Obesity vs. Metabolically Healthy Obesity in East Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Asian Obesity: A Focus on Metabolic Health
The Crisis Point: Expected Life and Public Costs for East Asia
1.2. Obesity, Diabetes, the Heart, and the Brain: A Troublesome Tetrad
1.3. General Interventions Available against Obesity
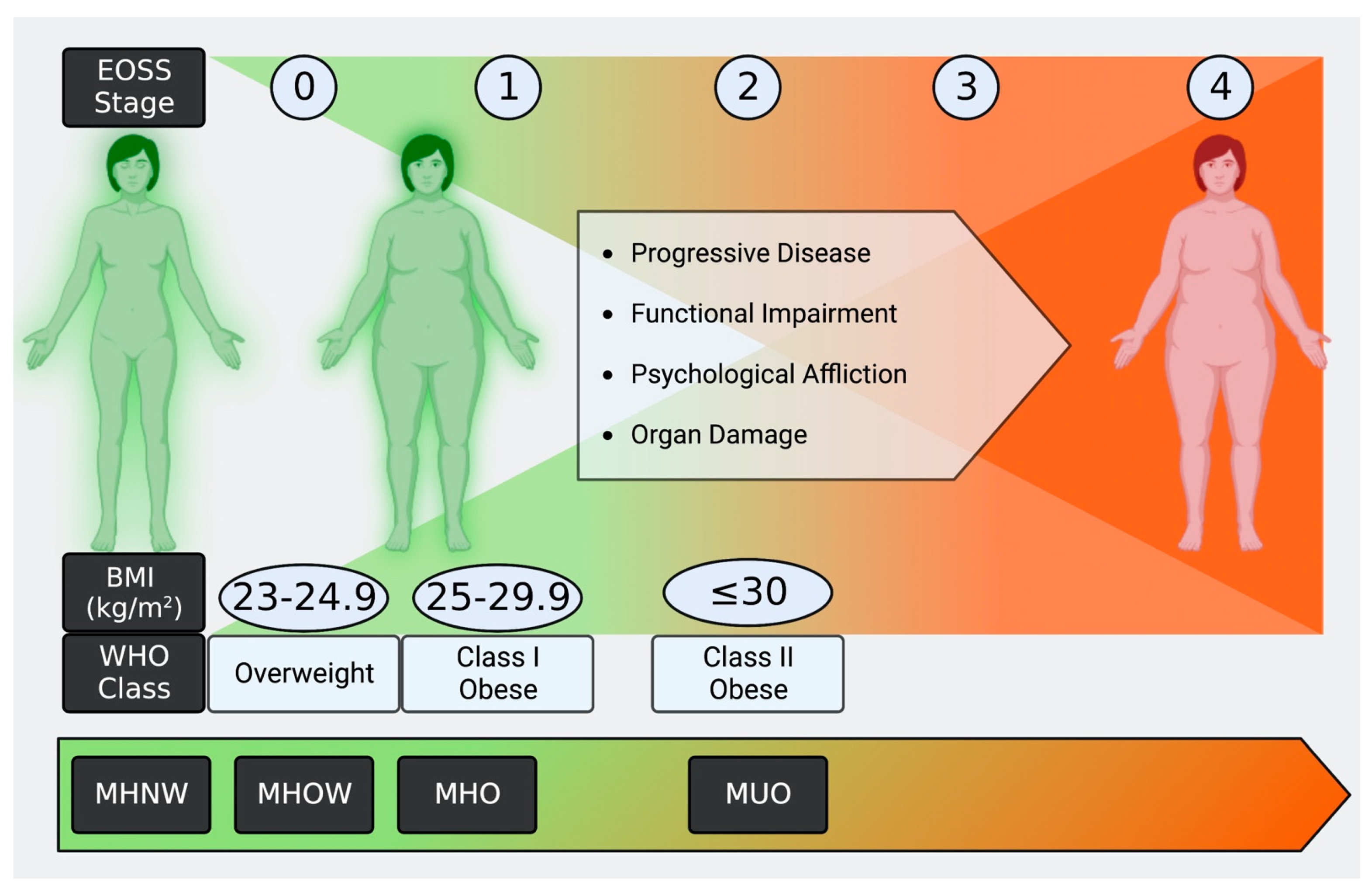
2. Obesity and Metabolically Healthy Obesity Criteria: Impact
Obesity by BMI: The WHO and International Obesity Task Force
| (a) | ||||
| BMI in kg/m2 | ||||
| Class | BMI–Non-Asian | Asian | ||
| Underweight | <18.5 | <18.5 | ||
| Normal | 18.5–24.9 | 18.5–22.9 | ||
| Pre-Obese | 25.0–29.9 | 23–24.9 | ||
| Class I | 30.0–34.9 | 25–29.9 | ||
| Class II | 35.0–39.9 | ≤30 | ||
| Class III | ≤40 | |||
| (b) | ||||
| Stage | Grade | Mental Symptoms | Functional Limits | Medical Condition |
| 0 | Mild | None | None | None |
| 1 | Mild | No quality of life impact | Aches and pains, some dyspnea during exercise | No active diseases but subclinical markers (borderline high blood pressure, high cholesterol, abnormal liver enzymes) |
| 2 | Moderate | Depression, anxiety, low self-esteem | Limits on daily activities | Type 2 diabetes, NAFLD, sleep apnea, etc. |
| 3 | Significant | Chronic depression/anxiety, suicidal thoughts | Reduced mobility, reduced work capacity | Severe diabetes, organ damage, gout or joint damage |
| 4 | Severe | Psychologically disabled | Immobile, unable to work | End-stage organ failures, uncontrolled diabetes |
3. Metabolically Healthy Obesity
3.1. What Is Metabolically Healthy Obesity?
3.2. MHO Effect on Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Risks
3.3. MHO to MUO Transition and Reversals in Eastern Asia
4. Country-Level Analysis: China
4.1. Prevalence of Obesity-Related Diseases
4.2. Public Health Costs: Deaths
4.3. Public Health Costs: Funding
4.4. Cause Analysis: China
4.5. MHO Prevalence
4.6. Potential Reductions in Death and Funding Costs with MHO
4.7. China-Specific Public Health Interventions
5. Japan
5.1. Prevalence of Obesity-Related Diseases
5.2. Public Health Costs: Deaths
5.3. Public Health Costs: Funding
5.4. Cause Analysis: Japan
5.5. MHO Prevalence
5.6. Potential Reductions in Death and Funding Costs with MHO
5.7. Japan-Specific Public Health Interventions
6. Comparisons and Contrasts from Country Analyses
