High Glucose Concentration on the Metabolic Activity of C6 Glia Cells: Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. C6 Cell Culture
2.2. Culture of C6 Cells Under High Glucose Conditions
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Indirect Evaluation of Cellular Glucose Uptake
2.5. Evaluation of Mitochondrial Activity
2.6. Analysis of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm)
2.7. Determination of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
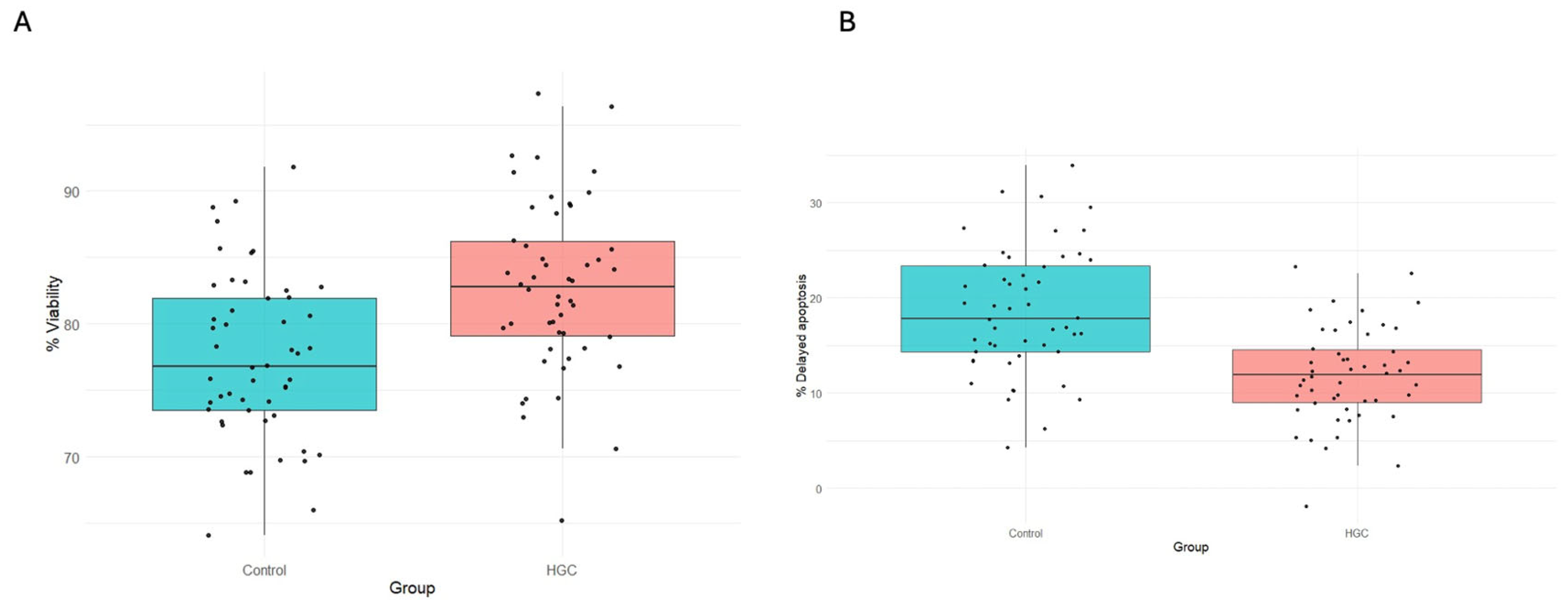
3.1. Cell Viability and Proliferation
3.2. Measurement of Residual Glucose in the Culture Medium
3.3. Assessment of Mitochondrial Activity
3.4. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm)
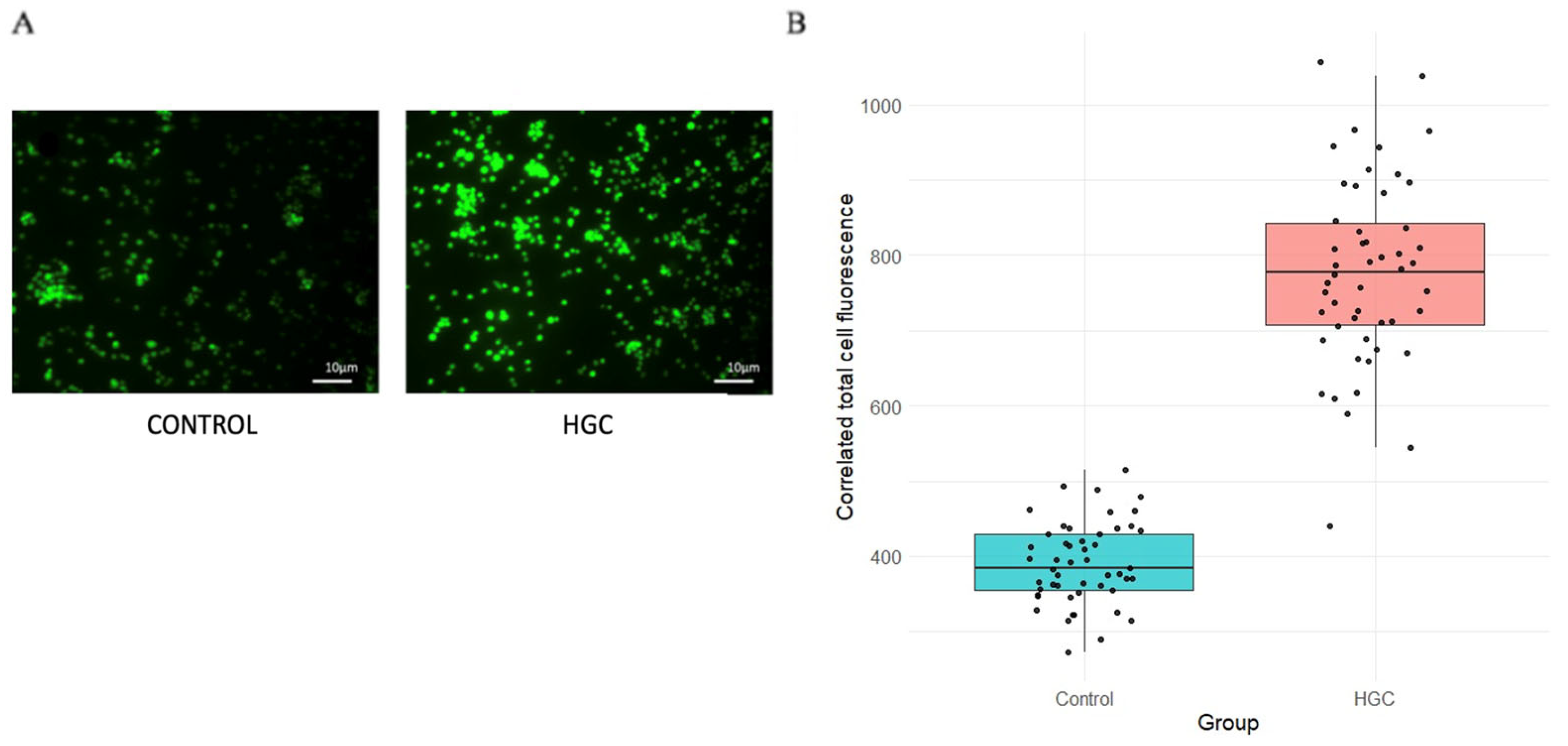
3.5. Intracellular ROS Estimation
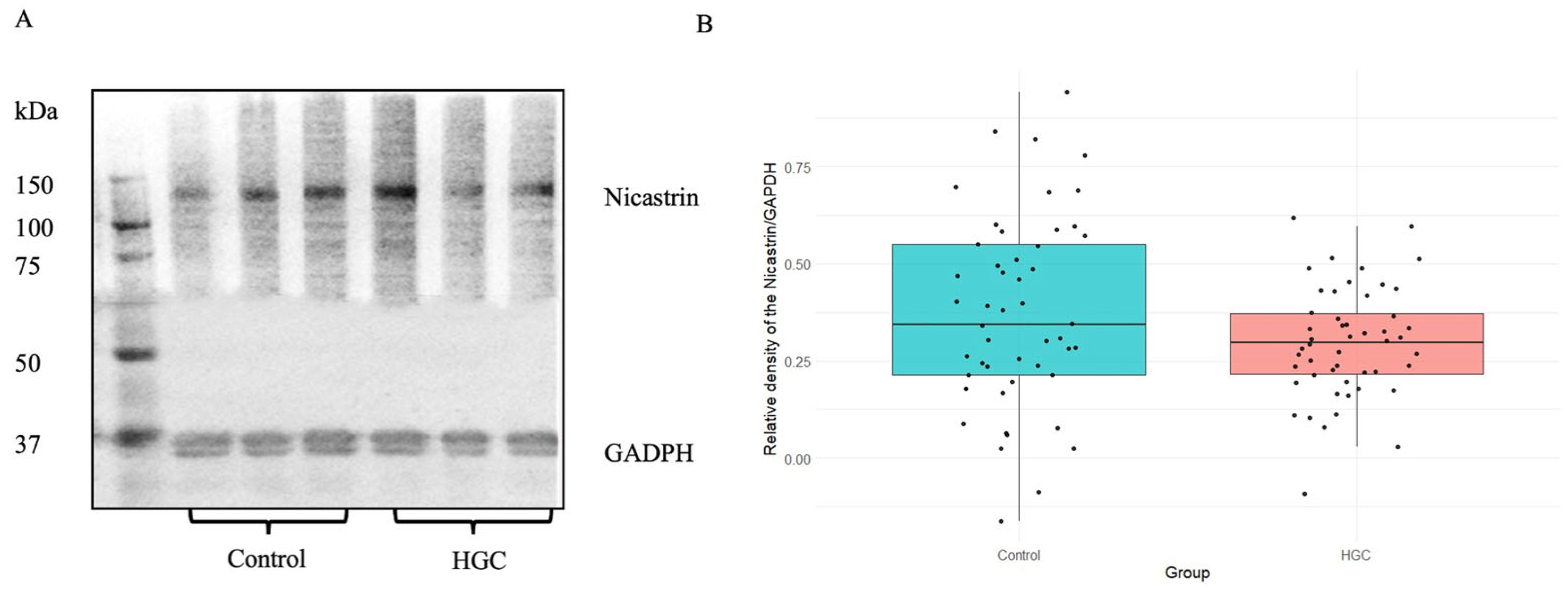
3.6. Immunodetection of GFAP and Nicastrin by Western Blot Method
3.7. Estimation of Tau and pTau by the Sandwich ELISA Method
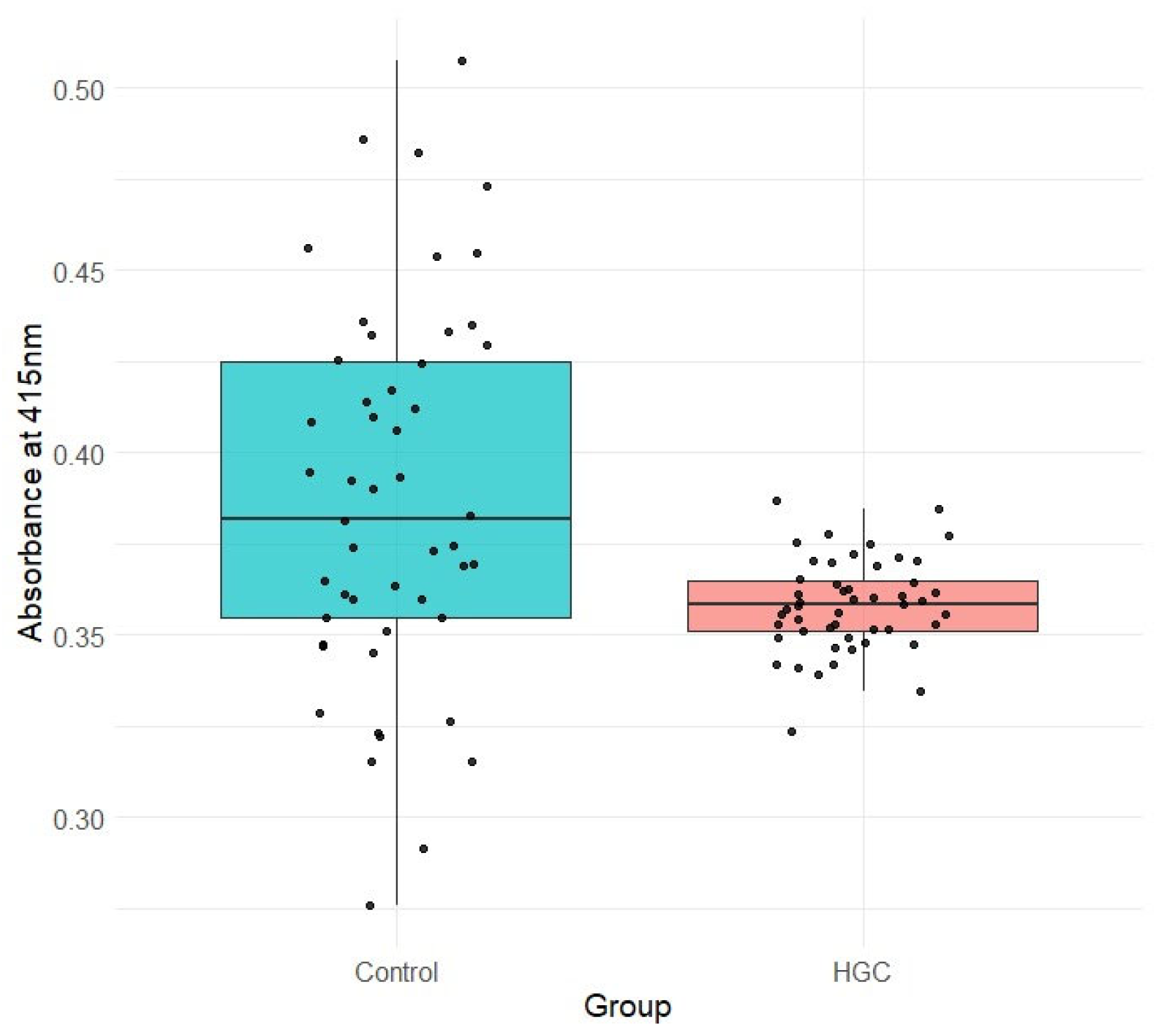
3.8. Estimation β Amyloid by Sandwich ELISA Method
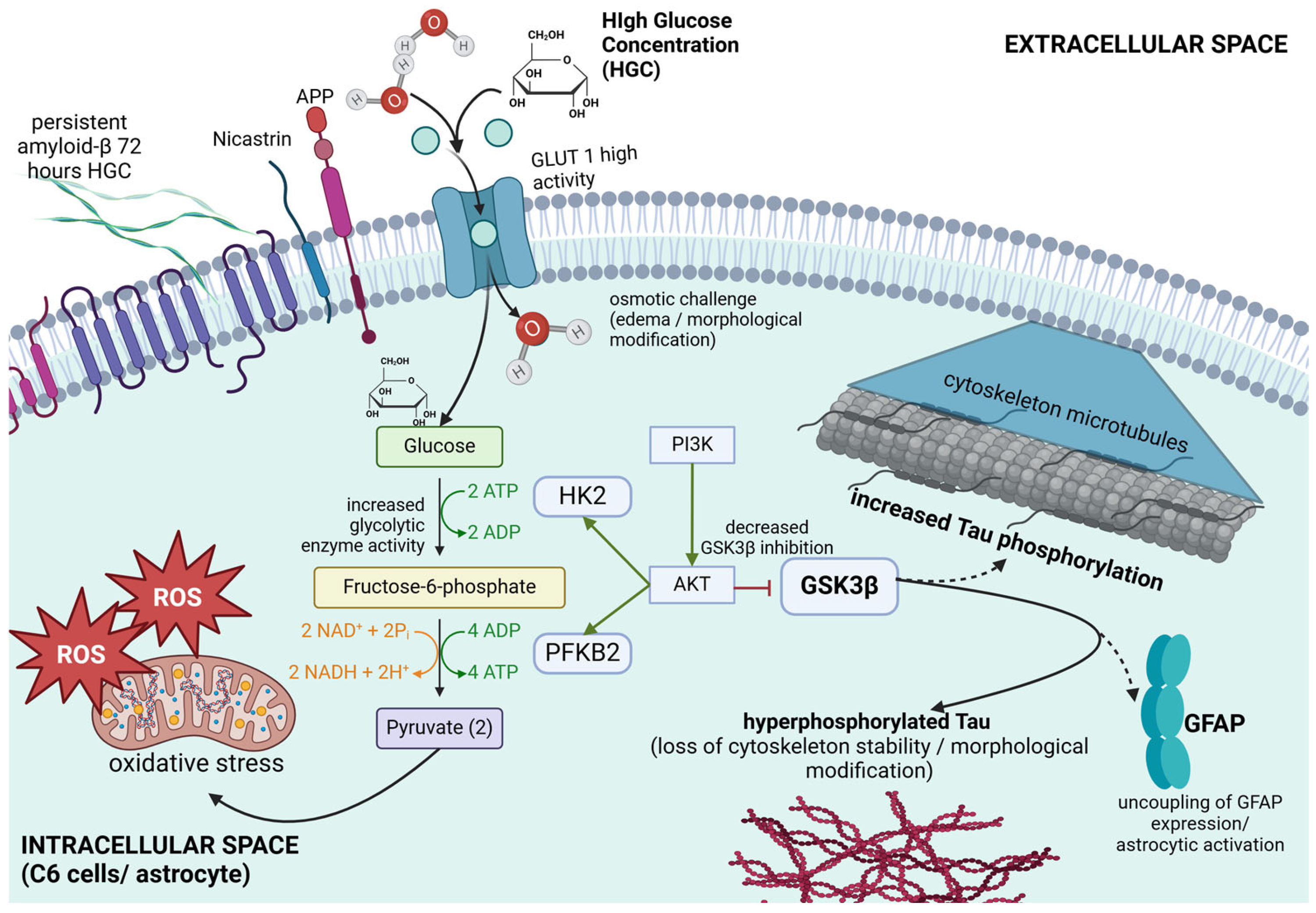
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Better, M.A. Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 1598–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolós, M.; Perea, J.R.; Avila, J. Alzheimer’s Disease as an Inflammatory Disease. Biomol. Concepts 2017, 8, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Zhang, D.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, T.Y.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Underlying the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagelatos, N.T.; Eslick, G.D. Type 2 Diabetes as a Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease: The Confounders, Interactions, and Neuropathology Associated with This Relationship. Epidemiol. Rev. 2013, 35, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, C.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Peng, W.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Pi, C.; Shi, Y.; He, X. Metabolism: A Novel Shared Link between Diabetes Mellitus and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 4981814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.M.M.; Chua, Z.J.Y.; Tan, J.C.