Abstract
This review discusses the principle of typical bandgap reference circuits and analyzes their sources of errors. In order to provide readers with a clear perspective, we categorize the error sources into four types: (a) amplifier offset; (b) high-order nonlinearity of ; (c) current mirror mismatch; and (d) other error sources. For these error sources, the most commonly used methods to reduce or minimize them to achieve high accuracy are summarized. Furthermore, this review explores sub-1V bandgap reference design techniques, addressing the increasing demand for low-power and low-voltage applications. Finally, we provide some suggestions for a future high-accuracy reference design.
1. Introduction
The bandgap reference (BGR) is a critical component used in analog and mixed-signal circuits, such as A/D data converters, phase-locked loops, DRAMs, and supply voltage regulators [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. It can generate a stable reference voltage or current for maintaining the performance of circuits across varying operating conditions because of its temperature independence. The accuracy of the bandgap reference limits the accuracy of the circuits mentioned above. Therefore, a high-accuracy bandgap reference is necessary.
The principle of a bandgap reference is summing the proportional-to-absolute temperature (PTAT) signal and a complementary-to-absolute temperature (CTAT) signal in a certain proportion to obtain a temperature-independent voltage or current. However, the output voltage or current of the bandgap reference is not strictly temperature-independent. Quite a few factors contribute to the temperature drift of the output such as the process variation [1,12]; the nonlinearity of [1,4,6,12], which is the base-emitter voltage of BJTs and used as the CTAT term; the variation in the common emitter current gain () of the BJT [12,13,14]; and the offset and noise of the error amplifier [1,12,13,14,15].
In this paper, we summarize the factors that influence the accuracy of the bandgap reference as well as the corresponding solutions proposed by former researchers. The reminder of the paper is organized as follows. The principle of the bandgap reference is introduced in Section 2. The sources of errors are discussed in Section 3, and the techniques to reduce or minimize them are presented in Section 4. The sub-1V references are presented in Section 5. Finally, the conclusion is drawn in Section 6.
2. Principle of Bandgap Reference
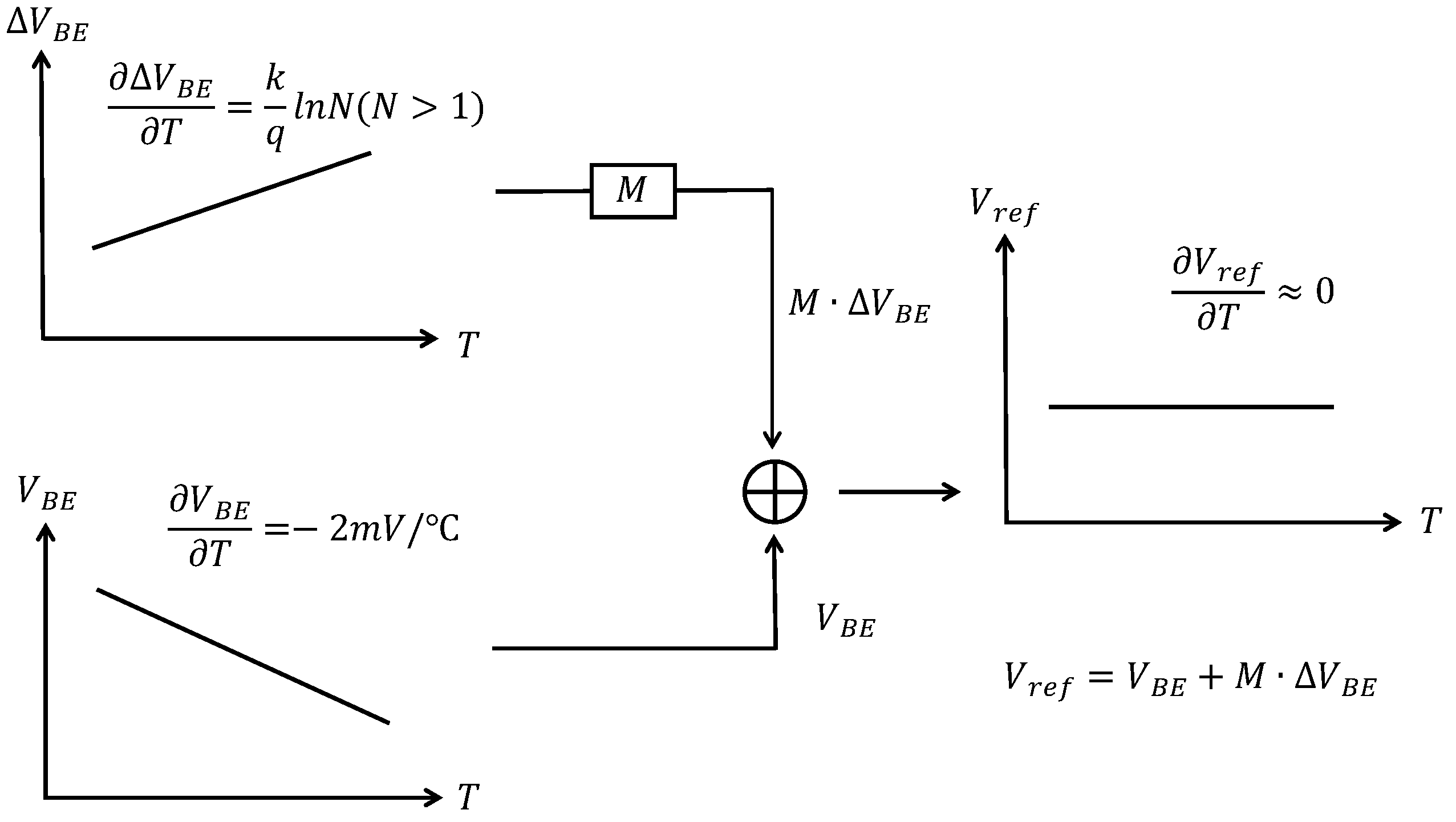
The main idea of a bandgap reference is to sum a PTAT signal and a CTAT signal in a certain proportion to reduce the temperature coefficient (TC) of the reference voltage, as shown in Figure 1. BJT-based bandgap references are the most widely used as they are insensitive to PVT variations [3,16,17]. The base-emitter voltage () of a BJT has a negative TC, while the difference in between two BJTs biased at different current densities has a positive TC. We could obtain a theoretically zero-TC reference voltage by designing a circuit which combines and in a proper proportion. Also, there has been a lot of research on -based CMOS voltage references for low supply voltage and low power consumption. However, -based references always suffer from poor accuracy, as is sensitive to process variations [16,17,18,19]. Therefore, -based references are not suitable for high-accuracy applications.
Figure 1.
Ideal bandgap reference.
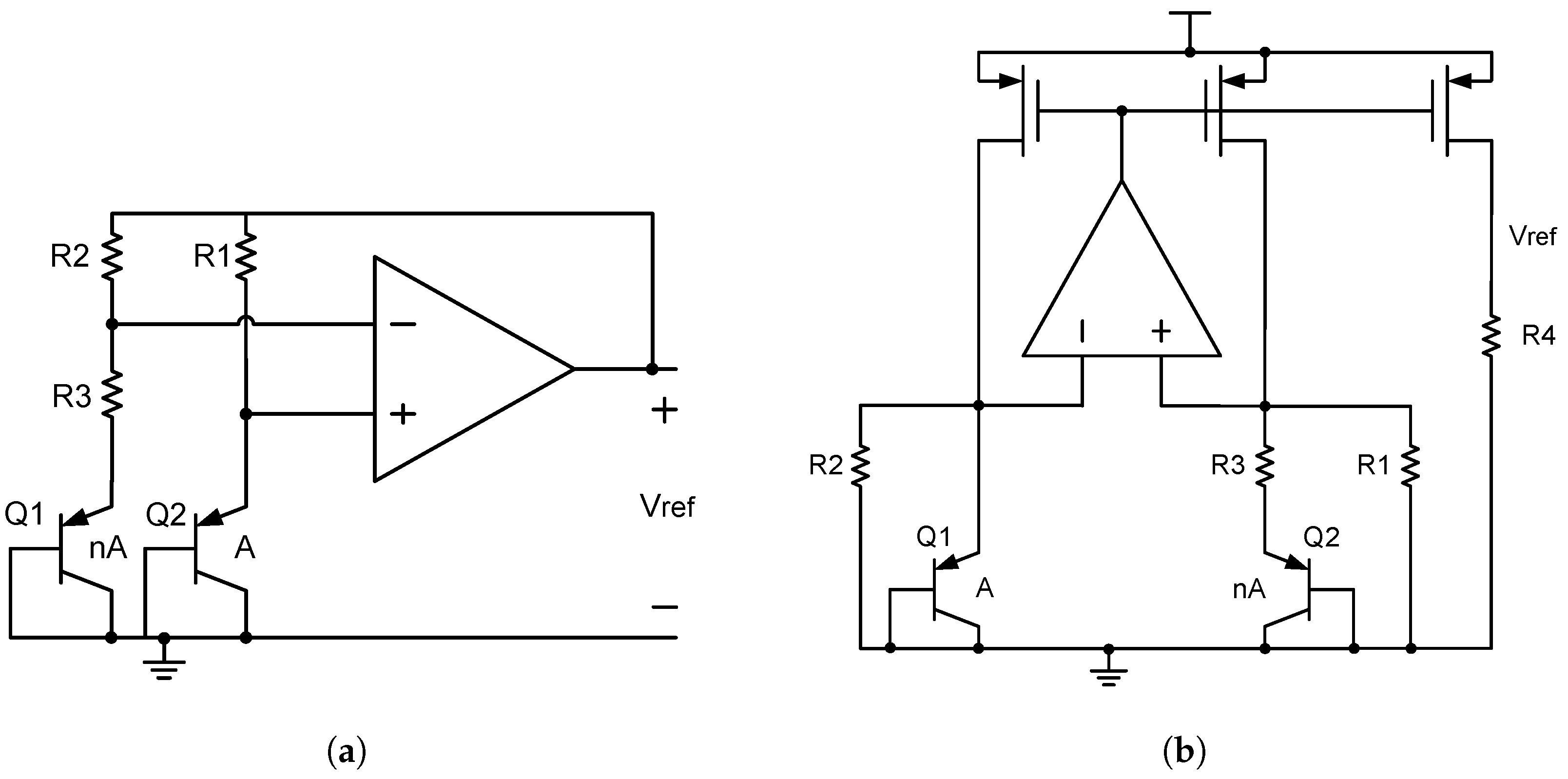
BJT-based bandgap references developed to date can be divided into two categories, i.e., voltage-mode BGRs, proposed by Kuijk [20]; and current-mode BGRs, proposed by Banba [9]. The main difference between them is that the PTAT signal and the CTAT signal are summed in either the voltage mode or the current mode, as shown in Figure 2a,b. A voltage-mode BGR has a reference voltage of about 1.25 V [8], and it usually works with a relatively high supply voltage. A current-mode BGR allows for operation under a low supply voltage, thus possibly resulting in less power consumption. Since its reference voltage is not limited to around 1.25 V, it can be used in sub-1V designs. In addition, voltage-mode BGRs have only two operating points, while current-mode BGRs have more operating points due to their symmetry. Therefore, the start-up circuit of a voltage-mode BGR is easier than for a current-mode BGR [5,8]. Some researchers also proposed a mixed-mode BGR to obtain a sub-1V voltage reference as well as to decrease the number of operating points [8].
Figure 2.
(a) Classic voltage-mode BGR; and (b) classic current-mode BGR.
The output voltage in Figure 2a can be expressed as
where is the thermal voltage.
Apart from that, the output voltage in Figure 2b can be expressed as
3. Sources of Errors
There are many factors that affect the output accuracy of BGRs. Among them, the most significant factors are the operational amplifier offset, nonlinearity of , and current mirror mismatch in most cases.
3.1. Amplifier Offset
An amplifier is usually indispensable in the design of a BGR. We use the “virtual short” characteristic of the input terminals of the operational amplifier (opamp) to force the voltages between two nodes to be equal. However, the opamp has input offset [1,4,5,6,8,12,13,14,15,17,21], that is, the input voltage difference is unexpectedly not zero, which contributes to the output of the BGR. When the offset of the amplifier is considered, the output voltage in Figure 2a can be expressed as
and the output voltage in Figure 2b can be expressed as
3.2. High-Order Nonlinearity of
The I-V characteristic of a diode-connected BJT can be expressed as [6,22,23]
where A is the emitter area, and are both process-dependent constants, T is the absolute temperature, and is the bandgap voltage at T and can be modeled as [6,22,23]
where is the bandgap voltage at 0 K, and and are temperature-independent parameters. Equation (5) can be equivalently rewritten in logarithmic form as follows [22,24]:
Usually, we use a linear approximation to estimate :
where is an extrapolated bandgap voltage at 0 K, and a is a constant.
Combining Equations (7) and (8), if is proportional to , the base-emitter voltage can be expressed as [1,4,6,12,13,22,24]
where is the base-emitter voltage at the reference temperature, and is the order of temperature dependency of the collector current. In this equation, is the first-order temperature-dependent term, which can be compensated by a PTAT source, and is the high-order nonlinearity, which contributes to the systematic output variation and thus must be canceled or at least reduced in order to obtain a high-accuracy reference [25]. If we express in the form of the tangent at the temperature plus a nonlinear term, then can be expressed as
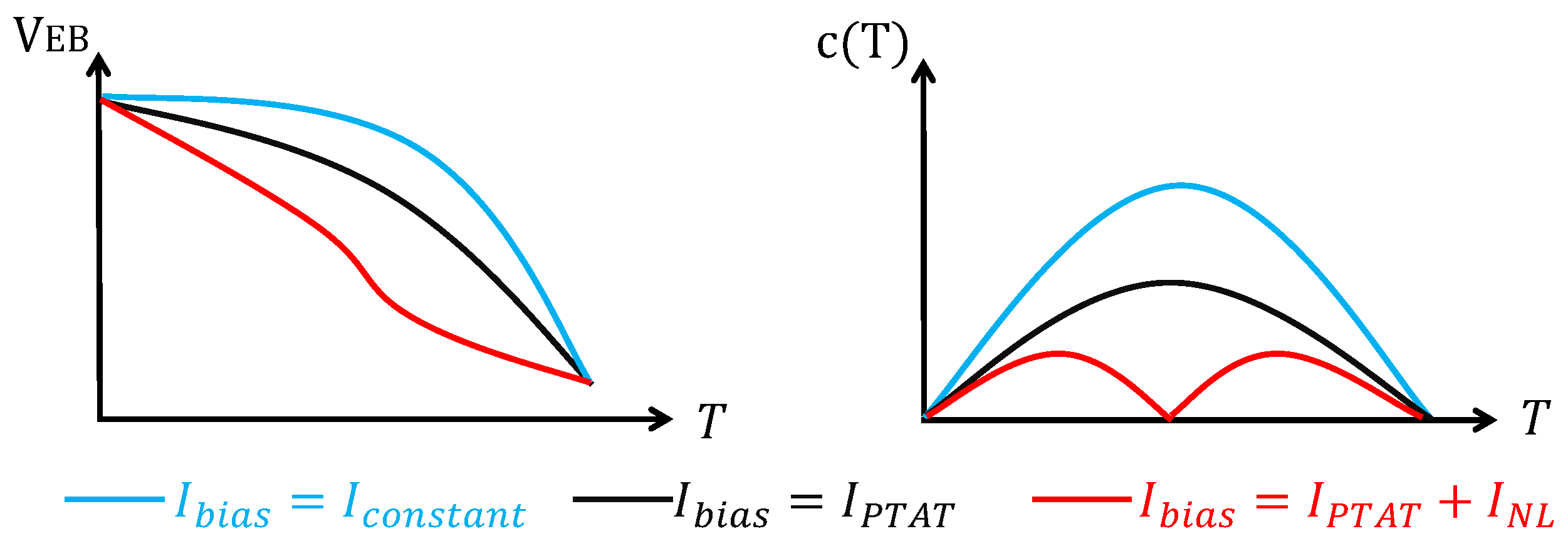
where is the slope of the tangent at the temperature , and is a nonlinear term that can be expressed as
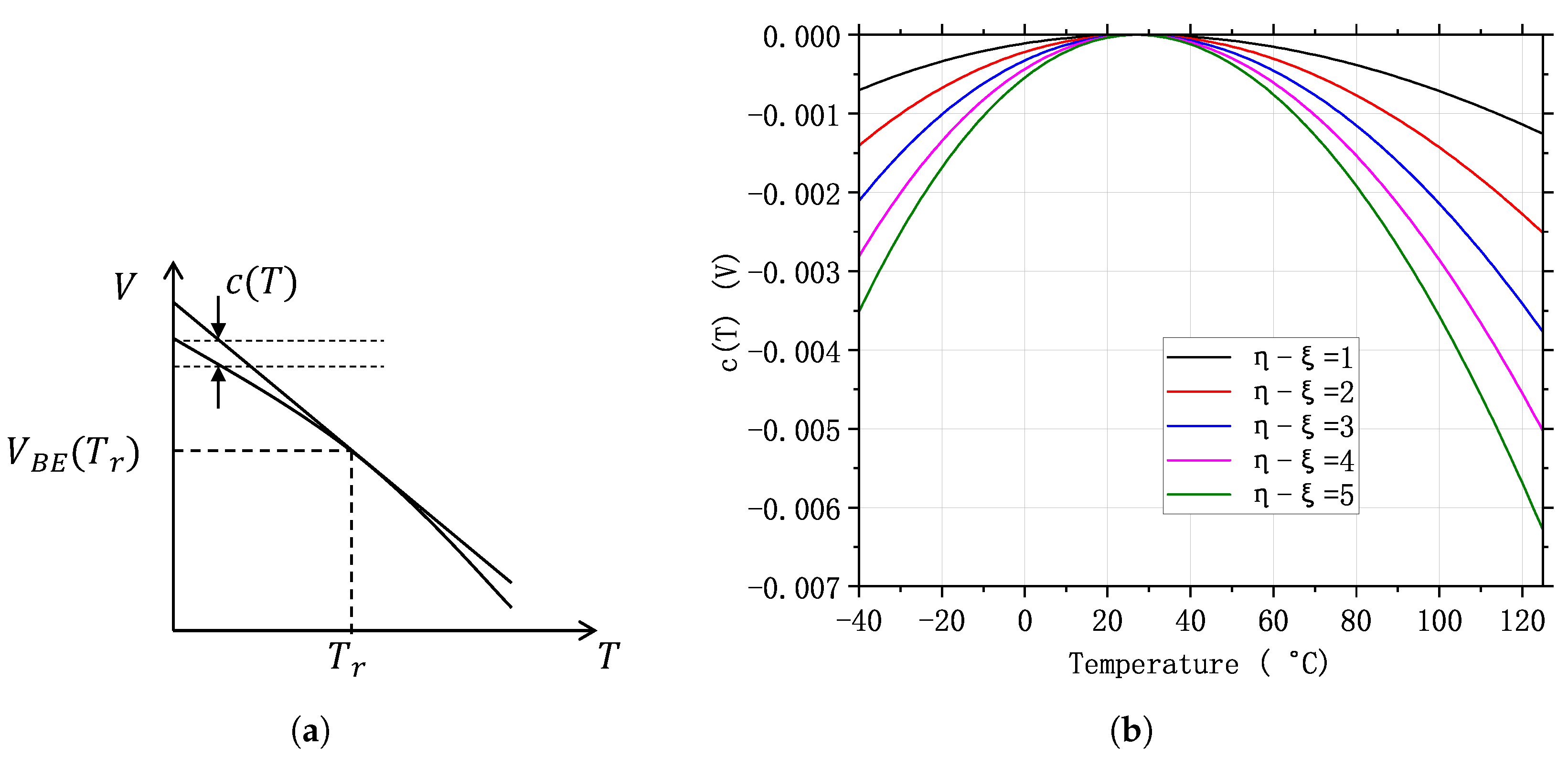
Figure 3a shows a and its tangent at [26]; and Figure 3b shows the at a reference temperature C and a temperature range C to C [26]. It can be seen that the larger is, the smaller will be. Due to this reason, it is desirable to have a larger . Nevertheless, this means that we need to generate a current that changes with temperature with a higher-order relationship. And this is usually not easy to realize. Therefore, a more practical way is to use a PTAT current to bias the BJT ().
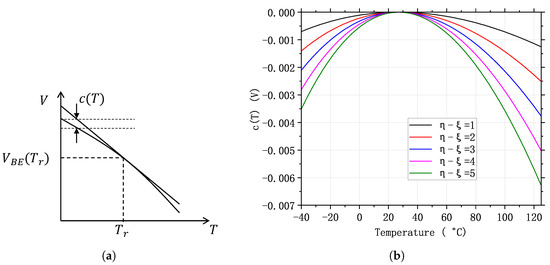
Figure 3.
(a) and its tangent at ; and (b) curves of c(T) under different biasing currents.