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Managing Overweight and Obesity in Adults; National Heart Lung and Blood Institute: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2013; p. 501. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/sites/default/files/media/docs/obesity-evidence-review.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Cawley, J.; Biener, A.; Meyerhoefer, C.; Ding, Y.; Zvenyach, T.; Smolarz, B.G.; Ramasamy, A. Direct medical costs of obesity in the United States and the most populous states. J. Manag. Care Spéc. Pharm. 2021, 27, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helble, M.; Francisco, K. The Upcoming Obesity Crisis in Asia and the Pacific: First Cost Estimates; Asian Development Bank Institute: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; p. 33. Available online: https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/231516/adbi-wp679.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Oku, A.; Ichimura, E.; Tsukamoto, M. Aging population in Asian Countries—Lessons from Japanese Experiences—PRI Discussion Paper Series. 2017. Available online: https://www.mof.go.jp/pri/research/discussion_paper/ron299.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Chen, R.; Xu, P.; Song, P.; Wang, M.; He, J. China has faster pace than Japan in population aging in next 25 years. Biosci. Trends 2019, 13, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, I.-Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, F. The 50th Anniversary Committee of Korean Geriatrics Society Geriatrics Fact Sheet in Korea 2018 from National Statistics. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 2019, 23, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zanella, M.T.; Kohlmann, O., Jr.; Ribeiro, A.B. Treatment of Obesity Hypertension and Diabetes Syndrome. Hypertension 2001, 38, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nianogo, R.A.; Arah, O.A. Forecasting Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Incidence and Burden: The ViLA-Obesity Simulation Model. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 818816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondmkun, Y.T. Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes: Associations and Therapeutic Implications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fang, W.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Cai, Z.; Chen, G.; Wu, W.; Chen, Z.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y. Association between age at onset of overweight and risk of hypertension across adulthood. Heart 2022, 108, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.I.; Mittendorfer, B.; Klein, S. Metabolically healthy obesity: Facts and fantasies. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3978–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.D.; Liang, D.L.; Xie, Y. Prediabetes and risk of heart failure: The link grows stronger. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, K.; Wang, J.; Qian, W.-L.; Yan, W.-F.; Pang, T.; Yang, Z.-G. The additive effect of essential hypertension on coronary artery plaques in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A coronary computed tomography angiography study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konwar, M.; Bose, D.; Jaiswal, S.K.; Maurya, M.K.; Ravi, R. Efficacy and Safety of Liraglutide 3.0 mg in Patients with Overweight and Obese with or without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 1201977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritchevsky, S.B.; Beavers, K.M.; Miller, M.E.; Shea, M.K.; Houston, D.; Kitzman, D.W.; Nicklas, B.J. Intentional Weight Loss and All-Cause Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.K.; Han, K.; Koh, E.S.; Kim, E.S.; Lee, M.-K.; Nam, G.E.; Kwon, H.-S. Weight change and mortality and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with new-onset diabetes mellitus: A nationwide cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, W.; Lundberg, D.J.; Collins, J.M.; Johnston, S.S.; Waggoner, J.R.; Hsiao, C.-W.; Preston, S.H.; Manson, J.E.; Stokes, A.C. Association of Weight Loss Between Early Adulthood and Midlife With All-Cause Mortality Risk in the US. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2013448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, A.L.; Griffin, S.J.; Ahern, A.L.; Long, G.H.; Weinehall, L.; Fhärm, E.; Norberg, M.; Wennberg, P. Impact of weight maintenance and loss on diabetes risk and burden: A population-based study in 33,184 participants. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Targher, G.; Corey, K.E.; Byrne, C.D.; Roden, M. The complex link between NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus—Mechanisms and treatments. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B. Hypertension in Obesity and the Impact of Weight Loss. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2017, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, E.L.; Patnode, C.D.; Webber, E.M.; Redmond, N.; Rushkin, M.; O’Connor, E.A. Behavioral and Pharmacotherapy Weight Loss Interventions to Prevent Obesity-Related Morbidity and Mortality in Adults: An Updated Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force; U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Evidence Syntheses, Formerly Systematic Evidence Reviews; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2018.
