Identification of Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Head and Neck Cancer: Bioinformatics Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
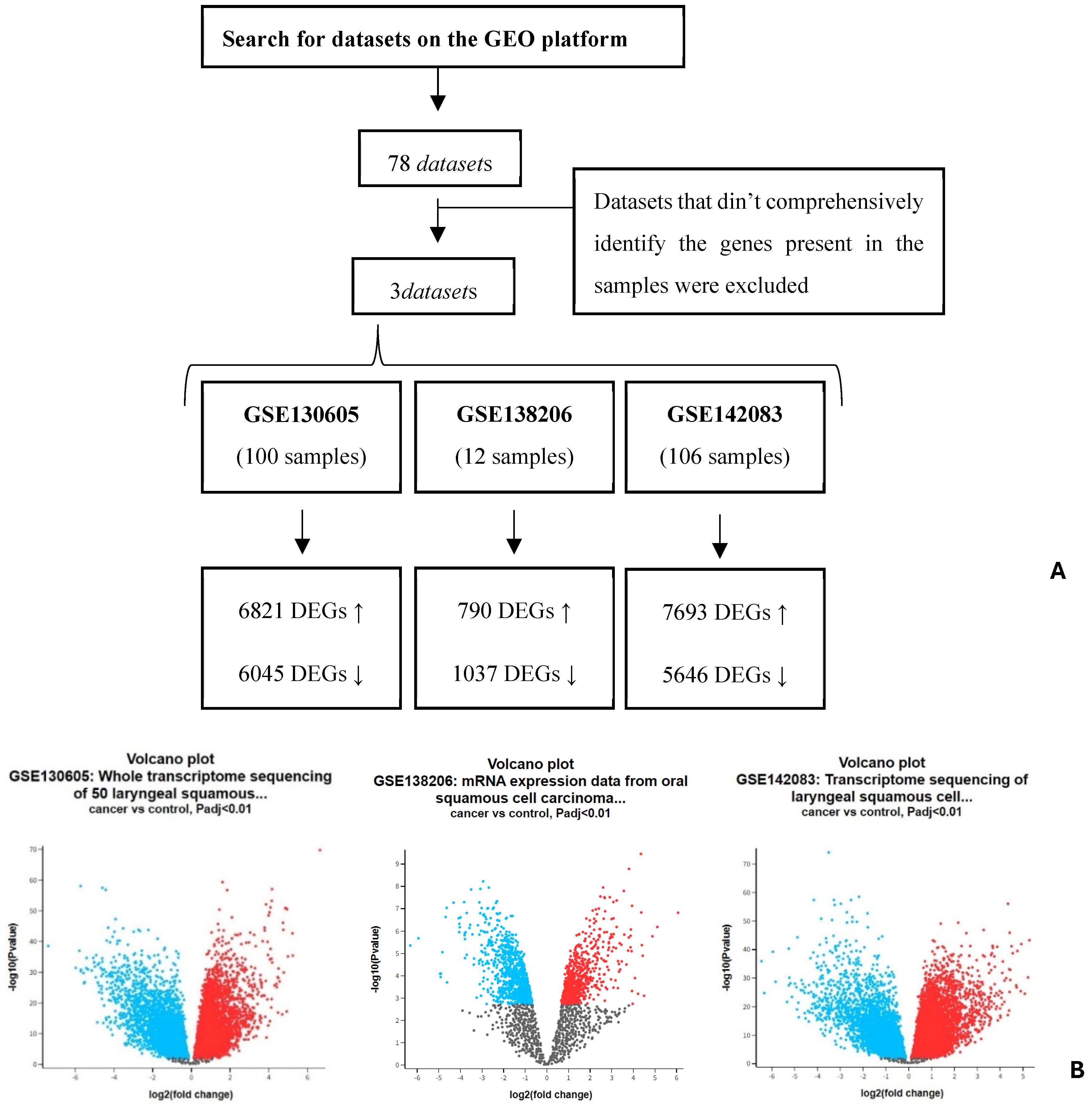
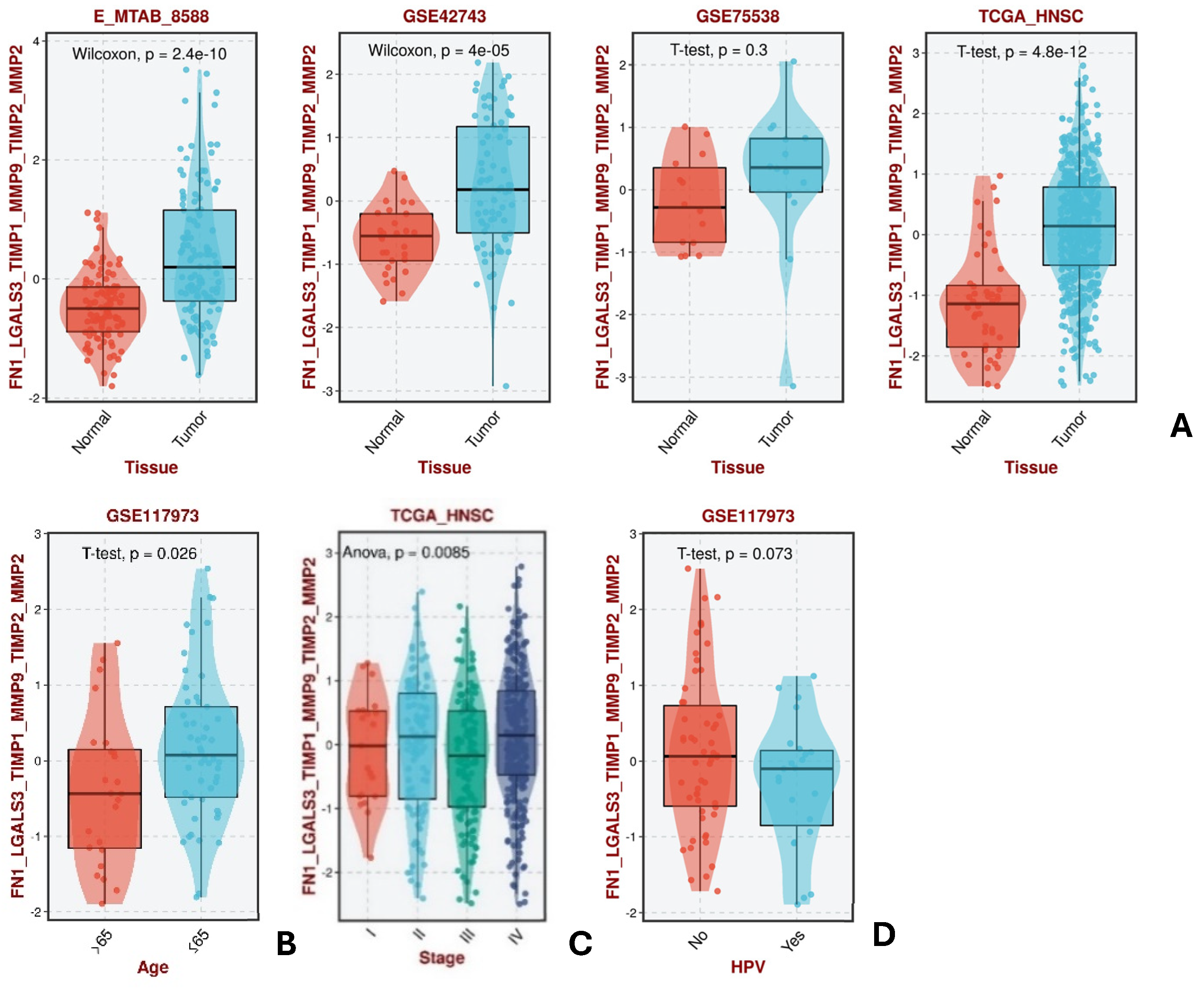
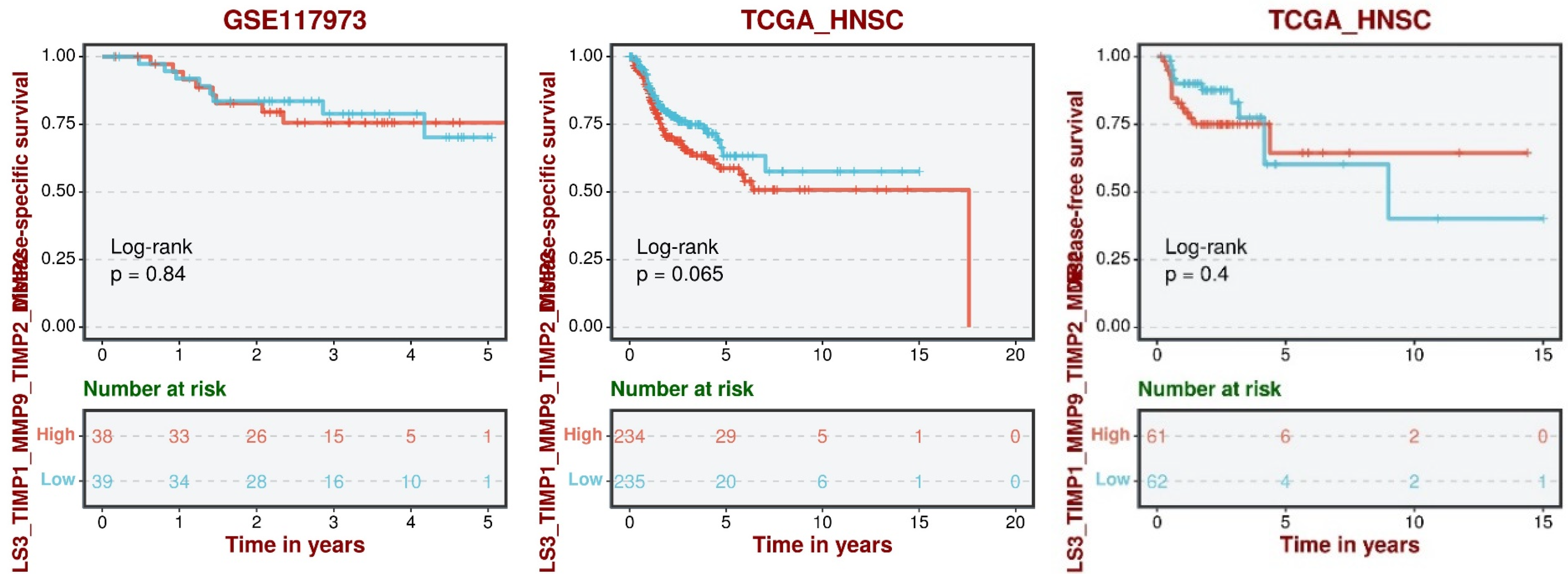
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yiu, C.Y.; Liu, C.C.; Wu, J.Y.; Tsai, W.W.; Liu, P.H.; Cheng, W.J.; Chen, J.Y.; Hung, K.C. Efficacy of the Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index for Predicting Overall Survival in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakili, S.; Barzegar Behrooz, A.; Wichelo, R.; Fernades, A.; Emwas, A.-H.; Jaremko, M.; Markowski, J.; Łos, M.J.; Ghavami, S.; Vitorino, R. Progress in Precision Medicine for Head and Neck Cancer. Preprints 2024, 16, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marur, S.; Forastiere, A.A. Head and neck cancer: Changing epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, O.; D'Agostino, V.G.; Santos, L.; Ferreira, R.; Vitorino, R. Multi-omics approach reveals promising salivary protein markers for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma prognosis. Oral. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 7, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettig, E.M.; D'Souza, G. Epidemiology of head and neck cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 24, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbiatti, A.L.; Padovani-Junior, J.A.; Maníglia, J.V.; Rodrigues, C.D.; Pavarino, É.C.; Goloni-Bertollo, E.M. Head and neck cancer: Causes, prevention and treatment. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 79, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gormley, M.; Creaney, G.; Schache, A.; Ingarfield, K.; Conway, D.I. Reviewing the epidemiology of head and neck cancer: Definitions, trends and risk factors. Br. Dent. J. 2022, 233, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza de Oliveira, N.; Rech, N. Biological aspects of Head and Neck Cancer. Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2023, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassirian, S.; Dzioba, A.; Hamel, S.; Patel, K.; Sahovaler, A.; Palma, D.A.; Read, N.; Venkatesan, V.; Nichols, A.C.; Yoo, J.; et al. Delay in diagnosis of patients with head-and-neck cancer in Canada: Impact of patient and provider delay. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 27, e467–e477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Hsueh, C.Y.; Shen, Y.J.; Guo, Y.; Huang, J.M.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, J.Y.; Gong, H.L.; Zhou, L. Small extracellular vesicle-packaged TGFβ1 promotes the reprogramming of normal fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts by regulating fibronectin in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2021, 517, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.; Guo, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Huo, Z. Aberrant Methylation and Immune Microenvironment Are Associated With Overexpressed Fibronectin 1: A Diagnostic and Prognostic Target in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 753563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funasaka, T.; Raz, A.; Nangia-Makker, P. Galectin-3 in angiogenesis and metastasis. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, A.; Niwa, M.; Noguchi, K.; Kanayama, T.; Niwa, A.; Matsuo, M.; Hatano, Y.; Tomita, H. Galectin-3 as a Next-Generation Biomarker for Detecting Early Stage of Various Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, D.; Sun, Z.; Yang, H.; Yin, Q. Galectin-3: A key player in microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokmak, S.; Arık, D.; Pınarbaşlı, Ö.; Gürbüz, M.K.; Açıkalın, M.F. Evaluation and Prognostic Significance of Galectin-3 Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100, 578s–583s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Zheng, Z.; Bai, Z.; Ouyang, K.; Wu, Q.; Xu, S.; Huang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Gao, J.; et al. Overexpression of angiogenic factors and matrix metalloproteinases in the saliva of oral squamous cell carcinoma patients: Potential non-invasive diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornieles, G.; Núñez, M.I.; Expósito, J. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors as Potential Prognostic Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer after Radiotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietruszewska, W.; Bojanowska-Poźniak, K.; Kobos, J. Matrix metalloproteinases MMP1, MMP2, MMP9 and their tissue inhibitors TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3 in head and neck cancer: An immunohistochemical study. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2016, 70, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zheng, A.; Li, F.; Wen, S.; Chen, S.; Tao, Z. Screening and identification of potential target genes in head and neck cancer using bioinformatics analysis. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 2955–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayanloo-Beik, A.; Sarvari, M.; Payab, M.; Gilany, K.; Alavi-Moghadam, S.; Gholami, M.; Goodarzi, P.; Larijani, B.; Arjmand, B. OMICS insights into cancer histology; Metabolomics and proteomics approach. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 84, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, C.; Han, W.; Luo, G.; Huang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Lu, W.; Hu, Q.; Shang, Z.; Yang, X. Advanced progress of spatial metabolomics in head and neck cancer research. Neoplasia 2024, 47, 100958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clough, E.; Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for gene expression and epigenomics data sets: 23-year update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 52, D138–D144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Weng, S.; Hui, X.; Xing, Z.; Ren, Y.; Ge, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, C.; Li, L.; et al. BEST: A web application for comprehensive biomarker exploration on large-scale data in solid tumors. J. Big Data 2022, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
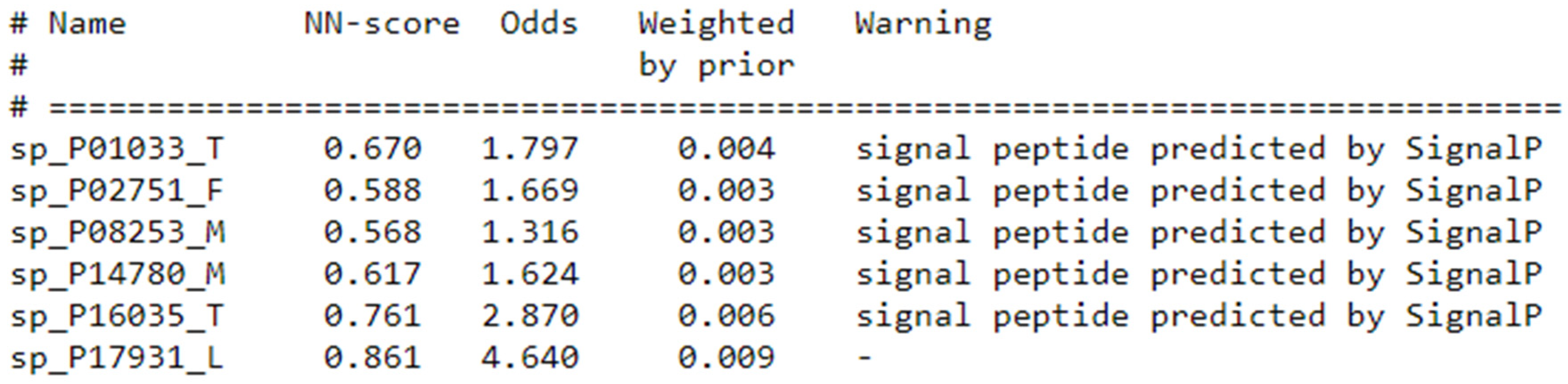