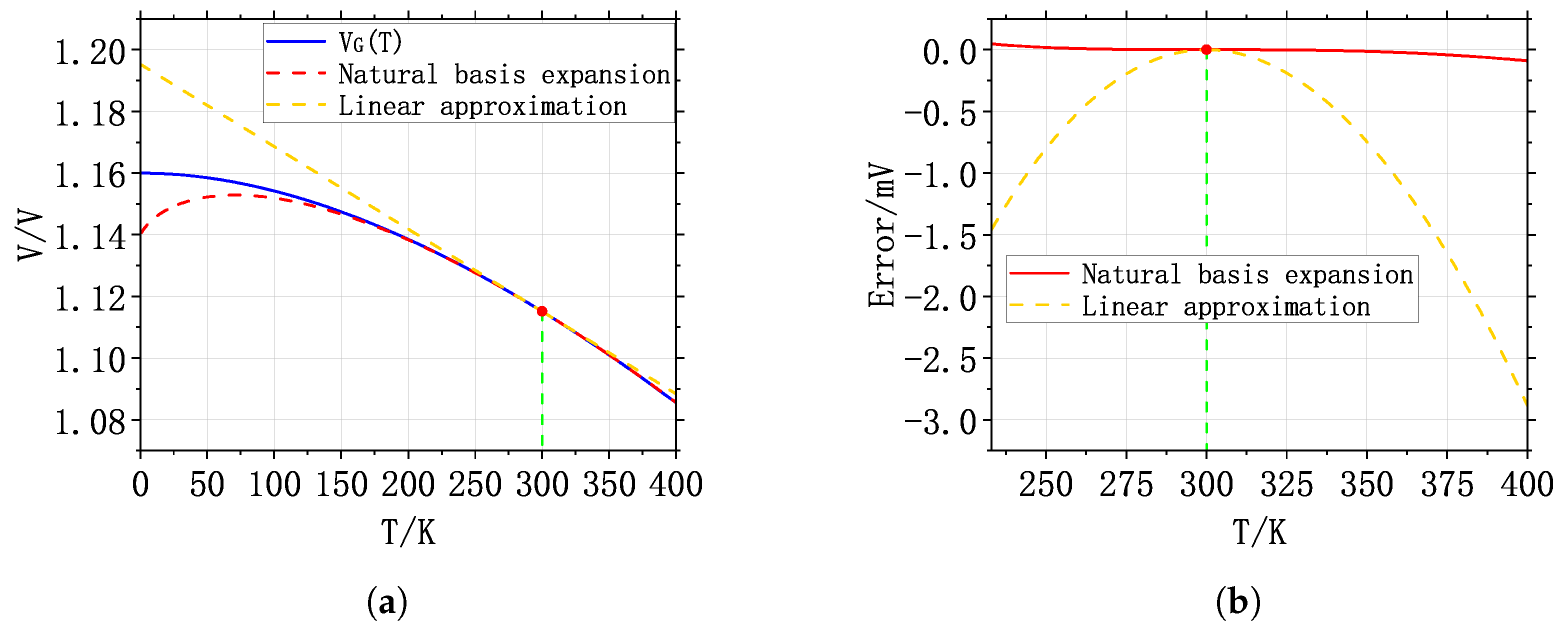
Although the above discussion is useful, Equation (8) may not be accurate enough in some cases. For example, in the design of some ultra-high-accuracy C BGRs, the is expanded by two basis functions, T and , instead of Equation (8). This method of expansion is more accurate and is called the natural basis expansion [6,22,23]. In this circumstance, can be approximated in the following way [22]:
where a and b are temperature-independent coefficients.
For easy understanding, the fitting curves of Equations (8) and (12) are shown in Figure 4a, and the fitting error is shown in Figure 4b [22].
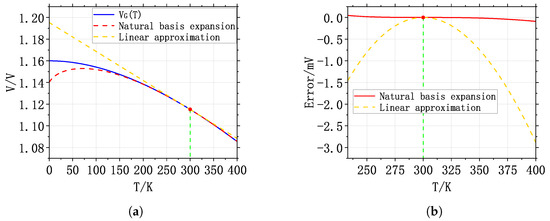
Figure 4.
(a) and its fitting curves and (b) fitting error.
3.3. Current Mirror Mismatch
The mismatch of CMOS current mirrors is mainly caused by variations in the threshold voltage and current gain (), both of which are influenced by the temperature and process [3]. Specifically, the current mirror mismatch can be expressed as follows [3,27]:
where is the mismatch coefficient of the threshold voltage; is the mismatch coefficient of the current gain ; W and L are the channel width and length of transistor, respectively; and is the transistor current efficiency in the strong inversion region. Because in the strong inversion region, the current mirror mismatch can be re-written as [3]
It can be seen in Equation (15) that to reduce the current mirror mismatch, we can increase the transistor size or increase the drain current. Nevertheless, an increased size means a larger chip area, and an increased drain current means a larger power consumption and a higher supply voltage. Therefore, there is a trade-off in the circuit design, since it is desirable to have a smaller area, a lower power consumption, and a lower supply voltage. On the other hand, if the drain current is so small that the transistor enters the sub-threshold region, then the current mirror mismatch will increase significantly. This is because there is an exponential relationship between the drain current and the gate-source voltage at this moment, and any small changes in the threshold voltage can be exponentially amplified, which leads to significant changes in the current. This should be avoided in a high-accuracy design.
Usually, a current mirror mismatch is undesirable. For example, it can result in variations in the current ratio, leading to a non-PTAT error in the generated PTAT current as well as the final reference voltage [12].
3.4. Other Error Sources
3.4.1. Variation in Saturation Current
The base-emitter voltage of a BJT is closely related to its saturation current and its collector current . Due to this reason, if deviates from its nominal value under process variations, then the can be influenced as well. The following equation shows this phenomenon [12]:
It can be assumed that is process-dependent but temperature-independent. And therefore, the saturation current spread results in a PTAT error in , which can be reduced by a PTAT trim [12].
3.4.2. Resistor Mismatch
The mismatch of and in Figure 2a can influence the by changing the . If we define the mismatch as a fractional deviation , then the can be written as [12]
As can be seen, since is mainly temperature-independent, it only results in a PTAT error in as well, which can also be reduced by a PTAT trim [12].
3.4.3. Finite Current Gain
The limited BJT current gain also affects the accuracy of the BGR. Especially, is usually small in standard CMOS technology [28] and it can easily vary with temperature and process. Under this circumstance, the can be expressed in the following way [12]:
where is the emitter current of the BJT. It can be seen in the above equation that the variation results in a non-PTAT error which cannot be canceled by a PTAT trim. This non-PTAT error is also one of the factors that limits the accuracy of a single-trim BGR.
3.4.4. Parasitic Base Resistance
The parasitic base resistance also affects the output of a BGR. If both the parasitic base resistance and are taken into account, then the can be rewritten as follows [14]:
where is the parasitic base resistor of the BJT. Similar to variations, this error is also non-PTAT and it is also a factor that limits the accuracy of a single-trim BGR.
4. Methods for Eliminating the Error Sources
In order to improve the accuracy of the BGR, the following summarizes the commonly used solutions to cancel out the error sources.
4.1. Techniques to Reduce the Amplifier Offset
4.1.1. Self-Biasing Technique
The self-biasing technique [5,8,13,29,30,31,32] is a circuit design method that allows key components in a circuit, such as operational amplifiers or other active components, to automatically adjust their operating points without an extra biasing circuit. This technique is sometimes suitable for analog circuits that require high accuracy and robustness, such as bandgap reference circuits, as they can maintain a consistent performance under different operating conditions and under PVT variations.
In bandgap reference circuits, the self-biasing technique can reduce system errors caused by device mismatches through ensuring current density matching within the circuit. Specifically, the self-biasing technique can reduce the system offset of operational amplifiers.
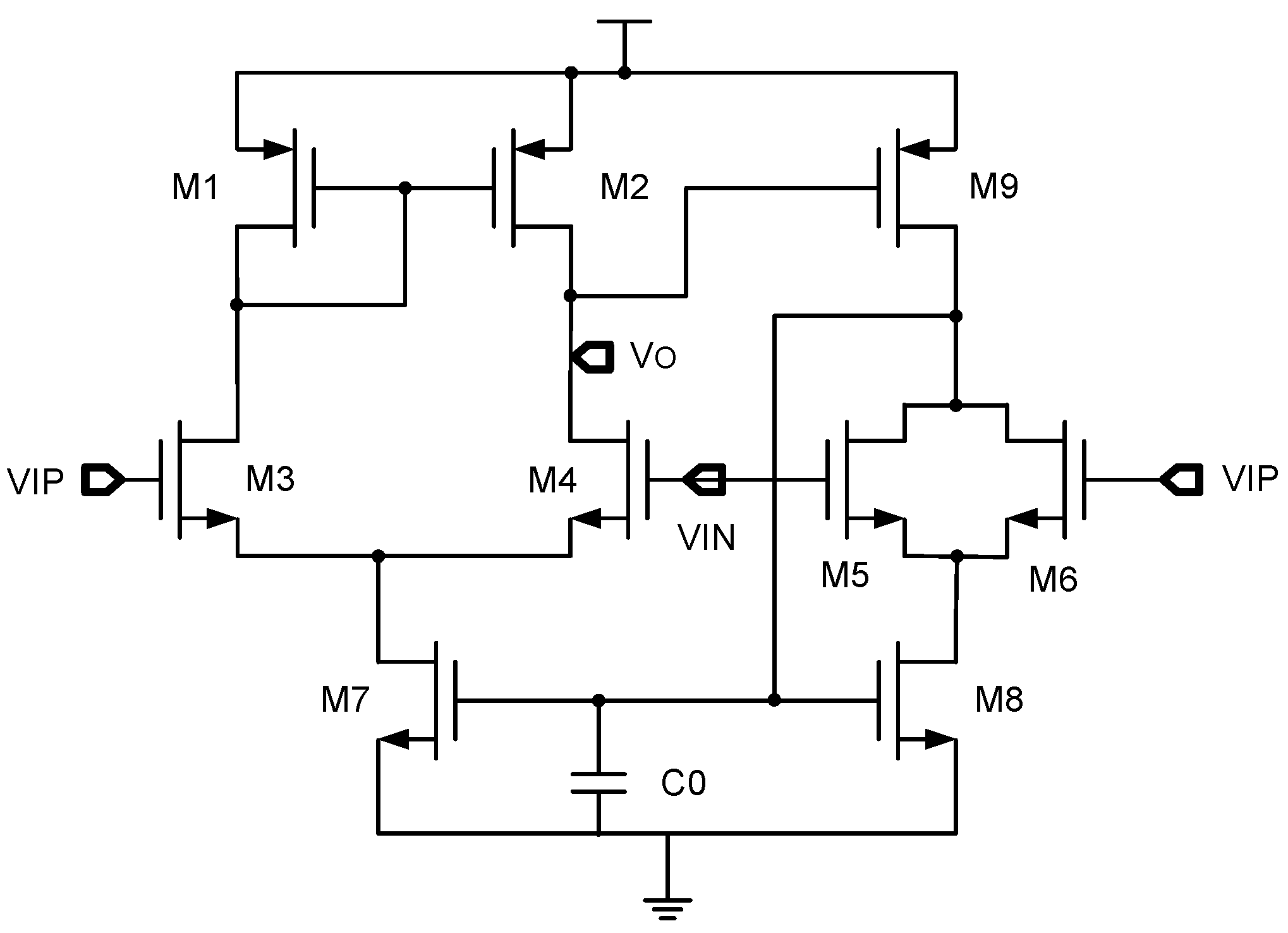
In operational amplifiers, the input stage is typically composed of a pair of differential transistors that require precise matching in order to ensure the circuit performance, such as a low input-referred offset and a good common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR). Nevertheless, in an actual manufacturing process, even transistors on the same chip may have slight differences in their physical parameters, which leads to mismatched current density of input-stage transistors, and thus affects the performance of the circuit. In the design of operational amplifiers, for example, in Figure 5, the self-biasing technique [5] helps control the biasing point of the amplifier by using the output of the circuit to guarantee that the circuit operates in the optimal linear region. This typically involves using a negative feedback loop that detects the current at the output or detects the internal nodes of the amplifier, and thus adjusts the bias circuit to maintain the desired current density or operating point [5,33].
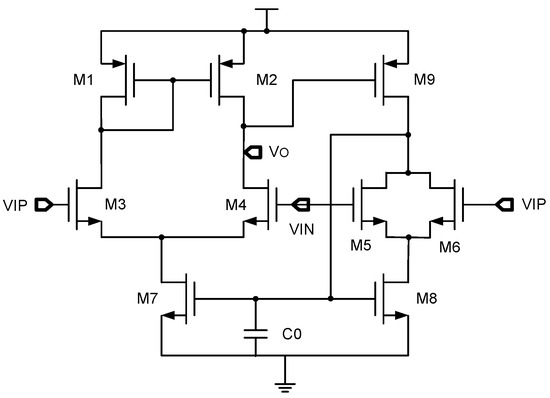
Figure 5.
Typical self-biased opamp.
4.1.2. Chopping Technique
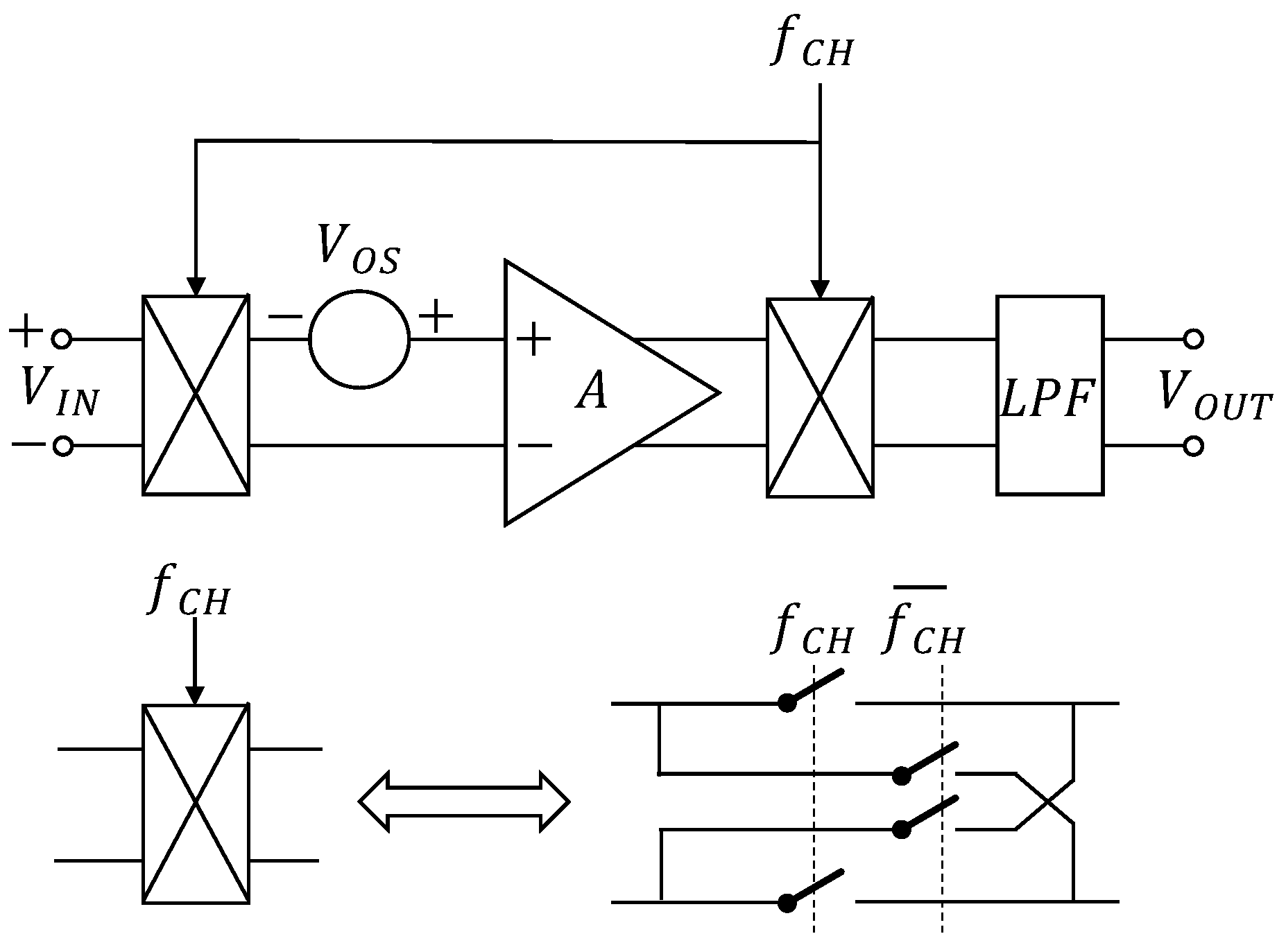
The chopping technique is often used to reduce the random offset or low-frequency noise of error opamp [5,12,34,35,36,37]. The principle of the chopping technique is to perform a square-wave modulation on the input signal before inputting it into the operational amplifier, and then to perform a square-wave modulation on the output of the operational amplifier. During the entire process, the input signal is modulated twice, but the offset signal or low-frequency noise is modulated only once. This helps demodulate the input signal and modulate the offset and low-frequency noise to a high frequency [34,38]. Finally, after filtering, an amplified input signal can be obtained, which realizes the elimination of offset and low-frequency noise. The principle of the chopping technique [12] is shown in Figure 6, where is the clock frequency, A is the gain of the opamp, and LPF is a low-pass filter.
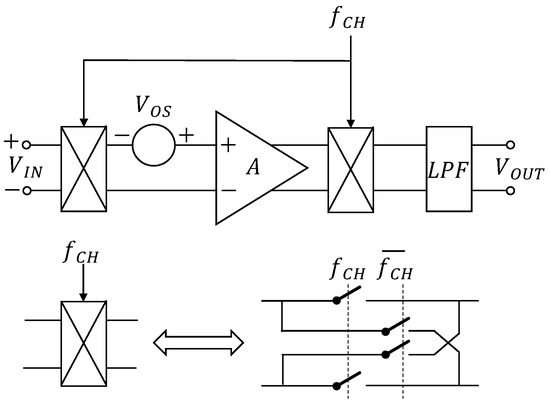
Figure 6.
Chopping technique.
4.1.3. Auto-Zeroing Technique
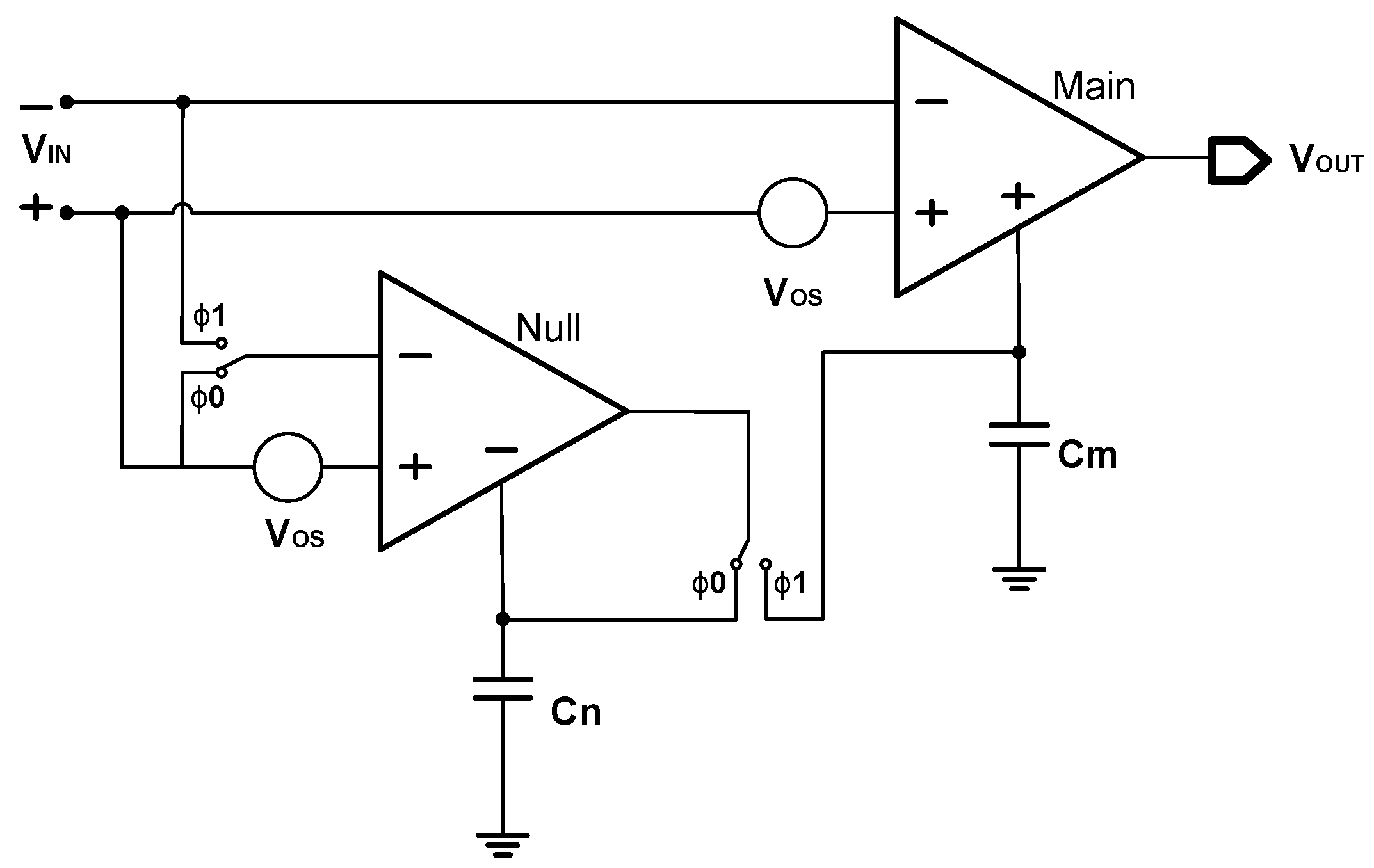
The basic principle of the auto-zeroing technique [1,14,35,37,38,39] is to sample the unwanted offset voltage and subtract it from the input signal or output signal [38]. A typical continuous-output auto-zeroing amplifier [1,38] is shown in Figure 7. It includes two amplifiers, one of which is the main amplifier and the other is the nulling amplifier, also known as the auxiliary amplifier or zeroing amplifier. The auto-zeroing process consists of at least two successive phases. In the first phase, , the nulling amplifier is disconnected from the main amplifier and its input ports are shorted to perform its own auto-zeroing operation. As a result, its auto-zeroing correction signal is generated and held on the capacitor for its nulling amplifier correction. In the second phase, , the nulling amplifier is connected in parallel with the main amplifier to obtain its input offset and to generate another correction signal . This correction signal is held on the capacitor for the main amplifier correction [39]. Finally, an output without offset is realized.
