Regular Intermittent Aerobic Exercise Reduces Arterial Stiffness Associated with Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Middle-Aged and Older Individuals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Physical Characteristics
2.4. Arterial Stiffness
2.5. Upper Arm and Ankle Blood Pressure
2.6. Heart Rate
2.7. Blood Glucose
2.8. The 75 g OGTT
2.9. VO2max
2.10. Intermittent Aerobic Training
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Characteristics
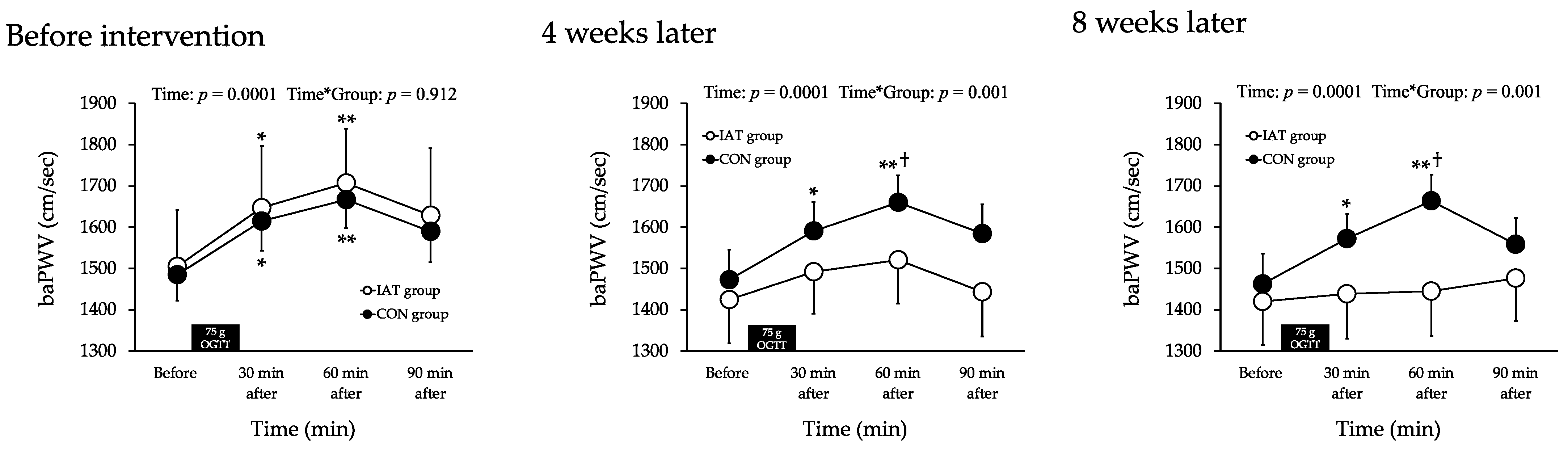
3.2. Arterial Stiffness
3.3. Brachial Blood Pressure
3.4. Ankle Blood Pressure
3.5. Heart Rate
3.6. Blood Glucose
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DECODE Study Group; the European Diabetes Epidemiology Group. Glucose Tolerance and Cardiovascular Mortality: Comparison of Fasting and 2-Hour Diagnostic Criteria. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacome-Sosa, M.; Parks, E.J.; Bruno, R.S.; Tasali, E.; Lewis, G.F.; Schneeman, B.O.; Rains, T.M. Postprandial Metabolism of Macronutrients and Cardiometabolic Risk: Recent Developments, Emerging Concepts, and Future Directions. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, R.; Sato, K.; Takahashi, T.; Asaki, K.; Iwanuma, S.; Ohashi, N.; Hashiguchi, T. Arterial Stiffness During Hyperglycemia in Older Adults with High Physical Activity vs Low Physical Activity. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2019, 65, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.W. The Association of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Acute Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Korean Prediabetic and Diabetic Subjects. Korean Diabetes J. 2010, 34, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, R.; Sato, K.; Takahashi, T.; Asaki, K.; Iwanuma, S.; Ohashi, N.; Hashiguchi, T. Effects of a Short-Term Increase in Physical Activity on Arterial Stiffness during Hyperglycemia. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2020, 66, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikael, L.D.R.; De Paiva, A.M.G.; Gomes, M.M.; Sousa, A.L.L.; Jardim, P.C.B.V.; Vitorino, P.V.D.O.; Euzébio, M.B.; Sousa, W.D.M.; Barroso, W.K.S. Vascular Aging and Arterial Stiffness. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2017, 109, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, C.W.; Egan, J.M.; Ferrucci, L. Age-Related Changes in Glucose Metabolism, Hyperglycemia, and Cardiovascular Risk. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 886–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, R.; Asaki, K.; Hashiguchi, T.; Negoro, H. The Effect of Aerobic Exercise Training Frequency on Arterial Stiffness in a Hyperglycemic State in Middle-Aged and Elderly Females. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manley, A.F. Physical Activity and Health: A Report of the Surgeon General; Public Health Service; Office of the Surgeon General, Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Xiao, H.; Wang, P. Acute Effects of the Interval and Duration of Intermittent Exercise on Arterial Stiffness in Young Men. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Yan, S. Acute Effects of Moderate-Intensity Continuous and Accumulated Exercise on Arterial Stiffness in Healthy Young Men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 115, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; He, Z.; Yuan, M.; Yin, Z.; Dang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, W. Longer Rest Intervals Do Not Attenuate the Superior Effects of Accumulated Exercise on Arterial Stiffness. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 115, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, R.; Hatakeyama, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Okamoto, T. Acute Effects of Accumulated Aerobic Exercise on Aortic and Peripheral Pulse Wave Velocity in Young Males. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, R.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Okamoto, T. Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise Intensity on Arterial Stiffness after Glucose Ingestion in Young Men. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2018, 38, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kario, K. Key Points of the 2019 Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension. Korean Circ. J. 2019, 49, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H. Sample Size Determination and Power Analysis Using the G*Power Software. J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 2021, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, J.; Hayashi, K.; Yokoi, T.; Cortez-Cooper, M.Y.; DeVan, A.E.; Anton, M.A.; Tanaka, H. Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity: An Index of Central Arterial Stiffness? J. Hum. Hypertens. 2005, 19, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, S.; Stone, K.; Paterson, C.; Brown, M.; Faulkner, J.; Lambrick, D.; Credeur, D.; Zieff, G.; Martínez Aguirre-Betolaza, A.; Stoner, L. Central and Peripheral Arterial Stiffness Responses to Uninterrupted Prolonged Sitting Combined with a High-Fat Meal: A Randomized Controlled Crossover Trial. Hypertens. Res. 2021, 44, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, R.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Okamoto, T. Acute Effects of Repeated Bouts of Aerobic Exercise on Arterial Stiffness after Glucose Ingestion. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2019, 41, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordin, D.; Saraheimo, M.; Tuomikangas, J.; Soro-Paavonen, A.; Forsblom, C.; Paavonen, K.; Steckel-Hamann, B.; Vandenhende, F.; Nicolaou, L.; Pavo, I.; et al. Influence of Postprandial Hyperglycemic Conditions on Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murai, N.; Saito, N.; Nii, S.; Nishikawa, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Kodama, E.; Iida, T.; Mikura, K.; Imai, H.; Hashizume, M.; et al. Postloading Insulinemia Is Independently Associated with Arterial Stiffness in Young Japanese Persons. Hypertens. Res. 2021, 44, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, R.; Sakazaki, M.; Nagai, Y.; Asaki, K.; Hashiguchi, T.; Negoro, H. Effects of Different Types of Carbohydrates on Arterial Stiffness: A Comparison of Isomaltulose and Sucrose. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, R.; Sato, K.; Sakazaki, M.; Nagai, Y.; Iwanuma, S.; Ohashi, N.; Hashiguchi, T. Acute Effects of Difference in Glucose Intake on Arterial Stiffness in Healthy Subjects. Cardiol. J. 2021, 28, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baynard, T.; Carhart, R.L.; Weinstock, R.S.; Ploutz-Snyder, L.L.; Kanaley, J.A. Short-Term Exercise Training Improves Aerobic Capacity with No Change in Arterial Function in Obesity. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, R.; Yoshida, S.; Okamoto, T. Arterial Stiffness After Glucose Ingestion in Exercise-Trained versus Untrained Men. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 40, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashina, A.; Tomiyama, H.; Arai, T.; Koji, Y.; Yambe, M.; Motobe, H.; Glunizia, Z.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hori, S. Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure. Hypertens. Res. 2003, 26, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, R.; Yoshida, S.; Okamoto, T. Effects of Acute Aerobic Exercise on Arterial Stiffness before and after Glucose Ingestion. Int. J. Sport. Med. 2017, 38, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciolac, E.G.; Guimarães, G.V.; D Avila, V.M.; Bortolotto, L.A.; Doria, E.L.; Bocchi, E.A. Acute Effects of Continuous and Interval Aerobic Exercise on 24-h Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Long-Term Treated Hypertensive Patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009, 133, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Rink, L.D.; Wallace, J.P. Accumulation of Physical Activity Leads to a Greater Blood Pressure Reduction than a Single Continuous Session, in Prehypertension. J. Hypertens. 2006, 24, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, R.; Sakazaki, M.; Nagai, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Sato, K.; Seki, S.; Hata, U.; Esaki, K.; Tanigawa, R.; et al. Habitual isomaltulose intake reduces arterial stiffness associated with postprandial hyperglycemia in middle-aged and elderly people: A randomized controlled trial. Heart Vessels 2024, 39, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmstrup, M.; Fairchild, T.; Keslacy, S.; Weinstock, R.; Kanaley, J. Multiple Short Bouts of Exercise over 12-h Period Reduce Glucose Excursions More than an Energy-Matched Single Bout of Exercise. Metabolism 2014, 63, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Measurement Item | IAT (n = 15) | CON (n = 15) | p-Value (Group) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Intervention | 4 Weeks Later | 8 Weeks Later | before Intervention | 4 Weeks Later | 8 Weeks Later | ||
| Age, years | 63.6 ± 1.2 | NA | NA | 63.2 ± 1.1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Height, cm | 152.2 ± 2.2 | NA | NA | 152.5 ± 3.4 | NA | NA | NA |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.4 ± 0.4 | 22.7 ± 0.5 | 22.7 ± 0.5 | 22.4 ± 0.5 | 22.2 ± 0.5 | 22.3 ± 0.5 | p > 0.05 |