- Nielsen, H.; Petsalaki, E.I.; Zhao, L.; Stühler, K. Predicting eukaryotic protein secretion without signals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 140174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Madrigal, P.; Tarazona, S.; Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Cervera, A.; McPherson, A.; Szcześniak, M.W.; Gaffney, D.J.; Elo, L.L.; Zhang, X.; et al. A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, I.; Cordes, N. Focal adhesion signaling and therapy resistance in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 31, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyytiäinen, A.; Wahbi, W.; Väyrynen, O.; Saarilahti, K.; Karihtala, P.; Salo, T.; Al-Samadi, A. Angiogenesis Inhibitors for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatment: Is There Still Hope? Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 683570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, M.; Rüdiger, D.; Zahler, S. Mechanical Aspects of Angiogenesis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.L.; Veras, S.S.; Silveira, E.J.; Seabra, F.R.; Pinto, L.P.; Souza, L.B.; Freitas, R.A. The role of matrix extracellular proteins and metalloproteinases in head and neck carcinomas: An updated review. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2005, 71, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.J.; Ko, A.; Kil, S.H.; Mallen-St Clair, J.; Shin, D.S.; Wang, M.B.; Srivatsan, E.S. EGFR pathway targeting drugs in head and neck cancer in the era of immunotherapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Huang, L.; Lu, Y.G.; Zheng, D.L. Roles of the Wnt Signaling Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 590912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortuna-Costa, A.; Gomes, A.M.; Kozlowski, E.O.; Stelling, M.P.; Pavão, M.S. Extracellular galectin-3 in tumor progression and metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, L. Galectin-3 Is a Potential Mediator for Atherosclerosis. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 5284728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Shen, R.; Yu, L.; Zheng, X.; Cui, R.; Song, Y.; Wang, D. Roles of galectin-3 in the tumor microenvironment and tumor metabolism (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 1799–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Chun, K.H. Non-classical role of Galectin-3 in cancer progression: Translocation to nucleus by carbohydrate-recognition independent manner. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, N.; Halder, A.K.; Mallick, S.; Saha, A.; Saha, K.D.; Jha, T. Robust design of some selective matrix metalloproteinase-2 inhibitors over matrix metalloproteinase-9 through in silico/fragment-based lead identification and de novo lead modification: Syntheses and biological assays. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4291–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Wang, C.; Jian, S.; Gang, Y.; Wen, C.; Hu, B. Construction of wound repair model and function of recombinant TIMP from Hyriopsis cumingii. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 119, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feser, R.; Opperman, R.; Nault, B.; Maiti, S.; Chen, V.; Majumder, M. Breast Cancer Cell Secretome Analysis to Decipher miRNA Tumor Biology and Discover Potential. Biomarkers. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Dong, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 3872367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeney, D.; Liu, Y.; Lazaroff, C.; Gurung, S.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Unravelling the distinct biological functions and potential therapeutic applications of TIMP2 in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2022, 43, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakiyanov, O.; Kalousová, M.; Zima, T.; Tesař, V. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases in kidney disease. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 105, 141–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Dey, M.K.; Devireddy, R.; Gartia, M.R. Biomarkers in Cancer Detection, Diagnosis, and Prognosis. Sensors 2023, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakari, S.; Niels, N.K.; Olagunju, G.V.; Nnaji, P.C.; Ogunniyi, O.; Tebamifor, M.; Israel, E.N.; Atawodi, S.E.; Ogunlana, O.O. Emerging biomarkers for non-invasive diagnosis and treatment of cancer: A systematic review. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1405267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Protein of Interest | Negative Regulators | Positive Regulators |
|---|---|---|
