Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) Methods and Concepts
Definition
:1. Introduction
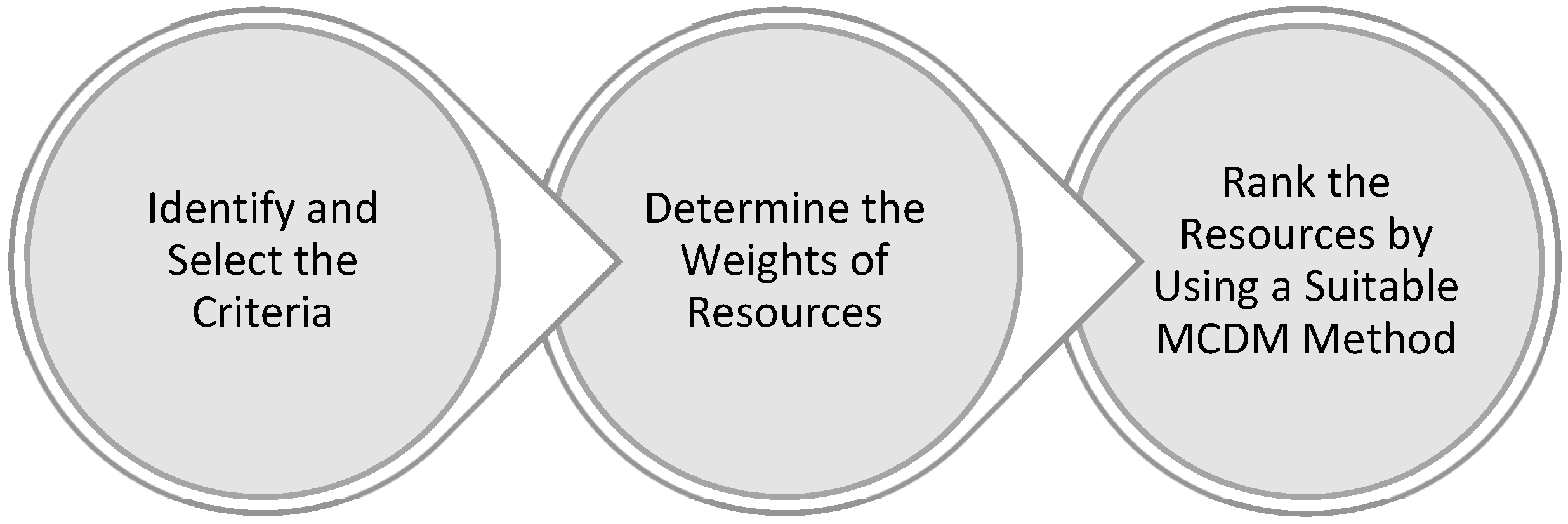
2. Solving an MCDM Problem—General Approach
- Alternatives are “different possible courses of action”
- The attribute is defined as “a measurable characteristic of an alternative”
- Aggregation refers to “considering the performances of an alternative on the specific criteria for deciding on the alternative”
- Decision variables are defined as “components of alternatives’ vector”
- Decision space is represented as “feasible alternatives”
- Measures are defined as “elements utilized to quantify an alternative to its attribute by assigning to the attribute numbers or symbols”
- Criteria are defined as “tools for evaluating and comparing alternatives from the viewpoint of the consequences of their selection”
- Preferences are defined as “how an alternative fulfills the need of a decision-maker regarding a given attribute”
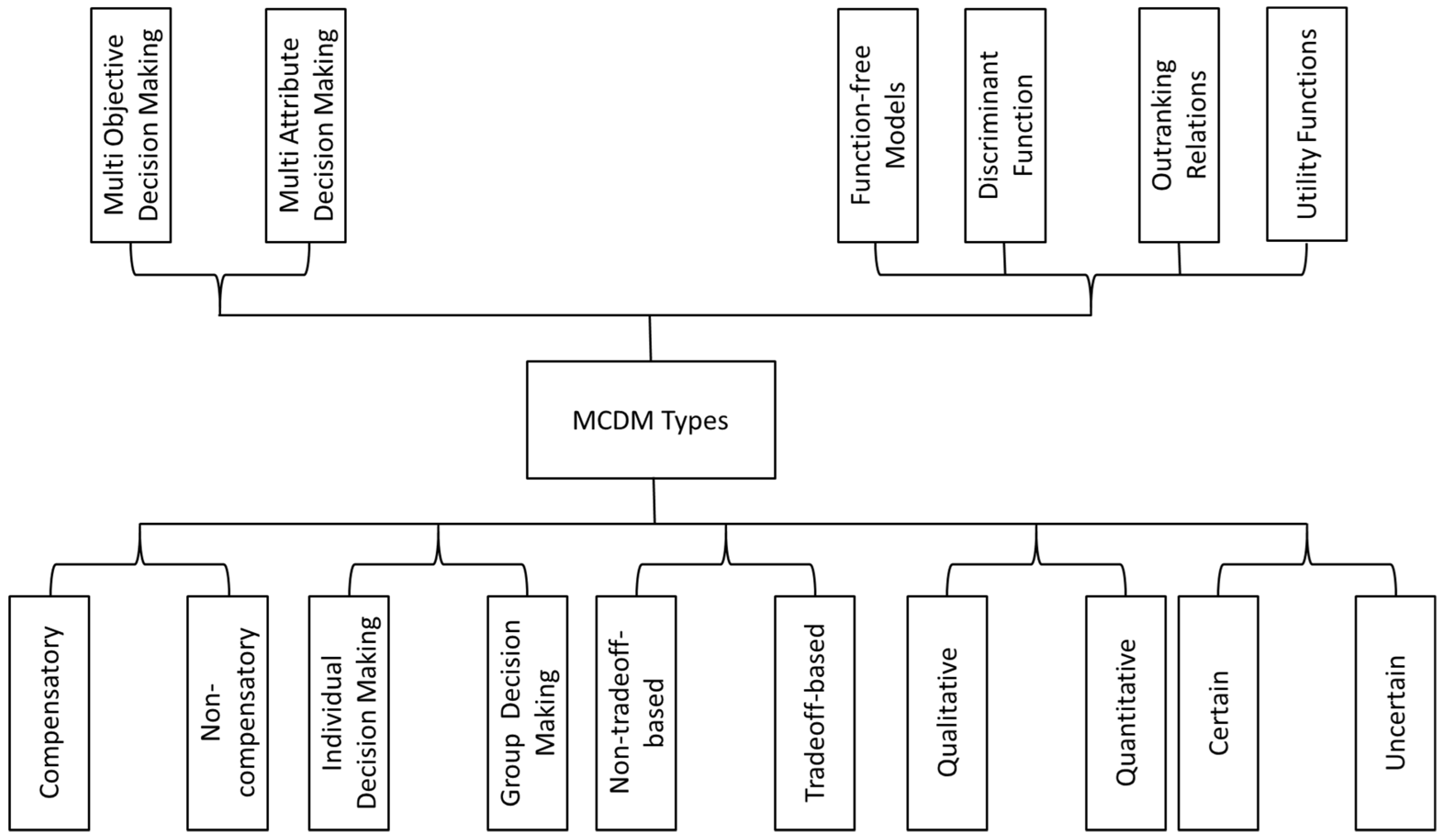
3. Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Categories
4. Research on Multi-Criteria Decision Making
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aruldoss, M.; Lakshmi, M.T.; Venkatesan, V.P. A survey on multi criteria decision making methods and its applications. Am. J. Inf. Syst. 2013, 1, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Velasquez, M.; Hester, P.T. An analysis of multi-criteria decision making methods. Int. J. Oper. 2013, 10, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hajduk, S. Multi-Criteria Analysis in the Decision-Making Approach for the Linear Ordering of Urban Transport Based on TOPSIS Technique. Energies 2021, 15, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavarani, A.M.; Azad Marz Abadi, E. The Bases, Principles, and Methods of Decision-Making: A review of literature. IJMR 2015, 2, 214–225. [Google Scholar]
- Bączkiewicz, A.; Wątróbski, J.; Kizielewicz, B.; Sałabun, W. Towards Objectification of Multi-Criteria Assessments: A Comparative Study on MCDA Methods. In Proceedings of the 2021 16th Conference on Computer Science and Intelligence Systems (FedCSIS), online, 2–5 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik, P.K.D.; Biswas, S.; Pal, S.; Marinković, D.; Choudhury, P. A Comparative Analysis of Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Methods for Resource Selection in Mobile Crowd Computing. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habenicht, W.; Scheubrein, B.; Scheubrein, R. Multiple-criteria Decision Making. Optim. Oper. Res. 2002, 4, 257–279. [Google Scholar]
- Trendowicz, A.; Kopczyńska, S. Adapting Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis for Assessing the Quality of Software Products. Current Approaches and Future Perspectives. In Advances in Computers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 153–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ceballos, B.; Lamata, M.T.; Pelta, D.A. A comparative analysis of multi-criteria decision-making methods. Prog. Artif. Intell. 