Abstract
The identification of genes that are expressed differentially in the diseased versus healthy individual give relevant information regarding the pathology of the disease. The identification of DEGs can be a significant step in the field of clinical and pharmaceutical research. They can act as a potent biomarker, therapeutic target, or gene signature for the early diagnosis of the disease. Intellectual disability is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects those at the fetal stage. Timely diagnosis of the disease can help in preventing severe neurodevelopmental delay in the child. In the current study, a meta-analysis approach was applied for the identification of the DEGs in patients of intellectual disability disorder. Six intellectual disability datasets were retrieved from the GEO database of NCBI and were subjected to quality check, trimming, and alignment. Post-alignment, FeatureCounts was used to form a raw gene count file for differential analysis. The differentially expressed genes were analyzed using the EdgeR statistical package of R Studio. The genes which had an FDR p-value less than 0.05 and log2foldchange greater than 0 were considered upregulated and significantly expressed genes. The study found MTRNR2L1, PAPSS2, L1CAM, IGLV1-47, IGLV3-19, and IGKV1-16 genes to be upregulated in the patient sample. These genes can thus play an important role in the progression of intellectual disability disorder that facilitates early diagnosis of the disease.
1. Introduction
High-throughput sequencing technology is the standard method used for determining the expression levels of RNA []. The detailed profiling of gene expression is now a part of every field of life sciences due to the reduced cost and rapid sequencing technologies []. The main objective of high-throughput sequencing technology is to identify the genes that are differentially expressed (DEGs) under certain specific conditions. The number of sequenced fragments that map to the transcript determines the level of expression of each RNA unit. The identification of DEGs is essential in understanding the mechanism and progression of disease, for the early diagnosis of the disease, and for the identification of biomarkers related to the disease as well [].
Intellectual disability disorder (IDD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting the functioning of the brain. Intellectual disability is characterised by greater difficulty in learning new things, understanding concepts, solving problems, concentrating and remembering. The diagnosis of intellectual disability at a developmental stage itself can prevent the occurrence of more severe neurodevelopmental disorder in growing children. Thus, it is essential to consider intellectual disability as a disorder instead of representing it as a symptom to other neurological disorders.
In this study, we have aimed to identify the significantly expressed genes in the samples of patients with intellectual disability disorder when compared with heavy individuals using the meta-analysis transcriptomics approach.
2. Methods
An intensive literature survey was performed to organize a well-defined pipeline for the study. The complete workflow used in the present study is illustrated in Figure 1.
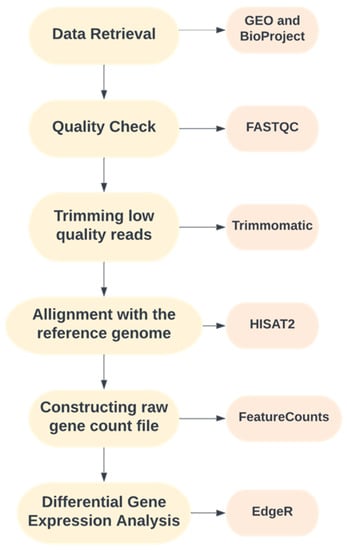
Figure 1.
Pipeline adopted for the current study.
2.1. Data Retrieval
In the current study, we used studies that were based on transcriptomic sequencing of patients, and control samples were taken for analytical consideration. The GEO [], SRA [] and BioProject [] databases from National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) were used as the major platform for data retrieval and collection.
2.2. Quality Control, Trimming and Alignment
The quality assessment of each sample present in each study was performed using FASTQC []. FASTQC is an analysis tool that performs quality control checks on raw sequence data derived from high-throughput sequencing pipelines. The low-quality reads and duplicated sequences were trimmed off from the sample sequence using Trimmomatic tool []. Trimmomatic tool performs different trimming jobs for illumine paired-end and single-ended data. FASTQC and Trimmomatic were accessed from the GALAXY platform [].
