Journal Description
Targets
Targets
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on chemical measurement science, biology, material science, pharmacy, clinical diagnostics, molecular medicine and biomedicine published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 24.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Companion journal: Sensors.
- Journal Clusters of Oncology: Cancers, Current Oncology, Onco and Targets.
Latest Articles
Extracellular Vesicle-Associated miRNAs in Cornea Health and Disease: Diagnostic Potential and Therapeutic Implications
Targets 2025, 3(4), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3040032 - 17 Oct 2025
Abstract
Extracellular Vesicle-associated microRNAs (EV-miRNAs) are emerging as pivotal regulators of corneal health and disease, holding exceptional promise for transforming both diagnostics and therapeutics. These vesicles carry distinct miRNA signatures in biofluids such as tears, offering a powerful, non-invasive approach for early detection, risk
[...] Read more.
Extracellular Vesicle-associated microRNAs (EV-miRNAs) are emerging as pivotal regulators of corneal health and disease, holding exceptional promise for transforming both diagnostics and therapeutics. These vesicles carry distinct miRNA signatures in biofluids such as tears, offering a powerful, non-invasive approach for early detection, risk stratification, and dynamic monitoring of corneal disorders. In addition, EV-miRNAs act as key mediators of critical biological processes, including inflammation, fibrosis, and tissue repair. Consequently, they represent attractive therapeutic targets; for example, engineered EVs loaded with miRNA mimics or inhibitors can precisely modulate these pathways to promote regeneration and suppress disease progression. Yet, despite this considerable promise, the translation of EV-miRNA research into clinical practice remains constrained by several challenges. Topmost among these are the lack of standardized EV isolation methods, variability in miRNA quantification, and the pressing need for regulatory frameworks tailored to the complexity of these biological therapeutics. Addressing these barriers is essential to ensure reproducibility, scalability, and safety in clinical applications. Accordingly, this review synthesizes current knowledge on EV-miRNA profiles in corneal diseases, critically evaluates their diagnostic and therapeutic potential, and highlights strategies to overcome existing technical and regulatory limitations. Ultimately, the successful integration of EV-miRNA-based approaches into personalized medicine frameworks could revolutionize the management of corneal diseases and substantially improve patient outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Biomarkers of Disease: Discovery and Clinical Applications)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Integrating Nanotechnology and Artificial Intelligence for Early Detection and Prognostication of Glioblastoma: A Translational Perspective
by
Meghraj Vivekanand Suryawanshi, Imtiyaz Bagban and Akshata Yashwant Patne
Targets 2025, 3(4), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3040031 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and aggressive malignant brain tumor in adults. This review explains the connections between the genesis and progression of GBM and particular cellular tumorigenic mechanisms, such as angiogenesis, invasion, migration, growth factor overexpression, genetic instability, and apoptotic disorders,
[...] Read more.
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and aggressive malignant brain tumor in adults. This review explains the connections between the genesis and progression of GBM and particular cellular tumorigenic mechanisms, such as angiogenesis, invasion, migration, growth factor overexpression, genetic instability, and apoptotic disorders, as well as possible therapeutic targets that help predict the course of the disease. Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) diagnosis relies heavily on histopathological features, molecular markers, extracellular vesicles, neuroimaging, and biofluid-based glial tumor identification. In order to improve miRNA stability and stop the proliferation of cancer cells, nanoparticles, magnetic nanoparticles, contrast agents, gold nanoparticles, and nanoprobes are being created for use in cancer treatments, neuroimaging, and biopsy. Targeted nanoparticles can boost the strength of an MRI signal by about 28–50% when compared to healthy tissue or controls in a preclinical model like mouse lymph node metastasis. Combining the investigation of CNAs and noncoding RNAs with deep learning-driven global profiling of genes, proteins, RNAs, miRNAs, and metabolites presents exciting opportunities for creating new diagnostic markers for malignancies of the central nervous system. Artificial intelligence (AI) advances precision medicine and cancer treatment by enabling the real-time analysis of complex biological and clinical data through wearable sensors and nanosensors; optimizing drug dosages, nanomaterial design, and treatment plans; and accelerating the development of nanomedicine through high-throughput testing and predictive modeling.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
The Expanding E3 Ligase-Ligand Landscape for PROTAC Technology
by
Zhenzhen Li, Xiaoli Huang, Xuchi Zhao, Yunxiu Zhang and Ping Li
Targets 2025, 3(4), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3040030 - 27 Sep 2025
Abstract
Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) are a transformative therapeutic modality that co-opts the ubiquitin-proteasome system for selective protein degradation. To date, the development of PROTACs has been overwhelmingly dominated by the recruitment of four canonical E3 ligases: CRBN, VHL, MDM2, and IAP. This limited repertoire
[...] Read more.
Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) are a transformative therapeutic modality that co-opts the ubiquitin-proteasome system for selective protein degradation. To date, the development of PROTACs has been overwhelmingly dominated by the recruitment of four canonical E3 ligases: CRBN, VHL, MDM2, and IAP. This limited repertoire represents a critical bottleneck, restricting the scope of degradable proteins and potential therapeutic applications. Addressing this challenge, recent years have witnessed a surge in the successful recruitment of novel E3 ligases. This review provides a dedicated and comprehensive summary of this progress, focusing exclusively on the emerging E3 ligases and their cognate ligands reported for PROTAC technology outside of the well-established quartet. We detail their discovery and strategic application, highlighting how this rapidly expanding toolbox promises to overcome existing limitations and unlock the full potential of targeted protein degradation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Comprehending Molecular Targets: Mechanisms and Actions in Drug Development)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Contrast-Enhanced Mammography as a Functional Biomarker in Breast Cancer: Correlation of Enhancement Patterns with Ki-67 and Histological Grade
by
Marina Balbino, Manuela Montatore, Federica Masino, Antonietta Ancona, Francesca Anna Carpagnano, Giulia Capuano, Riccardo Guglielmi and Giuseppe Guglielmi
Targets 2025, 3(3), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3030029 - 17 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) combines anatomical and functional imaging, showing promise in breast cancer diagnosis. Despite well-established lesion detection accuracy, few studies have investigated the link between CESM enhancement patterns and tumor aggressiveness biomarkers. Methods: We retrospectively evaluated 100 patients (mean age
[...] Read more.
Background: Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) combines anatomical and functional imaging, showing promise in breast cancer diagnosis. Despite well-established lesion detection accuracy, few studies have investigated the link between CESM enhancement patterns and tumor aggressiveness biomarkers. Methods: We retrospectively evaluated 100 patients (mean age 59.5 years) undergoing CESM with complete histopathological data. Lesions were categorized by enhancement intensity (high, medium, low) and contrast homogeneity (homogeneous vs. heterogeneous), correlated with Ki-67 index and histological grade. Results: Lesion size measured by CESM closely matched histology (mean 2.16 cm vs. 2.25 cm). Mass-like lesions corresponded mainly to invasive ductal carcinoma, while non-mass patterns aligned with lobular or in situ carcinomas. Enhancement intensity correlated moderately with Ki-67 (Spearman ρ = 0.56, p < 0.001), and contrast heterogeneity showed a weaker but significant correlation with tumor grade (ρ = 0.22, p < 0.05). Conclusions: CESM accurately assesses tumor size and provides functional insight into tumor biology. Enhancement intensity may serve as a non-invasive proliferation marker, while contrast heterogeneity offers additional prognostic data, supporting CESM’s role in personalized breast cancer management.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Use of Particle Radiotherapy and Radiation Sensitizers for Treatment of Chordomas: A Narrative Review
by
Aarti Kishore Jain, Sahdev S. Baweja, Beatrice Campilan, Madison J. Michles, Aviva Berkowitz and Patricia L. Zadnik Sullivan
Targets 2025, 3(3), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3030028 - 15 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Chordomas are primary tumors of the skull base and vertebral column typically derived from the notochord. Treatment options consist of surgical resection, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. This study reviews clinical trials focused on radiotherapy techniques, such as photon therapy and carbon ion radiotherapy, as
[...] Read more.
