Macroplastics and Microplastics in Intertidal Sediment of Vinces and Los Tintos Rivers, Guayas Province, Ecuador
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
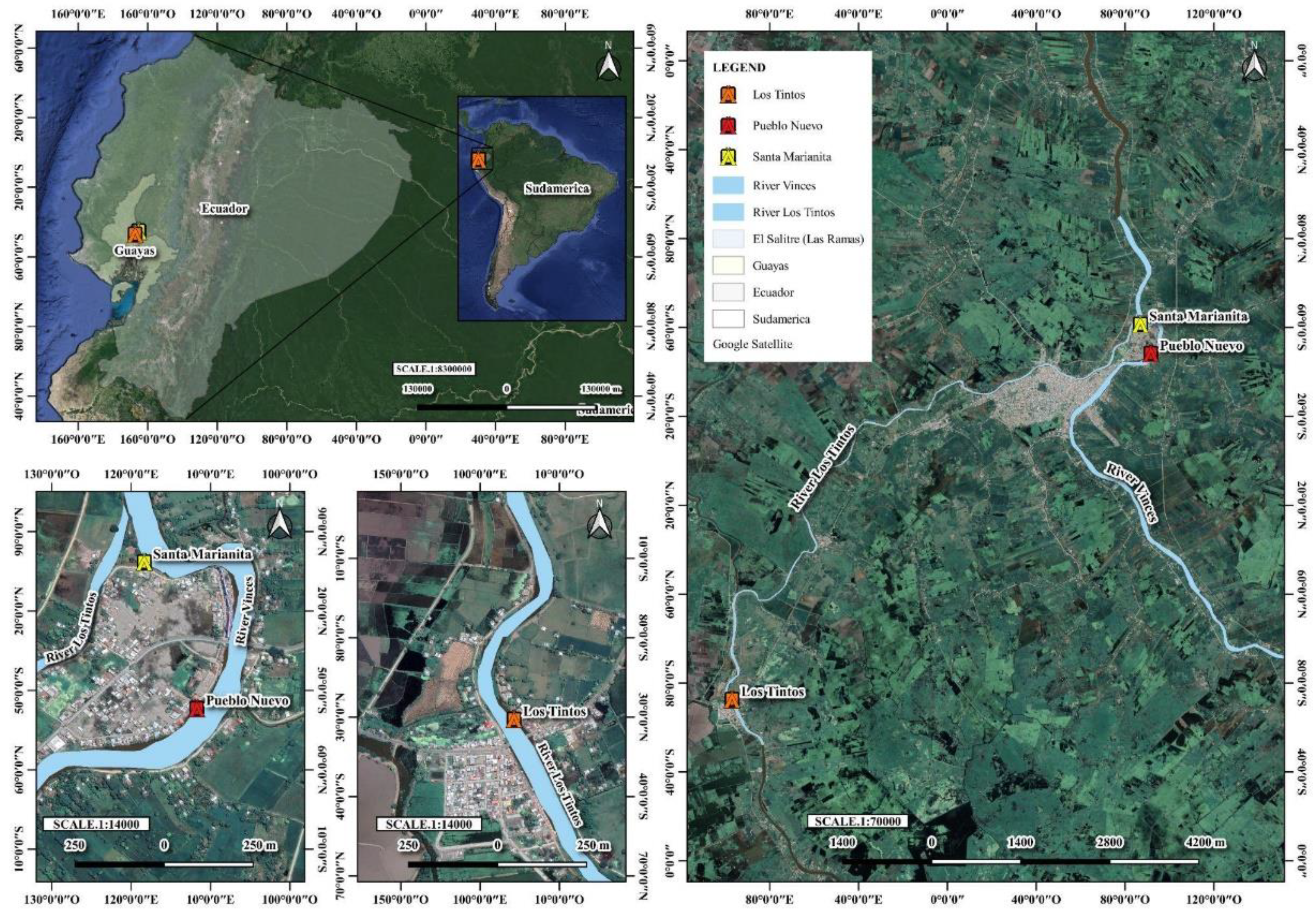
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Contamination Prevention Measures
2.4. Macroplastic Standing Stock Survey
2.5. Microplastic Sediment Sampling
2.6. Laboratory Analysis
2.6.1. Microplastic Extraction
2.6.2. Grain Size Analysis
2.7. Plastic Categories
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
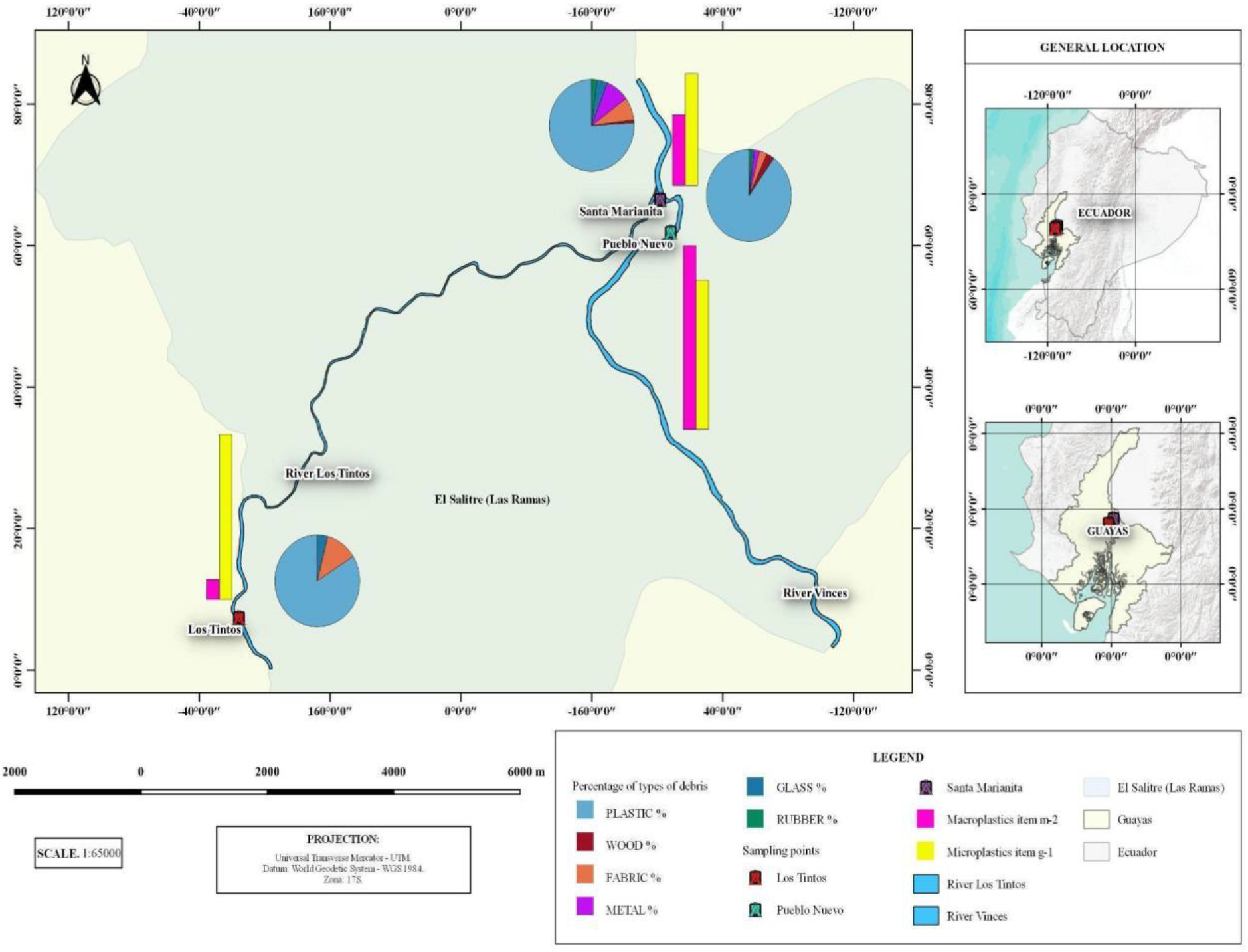
3.1. Macro Items
3.2. Microplastic Composition in Sediment
3.3. Microplastic Colours
3.4. Contamination
3.5. Sediment Weight and Grain Size
3.6. Anthropogenic Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chilton, D.; Hamilton, D.P.; Nagelkerken, I.; Cook, P.; Hipsey, M.R.; Reid, R.; Sheaves, M.; Waltham, N.J.; Brookes, J. Environmental Flow Requirements of Estuaries: Providing Resilience to Current and Future Climate and Direct Anthropogenic Changes. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhankar, C.; Shivika, S. Microplastics in Our Oceans and Marine Health. Available online: http://journals.openedition.org/factsreports/5257 (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Blumenröder, J.; Sechet, P.; Kakkonen, J.E.; Hartl, M.G.J. Microplastic Contamination of Intertidal Sediments of Scapa Flow, Orkney: A First Assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.; Lusher, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Morley, A. The Deposition and Accumulation of Microplastics in Marine Sediments and Bottom Water from the Irish Continental Shelf. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelia, T.S.M.; Khalik, W.M.A.W.M.; Ong, M.C.; Shao, Y.T.; Pan, H.J.; Bhubalan, K. Marine Microplastics as Vectors of Major Ocean Pollutants and its Hazards to the Marine Ecosystem and Humans. Prog. Earth Planet Sci. 2021, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenon, F.; Carroll, C.; Sousa, J. Plastic Debris in the Ocean. The Characterization of Marine Plastics and their Environmental Impacts, Situation Analysis Report. In International Union for Conservation of Nature Global Marine and Polar Programme (IUCN); IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2014; p. 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sebille, E.; Wilcox, C.; Lebreton, L.; Maximenko, N.; Hardesty, B.D.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Eriksen, M.; Siegel, D.; Galgani, F.; Law, K.L. A Global Inventory of Small Floating Plastic Debris. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, T.S.; Cole, M.; Lewis, C. Interactions of Microplastic Debris throughout the Marine Ecosystem. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 116, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, J.N.; Mitrovic, S.M. Microplastic Pollution in Estuaries across a Gradient of Human Impact. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.N.; Duong, T.T.; Quynh Le, T.P.; Hoang, T.K.; Ngo, H.M.; Phuong, N.A.; Pham, Q.T.; Doan, T.O.; Ho, T.C.; Le, N.D.; et al. Microplastics in Asian Freshwater Ecosystems: Current Knowledge and Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 151989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H. Transport of Microplastics in Coastal Seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 199, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M. Oceans of Plastic Waste. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.G.; Reisser, J. Plastic Pollution in the World’s Oceans: More than 5 Trillion Plastic Pieces Weighing over 250,000 Tons Afloat at Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 12, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadri, S.S.; Thompson, R.C. On the Quantity and Composition of Floating Plastic Debris Entering and Leaving the Tamar Estuary, Southwest England. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, M.; Maximenko, N.; Thiel, M.; Cummins, A.; Lattin, G.; Wilson, S.; Hafner, J.; Zellers, A.; Rifman, S. Plastic Pollution in the South Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 68, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcgoran, A.; Morritt, D.; Clark, P.F.; Cowie, P.R.; McEvoy, J.P. Ingestion of plastic by fish: A comparison of Thames Estuary and Firth of Clyde populations. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, F.; Gilbert, B.; Compère, P.; Eppe, G.; Das, K.; Jauniaux, T.; Parmentier, E. Microplastics in Livers of European Anchovies (Engraulis encrasicolus, L.). Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendel, A.L.; Bessa, F.; Alves, V.E.N.; Amorim, A.L.A.; Patrício, J.; Palma, A.R.T. Widespread Microplastic Ingestion by Fish Assemblages in Tropical Estuaries Subjected to Anthropogenic Pressures. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruge, A.; Barreau, C.; Carlot, J.; Collin, H.; Moreno, C.; Maison, P. Monitoring Litter Inputs from the Adour River (Southwest France) to the Marine Environment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, T.; Glassom, D.; Smit, A.J. Plastic Pollution in Five Urban Estuaries of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, K.; Xiong, X. Microplastic Pollution in Inland Waters Focusing on Asia. In Freshwater Microplastics: The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry, 58; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.F.; Barletta, M. Microplastics in Coastal and Marine Environments of the Western Tropical and Sub-Tropical Atlantic Ocean. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1868–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, N.; Chagnon, C.; Felix, F.; Fernández, C.; Ferreira, J.L.; Gallardo, C.; Ordóñez, O.G.; Henostroza, A.; Laaz, E.; Mizraji, R.; et al. Low Prevalence of Microplastic Contamination in Planktivorous Fish Species from the Southeast Pacific Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Pico, J.; Mero del Valle, D.; Castillo, R.; Macias-Mayorga, D. Marine debris: Implications for conservation of rocky reefs in Manabi, Ecuador (Se Pacific Coast). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestanza, C.; Botero, C.M.; Anfuso, G.; Chica-Ruiz, J.A.; Pranzini, E.; Mooser, A. Beach Litter in Ecuador and the Galapagos islands: A Baseline to Enhance Environmental Conservation and Sustainable Beach Tourism. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaibor, N.; Condo-Espinel, V.; Cornejo-Rodríguez, M.H.; Darquea, J.; Pernia, B.; Domínguez, G.; Briz, M.E.; Márquez, L.; Laaz, E.; Alemán-Dyer, C.; et al. Composition, Abundance and Sources of Anthropogenic Marine Debris on the Beaches from Ecuador—A volunteer-supported study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tercera Comunicación Nacional del Ecuador a la Convención Marco de las Naciones Unidas sobre el Cambio Climático. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/35703383/Tercera_Comunicaci%C3%B3n_Nacional_del_Ecuador_a_la_Convenci%C3%B3n_Marco_de_las_Naciones_Unidas_sobre_el_Cambio_Clim%C3%A1tico (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Constitución de la República del Ecuador. Available online: https://www.oas.org/juridico/pdfs/mesicic4_ecu_const.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Código Orgánico del Ambiente (COA). Registro Oficial de la República del Ecuador, Suplemento No. 983, Quito, Ecuador. Available online: http://www.ambiente.gob.ec/wp-content/uploads/downloads/2018/01/CODIGO_ORGANICO_AMBIENTE.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Jara-Samaniego, J.; Moral, M.R.; Perez-Murcia, D.; Parades, C.; Galvez-Sola, L.; Gavilanes-Teran, I.; Bustamante, M.A. Urban Waste Management and Potential Agricultural Use in South American Developing Countries: A Case Study of Chimborazo Region (Ecuador). Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 46, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INEC 2010. Fascículo Provincial Guayas. Available online: https://www.ecuadorencifras.gob.ec/wp-content/descargas/Manu-lateral/Resultados-provinciales/guayas.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Plan de Desarrollo de la Provincia del Guayas 2012–2021. Available online: https://studylib.es/doc/5697708/plan-de-desarrollo-de-la-provincia-del-guayas-2012 (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Chinacalle-Martinez, N.; Garcia-Rada, E.; Lopez-Macias, J.; Pinoargote, S.; Loor, G.; Zevallos-Rosado, J.; Cruz, P.; Pablo, D.; Andrade, B.; Robalino-Mejia, C.; et al. Oceanic Primary Production Trend Patterns Along Coast of Ecuador. Neotrop. Biodivers. 