochem. Health 2008, 30, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edirisinghe, E.A.N.V.; Manthrithilake, H.; Pitawala, H.M.T.G.A.; Dharmagunawardhane, H.A.; Wijayawardane, R.L. Geochemical and isotopic evidences from groundwater and surface water for understanding of natural contamination in chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) endemic zones in Sri Lanka. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2018, 54, 244–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thammitiyagodage, M.G.; Gunatillaka, M.M.; Ekanayaka, N.; Rathnayake, C.; Horadagoda, N.U.; Jayathissa, R.; Gunaratne, U.K.; Kumara, W.G.; Abeynayake, P. Ingestion of dug well water from an area with high prevalence of chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) and development of kidney and liver lesions in rats. Ceylon Med. J. 2017, 62, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wasana, H.M.S.; Aluthpatabendi, D.; Kularatne, W.M.T.D.; Wijekoon, P.; Weerasooriya, R.; Bandara, J. Drinking water quality and chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu): Synergic effects of fluoride, cadmium and hardness of water. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasana, H.; Perera, G.D.; Gunawardena, P.D.S.; Fernando, P.S.; Bandara, J. WHO water quality standards Vs Synergic effect(s) of fluoride, heavy metals and hardness in drinking water on kidney tissues. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulathunga, M.R.D.L.; Wijayawardena, M.A.A.; Naidu, R.; Wijeratne, A.W. Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in Sri Lanka and the exposure to environmental chemicals: A review of literature. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogo, A.B. Mechanisms of progression of chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2007, 22, 2011–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anand, S.; Montez-Rath, M.E.; Adasooriya, D. Prospective Biopsy-Based Study of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in Sri Lanka. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nanayakkara, S.; Komiya, T.; Ratnatunga, N.; Senevirathna, S.T.M.L.D.; Harada, K.H.; Hitomi, T.; Gobe, G.; Muso, E.; Abeysekera, T.; Koizumi, A. Tubulointerstitial damage as the major pathological lesion in endemic chronic kidney disease among farmers in North Central Province of Sri Lanka. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2012, 17, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wijkström, J.; Leiva, R.; Elinder, C.-G.; Leiva, S.; Trujillo, Z.; Trujillo, L.; Söderberg, M.; Hultenby, K.; Wernerson, A. Clinical and pathological characterization of Mesoamerican nephropathy: A new kidney disease in Central America. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 62, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, S.; Senevirathna, L.; Karunaratne, U.; Chandrajith, R.; Harada, K.H.; Hitomi, T.; Watanabe, T.; Abeysekara, T.; Aturaliya, T.N.C.; Koizumi, A. Evidence of tubular damage in the very early stage of chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology in the North Central Province of Sri Lanka: A cross-sectional study. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2012, 17, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernando, B.N.T.W.; Alli-Shaik, A.; Hemage, R.K.D.; Badurdeen, Z.; Hettiarachchi, T.W.; Abeysundara, H.T.K.; Abeysekara, T.D.J.; Wazil, A.; Rathnayake, S.; Gunaratne, J.; et al. Pilot Study of Renal Urinary Biomarkers for Diagnosis of CKD of Uncertain Etiology. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayanthooran, S.; Magana-Arachchi, D.N.; Gunerathne, L.; Abeysekera, T. Potential diagnostic biomarkers for chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka: A pilot study. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Silva, P.M.C.S.; Abdul, K.S.M.; Eakanayake, E.M.D.V.; Jayasinghe, S.S.; Jayasumana, C.; Asanthi, H.B.; Perera, H.S.D.; Chaminda, G.G.T.; Chandana, E.P.S.; Siribaddana, S.H. Urinary Biomarkers KIM-1 and NGAL for Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease of Uncertain Etiology (CKDu) among Agricultural Communities in Sri Lanka. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wanigasuriya, K.; Jayawardene, I.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Wickremasinghe, R. Novel urinary biomarkers and their association with urinary heavy metals in chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in Sri Lanka: A pilot study. Ceylon Med. J. 2017, 62, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paci, E.; Greene, L.H.; Jones, R.M.; Smith, L.J. Characterization of the molten globule state of retinol-binding protein using a molecular dynamics simulation approach. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 4826–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, D.S. 8 Plasma Retinol-Binding Protein. In The Retinoids; Sporn, M.B., Roberts, A.B., Goodman, D.S., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 41–88. [Google Scholar]