| FN1 | FGG; SERPINA5; Viocristine sulfate | TWIST1; SNAIL/RELA/RAPP1; DLK1 |
| LGALS3 | ND | CSNK1A1; ABL2; GSK3B |
| MMP9 | SPRY4; SPDEF; PZP; A2M | ETS1; SANI2; USP6; Nfkb-p65/p50 |
| TIMP1 | ND | SPRY4 |
| MMP2 | NME1; PZP; A2M | MMP25; TWIST1; TP53; RUNX2; NODAL |
| TIMP2 | DNMT3A; PTTG1 | ND |
| Dataset | Main Conclusion on Gene Expression Pattern |
|---|---|
| GSE130605 | Only MMP9 and MMP2 were identified with statistical significance, and they exhibited a similar increased expression profile. Their positive regulators were found to be upregulated and negative ones downregulated. |
| GSE138206 | Only MMP9 and TIMP1 were identified with statistical significance, and the results obtained support the inverse expression relationship between these two proteins. For MMP9, only positive regulators were found to be upregulated. |
| GSE142083 | For FN1, LGALS3, MMP2, and MMP9, a statistically significant difference in expression levels was identified between the control group and HNC. All showed increased expression in HNC except for LGALS3, which was downregulated. The pattern expression of FN1, MMP2, and MMP9 seemed to show to a lack of negative regulators, while LGALS3 did not seem to be affected by its regulators. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes, A.; Vitorino, R. Identification of Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Head and Neck Cancer: Bioinformatics Approach. Targets 2024, 2, 470-480. https://doi.org/10.3390/targets2040026
Fernandes A, Vitorino R. Identification of Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Head and Neck Cancer: Bioinformatics Approach. Targets. 2024; 2(4):470-480. https://doi.org/10.3390/targets2040026
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes, Alexandra, and Rui Vitorino. 2024. "Identification of Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Head and Neck Cancer: Bioinformatics Approach" Targets 2, no. 4: 470-480. https://doi.org/10.3390/targets2040026
APA StyleFernandes, A., & Vitorino, R. (2024). Identification of Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Head and Neck Cancer: Bioinformatics Approach. Targets, 2(4), 470-480. https://doi.org/10.3390/targets2040026







