Of Soldiers and Their Ghosts: Are We Ready for a Review of PTSD Evidence?
Abstract
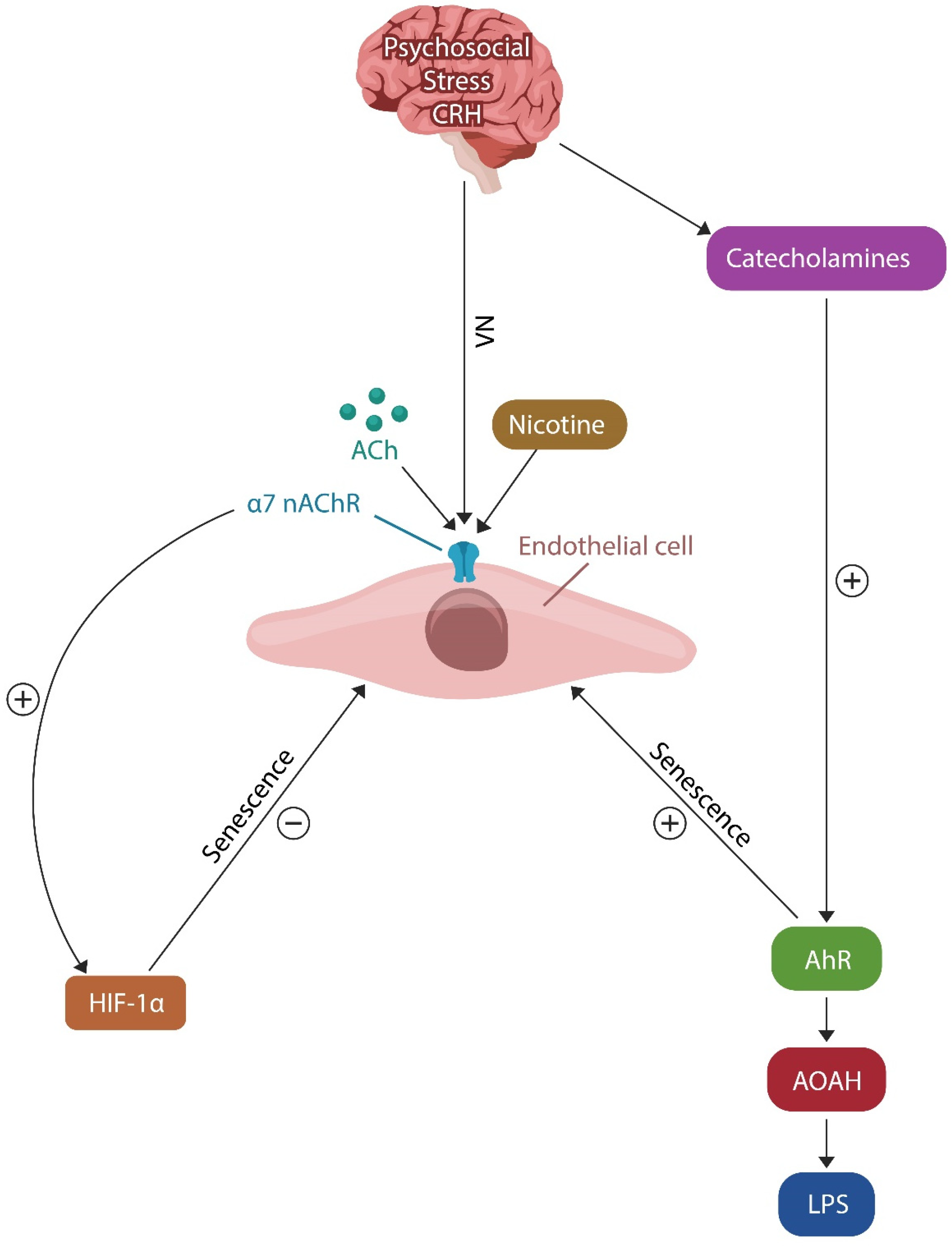
:1. Introduction
2. PTSD and Interoceptive Awareness
2.1. Heart Rate Variability as a PTSD Risk Factor
2.2. PTSD-Associated Hypertension (HTN)
3. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and Enteric Nervous System: Quick Reminder
3.1. AhR and Cellular Senescence
3.2. PTSD, Premature EC Senescence, and Barrier Function
4. PTSD Resilience Systems
4.1. Resilience Mechanism #1: The Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway (CAP)
4.2. Resilience Mechanism #2: HIF-1α and PTSD Resilience
5. Early Detection Markers
5.1. LPS
5.2. LBP and CD14
5.3. Microbial Cell-Free DNA (mcfDNA)
5.4. Acyloxyacyl Hydrolase (AOAH)
5.5. IL22
| Markers | Origin or Function | References |
|---|---|---|
| HRV | GI tract inflammation lowers HRV | [68] |
| BP | Right vs. left IC = vasopressor vs. vasodilation | [79] |
| LPS (elevated) | Gut, oral microbiome, food origin | [198,199,200] |
| sCD14 (elevated) | Receptor for LPS/LBP heterodimer | [229] |
| LBP (elevated) | Enhances the action of LPS | [230] |
| AOAH (low) | Neutralizes translocated LPS | [124] |
| IL22 (low) | Impaired barrier function | [239] |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdul-Hamid, W.K.; Hughes, J.H. Nothing new under the sun: Post-traumatic stress disorders in the ancient world. Early Sci. Med. 2014, 19, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraenkel, E. (Ed.) Aeschylus: Agamemnon; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Euben, J.P. The Tragedy of Political Theory: The Road Not Taken; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, M.A.; Holowka, D.W.; Vasterling, J.J.; Keane, T.M.; Marx, B.P.; Rosen, R.C. Posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans and military personnel: Epidemiology, screening, and case recognition. Psychol. Serv. 2012, 9, 361–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalev, A.; Liberzon, I.; Marmar, C. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2459–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbogen, E.B.; Johnson, S.C.; Wagner, H.R.; Sullivan, C.; Taft, C.T.; Beckham, J.C. Violent behaviour and post-traumatic stress disorder in US Iraq and Afghanistan veterans. Br. J. Psychiatry 2014, 204, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, H.; Yang, Z.; Satterthwaite, T.D.; Cook, P.A.; Bruce, S.E.; Shinohara, R.T.; Rosenberg, B.; Sheline, Y.I. Cognitive behavioral therapy increases amygdala connectivity with the cognitive control network in both MDD and PTSD. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 14, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisler, J.M.; Sigel, B.A.; Kramer, T.L.; Smitherman, S.; Vanderzee, K.; Pemberton, J.; Kilts, C.D. Amygdala response predicts trajectory of symptom reduction during Trauma-Focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy among adolescent girls with PTSD. J. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 71, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schottenbauer, M.A.; Glass, C.R.; Arnkoff, D.B.; Tendick, V.; Gray, S.H. Nonresponse and dropout rates in outcome studies on PTSD: Review and methodological considerations. Psychiatry 2008, 71, 134–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytwinski, N.K.; Scur, M.D.; Feeny, N.C.; Youngstrom, E.A. The co-occurrence of major depressive disorder among individuals with posttraumatic stress disorder: A meta-analysis. J. Trauma. Stress 2013, 26, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, L.E.; Sprang, K.R.; Rothbaum, B.O. Treating PTSD: A Review of Evidence-Based Psychotherapy Interventions. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Burgo-Black, L.; Hunt, S.C.; Miller, M.; Spelman, J.F. A Practical Review of Suicide Among Veterans: Preventive and Proactive Measures for Health Care Institutions and Providers. Public Health Rep. 2023, 138, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayfert, C.; DeViva, J.C.; Becker, C.B.; Pike, J.L.; Gillock, K.L.; Hayes, S.A. Exposure utilization and completion of cognitive behavioral therapy for PTSD in a “real world” clinical practice. J. Trauma. Stress 2005, 18, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribl, G.G.; Wetter, T.C.; Schredl, M. Dreaming under antidepressants: A systematic review on evidence in depressive patients and healthy volunteers. Sleep Med. Rev. 2013, 17, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabat-Zinn, J. Mindfulness-based interventions in context: Past, present, and future. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 2003, 10, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, K.D.; Laska, K.M.; Wampold, B.E. The evidence for present-centered therapy as a treatment for posttraumatic stress disorder. J. Trauma. Stress 2014, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, L.L.; Whetsell, C.; Hamner, M.B.; Carmody, J.; Rothbaum, B.O.; Allen, R.S.; Al Bartolucci, A.B.P.P.; Southwick, S.M.; Bremner, J.D. A Multisite Randomized Controlled Trial of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction in the Treatment of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Psychiatry Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 1, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouchou, F.; Mauguière, F.; Vallayer, O.; Catenoix, H.; Isnard, J.; Montavont, A.; Jung, J.; Pichot, V.; Rheims, S.; Mazzola, L. How the insula speaks to the heart: Cardiac responses to insular stimulation in humans. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, T.A.; Ullsperger, M.; Danielmeier, C. Error awareness and the insula: Links to neurological and psychiatric diseases. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Lievana, E.; Ramírez-Mejía, G.; Urrego-Morales, O.; Luis-Islas, J.; Gutierrez, R.; Bermúdez-Rattoni, F. Photostimulation of Ventral Tegmental Area-Insular Cortex Dopaminergic Inputs Enhances the Salience to Consolidate Aversive Taste Recognition Memory via D1-like Receptors. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 823220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnath, H.O.; Baier, B.; Nägele, T. Awareness of the functioning of one’s own limbs mediated by the insular cortex? J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 7134–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullsperger, M.; Harsay, H.A.; Wessel, J.R.; Ridderinkhof, K.R. Conscious perception of errors and its relation to the anterior insula. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghozi, J.L.; Saad, M.A.; Huerta, F.; Trancard, J. Ischaemia of the insular cortex increases the vagal contribution to the baroreceptor reflex in the rat. J. Hypertens Suppl. 1989, 7, S36–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppa, T.; Benschop, L.; Horczak, P.; Vanderhasselt, M.A.; Carrette, E.; Bechara, A.; Baeken, C.; Vonck, K. Auricular transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation modulates the heart-evoked potential. Brain Stimul. 2022, 15, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taft, T.H.; Quinton, S.; Jedel, S.; Simons, M.; Mutlu, E.A.; Hanauer, S.B. Posttraumatic Stress in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Prevalence and Relationships to Patient-Reported Outcomes. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A.; Tillisch, K. The brain-gut axis in abdominal pain syndromes. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, F.; Wu, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, G.; Piao, R.; Geng, B.; Xu, K.; Liu, P. Altered structural covariance and functional connectivity of the insula in patients with Crohn’s disease. Quant Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 1020–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruki, Y.; Ogawa, K. Role of anatomical insular subdivisions in interoception: Interoceptive attention and accuracy have dissociable substrates. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 2669–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, K.; Stewart, C.J.; Robinson, M.; Molfese, D.L.; Gosnell, S.N.; Kosten, T.R.; Petrosino, J.F.; De La Garza, R., II; Salas, R. Insular resting state functional connectivity is associated with gut microbiota diversity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2019, 50, 2446–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morey, R.A.; Gold, A.L.; LaBar, K.S.; Beall, S.K.; Brown, V.M.; Haswell, C.C.; Nasser, J.D.; Wagner, H.R.; McCarthy, G. Mid-Atlantic MIRECC Workgroup. Amygdala volume changes in posttraumatic stress disorder in a large case-controlled veterans group. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousdal, O.T.; Milde, A.M.; Hafstad, G.S.; Hodneland, E.; Dyb, G.; Craven, A.R.; Melinder, A.; Endestad, T.; Hugdahl, K. The association of PTSD symptom severity with amygdala nuclei volumes in traumatized youths. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palgi, Y.; Avidor, S.; Shrira, A.; Bodner, E.; Ben-Ezra, M.; Zaslavsky, O.; Hoffman, Y. Perception Counts: The Relationships of Inner Perceptions of Trauma and PTSD Symptoms Across Time. Psychiatry 2018, 81, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, G.J.; Berntson, G.G.; Cacioppo, J.T. Emotion, Somatovisceral Afference, and Autonomic Regulation. Emot. Rev. 2014, 6, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Rivera, M.; Kim, S.; Coleman, T.P.; Maldonado, P.E.; Torrealba, F. Interoceptive insular cortex participates in sensory processing of gastrointestinal malaise and associated behaviors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, N.S.; Varela, J.A.; Ng, A.J.; Granata, L.; Djerdjaj, A.; Brenhouse, H.C.; Christianson, J.P. Insular cortex corticotropin-releasing factor integrates stress signaling with social affective behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terasawa, Y.; Kurosaki, Y.; Ibata, Y.; Moriguchi, Y.; Umeda, S. Attenuated sensitivity to the emotions of others by insular lesion. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Hof, P.R.; Friston, K.J.; Fan, J. Anterior insular cortex and emotional awareness. J. Comp. Neurol. 2013, 521, 3371–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrushina, O.R.; Dobrynina, L.A.; Arina, G.A.; Kremneva, E.I.; Suslina, A.D.; Gubanova, M.V.; Belopasova, A.V.; Solodchik, P.O.; Urazgildeeva, G.R.; Krotenkova, M.V. Interaction of Interoceptive Perception and Emotional Intelligence: A Functional Neuroimaging Study. Neurosci. Behav. Physi. 2020, 50, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, C.; Singer, T. The role of anterior insular cortex in social emotions. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalley, M.G.; Kroes, M.C.; Huntley, Z.; Rugg, M.D.; Davis, S.W.; Brewin, C.R. An fMRI investigation of posttraumatic flashbacks. Brain Cogn. 2013, 81, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, M.; Espinal, E.; Aupperle, R.L.; Nikulina, V.; Stewart, J.L. The Electrical Aftermath: Brain Signals of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Filtered Through a Clinical Lens. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, G.; Feng, C.; Camilleri, J.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Krueger, F. The role of the anterior insula in social norm compliance and enforcement: Evidence from coordinate-based and functional connectivity meta-analyses. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 92, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogolla, N.; Takesian, A.E.; Feng, G.; Fagiolini, M.; Hensch, T.K. Sensory integration in mouse insular cortex reflects GABA circuit maturation. Neuron 2014, 83, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D. Retrieving immune responses stored in the insular cortex. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 23, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovikova, L.V.; Ivanova, S.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Botchkina, G.I.; Watkins, L.R.; Wang, H.; Abumrad, N.; Eaton, J.W.; Tracey, K.J. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 2000, 405, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Jin, U.H.; Karki, K.; Jayaraman, A.; Allred, C.; Michelhaugh, S.K.; Mittal, S.; Chapkin, R.S.; Safe, S. Dopamine is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 3899–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, Y.; Kado, S.Y.; Bein, K.J.; He, Y.; Pouraryan, A.A.; Urban, A.; Haarmann-Stemmann, T.; Sweeney, C.; Vogel, C.F.A. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling Synergizes with TLR/NF-κB-Signaling for Induction of IL-22 Through Canonical and Non-Canonical AhR Pathways. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 3, 787360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beekum, C.J.; von Websky, M.W.; Willis, M.A.; Panknin, C.; Coenen, M.; Fimmers, R.; Kalff, J.C.; Wehner, S.; Vilz, T.O. Transcutaneous vagal nerve simulation to reduce a systemic inflammatory response syndrome and the associated intestinal failure: Study protocol of a prospective, two-armed, sham-controlled, double-blinded trial in healthy subjects (the NeuroSIRS-Study). Int. J. Color. Dis. 2022, 37, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaram, R.; Caria, A.; Veit, R.; Gaber, T.; Ruiz, S.; Birbaumer, N. Volitional control of the anterior insula in criminal psychopaths using real-time fMRI neurofeedback: A pilot study. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, W.W. Anterior insula degeneration in frontotemporal dementia. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, R.C.; Chow, D.C.; Lum, C.J.; Shikuma, C.M.; Kallianpur, K.J. Reply to “The insular cortex and QTc interval in HIV+ and HIV- individuals: Is there an effect of sympathetic nervous system activity?”. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 337–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voruz, P.; Cionca, A.; Jacot de Alcântara, I.; Nuber-Champier, A.; Allali, G.; Benzakour, L.; Thomasson, M.; Lalive, P.H.; Lövblad, K.O.; Braillard, O.; et al. Functional connectivity underlying cognitive and psychiatric symptoms in post-COVID-19 syndrome: Is anosognosia a key determinant? Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juengst, S.; Skidmore, E.; Pramuka, M.; McCue, M.; Becker, J. Factors contributing to impaired self-awareness of cognitive functioning in an HIV positive and at-risk population. Disabil. Rehabil. 2012, 34, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszewska, D.A.; Lang, A.E. The Role of Insular Cortex in Gut-Inflammation Memory: What Does It Mean for Parkinson’s Disease? Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 700–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouhmad, N.; Deperrois, R.; Combalbert, N.; El Hage, W. The Role of Anxiety and Depression in the Emotion Regulation Strategies of People Suffering from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. J. Psychol. 2023, 157, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berntson, G.G.; Khalsa, S.S. Neural Circuits of Interoception. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmedt, A.; Marighetto, A.; Piazza, P.V. Abnormal Fear Memory as a Model for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A.; Flynn, P.; Rischbieth, S.; McKellar, D. Managing severe aggression in frontotemporal dementia. Australas Psychiatry 2014, 22, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiesa, A.; Serretti, A. Mindfulness based cognitive therapy for psychiatric disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2011, 187, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutschler, I.; Reinbold, C.; Wankerl, J.; Seifritz, E.; Ball, T. Structural basis of empathy and the domain general region in the anterior insular cortex. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.A.; Chao, L.; Neylan, T.C.; O’Donovan, A.; Metzler, T.J.; Inslicht, S.S. Association among anterior cingulate cortex volume, psychophysiological response, and PTSD diagnosis in a Veteran sample. Neurobiol. Learn Mem. 2018, 155, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ojeda, W.; Hurley, R.A. Von Economo Neuron Involvement in Social Cognitive and Emotional Impairments in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 34, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allman, J.M.; Tetreault, N.A.; Hakeem, A.Y.; Manaye, K.F.; Semendeferi, K.; Erwin, J.M.; Park, S.; Goubert, V.; Hof, P.R. The von Economo neurons in frontoinsular and anterior cingulate cortex in great apes and humans. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 495–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillo, A.F.; Nilsson, C.; Englund, E. von Economo neurones are selectively targeted in frontotemporal dementia. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2013, 39, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, A.A.; Lin, L.-C.; Nana, A.L.; Gaus, S.E.; Seeley, W.W. Von Economo neurons and fork cells: A neurochemical signature linked to monoaminergic function. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibegbu, A.O.; Umana, U.E.; Hamman, W.O.; Adamu, A.S. Von Economo neurons: A Review of the Anatomy and Functions. Austin J. Anat. 2014, 1, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, S.K.; Yin, C.; Weber, C.; Godinho-Silva, C.; Veiga-Fernandes, H.; Xu, Q.J.; Chang, R.B.; Habenicht, A.J.R. Cardiovascular Brain Circuits. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 1546–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Yao, Y.; Ju, S.Y. Heart rate variability and inflammatory bowel disease in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e23430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeppl, T.B.; Donges, M.R.; Mokros, A.; Rupprecht, R.; Fox, P.T.; Laird, A.R.; Bzdok, D.; Langguth, B.; Eickhoff, S.B. A view behind the mask of sanity: Meta-analysis of aberrant brain activity in psychopaths. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, A.; Fung, A.L.; Portnoy, J.; Choy, O.; Spring, V.L. Low heart rate as a risk factor for child and adolescent proactive aggressive and impulsive psychopathic behavior. Aggress Behav. 2014, 40, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segarra, P.; Poy, R.; Branchadell, V.; Ribes-Guardiola, P.; Moltó, J. Psychopathy and heart rate variability: A new physiological marker for the adaptive features of boldness. Pers. Disord. 2022, 13, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, L.; Nana, A.L.; Toller, G.; Brown, J.A.; Deng, J.; Staffaroni, A.; Kim, E.J.; Hwang, J.L.; Li, L.; Park, Y.; et al. Salience Network Atrophy Links Neuron Type-Specific Pathobiology to Loss of Empathy in Frontotemporal Dementia. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 5387–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banovac, I.; Sedmak, D.; Judaš, M.; Petanjek, Z. Von Economo Neurons-Primate-Specific or Commonplace in the Mammalian Brain? Front. Neural Circuits 2021, 15, 714611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Boxtel, G.J.M.; Cluitmans, P.J.M.; Raymann, R.J.E.M.; Ouwerkerk, M.; Denissen, A.J.M.; Dekker, M.K.J.; Sitskoorn, M.M. Heart Rate Variability, Sleep, and the Early Detection of Post-traumatic Stress Disorder. In Sleep and Combat-Related Post Traumatic Stress Disorder; Vermetten, E., Germain, A., Neylan, T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, B.F. Heart Rate Variability Following Treatment for PTSD: Testing the Polyvagal Theory. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Missouri-St. Louis, St. Louis, MI, USA, 2022. Available online: https://irl.umsl.edu/dissertation/1150 (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Soder, H.E.; Wardle, M.C.; Schmitz, J.M.; Lane, S.D.; Green, C.; Vujanovic, A.A. Baseline resting heart rate variability predicts post-traumatic stress disorder treatment outcomes in adults with co-occurring substance use disorders and post-traumatic stress. Psychophysiology 2019, 56, e13377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheimer, S.M.; Gelb, A.; Girvin, J.P.; Hachinski, V.C. Cardiovascular effects of human insular cortex stimulation. Neurology 1992, 42, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marins, F.R.; Iddings, J.A.; Fontes, M.A.; Filosa, J.A. Evidence that remodeling of insular cortex neurovascular unit contributes to hypertension-related sympathoexcitation. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Larsen, A.; Principe, A.; Ley, M.; Navarro-Cuartero, J.; Rocamora, R. Characterization of the Insular Role in Cardiac Function through Intracranial Electrical Stimulation of the Human Insula. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.M.; Mendes, W.B. A large-scale study of stress, emotions, and blood pressure in daily life using a digital platform. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2105573118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubbin, J.A.; Nathan, A.; Hibdon, M.A.; Castillo, A.V.; Graham, J.G.; Switzer, F.S., III. Blood Pressure, Emotional Dampening, and Risk Behavior: Implications for Hypertension Development. Psychosom. Med. 2018, 80, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, J.A.; Kubzansky, L.D.; Roberts, A.L.; Gilsanz, P.; Chen, Q.; Winning, A.; Forman, J.P.; Rimm, E.B.; Koenen, K.C. Post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms and risk of hypertension over 22 years in a large cohort of younger and middle-aged women. Psychol. Med. 2016, 46, 3105–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkreli, L.; Woud, M.L.; Ramsbottom, R.; Rupietta, A.E.; Waldhauser, G.T.; Kumsta, R.; Reinecke, A. Angiotensin involvement in trauma processing-exploring candidate neurocognitive mechanisms of preventing post-traumatic stress symptoms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Yu, Y.; Wei, S.G.; Beltz, T.G.; Guo, F.; Felder, R.B.; Johnson, A.K. Stress-Induced Sensitization of Angiotensin II Hypertension Is Reversed by Blockade of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme or Tumor Necrosis Factor-α. Am. J. Hypertens. 2019, 32, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, W.; Qi, Z.; Xu, T.; Zhou, F.; Becker, B. Angiotensin II Regulates the Neural Expression of Subjective Fear in Humans: A Precision Pharmaco-Neuroimaging Approach. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2023, 8, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonia, R.; Empey, P.E.; Poloyac, S.M.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Klamerus, M.; Ozawa, H.; Wagner, A.K.; Ruppel, R.; Bell, M.J.; Feldman, K.; et al. Endothelin-1 is increased in cerebrospinal fluid and associated with unfavorable outcomes in children after severe traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janiri, D.; Carfì, A.; Kotzalidis, G.D.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F.; Sani, G. Gemelli Against COVID-19 Post-Acute Care Study Group. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Patients After Severe COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neigh, G.N.; Ali, F.F. Co-morbidity of PTSD and immune system dysfunction: Opportunities for treatment. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, N.M.; Marvar, P.J.; Gillespie, C.F.; Wingo, A.; Schwartz, A.; Bradley, B.; Kramer, M.; Ressler, K.J. The renin-angiotensin pathway in posttraumatic stress disorder: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers are associated with fewer traumatic stress symptoms. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2012, 73, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfera, A.; Osorio, C.; Rahman, L.; Zapata-Martín Del Campo, C.M.; Maldonado, J.C.; Jafri, N.; Cummings, M.A.; Maurer, S.; Kozlakidis, Z. PTSD as an Endothelial Disease: Insights from COVID-19. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 770387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbor, L.N.; Elased, K.M.; Walker, M.K. Endothelial cell-specific aryl hydrocarbon receptor knockout mice exhibit hypotension mediated, in part, by an attenuated angiotensin II responsiveness. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Yu, P.; Wang, Z.; Deng, W.; Bao, L.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, N.; Lv, Q.; et al. ACE2 expression is regulated by AhR in SARS-CoV-2-infected macaques. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1308–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, M.; Tatebe, J.; Watanabe, I.; Yamazaki, J.; Ikeda, T.; Morita, T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates indoxyl sulfate-induced cellular senescence in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2014, 21, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memari, B.; Bouttier, M.; Dimitrov, V.; Ouellette, M.; Behr, M.A.; Fritz, J.H.; White, J.H. Engagement of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Infected Macrophages Has Pleiotropic Effects on Innate Immune Signaling. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4479–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armando, I.; Seltzer, A.; Bregonzio, C.; Saavedra, J.M. Stress and angiotensin II: Novel therapeutic opportunities. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2003, 2, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, J.; Benicky, J.; Murakami, Y.; Sanchez-Lemus, E.; Saavedra, J.M. Peripherally administered angiotensin II AT1 receptor antagonists are anti-stress compounds in vivo. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1148, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, A.M.; Higashiguchi, S.; Horie, K.; Kim, M.; Hatta, H.; Yokogoshi, H. Relaxation and immunity enhancement effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) administration in humans. Biofactors 2006, 26, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furness, J.B.; Callaghan, B.P.; Rivera, L.R.; Cho, H.J. The enteric nervous system and gastrointestinal innervation: Integrated local and central control. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 39–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.; Micci, M.A.; Leser, J.; Shin, C.; Tang, S.C.; Fu, Y.Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Saha, M.; Li, C.; et al. Adult enteric nervous system in health is maintained by a dynamic balance between neuronal apoptosis and neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3709–E3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Foong, J.P.P.; Harris, N.L.; Bornstein, J.C. Enteric neuroimmune interactions coordinate intestinal responses in health and disease. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, A.; Kende, A. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: Environmental contaminant and molecular probe. Fed. Proc. 1976, 35, 2404–2411. [Google Scholar]
- Fehsel, K.; Schwanke, K.; Kappel, B.A.; Fahimi, E.; Meisenzahl-Lechner, E.; Esser, C.; Hemmrich, K.; Haarmann-Stemmann, T.; Kojda, G.; Lange-Asschenfeldt, C. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by clozapine induces preadipocyte differentiation and contributes to endothelial dysfunction. J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G. Tumour Microenvironment: Roles of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor, O-GlcNAcylation, Acetyl-CoA and Melatonergic Pathway in Regulating Dynamic Metabolic Interactions across Cell Types-Tumour Microenvironment and Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzella, C.; Singhal, M.; Alrefai, W.A.; Saksena, S.; Dudeja, P.K.; Gill, R.K. Serotonin is an endogenous regulator of intestinal CYP1A1 via AhR. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giaimo, R.; Durovic, T.; Barquin, P.; Kociaj, A.; Lepko, T.; Aschenbroich, S.; Breunig, C.T.; Irmler, M.; Cernilogar, F.M.; Schotta, G.; et al. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Pathway Defines the Time Frame for Restorative Neurogenesis. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 3241–3251.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madison, C.A.; Hillbrick, L.; Kuempel, J.; Albrecht, G.L.; Landrock, K.K.; Safe, S.; Chapkin, R.S.; Eitan, S. Intestinal epithelium aryl hydrocarbon receptor is involved in stress sensitivity and maintaining depressive symptoms. Behav. Brain Res. 2023, 440, 114256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.K.; Peng, V.; Sudan, R.; Ulezko Antonova, A.; Di Luccia, B.; Ohara, T.E.; Fachi, J.L.; Grajales-Reyes, G.E.; Jaeger, N.; Trsan, T.; et al. Repression of the aryl-hydrocarbon receptor prevents oxidative stress and ferroptosis of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Immunity 2023, 56, 797–812.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logue, M.W.; Miller, M.W.; Wolf, E.J.; Huber, B.R.; Morrison, F.G.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Smith, A.K.; Daskalakis, N.P.; Ratanatharathorn, A.; et al. An epigenome-wide association study of posttraumatic stress disorder in US veterans implicates several new DNA methylation loci. Clin. Epigenetics 2020, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiniga, L.M.; Yang, W.; Yaggie, R.E.; Schaeffer, A.J.; Klumpp, D.J.; MAPP Research Network Study Group. Acyloxyacyl hydrolase modulates depressive-like behaviors through aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2019, 317, R289–R300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Feng, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, F.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, W. Stress-altering anterior insular cortex activity affects risk decision-making behavior in mice of different sexes. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1094808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) reveals evidence of antagonistic pleiotropy in the regulation of the aging process. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A. Mutual antagonism between aryl hydrocarbon receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (AhR/HIF-1α) signaling: Impact on the aging process. Cell. Signal. 2022, 99, 110445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, N.; Fukuda, K.; Nagata, Y.; Okada, H.; Haga, A.; Hatakeyama, S.; Yoshida, S.; Okamoto, T.; Hosaka, M.; Sekine, K.; et al. The activation mechanism of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) by molecular chaperone HSP90. FEBS Open Bio. 2014, 4, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, K.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, M.; Doyle, F.J., III. A detailed modular analysis of heat-shock protein dynamics under acute and chronic stress and its implication in anxiety disorders. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B.R.; Karchner, S.I.; Allan, L.L.; Pollenz, R.S.; Tanguay, R.L.; Jenny, M.J.; Sherr, D.H.; Hahn, M.E. Repression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) signaling by AHR repressor: Role of DNA binding and competition for AHR nuclear translocator. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, T.; Wang, J.; Zhu, K.; Tang, Y.; Huang, S.; Shui, X.; Ding, Y.; Chen, C.; Lei, W. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor: A New Player of Pathogenesis and Therapy in Cardiovascular Diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6058784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, E.S.; Tischkau, S.A. The Role of AhR in the Hallmarks of Brain Aging: Friend and Foe. Cells 2021, 10, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Tian, H.; Tian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Wang, X. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor/IL-22/Stat3 signaling pathway is involved in the modulation of intestinal mucosa antimicrobial molecules by commensal microbiota in mice. Innate Immun. 2018, 24, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nacarino-Palma, A.; Rico-Leo, E.M.; Campisi, J.; Ramanathan, A.; González-Rico, F.J.; Rejano-Gordillo, C.M.; Ordiales-Talavero, A.; Merino, J.M.; Fernández-Salguero, P.M. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor blocks aging-induced senescence in the liver and fibroblast cells. Aging 2022, 14, 4281–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Ren, Q.; Guo, F.; Du, X.; Yang, H.; Fu, P.; Ma, L. Tubular aryl hydratocarbon receptor upregulates EZH2 to promote cellular senescence in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alique, M.; Sánchez-López, E.; Bodega, G.; Giannarelli, C.; Carracedo, J.; Ramírez, R. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α: The Master Regulator of Endothelial Cell Senescence in Vascular Aging. Cells 2020, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pral, L.P.; Fachi, J.L.; Corrêa, R.O.; Colonna, M.; Vinolo, M.A.R. Hypoxia and HIF-1 as key regulators of gut microbiota and host interactions. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 604–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfera, A.; Klein, C.; Anton, J.J.; Kozlakidis, Z.; Andronescu, C.V. The Role of Lactylation in Mental Illness: Emphasis on Microglia. Neuroglia 2023, 4, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munford, R.S.; Weiss, J.P.; Lu, M. Biochemical transformation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides by acyloxyacyl hydrolase reduces host injury and promotes recovery. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 17842–17851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerville, M.; Boudry, G. Gastrointestinal and hepatic mechanisms limiting entry and dissemination of lipopolysaccharide into the systemic circulation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 311, G1–G15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.J.; Tong, J.; Zeng, F.Y.; Guo, M.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Wang, P. Nicotinic ACh receptor α7 inhibits PDGF-induced migration of vascular smooth muscle cells by activating mitochondrial deacetylase sirtuin 3. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 4388–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Cabezudo, M.J.; Lorke, D.E.; Azimullah, S.; Mechkarska, M.; Hasan, M.Y.; Petroianu, G.A.; al-Ramadi, B.K. Cholinergic stimulation of the immune system protects against lethal infection by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Immunology 2010, 130, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.; Kirk, J.; Dolezalova, N.; Guyot, M.; Panzolini, C.; Bondue, A.; Lavergne, J.; Hugues, S.; Hypolite, N.; Saeb-Parsy, K.; et al. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway inhibits inflammation without lymphocyte relay. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1125492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnawski, L.; Shavva, V.S.; Kort, E.J.; Zhuge, Z.; Nilsson, I.; Gallina, A.L.; Martínez-Enguita, D.; Heller Sahlgren, B.; Weiland, M.; Caravaca, A.S.; et al. Cholinergic regulation of vascular endothelial function by human ChAT+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2212476120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, C.; Kilcoyne, C.M.; Quyyumi, A.A.; Cannon, R.O., III; Panza, J.A. Role of nitric oxide in the vasodilator response to mental stress in normal subjects. Am. J. Cardiol. 1997, 80, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Ding, Q.; Lin, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Zhu, Y. New insights of epigenetics in vascular and cellular senescence. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2021, 9, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Shao, C.; Rose, P.; Zhu, Y.Z. Epigenetics and Vascular Senescence-Potential New Therapeutic Targets? Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 535395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, S.; Ikeda, K.; Urata, R.; Yamazaki, E.; Emoto, N.; Matoba, S. Cellular senescence promotes endothelial activation through epigenetic alteration, and consequently accelerates atherosclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Beier, F.; Gusmao, E.G.; Koch, C.M.; Hummel, S.; Charapitsa, I.; Joussen, S.; Benes, V.; Brümmendorf, T.H.; Reid, G.; et al. Replicative senescence is associated with nuclear reorganization and with DNA methylation at specific transcription factor binding sites. Clin. Epigenet. 2015, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, D.S.; Moser, D.A.; Paoloni-Giacobino, A.; Stenz, L.; Gex-Fabry, M.; Aue, T.; Adouan, W.; Cordero, M.I.; Suardi, F.; Manini, A.; et al. Methylation of NR3C1 is related to maternal PTSD, parenting stress and maternal medial prefrontal cortical activity in response to child separation among mothers with histories of violence exposure. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukojevic, V.; Kolassa, I.T.; Fastenrath, M.; Gschwind, L.; Spalek, K.; Milnik, A.; Heck, A.; Vogler, C.; Wilker, S.; Demougin, P.; et al. Epigenetic modification of the glucocorticoid receptor gene is linked to traumatic memory and post-traumatic stress disorder risk in genocide survivors. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 10274–10284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-J.; Stewart, R.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, S.-W.; Shin, I.-S.; Kim, M.-C.; Hong, Y.J.; Ahn, Y.; Shin, M.-G.; Jeong, M.H.; et al. Synergistic effects of depression and NR3C1 methylation on prognosis of acute coronary syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philibert, R.A.; Dogan, M.V.; Mills, J.A.; Long, J.D. AHRR Methylation is a Significant Predictor of Mortality Risk in Framingham Heart Study. J. Insur. Med. 2019, 48, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.K.; Ratanatharathorn, A.; Maihofer, A.X.; Naviaux, R.K.; Aiello, A.E.; Amstadter, A.B.; Ashley-Koch, A.E.; Baker, D.G.; Beckham, J.C.; Boks, M.P.; et al. Epigenome-wide meta-analysis of PTSD across 10 military and civilian cohorts identifies methylation changes in AHRR. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.W.; Xu, H. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Repressor Methylation: A Link Between Smoking and Atherosclerosis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2015, 8, 640–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic Eren, M.; Tabor, V. The role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha in bypassing oncogene-induced senescence. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101064, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winans, B.; Nagari, A.; Chae, M.; Post, C.M.; Ko, C.I.; Puga, A.; Kraus, W.L.; Lawrence, B.P. Linking the aryl hydrocarbon receptor with altered DNA methylation patterns and developmentally induced aberrant antiviral CD8+ T cell responses. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4446–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severance, E.G.; Gressitt, K.L.; Stallings, C.R.; Origoni, A.E.; Khushalani, S.; Leweke, F.M.; Dickerson, F.B.; Yolken, R.H. Discordant patterns of bacterial translocation markers and implications for innate immune imbalances in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2013, 148, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevin, A.S.; McKinnon, L.; Burgener, A.; Klatt, N.R. Microbial translocation and microbiome dysbiosis in HIV-associated immune activation. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2016, 11, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, R.; Francés, R.; Gutiérrez, A.; Juanola, O. Bacterial Translocation as Inflammatory Driver in Crohn’s Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 703310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishido, A.A.; Noe, M.; Saharia, K.; Luethy, P. Clinical impact of a metagenomic microbial plasma cell-free DNA next-generation sequencing assay on treatment decisions: A single-center retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Leung, C.H.C.; Wu, A.R. Cell-Free DNA as Biomarker for Sepsis by Integration of Microbial and Host Information. Clin. Chem. 2022, 68, 1184–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaler, C.R.; Parco, A.A.; Elhenawy, W.; Dourka, J.; Jury, J.; Verdu, E.F.; Coombes, B.K. Psychological stress impairs IL22-driven protective gut mucosal immunity against colonising pathobionts. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengil, S.; Laloğlu, E. Evaluation of Serum Zonulin and Occludin Levels in Bipolar Disorder. Psychiatry Investig. 2023, 20, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karailiev, P.; Hlavacova, N.; Chmelova, M.; Homer, N.Z.M.; Jezova, D. Tight junction proteins in the small intestine and prefrontal cortex of female rats exposed to stress of chronic isolation starting early in life. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e14084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Y.; Guo, C.C.; Li, M.Y.; Lou, Y.H.; Chen, Z.R.; Liu, B.W.; Lan, L. Brain-gut-liver axis: Chronic psychological stress promotes liver injury and fibrosis via gut in rats. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1040749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.J.; Nazli, A.; Rojas, O.L.; Chege, D.; Alidina, Z.; Huibner, S.; Mujib, S.; Benko, E.; Kovacs, C.; Shin, L.Y.; et al. A role for mucosal IL-22 production and Th22 cells in HIV-associated mucosal immunopathogenesis. Mucosal Immunol. 