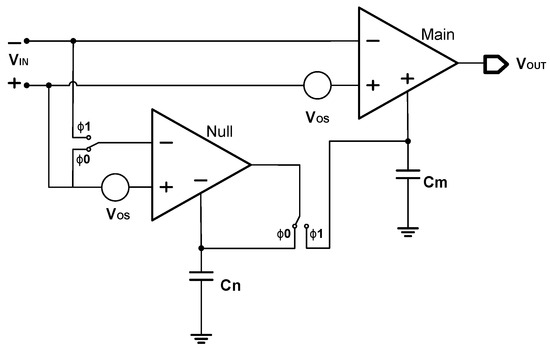
Figure 7.
Auto-zeroing technique.
Overall, the core idea of the auto-zeroing technique is to store the offset voltage on a capacitor and use it to eliminate the offset voltage later. Therefore, it is also known as the offset storage technique.
As mentioned above, the auto-zeroing technique is useful, but it needs a nulling amplifier, which consumes energy. Especially, if there are many main amplifiers, then each main amplifier will need a nulling amplifier, wasting a lot of energy. To solve this issue, ref. [1] proposed a shared offset cancellation method to share the same nulling amplifier among different main amplifiers, so that energy, as well as die area, could be saved.
4.1.4. Switched-Capacitor Bandgap Reference
Another idea to cancel out the amplifier offset is to use a switched-capacitor bandgap reference. For example, if the amplifier offset is difficult to eliminate for some reason, then a bandgap reference without an amplifier can be used. In this situation, a switched-capacitor bandgap reference (SCBGR) [31,35,40,41] is a possible solution. Usually, SCBGRs are based on sampling. This means that, in the first phase, we can first sample the voltages through capacitors, and then, in the second phase, the operation of summation or subtraction can be performed on the sampled voltages by using the charge redistribution of capacitors. Since, in this operation, it is not necessary to use an amplifier, the amplifier offset is no longer a problem either. Here, for easy understanding, this technique is illustrated with the circuit of [31], as shown in Figure 8.
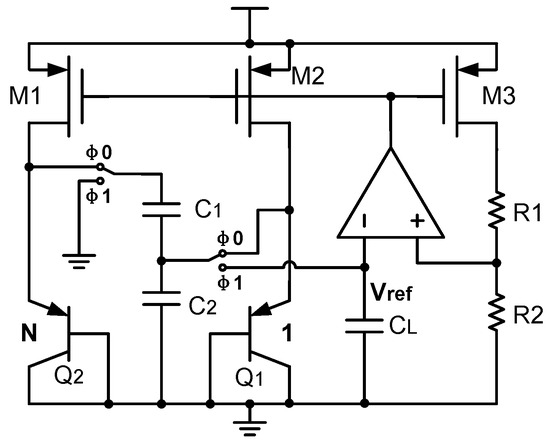
Figure 8.
Switched-capacitor bandgap reference.
This technique can be understood easily by looking at the expression of reference voltage. Usually, the reference voltage is expressed in the following way:
For easy understanding, this expression can be rewritten as follows:
As can be seen, the reference voltage is a scaled subtraction of two base-emitter voltages of BJTs with different current densities [31]. To realize this scaled subtraction, Figure 8 shows the switched-capacitor bandgap reference in [31]. It is controlled by clock signals. In the first phase, , the voltage is sampled onto the capacitor , while the voltage is sampled onto the capacitor . After that, in the second phase, , the capacitors , , and are connected together, so that there is a charge redistribution among these capacitors. As a result, a is generated that can be expressed in the following way [31]:
As can be seen, this realizes the desired scaled subtraction of two base-emitter voltages. And if the ratio between and is designed as , then it can be demonstrated that the generated is a temperature-independent reference voltage.
Here, the problem is that, in Figure 8, there is also an amplifier in the bandgap reference circuit. This seems to contradict the above statement that this technique does not need an amplifier. Nevertheless, this is not a real problem. This is because this amplifier is only used for generating a biasing current. If it is necessary, we can also use other methods without an amplifier to generate the biasing current. From this perspective, it is true that the technique in Figure 8 does not need an amplifier.
Apart from that, since the amplifier is only used for generating the biasing current, its amplifier offset has almost no influence on the accuracy of the reference voltage. And therefore, we do not need to care about the amplifier offset here. For easy understanding, we calculate the influence of the amplifier offset on the generated reference voltage as follows [31]:
where is the transconductance of the BJT , and is the amplifier offset mentioned above. As can be seen, the amplifier offset is greatly attenuated, by times, when generating the reference voltage . This demonstrates that the amplifier offset indeed does not influence the reference voltage accuracy in the structure of Figure 8.
Overall, the amplifier offset can be significantly reduced by using the auto-zeroing technique, the chopping technique, and the switched-capacitor bandgap reference. Their disadvantages are that all of them are clock-controlled circuits. This kind of circuit has the issue of charge injection and clock feedthrough, which should be treated carefully in high-accuracy bandgap references. Apart from that, they also require extra clock generators to generate the clock signals. This also wastes some energy and chip area.
4.1.5. Feedback Coefficient Enhancement Technique
In the previous sections, we have introduced some techniques to eliminate the amplifier offset error. Here, as an alternative, we also introduce a technique to reduce, but not eliminate, the amplifier offset error. It is called the feedback coefficient enhancement technique; it uses a better feedback coefficient in the feedback loop to help reduce the amplifier offset error.
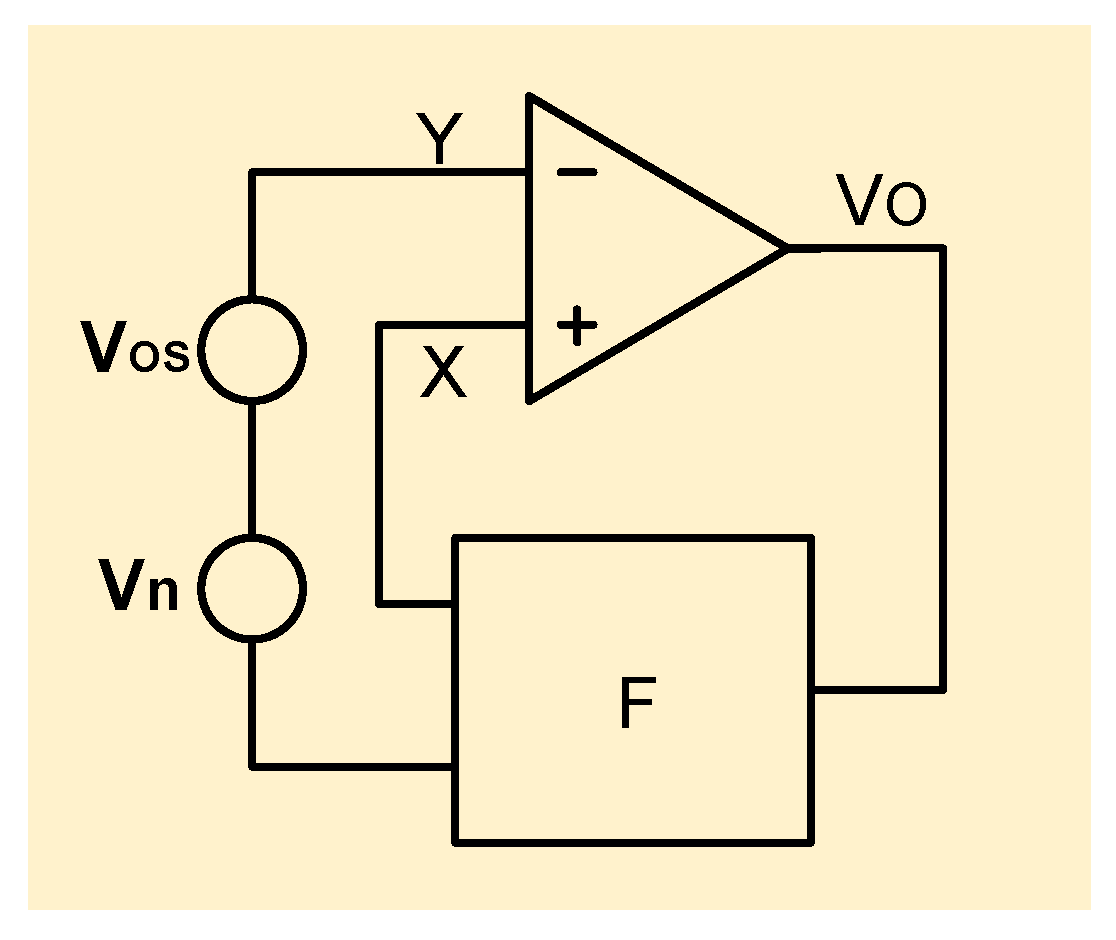
For example, in order to calculate the feedback coefficient, Figure 9 shows the equivalent small-signal model of both a voltage-mode BGR and current-mode BGR. Since both of them have a feedback loop, their feedback coefficients can be calculated. Here, and represent the input-referred offset and noise of the amplifier, respectively. And the feedback network in the yellow rectangle can be simplified as shown in Figure 10.
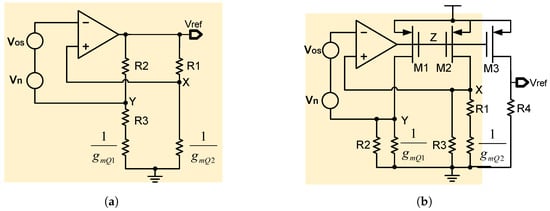
Figure 9.
Small-signal model of (a) voltage-mode BGR and (b) current-mode BGR.
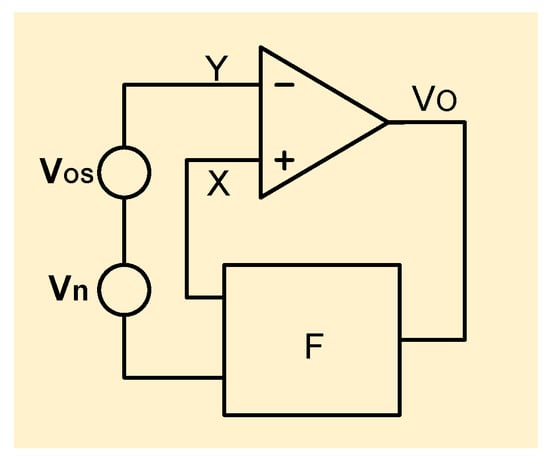
Figure 10.
Feedback network.
In Figure 10, F is the feedback coefficient. And its value can be calculated in the following way:
By using this concept of feedback coefficient F, the amplifier input-referred offset that is transferred to the reference voltage output can be calculated as follows:
Take Figure 9a as an example, its feedback coefficient F can be expressed as
From its equivalent small-signal circuit, it is easy to know that the voltage change at node X is as follows:
And the voltage change at node Y is as follows:
And therefore, with Equations (26)–(28), the feedback coefficient F can be calculated as follows:
According to Equation (25), we can calculate the reference voltage change that is caused by the amplifier input-referred offset :
As can be seen in Equation (30), the amplifier input-referred offset is amplified by a factor of () towards the reference voltage. This satisfies the previously mentioned Equation (3). In general, this factor of () is approximately equal to 10 [21]. And as long as this factor is greatly reduced, the error in the reference voltage will also be greatly reduced as well.
Similarly, for the current-mode BGR in Figure 9b, we can also calculate the reference voltage change that is caused by the amplifier input-referred offset as follows [42]:
As can be seen in Equation (31), the amplifier input-referred offset is amplified by a factor of towards the reference voltage. This approximately satisfies the previously mentioned Equation (4). Typically, this factor of is also a large value. And it is desirable if this factor can be greatly reduced as much as possible.
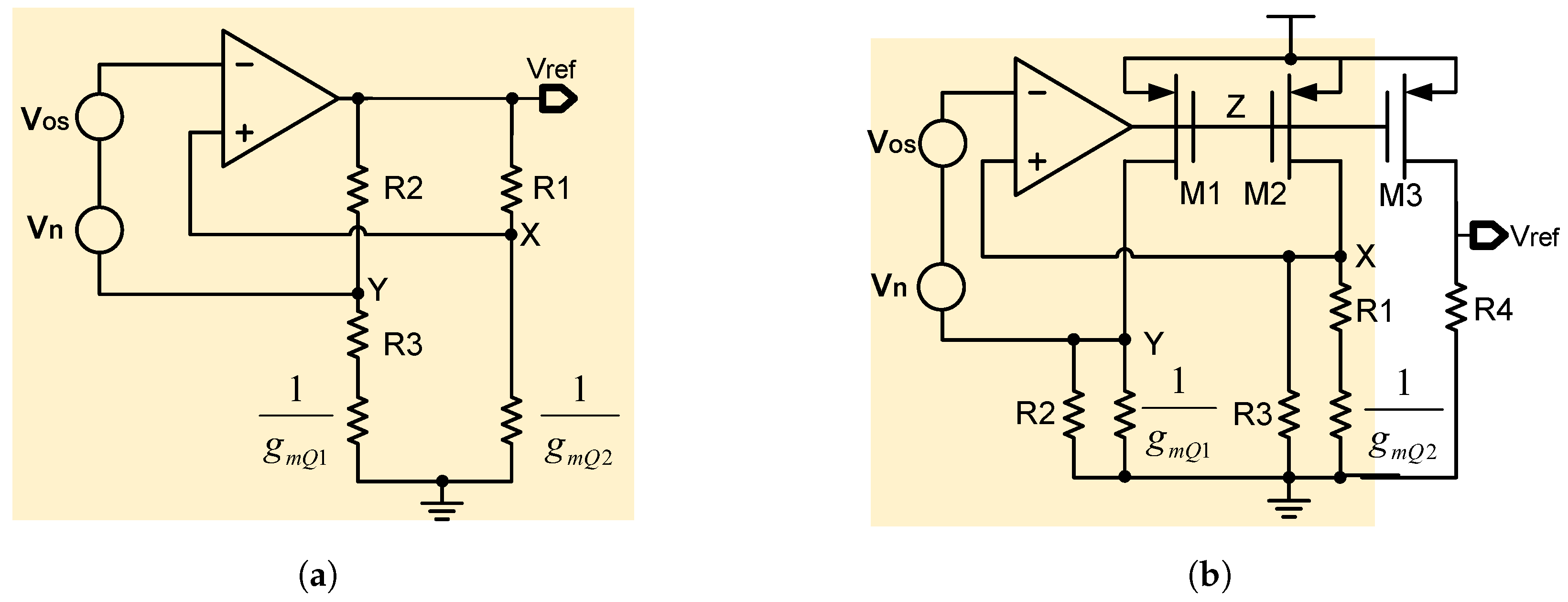
From the above analysis, we can see that increasing the feedback coefficient F is helpful for reducing the impact of amplifier offset. This is the basic idea of the feedback coefficient enhancement technique, which is also called the offset suppression technique [16,21,42,43]. Based on this technique, refs. [21,43] proposed improved versions of voltage-mode and current-mode BGRs, which are shown in Figure 11a and Figure 11b, respectively.
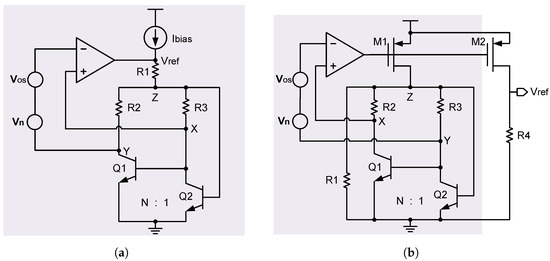
Figure 11.
Improved versions of (a) voltage-mode BGR and (b) current-mode BGR.
Here, still using the improved voltage-mode BGR in Figure 11a as an example, we can calculate its feedback coefficient F in a similar way. The only difference is that an intermediate node Z is added here for easy calculation. As a result, we have
Based on this way of calculation, we first calculate the equivalent resistor looking from node Z, which is given by [21]
Then, we can obtain the relation between and as follows:
In addition, and can be calculated easily with the help of in the following way:
Finally, according to Equations (32)–(36), the feedback coefficient F can be calculated as follows [21]:
As can be seen in the above equation, the feedback coefficient F becomes a large value. This helps to greatly reduce the error in the reference voltage that is caused by the amplifier offset. Specifically, N is chosen to be 6 in [21] as an example. This leads to an F of 1/1.02, which is much larger than the previous F of 1/10. This improvement is desirable in high-accuracy applications.
Similarly, we can also calculate the feedback coefficient F in the improved current-mode BGR in Figure 11b, as follows [43]:
where is the transconductance of . As can be seen, the feedback coefficient F is greatly increased, since is a large value. This is helpful for suppressing the amplifier offset effectively. As a result, the accuracy of BGR is greatly improved.
4.2. Curvature Compensation to Reduce Nonlinearity
4.2.1. Piecewise Compensation Technique
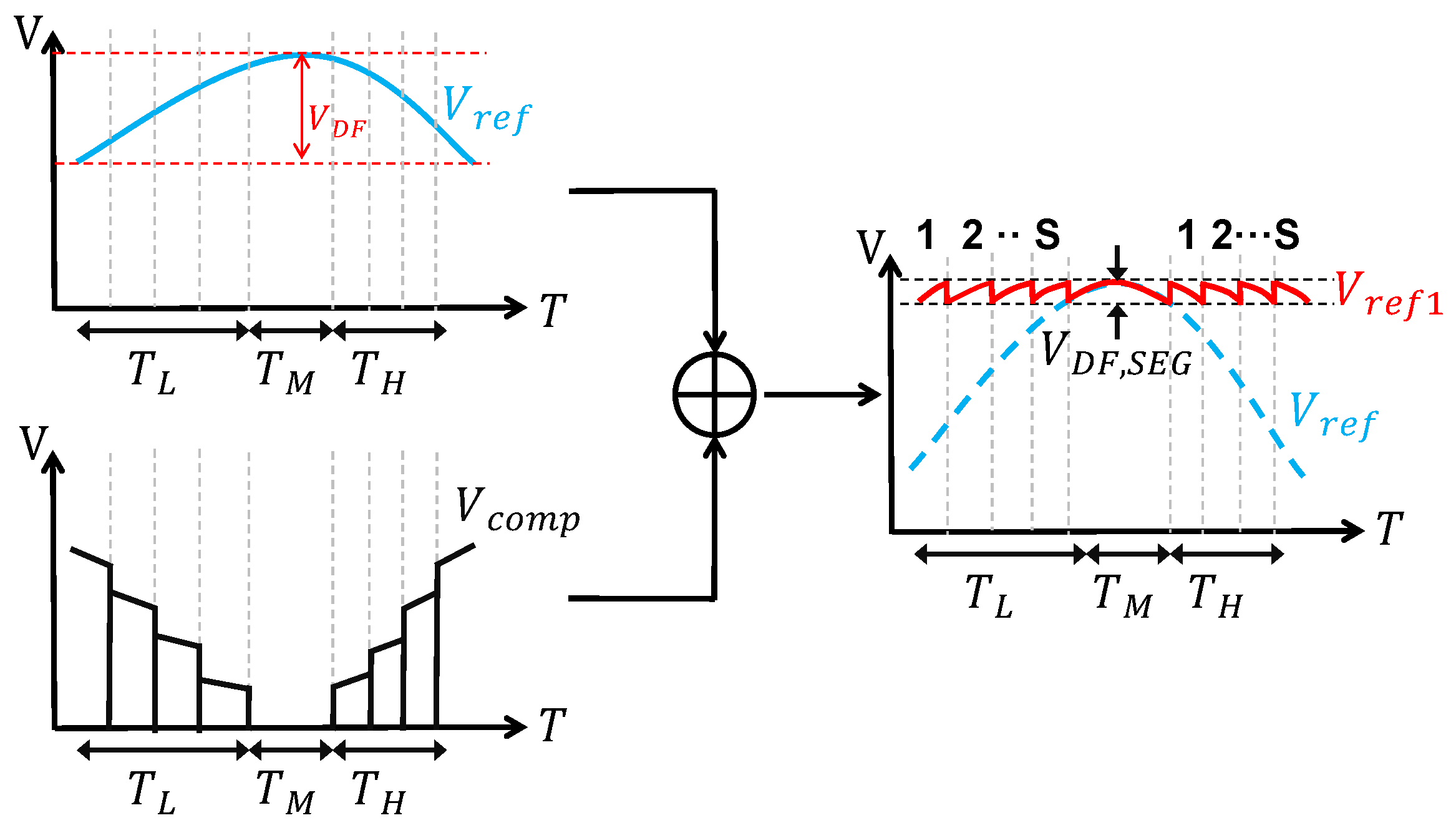
In a typical BGR circuit, the output reference voltage usually has a convex curvature due to the nonlinear term in . The piecewise compensation technique [1,6,10,11,21,43,44] is usually used to reduce this nonlinearity by dividing the entire temperature range into several intervals and using different compensation currents in each interval.