2016, 5, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zopounidis, C.; Doumpos, M. Multicriteria classification and sorting methods: A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 138, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaei, D.; Erkoyuncu, J.; Roy, R. A review of multi-criteria decision making methods for enhanced maintenance delivery. Procedia CIRP 2015, 37, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, C.-L.; Yoon, K. Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications—A State-of-the-Art Survey; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981; Volume 186. [Google Scholar]
- Baizyldayeva, U.; Vlasov, O.; Kuandykov, A.A.; Akhmetov, T.B. Multi-criteria decision support systems. Comparative analysis. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2013, 16, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar]
- Sotoudeh-Anvari, A. The applications of MCDM methods in COVID-19 pandemic: A state of the art review. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 126, 109238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplinski, O.; Peldschus, F.; Nazarko, J.; Kaklauskas, A.; Baušys, R. MCDM, operational research and sustainable development in the trans-border Lithuanian–German–Polish co-operation. Eng. Manag. Prod. Serv. 2019, 11, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process McGraw-Hill; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W. Management Models and Industrial Applications of Linear Programming; Johhn Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1961; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner, J.L. Understanding Creativity: A Case-Based Approach. In European Workshop on Case-Based Reasoning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ju-Long, D. Control problems of grey systems. Syst. Control Lett. 1982, 1, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision Making with Dependence and Feedback: The Analytic Network Process; RWS Publications: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Van Laarhoven, P.J.; Pedrycz, W. A fuzzy extension of Saaty’s priority theory. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1983, 11, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banayoun, R.; Roy, B.; Sussman, N. Manual de Reference du Programme Electre, Note de Synthese et Formation 25; Direction Scientifique SEMA: Paris, France, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Brans, J.-P. L’ingénierie de la Décision: L’élaboration D’instruments D’aide a la Décision; Université Laval, Faculté des Sciences de L’administration: Québec, QC, Canada, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Opricovic, S. Multicriteria Optimization of Civil Engineering Systems; Faculty of Civil Engineering: Belgrade, Serbia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-T. Extensions of the TOPSIS for Group Decision-Making under Fuzzy Environment. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2000, 114, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-J.; Liu, T.-Y.; Hwang, C.-L. Topsis for MODM. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1994, 76, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabus, A.; Fontela, E. World Problems, an Invitation to Further Thought within the Framework of DEMATEL; Battelle Geneva Research Center: Geneva, Switzerland, 1972; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Matarazzo, B. Preference Ranking Global Frequencies in Multicriterion Analysis (PRAGMA). Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1988, 36, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchman, C.W.; Ackoff, R.L. An approximate measure of value. J. Oper. Res. Soc. Am. 1954, 2, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeney, R.L.; Raiffa, H.; Meyer, R.F. Decisions with Multiple Objectives: Preferences and Value Trade-Offs; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, J. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method. Omega 2015, 53, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, W. The engineering economic summer symposium series. Soc. Util. 1971, 6, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailov, L.; Singh, M.G. Fuzzy analytic network process and its application to the development of decision support systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 2003, 33, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Application Fields | Examples of the Application Focus |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | The assessment of COVID-19 regional safety, occupational health, and safety risk assessment |
| Energy sector | Ranking renewable energy sources, techniques for energy policy |
| Engineering and Production | Engineering, material selection for optimal design, Optimum Process Parameters |
| Career and Job | Occupational stressors among firefighters, personnel selection problems, Job Choice |
| Supply chain management | Supporting sustainable supplier selection, green supplier evaluation, and selection |
| Organizations and corporates | System Selection Process in Enterprises, corporate sustainability |
| Education | Contextual Learner Modelling in Personalized and Ubiquitous Learning, E-learning |
| Transportation | Urban passenger transport systems, integrated transportation systems |
| Civil Engineering | Flood disaster risk analysis |
| Finance/economics | Project portfolio management |
| MCDM Matrix | C1 | C2 | … | Cn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | x11 | x12 | … | x1n |
| A2 | x21 | x22 | … | x2n |
| … | … | … | xij | … |
| Am | xm1 | xm2 | … | xmn |
| Method | Number of Results | Method | Number of Results | Method | Number of Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) | 8241 | Fuzzy analytic network process (ANP) | 586 | Complex Proportional Assessment (COPRAS) | 445 |
| VIseKriterijumska Optimizacija I Kompromisno Resenje (VIKOR) | 2691 | Grey analysis: Grey Relational Analysis/Grey Relational Model (GRA/GRM) | 3176 | COmbined COmpromise SOlution (CoCoSo) | 75 |
| Multi-Objective Optimization by Ratio Analysis (Multi-MOORA) | 165 | Weighted Sum Model (WSM) | 470 | Measurement of Alternatives and Ranking according to COmpromise Solution (MARCOS) | 35 |
