A Simplified Algorithm for a Full-Rank Update Quasi-Newton Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Notations
3. Linearization Methods
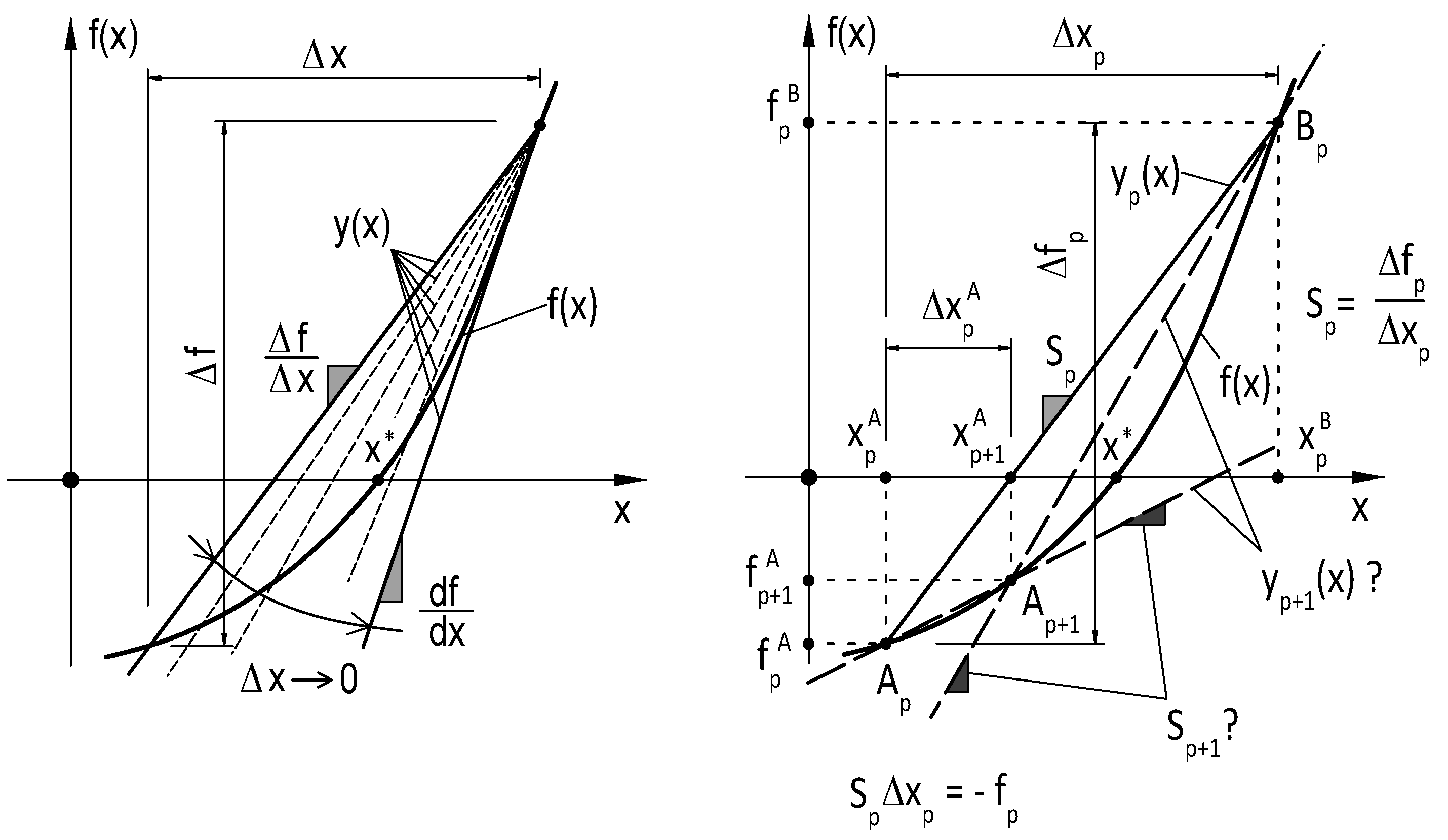
3.1. Single-Variable Case
3.2. Multi-Variable Case
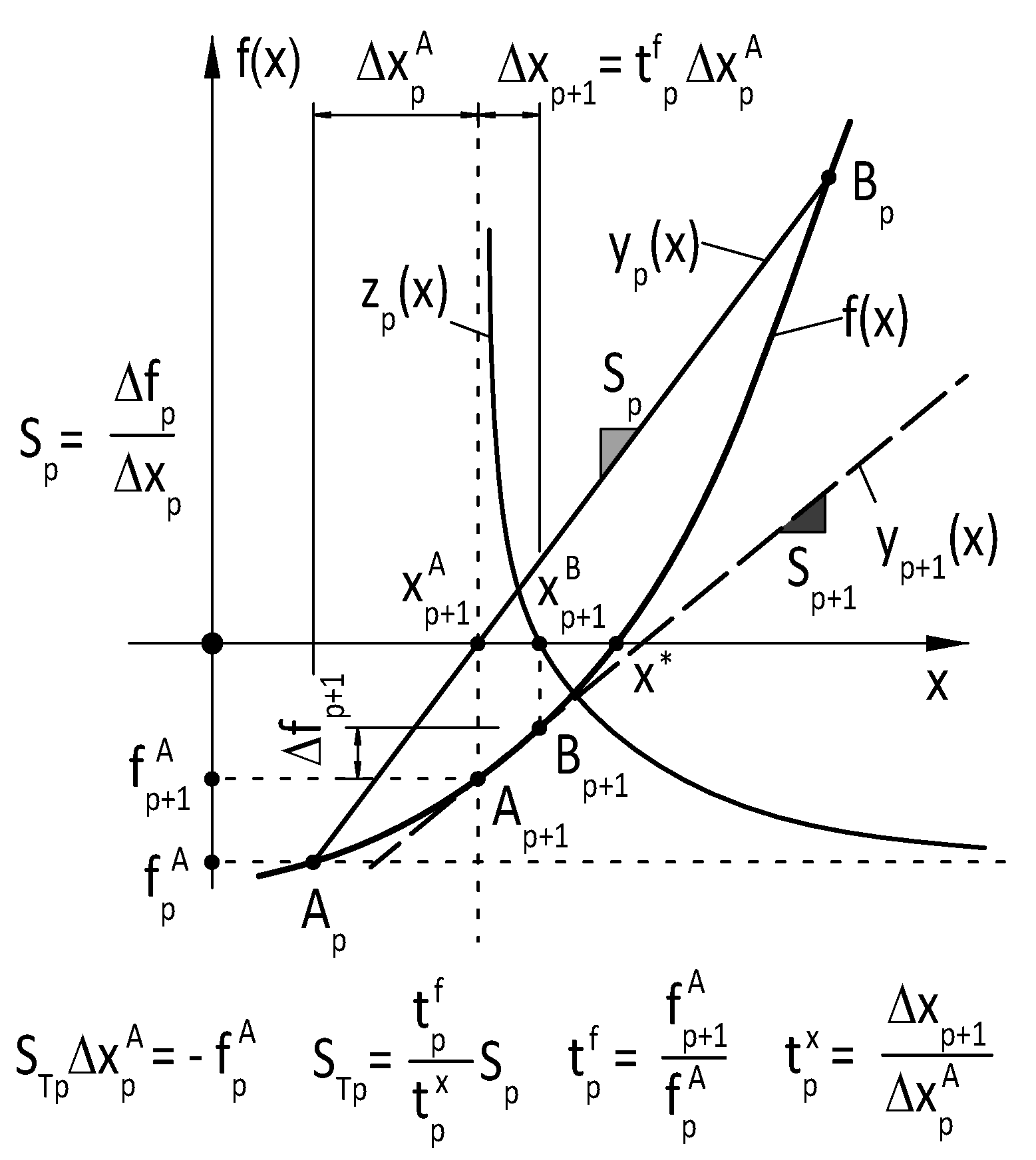
4. T-Secant Method
4.1. Single-Variable Case
4.2. Multi-Variable Case
5. Algorithm
- Step 1: Generate a set of additional approximates (Equation (64)) and evaluate function values . Assure that .
- Step 3: If , then terminate iteration, else continue with Step 4.
- Step 5 : Continue iteration from Step 1 with , and .