The most commonly used compensation technique is piecewise linear compensation, which typically uses a CTAT current for compensation in the lower-temperature range and a PTAT current in the higher-temperature range, with no compensation applied in the intermediate temperature range. The principle of piecewise linear compensation is shown in Figure 12. As can be seen, it uses three-piece linear compensation. Similarly, ref. [21] even uses five-piece linear compensation.
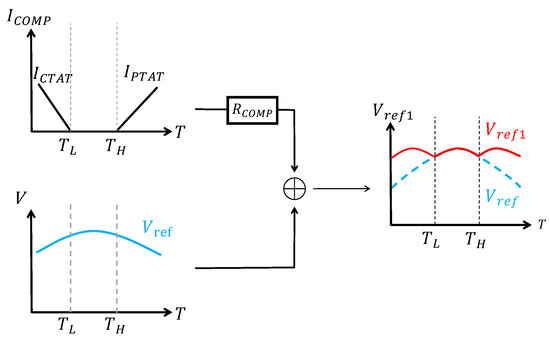
Figure 12.
Piecewise linear compensation.
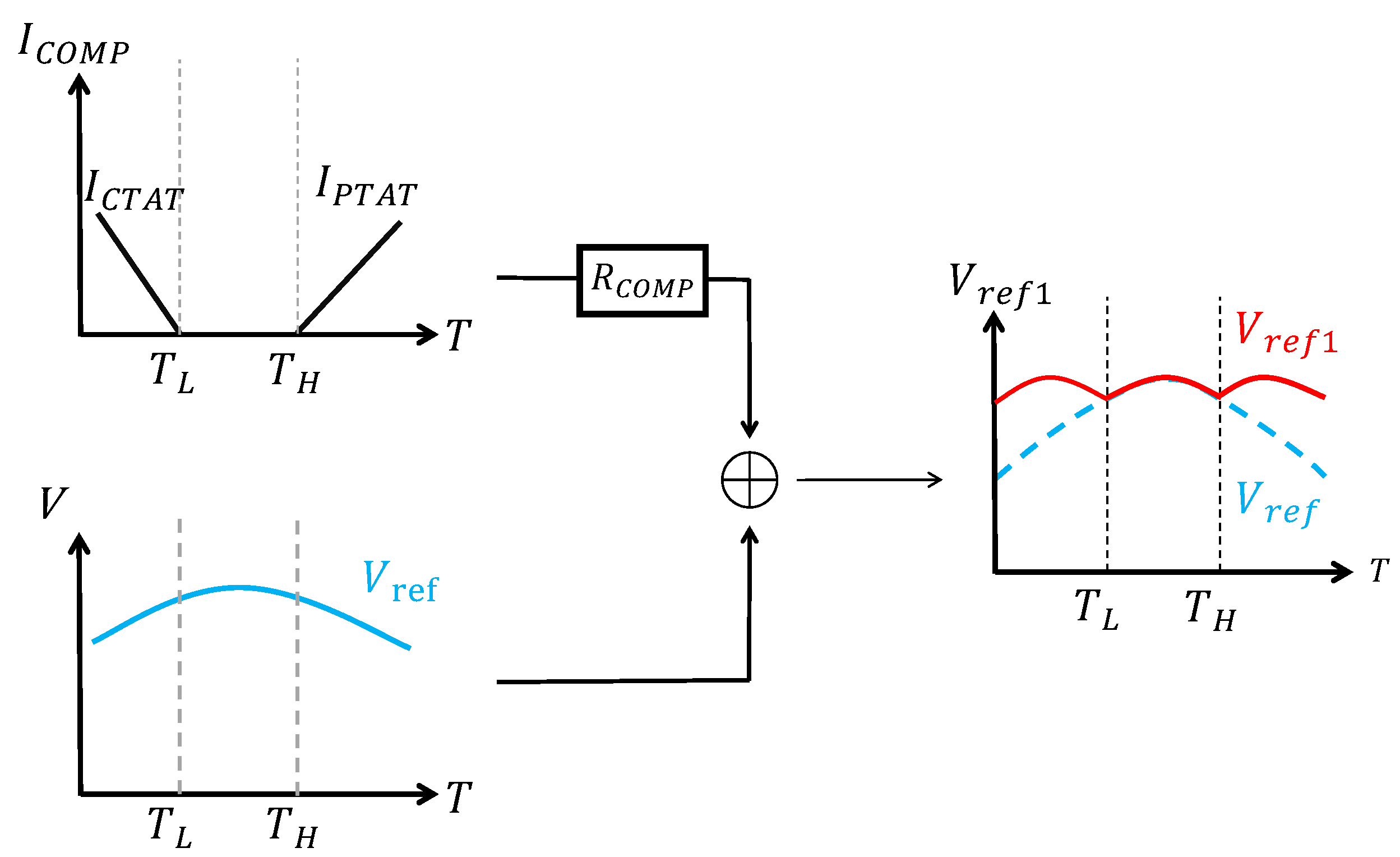
Apart from the linear compensation current mentioned above, piecewise compensation can also be realized by using a variety of nonlinear currents in different temperature ranges [7,37,42,45]. For example, ref. [45] realized compensation with an exponential current in the low-temperature range and a logarithmic current in the high-temperature range. Ref. [42] used two exponential currents in the low- and high-temperature ranges, respectively, in order to form a bowl-shaped curvature compensation current, as shown in Figure 13. As can be seen, nonlinear compensation currents have a better compensation effect. And generally, the selection of the compensation current within different temperature ranges depends on the specific application.
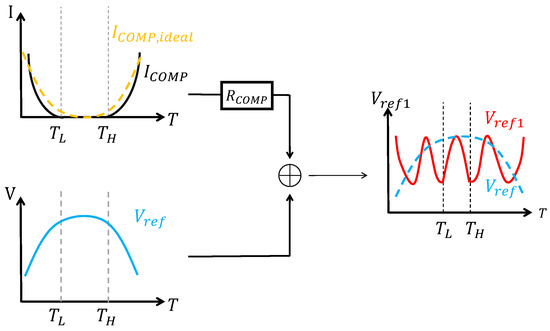
Figure 13.
Bowl-shaped curvature compensation.
In order to cater to different applications, ref. [7] designed an adjustable-temperature curvature compensation circuit that generates different compensation currents based on the curvature type of the reference voltage. This allows it to compensate for the reference voltage with an arbitrary curvature type.
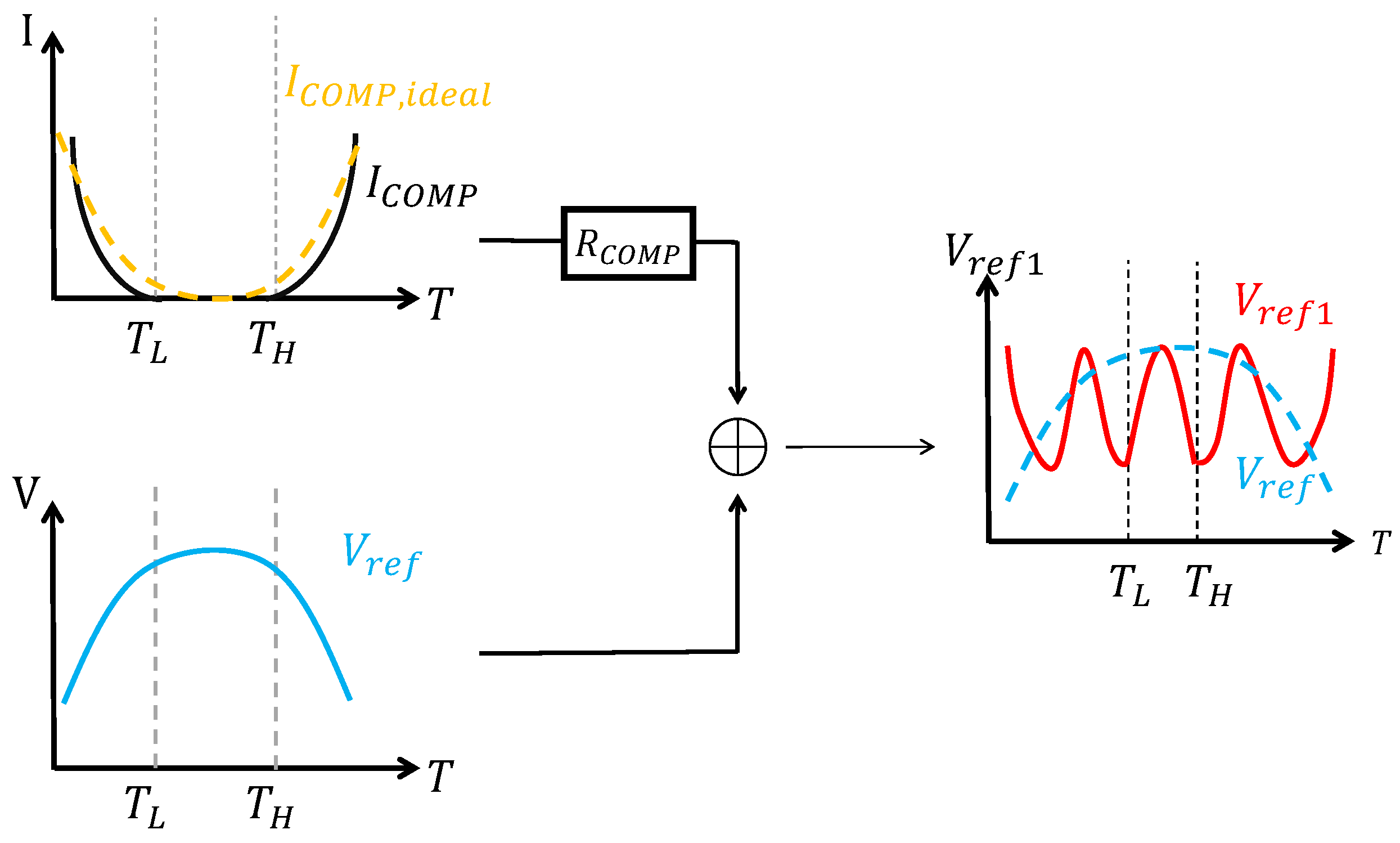
Up to now, the above-mentioned piecewise compensations are limited in the number of temperature segments. To break this limitation, ref. [1] proposed an interesting idea of using multiple piecewise linear compensations, with each compensation current having a different threshold voltage. This approach of increasing the number of segments is called multi-section curvature compensation, which provides more flexibility during the design of compensation and over a wider temperature range. The principle of multi-section curvature compensation is illustrated in Figure 14.
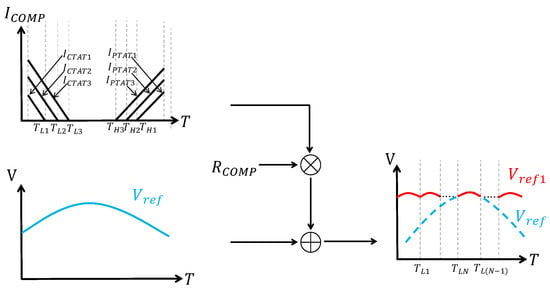
Figure 14.
Multi-section curvature compensation.
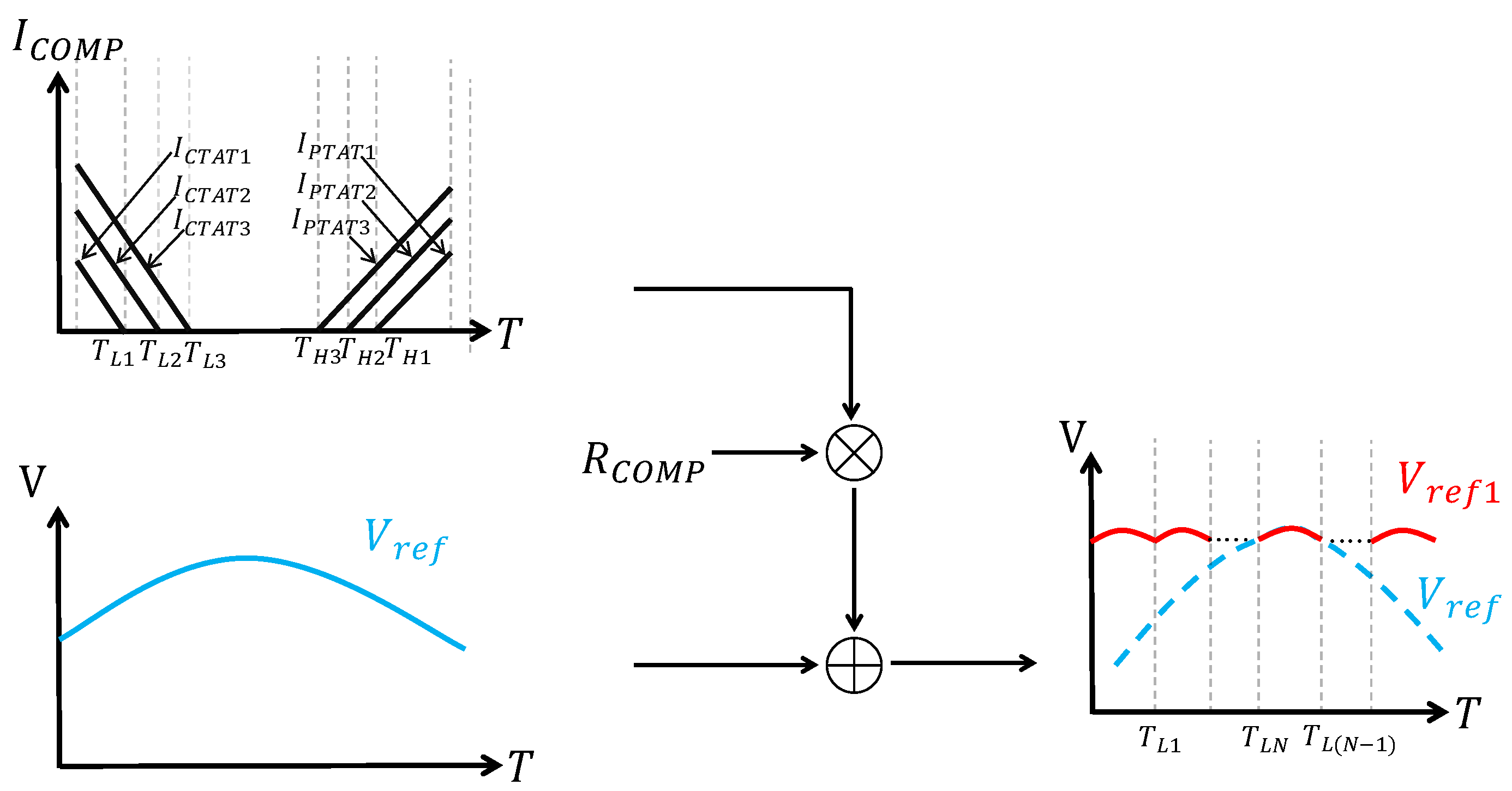
Similarly, ref. [46] proposed a method called segmented curvature compensation. It also divides the reference voltage into many pieces as well. This makes it similar to the multi-section curvature compensation that is mentioned above. Nevertheless, they are actually very different. This difference can be observed in Figure 15. As can be seen, segmented curvature compensation has a different reference voltage after compensation. Its shape is very different. Specifically, its shape is like dividing the into segments. And if the total change in reference voltage before compensation is , then the total change in reference voltage after compensation can be calculated in the following way [46]:
where S is the number of segments in the lower-temperature range or higher-temperature range . And its temperature coefficient can be expressed in the following way [46]:
where is the maximum operating temperature and is the minimum operating temperature. From Equations (39) and (40), it can be found that, in an ideal situation, the greater the number of segments, the lower the temperature coefficient will be. However, there is a trade-off. This is because a large number of segments means a large number of comparators as well. This consumes much energy and area.
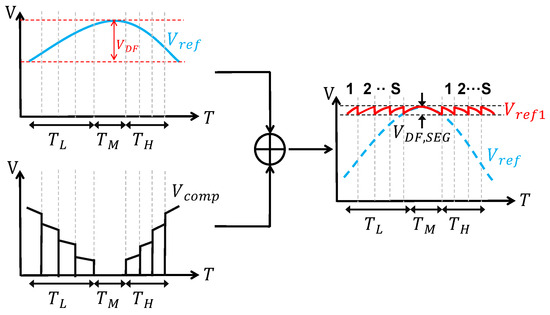
Figure 15.
Segmented curvature compensation.
4.2.2. Second-Order Curvature Compensation
Another type of compensation is called second-order curvature compensation. This compensation can be understood easily by looking at the curvature in . If we perform a Taylor expansion on in Equation (9), then we can obtain the following expression:
where ranges from to when the temperature is in the range of −123 °C to 127 °C [4]. Due to this negative , the usually has a curvature-down characteristic. Apart from that, other terms in the above equation, such as the third-order term, fourth-order term, and so on, only have a negligible impact on the BGR accuracy. And the first-order term can also be canceled out by a PTAT voltage. Therefore, the most important thing here is the second-order term. To eliminate this term, second-order curvature compensation is usually used, which introduces a component into the reference voltage.
There are several methods to generate the second-order compensation current or voltage in the BGR circuit. For example, refs. [47,48] use the temperature coefficient difference between the poly resistor and diffusion resistor to generate a term for the second-order curvature compensation.
Similarly, ref. [14] generates a second-order term in by adding a PTAT current into the bias current of one BJT and subtracting a PTAT current from another BJT. As a result, its can be expressed in the following way [14]:
where is a PTAT current, is a temperature-independent current, and N is the ratio between the two BJTs. As can be seen in the above equation, the second term is a desirable term.
As another example, ref. [49] realizes the second-order compensation by combining an MOS-based compensation circuit and a BJT-based reference circuit with correct weights, and using their outputs with opposite curvatures for the second-order and partial third-order compensation. By using the parameter n in Equation (46) (to be discussed later) that is a function of temperature, it generates a positive second-order term in the expression of as follows [49]:
where E, F, and G are positive constants, w is equal to , and are the currents flowing through two MOSFETs, and and are the width–length ratios of the two MOSFETs. As can be seen, this voltage difference includes a desirable second-order term, which can be used to perform the curvature compensation.
In sum, although second-order compensation cannot completely eliminate the curvature in the reference voltage, it cancels out the most significant term among the high-order terms. As a result, the BGR accuracy is greatly improved.
4.2.3. Compensation
Another commonly used technique is compensation. From Equation (9), it can be seen that the nonlinearity in is totally caused by the term. Therefore, as long as the term is eliminated, we can completely remove the curvature in .
There are several methods to generate the term for curvature compensation. The first method is called the extraction technique [11,12,22,23,24,35,50,51], which is based on the fact that the of two BJTs biased at a ZTAT current and a PTAT current has exactly the same term that we need in the curvature compensation. Specifically, according to Equation (9), if we have a BJT (Q3 as an example) with a ZTAT current and a BJT (Q2) with a PTAT current, then the between them can be calculated as follows:
By carefully combining , , and , we can extract from and use this extracted as the reference voltage. For easy understanding, this combination can be expressed in the following way:
where and are the scaling factors, which can be determined by solving both and simultaneously.
The second method also generates the term for the curvature compensation. The only difference is that it uses the gate-source voltage of the MOSFET in the sub-threshold region to generate this term [6,25,52,53]. Specifically, it is based on the drain current of the MOSFET in the sub-threshold region as follows [54]:
where is the gate oxide capacitance, n is the sub-threshold slope factor, is the mobility, is the gate-source voltage, is the drain-source voltage, and is the threshold voltage. For , the term can be neglected, so that we can obtain the expression of as follows [6]:
Here, the relationship between the mobility and the temperature T is usually modeled in the following way [55]:
where is the mobility at temperature , and is the mobility temperature exponent.
Apart from that, the threshold voltage is usually modeled in the following way [55]:
where is the threshold voltage at 0 K and is the temperature coefficient of .
Combining Equation (47), Equation (48), and Equation (49), the can be expressed in the following way, if we set to be equal to (where G is a coefficient) [6]:
As can be seen in this equation, the last term is the desirable term. By summing , , and in an appropriate proportion, we can finally obtain a reference voltage which no longer has the nonlinear term . For easy understanding, this summation is also expressed below:
Apart from the methods discussed above, there are also other methods. For example, ref. [56] realizes an approximate value of . Although not accurately equal to , it is approximately equal to . It generates an approximate value, because the accurate value of is hard to generate, since complicated circuits are usually required. Due to this reason, a compensation term that is equal to is generated instead. Although it seems to be very different from , their values are very close to each other as long as the circuit is properly designed.