| VO2max, ml/kg/min | 22.2 ± 2.0 | 26.8 ± 1.8 * | 29.9 ± 1.0 *† | 21.8 ± 1.1 | 22.7 ± 1.1 | 22.4 ± 1.2 | p > 0.05 |
| Measurement Item | Intervention | Group | before | 30 min after | 60 min after | 90 min after | p-Value (Group) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brachial SBP, mmHg | Pre | IAT | 121.9 ± 5.0 | 122.8 ± 4.6 | 125.9 ± 4.4 | 129.8 ± 4.8 | p > 0.05 |
| CON | 120.7 ± 5.3 | 123.4 ± 6.3 | 126.3 ± 7.1 | 126.6 ± 6.7 | |||
| 4 weeks later | IAT | 120.2 ± 5.4 | 120.9 ± 4.5 | 122.4 ± 4.7 | 125.3 ± 3.5 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 118.9 ± 5.9 | 119.9 ± 6.6 | 123.2 ± 7.2 | 122.3 ± 7.2 | |||
| 8 weeks later | IAT | 120.8 ± 4.8 | 121.4 ± 3.5 | 120.9 ± 4.3 | 124.2 ± 4.7 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 118.3 ± 4.8 | 120.2 ± 5.2 | 122.4 ± 6.4 | 121.0 ± 6.4 | |||
| Brachial MBP, mmHg | Pre | IAT | 88.7 ± 1.9 | 89.4 ± 1.9 | 90.0 ± 2.3 | 91.7 ± 1.9 | p > 0.05 |
| CON | 87.6 ± 3.7 | 88.6 ± 3.8 | 89.8 ± 4.3 | 89.2 ± 4.4 | |||
| 4 weeks later | IAT | 86.9 ± 2.4 | 87.2 ± 2.6 | 87.4 ± 2.7 | 90.0 ± 2.0 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 86.2 ± 4.1 | 86.4 ± 4.3 | 87.6 ± 4.2 | 87.1 ± 4.7 | |||
| 8 weeks later | IAT | 87.4 ± 1.5 | 87.9 ± 1.4 | 87.8 ± 2.4 | 89.8 ± 2.0 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 85.2 ± 3.5 | 85.7 ± 3.3 | 86.9 ± 3.7 | 88.0 ± 3.9 | |||
| Brachial DBP, mmHg | Pre | IAT | 72.2 ± 1.8 | 72.7 ± 1.5 | 72.0 ± 2.1 | 72.7 ± 1.9 | p > 0.05 |
| CON | 71.1 ± 3.0 | 71.2 ± 2.6 | 71.5 ± 3.1 | 70.5 ± 3.5 | |||
| 4 weeks later | IAT | 70.3 ± 1.9 | 70.4 ± 2.2 | 69.9 ± 2.8 | 72.3 ± 2.1 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 69.9 ± 3.3 | 69.6 ± 3.4 | 69.8 ± 2.8 | 69.5 ± 3.6 | |||
| 8 weeks later | IAT | 70.7 ± 1.7 | 71.2 ± 1.6 | 71.3 ± 2.3 | 72.7 ± 1.8 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 68.7 ± 3.0 | 68.5 ± 2.5 | 69.2 ± 2.5 | 71.5 ± 2.8 |
| Measurement Item | Intervention | Group | before | 30 min after | 60 min after | 90 min after | p-Value (Group) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankle SBP, mmHg | Pre | IAT | 143.0 ± 9.2 | 156.1 ± 7.7 * | 163.1 ± 9.1 * | 160.4 ± 8.4 | p > 0.05 |
| CON | 146.3 ± 6.3 | 157.5 ± 6.1 * | 162.9 ± 6.6 * | 156.9 ± 7.6 | |||
| 4 weeks later | IAT | 141.7 ± 9.8 | 144.1 ± 8.1 | 146.6 ± 8.3 | 144.8 ± 7.5 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 145.3 ± 6.7 | 156.5 ± 5.4 * | 163.1 ± 4.9 *† | 153.5 ± 3.7 | |||
| 8 weeks later | IAT | 142.6 ± 6.7 | 145.4 ± 7.1 | 148.2 ± 7.6 | 145.9 ± 7.8 | p < 0.05 | |
| CON | 144.2 ± 6.3 | 154.2 ± 5.5 * | 163.2 ± 5.0 *† | 157.2 ± 4.7 | |||
| Ankle MBP, mmHg | Pre | IAT | 96.5 ± 3.2 | 101.0 ± 2.7 | 103.3 ± 2.8 | 105.2 ± 2.4 | p > 0.05 |
| CON | 96.8 ± 3.7 | 100.4 ± 3.5 | 102.0 ± 4.1 | 100.4 ± 4.8 | |||
| 4 weeks later | IAT | 94.4 ± 3.8 | 95.4 ± 2.9 | 96.4 ± 2.9 | 96.9 ± 2.6 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 93.9 ± 3.5 | 97.9 ± 3.0 | 99.9 ± 3.3 | 96.6 ± 3.2 | |||
| 8 weeks later | IAT | 94.5 ± 2.1 | 95.0 ± 2.1 | 96.5 ± 2.4 | 98.0 ± 2.6 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 94.2 ± 4.3 | 97.2 ± 3.4 | 101.0 ± 3.5 | 99.4 ± 3.7 | |||
