Adaptive Importance Sampling for Equivariant Group-Convolution Computation †
Abstract
1. Introduction and Motivations
2. Group Convolution and Expectation
3. Adaptive Importance Sampling
3.1. Monte Carlo Estimator and Convergence
3.2. Natural Gradient Descent
3.3. About IGO Algorithms
4. Application to -Convolutions
4.1. Fisher Information Metric
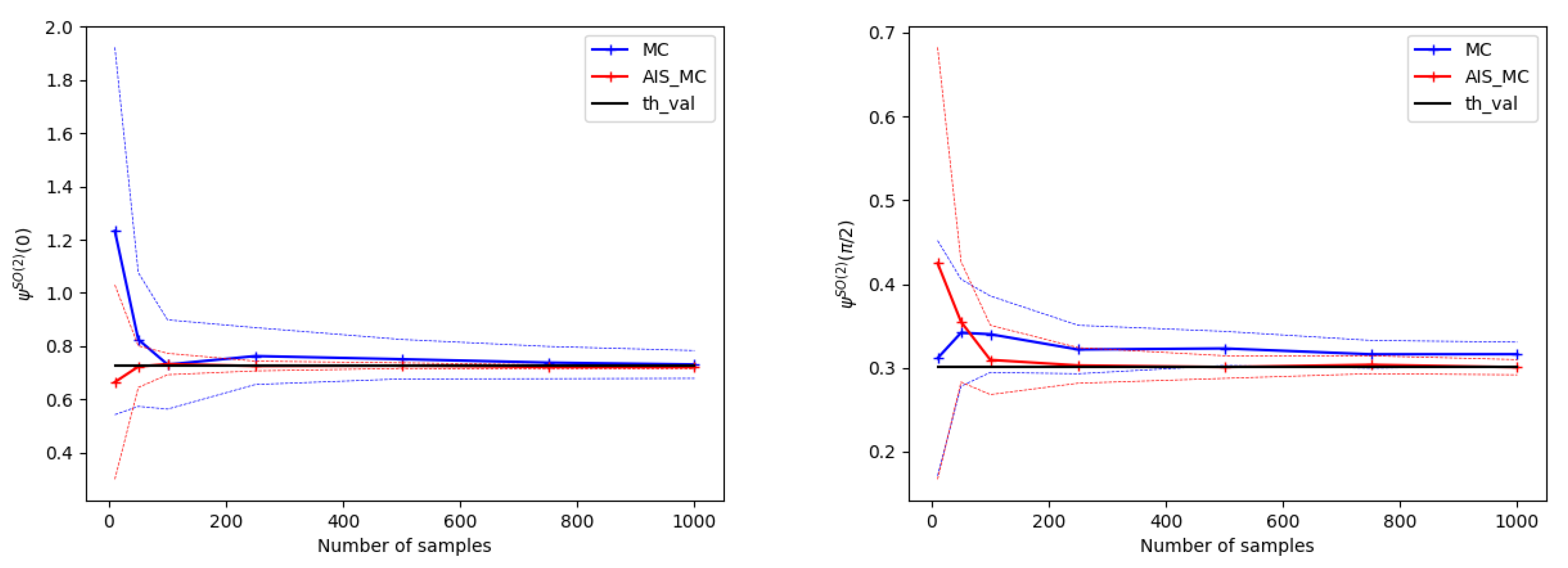
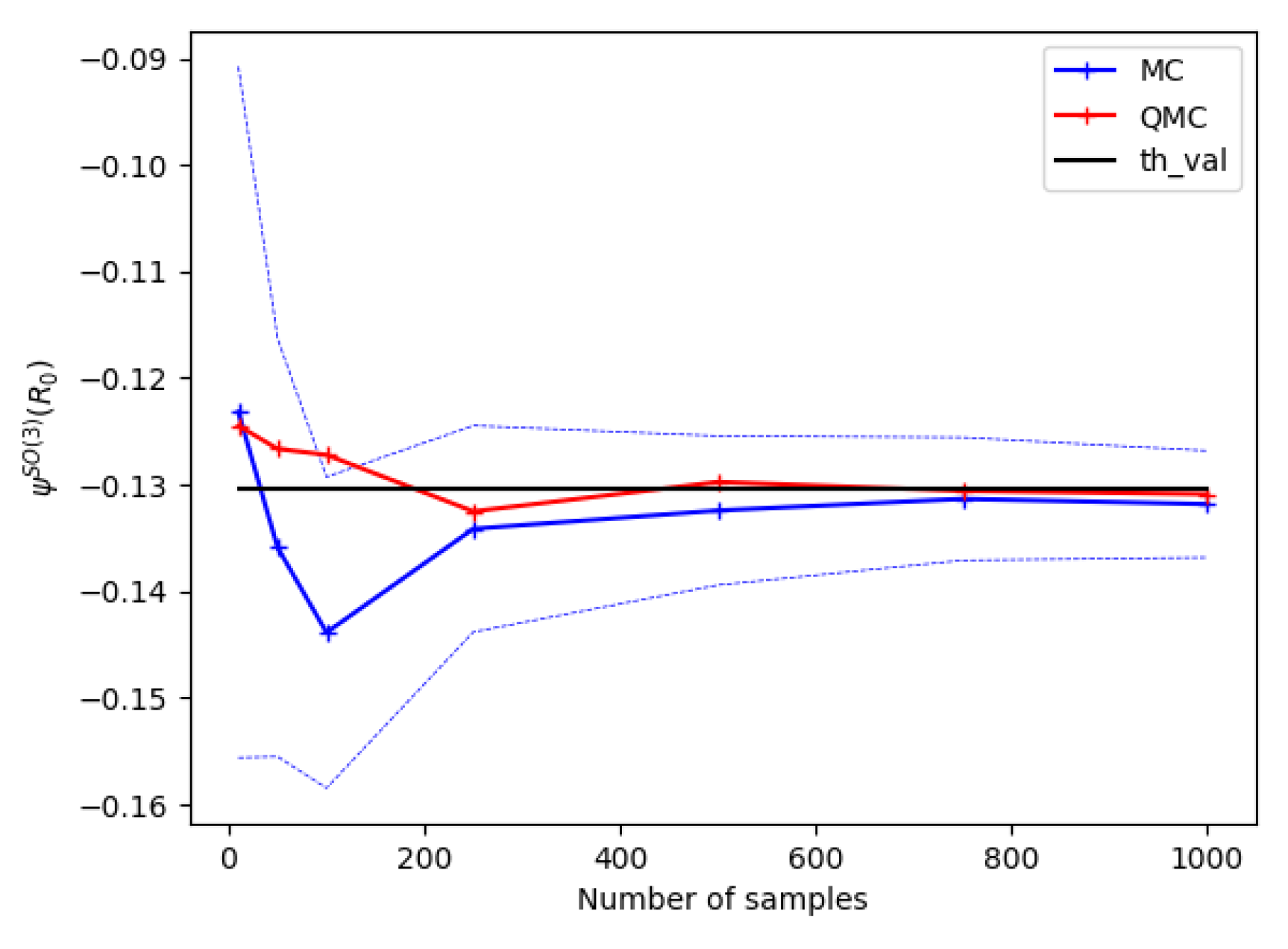
4.2. Numerical Experiments
4.3. Extension to -Convolutions
5. Monte Carlo Methods in the Quantum Set-Up
6. Conclusions and Further Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bronstein, M.M.; Bruna, J.; Cohen, T.; Veličković, P. Geometric Deep Learning: Grids, Groups, Graphs, Geodesics, and Gauges. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.13478. [Google Scholar]
- Finzi, M.; Stanton, S.; Izmailov, P.; Wilson, A.G. Generalizing Convolutional Neural Networks for Equivariance to Lie Groups on Arbitrary Continuous Data. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.12880. [Google Scholar]
- Lafarge, M.W.; Bekkers, E.J.; Pluim, J.P.W.; Duits, R.; Veta, M. Roto-Translation Equivariant Convolutional Networks: Application to Histopathology Image Analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.08725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, T.S.; Geiger, M.; Köhler, J.; Welling, M. Spherical CNNs. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.10130. [Google Scholar]
- Gerken, J.E.; Aronsson, J.; Carlsson, O.; Linander, H.; Ohlsson, F.; Petersson, C.; Persson, D. Geometric Deep Learning and Equivariant Neural Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.13926. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Dobriban, E.; Lee, J.H. A Group-Theoretic Framework for Data Augmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1907.10905. [Google Scholar]
- Kondor, R.; Trivedi, S. On the Generalization of Equivariance and Convolution in Neural Networks to the Action of Compact Groups. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; Dy, J., Krause, A., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 80, pp. 2747–2755. [Google Scholar]
- Lagrave, P.Y.; Cabanes, Y.; Barbaresco, F. SU(1,1) Equivariant Neural Networks and Application to Robust Toeplitz Hermitian Positive Definite Matrix Classification. In Geometric Science of Information; Nielsen, F., Barbaresco, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- Finzi, M.; Welling, M.; Wilson, A.G. A Practical Method for Constructing Equivariant Multilayer Perceptrons for Arbitrary Matrix Groups. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.09459. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, T.S.; Geiger, M.; Weiler, M. A General Theory of Equivariant CNNs on Homogeneous Spaces. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., Alché-Buc, F., Fox, E., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 32, pp. 9145–9156. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, T.; Welling, M. Group Equivariant Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; Balcan, M.F., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 48, pp. 2990–2999. [Google Scholar]
- Egloff, D.; Leippold, M. Quantile estimation with adaptive importance sampling. Ann. Stat. 2010, 38, 1244–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ollivier, Y.; Arnold, L.; Auger, A.; Hansen, N. Information-Geometric Optimization Algorithms: A Unifying Picture via Invariance Principles. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 18, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrave, P.Y.; Barbaresco, F. Generalized SU(1,1) Equivariant Convolution on Fock-Bargmann Spaces for Robust Radar Doppler Signal Classification. 2021; working paper or preprint. [Google Scholar]
- von Mises, R. Uber die “Ganzzahligkeit” der Atomgewicht und verwandte Fragen. Phys. Z. 1981, 19, 490–500. [Google Scholar]
- Amari, S.I.; Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E.; Kass, R.E.; Lauritzen, S.L.; Rao, C.R. Differential Geometry in Statistical Inference; Lecture Notes–Monograph Series; Institute of Mathematical Statistics: Hayward, CA, USA, 1987; Volume 10, pp. 1–240. [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro, A. Quantum speedup of Monte Carlo methods. Proc. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 471, 20150301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, S. Quantum Monte-Carlo Integration: The Full Advantage in Minimal Circuit Depth. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.09100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Linden, N.; Liu, J.P.; Montanaro, A.; Shao, C.; Wang, J. Quantum-accelerated multilevel Monte Carlo methods for stochastic differential equations in mathematical finance. Quantum 2021, 5, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelazo, G.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Palma, G.D.; Englund, D.; Lloyd, S.; Kiani, B.T. Quantum algorithms for group convolution, cross-correlation, and equivariant transformations. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botev, Z.; Ridder, A. Variance Reduction. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdain, B. Adaptive variance reduction techniques in finance. Adv. Financ. Model. 2009, 8, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, H.; Monro, S. A Stochastic Approximation Method. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Lagrave, P.Y. On the Benefits of SO(3)-Equivariant Neural Networks for Spherical Image Processing. 2022, working paper or preprint. 2022; working paper or preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, J.T. The Fisher-Bingham Distribution on the Sphere. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. (Methodol.) 1982, 44, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederreiter, H. Random Number Generation and Quasi-Monte Carlo Methods; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol’, I. On the distribution of points in a cube and the approx imate evaluation of integrals. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 1967, 7, 86–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orús, R.; Mugel, S.; Lizaso, E. Quantum computing for finance: Overview and prospects. Rev. Phys. 2019, 4, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, G.; Høyer, P.; Mosca, M.; Tapp, A. Quantum amplitude amplification and estimation. Contemp. Math. 2002, 305, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaresco, F. Lie Group Statistics and Lie Group Machine Learning Based on Souriau Lie Groups Thermodynamics & Koszul-Souriau-Fisher Metric: New Entropy Definition as Generalized Casimir Invariant Function in Coadjoint Representation. Entropy 2020, 22, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larocca, M.; Sauvage, F.; Sbahi, F.M.; Verdon, G.; Coles, P.J.; Cerezo, M. Group-Invariant Quantum Machine Learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.02261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.J.; Mularski, M.; Gil-Fuster, E.; Mele, A.A.; Arzani, F.; Wilms, A.; Eisert, J. Exploiting symmetry in variational quantum machine learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.06217. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lagrave, P.-Y.; Barbaresco, F. Adaptive Importance Sampling for Equivariant Group-Convolution Computation. Phys. Sci. Forum 2022, 5, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2022005017
Lagrave P-Y, Barbaresco F. Adaptive Importance Sampling for Equivariant Group-Convolution Computation. Physical Sciences Forum. 2022; 5(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2022005017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLagrave, Pierre-Yves, and Frédéric Barbaresco. 2022. "Adaptive Importance Sampling for Equivariant Group-Convolution Computation" Physical Sciences Forum 5, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2022005017
APA StyleLagrave, P.-Y., & Barbaresco, F. (2022). Adaptive Importance Sampling for Equivariant Group-Convolution Computation. Physical Sciences Forum, 5(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2022005017