2012, 5, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirumalaraju, V.; Suchting, R.; Evans, J.; Goetzl, L.; Refuerzo, J.; Neumann, A.; Anand, D.; Ravikumar, R.; Green, C.E.; Cowen, P.J.; et al. Risk of Depression in the Adolescent and Adult Offspring of Mothers with Perinatal Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e208783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, J.D.; Mashburn-Warren, L.; Blalock, L.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Carroll, J.E.; Ross, K.M.; Hobel, C.; Coussons-Read, M.; Dunkel Schetter, C.; Gur, T.L. Maternal anxiety, depression and stress affects offspring gut microbiome diversity and bifidobacterial abundances. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 107, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Giollabhui, N.; Breen, E.C.; Murphy, S.K.; Maxwell, S.D.; Cohn, B.A.; Krigbaum, N.Y.; Cirillo, P.M.; Perez, C.; Alloy, L.B.; Drabick, D.A.G.; et al. Maternal inflammation during pregnancy and offspring psychiatric symptoms in childhood: Timing and sex matter. J. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 111, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, X.; Chen, C.; Fang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Fei, W.; Chen, F.; Zheng, C. The Role of Microbiomes in Pregnant Women and Offspring: Research Progress of Recent Years. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hine, A.M.; Loke, P. Intestinal Macrophages in Resolving Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ask, T.F.; Lugo, R.G.; Sütterlin, S. The Neuro-Immuno-Senescence Integrative Model (NISIM) on the Negative Association Between Parasympathetic Activity and Cellular Senescence. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, C.C.; Schridde, A. Origin, Differentiation, and Function of Intestinal Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, C.C.; Mowat, A.M. Macrophages in intestinal homeostasis and inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, T.W.; Bansal, V.; Peterson, C.Y.; Loomis, W.H.; Putnam, J.G.; Rankin, F.; Wolf, P.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Baird, A.; Coimbra, R. Efferent vagal nerve stimulation attenuates gut barrier injury after burn: Modulation of intestinal occludin expression. J. Trauma. 2010, 68, 1349–1354; discussion 1354–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyzaniak, M.; Peterson, C.; Loomis, W.; Hageny, A.M.; Wolf, P.; Reys, L.; Putnam, J.; Eliceiri, B.; Baird, A.; Bansal, V.; et al. Postinjury vagal nerve stimulation protects against intestinal epithelial barrier breakdown. J. Trauma. 2011, 70, 1168–1175; discussion 1175–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottari, S.A.; Lamb, D.G.; Porges, E.C.; Murphy, A.J.; Tran, A.B.; Ferri, R.; Jaffee, M.S.; Davila, M.I.; Hartmann, S.; Baumert, M.; et al. Preliminary evidence of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation effects on sleep in veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder. J. Sleep Res. 2023, e13891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, S.; Maueröder, C.; Ravichandran, K.S. Living on the Edge: Efferocytosis at the Interface of Homeostasis and Pathology. Immunity 2019, 50, 1149–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, T.; Otsubo, W.; Horiguchi, K.; Mikawa, S.; Kaji, N.; Iino, S.; Ozaki, H.; Hori, M. The anti-inflammatory pathway regulated via nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat intestinal mesothelial cells. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, W.; Su, Z.; Wazir, J.; Zhao, C.; Wei, L.; Wang, R.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H. Protective effect of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation on experimental colitis and its mechanism. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, E.R.; Sansgiry, S.; Kramer, J.R.; Waljee, A.K.; Gaidos, J.K.; Feagins, L.A.; Govani, S.M.; Dindo, L.; El-Serag, H.B.; Hou, J.K. The Incidence and Prevalence of Anxiety, Depression, and Post-traumatic Stress Disorder in a National Cohort of US Veterans With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Huang, M.; Yao, Y.M. Efferocytosis and Its Role in Inflammatory Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 839248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppe, J.P.; Desprez, P.Y.; Krtolica, A.; Campisi, J. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: The dark side of tumor suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2010, 5, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayflick, L. The limited in vitro lifetime of human diploid cell strains. Exp. Cell Res. 1965, 37, 614–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, C.B.; Futcher, A.B.; Greider, C.W. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature 1990, 345, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Huang, P.; Li, J. The association between post-traumatic stress disorder and shorter telomere length: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 218, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.M.; Coimbra, B.M.; Xavier, G.; Bugiga, A.V.G.; Fonseca, T.; Olff, M.; Polimanti, R.; Mello, A.F.; Ota, V.K.; Mello, M.F.; et al. Shorter Telomeres Related to Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Re-experiencing Symptoms in Sexually Assaulted Civilian Women. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 835783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, J.A.; Chen, Q.; Roberts, A.L.; Winning, A.; Rimm, E.B.; Gilsanz, P.; Glymour, M.M.; Tworoger, S.S.; Koenen, K.C.; Kubzansky, L.D. Posttraumatic stress disorder onset and inflammatory and endothelial function biomarkers in women. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, E.J.; Morrison, F.G. Traumatic Stress and Accelerated Cellular Aging: From Epigenetics to Cardiometabolic Disease. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2017, 19, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohr, J.B.; Palmer, B.W.; Eidt, C.A.; Aailaboyina, S.; Mausbach, B.T.; Wolkowitz, O.M.; Thorp, S.R.; Jeste, D.V. Is Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Associated with Premature Senescence? A Review of the Literature. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2015, 23, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.M.; Mackos, A.R.; Jaggers, R.M.; Brewster, P.C.; Webb, M.; Lin, C.H.; Ladaika, C.; Davies, R.; White, P.; Loman, B.R.; et al. Psychological stress disrupts intestinal epithelial cell function and mucosal integrity through microbe and host-directed processes. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2035661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alique, M.; Bodega, G.; Giannarelli, C.; Carracedo, J.; Ramírez, R. MicroRNA-126 regulates Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α which inhibited migration, proliferation, and angiogenesis in replicative endothelial senescence. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welford, S.M.; Bedogni, B.; Gradin, K.; Poellinger, L.; Broome Powell, M.; Giaccia, A.J. HIF1alpha delays premature senescence through the activation of MIF. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 3366–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.J.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, W.D.; Yuan, J.Q.; Yuan, K. HIF-2α not HIF-1α overexpression confers poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317709637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.A.; Waypa, G.B.; Dudley, V.J.; Budinger, G.R.S.; Abdala-Valencia, H.; Bartom, E.; Schumacker, P.T. Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Regulating Right Ventricular Function and Remodeling during Chronic Hypoxia-induced Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 63, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Tokunou, T.; Takahara, Y.; Sunagawa, K.; Hirooka, Y.; Ichiki, T.; Tsutsui, H. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 α deletion in myeloid lineage attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, B.S.; Katz, W.F.; Van Enkevort, E.A.; Khawaja, I.S. Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Comorbid With Mood Disorder: Significantly Higher Incidence Than in Either Diagnosis Alone. Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2018, 20, 18m02281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvonen, P.J.; Masino, T.; Drummond, S.P.; Myers, U.S.; Angkaw, A.C.; Norman, S.B. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder among OEF/OIF/OND Veterans. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doenyas-Barak, K.; Catalogna, M.; Kutz, I.; Levi, G.; Hadanny, A.; Tal, S.; Daphna-Tekoha, S.; Sasson, E.; Shechter, Y.; Efrati, S. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves symptoms, brain’s microstructure and functionality in veterans with treatment resistant post-traumatic stress disorder: A prospective, randomized, controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, B.B.; Weaver, L.K.; Gupta, A.; Wilson, S.H.; Vijayarangan, A.; Deru, K.; Hebert, D. Hyperbaric oxygen for mTBI-associated PCS and PTSD: Pooled analysis of results from Department of Defense and other published studies. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2019, 46, 353–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.I.; Yi, E.J.; Kim, Y.D.; Lee, A.R.; Chung, J.; Ha, H.C.; Cho, J.M.; Kim, S.R.; Ko, H.J.; Cheon, J.H.; et al. Local Stabilization of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Controls Intestinal Inflammation via Enhanced Gut Barrier Function and Immune Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 609689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muenchau, S.; Deutsch, R.; de Castro, I.J.; Hielscher, T.; Heber, N.; Niesler, B.; Lusic, M.; Stanifer, M.L.; Boulant, S. Hypoxic Environment Promotes Barrier Formation in Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells through Regulation of MicroRNA 320a Expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 39, e00553-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budda, S.A.; Girton, A.; Henderson, J.G.; Zenewicz, L.A. Transcription Factor HIF-1α Controls Expression of the Cytokine IL-22 in CD4 T Cells. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 2646–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yu, T.; Huang, X.; Bilotta, A.J.; Xu, L.; Lu, Y.; Sun, J.; Pan, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Intestinal microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulation of immune cell IL-22 production and gut immunity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M. Leaky gut: Mechanisms, measurement and clinical implications in humans. Gut 2019, 68, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.K.; Nakamura, T.; Byrne, R.J.; Naicker, S.; Tynan, R.J.; Hunter, M.; Hodgson, D.M. Neonatal lipopolysaccharide and adult stress exposure predisposes rats to anxiety-like behaviour and blunted corticosterone responses: Implications for the double-hit hypothesis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Luo, B.L.; Yang, Q.G.; Ni, M.Z.; Wu, Q.T.; Li, Y.; Li, X.W.; Chen, G.H. Prenatal exposure to inflammation increases anxiety-like behaviors in F1 and F2 generations: Possible links to decreased FABP7 in hippocampus. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 973069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Lin, S.Y.; Wang, S. Prenatal lipopolysaccharide exposure increases anxiety-like behaviors and enhances stress-induced corticosterone responses in adult rats. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagliato, L.A.; de Matos, U.; Nardi, A.E. Maternal immune activation generates anxiety in offspring: A translational meta-analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Haddad, B.J.S.; Oler, E.; Armistead, B.; Elsayed, N.A.; Weinberger, D.R.; Bernier, R.; Burd, I.; Kapur, R.; Jacobsson, B.; Wang, C.; et al. The fetal origins of mental illness. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 221, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, S.H. Lipopolysaccharide: Basic biochemistry, intracellular signaling, and physiological impacts in the gut. Intest. Res. 2014, 12, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, N.; Chadwick, J.; Sun, C.; Parbhakar, K.; Khoury, N.; Barbour, A.; Goldberg, M.; Tenenbaum, H.; Glogauer, M. Periodontal inflammation primes the systemic innate immune response. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassenaar, T.M.; Zimmermann, K. Lipopolysaccharides in Food, Food Supplements, and Probiotics: Should We be Worried? Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 8, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maric, S.; Restin, T.; Muff, J.L.; Camargo, S.M.; Guglielmetti, L.C.; Holland-Cunz, S.G.; Crenn, P.; Vuille-Dit-Bille, R.N. Citrulline, Biomarker of Enterocyte Functional Mass and Dietary Supplement. Metabolism, Transport, and Current Evidence for Clinical Use. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanelle, S.T.; McLaughlin, K.L.; Crouse, S.F. One Week of L-Citrulline Supplementation Improves Performance in Trained Cyclists. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossenaar, E.R.; van Venrooij, W.J. Citrullinated proteins: Sparks that may ignite the fire in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielski, O.; Biesiekierska, M.; Panthu, B.; Soszyński, M.; Pirola, L.; Balcerczyk, A. Citrullination in the pathology of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders: Recent advances and future perspectives. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T. Toll-like receptors: Critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deslauriers, J.; van Wijngaarde, M.; Geyer, M.A.; Powell, S.; Risbrough, V.B. Effects of LPS-induced immune activation prior to trauma exposure on PTSD-like symptoms in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 323, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, C.; Wolfensberger, C. Interferon in human serum after injection of endotoxin. Lancet 1980, 316, 852–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gola, H.; Engler, H.; Sommershof, A.; Adenauer, H.; Kolassa, S.; Schedlowski, M.; Groettrup, M.; Elbert, T.; Kolassa, I.T. Posttraumatic stress disorder is associated with an enhanced spontaneous production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. BMC Psychiatry 2013, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Susaki, E.A.; Nagaoka, I. Lipopolysaccharides and Cellular Senescence: Involvement in Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quave, C.B.; Nieto, S.J.; Haile, C.N.; Kosten, T.A. Immune receptor toll-like receptor 4 contributes to stress-induced affective responses in a sex-specific manner. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 14, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lin, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, M. Effect of Toll-like receptor 4 on depressive-like behaviors induced by chronic social defeat stress. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, T. Psychogenic fever: How psychological stress affects body temperature in the clinical population. Temperature 2015, 2, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Lin, C.; Marinova, M.; Brugnolo, L.; Rubino, G.; Plebani, M.; Iliceto, S.; Tona, F. Rapid changes of miRNAs-20, -30, -410, -515, -134, and -183 and telomerase with psychological activity: A one year study on the relaxation response and epistemological considerations. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2021, 11, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.Y.; Huang, K.W.; Kang, H.Y.; Huang, G.Y.; Huang, T.L. Antidepressants normalize elevated Toll-like receptor profile in major depressive disorder. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, L.; Wei, Y.; Fang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhou, F.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G.; Guo, Z.; Luo, Y.; et al. Exercise suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mice with diet-induced NASH: A plausible role of adropin. Lab. Investig. 2021, 101, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Jiang, S.