Chordomas are primary tumors of the skull base and vertebral column typically derived from the notochord. Treatment options consist of surgical resection, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. This study reviews clinical trials focused on radiotherapy techniques, such as photon therapy and carbon ion radiotherapy, as well as the concomitant use of radia-tion sensitizers. We completed a literature review on all published clinical trials on the usage of photon, proton, and carbon ion radiotherapy (CIRT) for chordoma in adults and all published literature on radiation sensitizers used for treatment in chordoma from 2000 to 2025. We reviewed all nine current clinical trials on radiotherapy for chordoma in adults. All clinical trials were able to achieve an overall survival rate above 50% at 3-year follow-up. Seven publications were found on the use of radiation sensitizers for chordomas, both in vitro and in vivo. The completed clinical trials evaluate the effectiveness of proton, photon, and CIRT for treatment of the skull base, spine, and sacral chordoma. Current trials continue these efforts and compare the different radiotherapies and determine appropriate doses. Research on radiation sensitizers for chordomas shows various therapies, ranging from hyperthermia to pharmaceutical options, that require further study.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Approaches for Identifying LncRNA-Associated Proteins for Therapeutic Targets and Cancer Biomarker Discovery
by
Mohammad Shabir Hussain, Puneet Vij, Sudhir Kotnala, Shadab Ahmad, Subhash C. Chauhan and Manish K. Tripathi
Targets 2025, 3(3), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3030027 - 11 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are increasingly recognized as key regulators of gene expression and cellular signaling in cancer. Their functions are primarily mediated through interactions with specific protein partners that modulate chromatin structure, epigenetic remodeling, transcription, and signal transduction. In this review, we
[...] Read more.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are increasingly recognized as key regulators of gene expression and cellular signaling in cancer. Their functions are primarily mediated through interactions with specific protein partners that modulate chromatin structure, epigenetic remodeling, transcription, and signal transduction. In this review, we explore reports and strategies for the proteomic characterization of lncRNA-associated proteins, particularly emphasizing high-throughput liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS)-based techniques. Affinity-based methods such as RNA pull-down, ChIRP MS, RAP-MS, BioID-MS, and SILAC-MS enable sensitive and specific mapping of lncRNA and protein complexes. These approaches reveal cancer-specific proteomic signatures, post-translational modifications, and mechanistic insights into tumor biology. The use of label-free quantification, bituminization, and crosslinking strategies further enhances the resolution of dynamic RNA–protein networks. Validation tools following bioinformatic analyses, such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and ELISA, are used to prioritize and confirm findings. Candidate biomarkers from hepatocellular carcinoma to colorectal and prostate cancers, profiling lncRNA-associated proteins, hold promise for identifying clinically actionable biomarkers and therapeutic targets. This review highlights the translational relevance of lncRNA protein studies and advocates for their broader adoption in oncological research. In LC-MS workflows, proteins bound to lncRNAs are enzymatically digested into peptides, separated via nano-LC, and analyzed using high-resolution tandem MS. Label-free or isotope-labeled methods quantify differential enrichment, followed by bioinformatics-driven pathway annotation.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Skeletal Health in Pituitary and Neuroendocrine Diseases: Prevention and Treatments of Bone Fragility
by
Flavia Costanza, Antonella Giampietro, Laura De Marinis, Antonio Bianchi, Sabrina Chiloiro and Alfredo Pontecorvi
Targets 2025, 3(3), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3030026 - 8 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Bone loss is common in patients affected by pituitary and neuroendocrine disorders as both hormone excess and hormone deficiency can affect bone structure. There is increasing evidence that pituitary hormones directly influence bone cells turnover by bypassing endocrine organs. Osteopenia, osteoporosis, and vertebral
[...] Read more.
Bone loss is common in patients affected by pituitary and neuroendocrine disorders as both hormone excess and hormone deficiency can affect bone structure. There is increasing evidence that pituitary hormones directly influence bone cells turnover by bypassing endocrine organs. Osteopenia, osteoporosis, and vertebral fractures often result from these skeletal changes; however, diagnosing and managing bone frailty in pituitary and neuroendocrine disorders is still challenging because of the unpredictable outcomes in terms of fracture risk, even after the improvement of pituitary dysfunction, and the limited evidence for the use of bone-active drugs in these pathologies. The use of vitamin D supplements for fracture prevention is still debated in these secondary forms of bone frailty, although some studies have shown similar benefits to those derived in the general population. This review offers an overview on the characteristics of bone fragility in different pituitary and neuroendocrine diseases, and focuses on the prevention and treatment of skeletal disorders with bone-active drugs and vitamin D formulations currently available in this setting.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Bacteriophages: Potential Candidates for the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Environment
by
Shahid Sher, Husnain Ahmad Khan, Zaman Khan, Muhammad Sohail Siddique, Dilara Abbas Bukhari and Abdul Rehman
Targets 2025, 3(3), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3030025 - 22 Jul 2025
Abstract
The invention of antibacterial agents (antibiotics) was a significant event in the history of the human race, and this invention changed the way in which infectious diseases were cured; as a result, many lives have been saved. Recently, antibiotic resistance has developed as
[...] Read more.
