Research on Finite Permeability Semi-Analytical Harmonic Modeling Method for Maglev Planar Motors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Semi-Analytic Harmonic Modeling Method
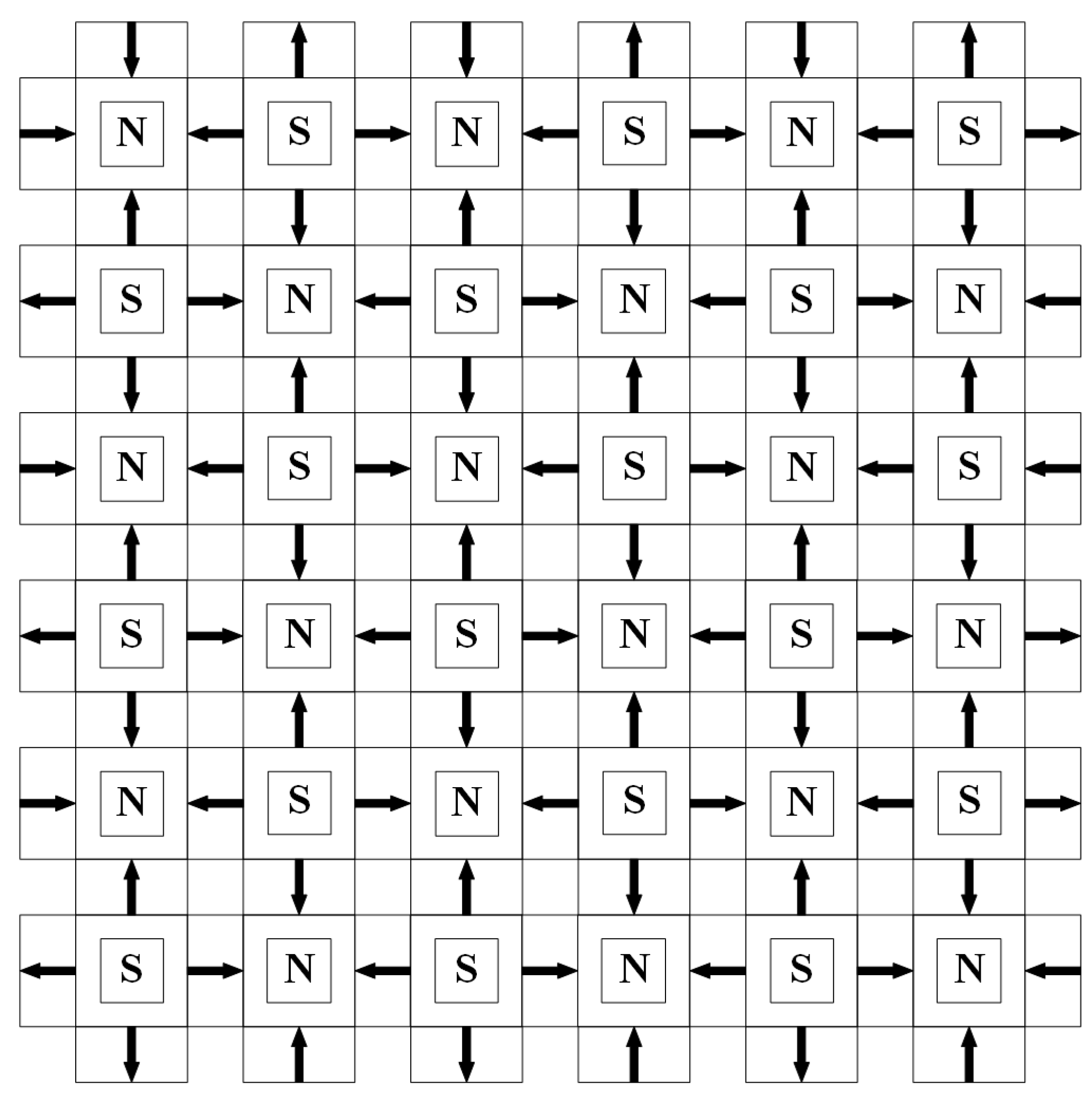
2.1. Traditional Magnet Array Model
- , , ,
- ,
- .