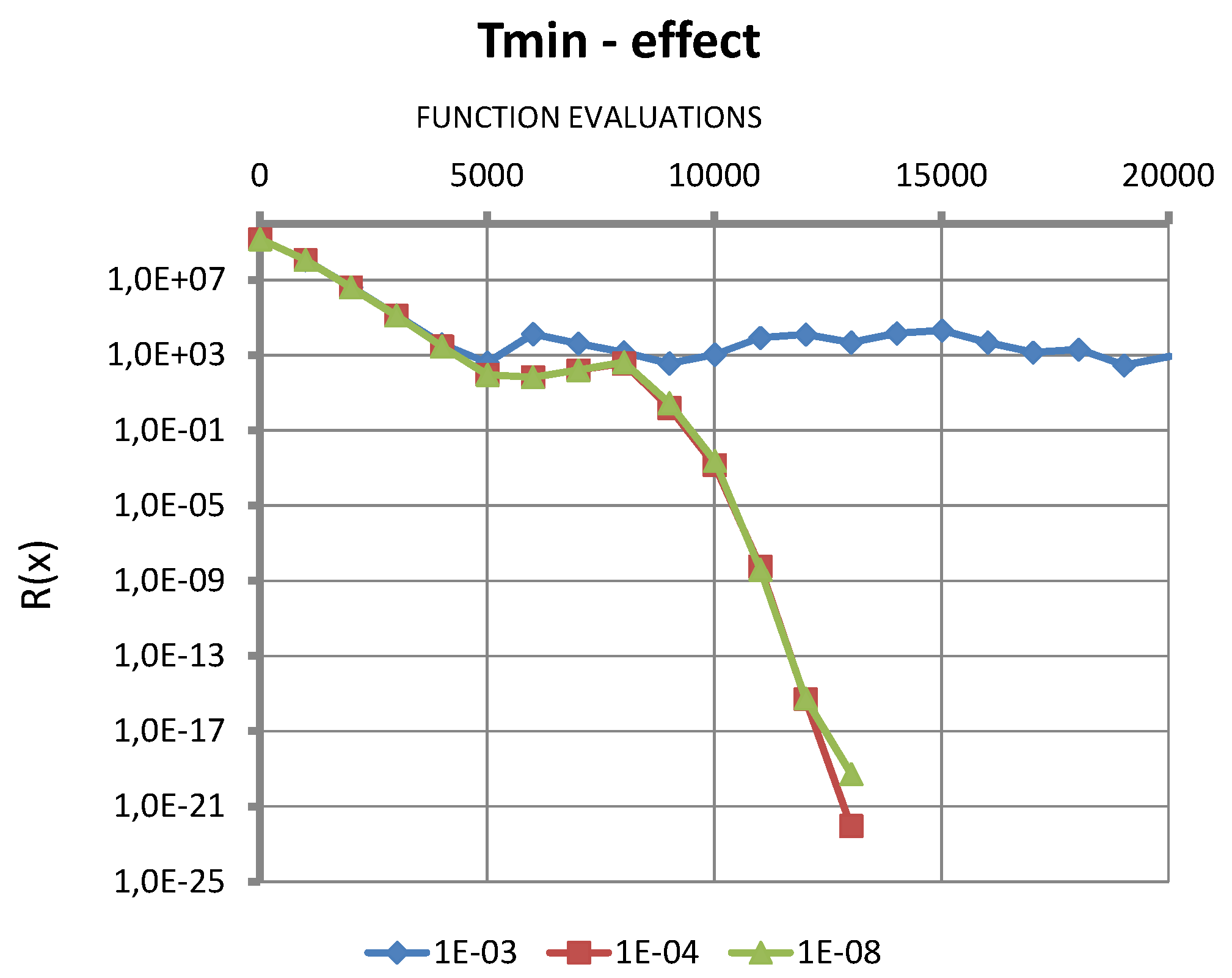
6. Numerical Tests Results
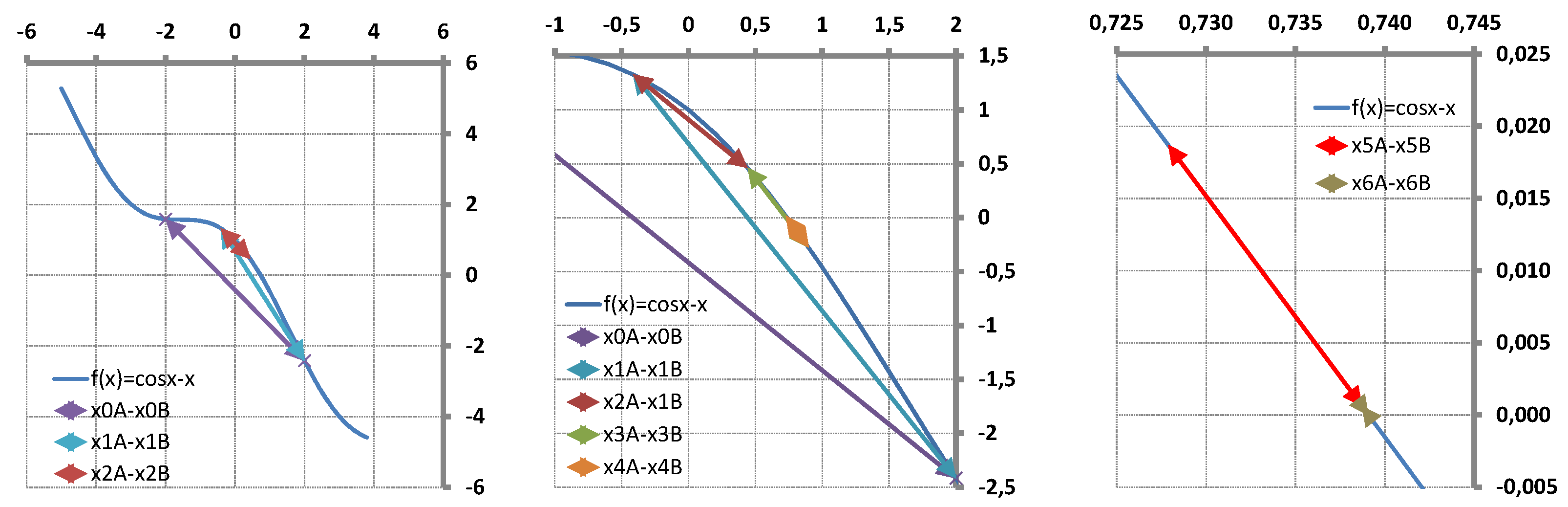
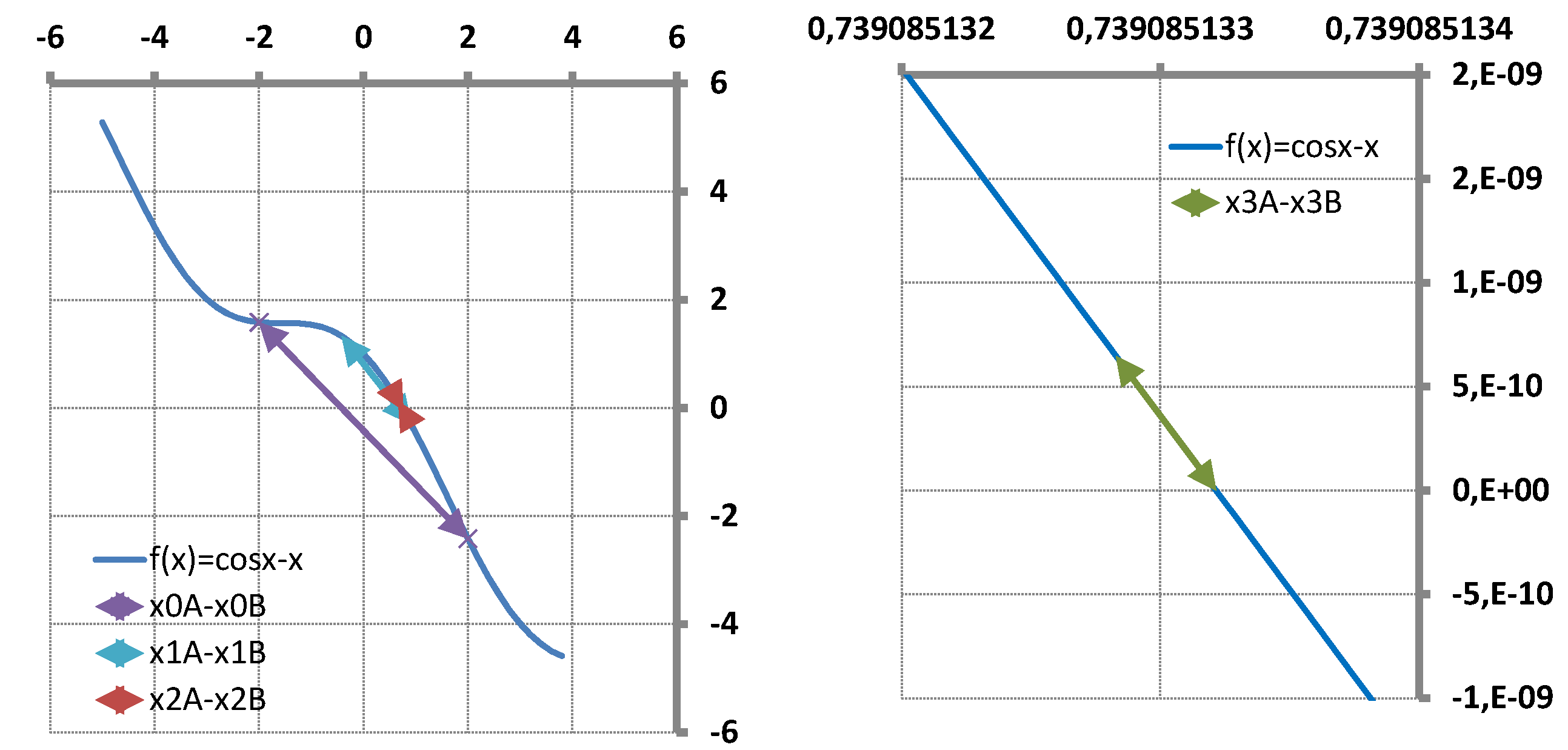
6.1. Single-Variable Test Function
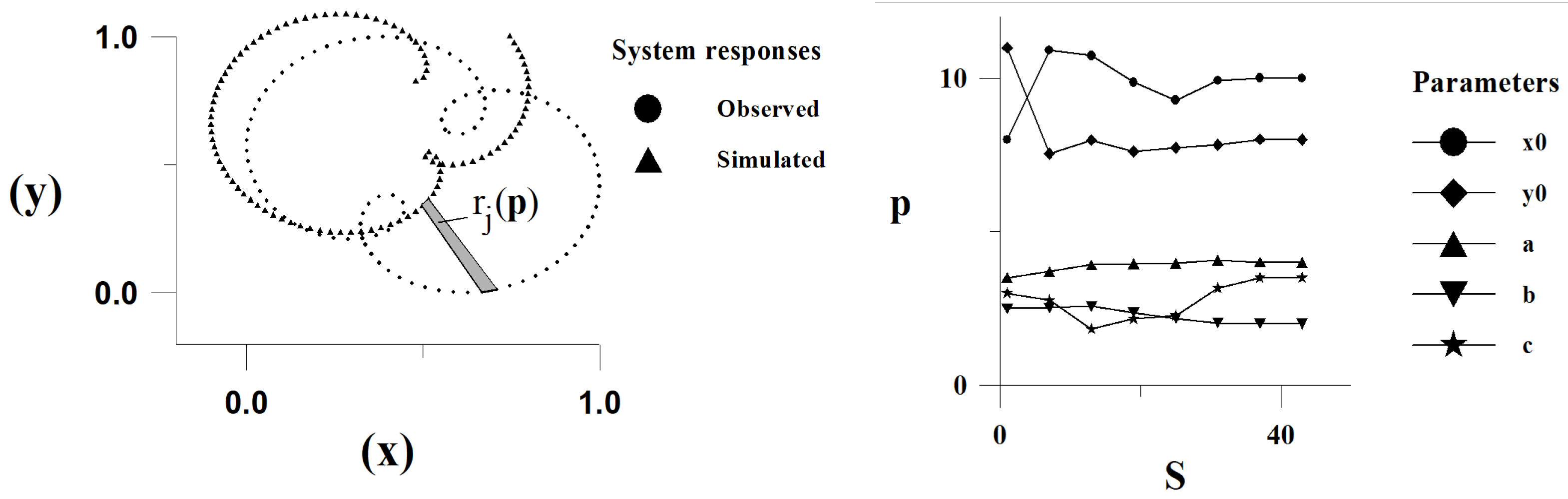
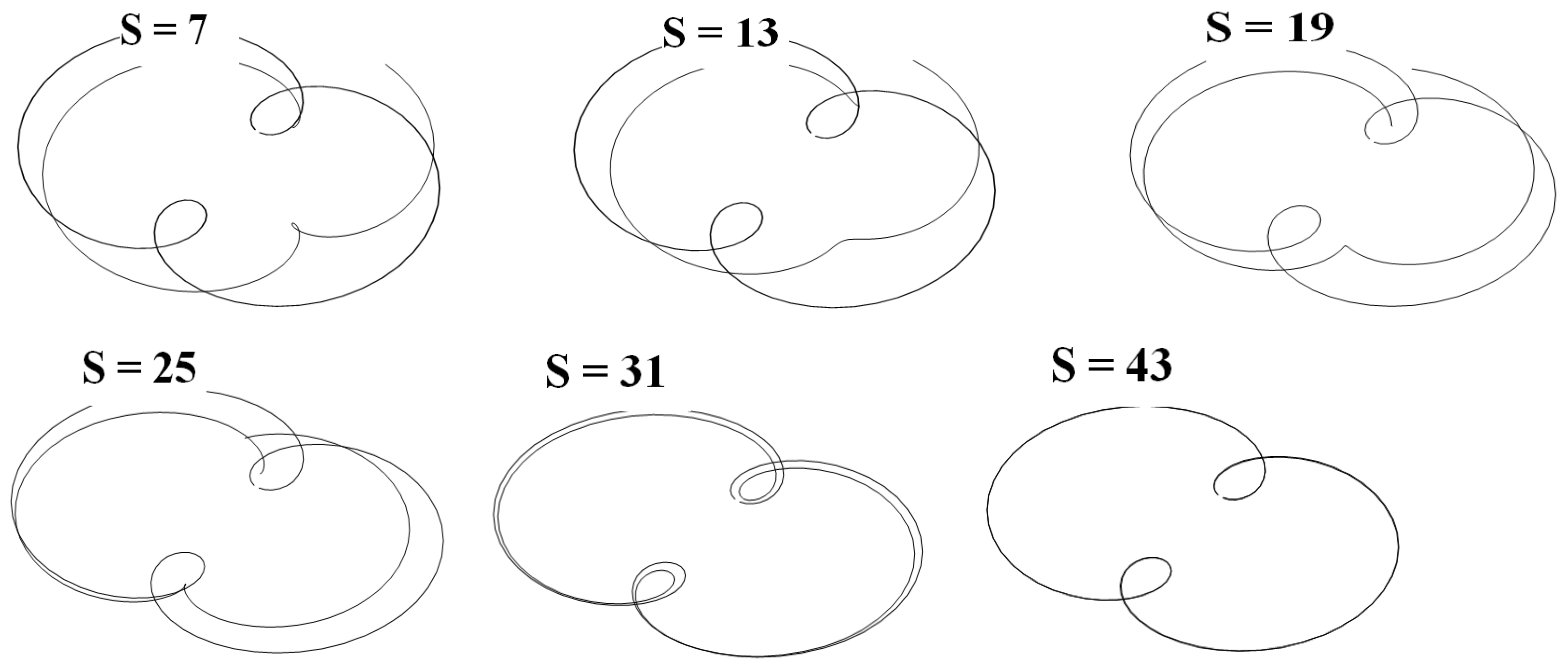
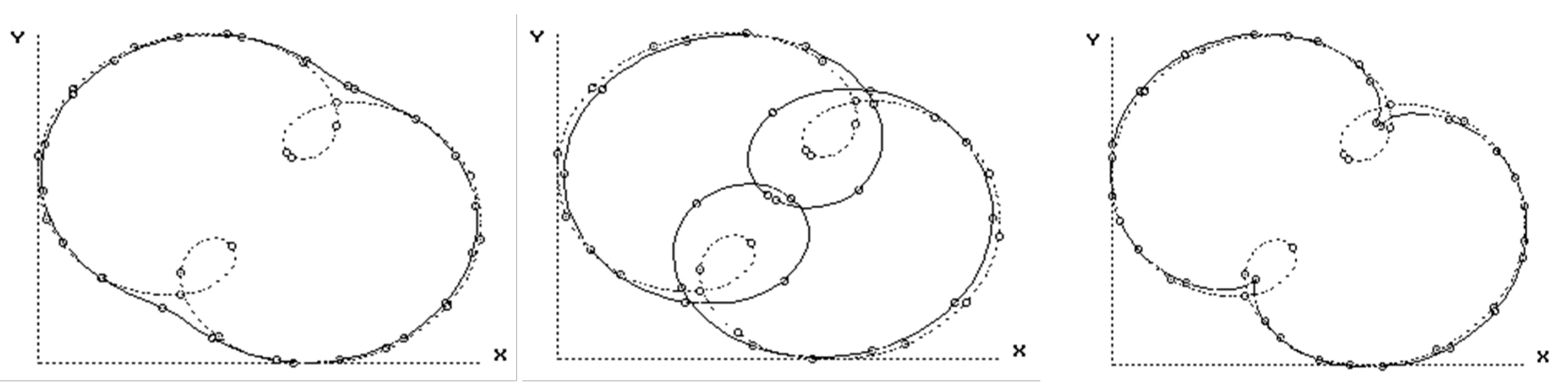
6.2. Solution of an Inverse Problem
7. Efficiency
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dennis, J.E., Jr.; Schnabel, R.B. Numerical Methods for Unconstrained Optimization and Nonlinear Equations; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, J.M.; Rheinboldt, W.C. Iterative Solution of Nonlinear Equations in Several Variables; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Hegedus, C. Numerical Methods I; ELTE, Faculty of Informatics: Budapest, Hungary, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Press, W.H.; Flannery, B.P.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Wetterling, W.T. Numerical Recepies; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Berzi, P. Convergence and Stability Improvement of Quasi-Newton Methods by Full-Rank Update of the Jacobian Approximates. AppliedMath 2024, 4, 143–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzi, P.; Beccu, R.; Lundberg, B. Identification of a Percussive Drill Rod Joint from its Response to Stress Wave Loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1994, 18, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzi, P. Pile-Soil Interaction due to Static and Dynamic Load. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, New Delhi, India, 5–10 January 1994; pp. 609–612. [Google Scholar]