2021, 7, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanik-Ambarita, M.N.; Lock, K.; Boets, P.; Everaert, G.; Nguyen, T.H.T.; Forio, M.A.E.; Musonge, P.L.S.; Suhareva, N.; Bennetsen, E.; Landuyt, D.; et al. Ecological Water Quality Analysis of the Guayas River Basin (Ecuador) Based on Macroinvertebrates Indices. Limnologica 2016, 57, 27–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, M.E.A. A Decision Framework for Integrated Wetland-River Basin Management in a Tropical and Data Scarce Environment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B. The Guayas River Basin. Guayaquil. Available online: http://repositorio.educacionsuperior.gob.ec/bitstream/28000/1039/1/T-SENESCYT-0415.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Ecured. Cantόn Vinces (Ecuador). Available online: https://www.ecured.cu/Cantόn_Vinces_(Ecuador) (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Ilbay Yupa, M.L.; Ruiz Depablos, J.L.; Cueva Jaramillo, E.G.; Ortiz Bustamante, V.M.; Morales Alarco, D.O. Empirical Model for Estimating the Ecological Footprint in Ecuador Based on Demographic, Economic and Environmental Indicators. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desarrollo y Problemática Ambiental del Área del Golfo de Guayaquil. Available online: https://books.google.com.sv/books/about/Desarrollo_y_problem%C3%A1tica_ambiental_del.html?id=fQJjAAAAMAAJ&utm_source=gb-gplus-shareDesarrollo (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Owens, K.A.; Divakaran Sarasamma, J.; Conlon, K.; Kiruba, S.; Biju, A.; Vijay, N.; Subramanian, M.; Asok Vijayamma, S.; Jayadev, A.; Hoon, V.; et al. Empowering Local Practitioners to Collect and Report on Anthropogenic Riverine and Marine Debris Using Inexpensive Methods in India. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippiatt, S.; Opfer, S.; Arthur, C. Marine Debris Monitoring and Assessment: Recommendations for Monitoring Debris Trends in the Marine Environment. In NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-46; NOAA Marine Debris Division: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013; p. 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GESAMP. Guidelines for the Monitoring and Assessment of Plastic Litter and Microplastics in the Ocean; Kershaw, P.J., Turra, A., Galgani, F., Eds.; IMO/FAO/UNESCO-IOC/UNIDO/WMO/IAEA/UN/UNEP/UNDP/ISA Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection: London, UK, 2019; Volume 99, p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods Used for Identification and Quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. In R Foundation for Statistical Computing; European Environment Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Getting Started with PRIMER v7; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2015; Volume 20, p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Determinación de la Calidad del Río Babahoyo, Informe Técnico no Publicado. Available online: file:///C:/Users/MDPI/Downloads/INFORMEBABAHOYO03DEAGOSTODEL2012-1.