2.2. New Halbach Array Model
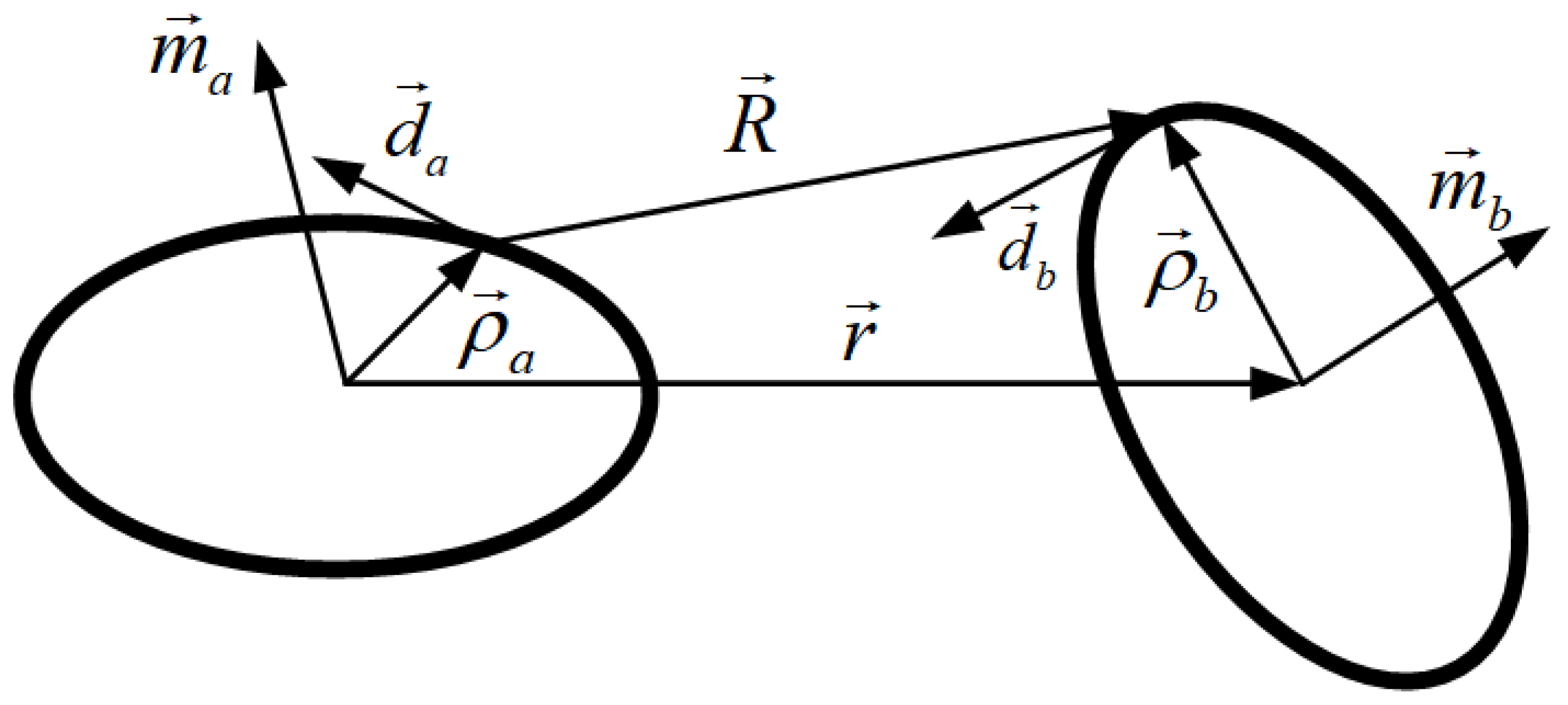
2.3. Analytical Model of Magnetic Dipole
3. Finite Permeability Model
3.1. Variable Permeability Model
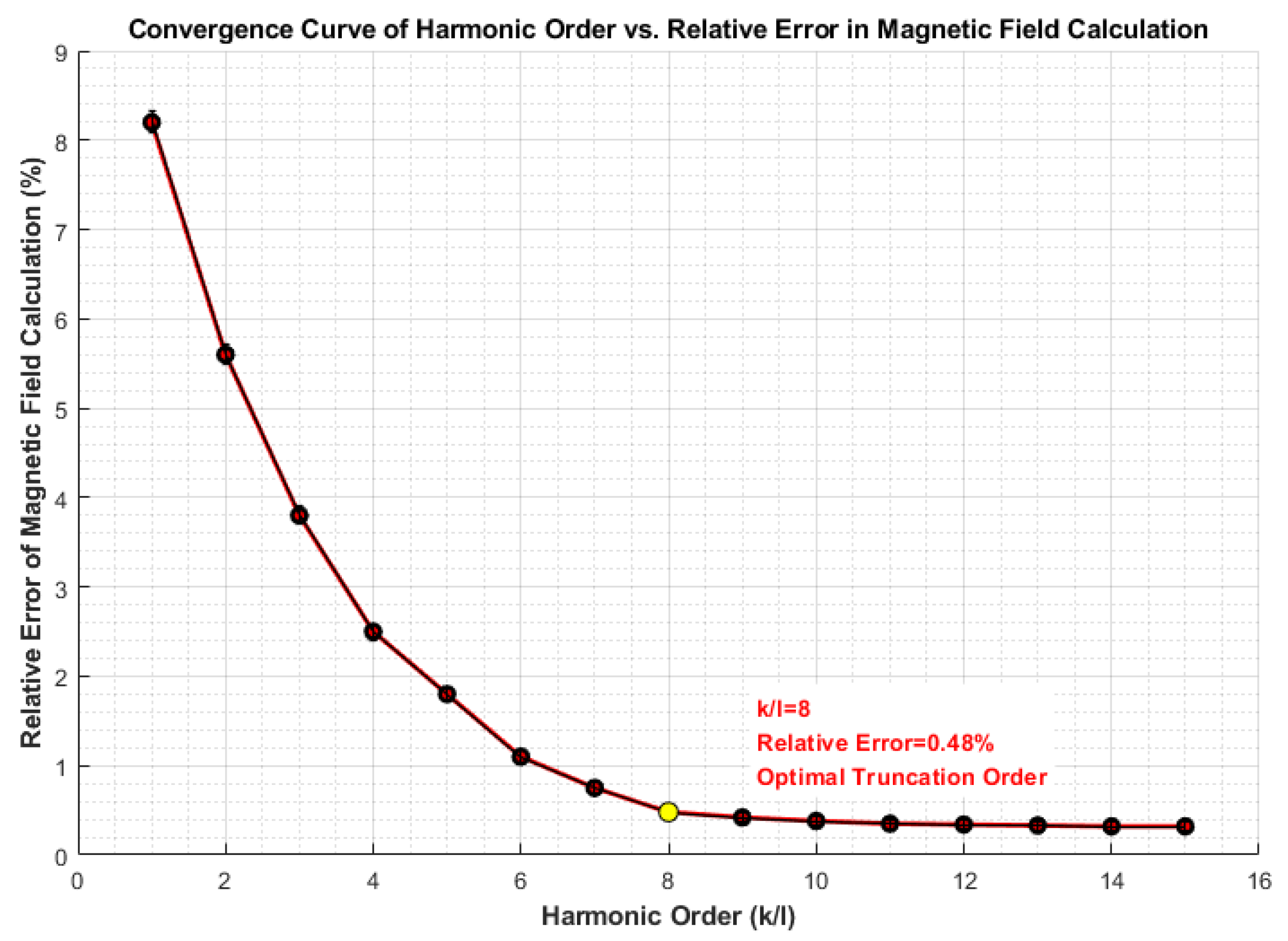
3.2. Scalar Potential Energy Solution
4. Simulation Analysis
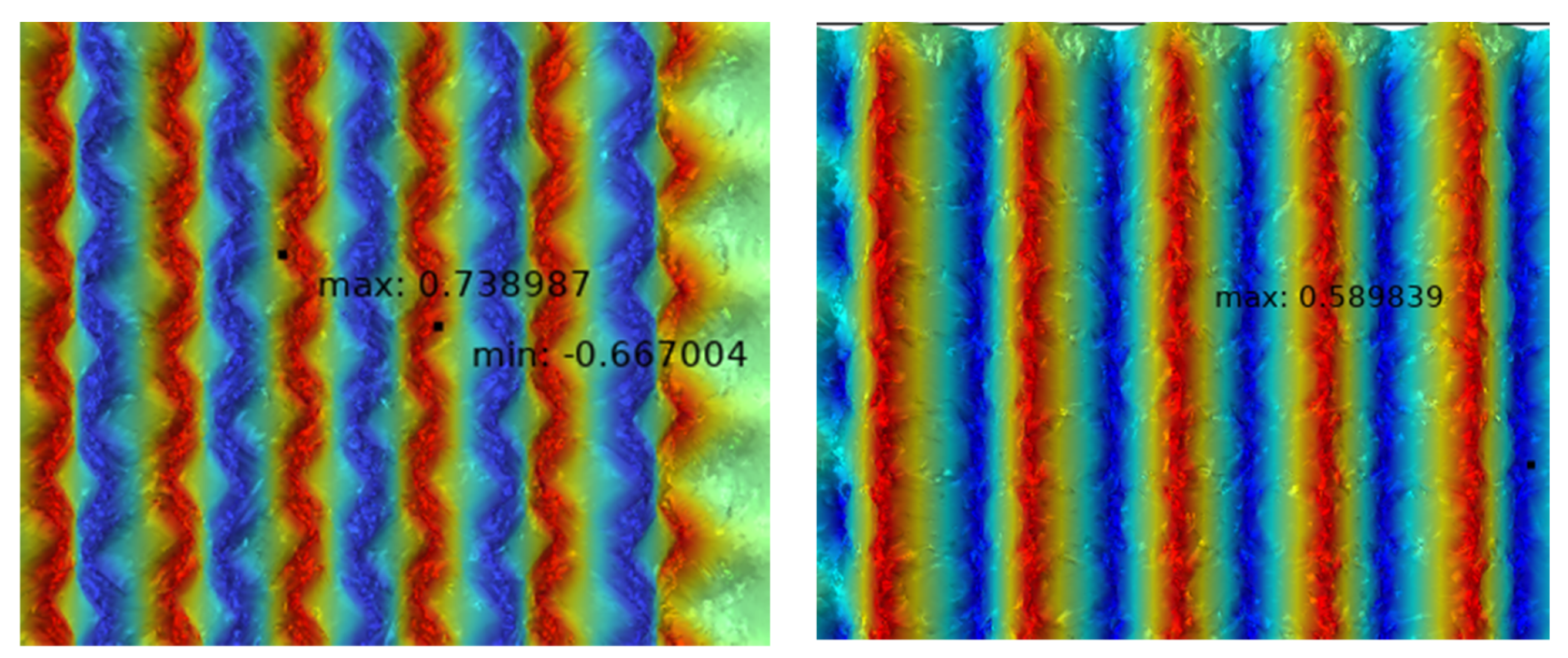
4.1. Comparison Simulation of Magnetic Field of New Halbach Array
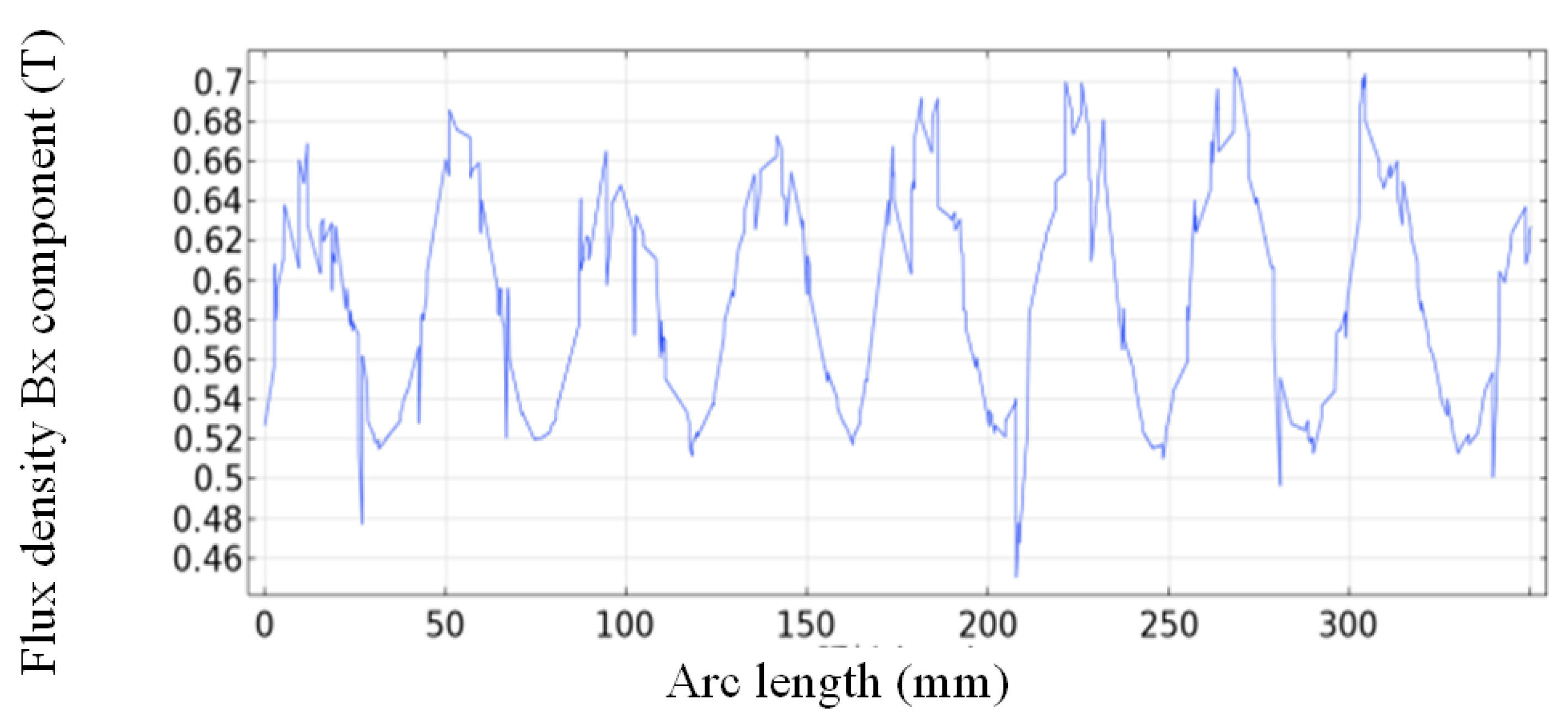
4.2. Simulation of Semi-Analytic Harmonic Model
5. Experimental Verification
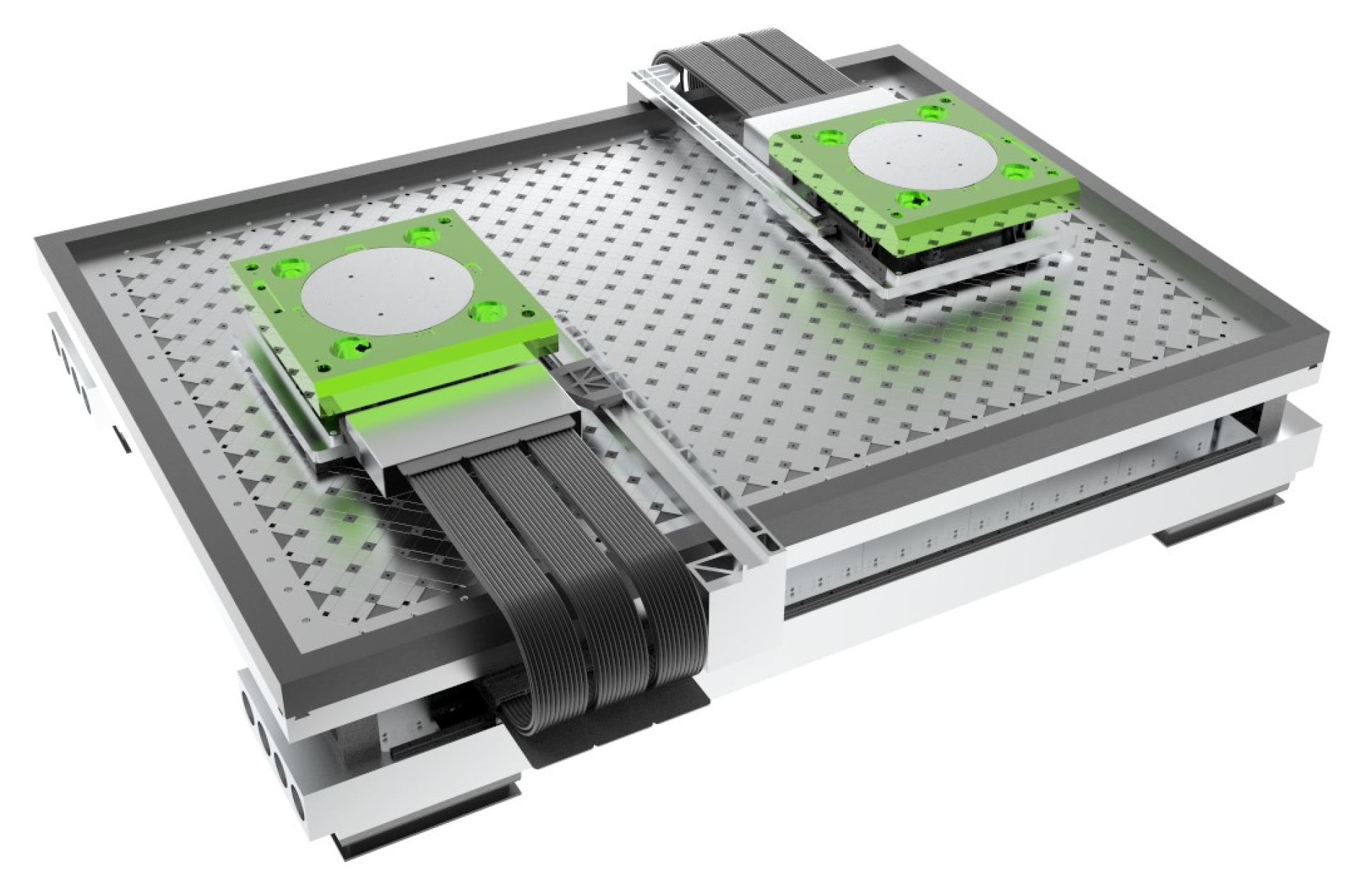
5.1. Experimental Setup
5.2. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klocke, F.; Beck, T.; Hoppe, S.; Krieg, T.; Müller, N.; Nöthe, T.; Raedt, H.W.; Sweeney, K. Examples of FEM application in manufacturing technology. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 120, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskos, D. Boundary Element Methods in Dynamic Analysis. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1987, 40, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipa, A.V.; Koskulics, J.; Brandenburg, R.; Hoder, T. The simplest equivalent circuit of a pulsed dielectric barrier discharge and the determination of the gas gap charge transfer. Rev. Sci. Instruments 2012, 83, 