- Berzi, P.; Popper, G. Evaluation of dynamic load test results on piles. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Identification of Nonlinear Mechanical Systems from Dynamic Tests (Euromech 280), Ecully, France, 29–31 October 1991; pp. 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Popper, G. Numerical method for least square solving of nonlinear equations. Period. Polytech. 1985, 29, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe, P. The Secant Method for Simultaneous Nonlinear Equations. Commun. ACM 1959, 2, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, J.M.; Tapia, R.A. Origin and evolution of the secant method in one dimension. Am. Math. Mon. 2013, 120, 500–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broyden, C.G.; Dennis, J.E.; Mor, J.J. On the local and superlinear convergence of quasi-Newton methods. J. Inst. Math. Appl. 1973, 12, 223–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, J.E.; Mor, J.J. A characterization of superlinear convergence and its application to quasi-Newton methods. Math. Comput. 1974, 28, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, A.M. Solution of Equations and Systems of Equations; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Traub, J.F. Iterative Methods for the Solution of Equations, 1st ed.; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Weerakoon, S.; Fernando, T.G.I. A variant of Newton’s method with accelerated third-order convergence. Appl. Math. Lett. 2000, 13, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, J. Accelerated convergence in Newton’s method. SIAM Rev. 1994, 36, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homeier, H.H.H. On Newton-type methods with cubic convergence. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2005, 176, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Third-order modification of Newton’s method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2007, 205, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar, V.; Sharma, J.R.; Mamta, J. A new family of Secant-like method with super-linear convergence. Appl. Math. Comput. 