Each study of each sample was aligned to the reference genome of Homo sapiens (hg38) using HISAT2 []. HISAT2 is a fast and sensitive alignment program that is more than 50 times faster as compared to TopHat2 and requires moderate amount of storage. It gives better alignment quality than the pre-existing alignment tools. After alignment, the counts per million (CPM) of each transcript mapped onto the reference genome were estimated using FeatureCounts []. FeatureCounts is a program written in C language and is a part of Subread package that count reads for genomic features in SAM/BAM files. The GALAXY platform was again used to access these software.
2.3. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
The expression of genes in patient sample as compared to the control sample were analyzed using the EdgeR (empirical analysis of DGE in R) [] package of R Studio []. EdgeR is a software package that is part of Bioconductor project. The package is used for examining the differential expression of replicated count data. It uses the Poisson model for biological variability and empirical Bayes method for moderating the degree of overdispersion across transcripts which helps in increasing the reliability of results []. The significantly expressed genes in intellectual disability patients were identified through the p value and log fold change value. Genes defining adjusted p-value less than 0.05 were considered significantly expressed in relation to the study. Out of significantly expressed genes, the genes which have positive log2FoldChange are upregulated and genes with negative Log2FoldChange are considered to be down regulated.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data Retrieved
GEO and BioProject database of NCBI were browsed to select studies related to transcriptomic sequencing of intellectual disability patient. In each of the six studies, all samples were taken for the analysis. Table 1 lists the details of the studies selected for the analysis.

Table 1.
Details of study included for analysis.
3.2. Pre-Processing and Alignment
Each sample of all the studies was independently run through FASTQC to check the quality of the reads. The poor-quality reads and duplicated sequences were deleted. All the sequences included in the study were aligned with the human genome (hg39, 2013 release). The aligned sequences were further used to count the expression of genes in each sample using FeatureCounts tool from galaxy platform.
3.3. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
The meta-analysis of all the 60 samples was performed using EdgeR package of R Studio to identify DEGs. The aligned files were used to count the expression of each gene through the FeatureCounts tool available on the galaxy platform. The counts file generated from FeatureCounts was merged for meta-analysis. TMM method was used for the normalization of the complete raw data count file that calculates normalization factor representing sample specific biasness. DEG analysis was carried out using the normalized gene count file. For the identification of significantly expressed genes, the p-value was set to 0.05 and the positive log2foldchange value represented upregulated genes whereas a negative log2foldchange value represented downregulated genes. The meta-analysis studies done in the current study determined six upregulated genes and five downregulated genes which were significantly expressed in intellectual disability patients. Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 represent the results of EdgeR in the form of heatmap, BCV, and MA plot.
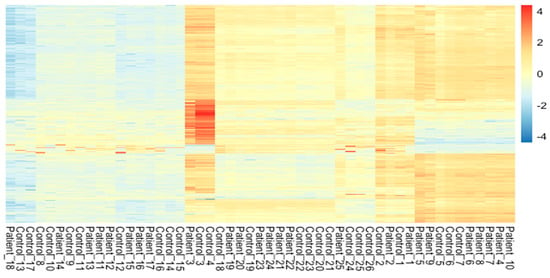
Figure 2.
Heatmap representing the results of EdgeR package.
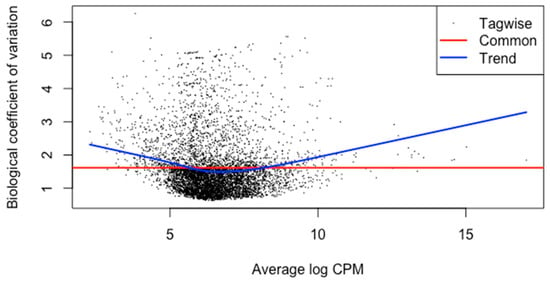
Figure 3.
BCV Plot representing the results of EdgeR package.
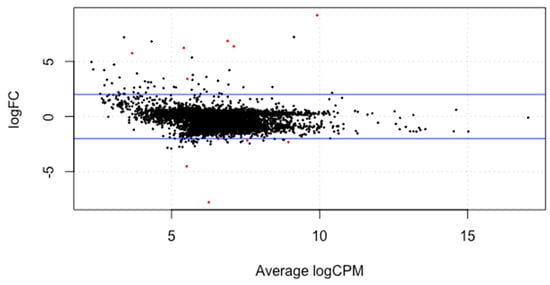
Figure 4.