The invention of antibacterial agents (antibiotics) was a significant event in the history of the human race, and this invention changed the way in which infectious diseases were cured; as a result, many lives have been saved. Recently, antibiotic resistance has developed as a result of excessive use of antibiotics, and it has become a major threat to world health. ARGs are spread across biomes and taxa of bacteria via lateral or horizontal gene transfer (HGT), especially via conjugation, transformation, and transduction. This review concerns transduction, whereby bacteriophages or phages facilitate gene transfer in bacteria. Bacteriophages are just as common and many times more numerous than their bacterial prey, and these phages are much more influential in controlling the population of bacteria. It is estimated that 25% of overall genes of Escherichia coli have been copied by other species of bacteria due to the HGT process. Transduction may take place via a generalized or specialized mechanism, with phages being ubiquitous in nature. Phage and virus-like particle (VLP) metagenomics have uncovered the emergence of ARGs and mobile genetic elements (MGEs) of bacterial origins. These genes, when transferred to bacteria through transduction, confer resistance to antibiotics. ARGs are spread through phage-based transduction between the environment and bacteria related to people or animals, and it is vital that we further understand and tackle this mechanism in order to combat antimicrobial resistance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Small-Molecule Antibiotic Drug Development)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Current Pharmacotherapies for Alcohol Use Disorder in Italy: From Neurobiological Targets to Clinical Practice
by
Andrea Mastrostefano, Giuseppe Greco, Chiara De Bacco, Flavio Davini, Giacomo Polito, Edoardo Carnevale, Giuseppe Anastasi and Sergio Terracina
Targets 2025, 3(3), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3030024 - 11 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Alcohol is a prevalent psychoactive substance and a risk factor for developing injuries and non-communicable diseases, representing a significant health and economic burden. Alcohol involves numerous molecular pathways. Its metabolism is regulated by alcohol dehydrogenases and aldehyde dehydrogenases; it also stimulates cholinergic interneurons,
[...] Read more.
Alcohol is a prevalent psychoactive substance and a risk factor for developing injuries and non-communicable diseases, representing a significant health and economic burden. Alcohol involves numerous molecular pathways. Its metabolism is regulated by alcohol dehydrogenases and aldehyde dehydrogenases; it also stimulates cholinergic interneurons, increasing the sensitivity of 5-HT3 receptors, while chronic alcohol consumption alters the mesolimbic dopaminergic system involved in reward processing. The treatment of alcohol use disorder (AUD) is essential to manage complex patients, following an evidence-based approach. The aim of this narrative review is to provide a clear and practical summary to support and assist healthcare professionals in the Italian context. Approved pharmacological treatments for AUD include oral naltrexone and acamprosate, sodium oxybate, disulfiram, and nalmefene. Off-label therapies include baclofen, topiramate, gabapentin, pregabalin, ondansetron, and cytisine. A more informed clinical and practical approach that understands the altered neuronal signaling pathways is essential for offering effective, efficient, appropriate, and safe therapeutic algorithms for complex patients with alcohol use disorder. A comprehensive framework should include integrated treatments with a personalized approach.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Natural Products Acting as Senolytics and Senomorphics Alleviate Cardiovascular Diseases by Targeting Senescent Cells
by
Hejing Tang, Xu Zhang, Senyang Hu, Yuhan Song, Wenhua Jin, Jianmin Zou, Yan Zhang, Jiayue Guo, Peng An, Junjie Luo, Pengjie Wang, Yongting Luo and Yinhua Zhu
Targets 2025, 3(3), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3030023 - 25 Jun 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Taken together, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) have become one of the prime causes of the global disease burden. Aging is closely related to CVDs and is considered to be one of the crucial factors in the incidence of CVDs. In the process of aging,
[...] Read more.
Taken together, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) have become one of the prime causes of the global disease burden. Aging is closely related to CVDs and is considered to be one of the crucial factors in the incidence of CVDs. In the process of aging, cellular senescence is an important cause of CVDs such as atherosclerosis and atrial fibrillation. The treatment for CVDs by targeting senescent cells has been carried out in cellular models, animal experiments, and anti-aging clinical trials. Chemical approaches to regulate the fate of senescent cells by senolytics and senomorphics, which could selectively eliminate senescent cells or inhibit their senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) secretion, have been increasingly explored. Importantly, many natural products with promising biological activity extracted from food or medicine–food homology have the above-mentioned effects. Furthermore, the identification of the target cells or target proteins of these natural products is of great significance for the indication of their mechanism of action, and it also lays a scientific foundation for the realization of precision nutrition intervention in the future. This review details how senescent cells affect CVDs, how natural products target senescent cells through nutritional intervention, and research methods for natural products in cardiovascular aging.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Report on the Antidepressant-like Activity of Paullinia pinnata Methanol Leaf Extract in Mice and Possible Involvement of Monoaminergic Mechanisms
by
Raymond I. Ozolua, Muideen A. Ajibade, Dickson O. Uwaya, Abigail M. Akhigbemen and Israel O. Bolanle
Targets 2025, 3(2), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3020022 - 16 Jun 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In West Africa, Paullinia pinnata (P. pinnata) alcohol leaf extracts are used to treat disorders such as depression and anxiety with no documented scientific justification. We have therefore evaluated the potential anxiolytic and antidepressant effects of Paullinia pinnata methanol leaf extract
[...] Read more.