- Klisic, A.; Kavaric, N.; Ninic, A. Retinol-binding protein 4 versus albuminuria as predictors of estimated glomerular filtration rate decline in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2018, 23, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, F.; Moosaie, F.; Khaloo, P.; Firouzabadi, F.D.; Abhari, S.M.F.; Atainia, B.; Ardeshir, M.; Nakhjavani, M.; Esteghamati, A. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Retinol-Binding Protein-4 as Biomarkers for Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2020, 45, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, C. Circulating RBP4 Increase and Its Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 48, 205–207. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, F.R.; Goodman, D.S. The effects of diseases of the liver, thyroid, and kidneys on the transport of vitamin A in human plasma. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 2426–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, W.K.; Fleming, L.W. Plasma retinol and retinol binding protein concentrations in patients on maintenance haemodialysis with and without vitamin A supplements. Nephron 1982, 30, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasekara, K.B.; Dissanayake, D.M.; Sivakanesan, R.; Ranasinghe, A.; Karunarathna, R.H.; Kumara, G.W.G.P. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease, with special emphasis on chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology, in the north central region of Sri Lanka. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Hostetter, T. Automatic reporting of estimated glomerular filtration rate--just what the doctor ordered. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 2188–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.H.; Levine, K.E.; Lebov, J.; Harrington, J.; Kondash, A. A comparative review: Chronic Kidney Disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) research conducted in Latin America versus Asia. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, G.A.; Brehm, M.; Groß, R.; Heider, J.; Sauter, J.; Baier, D.M.; Wehde, T.; Castriciano, S.; Schmidt, A.H.; Lange, V. Non-invasive determination of CMV serostatus from dried buccal swab samples: Assay development, validation and application to 1.2 million samples. J. Infect Dis. 2021, 224, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, J.; Isoherranen, N.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; Petrie, I.; Kestenbaum, B.; Yeung, C. Chronic Kidney Disease Alters Vitamin A Homeostasis via Effects on Hepatic RBP4 Protein Expression and Metabolic Enzymes. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2016, 9, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervaet, B.A.; Nast, C.C.; Jayasumana, C.; Schreurs, G.; Roels, F.; Herath, C.; Kojc, N.; Samaee, V.; Rodrigo, S.; Gowrishankar, S.; et al. Chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities is a toxin-induced proximal tubular nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vahlquist, A.; Peterson, P.A.; Wibell, L. Metabolism of the vitamin A transporting protein complex. I. Turnover studies in normal persons and in patients with chronic renal failure. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1973, 3, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.A.; Strober, W.; Mogielnicki, R.P. The renal handling of low molecular weight proteins. II. Disorders of serum protein catabolism in patients with tubular proteinuria, the nephrotic syndrome, or uremia. J. Clin. Investig. 1972, 51, 2162–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Variable | Average ± SD or Cases (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CKDu (n = 44) | NECKD (n = 45) | NEC (n = 45) | |
| Age, years | 51.7 ± 9.3 | 49.62 ± 13.5 | 48.1 ± 12.1 |
| Gender distribution, males | 40 (90.9) | 23 (51) | 18 (40) |
| Family history of CKD | 22 (50) | 7 (15.5) | 4 (8.9) |
| Smoking | 21 (47.7) | 11 (24.4) | 7 (15.5) |
| Chewing betel | 36 (81.8) | 6 (13.3) | 23 (51) |
| Alcohol consumption | 19 (43.2) | 8 (17.8) | 12 (26.7) |
| Hypertension | 14 (31.8) | 36 (80) | 0 (0) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 2 (4.5) | 21 (46.7) | 0 (0) |
| History of malaria | 18 (40.9) | 7 (15.6) | 0 (0) |
| S.Cr | eGFR | Raw RBP4 | Normalized RBP4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBP4 | RBP4:SCr | RBP4:eGFR | RBP4 | RBP4:SCr | RBP4:eGFR | ||||
| CKD vs. NEC | AUC | 0.939 | 0.917 | 0.709 | 0.934 | 0.916 | 0.584 | 0.937 | 0.897 |
| Sensitivity | 0.800 | 0.844 | 0.844 | 0.800 | 0.844 | 0.733 | 0.844 | 0.800 | |
| Specificity | 1.000 | 0.978 | 0.578 | 1.000 | 0.978 | 0.556 | 0.933 | 0.978 | |
| CKDu vs. NEC | AUC | 0.909 | 0.883 | 0.699 | 0.880 | 0.893 | 0.762 | 0.847 | 0.912 |
| Sensitivity | 0.750 | 0.841 | 0.841 | 0.750 | 0.841 | 0.733 | 0.867 | 0.841 | |
| Specificity | 0.956 | 0.911 | 0.533 | 0.933 | 0.889 | 0.773 | 0.727 | 0.956 | |
| CKD vs. CKDu | AUC | 0.688 | 0.674 | 0.523 | 0.699 | 0.670 | 0.663 | 0.743 | 0.619 |
| Sensitivity | 0.600 | 0.568 | 0.822 | 0.667 | 0.444 | 0.556 | 0.778 | 0.864 | |
| Specificity | 0.727 | 0.733 | 0.318 | 0.727 | 0.841 | 0.773 | 0.682 | 0.444 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Swa, H.L.F.; Fernando, B.N.T.; Premarathna, S.; Alli-Shaik, A.; Badurdeen, Z.; Gunarathna, J.; Nanayakkara, N. Evaluating Serum RBP4 as an Auxiliary Biomarker for CKDu Diagnosis. Kidney Dial. 2022, 2, 576-587. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial2040052
Swa HLF, Fernando BNT, Premarathna S, Alli-Shaik A, Badurdeen Z, Gunarathna J, Nanayakkara N. Evaluating Serum RBP4 as an Auxiliary Biomarker for CKDu Diagnosis. Kidney and Dialysis. 2022; 2(4):576-587. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial2040052
Chicago/Turabian StyleSwa, Hannah L. F., Buddhi N. T. Fernando, Shakila Premarathna, Asfa Alli-Shaik, Zeid Badurdeen, Jayantha Gunarathna, and Nishantha Nanayakkara. 2022. "Evaluating Serum RBP4 as an Auxiliary Biomarker for CKDu Diagnosis" Kidney and Dialysis 2, no. 4: 576-587. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial2040052
APA StyleSwa, H. L. F., Fernando, B. N. T., Premarathna, S., Alli-Shaik, A., Badurdeen, Z., Gunarathna, J., & Nanayakkara, N. (2022). Evaluating Serum RBP4 as an Auxiliary Biomarker for CKDu Diagnosis. Kidney and Dialysis, 2(4), 576-587. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial2040052