MA plot representing the results of EdgeR package. Red spots represent the significantly expressed genes obtained in the study.
4. Conclusions
The present meta-analysis study identified 11 significant genes, out of which 6 are upregulated genes and 5 are downregulated genes. The upregulated genes include MTRNR2L1, L1CAM, PAPSS2, IGLV1-47, IGLV3-19, and IGKV1-16. The downregulated genes identified in the study include IGLV3-9, IGLV3-1, LSM14B, ZNF75D, and NOTCH1. These upregulated genes can play a significant role in the progression of intellectual disability. The increased levels of these genes in the fetal sample can be an indication of the possibility of occurrence of intellectual disability disorder. Thus, these genes can also act as a biomarker for the diagnosis of intellectual disability disorder.
Author Contributions
P.G., F.J. and P.S. contributed equally to the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The manuscript is found suitable for publication in the present state.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in the present study is available at NCBI.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L. Wold B: Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.F.; Levin, J.Z.; Vijayendran, K.; Sivachenko, A.; Adiconis, X.; Maguire, J.; Johnson, L.A.; Robinson, J.; Verhaak, R.G.; Sougnez, C.; et al. Integrative analysis of the melanoma transcriptome. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapaport, F.; Khanin, R.; Liang, Y.; Pirun, M.; Krek, A.; Zumbo, P.; Mason, C.E.; Socci, N.D.; Betel, D. Comprehensive evaluation of differential gene expression analysis methods for RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clough, E.; Barrett, T. The Gene Expression Omnibus Database. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1418, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leinonen, R.; Sugawara, H.; Shumway, M. International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration. The sequence read archive. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D19–D21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, T.; Clark, K.; Gevorgyan, R.; Gorelenkov, V.; Gribov, E.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Kimelman, M.; Pruitt, K.D.; Resenchuk, S.; Tatusova, T.; et al. BioProject and BioSample databases at NCBI: Facilitating capture and organization of metadata. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D57–D63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High throughput Sequence Data. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili, V.; EnisAfgan; Gu, Q.; Clements, D.; Blankenberg, D.; Goecks, J.; Taylor, J.; Nekrutenko, A. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2020 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 8205–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2013, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.J.; Chen, Y.; Smyth, G.K. Differential expression analysis of multifactor RNA-Seq experiments with respect to biological variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4288–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio; PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maduro, V.; Pusey, B.N.; Cherukuri, P.F.; Atkins, P.; du Souich, C.; Rupps, R.; Limbos, M.; Adams, D.R.; Bhatt, S.S.; Eydoux, P.; et al. Complex translocation disrupting TCF4 and altering TCF4 isoform expression segregates as mild autosomal dominant intellectual disability. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2016, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, F.L.; Girisha, K.M.; Hardigan, A.A.; Kortüm, F.; Shukla, A.; Alawi, M.; Dalal, A.; Brady, L.; Tarnopolsky, M.; Bird, L.M.; et al. Mutations in EBF3 Disturb Transcriptional Profiles and Cause Intellectual Disability, Ataxia, and Facial Dysmorphism. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 100, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriele, M.; Vulto-van Silfhout, A.T.; Germain, P.L.; Vitriolo, A.; Kumar, R.; Douglas, E.; Haan, E.; Kosaki, K.; Takenouchi, T.; Rauch, A.; et al. YY1 Haploinsufficiency Causes an Intellectual Disability Syndrome Featuring Transcriptional and Chromatin Dysfunction. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 100, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Khan, K.; Armfield-Uhas, K.; Srikanth, S.; Thompson, N.A.; Pardo, M.; Yu, L.; Norris, J.W.; Peng, Y.; Gripp, K.W.; et al. Mutations in FAM50A suggest that Armfield XLID syndrome is a spliceosomopathy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).