2005, 171, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melman, A. Geometry and convergence of Euler’s and Halley’s methods. SIAM Rev. 1997, 39, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özban, A.Y. Some new variants of Newton’s method. Appl. Math. Letter. 2004, 17, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavo, T.R.; Thoo, J.B. On the geometry of Halley’s method. Am. Math. Mon. 1995, 102, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.; Mukhopadhyay, B. An improved regula falsi method for finding simple roots of nonlinear equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 254, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.E. A Method for Solving Algebraic Equations Using an Automatic Computer. Math. Tables Other Aids Comput. 1956, 10, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thukral, R. A New Secant-type method for solving nonlinear equations. Am. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2018, 8, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Amat, S.; Busquier, S.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Geometric constructions of iterative functions to solve nonlinear equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2003, 157, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ma, Y. A new modified King–Werner method for solving nonlinear equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 2011, 62, 3700–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Li, D.-S.; Liu, Y.-Z. A new method of secant-like for nonlinear equations. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2009, 14, 2923–2927. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Kou, J.; Gu, C. A new modified secant-like method for solving nonlinear equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 60, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martínez, J.M. Practical quasi-Newton methods for solving nonlinear systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2000, 124, 97–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoer, J.; Bulirsch, R. Introduction to Numerical Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Birgin, E.G.; Krejic, N.; Martinez, J.M. Globally convergent inexact quasi-Newton methods for solving nonlinear systems. Num. Algorithms 2003, 32, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembo, R.S.; Eisenstat, S.C.; Steihaug, T. Inexact Newton methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1971, 19, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.M.; Qi, L. Inexact Newton methods for solving non-smooth equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1995, 60, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broyden, C.G. A class of Methods for Solving Nonlinear Simultaneous Equations. Math. Comput. Am. Math. 1965, 19, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strang, G. Introduction to Linear Algebra, revised international ed.; Wellesley-Cambridge Press: Wellesley, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- King, R.F. Tangent method for nonlinear equations. Numer. Math. 1972, 18, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, W. Über ein Verfarhren der Ordnung 1 + √ 2 zur Nullstellenbestimmung. Numer. Math. 1979, 32, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Wu, Q.; Bi, W. On convergence of a new secant-like method for solving nonlinear equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 2010, 217, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.J.D. An efficient method for finding the minimum of a function of several variables without calculating derivatives. Comput. J. 1964, 7, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loshchilov, I.; Schoenauer, M.; Sebag, M. Adaptive Coordinate Descent. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference (GECCO), Dublin, Ireland, 12–16 July 2011; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 885–892. [Google Scholar]
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A simplex method for function minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Single-Variable | Multi-Variable | Equations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (37) | ||
| 2 | (36) | ||
| 3 | (21) and (35) | ||
| 4 | (24) and (40) | ||
| 5 | (27) and (45) |
| Classic Secant Method | Suggested Update Method | Equations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (64) | ||
| 2 | (37) and (65) | ||
| 3 | (36) | ||
| 4 | (67) | ||
| 5 | (66) | ||
| 6 | (35) and (69) | ||
| 7 | (43) and (68) | ||
| 8 | (42) and (72) | ||
| 9 | (41) and (73) | ||
| 10 | (74) | ||
| 11 | (75) |
| 0 | 1.700 | 2.000 | 0.421 | −0.085 | 0.036 | 2 | 1.23 | ||
| 1 | 2.121 | 2.156 | −0.036 | −0.359 | −0.013 | 4 | 0.87 | ||
| 2 | 2.085 | 2.072 | 0.013 | −0.342 | 0.0044 | 1.08 | 6 | 0.76 | |
| 3 | 2.098 | 2.102 | −0.0044 | −0.348 | −0.0015 | 0.97 | 8 | 0.70 | |
| 4 | 2.093 | 2.092 | 0.0015 | −0.346 | 0.00053 | 1.01 | 10 | 0.67 | |
| 5 | 2.0949 | 2.0955 | −0.00053 | −0.347 | −0.00018 | 0.997 | 12 | 0.65 | |
| 6 | 2.0944 | 2.0942 | 0.00018 | −0.346 | 0.000063 | 1.001 | 14 | 0.63 | |
| 7 | 2.0946 | 2.0947 | −0.000063 | −0.346 | 0.000022 | 0.9997 | 16 | 0.62 |
| Method | [15] | [14] | [36] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Secant | 1 | 1.618… | 1.618… | 1.618… | 4.0 |
| 2 | Newton | 2 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 1.414… | 3.0 |
| 3 | T-Secant | 2 | 2.618… | 1.309… | 1.618… | 4.5 |
| 4 | TS-const. | 2 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
