High-Speed 3D Vision Based on Structured Light Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. High-Speed Vision Devices
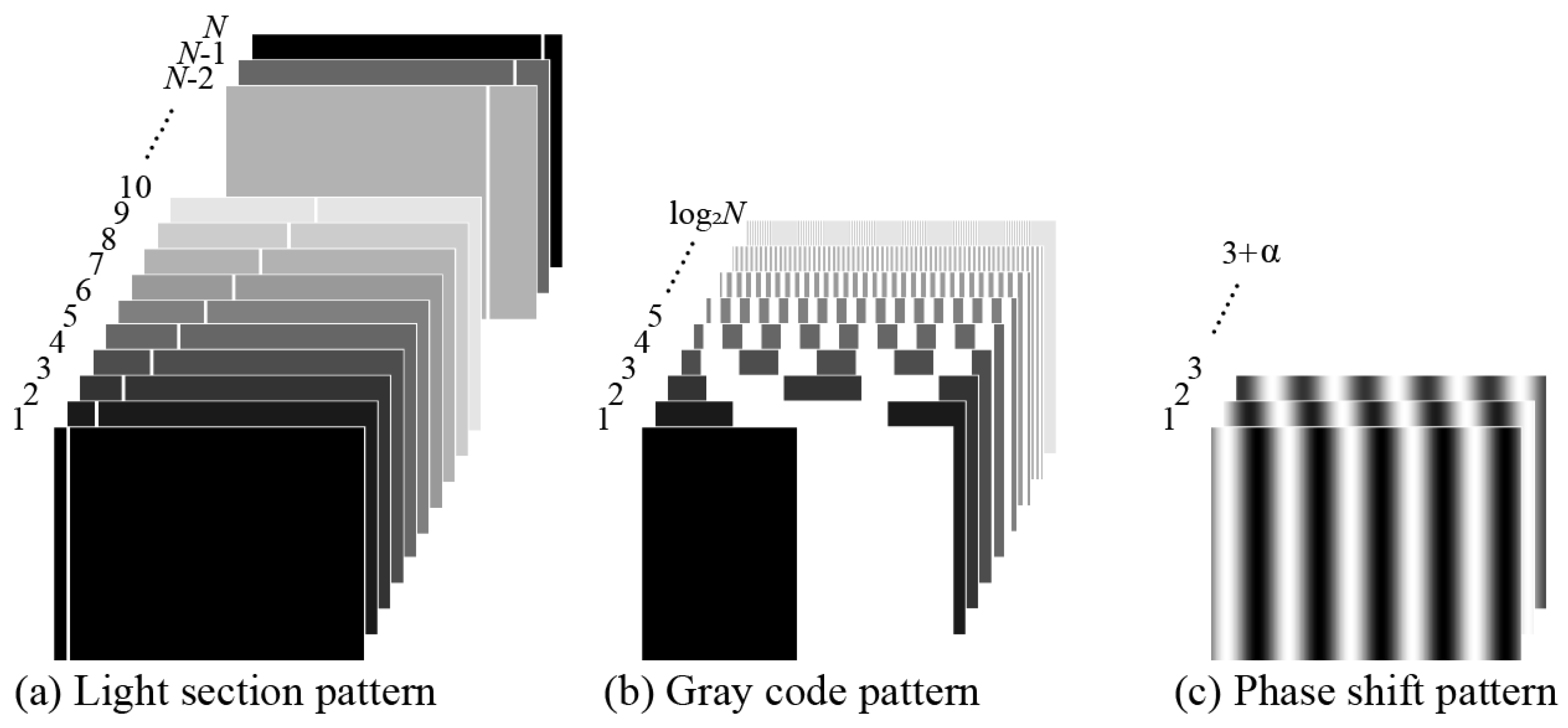
3. Conventional Structured Light Patterns
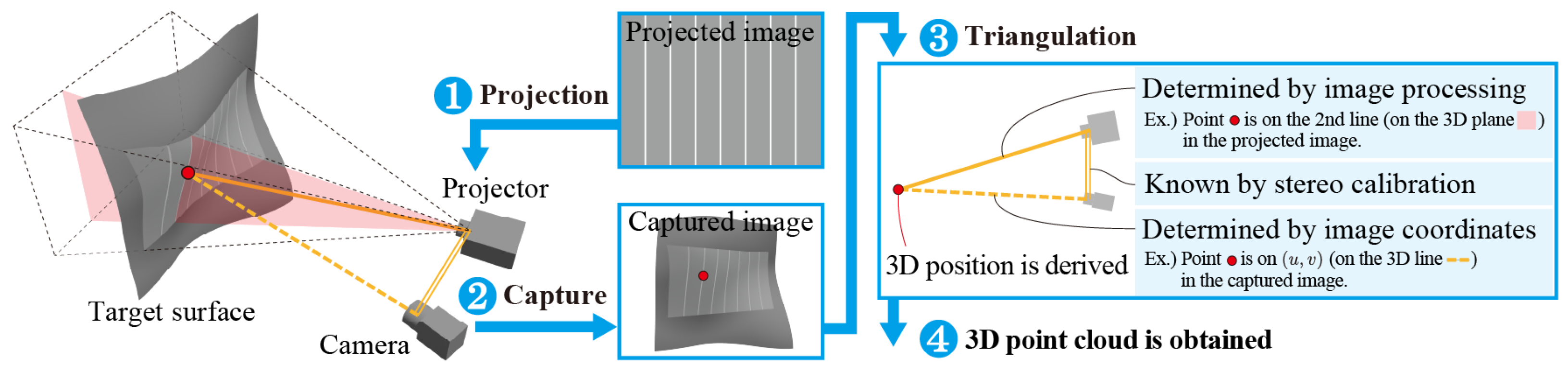
4. High-Speed 3D Measurement
4.1. Multi-Shot Methods
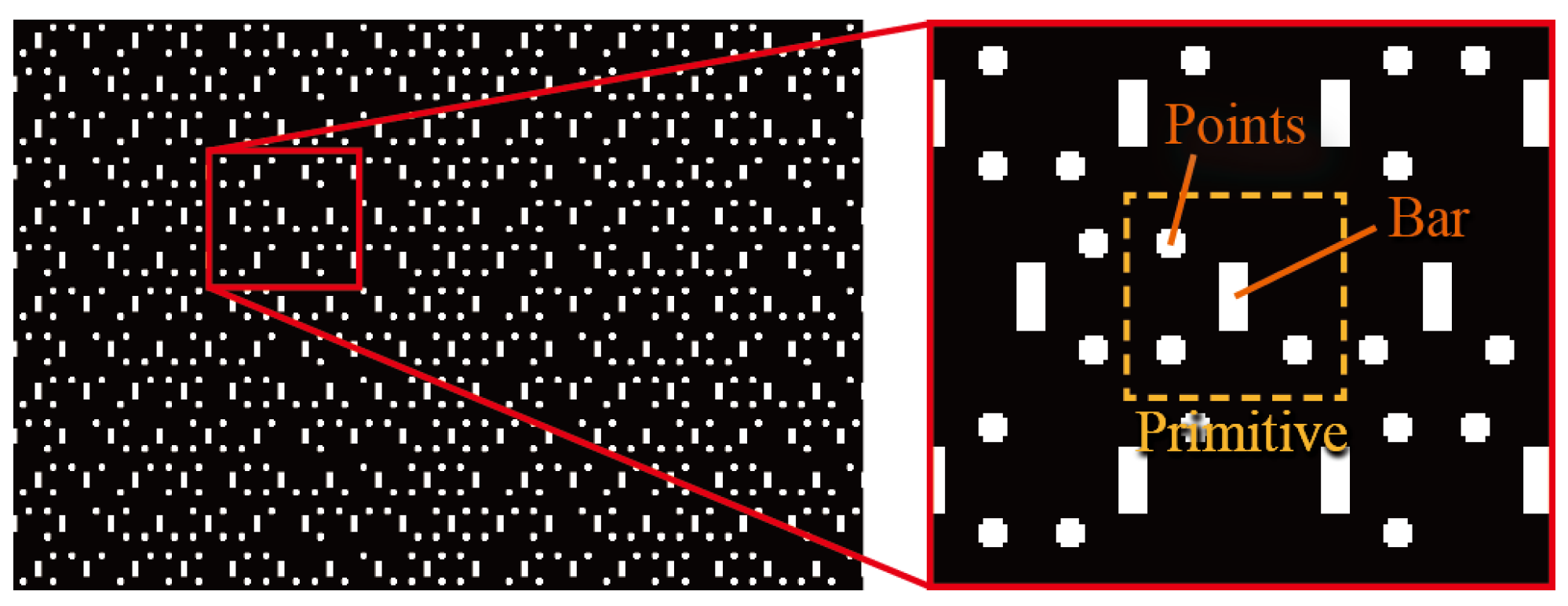
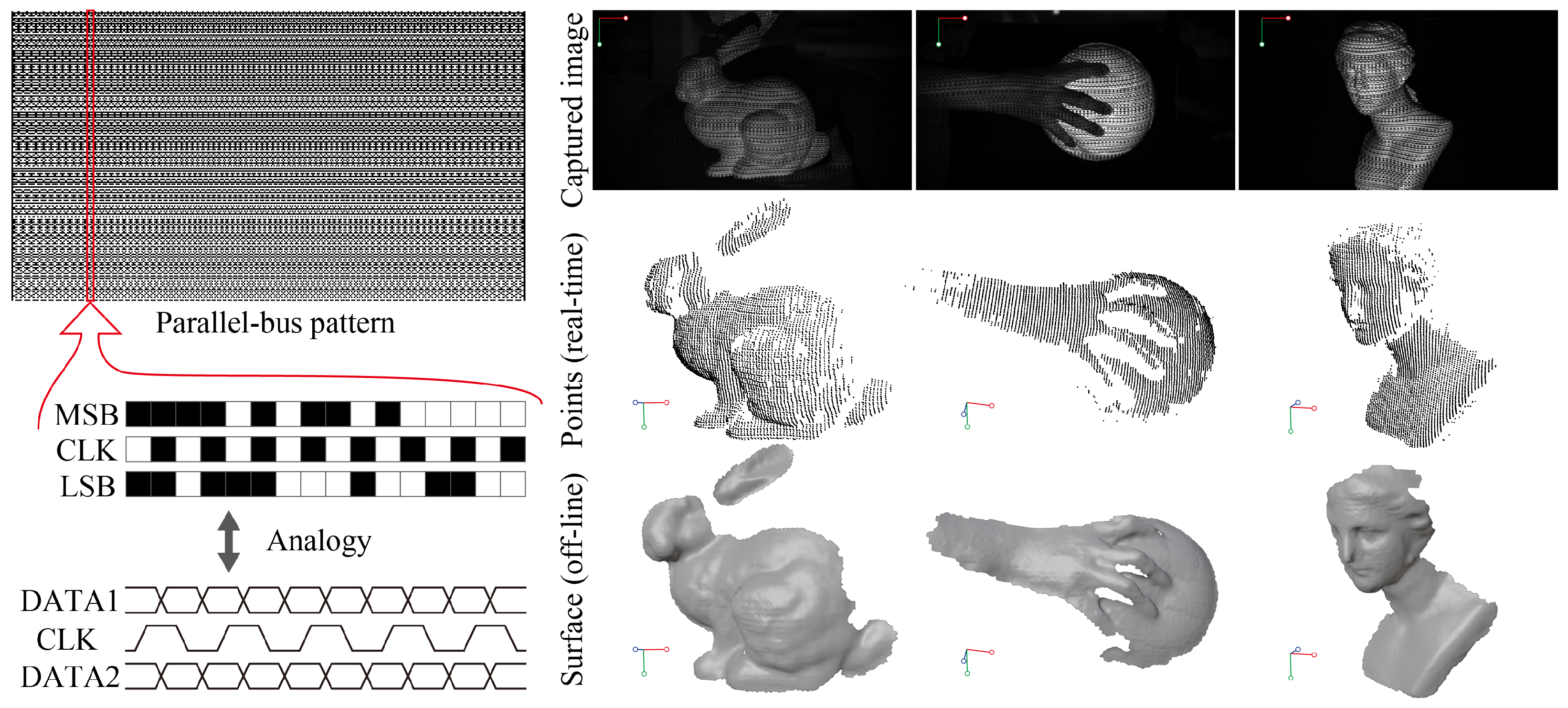
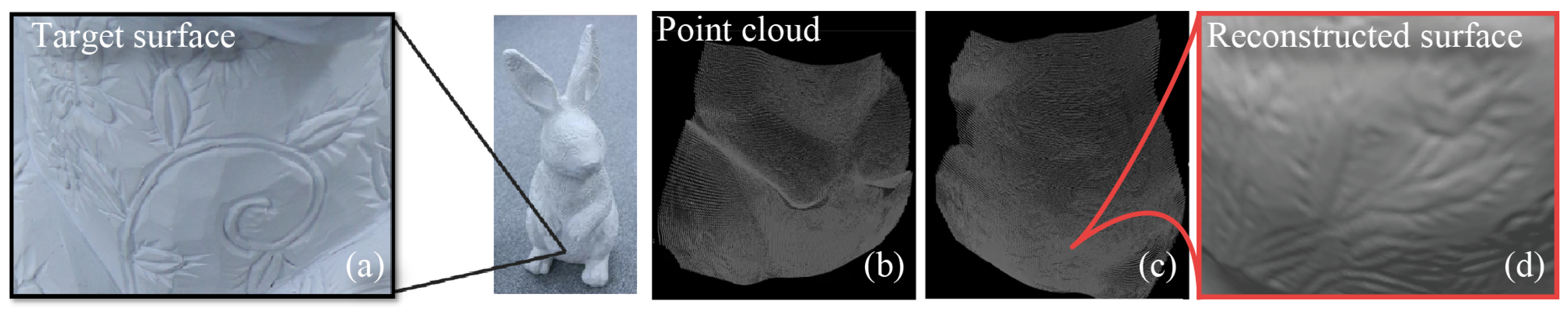
4.2. One-Shot Methods
5. Applications of High-Speed 3D Measurement
5.1. High-Speed Measurement and Integration of Depth and Normal
5.2. Three-Dimensional Motion Estimation and Reconstruction
5.3. Application in Robotics and XR
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.; Xi, N.; Zhang, C.; Shi, Q.; Gregory, J. Real-time 3D shape inspection system of automotive parts based on structured light pattern. Opt. Laser Technol. 2011, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ibanez-Guzman, J. Lidar for Autonomous Driving: The Principles, Challenges, and Trends for Automotive Lidar and Perception Systems. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 37, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Cai, L. Robust Hand Gesture Recognition Based on RGB-D Data for Natural Human–Computer Interaction. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 54549–54562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lin, X.; Xin, Y.; Duan, K.; Tang, Q. Large depth-of-view portable three-dimensional laser scanner and its segmental calibration for robot vision. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2007, 45, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosarevsky, S. Practical way to measure large-scale 2D parts using repositioning on coordinate-measuring machines. Measurement 2010, 43, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.H. Frequency-Based 3D Reconstruction of Transparent and Specular Objects. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadambi, A.; Taamazyan, V.; Shi, B.; Raskar, R. Depth Sensing Using Geometrically Constrained Polarization Normals. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2017, 125, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Chiba, H.; Yamato, K.; Oku, H. Development of a coded exposure camera for high-speed 3D measurement using microscope. In Imaging Systems and Applications; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; p. ITu3B.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhou, H.; Banerjee, P.P. Use of structured light in 3D reconstruction of transparent objects. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, B314–B324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Qin, L.; Li, Y.; Hou, J.; Xiao, C. An Adaptive Multiexposure Scheme for the Structured Light Profilometry of Highly Reflective Surfaces Using Complementary Binary Gray Code. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Q.; Aoyama, T.; Takaki, T.; Ishii, I. Robot-mounted 500-fps 3-D shape measurement using motion-compensated coded structured light method. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO 2014), Bali, Indonesia, 5–10 December 2014; pp. 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiki, A.; Shimada, K.; Kin, Y.; Ishii, I. Development of an Active High-Speed 3-D Vision System. Sensors 2019, 19, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, L.; Watanabe, Y.; Ishikawa, M. MIDAS Projection: Markerless and Modelless Dynamic Projection Mapping for Material Representation. ACM Trans. Graph. 2018, 37, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, T.; Leibe, B.; Van Gool, L. Fast 3D Scanning with Automatic Motion Compensation. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisvert, J.; Drouin, M.A.; Dicaire, L.G.; Picard, M.; Godin, G. Motion Compensation for Phase-Shift Structured-Light Systems Based on a Total-Variation Framework. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Qingdao, China, 10–12 October 2017; pp. 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansard, M.; Lee, S.; Choi, O.; Horaud, R. Time-of-Flight Cameras: Principles, Methods and Applications; Springer Publishing Company: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J. Structured-light 3D surface imaging: A tutorial. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2011, 3, 128–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, P. Quantum-Noise Limited Distance Resolution of Optical Range Imaging Techniques. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2008, 55, 2368–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, R.M.; Dorrington, A.A.; Künnemeyer, R.; Cree, M.J. Range imager performance comparison in homodyne and heterodyne operating modes. Three-Dimens. Imaging Metrol. 2009, 7239, 723905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamji, C.; Godbaz, J.; Oh, M.; Mehta, S.; Payne, A.; Ortiz, S.; Nagaraja, S.; Perry, T.; Thompson, B. A Review of Indirect Time-of-Flight Technologies. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2022, 69, 2779–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, L.; Tabata, S.; Ishikawa, M. 3D Sensing Based on High-speed Image Processing and Applications (in Japanese). Laser Soc. Jpn. Rev. Laser Eng. 2023, 51, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Nose, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Katayama, H.; Uehara, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Shida, S.; Odahara, M.; Takamiya, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Miyashita, L.; et al. Design and Performance of a 1 ms High-Speed Vision Chip with 3D-Stacked 140 GOPS Column-Parallel PEs †. Sensors 2018, 18, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, K.; Oku, H.; Ishikawa, M. High-speed gaze controller for millisecond-order pan/tilt camera. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 6186–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, K.; Oku, H. Saccade Mirror 3: High-speed gaze controller with ultra wide gaze control range using triple rotational mirrors. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, H.; Ishikawa, M. High-speed liquid lens for computer vision. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 2643–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Narita, G.; Tatsuno, S.; Yuasa, T.; Sumino, K.; Ishikawa, M. High-speed 8-bit image projector at 1000 fps with 3 ms delay. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Display Workshops, Otsu, Japan, 9–11 December 2015; pp. 1421–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.; Ishikawa, M. High-speed and high-brightness color single-chip DLP projector using high-power LED-based light sources. In Proceedings of the 26th International Display Workshops, Sapporo, Japan, 27–29 November 2019; pp. 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lippmann, U.; Aswendt, P.; Hoefling, R.; Sumino, K.; Ueda, K.; Ono, Y.; Kasebe, H.; Yamashita, T.; Yuasa, T.; Watanabe, Y. High-Speed RGB+IR Projector Based on Coaxial Optical Design with Two Digital Mirror Devices. In Proceedings of the International Display Workshops, Sapporo, Japan, 4–6 December 2021; p. 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fei, Z.; Yang, J.; Tan, Z.; Luo, M. Line structured light calibration method and centerline extraction: A review. Results Phys. 2020, 19, 103637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.B.; Chen, Y.; Wu, M.Y.; Guan, C.R.; Yu, X.Y. 3D Measurement Technology by Structured Light Using Stripe-Edge-Based Gray Code. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 48, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Zhang, S. Flexible 3-D shape measurement using projector defocusing. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 3080–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, P.; Wang, H. A review for three-step phase-shifting algorithms. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2025, 186, 108751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lan, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, J.; Lee, H. Phase Unwrapping in InSAR: A Review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Nayar, S.K. Micro Phase Shifting. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, M.; Tabata, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Multi-pattern Embedded Phase Shifting Using a High-Speed Projector for Fast and Accurate Dynamic 3D Measurement. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, S.; Maruyama, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Pixelwise Phase Unwrapping Based on Ordered Periods Phase Shift. Sensors 2019, 19, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Takaki, T.; Ishii, I. GPU-based real-time structured light 3D scanner at 500 fps. In Real-Time Image and Video Processing 2012; Kehtarnavaz, N., Carlsohn, M.F., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8437, pp. 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S. Superfast multifrequency phase-shifting technique with optimal pulse width modulation. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 5149–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, C.; Tao, T.; Feng, S.; Huang, L.; Asundi, A.; Chen, Q. Micro Fourier Transform Profilometry (μFTP): 3D shape measurement at 10,000 frames per second. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2018, 102, 70–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zuo, C.; Guo, W.; Tao, T.; Zhang, Q. High-speed three-dimensional shape measurement based on cyclic complementary Gray-code light. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 1283–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. High-speed and high-efficiency three-dimensional shape measurement based on Gray-coded light. Photon. Res. 2020, 8, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Watanabe, Y. High-Frame-Rate Projection with Thousands of Frames Per Second Based on the Multi-Bit Superimposition Method. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Sydney, Australia, 16–20 October 2023; pp. 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zhu, J.; Jing, H. Optical 3-D surface reconstruction with color binary speckle pattern encoding. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 3452–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Zhao, H.; Ji, Y.; Deng, Z.; Jin, Z.; Feng, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; Zuo, C. High-Resolution, Wide-Field-of-View, and Real-Time 3D Imaging Based on Spatial-Temporal Speckle Projection Profilometry with a VCSEL Projector Array. ACS Photonics 2024, 11, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Komuro, T.; Ishikawa, M. 955-fps Real-time Shape