In West Africa, Paullinia pinnata (P. pinnata) alcohol leaf extracts are used to treat disorders such as depression and anxiety with no documented scientific justification. We have therefore evaluated the potential anxiolytic and antidepressant effects of Paullinia pinnata methanol leaf extract (PPME) in mice, along with probable underlying mechanisms. Adult Swiss albino mice were administered 100, 200, and 400 mg/kg of PPME orally before subjecting them through elevated plus maze (EPM) and hole-board tests to assess the anxiolytic effect. The tail suspension test (TST) and the forced swim test (FST) were used to assess the antidepressant-like effects. Reserpine, labetalol, and risperidone were used to investigate probable mechanisms of action. In both FST and TST, the duration of immobility was considerably reduced by PPME. Conversely, PPME had no significant effect on the number of mice who dipped their heads into the hole-board or entered the EPM’s open arm. Mechanistic analysis revealed that in mice given labetalol or risperidone beforehand, PPME dramatically reduced the length of immobility and reversed ptosis and akinesia caused by reserpine. Our findings suggest that PPME possesses antidepressant-like, but not anxiolytic-like, effects in mice, and antidepressant action may involve enhancing noradrenergic and serotonergic mechanisms.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Targeted Treatment Approaches for Gastrointestinal Metastases of Malignant Melanoma: Clinical Insights and Overcoming Drug Resistance
by
Tsvetelina Velikova, Marina Konaktchieva and Milena Peruhova
Targets 2025, 3(2), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3020021 - 11 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Gastrointestinal metastases of malignant melanoma are relatively common and pose significant challenges to clinical management due to their complex presentation and resistance to therapy. Early detection and a multidisciplinary treatment approach are critical to improve outcomes. This review highlights targeted treatment strategies for
[...] Read more.
Gastrointestinal metastases of malignant melanoma are relatively common and pose significant challenges to clinical management due to their complex presentation and resistance to therapy. Early detection and a multidisciplinary treatment approach are critical to improve outcomes. This review highlights targeted treatment strategies for gastrointestinal melanoma metastases, focusing on current therapeutic options and the mechanisms underlying drug resistance. Advances in immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and targeted therapies, such as BRAF and MEK inhibitors, have revolutionized melanoma treatment, yet their efficacy is often limited by the emergence of resistance mechanisms, including genetic mutations, tumor microenvironment factors, and immune escape. Herein, we explore potential resistance biomarkers for resistance and emerging targeting treatments targeting these pathways. Understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms driving drug resistance remains critical to overcoming therapeutic limitations, emphasizing the importance of collaborative efforts in research and clinical practice to refine therapeutic approaches and improve survival rates for patients with metastatic melanoma involving the gastrointestinal tract. Future directions include optimizing combination therapies and leveraging precision medicine to address resistance and disease progression.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Role of Osimertinib in Stage I–II Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Activating EGFR Mutation
by
Cesare Gridelli, Emanuela Nuccio and Francesca Casaluce
Targets 2025, 3(2), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3020020 - 11 Jun 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide with only approximately 30% of new diagnoses manifesting with localized stages IA–IIA. Osimertinib is a third-generation inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which is used for treating metastatic, locally
[...] Read more.
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide with only approximately 30% of new diagnoses manifesting with localized stages IA–IIA. Osimertinib is a third-generation inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which is used for treating metastatic, locally advanced, and early-stage NSCLC expressing common EGFR mutations. Two phase III clinical trials supported yresectable locally advanced disease, consisting of the ADAURA and LAURA studies, respectively. On the other hand, conflicting data on neoadjuvant efficacy led to the design of the ongoing Neo-ADAURA trial. In this review, we describe the pivotal trials that led to the approval of osimertinib use as an adjuvant treatment in radically resected NSCLC patients and as maintenance therapy after chemoradiotherapy. We also summarize the principal ongoing clinical trials in the neoadjuvant and adjuvant settings. Finally, we analyze several issues about the use of osimertinib in those different early settings while also depicting future perspectives and the potential evolution of treatment strategies.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic, and Anxiolytic Effects of Crude Extracts and Isolated Bioactive Fractional Compounds from Pouzolzia sanguinea
by
Md. Qamrul Ahsan, Rateep Nasim, Md. Talat Nasim and S. M. Shahinul Islam
Targets 2025, 3(2), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3020019 - 10 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pharmacological relevance: Ethnic people residing in the Chittagong Hill Tracts (CHTs) of Bangladesh use Pouzolzia sanguinea to alleviate flatulence, for menstruation, inflammation, insomnia, and analgesia. However, there is no scientific evidence regarding the bioactivity of these plants. Aim: This study aimed to isolate
[...] Read more.