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Lechthaler, S.; Waldschläger, K.; Stauch, G.; Schüttrumpf, H. The Way of Macroplastic through the Environment. Environments 2020, 2, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graca, B.; Szewc, K.; Zakrzewska, D.; Dołęga, A.; Szczerbowska-Boruchowska, M. Sources and Fate of Microplastics in Marine and Beach Sediments of the Southern Baltic Sea—A Preliminary Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7650–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiaras, K.; Hatzonikolakis, Y.; Kalaroni, S.; Pollani, A.; Triantafyllou, G. Modeling the Pathways and Accumulation Patterns of Micro- and Macro-Plastics in the Mediterranean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 743117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkajit, P.; Thongnonghin, S.; Sriraksa, S.; Pumsri, S. Preliminary Study of Distribution and Quantity of Plastic-debris on Beaches Along the Coast at Phuket Province. App. Envi. Res. 2019, 41, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capparelli, M.V.; Molinero, J.; Moulatlet, G.M.; Barrado, M.; Prado-Alcívar, S.; Cabrera, M.; Gimiliani, G.; Ñacato, C.; Pinos-Velez, V.; Cipriani-Avila, I. Microplastics in Rivers and Coastal Waters of the Province of Esmeraldas, Ecuador. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo-Lecompte, C.; Mehrvar, M. Slaughterhouse Wastewater: Treatment, Management and Resource Recovery. Phys. Chem. Wastewater Treat. Resour. Recovery 2017, 8, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddout, S.; Gimiliani, G.; Priya, K.L.; Hoguane, A.; Casila, J.C.; Ljubenkov, I. Microplastics in Surface Waters and Sediments in the Sebou Estuary and Atlantic Coast, Morocco. Anal. Lett. 2021, 66, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcivar, M.S.G.; Pérez, A.V.; Gilert, B.I.C.; Gámez, M.R. Zeolite in Wastewater Decontamination as a Local Development Solution. Int. J. Life Sci. 2017, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos (INEC). Documento Metodológico de la Estadística de Información Ambiental Económica en Gobiernos Autónomos Descentralizados Municipales; GAD Munic: Quito, Ecuador, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vera, W. Determinación de la Capacidad de Carga Turística del Balneario de Agua Dulce Santa Marianita, Canton Salitre para el Desarrollo Sostenible del Sector. 2017. Available online: http://repositorio.ug.edu.ec/handle/redug/18397 (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Astudillo, J.; Bravo, M.; Dumont, C.; Thiel, M. Detached Aquaculture Buoys in the SE Pacific: Potential Dispersal Vehicles for Associated Organisms. Aquat. Biol. 2009, 5, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeiren, P.; Lercari, D.; Munoz, C.C.; Ikejima, K.; Celentano, E.; Jorge-Romero, G.; Defeo, O. Sediment Grain Size Determines Microplastic Exposure Landscapes for Sandy Beach Macroinfauna. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, R.M.; Waldron, S.; Phoenix, V.R.; Gauchotte-Lindsay, C. Microscopy and Elemental Analysis Characterisation of Microplastics in Sediment of a Freshwater Urban River in Scotland, UK. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12491–12504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomar, C.; Estarellas, F.; Deudero, S. Microplastics in the Mediterranean Sea: Deposition in Coastal Shallow Sediments, Spatial Variation and Preferential Grain Size. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 115, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, W.J.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S.E. Identification Methods in Microplastics Analysis: A Review. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.; Slat, B.; Ferrari, F.; Sainte-Rose, B.; Aitken, J.; Marthouse, R.; Hajbane, S.; Cunsolo, S.; Schwarz, A.; Levivier, A.; et al. Evidence that the Great Pacific Garbage Patch is Rapidly Accumulating Plastic. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Pueblo Nuevo | Santa Marianita | Los Tintos | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | 1°49′31′′ S | 1°49′16′′ S | 1°52′29′′ S |
| Longitude | 79°48′9′′ W | 79°48′14′′ W | 79°51′42′′ W |
| Aspect | North-East | North | South-East |
| Location | Suburban town | Rural/suburban village | Suburban town |
| Major usage | Recreation and agriculture | Boats | Recreation, agriculture and fishing |
| River name | Vinces river | Vinces river | Los Tintos river |
| Water flow direction | East | South-East | South-West |
| Landward limit | Street (tyres used as barriers along shore) | Boat ramp | Vegetation |
| Description | Residential area, vehicle and boat activity, used for fishing and agriculture | Few residences surrounding riverside, small harbour area, canoe and boat access | Very residential, regular boat traffic, heavy fishing and agricultural use |
| Nearest landmarks | Beach and restaurants | Slaughterhouse | Bridge, shops, restaurants, residences |
| River | Total MAPs | Macro Average (Items/m2) | No of Black Fibres | No of White Fibres | No of Red Fibres | No of Blue Fibres | No of Green Fibres | No of Yellow Fibres | No of Particles | Size Classes (mm) | MPs (Item g−1) | Total Items (MAPS + MPs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vinces River: Pueblo Nuevo | 213 | 9.1 | 76 | 27 | 15 | 29 | 4 | 1 | 54 | 0.43–2.52 | 7.39 | 419 |
| Vinces River: Santa Marianita | 98 | 3.52 | 59 | 22 | 21 | 28 | 8 | 84 | 0.25–0.35 | 5.55 | 320 | |
| Los Tintos River: Los Tintos | 25 | 1 | 52 | 9 | 21 | 53 | 2 | 89 | 0.15–0.61 | 8.17 | 251 |