| Multi-Attribute Utility Theory (MAUT) | 948 | Weighted Product model (WPM) | 198 | Ranking of Alternatives through Functional mapping of criterion sub-intervals into a Single Interval (RAFSI) | 1 |
| AHP | 15,452 | Aggregated Indices Randomization method (AIRM) | 4 | Automatic Routine Generating and Updating System (ARGUS) method | 3 |
| FST | 8730 | ANP | 3126 | Lexicographic Method (LM) | 311 |
| Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) | 3258 | Treatment of the Alternatives according To the Importance of Criteria (TACTIC) | 1 | Measuring Attractiveness by a categorical Based Evaluation Technique (MACBETH) | 162 |
| Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) | 9367 | Intercriteria Decision Rule Approach (IDRA) | 183 | Multicriterion Analysis of Preferences by Pair-wise Actions and Criterion Comparisons (MAPPAC) | 3 |
| Simple Multi-Attribute Rating Technique (SMART) | 646 | Evaluation of Mixed Data (EVAMIX) | 65 | Multi-Attribute Value Theory (MAVT) | 315 |
| Goal Programming (GP) | 4113 | Passive and Active Compensability Multicriteria ANalysis (PACMAN) | 3 | Best-Worst Method (BWM) | 867 |
| ELimination Et Choix Traduisant la REalité (ELimination Et Choice Translating REality) (ELECTRE) | 2782 | Dominance-based rough set approach (DRSA) | 278 | Maximax | 195 |
| Preference Ranking Organization Method for Enrichment of Evaluations (PROMETHEE) | 2715 | Characteristic Objects METhod (COMET) | 102 | An acronym in Portuguese for “Interactive Multi-Criteria Decision Making” (TODIM) | 249 |
| Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) | 976 | Evaluation based on Distance from Average Solution (EDAS) | 143 | Méthode d’ELimination et de CHoix Includent les relations d’ORdre (MELCHIOR) | 0 |
| FUZZY TOPSIS | 2014 | Multi-Attribute Border Approximation Area Comparison (MABAC) | 245 | MIN_MAX | 22 |
| FUZZY AHP | 2804 | Additive Ratio Assessment (ARAS) | 173 | Novel Approach to Imprecise Assessment and Decision Environments (NAIADE) | 40 |
| Organisation, Rangement Et Synthese De Donnes Relationelles (ORESTE) | 35 | REGIonal Multicriteria Elimination (REGIME) | 217 | Ratio Estimation in Magnitudes or deci-Bells to Rate Alternatives which are Non-Dominated (REMBRANDT) | 4 |
| Procédure d’Agrégation Multicritère de type Surclassement de Synthèse pour Evaluations Mixtes (PAMSSEM) | 6 | TACTIC | 10 | Multi-Attribute Range Evaluations (MARE) | 3 |
| Preference Ranking Global Frequencies in Multicriterion Analysis (PRAGMA) | 1267 | UTilités Additives (UTA) | 31 | Weighted Aggregated Sum Product Assessment (WASPAS) | 270 |
| QUALIty by FLEXible multicriteria method (QUALIFLEX) | 117 | Decision making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) | 1378 | DEMATEL-based ANP (DANP) | 73 |
| Geometrical Analysis for Interactive Aid (GAIA) | 68 | Induced Ordered Weighted Averaging (IOWA) | 125 | KANO model/method (author’s name) | 476 |
| Method | Description | Original Reference or Underlying Source |
|---|---|---|
| AHP | Pairwise comparison of hierarchical criteria considering difference information. | Saaty [16] |
| DEA | Performance assessment of a set of homogeneous DM units with multiple inputs and outputs. | Charnes and Cooper [17] |