Measurement of a Moving/Deforming Object using High-speed Vision for Numerous-point Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Rome, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 3192–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, S.; Noguchi, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Ishikawa, M. High-speed 3D sensing with three-view geometry using a segmented pattern. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 3900–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharstein, D.; Szeliski, R.; Zabih, R. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 47, 7–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita, L.; Tabata, S.; Ishikawa, M. High-Speed and Low-Latency 3D Sensing with a Parallel-Bus Pattern. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Prague, Czech Republic, 12–16 September 2022; pp. 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, F.; Diaconis, P.; Graham, R. Universal cycles for combinatorial structures. Discret. Math. 1992, 110, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horan, V.; Stevens, B. Locating patterns in the de Bruijn torus. Discret. Math. 2016, 339, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehab, D.; Rusinkiewicz, S.; Davis, J.; Ramamoorthi, R. Efficiently Combining Positions and Normals for Precise 3D Geometry. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG); Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, L.; Kimura, Y.; Tabata, S.; Ishikawa, M. High-Speed Depth-Normal Measurement and Fusion Based on Multiband Sensing and Block Parallelization. J. Robot. Mechatronics 2022, 34, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoshi Tabata, Y.W.; Ishikawa, M. High-speed 6-DoF Tracking Based on Small-Displacement Assumption. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2018, J101-D, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar]