4.2.4. Indirect Curvature Compensation
Up to now, in all of the previously discussed compensation methods, the compensation signal is added directly onto the reference voltage or current. From this perspective, all of these methods are called direct curvature compensation. Different from this direct curvature compensation, ref. [40] proposed an indirect curvature compensation. This does not add the compensation signal directly onto the reference voltage or current. Instead, it performs the compensation by setting the biasing current of the BJT. Specifically, when a well-designed biasing current flows into the BJT, the curvature in the emitter-base voltage can be canceled out. This realizes the compensation operation. For easy understanding, Figure 16 shows this conception of indirect curvature compensation. As can be seen in Figure 16, the is the source-drain current of an MOS transistor operating in the sub-threshold region, which can be expressed as Equation (46).
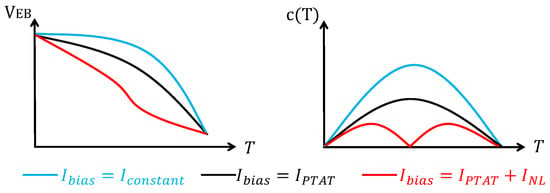
Figure 16.
Indirect curvature compensation.
Here, to understand indirect curvature compensation, we express the collector current of the BJT in the following way [40]:
where is the current gain of the BJT at the reference temperature , is the emitter current at the reference temperature , and and are the temperature exponents of and , respectively. After that, by combining Equation (52) and Equation (11), the nonlinear term in the emitter-base voltage can be expressed in the following way [40]:
Since the emitter current is , as shown in Figure 16, the temperature exponent of the emitter current can be controlled by adjusting the ratio between and . As a result, a desirable value of can be realized by designing and in a proper proportion. This eliminates the curvature in the emitter-base voltage .
4.2.5. Other Compensation Techniques
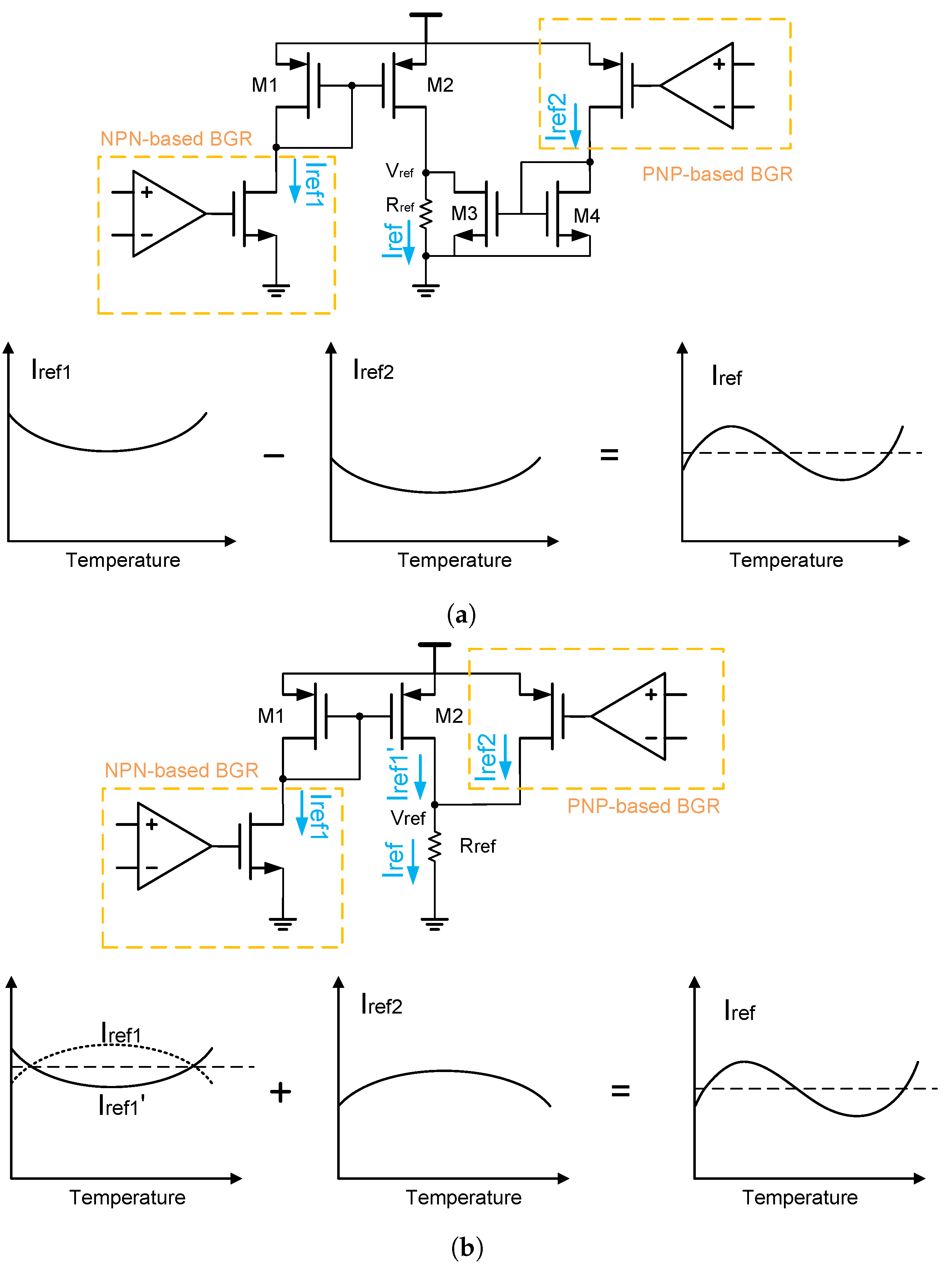
Apart from the previously mentioned methods, there are also many other compensation techniques. For example, refs. [4,28] propose two compensation methods, which are shown in Figure 17. Here, the first method [28] is to use a BGR circuit with NPN transistors and a BGR circuit with PNP transistors to generate two reference currents that have the same type of curvature but different reference currents. And then, these reference currents are subtracted from each other to cancel out the curvature in them [28].
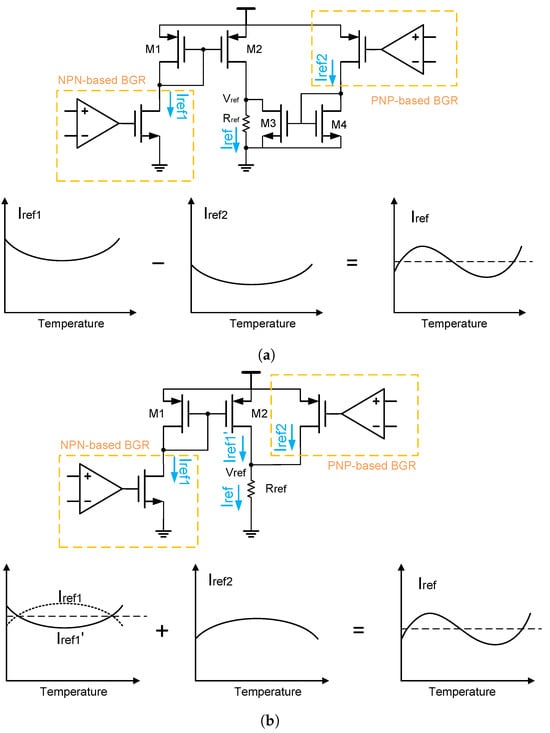
Figure 17.
Other compensation techniques: (a) the first method and (b) the second method.
The second method [4] uses a special current mirror to generate a curvature for the curvature compensation. Specifically, it causes the original reference current to flow through the current mirror, so that an opposite curvature is generated in the output current. After that, it adds this output current back to the original reference current, so that the curvature in them can be canceled out [4].
Overall, any signal, that can adjust the curvature in the reference voltage may be used as a curvature compensation signal.
4.3. Techniques to Reduce the Current Mirror Mismatch
4.3.1. Automatic Current-Controlled Feedback Loop
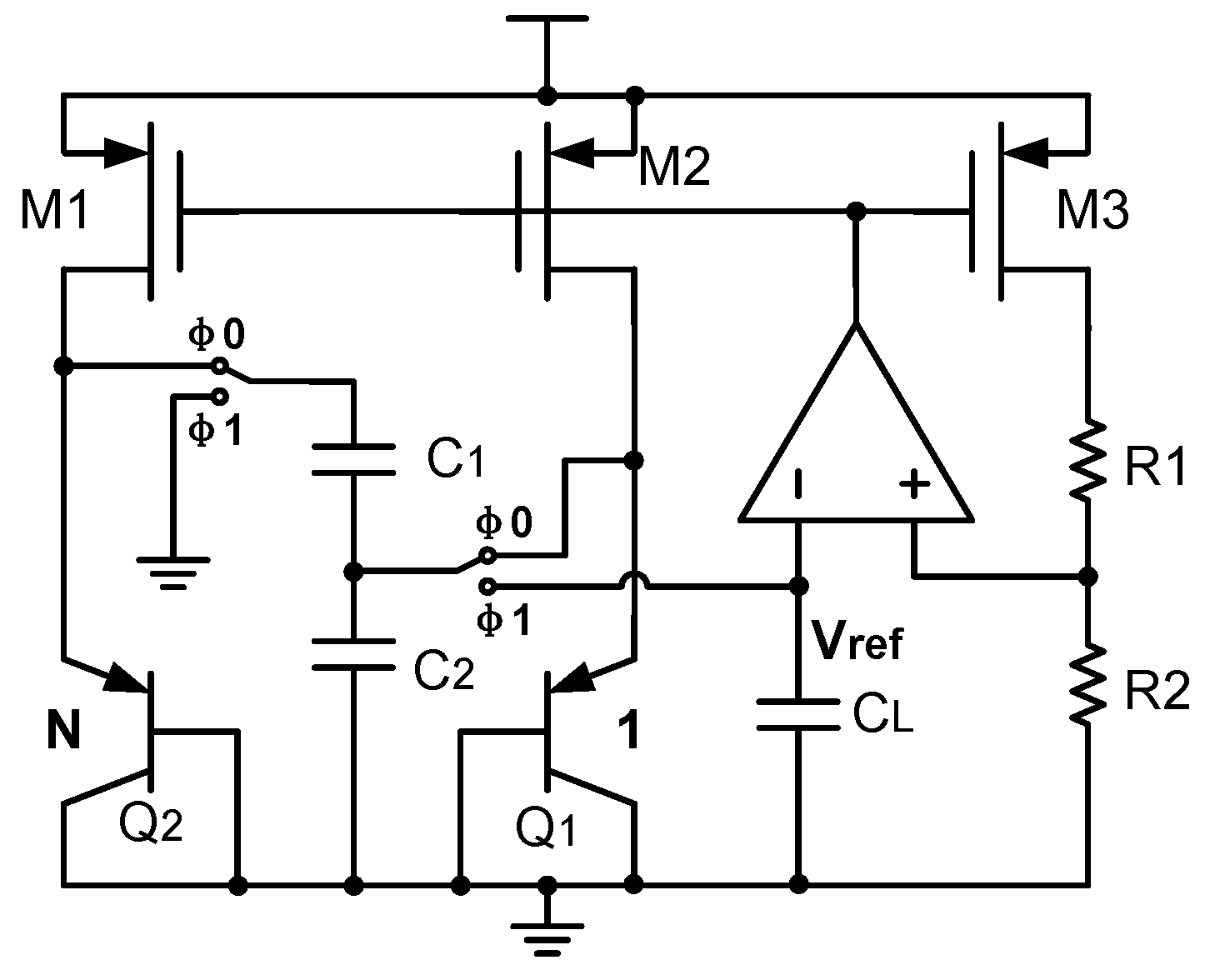
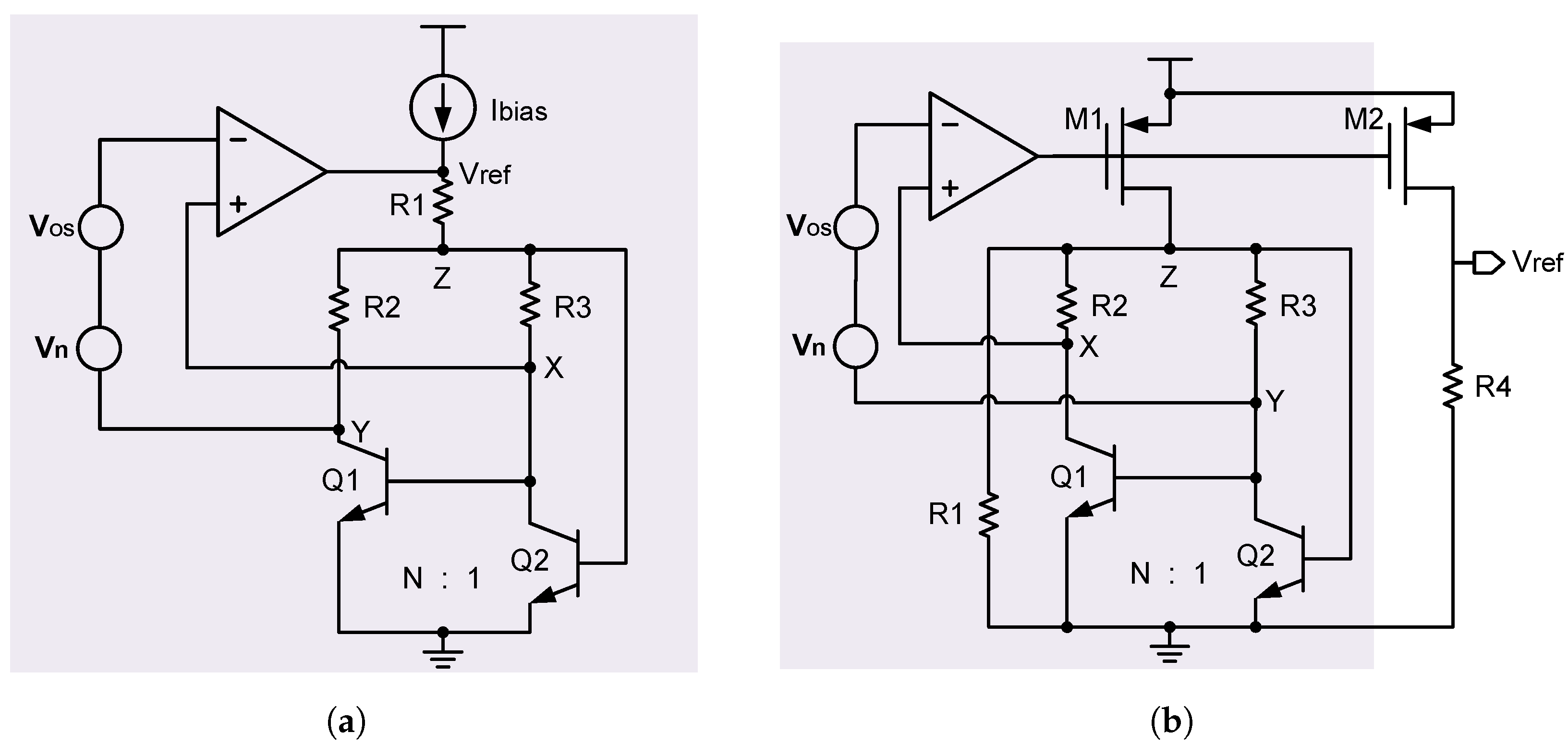
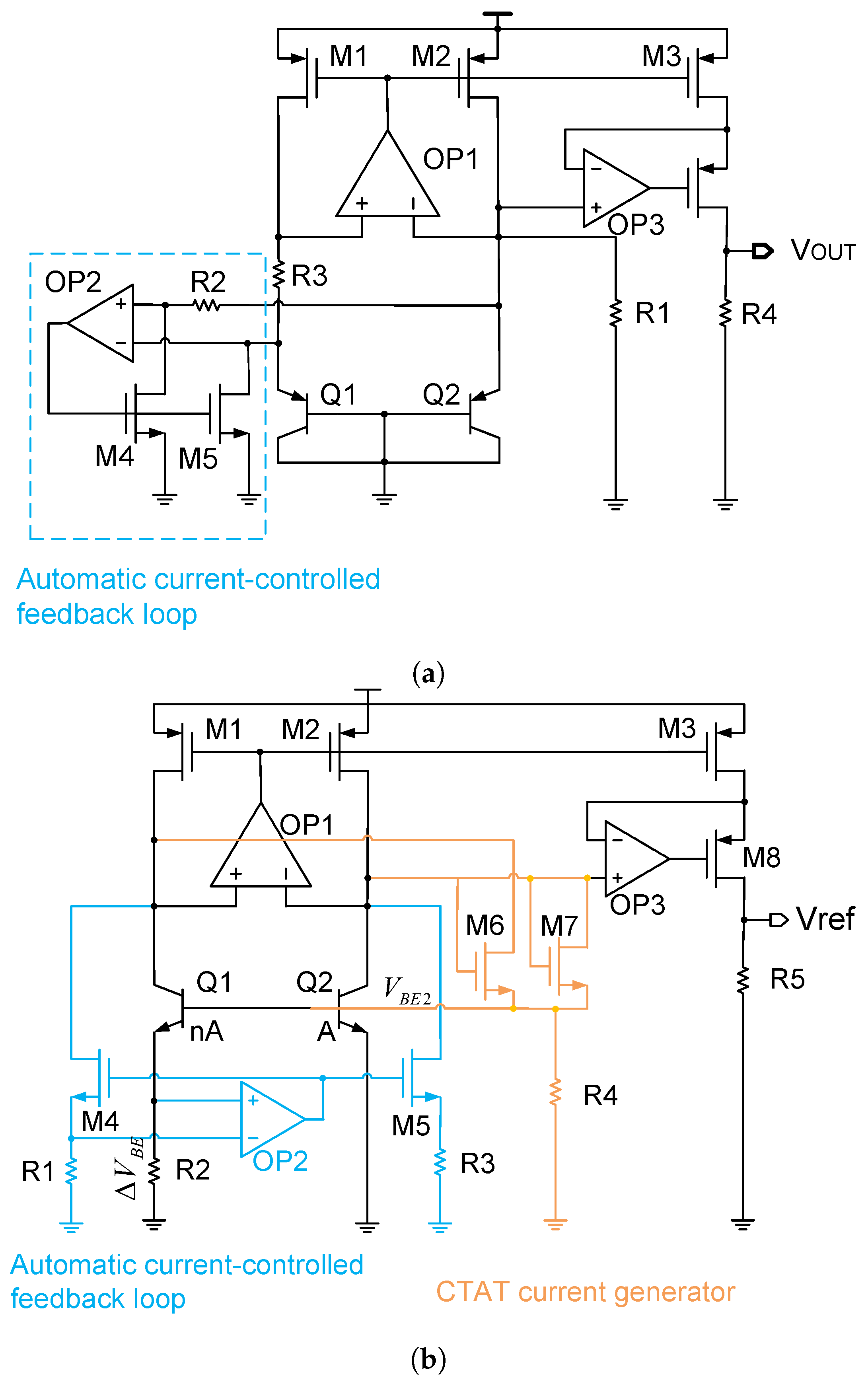
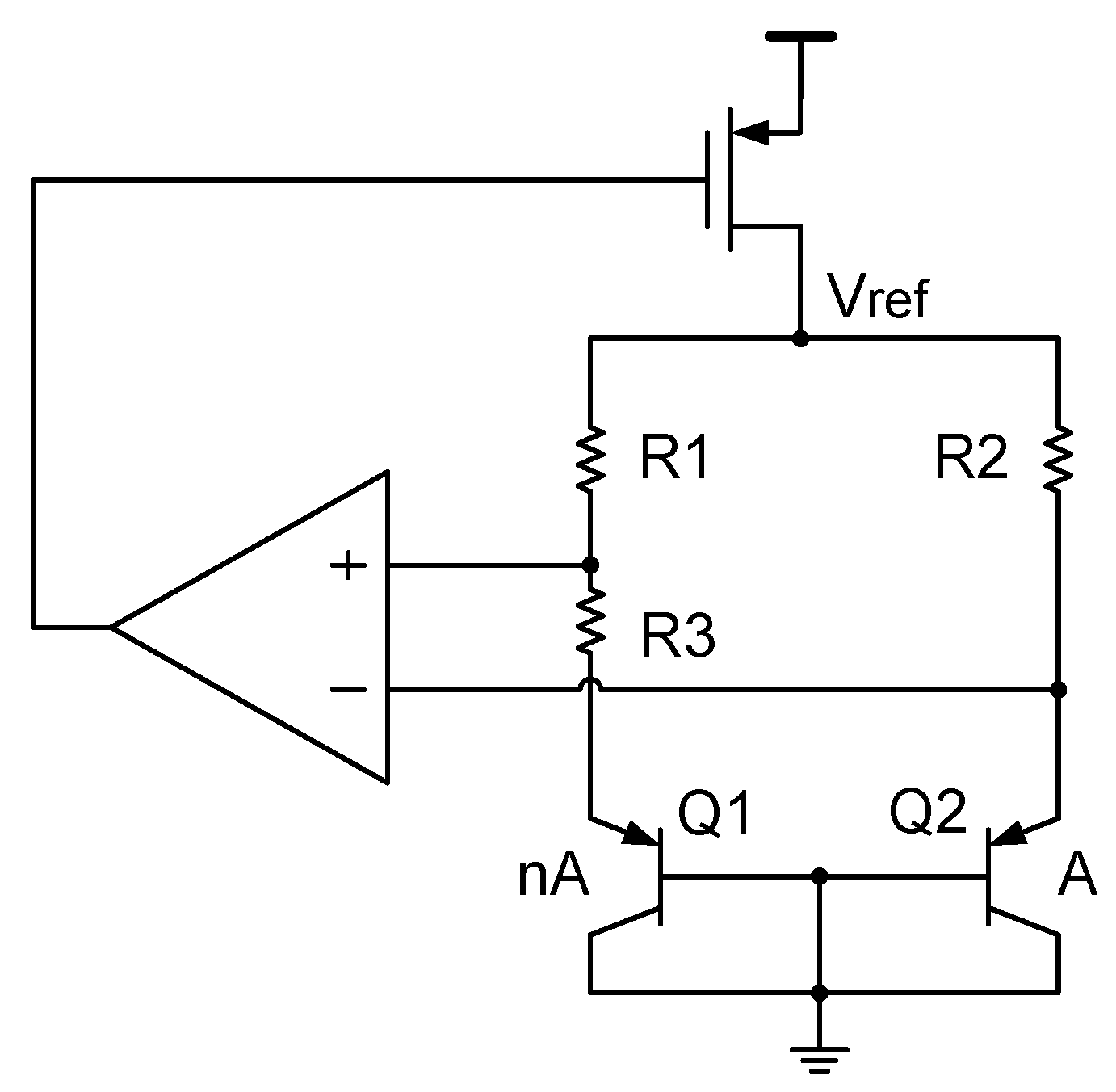
Current mirror mismatch can significantly affect the BGR accuracy. To solve this issue, an automatic current-controlled feedback loop can be used to reduce the current mirror mismatch. As mentioned in Equations (14) and (15), in order to reduce the current mirror mismatch, one possible solution is to increase the current in the current mirror. Nevertheless, this method goes against our need for low power consumption and a low power supply voltage, since a large current also means a large base-emitter voltage of the BJT that is used in the BGR circuit. By contrast, in order to realize both low power consumption and a low power supply voltage, ref. [18] proposed an automatic current-controlled feedback loop which reduces the current mirror mismatch without increasing the power consumption or power supply voltage. Figure 18a shows a schematic diagram of it.
