Black Fungi Research: Out-of-This-World Implications
Definition
:1. Introduction
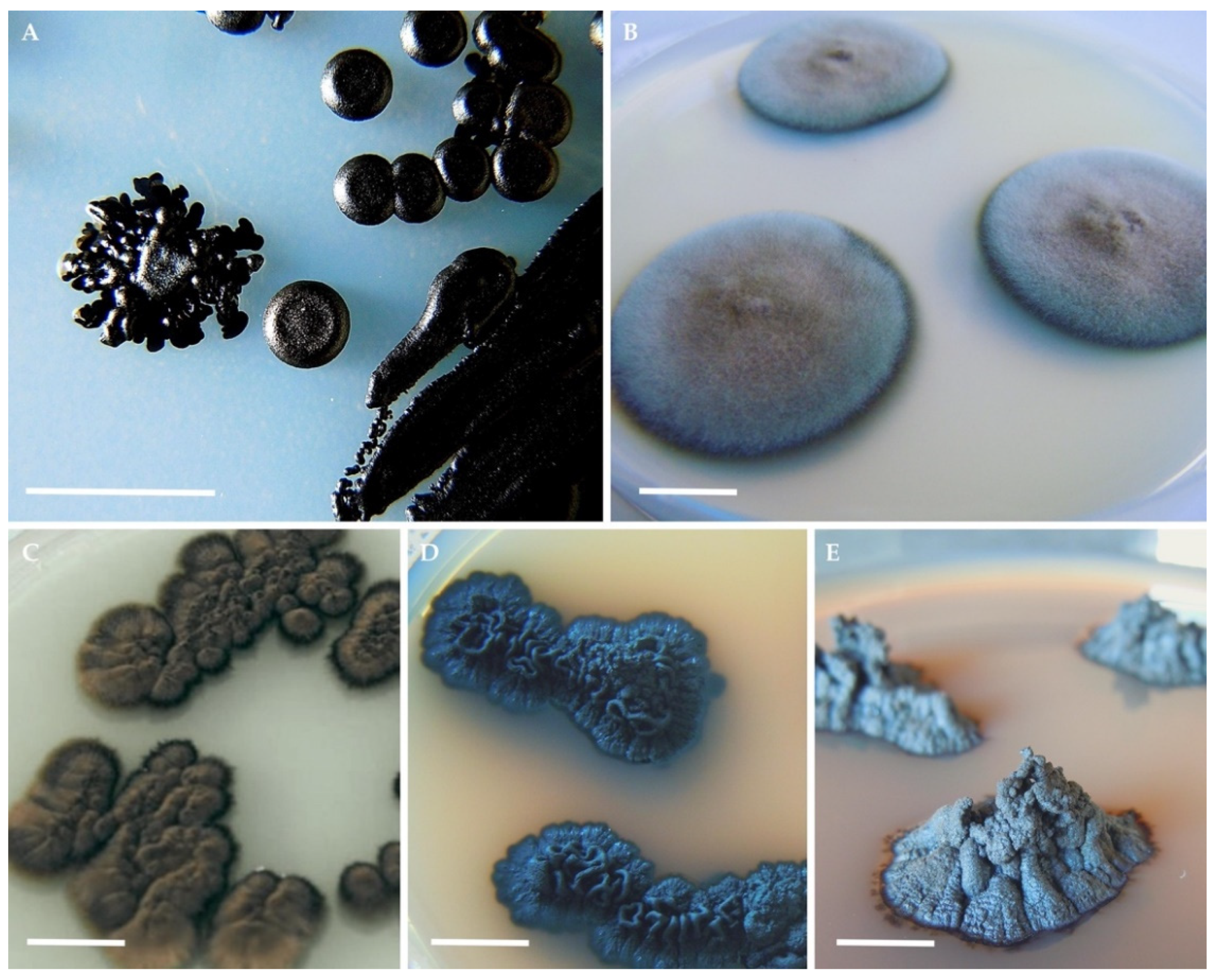
2. Black Fungi: An Exquisite Example of Fungal Extremophiles
3. Life Finds Its Way: Mechanisms of Stress Tolerance in Black Fungi
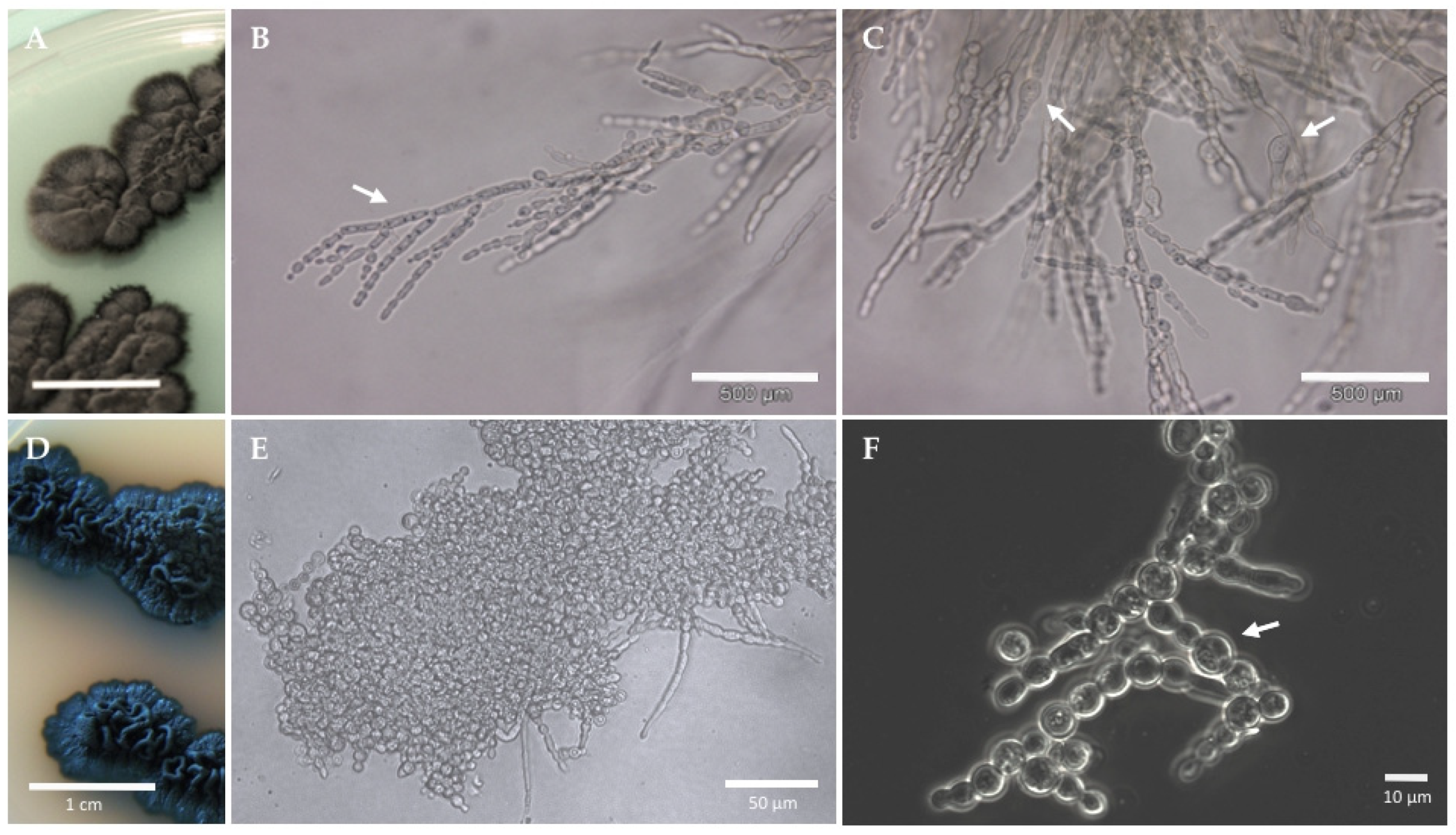
3.1. Morphophysiological Traits
3.2. Adaptations at the Molecular Level
4. From Stress Adaptation to Biotechnological Significance
4.1. Astrobiology Studies
4.2. Black Fungi as Biotechnologically Relevant Microorganisms
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Entry Link on the Encyclopedia Platform
References
- Merino, N.; Aronson, H.S.; Bojanova, D.P.; Feyhl-buska, J.; Wong, M.L.; Zhang, S.; Giovannelli, D. Living at the Extremes: Extremophiles and the Limits of Life in a Planetary Context. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibanda, T.; Selvarajan, R.; Tekere, M. Synthetic extreme environments: Overlooked sources of potential biotechnologically relevant microorganisms. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malo, M.; Dadachova, E. Melanin as an Energy Transducer and a Radioprotector in Black Fungi. In Fungi in Extreme Environments: Ecological Role and Biotechnological Significance; Tiquia-Arashiro, S., Grube, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 9783030190309. [Google Scholar]
- Rampelotto, P. Extremophiles and Extreme Environments. Life 2013, 3, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Jain, K.; Desai, C.; Tiwari, O.; Madamwar, D. Microbial Community Dynamics of Extremophiles/Extreme Environment. In Microbial Diversity in the Genomic Era; Das, S., Hirak, R.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 323–332. ISBN 9780128148495. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Wangi, W.; He, J.; Ma, Y.; Xiao, F.; He, S. Antioxidative system of Deinococcus radiodurans. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 171, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, A.; González-Toril, E. Eukaryotic Life in Extreme Environments: Acidophilic Fungi. In Fungi in Extreme Environments: Ecological Role and Biotechnological Significance; Tiquia-Arashiro, M.G., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 21–38. [Google Scholar]
- Shtarkman, Y.M.; Koçer, Z.A.; Edgar, R.; Veerapaneni, R.S.; D’Elia, T.; Morris, P.F.; Rogers, S.O. Subglacial Lake Vostok (Antarctica) Accretion Ice Contains a Diverse Set of Sequences from Aquatic, Marine and Sediment-Inhabiting Bacteria and Eukarya. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.L.; Lantz, H.; Pettersson, O.V.; Frisvad, J.C.; Thrane, U.; Heipieper, H.J.; Dijksterhuis, J.; Grabherr, M.; Pettersson, M.; Tellgren-roth, C.; et al. Genome and physiology of the ascomycete filamentous fungus Xeromyces bisporus, the most xerophilic organism isolated to date. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Ramos, J.; Plemenitaš, A. Halotolerant and halophilic fungi. Mycol. Res. 2009, 113, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostinčar, C.; Grube, M.; De Hoog, S.; Zalar, P.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Extremotolerance in fungi: Evolution on the edge. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 71, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckbach, J.; Rampelotto, P.H. Polyextremophiles. In Microbial Evolution under Extreme Conditions; Bakermans, C., Ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 153–170. ISBN 9783110389647. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, S.; Das, M. Extremophiles-A Clue to Origin of Life and Biology of Other Planets. Everyman’s Sci. 2016, 51, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ott, E.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kölbl, D.; Rabbow, E.; Rettberg, P.; Mora, M.; Moissl-eichinger, C.; Weckwerth, W.; Yamagishi, A.; Milojevic, T. Molecular repertoire of Deinococcus radiodurans after 1 year of exposure outside the International Space Station within the Tanpopo mission. Microbiome 2020, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesei, D.; Sterflinger, K.; Marzban, G. Global Proteomics of Extremophilic Fungi: Mission Accomplished? Tiquia-Arashiro, M.G., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 9783030190309. [Google Scholar]