| FST | Quantifying the linguistic facet of accessible data and preferences to address subjective and ambiguous problems. | Zadeh [18] |
| TOPSIS | Evaluating based on the distance of alternative to the ideal solution. | Hwang and Yoon [12] |
| GP | Minimizing the derivation of each objective from the desired target together with optimizing manifold goals. | Charnes and Cooper [19] |
| CBR | Making recommendations using the analysis of the historical data | Kolodner [20] |
| GRA/GRM | Dividing information to white, black, and grey (between known and unknown). | Deng [21] |
| ANP | A non-linear and more general type of AHP using Markov-chain-based aggregation. | Saaty [22] |
| FUZZY AHP | AHP with the fuzzy evaluation of the alternatives. | Van Laarhoven and Pedrycs [23] |
| ELECTRE | Outranking the relationship of the alternatives and using pairwise comparison | Benayoun et al. [24] |
| PROMETHEE | Outranking method (such as ELECTRE) including several iterations. | J.P. Brans [25] |
| VIKOR | A compensatory version of TOPSIS that is based on minimizing the distance to the ideal solution using a linear normalization approach. | Opricovic [26] |
| FUZZY TOPSIS | Based on TOPSIS under a fuzzy environment | Chen [27] Or Lai et al. 1994 [28] |
| DEMATEL | Verifying relationships/interdependence between variables. | Gabus and Fontela [29] |
| PRAGMA | Comparing partial profiles of alternatives considering all the possible criteria pairs. | Matarazzo [30] |
| SAW | Involving a simple addition of scores representing the goal achievements considering all criteria that is multiplied by the criteria weights. | Churchman and Ackoff [31] |
| MAUT | Based on incorporating uncertainty and risk preferences factors into multi criteria decision support methods. | Keeney [32] |
| BWM | Identifying the best and the worst criteria followed by conducting a pairwise comparisons between each of the best and worst criteria and other ones. | Rezaei [33] |
| SMART | weighting the criteria based on their importance and converting importance weights into real numbers. | Edwards [34] |
| Fuzzy ANP | Fuzzy expression of criteria weights in ANP method. | Mikhailov and Singh [35] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taherdoost, H.; Madanchian, M. Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) Methods and Concepts. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 77-87. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010006
Taherdoost H, Madanchian M. Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) Methods and Concepts. Encyclopedia. 2023; 3(1):77-87. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaherdoost, Hamed, and Mitra Madanchian. 2023. "Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) Methods and Concepts" Encyclopedia 3, no. 1: 77-87. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010006
APA StyleTaherdoost, H., & Madanchian, M. (2023). Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) Methods and Concepts. Encyclopedia, 3(1), 77-87. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010006