115112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, T.; Hu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, M. Generation Mechanism and Decoupling Strategy of Coupling Effect in Maglev Planar Motor. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2023, 28, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-S.; Im, C.-H.; Jung, H.-K. Magnetic field analysis of 2-D permanent magnet array for planar motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 3762–3766. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Mehrtash, M.; Khamesee, M.B. Dual-axial motion control of a magnetic levitation system using Hall-effect sensor. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2016, 21, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compter, I.J.C. Electro-dynamic planar motor. Precis. Eng. 2004, 28, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boeij, J.; Lomonova, E.; Vandenput, A. Modeling Ironless Permanent-Magnet Planar Actuator Structures. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.W.; van Lierop, C.M.M.; Lomonova, E.A.; Vandenput, A.J.A. Modeling of magnetically levitated planar actuators with moving magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovers, J.M.M.; Jansen, J.W.; Lomonova, E.A. Multiphysical analysis of moving-magnet planar motor topologies. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 5730–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boeij, J.; Lomonova, E.A.; Duarte, J.L. Contactless planar actuator with manipulator: A motion system without cables and physical contact between the mover and the fixed world. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Usman, I.U.R. 6D direct-drive technology for planar motion stages. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2012, 61, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, P.; Benkadda, S.; Garbet, X. Proper orthogonal decomposition and Galerkin projection for a three-dimensional plasma dynamical system. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 61, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genesio, R.; Tesi, A. Harmonic balance methods for the analysis of chaotic dynamics in nonlinear systems. Automatica 1990, 28, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbach, K. Design of permanent multipole magnets with oriented rare earth cobalt material. Nucl. Instruments Methods 1980, 169, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuidema, G.; Krop, D.C.J.; Lomonova, E.A. Semi-Analytical Modeling of a PM-based 6-DOF Actuator. In Proceedings of the 2021 Sixteenth