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, J.; Pan, K.; Zhou, J.; Xie, Y.; Kan, H.; Song, W.; Sun, Q.; et al. Air pollution is associated with the development of atherosclerosis via the cooperation of CD36 and NLRP3 inflammasome in ApoE−/− mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 290, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Tang, Y.; Xing, M.; Yao, P. Chronic high-fat diet induces galectin-3 and TLR4 to activate NLRP3 inflammasome in NASH. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 112, 109217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassel, S.L.; Joly, S.; Sutterwala, F.S. The NLRP3 inflammasome: A sensor of immune danger signals. Semin Immunol. 2009, 21, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngui, I.Q.H.; Perera, A.P.; Eri, R. Does NLRP3 Inflammasome and Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Play an Interlinked Role in Bowel Inflammation and Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer? Molecules 2020, 25, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanashi, T.; Iwata, M.; Shibushita, M.; Tsunetomi, K.; Nagata, M.; Kajitani, N.; Miura, A.; Matsuo, R.; Nishiguchi, T.; Kato, T.A.; et al. Beta-hydroxybutyrate, an endogenous NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor, attenuates anxiety-related behavior in a rodent post-traumatic stress disorder model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, W.; Zhao, R.; Song, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, C.; Han, L.; Zhao, W. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor negatively regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity by inhibiting NLRP3 transcription. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.O.; Huh, A.J.; Han, S.H.; Kim, J.M. Analysis of cellular senescence induced by lipopolysaccharide in pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 54, e35–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanuck, S.F. Microglial Phagocytosis of Neurons: Diminishing Neuronal Loss in Traumatic, Infectious, Inflammatory, and Autoimmune CNS Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanishi, K.; Sato, A.; Kihara, N.; Utsunomiya, R.; Tanaka, J. Synaptic elimination by microglia and disturbed higher brain functions. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 142, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, K.; Yamasue, H.; Gilbertson, M.W.; Shenton, M.E.; Rauch, S.L.; Pitman, R.K. Evidence for acquired pregenual anterior cingulate gray matter loss from a twin study of combat-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Jiang, J.; Jin, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, K.; Gong, Q. Trauma-specific Grey Matter Alterations in PTSD. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, K.; Feng, C.; Tang, L.; Zhang, J.; Huan, Y.; Cui, J.; Mu, Y.; Qi, S.; Xiong, L.; et al. Different regional gray matter loss in recent onset PTSD and non PTSD after a single prolonged trauma exposure. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, S.; Gallinat, J. Gray matter correlates of posttraumatic stress disorder: A quantitative meta-analysis. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.K.; Kim, S.J.; Rah, S.H.; Kang, J.I.; Jung, H.E.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, J.O.; Park, B.S.; Yoon, T.Y.; et al. Reconstruction of LPS Transfer Cascade Reveals Structural Determinants within LBP, CD14, and TLR4-MD2 for Efficient LPS Recognition and Transfer. Immunity 2017, 46, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roy, D.; Di Padova, F.; Adachi, Y.; Glauser, M.P.; Calandra, T.; Heumann, D. Critical role of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and CD14 in immune responses against gram-negative bacteria. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 2759–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweigner, J.; Gramm, H.J.; Singer, O.C.; Wegscheider, K.; Schumann, R.R. High concentrations of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in serum of patients with severe sepsis or septic shock inhibit the lipopolysaccharide response in human monocytes. Blood 2001, 98, 3800–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Li, Y.; Liao, Z.; Wang, G.; Cao, Q.; Li, Y.; Duan, Y.; Han, Y.; Deng, X.; Wu, F.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein expression is increased by stress and inhibits monoamine synthesis to promote depressive symptoms. Immunity 2023, 56, 620–634.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Tong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Luo, G.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J. Serum soluble CD14 is a potential prognostic indicator of recurrence of human breast invasive ductal carcinoma with Her2-enriched subtype. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgmann, H.; Winkler, S.; Locker, G.J.; Presterl, E.; Laczika, K.; Staudinger, T.; Knapp, S.; Thalhammer, F.; Wenisch, C.; Zedwitz-Liebenstein, K.; et al. Increased serum concentration of soluble CD14 is a prognostic marker in gram-positive sepsis. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 80 Pt 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauwkamp, T.A.; Thair, S.; Rosen, M.J.; Blair, L.; Lindner, M.S.; Vilfan, I.D.; Kawli, T.; Christians, F.C.; Venkatasubrahmanyam, S.; Wall, G.D.; et al. Analytical and clinical validation of a microbial cell-free DNA sequencing test for infectious disease. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Li, R.; Shi, J.; Tan, P.; Zhang, R.; Li, J. Liquid biopsy for infectious diseases: A focus on microbial cell-free DNA sequencing. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5501–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulthard, M.G.; Swindle, J.; Munford, R.S.; Gerard, R.D.; Meidell, R.S. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of a gene encoding acyloxyacyl hydrolase (AOAH) into mice increases tissue and plasma AOAH activity. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudakov, J.A.; Hanash, A.M.; Jenq, R.R.; Young, L.F.; Ghosh, A.; Singer, N.V.; West, M.L.; Smith, O.M.; Holland, A.M.; Tsai, J.J.; et al. Interleukin-22 drives endogenous thymic regeneration in mice. Science 2012, 336, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keir, M.; Yi, Y.; Lu, T.; Ghilardi, N. The role of IL-22 in intestinal health and disease. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20192195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilanges, A.; Xia, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, L.; Shiao, R.; Wang, C.; Jin, Z.; Feng, R.; Qi, Q.; Yi, H.; et al. Microbiota-stimulated Interleukin-22 regulates brain neurons and protects against stress-induced anxiety. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattapallil, M.J.; Kielczewski, J.L.; Zárate-Bladés, C.R.; St Leger, A.J.; Raychaudhuri, K.; Silver, P.B.; Jittayasothorn, Y.; Chan, C.C.; Caspi, R.R. Interleukin 22 ameliorates neuropathology and protects from central nervous system autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 102, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Santoro, J.; Bender, F.C.; Laterza, O.F. Quantitative determination of human interleukin 22 (IL-22) in serum using Singulex-Erenna® technology. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 390, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sfera, A.; Anton, J.J.; Imran, H.; Kozlakidis, Z.; Klein, C.; Osorio, C. Of Soldiers and Their Ghosts: Are We Ready for a Review of PTSD Evidence? BioMed 2023, 3, 484-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed3040039
Sfera A, Anton JJ, Imran H, Kozlakidis Z, Klein C, Osorio C. Of Soldiers and Their Ghosts: Are We Ready for a Review of PTSD Evidence? BioMed. 2023; 3(4):484-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed3040039
Chicago/Turabian StyleSfera, Adonis, Jonathan J. Anton, Hassan Imran, Zisis Kozlakidis, Carolina Klein, and Carolina Osorio. 2023. "Of Soldiers and Their Ghosts: Are We Ready for a Review of PTSD Evidence?" BioMed 3, no. 4: 484-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed3040039
APA StyleSfera, A., Anton, J. J., Imran, H., Kozlakidis, Z., Klein, C., & Osorio, C. (2023). Of Soldiers and Their Ghosts: Are We Ready for a Review of PTSD Evidence? BioMed, 3(4), 484-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed3040039