| 5 | T-Newton | 3 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 1.442… | 3.0 |
| 6 | Chen [28] | 3 | 1.618… | 0.539… | 1.173… | − |
| 7 | Wang [30] | 5 | 1.618… | 0.323… | 1.101… | − |
| Method | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | Broyden 1. [36] | 4.92 | - | 59 | 0.391 | 0.78 | |
| 2 | 2 | Broyden 2. [36] | 4.92 | - | 39 | 0.607 | 1.22 | |
| 3 | 2 | Powell [41] | 4.92 | - | 151 | 0.150 | 0.30 | |
| 4 | 2 | ACD [42] | 130.1 | - | 325 | 0.086 | 0.17 | |
| 5 | 2 | Nelder–Mead [43] | 2.00 | - | 185 | 0.127 | 0.25 | |
| 6 | 2 | T-secant [36,41] | 4.92 | 3 | 9 | 6.573 | 13.15 | |
| 7 | 2 | T-secant [42] | 130.1 | 3 | 9 | 6.937 | 13.87 | |
| 8 | 2 | T-secant [43] | 2.00 | 2 | 6 | 5.556 | 11.11 | |
| 9 | 3 | T-secant | 72.72 | 5 | 20 | 1.809 | 5.43 | |
| 10 | 3 | 32.47 | 4 | 16 | 3.815 | 11.45 | ||
| 11 | 5 | 93.53 | 8 | 48 | 0.760 | 3.80 | ||
| 12 | 5 | 7.19 | 4 | 24 | 1.351 | 6.76 | ||
| 13 | 10 | 202.6 | 14 | 154 | 0.408 | 4.08 | ||
| 14 | 200 | 92.78 | 10 | 2010 | 0.042 | 8.44 | ||
| 15 | 1000 | 212.4 | 6 | 6006 | 0.006 | 5.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berzi, P. A Simplified Algorithm for a Full-Rank Update Quasi-Newton Method. AppliedMath 2025, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath5010015
Berzi P. A Simplified Algorithm for a Full-Rank Update Quasi-Newton Method. AppliedMath. 2025; 5(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath5010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerzi, Peter. 2025. "A Simplified Algorithm for a Full-Rank Update Quasi-Newton Method" AppliedMath 5, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath5010015
APA StyleBerzi, P. (2025). A Simplified Algorithm for a Full-Rank Update Quasi-Newton Method. AppliedMath, 5(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath5010015