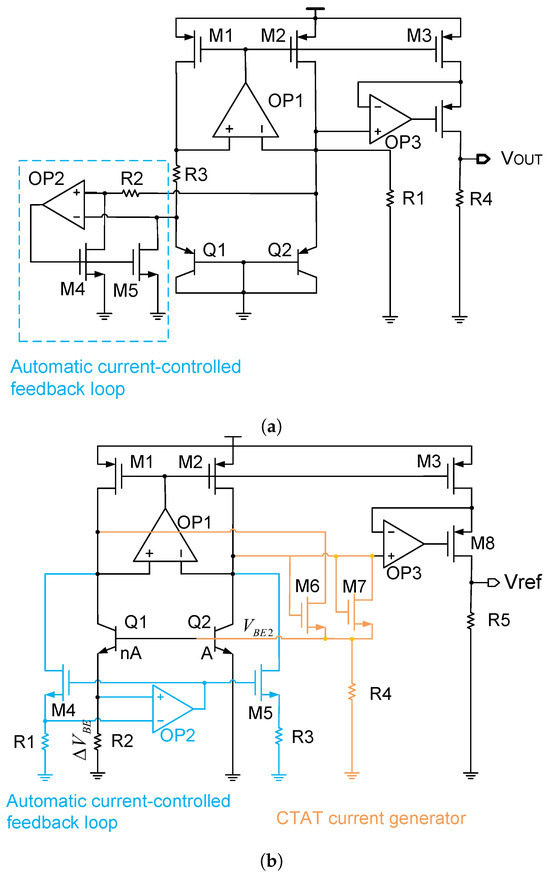
Figure 18.
(a) Bandgap reference with an automatic current-controlled feedback loop; and (b) bandgap reference with an improved version of automatic current-controlled feedback loop.
As can be seen in Figure 18a, the circuit ensures that the current flowing through the BJT is effectively limited to a small value for a low power supply voltage, and it ensures that the current in the current mirror is large enough for a good matching, and this does not require increasing the transistor size in the current mirror. Regardless of its effectiveness, this method also has a disadvantage. It is sensitive to the amplifier offset. Specifically, although the input-referred offset of amplifier OP2 in the feedback loop contributes little to the reference voltage, the reference voltage is quite sensitive to the amplifier OP1 offset. Therefore, to solve this issue, an improved version of the automatic current-controlled feedback loop is developed in [16], which makes the reference voltage insensitive to the amplifier OP1 offset. Figure 18b shows this improved version of the automatic current-controlled feedback loop.
4.3.2. Resistor Feedback Technique
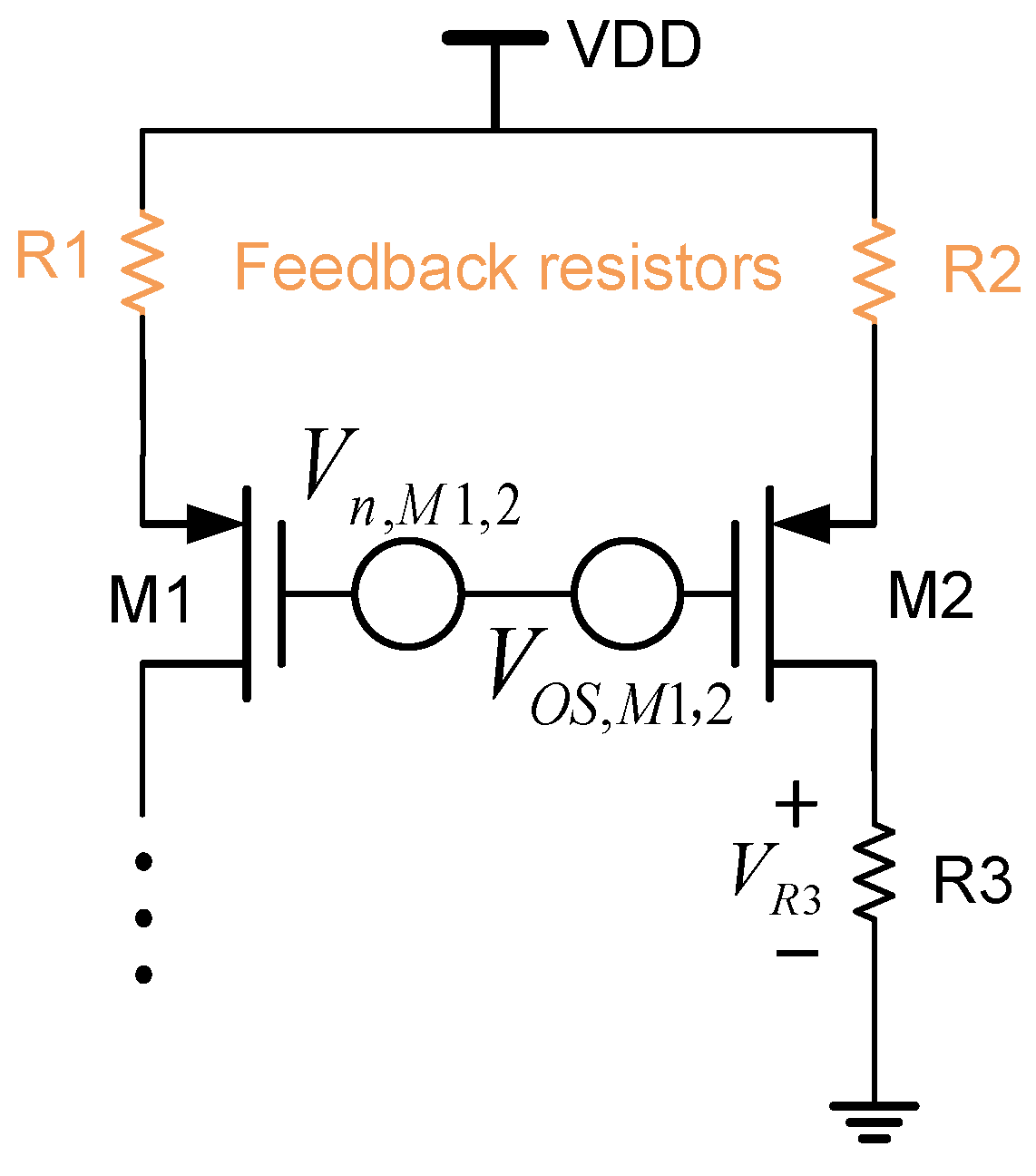
Another way to reduce the current mirror mismatch is to use the resistor feedback technique in [21,42,43], as shown in Figure 19. This technique can effectively reduce the error and low-frequency noise in the current mirror. Its principle is easy to understand. The feedback resistor adjusts the current distribution in the current mirror, making the current more uniform and thus reducing the errors caused by inconsistent transistor parameters. This kind of feedback resistor is added at the source of the current mirror (see Figure 19). Let us take the low-frequency noise of transistors and as an example. If there are no feedback resistors and , then the low-frequency noise is amplified by the current mirror in the following way, when the noise is transferred to :
where is the low-frequency noise at that is caused by . In addition, the transfer of the current mirror offset is similar to this low-frequency noise as well.
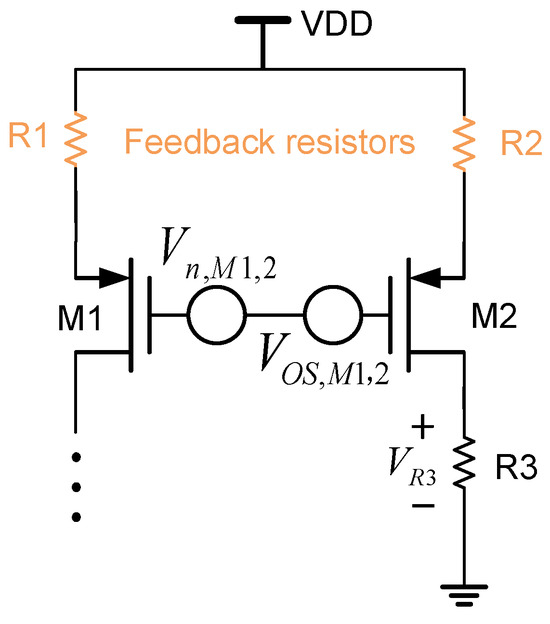
Figure 19.
Current mirror with feedback resistors.
After the feedback resistors and are added into the circuit, the noise transferred to becomes the following:
From Equations (54) and (55), it can be clearly seen that the influence of low-frequency noise is significantly reduced thanks to the resistor feedback technique. Nevertheless, regardless of its effectiveness, its disadvantage is that it sacrifices the voltage margin.
4.3.3. Stacked Multiple Transistors
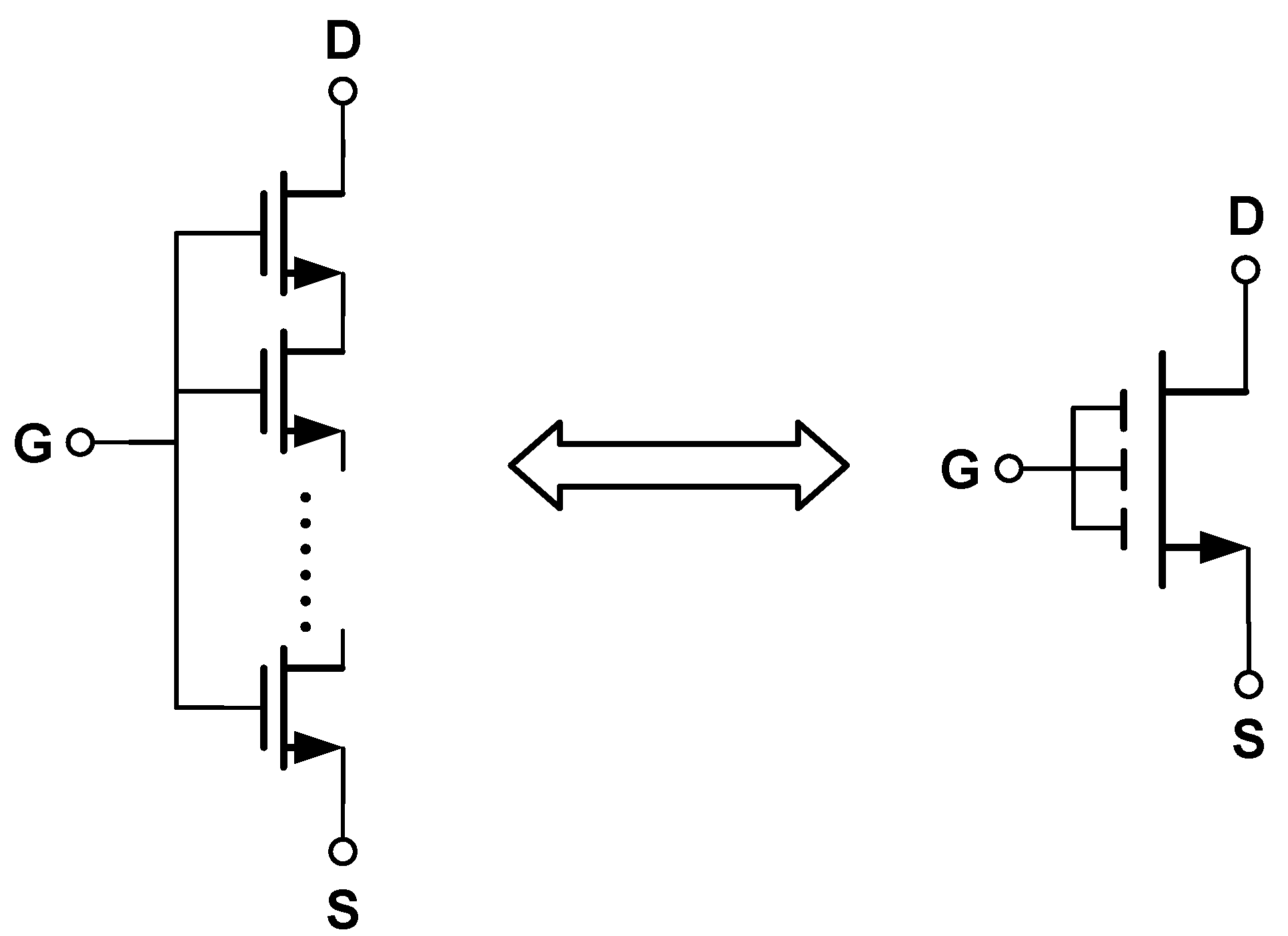
According to Equation (15), another possible way to reduce the current mirror mismatch is to increase the size (W and L) of the MOSFET. Nevertheless, in advanced technology nodes, the chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) process may affect the uniformity of the metal gate, especially for long-channel transistors. This may influence the performance of the transistor unexpectedly. Fortunately, this problem can be avoided by stacking multiple short-channel transistors together, as in [3,17]. This is because when the gate length of each small transistor is short enough, it is much easier to control the process variability and its defects, and thus the overall quality and performance of transistor can be improved. Apart from that, the design of stacked small transistors can also help alleviate the impact of temperature and process variations on the circuit performance. This is because, by spreading the small transistors across the entire chip, the effects of local temperature and process variations can be averaged out, thereby improving the stability and reliability of the circuit. In addition, by putting the small transistors into idle areas of the layout, the limited chip area can be effectively used to achieve a more compact layout, thus reducing the overall chip size [3]. As an example, Figure 20 shows the idea of stacked multiple transistors [57].
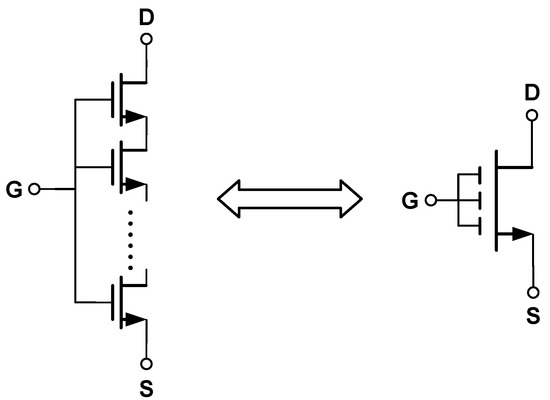
Figure 20.
Stacked multiple transistors.
4.3.4. Matched Resistor Topology
Refs. [12,21] used a matched resistor topology to avoid the problem of current mirror mismatch, as shown in Figure 21. In this topology, two resistors and are used to ensure the current matching between the two branches and therefore the MOSFET-based current mirror is no longer needed. Here, since and are equal, the reference voltage can be calculated in the following way:
This topology is advantageous compared to the MOSFET-based current mirror as its mismatch error is much smaller and can be easily removed. It only results in a PTAT error, which can be removed by a single trim [12]. This is different from the current mirror mismatch. The current mirror mismatch always results in non-PTAT errors, that are often more difficult to eliminate.
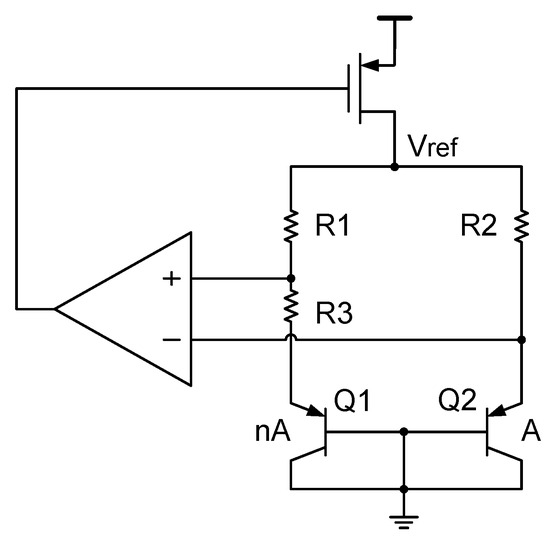
Figure 21.
Matched resistor topology.
4.3.5. Regulated Cascode Current Mirror
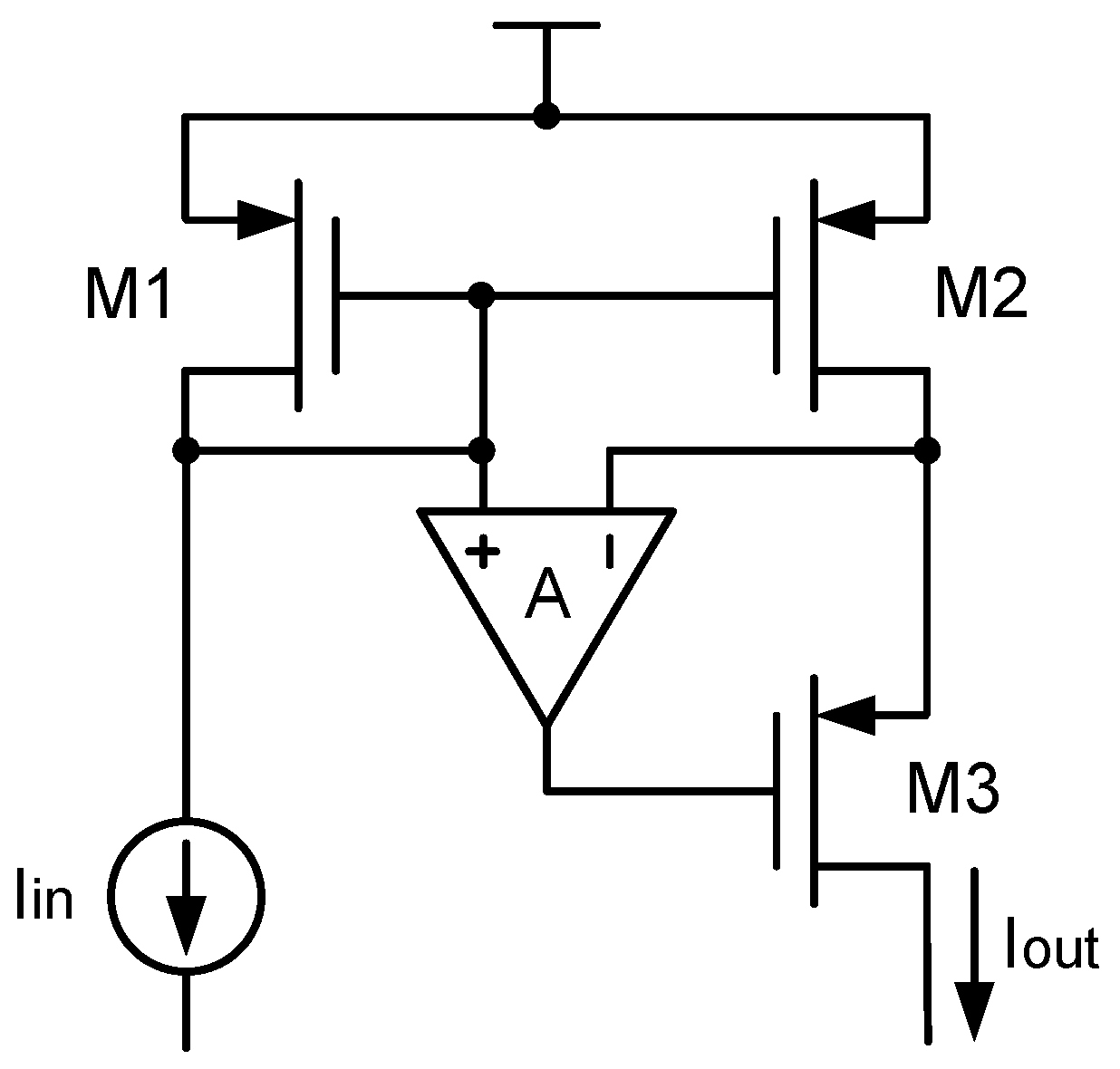
The inaccuracy of the current mirror is not only caused by the device mismatch, but also caused by channel-length modulation. Specifically, in a current mirror, the drain-source voltage variations of the MOS transistor can seriously affect the accuracy of its drain current. To solve this issue, the regulated cascode current mirror was proposed in [58], which is much more accurate than the classic cascode current mirror and Wilson current mirror.