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Zhao, Y. From Pre-Diabetes to Diabetes: Diagnosis, Treatments and Translational Research. Medicina 2019, 55, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechanick, J.I. Global Dimensions of Diabetes: Information and Synthesis. Ann. Glob. Health 2015, 81, 733–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Pan, X.; Xu, J.; Ding, Y.; Sun, X.; Song, X.; Ren, Y.; Shan, P.F. Global, Regional, and National Burden and Trend of Diabetes in 195 Countries and Territories: An Analysis from 1990 to 2025. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, E.; Terry, B.M.; Rivera, E.J.; Cannon, J.L.; Neely, T.R.; Tavares, R.; Xu, X.J.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Impaired Insulin and Insulin-like Growth Factor Expression and Signaling Mechanisms in Alzheimer’s Disease--Is This Type 3 Diabetes. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2005, 7, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, I.A.; Dwyer, D.; Malide, D.; Moley, K.H.; Travis, A.; Vannucci, S.J. The Facilitative Glucose Transporter GLUT3: 20 Years of Distinction. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E242–E253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Xue, M.; Zhang, J.; Leng, L. Brain Energy Metabolism: Astrocytes in Neurodegenerative Diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quincozes-Santos, A.; Bobermin, L.D.; de Assis, A.M.; Gonçalves, C.A.; Souza, D.O. Fluctuations in Glucose Levels Induce Glial Toxicity with Glutamatergic, Oxidative and Inflammatory Implications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staricha, K.; Meyers, N.; Garvin, J.; Liu, Q.; Rarick, K.; Harder, D.; Cohen, S. Effect of High Glucose Condition on Glucose Metabolism in Primary Astrocytes. Brain Res. 2020, 1732, 146702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, I.C.; Scarpa, M.; Malarte, M.L.; Rocha, F.M.; Ausellé-Bosch, S.; Bluma, M.; Bucci, M.; Chiotis, K.; Kumar, A.; Nordberg, A. Astrocyte Signature in Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum through a Multi-PET Tracer Imaging Perspective. Cells 2023, 12, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroja, S.R.; Gorbachev, K.; Julia, T.; Goate, A.M.; Pereira, A.C. Astrocyte-Secreted Glypican-4 Drives APOE4-Dependent Tau Hyperphosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2108870119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Gao, J.M.; Lv, C.; Lang, L.H.; Shi, J.S.; Yu, C.Y.; Gong, Q.H. Icariside II Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Amyloid Production in Rat Astrocytes by Regulating IKK/IκB/NF-ΚB/BACE1 Signaling Pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, R.H. The Mitochondrial Hypothesis: Dysfunction, Bioenergetic Defects, and the Metabolic Link to Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2020, 154, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Díaz, J.A.; Hernández-Aguilar, M.E.; Rojas-Durán, F.; Herrera-Covarrubias, D.; García-Hernández, L.I.; Mestizo-Gutiérrez, S.L.; Aranda-Abreu, G.E. Expression of Proteins Linked to Alzheimer’s Disease in C6 Rat Glioma Cells under the Action of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), Nimesulide, Resveratrol and Citalopram. Turk. J. Biochem. 2020, 45, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, R.F.; Kaur, B. Rat Brain Tumor Models in Experimental Neuro-Oncology: The C6, 9L, T9, RG2, F98, BT4C, RT-2 and CNS-1 Gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 94, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenting, K.; Verhaak, R.; Ter Laan, M.; Wesseling, P.; Leenders, W. Glioma: Experimental Models and Reality. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devan, S.; Janardhanam, V.A. Effect of Naringenin on Metabolic Markers, Lipid Profile and Expression of GFAP in C6 Glioma Cells Implanted Rat’s Brain. Ann. Neurosci. 2011, 18, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Loureiro, S.O.; Heimfarth, L.; Reis, K.; Wild, L.; Andrade, C.; Guma, F.T.; Gonçalves, C.A.; Pessoa-Pureur, R. Acute Ethanol Exposure Disrupts Actin Cytoskeleton and Generates Reactive Oxygen Species in C6 Cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2011, 25, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Atrache, Z.; Lopez, D.B.; Hingley, S.T.; Appelt, D.M. Astrocytes Infected with Chlamydia Pneumoniae Demonstrate Altered Expression and Activity of Secretases Involved in the Generation of β-Amyloid Found in Alzheimer Disease. BMC Neurosci. 2019, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.P.; Chu, J.M.; Hung, V.K.; Lee, D.K.; Cheng, C.H.; Yung, K.K.; Yue, K.K. Modulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Chaperone GRP78 by High Glucose in Hippocampus of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice and C6 Astrocytic Cells. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morato, E.; Mayor, F. Production of the Alzheimer’s Beta-Amyloid Peptide by C6 Glioma Cells. FEBS Lett. 1993, 336, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramontina, A.C.; Nardin, P.; Quincozes-Santos, A.; Tortorelli, L.; Wartchow, K.M.; Andreazza, A.C.; Braganhol, E.; de Souza, D.O.; Gonçalves, C.A. High-Glucose and S100B Stimulate Glutamate Uptake in C6 Glioma Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yao, L.; Wang, F.; Liu, S.; Yin, J.; Ling, E.A.; Wang, L.; et al. High Glucose-Induced Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines and Reactive Oxygen Species in Cultured Astrocytes. Neuroscience 2012, 202, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, A.; Stolk, R.P.; van Harskamp, F.; Pols, H.A.; Hofman, A.; Breteler, M.M. Diabetes Mellitus and the Risk of Dementia: The Rotterdam Study. Neurology 1999, 53, 1937–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Gibbons, C.H.; Giurini, J.M.; Hilliard, M.E.; et al. 12. Retinopathy, Neuropathy, and Foot Care: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S203–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Zhang, W.; Sima, A.A. Alzheimer-like Changes in Rat Models of Spontaneous Diabetes. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestizo-Gutiérrez, S.L.; Hernández-Aguilar, M.E.; Rojas-Durán, F.; Manzo-Denes, J.; Aranda-Abreu, G.E. La Enfermedad de Alzheimer y La Diabetes Mellitus. ENeurobiología 2014, 5, 070914. [Google Scholar]
- Baglietto-Vargas, D.; Shi, J.; Yaeger, D.M.; Ager, R.; LaFerla, F.M. Diabetes and Alzheimer’s Disease Crosstalk. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 64, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellerin, L.; Bouzier-Sore, A.K.; Aubert, A.; Serres, S.; Merle, M.; Costalat, R.; Magistretti, P.J. Activity-Dependent Regulation of Energy Metabolism by Astrocytes: An Update. Glia 2007, 55, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tönnies, E.; Trushina, E. Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosconi, L. Glucose Metabolism in Normal Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease: Methodological and Physiological Considerations for PET Studies. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2013, 1, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.E.; Ince, P.G.; Lace, G.; Forster, G.; Shaw, P.J.; Matthews, F.; Savva, G.; Brayne, C.; Wharton, S.B.; MRC, C.F. and A.N.S.G. Astrocyte Phenotype in Relation to Alzheimer-Type Pathology in the Ageing Brain. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Roy Choudhury, G.; Winters, A.; Prah, J.; Lin, W.; Liu, R.; Yang, S.H. Hyperglycemia Alters Astrocyte Metabolism and Inhibits Astrocyte Proliferation. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zuo, Y.X.; Jiang, R.T. Astrocyte Morphology: Diversity, Plasticity, and Role in Neurological Diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardin, P.; Tramontina, F.; Leite, M.C.; Tramontina, A.C.; Quincozes-Santos, A.; de Almeida, L.M.; Battastini, A.M.; Gottfried, C.; Gonçalves, C.A. S100B Content and Secretion Decrease in Astrocytes Cultured in High-Glucose Medium. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 50, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadó, G.; Milà-Alomà, M.; Shekari, M.; Ashton, N.J.; Operto, G.; Falcon, C.; Cacciaglia, R.; Minguillon, C.; Fauria, K.; Niñerola-Baizán, A.; et al. Reactive Astrogliosis Is Associated with Higher Cerebral Glucose Consumption in the Early Alzheimer’s Continuum. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 4567–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, S.M.; Harvey, D.; Madison, C.M.; Koeppe, R.A.; Reiman, E.M.; Foster, N.L.; Weiner, M.W.; Jagust, W.J.; Alzheimer’s, D.N.I. Associations between Cognitive, Functional, and FDG-PET Measures of Decline in AD and MCI. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, S.F.; Chiotis, K.; Nordberg, A.; Rodriguez-Vieitez, E. Longitudinal Association between Astrocyte Function and Glucose Metabolism in Autosomal Dominant Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuete, V.; Karaosmanoğlu, O.; Sivas, H. Anticancer Activities of African Medicinal Spices and Vegetables. In Medicinal Spices and Vegetables from Africa; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 271–297. [Google Scholar]