- Swaleh, R.; McGuckin, T.; Myroniuk, T.W.; Manca, D.; Lee, K.; Sharma, A.M.; Campbell-Scherer, D.; Yeung, R.O. Using the Edmonton Obesity Staging System in the real world: A feasibility study based on cross-sectional data. CMAJ Open 2021, 9, E1141–E1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho-Pham, L.T.; Campbell, L.V.; Nguyen, T.V. More on body fat cutoff points. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 584–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goda, A.; Masuyama, T. Obesity and Overweight in Asian People. Circ. J. 2016, 80, 2425–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, A.; Chamukuttan, S.; Shetty, S.A.; Arun, N.; Susairaj, P. Obesity in Asia—Is it different from rest of the world. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2012, 28 (Suppl. S2), 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, S.; Zimmet, P.; Caterson, I.; Chunming, C.; Ikeda, Y.; Khalid, A.; Kim, Y.S.; Bassett, J. The Asia—Pacific perspective: Redefining obesity and its treatment. Int. Obes. Task Force 2000, 2, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Fyhofer, S. Report of the Council on Science and Public Health—Report 3-A-13. 2013. Available online: https://www.ama-assn.org/sites/ama-assn.org/files/corp/media-browser/public/about-ama/councils/Council%20Reports/council-on-science-public-health/a13csaph3.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Eurostat Statistics Explained. Overweight and Obesity—BMI Statistics. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Overweight_and_obesity_-_BMI_statistics (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- April-Sanders, A.K.; Rodriguez, C.J. Metabolically Healthy Obesity Redefined. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e218860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, K.L.; Brown, R.E.; Wharton, S.; Sharma, A.M.; Kuk, J.L. Edmonton Obesity Staging System Prevalence and Association with Weight Loss in a Publicly Funded Referral-Based Obesity Clinic. J. Obes. 2015, 2015, 619734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blüher, M. Metabolically Healthy Obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, bnaa004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.M.; Kushner, R.F. A proposed clinical staging system for obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathis, B.J.; Tanaka, K.; Hiramatsu, Y. Factors of Obesity and Metabolically Healthy Obesity in Asia. Medicina 2022, 58, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Saredy, J.; Zhang, R.; Shao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, W.Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Drummer, C.I.; Johnson, C.; et al. Approaching Inflammation Paradoxes—Proinflammatory Cytokine Blockages Induce Inflammatory Regulators. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 554301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, F.; Patten, D.A.; Harper, M.-E. Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress in Obesity-Recent Findings and Empirical Approaches. Obesity 2016, 24, 2301–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Sandoval, D.; Reed, J.A.; Matter, E.K.; Tolod, E.G.; Woods, S.C.; Seeley, R.J. The role of GM-CSF in adipose tissue inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E1038–E1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wright, E., Jr.; Scism-Bacon, J.L.; Glass, L.C. Oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes: The role of fasting and postprandial glycaemia. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2006, 60, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safinowski, M.; Wilhelm, B.; Reimer, T.; Weise, A.; Thomé, N.; Hänel, H.; Forst, T.; Pfützner, A. Determination of nitrotyrosine concentrations in plasma samples of diabetes mellitus patients by four different immunoassays leads to contradictive results and disqualifies the majority of the tests. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2009, 47, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos-Palacios, L.; Ruiz-Moreno, M.I.; Vilches-Perez, A.; Vargas-Candela, A.; Muñoz-Úbeda, M.; Porres, J.B.; Navarro-Sanz, A.; Lopez-Carmona, M.D.; Sanz-Canovas, J.; Perez-Belmonte, L.M.; et al. Metabolically healthy obesity: Inflammatory biomarkers and adipokines in elderly population. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyśk, B.; Ostrowska, L.; Smarkusz-Zarzecka, J. Salivary Adipokine and Cytokine Levels as Potential Markers for the Development of Obesity and Metabolic Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.; Han, C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Dynamic status of metabolically healthy overweight/obesity and metabolically unhealthy and normal weight and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cohort study of a rural adult Chinese population. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 12, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Kaneko, H.; Kiriyama, H.; Kamon, T.; Fujiu, K.; Morita, K.; Michihata, N.; Jo, T.; Takeda, N.; Morita, H.; et al. Metabolically Healthy Obesity and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the General Population—Analysis of a Nationwide Epidemiological Database. Circ. J. 2021, 85, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.-L.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Tsai, M.-C.; Hsu, L.-Y.; Hwang, L.-C.; Chien, K.-L. Association between metabolically healthy obesity/overweight and cardiovascular disease risk: A representative cohort study in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Gomez, D.; Ortega, F.B.; Hamer, M.; Lopez-Garcia, E.; Struijk, E.; Sadarangani, K.P.; Lavie, C.J.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. Physical Activity and Risk of Metabolic Phenotypes of Obesity: A Prospective Taiwanese Cohort Study in More Than 200,000 Adults. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongraw-Chaffin, M.; Foster, M.C.; Anderson, C.A.; Burke, G.L.; Haq, N.; Kalyani, R.R.; Ouyang, P.; Sibley, C.T.; Tracy, R.; Woodward, M.; et al. Metabolically Healthy Obesity, Transition to Metabolic Syndrome, and Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvari, M.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Yannakoulia, M.; Georgousopoulou, E.; Critselis, E.; Chrysohoou, C.; Tousoulis, D.; Pitsavos, C.; ATTICA Study Investigators. Transition from meta-bolically benign to metabolically unhealthy obesity and 10-year cardiovascular disease incidence: The ATTICA cohort study. Metabolism 2019, 93, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-B.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, K.M.; Baik, S.H.; Park, Y.G.; Han, K.; Yoo, H.J. Hospitalization for heart failure incidence according to the transition in metabolic health and obesity status: A nationwide population-based study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, W. The prevalence and increasing trends of overweight, general obesity, and abdominal obesity among Chinese adults: A repeated cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Peng, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Z.; Song, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Huang, Z.; Sun, X.; et al. Prevalence and Treatment of Diabetes in China, 2013–2018. JAMA 2021, 326, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Teng, D.; Shi, X.; Qin, G.; Qin, Y.; Quan, H.; Shi, B.; Sun, H.; Ba, J.; Chen, B.; et al. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in mainland China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American Diabetes Association: National cross sectional study. BMJ 2020, 369, m997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Yin, L.; Li, L.; Silva-Nash, J.; Tan, J.; Pan, Z.; Zeng, J.; Yan, L.L. Hypertension in China: Burdens, guidelines and policy responses: A state-of-the-art review. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2022, 36, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Hao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, L.; Tian, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, C.; et al. Status of Hypertension in China. Circulation 2018, 137, 2344–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, G.; Wu, C.; Chen, B.; Lu, Y.; Lu, J.; Yan, X.; Zhu, Z.; Nasir, K.; et al. Obesity Prevalence and Risks Among Chinese Adults: Findings From the China PEACE Million Persons Project, 2014–2018. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2020, 14, e007292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakkar, E.E.; Stevens, J.; Truesdale, K.P.; Cai, J. BMI and all-cause mortality among Chinese and Caucasians: The People’s Republic of China and the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Studies. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 24, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qi, J.; Yin, P.; Liu, Y.; You, J.; Lin, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L. Cardiovascular Disease Mortality—China, 2019. China CDC Wkly. 2021, 3, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Hu, G.; Xu, Y.; Peng, X.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, X. Trends in Diabetes Mortality in Urban and Rural China, 1987–2019: A Joinpoint Regression Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 777654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, R.; An, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J. Cost-effectiveness of adding dapagliflozin to standard treatment for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction patients in China. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 3582–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, C.; Wu, J. Direct Medical Costs of Incident Complications in Patients Newly Diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes in China. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Khan, M.M.; Zhang, D.; Rajbhandari-Thapa, J.; Li, L. Pharmacoeconomics of obesity in China: A scoping review. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2021, 21, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Han, A.; Chai, L. Assessing the Nutrient Adequacy in China’s Food Supply from 1965 to 2018. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Fu, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Zheng, P.; Fu, H.; et al. Why are male Chinese smokers unwilling to quit? A multicentre cross-sectional study on smoking rationalisation and intention to quit. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Hu, M.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Luo, T.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; et al. Alcohol Consumption in China Before and During COVID-19: Preliminary Results From an Online Retrospective Survey. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 597826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Xue, H.; Wang, V.H.; Li, M.; Wang, Y. Are single children more likely to be overweight or obese than those with siblings? The influence of China’s one-child policy on childhood obesity. Prev. Med. 2017, 103, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, H. Grandparental care and childhood obesity in China. SSM-Popul. Health 2022, 17, 101003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gao, D.; Ma, T.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wen, B.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Could greenness modify the effects of physical activity and air pollutants on overweight and obesity among children and adolescents? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Xu, Z.; Hu, X.; Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, T.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, J.; et al. Air pollution, greenness and risk of overweight among middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study in China. Environ. Res. 2023, 216 Pt 1, 114372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; Li, H.; Song, C.; Yuan, F.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, R.; Fang, H.; Liu, A. Effects of Gene-Environment Interaction on Obesity among Chinese Adults Born in the Early 1960s. Genes 2021, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Ai, F.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, M.; Zhang, S.; et al. Obesity-Related Genetic Variants and Hyperuricemia Risk in Chinese Men. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Guo, X.; Li, G.X.; Yang, H.; Zheng, L.; Sun, Y. Metabolic healthy obesity is associated with higher incidence of mild decrease estimate glomerular rate in rural northeast Chinese. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, J.; Yang, S.; Yang, M.; Liu, A.; Wang, L.; Cao, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, D. Prevalence of metabolically obese but normal weight (MONW) and metabolically healthy but obese (MHO) in Chinese Beijing urban subjects. Biosci. Trends 2017, 11, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.Q.; Wei, B.; Song, Y.P.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X.H.; Wang, X.P.; Yan, Y.Z.; Ma, J.L.; Wang, K.; Keerman, M.; et al. Metabolically healthy obesity and unhealthy normal weight rural adults in Xinjiang: Prevalence and the associated factors. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, X.; Bloomgarden, Z.T.; Ning, G. The Jiangnan diet, a healthy diet pattern for Chinese. J. Diabetes 2020, 12, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, P.; Wang, D.; Shen, H.; Yu, L.; Gao, Q.; Mao, L.; Jiang, F.; Luo, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Physical activity and health in Chinese children and adolescents: Expert consensus statement (2020). Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M. Leisure-Time Physical Activity Among Chinese Adults—China, 2015. China CDC Wkly. 2020, 2, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.-B. The summit of a moral pilgrimage: Confucianism on healthy ageing and social eldercare. Nurs. Ethics 2021, 28, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Gao, W.; Cao, W.; Lv, J.; Yu, C.; Wang, S.; Huang, T.; Sun, D.; Liao, C.; Pang, Y.; et al. Education, income, and obesity: A nationwide Chinese twin study. Obesity 2022, 30, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, A.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Wen, D.; Wang, Y. Obesity intervention efforts in China and the 2022 World Obesity Day. Glob. Health J. 2022, 6, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, P. The Chinese governance system: Its strengths and weaknesses in a comparative development perspective. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 61, 101430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C. Policy style, consistency and the effectiveness of the policy mix in China’s fight against COVID-19. Policy Soc. 2020, 39, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Akter, S.; Hu, H.; Kashino, I.; Kuwahara, K.; Okazaki, H.; Sasaki, N.; Ogasawara, T.; Eguchi, M.; Kochi, T.; et al. Five-year cumulative incidence of overweight and obesity, and longitudinal change in body mass index in Japanese workers: The Japan Epidemiology Collaboration on Occupational Health Study. J. Occup. Health 2020, 62, e12095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazumitsu, N. Estimation of Diabetes Prevalence, and Evaluation of Factors Affecting Blood Glucose Levels and Use of Med-ications in Japan. Health 2021, 13, 1431–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Urakami, T.; Kuwabara, R.; Yoshida, K. Economic Impact of Diabetes in Japan. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, S.E.; Boye, K.S.; Montgomery, W.S.; Iwamoto, K.; Okamura, M.; Hayes, R.P. Diabetes in Japan: A review of disease burden and approaches to treatment. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2009, 25, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengoku, T.; Ishizaki, T.; Goto, Y.; Iwao, T.; Ohtera, S.; Sakai, M.; Kato, G.; Nakayama, T.; Takahashi, Y. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes by age, sex and geographical area among two million public assistance recipients in Japan: A cross-sectional study using a nationally representative claims database. J. Epidemiol. Commun. Health 2022, 76, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisamatsu, T.; Segawa, H.; Kadota, A.; Ohkubo, T.; Arima, H.; Miura, K. Epidemiology of hypertension in Japan: Beyond the new 2019 Japanese guidelines. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirawa, N.; Umemura, S.; Ito, S. Viewpoint on Guidelines for Treatment of Hypertension in Japan. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iso, H. Cardiovascular disease, a major global burden: Epidemiology of stroke and ischemic heart disease in Japan. Glob. Health Med. 2021, 3, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, Y.; Shimokawa, H. Epidemiology of Heart Failure in Asia. Circ. J. 2013, 77, 2209–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogata, S.; Nishimura, K.; Guzman-Castillo, M.; Sumita, Y.; Nakai, M.; Nakao, Y.M.; Nishi, N.; Noguchi, T.; Sekikawa, A.; Saito, Y.; et al. Explaining the decline in coronary heart disease mortality rates in Japan: Contributions of changes in risk factors and evidence-based treatments between 1980 and 2012. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 291, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imai, Y.; Tanaka, S.M.; Satoh, M.; Hirata, T.; Murakami, Y.; Miura, K.; Waki, T.; Hirata, A.; Sairenchi, T.; Irie, F.; et al. Prediction of Lifetime Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Deaths Stratified by Sex in the Japanese Population. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, 021753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, M.; Yatsuya, H.; Iso, H.; Li, Y.; Yamagishi, K.; Tanabe, N.; Wada, Y.; Ota, A.; Tamakoshi, K.; Tamakoshi, A. Impact of Body Mass Index on Obesity-Related Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality; The Japan Collaborative Cohort Study. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2022, 29, 1547–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyoshige, E.; Ogata, S.; O’Flaherty, M.; Capewell, S.; Takegami, M.; Iihara, K.; Kypridemos, C.; Nishimura, K. Projections of future coronary heart disease and stroke mortality in Japan until 2040: A Bayesian age-period-cohort analysis. Lancet Reg. Health-West. Pac. 2022, 31, 100637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokomichi, H.; Nagai, A.; Hirata, M.; Mochizuki, M.; Kojima, R.; Yamagata, Z.; Project, B.J. Cause-specific mortality rates in patients with diabetes according to comorbid macro- and microvascular complications: BioBank Japan Cohort. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2021, 4, e00181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, Z.; Akter, S.; Inoue, Y.; Hu, H.; Kuwahara, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Honda, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Okazaki, H.; Miyamoto, T.; et al. Prediabetes, Diabetes, and the Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in a Japanese Working Population: Japan Epidemiology Collaboration on Occupational Health Study. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, H.; Madin-Warburton, M.; Strizek, A.; Thornton-Jones, L.; Suzuki, S. The cost-effectiveness of dulaglutide versus insulin glargine for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japan. J. Med. Econ. 2018, 21, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaoka, K.; Okayama, S.; Nakai, M.; Sumita, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Kawakami, R.; Okura, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yasuda, S.; Tsutsui, H.; et al. Hospitalization Costs for Patients With Acute Congestive Heart Failure in Japan. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujihara, K.; Sone, H. Cardiovascular Disease in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2018, 11, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tatsumi, Y.; Ohkubo, T. Hypertension with diabetes mellitus: Significance from an epidemiological perspective for Japanese. Hypertens. Res. 2017, 40, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Johnston, K.; Nakayama, T.; Marra, C.; Tsuyuki, R.T. Economic Evaluation of Pharmacists Tackling the Burden of Hypertension in Japan. Hypertension 2019, 74, e54–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Ohde, S. PM2.5 and Diabetes in the Japanese Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, M.; Okamura, T.; Nishi, N.; Kadota, A.; Nakamura, M.; Kondo, K.; Okami, Y.; Kitaoka, K.; Ojima, T.; Yoshita, K.; et al. Trends in Prevalence, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension According to 40-Year-Old Life Expectancy at Prefectures in Japan from the National Health and Nutrition Surveys. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Akiyama, M.; Ishigaki, K.; Kanai, M.; Hosoe, J.; Shojima, N.; Hozawa, A.; Kadota, A.; Kuriki, K.; Naito, M.; et al. Identification of 28 new susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, H.; Odagiri, Y.; Ohya, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Shimomitsu, T.; Theorell, T.; Inoue, S. Association of overtime work hours with various stress responses in 59,021 Japanese workers: Retrospective cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakao, Y.M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ueshima, K.; Nakao, K.; Nakai, M.; Nishimura, K.; Yasuno, S.; Hosoda, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Itoh, H.; et al. Effectiveness of nationwide screening and lifestyle intervention for abdominal obesity and cardiometabolic risks in Japan: The metabolic syndrome and comprehensive lifestyle intervention study on nationwide database in Japan (MetS ACTION-J study). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, S.; Kurokawa, A. The Operation of School Lunches in Japan: Construction of a System Considering Sustainability. Jpn. J. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 76, S12–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Nakagawa, T.; Honda, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Kuwahara, K.; Okazaki, H.; Hu, H.; Imai, T.; Nishihara, A.; Miyamoto, T.; et al. Smoking, Smoking Cessation, and Risk of Mortality in a Japanese Working Population—Japan Epidemiology Collaboration on Occupational Health Study. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 3005–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okui, T. An analysis of predictors for heavy alcohol drinking using nationally representative survey data in Japan. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasawa, T.; Saito, J.; Odawara, M.; Imamura, H.; Kaji, Y.; Yuwaki, K.; Nogi, K.; Nakamura, M.; Shimazu, T. Smoking cessation interventions and implementations in Japan: A study protocol for a scoping review and supplemental survey. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e063912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Hashimoto, H. Associations of education and income with heavy drinking and problem drinking among men: Evidence from a population-based study in Japan. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, L.; Yuan, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X. SGLT2i: Beyond the glucose-lowering effect. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara, M.; Mita, T.; Katakami, N.; Wada, F.; Morita, N.; Kidani, Y.; Yajima, T.; Shimomura, I.; Watada, H. Three-Year Glycaemic Control and Management in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Initiating Second-Line Treatment in Japan: A Prospective Observational Study, J-DISCOVER. Diabetes Ther. 2022, 13, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | Thresholds | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Pressure | Systolic ≤ 130 mmHg | [29,31] |
| Diastolic ≤ 85 mmHg | ||
| Glucose Metabolism | Fasting ≤ 6.1 mmol/L | [29,31] |
| No type II diabetes | ||
| Serum Triglycerides | Fasting ≤ 1.7 mmol/L | [31] |
| HDL-C | >1.0 mmol/L for men | [31] |
| >1.3 mmol/L for women | ||
| Waist Circumference | <0.95 for women | [29] |
| (Waist-to-Hip Ratio) | <1.03 for men | |
| Inflammatory Biomarkers | Nominal | [39,40] |
| (TNFα, IL-6) | ||
| Body Mass Index | ≥30 kg/m2 Western | [26,31] |
| ≥25 kg/m2 Asian |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mathis, B.J.; Tanaka, K.; Hiramatsu, Y. Obesity vs. Metabolically Healthy Obesity in East Asia. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 730-745. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3020053
Mathis BJ, Tanaka K, Hiramatsu Y. Obesity vs. Metabolically Healthy Obesity in East Asia. Encyclopedia. 2023; 3(2):730-745. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3020053
Chicago/Turabian StyleMathis, Bryan J., Kiyoji Tanaka, and Yuji Hiramatsu. 2023. "Obesity vs. Metabolically Healthy Obesity in East Asia" Encyclopedia 3, no. 2: 730-745. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3020053
APA StyleMathis, B. J., Tanaka, K., & Hiramatsu, Y. (2023). Obesity vs. Metabolically Healthy Obesity in East Asia. Encyclopedia, 3(2), 730-745. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3020053