Pharmacological relevance: Ethnic people residing in the Chittagong Hill Tracts (CHTs) of Bangladesh use Pouzolzia sanguinea to alleviate flatulence, for menstruation, inflammation, insomnia, and analgesia. However, there is no scientific evidence regarding the bioactivity of these plants. Aim: This study aimed to isolate bioactive fractional compounds from Pouzolzia sanguinea (IFCPS) crude extract to assess the anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anxiolytic activities. Materials and Methods: Preparative TLC-bioautography and silica gel two-stage column chromatography were used to isolate bioactive fractional compounds from P. sanguinea methanol crude extracts. The anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anxiolytic activities of extracts and IFCPS were studied by inhibiting protein denaturation, acetic acid-induced writhing, Eddy’s hot plate, field cross, and hole cross methods. Results: The dried crude extract’s chemical analysis revealed alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, saponins, vitamin C, and tannins. Nine single isolated fractional compounds (IFC1PS to IFC9PS) were isolated through TLC. Among these, IFC2PS exhibited (p ˂ 0.01) the most potent anti-inflammatory activity in the inhibition of protein denaturation studies (70.51%), which was slightly lower than acetyl salicylic acid (82.29%), at160 µg/mL. This inhibitory effect occurred in a dose-dependent manner. IFC2PS exhibited the most potent peripheral analgesic and moderate central analgesic effects compared to the standard. In contrast, IFC1PS showed moderate effects in both areas. IFC8PS showed superior anxiolytic activities compared to crude extracts and other IFCPS. Conclusions: Out of the nine fractional compounds isolated, the IFC2PS reduced pain and inflammation, whilst IFC8PS exhibited anxiolytic activities. This is the first comprehensive study demonstrating the anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anxiolytic effects of crude extracts and isolated fractional compounds from the whole plant of P. sanguinea, which may have immediate experimental and clinical applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Recent Progress in Small Molecule Fluorescent Probes for Imaging and Diagnosis of Liver Injury
by
Shuo Liu, Fei Huang, Xinyi Huang, Fuxin Zhang, Dong Pei, Jinlong Zhang and Jun Hai
Targets 2025, 3(2), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3020018 - 28 May 2025
Abstract
The liver is an essential metabolic organ that is involved in energy metabolism, protein synthesis, and detoxification. Many endogenous and exogenous factors can cause liver injury, a complex pathological condition. It poses a serious risk to human health due to its extremely varied
[...] Read more.
The liver is an essential metabolic organ that is involved in energy metabolism, protein synthesis, and detoxification. Many endogenous and exogenous factors can cause liver injury, a complex pathological condition. It poses a serious risk to human health due to its extremely varied clinical manifestations, which range from mild fatty liver to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma. Because of their low specificity, lack of real-time monitoring, and invasiveness, traditional diagnostic techniques for liver injury, such as histopathological examination and serological analysis, have inherent limitations. Fluorescent probe technology, which offers high sensitivity, non-invasiveness, and real-time imaging capabilities, has become a potent tool in liver injury research and early diagnosis in recent years. The pathophysiology of liver injuries caused by alcohol, chemicals, drugs, and the immune system is methodically covered in this review, along with new developments in fluorescent probe development for their detection. The focused imaging properties of various fluorescent probes are highlighted, along with their possible uses in drug screening and early liver injury detection. This review attempts to offer theoretical insights to support the optimization of precision diagnostic and therapeutic approaches by summarizing these findings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Progress in Bioimaging and Targeted Therapy)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Targeting Obesity in Cardiovascular Disease Management: Cardiac Adipose Tissue Is a Real Biomarker!
by
Saverio D’Elia, Ettore Luisi, Achille Solimene, Chiara Serpico, Mariarosaria Morello, Gisella Titolo, Valentina Maria Caso, Francesco S. Loffredo, Paolo Golino, Giovanni Cimmino and Francesco Natale
Targets 2025, 3(2), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3020017 - 23 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Obesity has been defined as a true worldwide “pandemic” by the World Health Organization and represents one of the major public health problems. It is associated with a reduction in life expectancy of about 7–8 years due to related cardiovascular diseases such
[...] Read more.