| Ankle DBP, mmHg | Pre | IAT | 73.2 ± 1.5 | 73.5 ± 0.9 | 73.4 ± 1.4 | 77.6 ± 2.0 | p > 0.05 |
| CON | 72.0 ± 2.6 | 71.8 ± 2.5 | 71.6 ± 3.0 | 72.1 ± 3.6 | |||
| 4 weeks later | IAT | 70.8 ± 1.7 | 71.0 ± 1.6 | 71.4 ± 1.7 | 72.9 ± 1.5 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 68.2 ± 2.1 | 68.7 ± 2.0 | 68.3 ± 2.7 | 68.1 ± 3.2 | |||
| 8 weeks later | IAT | 70.5 ± 1.4 | 69.8 ± 1.3 | 70.7 ± 1.6 | 74.1 ± 1.3 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 69.2 ± 3.4 | 68.7 ± 2.8 | 69.9 ± 2.9 | 70.6 ± 3.6 |
| Measurement Item | Intervention | Group | before | 30 min after | 60 min after | 90 min after | p-Value (Group) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR, beats/min | Pre | IAT | 62.6 ± 2.5 | 62.8 ± 2.0 | 59.2 ± 1.8 | 58.9 ± 2.0 | p > 0.05 |
| CON | 63.0 ± 2.9 | 63.0 ± 1.8 | 61.4 ± 2.5 | 61.2 ± 1.8 | |||
| 4 weeks later | IAT | 59.1 ± 2.3 | 59.2 ± 2.2 | 58.7 ± 2.2 | 58.8 ± 2.0 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 62.8 ± 2.8 | 63.6 ± 2.2 | 62.6 ± 1.5 | 59.4 ± 2.3 | |||
| 8 weeks later | IAT | 58.3 ± 2.1 | 60.5 ± 1.6 | 57.4 ± 1.3 | 57.9 ± 1.2 | p > 0.05 | |
| CON | 59.4 ± 2.9 | 60.2 ± 2.7 | 61.9 ± 1.8 | 59.8 ± 2.4 |
| Measurement Item | Intervention | Group | Before | 30 min after | 60 min after | 90 min after | p-Value (Group) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BG, mg/dl | Pre | IAT | 98.1 ± 5.4 | 160.6 ± 8.4 * | 135.7 ± 8.1 * | 113.8 ± 4.4 | p > 0.05 |
| CON | 96.5 ± 5.0 | 148.0 ± 9.5 * | 131.2 ± 11.7 * | 95.8 ± 6.8 | |||
| 4 weeks later | IAT | 95.7 ± 5.3 | 112.0 ± 5.9 *† | 108.3 ± 4.8 | 104.6 ± 4.6 | p < 0.05 | |
| CON | 94.7 ± 7.2 | 139.6 ± 9.7 * | 128.2 ± 6.6 * | 108.9 ± 5.8 | |||
| 8 weeks later | IAT | 93.9 ± 4.3 | 114.2 ± 4.4 *† | 107.9 ± 4.1 | 101.6 ± 4.5 | p < 0.05 | |
| CON | 98.0 ± 5.3 | 145.9 ± 7.9 * | 128.3 ± 6.9 * | 106.6 ± 6.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, R.; Negoro, H. Regular Intermittent Aerobic Exercise Reduces Arterial Stiffness Associated with Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Middle-Aged and Older Individuals. BioMed 2024, 4, 39-49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4010003
Kobayashi R, Negoro H. Regular Intermittent Aerobic Exercise Reduces Arterial Stiffness Associated with Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Middle-Aged and Older Individuals. BioMed. 2024; 4(1):39-49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Ryota, and Hideyuki Negoro. 2024. "Regular Intermittent Aerobic Exercise Reduces Arterial Stiffness Associated with Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Middle-Aged and Older Individuals" BioMed 4, no. 1: 39-49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4010003
APA StyleKobayashi, R., & Negoro, H. (2024). Regular Intermittent Aerobic Exercise Reduces Arterial Stiffness Associated with Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Middle-Aged and Older Individuals. BioMed, 4(1), 39-49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4010003