| phi (Φ) | mm | Pueblo Nuevo (%) | Santa Marianita (%) | Los Tintos (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Granules | −1 | 2 | 0.25 | 0.36 | 0.08 |
| V. coarse sand | 0 | 1 | 0.57 | 0.22 | 0.05 |
| Coarse sand | 1 | 0.5 | 1.63 | 0.47 | 0.35 |
| Medium sand | 1.5 | 0.3 | 13.02 | 3.74 | 1.65 |
| Fine sand | 2 | 0.25 | 8.49 | 3.65 | 2.58 |
| V. fine sand | 3 | 0.125 | 48.25 | 65.50 | 70.27 |
| Silt clay | 3.5 | 0.063 | 27.80 | 26.06 | 25.02 |
| 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Sample ID | Polymer * | Density | Size | Colour | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | Average | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3(1-3) | LDPE | 0.93 | 500–710 µm | white | 89 | 95 | 90 | 91 (±3) | |
| 5(1-3) | PVC | 1.3 | <100 µm | white | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | too small |
| 12(1-3) | PVC | ≤1 mm | Grey | 60 | 90 | 90 | 80 (±17) | ||
| 4(1-3) | PET | 1.38 | 2 mm | Grey | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | did not float/easy to see |
| 6(1-3) | PET | 3 mm | White | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | did not float/easy to see | |
| 7(1-3) | PET | 1.38 | <1 mm | White | 90 | 60 | 90 | 80 (±17) | |
| 10(1-3) | PET | 1.38 | 1–2 mm | Grey | 90 | 70 | 100 | 86 (±15) | |
| 8(1-3) | HDPE | 0.97 | <1 mm | White | 100 | 90 | 90 | 93 (±5) | |
| 9(1-3) | PP | 0.946 | 1–2 mm | Red | 80 | 100 | 100 | 93 (±11) | |
| 11(1-3) | PS | 1.04 | 1–2 mm | Black | 100 | 100 | 80 | 93 (±11) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Talbot, R.; Cárdenas-Calle, M.; Mair, J.M.; López, F.; Cárdenas, G.; Pernía, B.; Hartl, M.G.J.; Uyaguari, M. Macroplastics and Microplastics in Intertidal Sediment of Vinces and Los Tintos Rivers, Guayas Province, Ecuador. Microplastics 2022, 1, 651-668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1040045
Talbot R, Cárdenas-Calle M, Mair JM, López F, Cárdenas G, Pernía B, Hartl MGJ, Uyaguari M. Macroplastics and Microplastics in Intertidal Sediment of Vinces and Los Tintos Rivers, Guayas Province, Ecuador. Microplastics. 2022; 1(4):651-668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1040045
Chicago/Turabian StyleTalbot, Rebecca, Maritza Cárdenas-Calle, James M Mair, Franklin López, Guillermo Cárdenas, Beatríz Pernía, Mark G. J. Hartl, and Miguel Uyaguari. 2022. "Macroplastics and Microplastics in Intertidal Sediment of Vinces and Los Tintos Rivers, Guayas Province, Ecuador" Microplastics 1, no. 4: 651-668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1040045
APA StyleTalbot, R., Cárdenas-Calle, M., Mair, J. M., López, F., Cárdenas, G., Pernía, B., Hartl, M. G. J., & Uyaguari, M. (2022). Macroplastics and Microplastics in Intertidal Sediment of Vinces and Los Tintos Rivers, Guayas Province, Ecuador. Microplastics, 1(4), 651-668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1040045