Background: Obesity has been defined as a true worldwide “pandemic” by the World Health Organization and represents one of the major public health problems. It is associated with a reduction in life expectancy of about 7–8 years due to related cardiovascular diseases such as arterial hypertension, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. Adipose tissue is not merely a fat storage site but a true endocrine and immunologically active organ that secretes hormones and mediators (adipokines), influencing cardiovascular risk and host physiology. Objective: This review summarizes the current understanding of the role of epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) in cardiovascular disease pathophysiology and discusses its clinical diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Methods: A narrative non-systematic review was conducted focusing on recent literature concerning the biological and clinical aspects of cardiac adipose tissue, with particular emphasis on epicardial adipose tissue. The review examined its gene expression profile, secretory function, and interaction with cardiovascular structures and diseases. Findings: There are different types of adipose tissue, including cardiac adipose tissue, which comprises epicardial and pericardial (or paracardiac) fractions. Epicardial adipose tissue is unique due to its proximity to the heart and a distinct gene expression profile compared to other adipose depots such as visceral and subcutaneous fat. EAT plays a crucial role in the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases with high morbidity and mortality, acting both as a metabolic and inflammatory mediator. Conclusion: Cardiac adipose tissue, particularly EAT, is a key player in cardiometabolic disease. Understanding its pathophysiological role and incorporating imaging tools to evaluate EAT may enhance cardiovascular risk stratification and disease management.
Full article
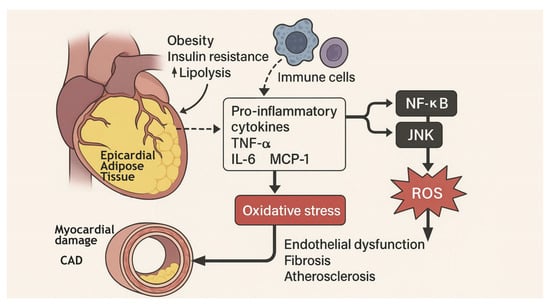
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Design and Prospects of Influenza Virus Vaccines Based on Conserved Epitopes and Adjuvant Optimization
by
Meng-Qian Zhang, Jin-Wei Bu, Zhi-Gang Wang and Shu-Lin Liu
Targets 2025, 3(2), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3020016 - 19 May 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Influenza viruses pose a significant threat to human health, and vaccination remains the most cost-effective and efficient strategy for controlling outbreaks. This review first introduces the molecular characteristics of influenza A virus (IAV) and examines how conserved epitopes contribute to overcoming its high
[...] Read more.
Influenza viruses pose a significant threat to human health, and vaccination remains the most cost-effective and efficient strategy for controlling outbreaks. This review first introduces the molecular characteristics of influenza A virus (IAV) and examines how conserved epitopes contribute to overcoming its high variability, laying the foundation for broadly protective vaccine design. Different vaccine platforms are then categorized and analyzed through representative examples to highlight their research significance and application potential. The discussion further extends to the role of adjuvants in modulating immune responses, with a focus on how their optimization enhances vaccine efficacy. We explore future directions in vaccine design, highlighting the synergistic potential of conserved epitope targeting and adjuvant improvement in advancing the next generation of influenza vaccines.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Progress in Bioimaging and Targeted Therapy)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
A Case Report on Magnetic Resonance-Guided Surveillance of a Giant Hydatid Cyst: Implications for Therapeutic Management and Other Modalities
by
Florian Stephan Bienenfeld, Marija Zubčić, Alessio Sciacqua, Giacomo Fascia, Manuela Montatore, Gianmichele Muscatella and Giuseppe Guglielmi
Targets 2025, 3(2), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3020015 - 1 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and Clinical Significance: Cystic echinococcosis (CE), also known as hydatid disease, is a zoonosis in whose life cycle humans can be an accidental intermediate host. The liver is the most commonly affected organ, with complications like cyst rupture, hematogenous spread, and
[...] Read more.
Background and Clinical Significance: Cystic echinococcosis (CE), also known as hydatid disease, is a zoonosis in whose life cycle humans can be an accidental intermediate host. The liver is the most commonly affected organ, with complications like cyst rupture, hematogenous spread, and infection. Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, CT, and MRI scans, play a vital role in diagnosing and classifying the disease, facilitating the appropriate therapeutic approach. Treatment options include albendazole for early stage cysts, with more invasive procedures like PAIR, MoCAT, and surgery for advanced cases. This article highlights the importance of imaging modalities in the diagnosis and therapeutic management of CE. Case Presentation: We report a case of a 23-year-old female patient presenting with nausea, fatigue, and loss of appetite to the emergency department, who was diagnosed with a giant echinococcosis lesion. The patient received ultrasound, MR, and CT diagnostics initially. The surveillance included ultrasound and MRI, as well as an anthelmintic therapy, and eventually led to an open resection. Conclusions: This case highlights the importance of imaging modalities in diagnosing and therapeutically managing CE. It explains the key features of each WHO classification stage of the disease for each modality, emphasizing the value of an MRI scan as a possibility for surveillance and a bridge to surgery.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Molecular and Immunological Mechanisms Associated with Diesel Exhaust Exposure
by
Naresh Singh and Samantha Sharma
Targets 2025, 3(2), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3020014 - 21 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Air pollution, particularly from vehicular emissions, has emerged as a critical environmental health concern, contributing to a global estimated 7 million premature deaths annually. Diesel exhaust, a major component of urban air pollution, contains fine particulate matter and gases that evade respiratory filtration,
[...] Read more.