- Tiquia-Arashiro, S.M. Thermophilic Fungi in Composts: Their Role in Composting and Industrial Processes. In Fungi in Extreme Environments: Ecological Role and Biotechnological Significance; Tiquia-Arashiro, G.M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-3-030-19029-3. [Google Scholar]
- Martorell, M.M.; Adolfo, L.; Ruberto, M.; de Castellanos, L.I.F.; Cormack, W.P. Mac Bioremediation Abilities of Antarctic Fungi. In Fungi in Extreme Environments: Ecological Role and Biotechnological Significance; Grube, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 517–534. ISBN 9783030190309. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, N.K.; Panosyan, H. Extremophiles: Applications and roles in environmental sustainability. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 2, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ametrano, C.G.; Muggia, L.; Grube, M. Extremotolerant Black Fungi from Rocks and Lichens. In Fungi in Extreme Environments: Ecological Role and Biotechnological Significance; Grube, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 119–143. ISBN 9783030190309. [Google Scholar]
- Selbmann, L.; Zucconi, L.; Isola, D.; Onofri, S. Rock black fungi: Excellence in the extremes, from the Antarctic to space. Curr. Genet. 2015, 63, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Sonjak, S.; Zalar, P.; Frisvad, J.C.; Diderichsen, B.; Plemenitaš, A. Extremophilic fungi in arctic ice: A relationship between adaptation to low temperature and water activity. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2003, 28, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Zalar, P.; de Hoog, G.S.; Plemenitaš, A. Hypersaline waters in salterns—Natural ecological niches for halophilic black yeasts. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2000, 32, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Selbmann, L.; de Hoog, G.S.; Zucconi, L.; Isola, D.; Ruisi, S.; van den Ende, A.H.G.; Ruibal, C.; De Leo, F.; Urzì, C.; Onofri, S. Drought meets acid: Three new genera in a dothidealean clade of extremotolerant fungi. Stud. Mycol. 2008, 61, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Zalar, P. Dishwasher and Car Wash: Man-made Environments Accommodating Human Opportunistic Black Yeasts. Emerg. Potential Black Yeasts 2011, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, V.N.; Cantrell, C.L.; Wedge, D.E.; Ferreira, M.C.; Soares, M.A.; Jacob, M.R.; Oliveira, F.S.; Galante, D.; Rodrigues, F.; Alves, T.M.A.; et al. Fungi associated with rocks of the Atacama Desert: Taxonomy, distribution, diversity, ecology and bioprospection for bioactive compounds. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ametrano, C.G.; Grewe, F.; Crous, P.W.; Goodwin, S.B.; Liang, C.; Selbmann, L.; Lumbsch, H.T.; Leavitt, S.D.; Muggia, L. Genome-scale data resolve ancestral rock- inhabiting lifestyle in Dothideomycetes (Ascomycota). IMA Fungus 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onofri, S.; Selbmann, L.; de Hoog, G.S.; Grube, M.; Barreca, D.; Ruisi, S.; Zucconi, L. Evolution and adaptation of fungi at boundaries of life. Adv. Sp. Res. 2007, 40, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de los Ríos, A.; Wierzchos, J.; Ascaso, C. The lithic microbial ecosystems of Antarctica’s McMurdo Dry Valleys. Antarct. Sci. 2014, 26, 459–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterflinger, K. Fungi as Geologic Agents. Geomicrobiol. J. 2000, 17, 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruibal, C.; Platas, G.; Bills, G.F. Isolation and characterization of melanized fungi from limestone formations in Mallorca. Mycol. Prog. 2005, 4, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak Babič, M.; Zalar, P.; Ženko, B.; Džeroski, S.