- Besl, P.; McKay, N.D. A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoshi Tabata, Y.W.; Ishikawa, M. Development of a Compact High-speed 3D Scanner. J. Robot. Soc. Jpn. Lett. 2024, 42, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Billinghurst, M. Marker tracking and HMD calibration for a video-based augmented reality conferencing system. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE and ACM International Workshop on Augmented Reality (IWAR’99), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–21 October 1999; pp. 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.; Murray, D. Parallel Tracking and Mapping for Small AR Workspaces. In Proceedings of the 2007 6th IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, Nara, Japan, 13–16 November 2007; pp. 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagami, S.; Hashimoto, K. Animated Stickies: Fast Video Projection Mapping onto a Markerless Plane through a Direct Closed-Loop Alignment. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2019, 25, 3094–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisaichi, S.; Sumino, K.; Ueda, K.; Kasebe, H.; Yamashita, T.; Yuasa, T.; Lippmann, U.; Aswendt, P.; Höfling, R.; Watanabe, Y. Depth-Aware Dynamic Projection Mapping using High-speed RGB and IR Projectors. In Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH Asia 2021 Emerging Technologies, Tokyo, Japan, 14–17 December 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
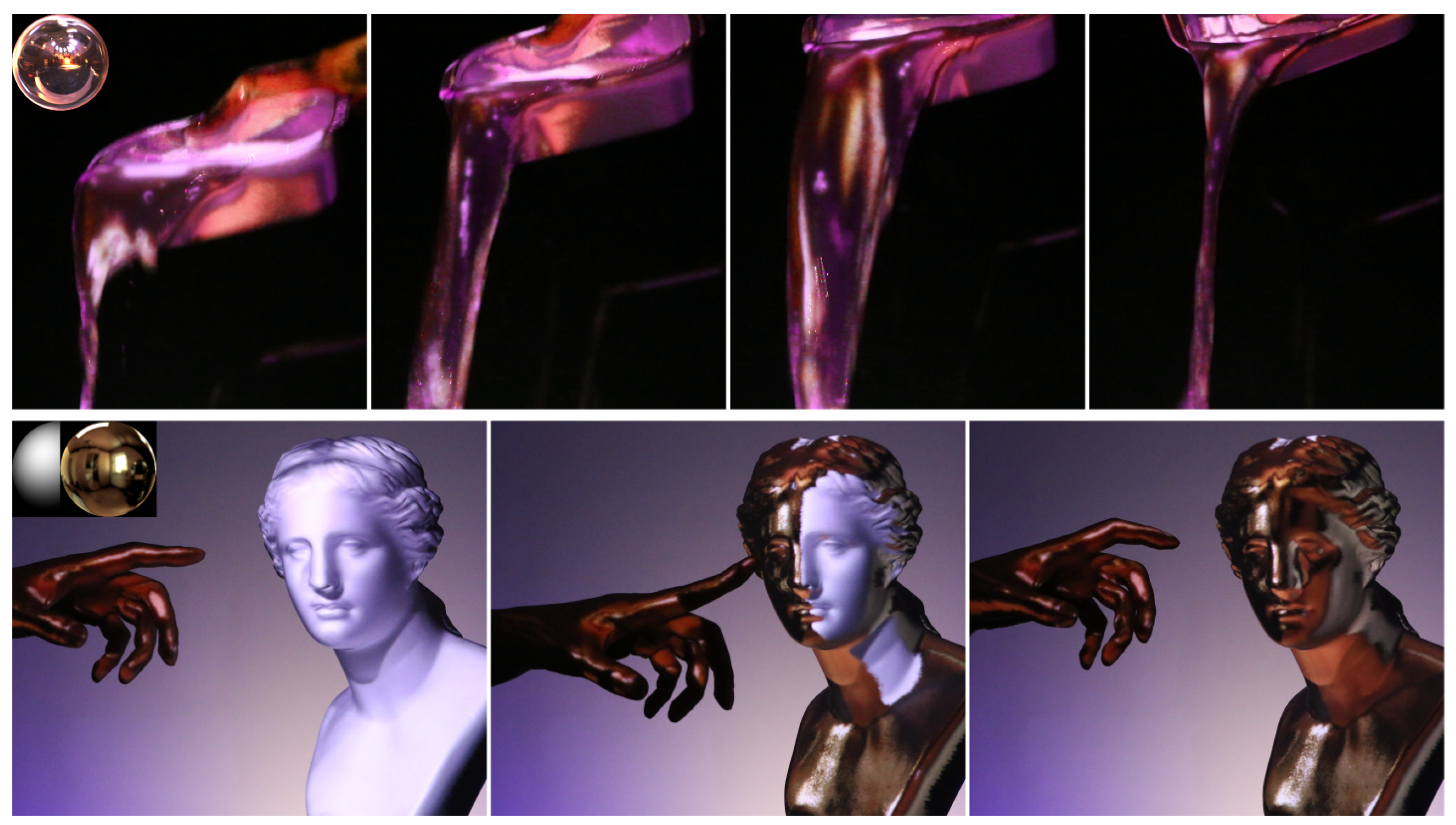

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyashita, L.; Tabata, S.; Ishikawa, M. High-Speed 3D Vision Based on Structured Light Methods. Metrology 2025, 5, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020024
Miyashita L, Tabata S, Ishikawa M. High-Speed 3D Vision Based on Structured Light Methods. Metrology. 2025; 5(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020024
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyashita, Leo, Satoshi Tabata, and Masatoshi Ishikawa. 2025. "High-Speed 3D Vision Based on Structured Light Methods" Metrology 5, no. 2: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020024
APA StyleMiyashita, L., Tabata, S., & Ishikawa, M. (2025). High-Speed 3D Vision Based on Structured Light Methods. Metrology, 5(2), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020024