Air pollution, particularly from vehicular emissions, has emerged as a critical environmental health concern, contributing to a global estimated 7 million premature deaths annually. Diesel exhaust, a major component of urban air pollution, contains fine particulate matter and gases that evade respiratory filtration, penetrating deep into the lungs and triggering oxidative stress, inflammation, and immune dysregulation. Epidemiological and in vitro studies have linked diesel exhaust exposure to respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary fibrosis, and lung cancer, with immunological mechanisms playing a central role. Diesel exhaust particles induce oxidative stress, impair macrophage phagocytosis, and skew T-cell polarization toward pro-inflammatory Th2 and Th17 responses, exacerbating chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Despite these insights, significant gaps remain in understanding the precise immunomodulatory pathways and long-term systemic effects of diesel exhaust exposure. While animal models and in vitro studies provide valuable data, they often fail to capture the complexity of human exposure and immune responses. Further research is needed to elucidate the mechanisms underlying diesel exhaust-induced immune dysregulation, particularly in vulnerable populations with pre-existing respiratory conditions. This review focuses on summarizing the current knowledge and identifying gaps that are essential for developing targeted interventions and policies to mitigate the adverse health impacts of diesel exhaust and improve respiratory health outcomes globally.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Semisynthetic Flavonoids as GSK-3β Inhibitors: Computational Methods and Enzymatic Assay
by
Heberth de Paula, Fernanda Souza, Lara Ferreira, Jéssica A. B. Silva, Rayssa Ribeiro, Juliana Vilachã, Flávio S. Emery, Valdemar Lacerda, Jr. and Pedro A. B. Morais
Targets 2025, 3(2), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/targets3020013 - 15 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3β) plays a crucial role in multiple cellular processes and is implicated in different types of cancers and neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease. Despite extensive efforts to develop novel GSK-3β inhibitors, the discovery of potent and selective lead compounds
[...] Read more.
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3β) plays a crucial role in multiple cellular processes and is implicated in different types of cancers and neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease. Despite extensive efforts to develop novel GSK-3β inhibitors, the discovery of potent and selective lead compounds remains a challenge. In this study, we evaluated the GSK-3β inhibitory potential of semisynthetic flavonoid derivatives, which exhibited sub-micromolar activity. To gain further insights, we employed molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, and pharmacokinetic profile predictions. The docking studies revealed that the most potent inhibitor, compound 10, establishes key interactions with the ATP-binding site. Molecular dynamics simulations further confirmed that compound 10 maintains stable interactions with GSK-3β throughout the simulation. Additionally, pharmacokinetic predictions identified compound 3 as a promising candidate for Alzheimer’s disease therapy due to its ability to cross the blood–brain barrier. These findings suggest that, within the studied flavonoid derivatives, these compounds (particularly 10 and 3) hold potential as lead compounds for GSK-3β inhibition. The combination of strong enzymatic inhibition, stable binding interactions, and favorable pharmacokinetic properties highlights their promise for further development in cancer and neurodegenerative disease research.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, Cancers, Diagnostics, JCM, Metabolites, Targets
Biomarkers of Disease: Discovery and Clinical Applications
Topic Editors: Ioannis Kanakis, Andreas TsakalofDeadline: 30 June 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Targets
Small-Molecule Antibiotic Drug Development
Guest Editor: Miguel García-CastroDeadline: 20 December 2025
Special Issue in
Targets
Comprehending Molecular Targets: Mechanisms and Actions in Drug Development
Guest Editors: Cristina Manuela Dragoi, Ion-Bogdan DumitrescuDeadline: 20 January 2026
Special Issue in
Targets
Multidisciplinary Approach to Oral Cavity Cancer: A Hard Enemy
Guest Editors: Francesco Perri, Agostino GuidaDeadline: 20 February 2026