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Yeasts and yeast-like fungi in tap water and groundwater, and their transmission to household appliances. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 20, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Ngan, A.H.Y.; Tsang, C.C.C.; Ling, I.W.H.; Chan, J.F.W.; Leung, S.-Y.; Yuen, K.-Y.; Lau, S.K.P. Clinical spectrum of exophiala infections and a novel Exophiala species, Exophiala hongkongensis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nienow, J.A. Terrestrial lithophytic (rock) communities. Antarct. Microbiol. 1993, 343–412. [Google Scholar]
- Coleine, C.; Stajich, J.E.; Ríos, A.D.L.; Selbmann, L. Beyond the extremes: Rocks as ultimate refuge for fungi in drylands Beyond the extremes. Mycologia 2021, 113, 108–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staley, J.T.; Palmer, F.; Adams, J.B. Microcolonial fungi: Common inhabitants on desert rocks? Science 1982, 215, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterflinger, K.; Krumbein, W.E. Dematiaceous fungi as a major agent of biopitting for Mediterranean marbles and limestones. Geomicrobiol. J. 1997, 14, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onofri, S.; Barreca, D.; Selbmann, L.; Isola, D.; Rabbow, E.; Horneck, G.; de Vera, J.P.P.; Hatton, J.; Zucconi, L. Resistance of Antarctic black fungi and cryptoendolithic communities to simulated space and Martian conditions. Stud. Mycol. 2008, 61, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalzi, G.; Selbmann, L.; Zucconi, L.; Rabbow, E.; Horneck, G.; Albertano, P.; Onofri, S. LIFE Experiment: Isolation of Cryptoendolithic Organisms from Antarctic Colonized Sandstone Exposed to Space and Simulated Mars Conditions on the International Space Station. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2012, 42, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, T.; De Hoog, G.S.; De Boer, A.G.; De Crom, I.; Haase, G. High prevalence of the neurotrope Exophiala dermatitidis and related oligotrophic black yeasts in sauna facilities Hohe Keimdichte der neurotropen Exophiala dermatitidis und verwandter oligotropher schwarzer Hefen in Sauna-Einrichtungen. Mycoses 2002, 35, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Miyaji, M.; Taguchi, H.; Tanaka, R. Fungi in bathwater and sludge of bathroom drainpipes. Mycopathologia 1987, 97, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döğen, A.; Kaplan, E.; Oksüz, Z.; Serin, M.S.; Ilkit, M.; de Hoog, G.S. Dishwashers are a major source of human opportunistic yeast-like fungi in indoor environments in Mersin, Turkey. Med. Mycol. 2013, 51, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, N.; Abe, N. Comparison of fungi found in bathrooms and sinks. Biocontrol Sci. 2010, 15, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, V.A.; Attili-Angelis, D.; Pie, M.R.; Queiroz-Telles, F.; Cruz, L.M.; Najafzadeh, M.J.; de Hoog, G.S.; Zhao, J.; Pizzirani-Kleiner, A. Environmental isolation of black yeast-like fungi involved in human infection. Stud. Mycol. 2013, 75, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, B.; Tafer, H.; Kustor, C.; Poyntner, C.; Lopandic, K.; Sterflinger, K. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the toluene degrading black yeast Cladophialophora immunda. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerbell, R.; De Hoog, G.S.; Prenafeta-boldu, F.X. Fungi growing on aromatic hydrocarbons: Biotechnology’s unexpected encounter with biohazard? FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Sterflinger, K. Temperature and NaCl-tolerance of rock-inhabiting meristematic fungi. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1998, 74, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacelli, C.; Bryan, R.A.; Onofri, S.; Selbmann, L.; Zucconi, L.; Shuryak, I.; Dadachova, E. Survival and redox activity of Friedmanniomyces endolithicus, an Antarctic endemic black meristematic fungus, after gamma rays exposure. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesei, D.; Quartinello, F.; Guebitz, G.M.; Ribitsch, D.; Nöbauer, K.; Razzazi-Fazeli, E.; Sterflinger, K. Shotgun proteomics reveals putative polyesterases in the secretome of the rock-inhabiting fungus Knufia chersonesos. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, B.; Poyntner, C.; Rudavsky, T.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.; de Hoog, G.; Tafer, H.; Sterflinger, K. Pathogenic yet environmentally friendly? Black fungal candidates for bioremediation of pollutants. Geomicrobiol. J. 2016, 33, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onofri, S.; de la Torre, R.; de Vera, J.-P.; Ott, S.; Zucconi, L.; Selbmann, L.; Scalzi, G.; Venkateswaran, K.J.; Rabbow, E.; Sánchez Iñigo, F.J.; et al. Survival of Rock-Colonizing Organisms After 1.5 Years in Outer Space. Astrobiology 2012, 12, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, K.; Marzban, G.; de Vera, J.-P.; Lorek, A.; Sterflinger, K. Protein patterns of black fungi under simulated Mars-like conditions. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesei, D.; Chiang, A.J.; Kalkum, M.; Stajich, J.E.; Mohan, G.B.M.; Sterflinger, K.; Venkateswaran, K. Effects of Simulated Microgravity on the Proteome and Secretome of the Polyextremotolerant Black Fungus Knufia chersonesos. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacelli, C.; Selbmann, L.; Zucconi, L.; Raguse, M.; Moeller, R.; Shuryak, I.; Onofri, S. Survival, DNA integrity, and ultrastructural damage in antarctic cryptoendolithic eukaryotic microorganisms exposed to ionizing radiation. Astrobiology 2017, 17, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onofri, S.; Selbmann, L.; Pacelli, C.; Zucconi, L.; Rabbow, E.; De Vera, J.P. Survival, DNA, and Ultrastructural Integrity of a Cryptoendolithic Antarctic Fungus in Mars and Lunar Rock Analogs Exposed Outside the International Space Station. Astrobiology 2019, 19, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterflinger, K.; de Hoog, G.S.; Haase, G. Phylogeny and ecology of meristematic ascomycetes. Stud. Mycol. 1999, 43, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Slepecky, R.A.; Starmer, W.T. Phenotypic plasticity in fungi: A review with observations on Aureobasidium pullulans. Mycologia 2009, 101, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenzien, U.; de Hoog, G.S.; Krumbein, W.E.; Urzi, C. On the isolation of microcolonial fungi occurring on and in marble and other calcareous rocks. Sci. Total Environ. 1995, 167, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbushina, A. a Life on the rocks. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1613–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterflinger, K. Black Yeasts and Meristematic Fungi: Ecology, Diversity and Identification. In Biodiversity and Ecophysiology of yeasts. The Yeast Handbook; Péter, G., Rosa, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 501–514. [Google Scholar]