Here, to understand the regulated cascode current mirror, let us look at channel-length modulation first. Channel-length modulation can be seen in the drain-source current of the MOS transistor as follows:
where is the current gain of the MOS transistor. As can be seen, when the drain-source voltage changes, the drain-source current changes as well. Specifically, if the drain-source voltage variation is , then the output current variation will be () due to the channel-length modulation effect. This means that the output resistance of the MOS transistor is . In order to increase the output resistance of the current mirror, the classic techniques include the cascode current mirror and the Wilson current mirror, whose output resistances are both . Nevertheless, the problem is that in a high-accuracy bandgap reference, especially a C bandgap reference, this kind of output resistance is still not large enough. To solve this issue, refs. [16,18,46,59] used a regulated cascode current mirror, which was first proposed by [58].
Figure 22 shows this regulated cascode current mirror. As can be seen, it uses an amplifier to accurately control the drain voltage of the MOS transistor, so that current matching between and is guaranteed. For easy understanding, the following equation shows the output resistance of the regulated cascode current mirror:
As can be seen, its output resistance is greatly increased, since the amplifier’s open-loop gain A can be designed to be very large. This helps guarantee accurate matching in the current mirror. Apart from that, this regulated cascode current mirror also has the advantage of a large output voltage swing. This is because the voltage drop across the output transistors and is as small as 2. This small voltage drop also makes it suitable for low-voltage applications. Apart from that, its disadvantage is that it uses an extra amplifier, wasting a lot of energy and area.
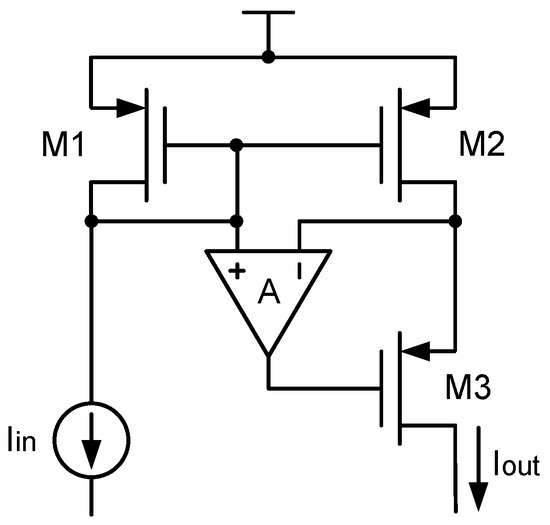
Figure 22.
Regulated cascode current mirror.
4.4. Summary
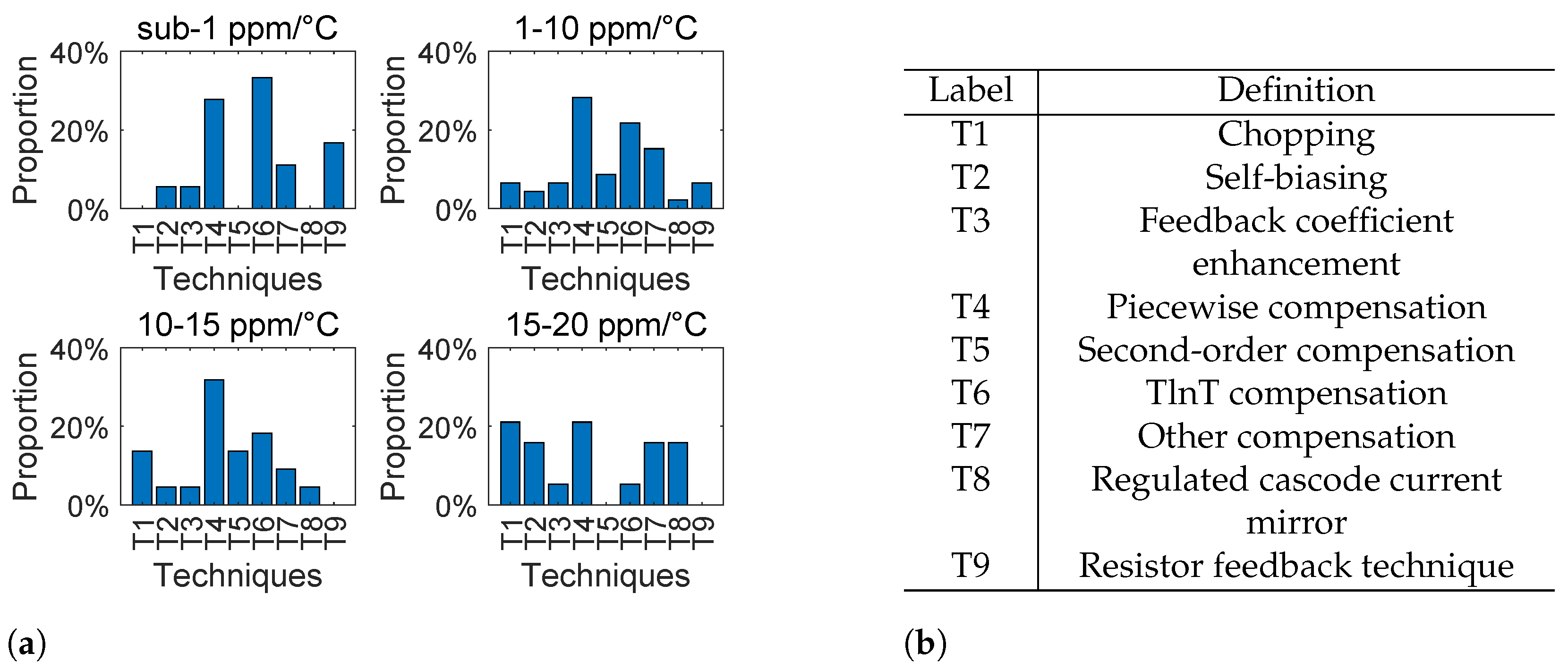
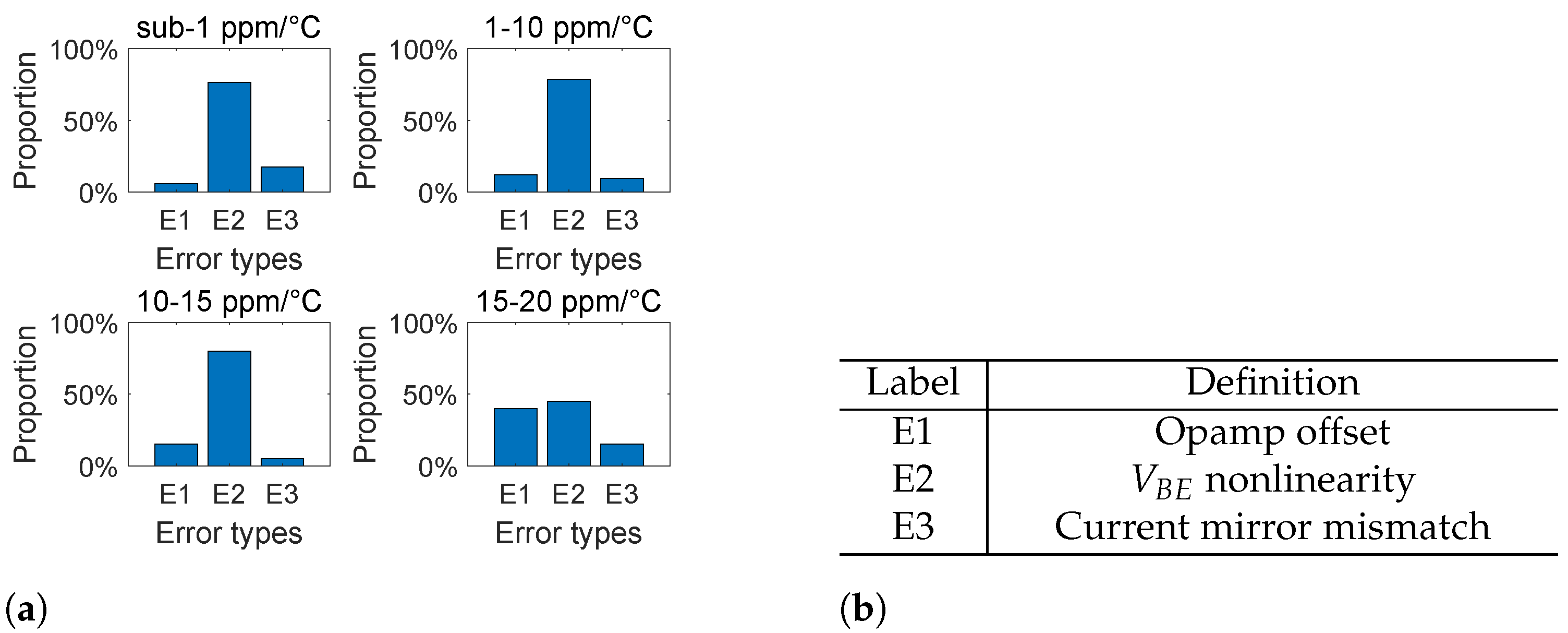
To gain an overall understanding of the above-mentioned techniques, we performed a statistical analysis of these techniques, summarized from 51 papers. This analysis is illustrated in Figure 23 and Figure 24, where Figure 23 shows the techniques for realizing the specific accuracy of the bandgap reference, and Figure 24 shows the important error sources that should be considered when realizing the specific accuracy of bandgap reference. Here, we focus on different accuracy ranges of the bandgap reference, including sub-1 ppm/°C, 1∼C, 10∼C, and 15∼C. This summary is important, since it provides us with clear guidance before we start to design the bandgap reference with a specific accuracy. In particular, for different accuracy ranges we have the following conclusions.
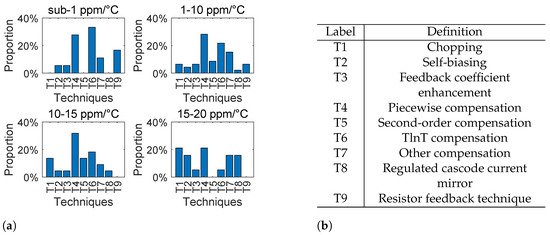
Figure 23.
Techniques for realizing a specific accuracy of the bandgap reference: (a) histogram of techniques (summarized from 51 papers); and (b) names of techniques.
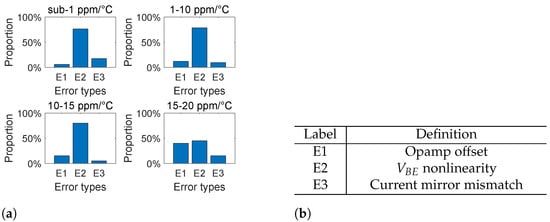
Figure 24.
Important error sources when realizing a specific accuracy of a bandgap reference: (a) histogram of important error sources (summarized from 51 papers); and (b) names of error sources.
For the 15∼C range, the most important error sources that should be considered include the opamp offset and the nonlinearity. In this situation, the most commonly used techniques to reduce the opamp offset include the chopping technique and the self-biasing technique. In addition, the techniques to reduce the nonlinearity include simple piecewise compensation. Since 15∼C accuracy is easy to realize, it is sufficient to use only a simple piecewise compensation.
For the 10∼C range, the nonlinearity starts to become a dominant error source. Under this circumstance, it is necessary to use more complicated curvature compensation techniques, such as piecewise compensation, second-order curvature compensation, and TlnT compensation. Apart from that, the chopping technique is also usually used in order to cancel out the opamp offset error.
For the 1∼C range, the nonlinearity is still a dominant error source. And therefore, it is necessary to use more effective curvature compensation techniques, such as piecewise compensation, TlnT compensation, and other high-order curvature compensation techniques. Apart from that, the chopping techniqe is still needed to cancel out the opamp offset error.
For the C range, the nonlinearity is not only a dominant error source, but also an error source that must be completely canceled out. Under this circumstance, the extremely accurate compensation techniques are required, which requires using several compensation techniques simultaneously, including multi-section piecewise compensation, TlnT compensation, and other high-order curvature compensation techniques. Apart from that, it is often necessary to design highly accurate current mirrors. And therefore, the resistor feedback technique is usually required as well.
Overall, across the entire accuracy range, we can see that the nonlinearity is always the most important error source in the bandgap reference. And for this reason, in recent decades, curvature compensation techniques have been a hot topic of research. And it can be anticipated that, in the near future, more accurate and low-cost compensation techniques are going to be invented.
5. Sub-1V Reference
The previous section mainly discusses how to improve the accuracy of the bandgap reference, but it does not investigate the way to reduce the supply voltage and the power consumption. Especially, with the development of portable battery-powered devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), there is an increasing demand to operate under a low supply voltage and with a low power consumption. Also, with the continual scaling down of modern CMOS processes, the supply voltage is going to decrease as well. For these reasons, sub-1V reference circuits have become more and more popular in recent years. In the following, this section focuses on the recent techniques to realize sub-1V reference circuits.
5.1. Current-Mode BGR
As mentioned before, there are two types of BGR circuits, which are voltage-mode BGRs and current-mode BGRs. Among them, voltage-mode BGRs have a relatively fixed reference voltage of approximately 1.25 V. And therefore, the supply voltage must be larger than this value [60] (for example, a 1.8 V supply voltage can be used). By contrast, current-mode BGRs are suitable for realizing a sub-1V design. The earliest sub-1V BGR was proposed by Banba in 1999 [9]. In this Banba structure, the supply voltage is greatly reduced to approximately [9], which was around 0.7 V in [61]. Overall, current-mode BGRs have been widely used in recent years in order to realize supply voltages of 0.7∼1 V.
5.2. BGR with Charge Pump
If we want to further reduce the supply voltage, it is a good choice to use a switched-capacitor reference with a charge pump. Specifically, the charge pump helps reduce the supply voltage by half, usually to around 0.5 V [62,63,64,65,66] or even below.
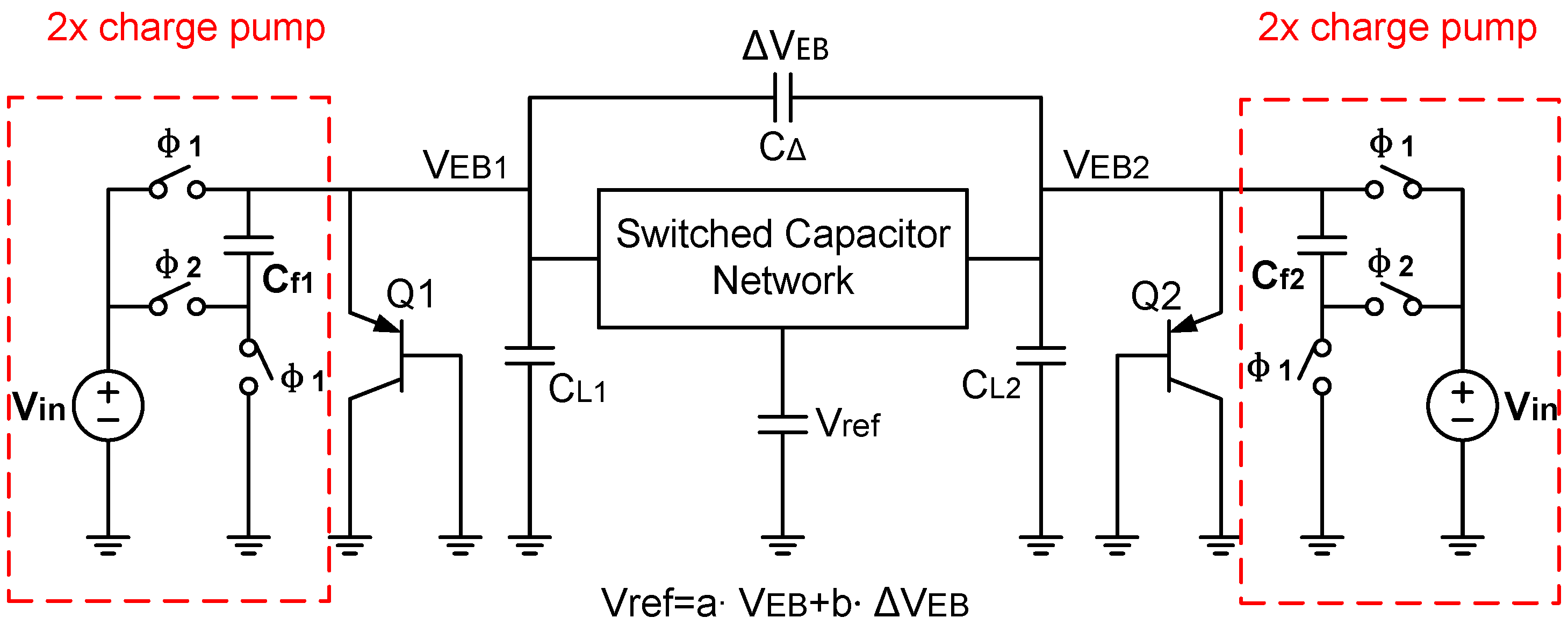
Figure 25 shows a typical BGR with charge pump. Its minimum supply voltage is equal to , which is as small as approximately 375 mV [65]. It uses a 2× charge pump to double the supply voltage. This doubled supply voltage drives the BJTs to generate and , which are stored onto and , respectively. Meanwhile, the difference between and is stored onto . And finally, the switched-capacitor network sums these PTAT and CTAT voltages together with appropriate weights in order to generate a reference voltage .
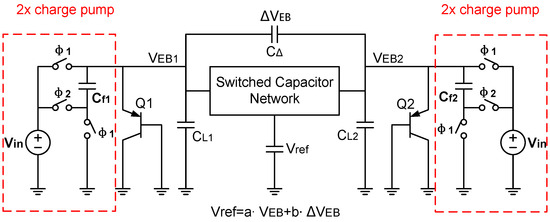
Figure 25.
A typical bandgap reference using a 2× charge pump cell.
Nevertheless, the limitation of such a BGR structure is that, since the driving capability is an important consideration, it cannot unconditionally reduce the supply voltage. As a result, it is not easy to design this structure [40].
5.3. MOSFET-Based Voltage Reference
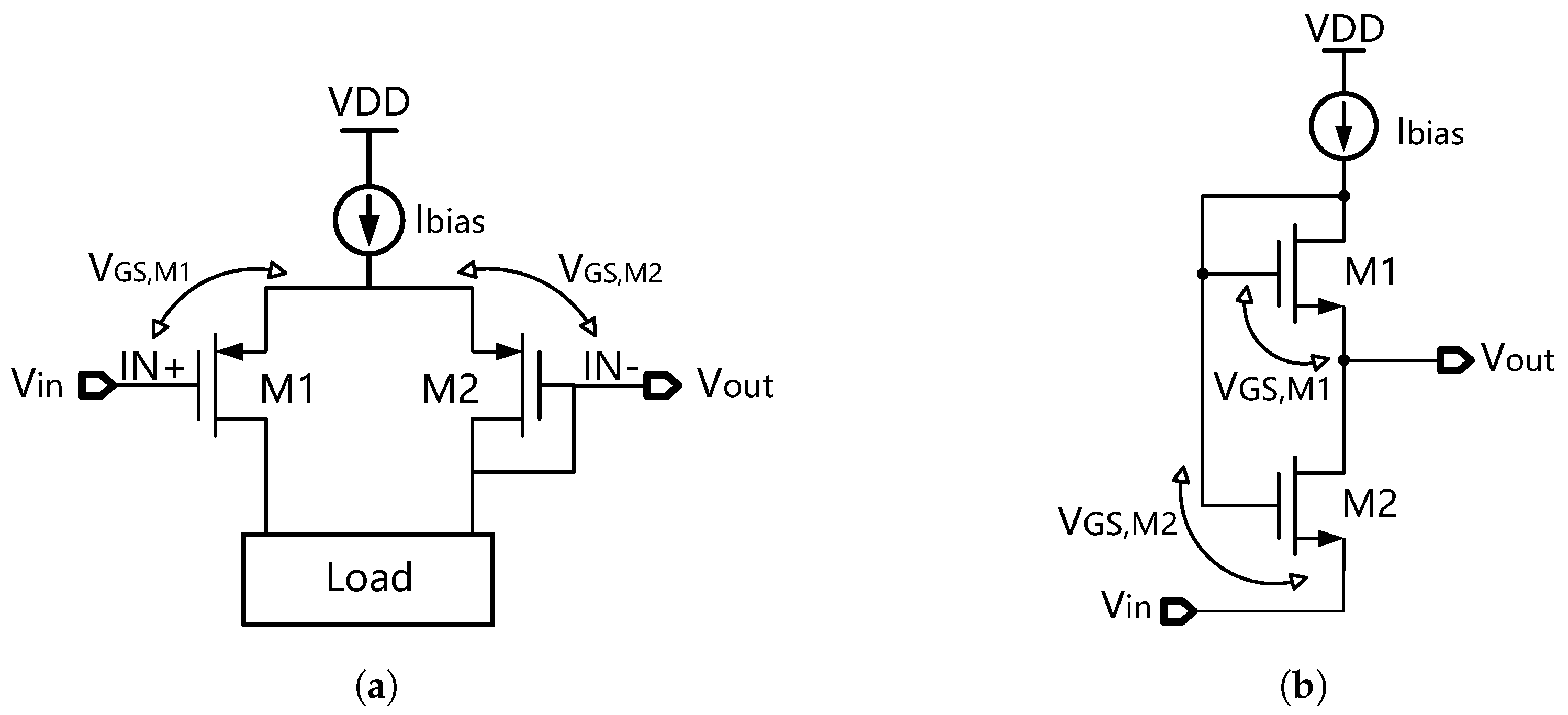
In a classic BGR circuit, the PTAT voltage is usually generated by the base-emitter voltage difference between two BJTs. Nevertheless, the disadvantage is that this requires a relatively high supply voltage. By contrast, an MOSFET-based PTAT generator is more suitable for low-voltage applications. It uses the gate-source voltage difference between two MOS transistors in the sub-threshold region in order to generate the PTAT voltage [61,64,67,68].