International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies, Monte-Carlo, Monaco, 5–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Liu, E.; Fan, C.; Zhao, B.; Tan, J. Honeycomb Halbach Flexible Permanent Magnet Array for Magnetically Levitated Planar Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2025, 61, 4900109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landecker, P.B.; Villani, D.D.; Yung, K.W. An Analytic Solution for the Torque Between Two Magnetic Dipoles. Magn. Electr. Sep. 1999, 10, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, T.H. The force on a magnetic dipole. Am. J. Phys. 1998, 56, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, H. Modeling and analysis of a magnetically levitated synchronous permanent magnet planar motor. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111 Pt 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H. Performance-oriented precision LARC tracking motion control of a magnetically levitated planar motor with comparative experiments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 5763–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| n | RMSE (C/m2) | Error (C/m2) | Time (s) | Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.156 | 0.213 | 0.02 | No |
| 2 | 0.089 | 0.127 | 0.04 | No |
| 3 | 0.045 | 0.063 | 0.06 | No |
| 4 | 0.021 | 0.038 | 0.08 | Yes |
| 5 | 0.020 | 0.036 | 0.15 | Yes (Redundancy) |
| 6 | 0.019 | 0.035 | 0.23 | Yes (Redundancy) |
| 7 | 0.018 | 0.034 | 0.31 | Yes (Redundancy) |
| 8 | 0.017 | 0.033 | 0.42 | Yes (Redundancy) |
| Symbol | Implication | Numerical Value |
|---|---|---|
| a | Large magnetic steel length | 40 mm |
| b | Large magnetic steel width | 40 mm |
| c | Large magnetic steel height | 40 mm |
| Small magnetic steel width | 20 mm | |
| Polar moment | 60 mm | |
| Polar moment (after magnetic steel rotation 45°) | mm | |
| M | Magnetization | 1040 KA/m |
| Remanence | 1440 mT | |
| Coercive Force | 836 KA/m | |
| Intrinsic Coercive Force | 955 KA/m | |
| Maximum energy Product | 374 KJ/m3 | |
| Working Temp | 80 °C |
| Modeling Dimension | Grid | Proposed Method | COMSOL FEM | Efficiency Multiple |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D magnetic field | Harmonic order k = l = 20 | 0.08 s | 124.3 s | 1554 times |
| 3D magnetic field | Harmonic order k = l = 30 | 0.32 s | 896.7 s | 2802 times |
| Dynamic magnetic field update | Harmonic order k = l = 20 | 0.012 s | 45.2 s | 3767 times |