- Pacelli, C.; Selbmann, L.; Zucconi, L.; De Vera, J.-P.; Rabbow, E.; Horneck, G.; de la Torre, R.; Onofri, S. BIOMEX Experiment: Ultrastructural Alterations, Molecular Damage and Survival of the Fungus Cryomyces antarcticus after the Experiment Verification Tests. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2016, 47, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenman, H.C.; Casadevall, A. Synthesis and assembly of fungal melanin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadachova, E.; Casadevall, A. Ionizing radiation: How fungi cope, adapt, and exploit with the help of melanin. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malo, M.E.; Frank, C.; Dadachova, P.E. Assessing Melanin Capabilities in Radiation Shielding and Radioadaptation. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2019, 50, S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, K.; Streibel, M.; Jahn, B.; Haase, G.; Brakhage, A. Biosynthesis of fungal melanins and their importance for human pathogenic fungi. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2003, 38, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brush, L.; Money, N.P. Invasive hyphal growth in Wangiella dermatitidis is induced by stab inoculation and shows dependence upon melanin biosynthesis. Fungal Genet. Biol. 1999, 28, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plemenitaš, A.; Vaupotič, T.; Lenassi, M.; Kogej, T. Adaptation of extremely halotolerant black yeast Hortaea werneckii to increased osmolarity: A molecular perspective at a glance. Stud. Mycol. 2008, 61, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Los Ríos, A.; Wierzchos, J.; Sancho, L.G.; Ascaso, C. Acid microenvironments in microbial biofilms of antarctic endolithic microecosystems. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nai, C.; Wong, H.Y.; Pannenbecker, A.; Broughton, W.J.; Benoit, I.; de Vries, R.P.; Gueidan, C.; Gorbushina, A.A. Nutritional physiology of a rock-inhabiting, model microcolonial fungus from an ancestral lineage of the Chaetothyriales (Ascomycetes). Fungal Genet. Biol. 2013, 56, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, S.C.; McDonald, I.R.; Barrett, J.E.; Cowan, D.A. On the rocks: The microbiology of Antarctic Dry Valley soils. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedmousavi, S.; Badali, H.; Chlebicki, A.; Zhao, J.; Prenafeta-boldú, F.X.; de Hoog, G.S. Exophiala sideris, a novel black yeast isolated from environments polluted with toxic alkyl benzenes and arsenic. Fungal Biol. 2011, 115, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenafeta-boldú, F.X.; Kuhn, A.; Luykx, D.M.A.M.; Anke, H.; van Groenestijn, J.W.; de Bont, J.A.M. Isolation and characterisation of fungi growing on volatile aromatic hydrocarbons as their sole carbon and energy source. Mycol. Res. 2001, 105, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.F.; Vicente, V.A.; Hoog, S. De Black yeasts in the omics era: Achievements and challenges. Med. Mycol. 2018, 56, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterflinger, K.; Lopandic, K.; Pandey, R.V.; Blasi, B.; Kriegner, A. Nothing Special in the Specialist? Draft Genome Sequence of Cryomyces antarcticus, the Most Extremophilic Fungus from Antarctica. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggia, L.; Ametrano, C.G.; Sterflinger, K.; Tesei, D. An Overview of Genomics, Phylogenomics and Proteomics Approaches in Ascomycota. Life 2020, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleine, C.; Masonjones, S.; Sterflinger, K.; Onofri, S.; Selbmann, L.; Stajich, J.E. Peculiar genomic traits in the stress-adapted cryptoendolithic Antarctic fungus Friedmanniomyces endolithicus. Fungal Biol. 2020, 124, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Flibotte, S.; Neira, M.; Formby, S.; Plemenita, A.; Cimerman, N.G.; Lenassi, M.; Gostinčar, C.; Stajich, J.E.; Nislow, C. Insight into the Recent Genome Duplication of the Halophilic Yeast Hortaea werneckii: Combining an Improved Genome with Gene Expression and Chromatin Structure. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 2015–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostinčar, C.; Stajich, J.E.; Zupan, J.; Zalar, P.; Gunde-cimerman, N. Genomic evidence for intraspecific hybridization in a clonal and extremely halotolerant yeast. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badali, H.; Gueidan, C.; Najafzadeh, M.J.; Bonifaz, A.; Gerrits van den Ende, A.H.G.; de Hoog, G.S. Biodiversity of the genus Cladophialophora. Stud. Mycol. 2008, 61, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesei, D.; Marzban, G.; Zakharova, K.; Isola, D.; Selbmann, L.; Sterflinger, K. Alteration of protein patterns in black rock inhabiting fungi as a response to different temperatures. Fungal Biol. 2012, 116, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakharova, K.; Tesei, D.; Marzban, G.; Dijksterhuis, J.; Wyatt, T.; Sterflinger, K. Microcolonial Fungi on Rocks: A Life in Constant Drought? Mycopathologia 2013, 175, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalar, P.; Novak, M.; de Hoog, G.S.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Dishwashers--a man-made ecological niche accommodating human opportunistic fungal pathogens. Fungal Biol. 2011, 115, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesei, D.; Marzban, G.; Marchetti-Deschmann, M.; Tafer, H.; Arcalis, E.; Sterflinger, K. Proteome of Tolerance Fine-Tuning in the Human Pathogen Black Yeast Exophiala dermatitidis. J. Proteom. 2015, 128, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultzhaus, Z.S.; Schultzhaus, J.N.; Romsdahl, J.; Chen, A.; Hervey, W.J., IV; Leary, D.H.; Wang, Z. Proteomics reveals distinct changes associated with increased gamma radiation resistance in the black yeast Exophiala dermatitidis. Genes 2020, 11, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, G.E.; Buckley, B.A.; Airaksinen, S.; Keen, J.E.; Somero, G.N. Heat-shock protein expression is absent in the antarctic fish Trematomus bernacchii (family Nototheniidae). J. Exp. Biol. 2000, 203, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, Z.; Kalapis, D.; Bódi, Z.; Szamecz, B.; Daraba, A.; Almási, K.; Kovács, K.; Boross, G.; Pál, F.; Horváth, P.; et al. Hsp70-associated chaperones have a critical role in buffering protein production costs. eLife 2018, 7, e29845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, B.; Tafer, H.; Tesei, D.; Sterflinger, K.; Blasi, B.; Tafer, H.; Tesei, D.; Sterflinger, K. From glacier to sauna: RNA-seq of the human pathogen black fungus Exophiala dermatitidis under varying temperature conditions exhibits common and novel fungal response. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Yang, M.; Chen, H.; Wu, B.; Liu, C. Identification and characterization of circular RNAs in Ganoderma lucidum. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malo, M.E.; Schultzhaus, Z.; Frank, C.; Romsdahl, J.; Wang, Z.; Dadachova, E. Transcriptomic and genomic changes associated with radioadaptation in Exophiala dermatitidis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargaud, M.; Amils, R.; Cleaves, H.J. Encyclopedia of Astrobiology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 1, ISBN 3642112714. [Google Scholar]
- COSPAR Planetary Protection Policy (20 Oct 2002, as Amended 24 Mar 2011); COSPAR: Paris, France, 2011. Available online: http://cosparhq.cnes.fr/Scistr/PPPolicy%20%2824-Mar2011%29.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- von Hegner, I. Extreme Exoworlds and the Extremophile Paradox Ian. 2021. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.06144 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Mustard, J.F.; Murchie, S.L.; Pelkey, S.M.; Ehlmann, B.L.; Milliken, R.E.; Grant, J.A.; Bibring, J.; Poulet, F.; Bishop, J.; Dobrea, E.N.; et al. Hydrated silicate minerals on Mars observed by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter CRISM instrument. Nature 2008, 454, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbmann, L.; Pacelli, C.; Zucconi, L.; Dadachova, E.; Moeller, R.; de Vera, J.P.; Onofri, S. Resistance of an Antarctic cryptoendolithic black fungus to radiation gives new insights of astrobiological relevance. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, B.R.H.; Radiobiology, C. The British Journal of Radiology. Br. J. Radiol. 1984, 57, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacelli, C.; Bryan, R.A.; Onofri, S.; Selbmann, L.; Shuryak, I.; Dadachova, E. Melanin is effective in protecting fast and slow growing fungi from various types of ionizing radiation. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1612–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiassi-nejad, M.; Mortazavi, S.M.J.; Cameron, J.R.; Niroomand-rad, A.; Karam, P.A. Very High Background Radiation Areas Of Ramsar, Iran: Preliminary Biological Studies. Health Phys 2002, 82, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.M.; Battista, J.R. Deinococcus Radiodurans—The Consummate Survivor. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Li, D.G.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C.T. Effects of spaceflight and simulated microgravity on microbial growth and secondary metabolism. Mil. Med. Res. 2018, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Middeleer, G.; Leys, N.; Sas, B.; De Saeger, S. Fungi and Mycotoxins in Space—A Review. Astrobiology 2019, 19, ast.2018.1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrhenius, S. The propagation of life in space. Umschau 1903, 7, 481–485. [Google Scholar]
- Israilides, C.; Smith, A.; Scanlon, B.; Barnett, C. Pullulan from Agro-industrial Wastes. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 1999, 16, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nieuwenhuijzen, E.J.; Centre, C.F.B. Aureobasidium. Encycl. Food Microbiol. 1999, 1, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, H.H.J.; Magielsen, F.J.; Doddema, H.J.; Harder, W. Influence of the water content and water activity on styrene degradation by Exophiala jeanselmei in biofilters. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 45, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, D.; Selbmann, L.; de Hoog, G.S.; Fenice, M.; Onofri, S.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X.; Zucconi, L. Isolation and Screening of Black Fungi as Degraders of Volatile Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Mycopathologia 2013, 175, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badali, H.; Prenafeta-boldu, F.X.; Guarro, J. Cladophialophora psammophila, a novel species of Chaetothyriales with a potential use in the bioremediation of volatile aromatic hydrocarbons. Fungal Biol. 2011, 115, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hoog, G.S.; Vicente, V.; Caligiorne, R.B.; Kantarcioglu, S.; Tintelnot, K.; Gerrits van den Ende, A.H.G.; Haase, G. Species Diversity and Polymorphism in the Exophiala spinifera Clade Containing Opportunistic Black Yeast-Like Fungi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4767–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, D.; Scano, A.; Orr, G.; Prenafeta-bold, F.X.; Zucconi, L. Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Sites: Is There Something More Than Exophiala xenobiotica? New Insights into Black Fungal Diversity Using the Long Cold Incubation Method. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimawi, B.H.; Rimawi, R.H.; Mirdamadi, M.; Steed, L.L.; Marchell, R.; Sutton, D.A.; Thompson, E.H.; Wiederhold, N.P.; Lindner, J.R.; Boger, M.S. A case of Exophiala oligosperma successfully treated with voriconazole. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2013, 2, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X.; Guivernau, M.; Gallastegui, G.; Viñas, M.; de Hoog, G.S.; Elías, A. Fungal/bacterial interactions during the biodegradation of TEX hydrocarbons (toluene, ethylbenzene and p-xylene) in gas biofilters operated under xerophilic conditions. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 80, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenafeta-Boldú, F.; Roca, N.; Villatoro, C.; Vera, L.; de Hoog, G.S. Prospective application of melanized fungi for the biofiltration of indoor air in closed bioregenerative systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 361, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, N.C.; Pagnocca, F.C.; Otsuka, A.A.; Prenafeta-boldú, F.X.; Vicente, V.A.; de Angelis, D.A. Black Fungi and Hydrocarbons: An Environmental Survey for Alkylbenzene Assimilation. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatheway, S.; Price, G.W. Analysis of Aspergillus Oryzae Degradation of Commercial Agricultural Mulch Films Composed of Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and Poly(lactic acid). 2014. Available online: https://divertns.ca/sites/default/files/researchreportsfiles/2021-09/RRFB%20Microbial%20plastics%20SHatheway%20Final%20Report.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Godwin, A.D. Plasticizers. In Plastics Design Library. Applied Plastics Engineering Handbook, 2nd ed.; Kutz, M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 533–553. ISBN 978-0-323-39040-8. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, O.; Lee, J.S.; Stote, R.; Kuehn, K.; Ruiz, O.N. Metagenomic characterization of microbial communities on plasticized fabric materials exposed to harsh tropical environments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 154, 105061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, O.; Ruiz, O.N. Black Yeast Genomes Assembled from Plastic Fabric Metagenomes Reveal an Abundance of Hydrocarbon. Microbiol. Resour. Annoucements 2021, 10, e01459-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostinčar, C.; Ohm, R.A.; Kogej, T.; Sonjak, S.; Turk, M.; Zajc, J.; Zalar, P.; Grube, M.; Sun, H.; Han, J.; et al. Genome sequencing of four Aureobasidium pullulans varieties: Biotechnological potential, stress tolerance, and description of new species. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, J.S.; Nixon, M.; Eastwood, I.M.; Greenhalgh, M.; Robson, G.D.; Handley, P.S. Fungal colonization and biodeterioration of plasticized polyvinyl chloride. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3194–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattoon, E.R.; Cordero, R.J.B.; Casadevall, A. Fungal Melanins and Applications in Healthcare, Bioremediation and Industry. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, A.; Chiang, A.J.; Elsaesser, A.; Kalkum, M.; Ehrenfreund, P.; Stajich, J.E.; Torok, T.; Wang, C.C.C.; Venkateswaran, K. Proteomic and metabolomic characteristics of extremophilic fungi under simulated Mars conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhdanova, N.N.; Tugay, T.; Dighton, J.; Zheltonozhsky, V.; Mcdermott, P. Ionizing radiation attracts soil fungi. Mycol. Res. 2004, 108, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.; Gadd, G.M. Biosorption of radionuclides by fungal biomass. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1990, 49, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tesei, D. Black Fungi Research: Out-of-This-World Implications. Encyclopedia 2022, 2, 212-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2010013
Tesei D. Black Fungi Research: Out-of-This-World Implications. Encyclopedia. 2022; 2(1):212-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleTesei, Donatella. 2022. "Black Fungi Research: Out-of-This-World Implications" Encyclopedia 2, no. 1: 212-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2010013
APA StyleTesei, D. (2022). Black Fungi Research: Out-of-This-World Implications. Encyclopedia, 2(1), 212-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2010013