- Dienel, G.A. Brain Glucose Metabolism: Integration of Energetics with Function. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 949–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, S.; Robinson, B.H. Mitochondria, Oxygen Free Radicals, and Apoptosis. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2001, 106, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and ROS-Induced ROS Release. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 909–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, S. Respiratory Chain Complex II as General Sensor for Apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1827, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarelli, R.; Sureda, F.X.; Casabona, G.; Di Iorio, P.; Caruso, A.; Spinella, F.; Condorelli, D.F.; Nicoletti, F.; Caciagli, F. Opposite Influence of the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtypes MGlu3 and -5 on Astrocyte Proliferation in Culture. Glia 1997, 21, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenić, A.; Boltze, J.; Deten, A.; Peters, M.; Andjus, P.; Radenović, L. Astrocytic Mitochondrial Membrane Hyperpolarization Following Extended Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liang, W.; Ding, G. Sirt6 Suppresses High Glucose-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Apoptosis in Podocytes through AMPK Activation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, C.; Massicotte, G.; Milot, M.; Trudeau, F.; Gagné, J. Impaired Modulation of AMPA Receptors by Calcium-Dependent Processes in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Brain Res. 1997, 768, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delyfer, M.N.; Forster, V.; Neveux, N.; Picaud, S.; Léveillard, T.; Sahel, J.A. Evidence for Glutamate-Mediated Excitotoxic Mechanisms during Photoreceptor Degeneration in the Rd1 Mouse Retina. Mol. Vis. 2005, 11, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jayanarayanan, S.; Smijin, S.; Peeyush, K.T.; Anju, T.R.; Paulose, C.S. NMDA and AMPA Receptor Mediated Excitotoxicity in Cerebral Cortex of Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rat: Ameliorating Effects of Curcumin. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 201, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borst, P. The Malate-Aspartate Shuttle (Borst Cycle): How It Started and Developed into a Major Metabolic Pathway. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 2241–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, W.; Ijaz, B.; Shabbiri, K.; Ahmed, F.; Rehman, S. Oxidative Toxicity in Diabetes and Alzheimer’s Disease: Mechanisms behind ROS/ RNS Generation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction-Linked Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurol. Res. 2017, 39, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchez, C.; Devin, A. Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): A Complex Relationship Regulated by the CAMP/PKA Signaling Pathway. Cells 2019, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, T.; Li, P.; Wei, N.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, H.; Ji, X.; Chen, W.; Xue, M.; Wei, J. The Ambiguous Relationship of Oxidative Stress, Tau Hyperphosphorylation, and Autophagy Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 352723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnsten, A.F.T.; Datta, D.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. Hypothesis: Tau Pathology Is an Initiating Factor in Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, B.A.; Bertram, L.; Miller, B.L.; Mullin, K.; Weintraub, S.; Johnson, N.; Bigio, E.H.; Mesulam, M.; Wiedau-Pazos, M.; Jackson, G.R.; et al. Association of GSK3B with Alzheimer Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, C.; Killick, R.; Lovestone, S. The GSK3 Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2008, 104, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, R.A.; Eissa, T.F.; Abdallah, D.M.; Saad, M.A.; El-Abhar, H.S. Peganum Harmala Enhanced GLP-1 and Restored Insulin Signaling to Alleviate AlCl3-Induced Alzheimer-like Pathology Model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Q.; Chiang, C.W.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, R.; Zhang, B.; Lewis, S.J.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Framework Identifies Candidate Targets for Drug Repurposing in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paspalas, C.D.; Carlyle, B.C.; Leslie, S.; Preuss, T.M.; Crimins, J.L.; Huttner, A.J.; van Dyck, C.H.; Rosene, D.L.; Nairn, A.C.; Arnsten, A.F.T. The Aged Rhesus Macaque Manifests Braak Stage III/IV Alzheimer’s-like Pathology. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Su, L.Y.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L.X.