Figure 26a shows an MOSFET-based PTAT generator with a differential pair structure [61,64,67], while Figure 26b shows a PTAT generator with a series-connected structure [69]. Both of these PTAT generators consist of two MOS transistors, and , operating in the sub-threshold region. And the gate-source voltage difference of these MOS transistors can be calculated as follows [61]:
where is the width-to-length ratio of the MOS transistor. As can be seen, it generates a PTAT voltage, which is desirable.
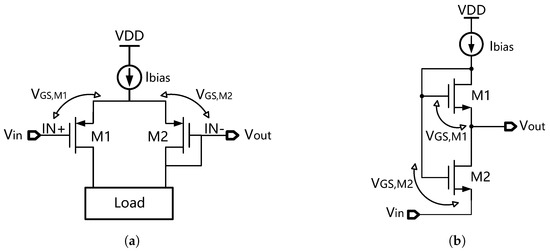
Figure 26.
MOSFET-based PTAT generator with (a) a differential pair structure and (b) a series-connected structure.
Apart from that, the CTAT voltage can be generated by using the gate-source voltage of a single MOS transistor operating in the sub-threshold region [70], since the threshold voltage is CTAT. And therefore, by combining these PTAT and CTAT voltages together in a proper proportion, a reference voltage can be generated. This kind of voltage reference circuit has the advantage of low-voltage operation. It only uses MOS transistors, and an MOS transistor usually has a much lower gate-source voltage than the base-emitter voltage of a BJT. And therefore, it can operate under a much lower supply voltage and with a much lower power consumption when compared to a BJT-based bandgap reference circuit. Nevertheless, its disadvantage is that the threshold voltage is sensitive to process variations. This causes its reference voltage to have a worse temperature coefficient when compared to the BJT-based bandgap reference circuit.
Overall, the MOSFET-based voltage reference uses only MOS transistors, and its generated reference voltage is no longer equal to the bandgap voltage [61,64,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81]. Therefore, this kind of circuit is called a voltage reference circuit, rather than a bandgap reference circuit. For this reason, we do not discuss this kind of circuit in more detail, as it is not the topic of this paper.
6. Conclusions
This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the operating principles and error sources in bandgap reference circuits, highlighting the key challenges in achieving high accuracy. By examining various error sources, including the amplifier offset, the nonlinearity, and the current mirror mismatch, this review summarizes different kinds of techniques to improve the accuracy. When discussing these techniques, this review focuses on different accuracy ranges of the bandgap reference, including C, 1∼C, 10∼C, and 15∼C. This classification is useful, since it helps us easily choose an appropriate technique in order to realize the target accuracy of the bandgap reference. Finally, apart from the discussion of accuracy, this review also summarizes low-voltage designs. Especially, it summarizes the advancements in recent sub-1V bandgap reference circuits.
Overall, in a high-accuracy bandgap reference design, the most important technique is the curvature compensation technique. And therefore, in the future, we believe that bandgap reference circuits will have the following two directions of development. The first direction is to propose a novel curvature compensation technique, in order to achieve an ultra-high accuracy, for example, <C. The second direction is to not only realize a high accuracy but also greatly reduce the cost, for example, reduce the circuit complexity, reduce the supply voltage, and reduce the power consumption.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z. and X.C.; methodology, H.Z. and X.C.; software, H.Z. and X.C.; validation, H.Z. and X.C.; formal analysis, H.Z. and X.C.; investigation, H.Z., X.C. and E.Z.; resources, H.Z. and X.C.; data curation, H.Z., X.C. and E.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Z. and X.C.; writing—review and editing, H.Z. and X.C.; visualization, H.Z. and X.C.; supervision, H.Z. and Q.L.; project administration, H.Z. and Q.L.; funding acquisition, H.Z. and Q.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62004023, 62090041), the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (2022NSFSC0492), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022M710624).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study.
References
- Chen, K.; Petruzzi, L.; Hulfachor, R.; Onabajo, M. A 1.16-V 5.8-to-13.5-ppm/°C Curvature-Compensated CMOS Bandgap Reference Circuit With a Shared Offset-Cancellation Method for Internal Amplifiers. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. Trimless second order curvature compensated bandgap reference using diffusion resistor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), San Jose, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2009; pp. 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Horng, J.J.; Kundu, A.; Chang, C.C.; Peng, Y.C. An ultra-compact, untrimmed CMOS bandgap reference with 3σ inaccuracy of ±0.64% in 16nm FinFET. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), KaoHsiung, Taiwan, 10–12 November 2014; pp. 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Roh, J. A 1.2-V 4.2- ppm/°C High-Order Curvature-Compensated CMOS Bandgap Reference. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2015, 62, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagulapalli, R.; Palani, R.K.; Bhagavatula, S. A 24.4 ppm/°C Voltage Mode Bandgap Reference With a 1.05V Supply. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadogbe, B.; Adjei, D.; Banahene, K.; Geiger, R.; Chen, D. Sub-ppm/°C High Performance Voltage Reference. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Monterey, CA, USA, 21–25 May 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Lee, C.C.; Jheng, S.H.; Chen, W.C.; Lee, B.Y. A Sub-1 ppm/°C Precision Bandgap Reference With Adjusted-Temperature-Curvature Compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 64, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagulapalli, R.; Hayatleh, K.; Yassine, N.; Barker, S. A Novel Sub-1V Bandgap Reference with 17.1 ppm/°C Temperature coefficient in 28nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Austin, TX, USA, 27 May–1 June 2022; pp. 1914–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banba, H.; Shiga, H.; Umezawa, A.; Miyaba, T.; Tanzawa, T.; Atsumi, S.; Sakui, K. A CMOS bandgap reference circuit with sub-1-V operation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1999, 34, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon-Mora, G.; Allen, P. A 1.1-V current-mode and piecewise-linear curvature-corrected bandgap reference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1998, 33, 1551–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, U.; Cullen, E.; Yu, T.; Jennings, J.; Wu, S.; Lim, P.; Farley, B.; Staszewski, R.B. A 1-V Bandgap Reference in 7-nm FinFET With a Programmable Temperature Coefficient and Inaccuracy of ±0.2% From −45 °C to 125 °C. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Zhang, C.; Hoogzaad, G.; Makinwa, K.A.A. A Single-Trim CMOS Bandgap Reference With a 3σ Inaccuracy of ±0.15% From −40 °C to 125 °C. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2011, 46, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagulapalli, R.; Palani, R.K.; Agarwal, S.; Hayatleh, S.C.K.; Barker, S. A 15 μW, 12 ppm/°C Curvature Compensated Bandgap in 0.85V Supply. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 22–28 May 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Gray, P. A precision curvature-compensated CMOS bandgap reference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1983, 18, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceekala, V.; Lewicki, L.; Wieser, J.; Varadarajan, D.; Mohan, J. A method for reducing the effects of random mismatches in CMOS bandgap references. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. Digest of Technical Papers (Cat. No.02CH37315), San Francisco, CA, USA, 7 February 2002; Volume 1, pp. 392–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Li, Q. A 0.8-V Supply, 1.58% 3σ-Accuracy, 1.9-μW Bandgap Reference in 0.13-μm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 1884–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Z. A Sub-200nW All-in-One Bandgap Voltage and Current Reference Without Amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Horng, J.J.; Chang, C.H.; Kundu, A.; Peng, Y.C.; Chen, M. 18.7 A 0.7V, 2.35% 3σ-Accuracy Bandgap Reference in 12nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–21 February 2019; pp. 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagulapalli, R.; Hayatleh, K.; Barker, S.; Tammam, A.A.; Georgiou, P.; Lidgey, F.J. A 0.55 V Bandgap Reference with a 59 ppm/°C Temperature Coefficient. J. Circuits, Syst. Comput. 2019, 28, 1950120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijk, K. A precision reference voltage source. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1973, 8, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liao, X.; Mu, J. A 3.6 μVrms Noise, 3 ppm/°C TC Bandgap Reference With Offset/Noise Suppression and Five-Piece Linear Compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2019, 66, 3786–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Geiger, R.L.; Chen, D. Sub-ppm/°C Bandgap References With Natural Basis Expansion for Curvature Cancellation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 3551–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Geiger, R.; Chen, D. Bandgap Voltage VGO Extraction with Two-Temperature Trimming for Designing Sub-ppm/°C Voltage References. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Sapporo, Japan, 26–29 May 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjei, D.; Gadogbe, B.; Chen, D.; Geiger, R. A Resistorless Precision Curvature-Compensated Bandgap Voltage Reference Based on the VGO Extraction Technique. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Monterey, CA, USA, 21–25 May 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, D.; Wirth, G.; Bampi, S.; Nabki, F.; Fayomi, C. Curvature correction method based on subthreshold currents for bandgap voltage references. In Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd Latin American Symposium on Circuits and Systems (LASCAS), Playa del Carmen, Mexico, 29 February–2 March 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, G.; Schmale, P.; Van Zalinge, K. A new curvature-corrected bandgap reference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1982, 17, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelgrom, M.J.; Duinmaijer, A.C. Matching properties of MOS transistors. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth European Solid-State Circuits Conference, Manchester, UK, 21–23 September 1988; pp. 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ker, M.D.; Chen, J.S.; Chu, C.Y. New curvature-compensation technique for CMOS bandgap reference with sub-1-V operation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Kobe, Japan, 23–26 May 2005; Volume 4, pp. 3861–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.H.; Ki, W.H. CMOS Bandgap References With Self-Biased Symmetrically Matched Current–Voltage Mirror and Extension of Sub-1-V Design. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2010, 18, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.T.; Lewis, S.H.; Brokaw, A.P.; Viswanathan, T.R. A 1.4 V Supply CMOS Fractional Bandgap Reference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 2180–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palani, R.K.; Bhagavatula, S.; Yuen, D.K. A Sub-1-V 8.5-ppm/°C Sampled Bandgap Voltage Reference. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 4153–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Jeon, C.; Son, H.; Kim, B.; Park, H.J.; Sim, J.Y. A 9.3 nW all-in-one bandgap voltage and current reference circuit using leakage-based PTAT generation and DIBL characteristic. In Proceedings of the Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 22–25 January 2018; pp. 309–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Ch, V.; Thouti, S.; Kumar, G.P.; Rajeswaran, N. High Gain More Stable Self Biased Two Stage Differential Amplifier for Bio-signal Processing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 17–18 March 2023; Volume 1, pp. 1859–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.H.; Fu, D.B.; Chen, G.B.; Ye, R.K.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, C. High precision bandgap reference with chopping offset reducing technique. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), Hangzhou, China, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 1381–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, J.H.; Cho, K.I.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, J.G.; Kwak, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, G.C. A Single-Trim Switched Capacitor CMOS Bandgap Reference With a 3σ Inaccuracy of +0.02%, -0.12% for Battery-Monitoring Applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lu, W.; Zhao, M.; Niu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. A Sub-1ppm/°C Current-Mode CMOS Bandgap Reference With Piecewise Curvature Compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Colombo, D.M.; Yin, Y.; El-Sankary, K. Low Noise, High PSRR, High-Order Piecewise Curvature Compensated CMOS Bandgap Reference. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 110970–110982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enz, C.; Temes, G. Circuit techniques for reducing the effects of op-amp imperfections: Autozeroing, correlated double sampling, and chopper stabilization. Proc. IEEE 1996, 84, 1584–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzahini, D.; Ghazlane, H. Auto-zero stabilized CMOS amplifiers for very low voltage or current offset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium. Conference Record (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37515), Portland, OR, USA, 19–25 October 2003; Volume 1, pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.F.; U, C.W.; Martins, R.P.; Lam, C.S. 0.4-V Supply, 12-nW Reverse Bandgap Voltage Reference With Single BJT and Indirect Curvature Compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.; Brederlow, R.; Gerber, J. An Ultra Low Power Bandgap Operational at Supply From 0.75 V. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L. A 3.0 μVrms, 2.4 ppm/°C BGR With Feedback Coefficient Enhancement and Bowl-Shaped Curvature Compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L. A High-Precision Current-Mode Bandgap Reference With Low-Frequency Noise/Offset Elimination. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 3993–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Zhang, X.b.; Yu, M.y. A 1.2-V Piecewise Curvature-Corrected Bandgap Reference in 0.5 μm CMOS Process. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2011, 19, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.K.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, P.S.; Ma, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, Z.; Ming, X.; Zhang, B. A 1.6-V 25-μ A 5-ppm/°C Curvature-Compensated Bandgap Reference. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2012, 59, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U, C.W.; Liu, C.; Martins, R.P.; Lam, C.S. An 1 V Supply, 740 nW, 8.7 ppm/°C Bandgap Voltage Reference With Segmented Curvature Compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2023, 70, 4755–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.W.; Huang, Y.C.; Liang, D.; Chen, H.W.; Chen, H.S. A 1.5-V 10-ppm/°C 2nd-order curvature-compensated CMOS bandgap reference with trimming. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Kos, Greece, 21–24 May 2006; p. 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.N.; Mok, P.; Leung, C.Y. A 2-V 23-μA 5.3-ppm/°C curvature-compensated CMOS bandgap voltage reference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2003, 38, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Yu, F. A Novel 1.2–V 4.5-ppm/°C Curvature-Compensated CMOS Bandgap Reference. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2014, 61, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Sun, J.; Bai, Y.; Xu, H.; Du, T.; Li, G.; Chen, Y. A Novel 1.03 ppm/°C Wide-Temperature-Range Curvature-Compensated Bandgap Voltage Reference. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Conference on Circuits, System and Simulation (ICCSS), Guangzhou, China, 14–16 July 2018; pp. 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, C.M.; Koudounas, S.; Georgiou, J. A Novel Wide-Temperature-Range, 3.9 ppm/°C CMOS Bandgap Reference Circuit. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Kong, F.; Cheung, C.; Najafizadeh, L. BiCMOS-Based Compensation: Toward Fully Curvature-Corrected Bandgap Reference Circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 1210–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Hu, L.; Xin, Y.L.; Zhang, X.; Gao, D.; Zhang, B. A High-Precision Resistor-Less CMOS Compensated Bandgap Reference Based on Successive Voltage-Step Compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 4086–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittoz, E.; Fellrath, J. CMOS analog integrated circuits based on weak inversion operations. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1977, 12, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsividis, Y.P. Operation and Modeling of the MOS Transistor; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Yin, P.; Shu, Z.; Bermak, A.; Tang, F. A Sub-1 ppm/°C Bandgap Voltage Reference With High-Order Temperature Compensation in 0.18-μm CMOS Process. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2022, 69, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galup-Montoro, C.; Schneider, M.; Loss, I. Series-parallel association of FET’s for high gain and high frequency applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1994, 29, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, W. Current Mirror. EP0356570A1, 7 March 1990. [Google Scholar]
- U, C.W.; Law, M.K.; Martins, R.P.; Lam, C.S. Sub-μW Auto-Calibration Bandgap Voltage Reference With 1σ Inaccuracy of ±0.12% Within −40 °C to 120 °C. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2024, 59, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanborn, K.; Ma, D.; Ivanov, V. A Sub-1-V Low-Noise Bandgap Voltage Reference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 2466–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, Y.; Hirose, T.; Kuroki, N.; Numa, M. 1.2-V Supply, 100-nW, 1.09-V Bandgap and 0.7-V Supply, 52.5-nW, 0.55-V Subbandgap Reference Circuits for Nanowatt CMOS LSIs. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U, C.W.; Law, M.K.; Lam, C.S.; Martins, R.P. Switched-Capacitor Bandgap Voltage Reference for IoT Applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2022, 69, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Yerragudi, S.B.; Dasari, N.; Lee, I.; Abbas, Z. An 18.5nW, 62.9dB PSRR, Switched-Capacitor Bandgap Voltage Reference using Low Power Clock Generator Circuit for Biomedical Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Monterey, CA, USA, 21–25 May 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y. A 58-ppm/°C 40-nW BGR at Supply From 0.5 V for Energy Harvesting IoT Devices. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 64, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Craig, K.; Roberts, N.E.; Wentzloff, D.D.; Calhoun, B.H. 5.4 A 32nW bandgap reference voltage operational from 0.5V supply for ultra-low power systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—(ISSCC) Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi-Wa, U.; Zeng, W.L.; Law, M.K.; Lam, C.S.; Martins, R.P. A 0.5-V Supply, 36 nW Bandgap Reference With 42 ppm/°C Average Temperature Coefficient Within −40 °C to 120 °C. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2020, 67, 3656–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossanov, A.; Ziegler, C.; Issakov, V. Ultra-Low-Power High PSRR Sub-1 V Voltage Reference Circuit in 22 nm FDSOI CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 4643–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Li, Q. A 0.5-V Voltage Reference Using Simple Common-Source Amplifier With Improved Gain. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 4723–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhan, C.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, G. A 0.9-V 33.7-ppm/°C 85-nW Sub-Bandgap Voltage Reference Consisting of Subthreshold MOSFETs and Single BJT. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2018, 26, 2190–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi Nowruzabadi, R.; Mostofi Sharq, J.; Ebrahimi, E. An ultra-low power fully CMOS sub-bandgap reference in weak inversion. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2024, 120, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, H.; Makinwa, K.A.A.; Lee, I.; Chae, Y. A Sub-1-V Capacitively-Biased Voltage Reference With an Auto-Zeroed Buffer and a TC of 18-ppm/°C. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.Z.; Kuo, S.C.; Liao, Y.T. A 1.8-nW, -73.5-dB PSRR, 0.2-ms Startup Time, CMOS Voltage Reference With Self-Biased Feedback and Capacitively Coupled Schemes. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 1795–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.C.; Cordova, D.; Klimach, H.; Bampi, S. A 0.12–0.4 V, Versatile 3-Transistor CMOS Voltage Reference for Ultra-Low Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 3790–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Shu, W.; Chang, J.; Liu, J. A novel subthreshold voltage reference featuring 17 ppm/°C TC within −40°C to 125°C and 75 dB PSRR. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Lisbon, Portugal, 24–27 May 2015; pp. 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.; Lei, K.M.; Martins, R.P.; Mak, P.I. A 0.4-V 8400-μm2 Voltage Reference in 65-nm CMOS Exploiting Well-Proximity Effect. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 3822–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, D.; Jin, J.; Mercier, P.P.; Wang, H. Design and Analysis of a Family of pW-Level Sub-1V CMOS VRGs by Stacking a Current-Source Transistor and a Resistive-Load Transistor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Singapore, 19–22 May 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Cheng, L. A Picowatt CMOS Voltage Reference Operating at 0.5-V Power Supply With Process and Temperature Compensation for Low-Power IoT Systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, M. A 23-pW NMOS-Only Voltage Reference With Optimum Body Selection for Process Compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 4213–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnelli, L.; Crupi, F.; Corsonello, P.; Pace, C.; Iannaccone, G. A 2.6 nW, 0.45 V Temperature-Compensated Subthreshold CMOS Voltage Reference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2011, 46, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venezia, C.; Ballo, A.; Grasso, A.D.; Rizzo, A.; Ribellino, C.; Pennisi, S. 46-nA High-PSR CMOS Buffered Voltage Reference With 1.2–5 V and −40 °C to 125 °C Operating Range. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Palani, R.K.; Tripathi, S. Analysis and Design of Ripple-Free Bandgap Reference Circuit With p-n-p Bipolars. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).