| Verify Height | Proposed vs. Experiment | Equivalent vs. Experiment | FEM vs. Experiment | Proposed vs. FEM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z = 2 mm | Mean absolute error | 0.028 T | 0.097 T | 0.021 T | 0.015 T |
| z = 2 mm | Maximum relative error | 3.67% | 12.8% | 2.79% | 1.92% |
| z = 5 mm | Mean absolute error | 0.021 T | 0.076 T | 0.016 T | 0.012 T |
| z = 5 mm | Maximum relative error | 3.24% | 10.9% | 2.45% | 1.63% |
| Method | Preprocessing | Single Modeling | Dynamic Update | Total Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed method | 0.25 s | 0.32 s | 0.012 s | 1.45 s |
| COMSOL FEM | 15.6 s | 896.7 s | 45.2 s | 4671.6 s |
| Equivalent charge method (only static magnetic field solution) | 0.18 s | 0.21 s | 0.008 s | 1.01 s |
| Equivalent charge method (Total time consumption in engineering scenarios) | 0.18 s | 3.04 s | 2.838 s | 3.84 s |
| Serial | Integration Step (mm) | Relative Error (%) | Integration Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.10 | 1.23 | 401 × 301 |
| 2 | 0.05 | 0.37 | 801 × 601 |
| 3 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 2001 × 1501 |
| 4 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 4001 × 3001 |
| Parameters | (2 mm) Traditional | (2 mm) New | (5 mm) Traditional | (5 mm) New |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean value/T | 0.6010 | 0.7395 | 0.4776 | 0.5917 |
| Standard deviation/T | 0.1134 | 0.1082 | 0.0596 | 0.0562 |
| Minimum value/T | 0.3338 | 0.5818 | 0.3248 | 0.4956 |
| Maximum value/T | 0.8443 | 0.9771 | 0.6019 | 0.7069 |
| Extreme value difference/T | 0.5105 | 0.3953 | 0.2771 | 0.2113 |
| Dispersion coefficient/T | 18.87% | 14.63% | 12.48% | 9.50% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; Yu, C. Research on Finite Permeability Semi-Analytical Harmonic Modeling Method for Maglev Planar Motors. Magnetism 2025, 5, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5040027
Zhang Y, Fan C, Yu C. Research on Finite Permeability Semi-Analytical Harmonic Modeling Method for Maglev Planar Motors. Magnetism. 2025; 5(4):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5040027
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yang, Chunguang Fan, and Chenglong Yu. 2025. "Research on Finite Permeability Semi-Analytical Harmonic Modeling Method for Maglev Planar Motors" Magnetism 5, no. 4: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5040027
APA StyleZhang, Y., Fan, C., & Yu, C. (2025). Research on Finite Permeability Semi-Analytical Harmonic Modeling Method for Maglev Planar Motors. Magnetism, 5(4), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5040027