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhou, H.; Xu, M.; Fan, Y.; et al. Activation of PPARA-Mediated Autophagy Reduces Alzheimer Disease-like Pathology and Cognitive Decline in a Murine Model. Autophagy 2020, 16, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, T.; Deshayes, N.A.C.; Borchelt, D.R.; Kamphuis, W.; Middeldorp, J.; Hol, E.M. Reactive Astrocytes as Treatment Targets in Alzheimer’s Disease-Systematic Review of Studies Using the APPswePS1dE9 Mouse Model. Glia 2021, 69, 1852–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadleir, K.R.; Kandalepas, P.C.; Buggia-Prévot, V.; Nicholson, D.A.; Thinakaran, G.; Vassar, R. Presynaptic Dystrophic Neurites Surrounding Amyloid Plaques Are Sites of Microtubule Disruption, BACE1 Elevation, and Increased Aβ Generation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Contreras, K.A.; Rojas-Durán, F.; Hernández-Aguilar, M.E.; Herrera-Covarrubias, D.; Godinez-Victoria, M.; Manzo-Denes, J.; Pérez-Estudillo, C.A.; Ramos-Morales, F.R.; Toledo-Cárdenas, R.; Aranda-Abreu, G.E. High Glucose Concentration on the Metabolic Activity of C6 Glia Cells: Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease. BioMed 2025, 5, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5010003
Hernández-Contreras KA, Rojas-Durán F, Hernández-Aguilar ME, Herrera-Covarrubias D, Godinez-Victoria M, Manzo-Denes J, Pérez-Estudillo CA, Ramos-Morales FR, Toledo-Cárdenas R, Aranda-Abreu GE. High Glucose Concentration on the Metabolic Activity of C6 Glia Cells: Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease. BioMed. 2025; 5(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Contreras, Karla Aketzalli, Fausto Rojas-Durán, María Elena Hernández-Aguilar, Deissy Herrera-Covarrubias, Marycarmen Godinez-Victoria, Jorge Manzo-Denes, César Antonio Pérez-Estudillo, Fernando Rafael Ramos-Morales, Rebeca Toledo-Cárdenas, and Gonzalo Emiliano Aranda-Abreu. 2025. "High Glucose Concentration on the Metabolic Activity of C6 Glia Cells: Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease" BioMed 5, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5010003
APA StyleHernández-Contreras, K. A., Rojas-Durán, F., Hernández-Aguilar, M. E., Herrera-Covarrubias, D., Godinez-Victoria, M., Manzo-Denes, J., Pérez-Estudillo, C. A., Ramos-Morales, F. R., Toledo-Cárdenas, R., & Aranda-Abreu, G. E. (2025). High Glucose Concentration on the Metabolic Activity of C6 Glia Cells: Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease. BioMed, 5(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5010003








