Trilobite Eyes and Their Evolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
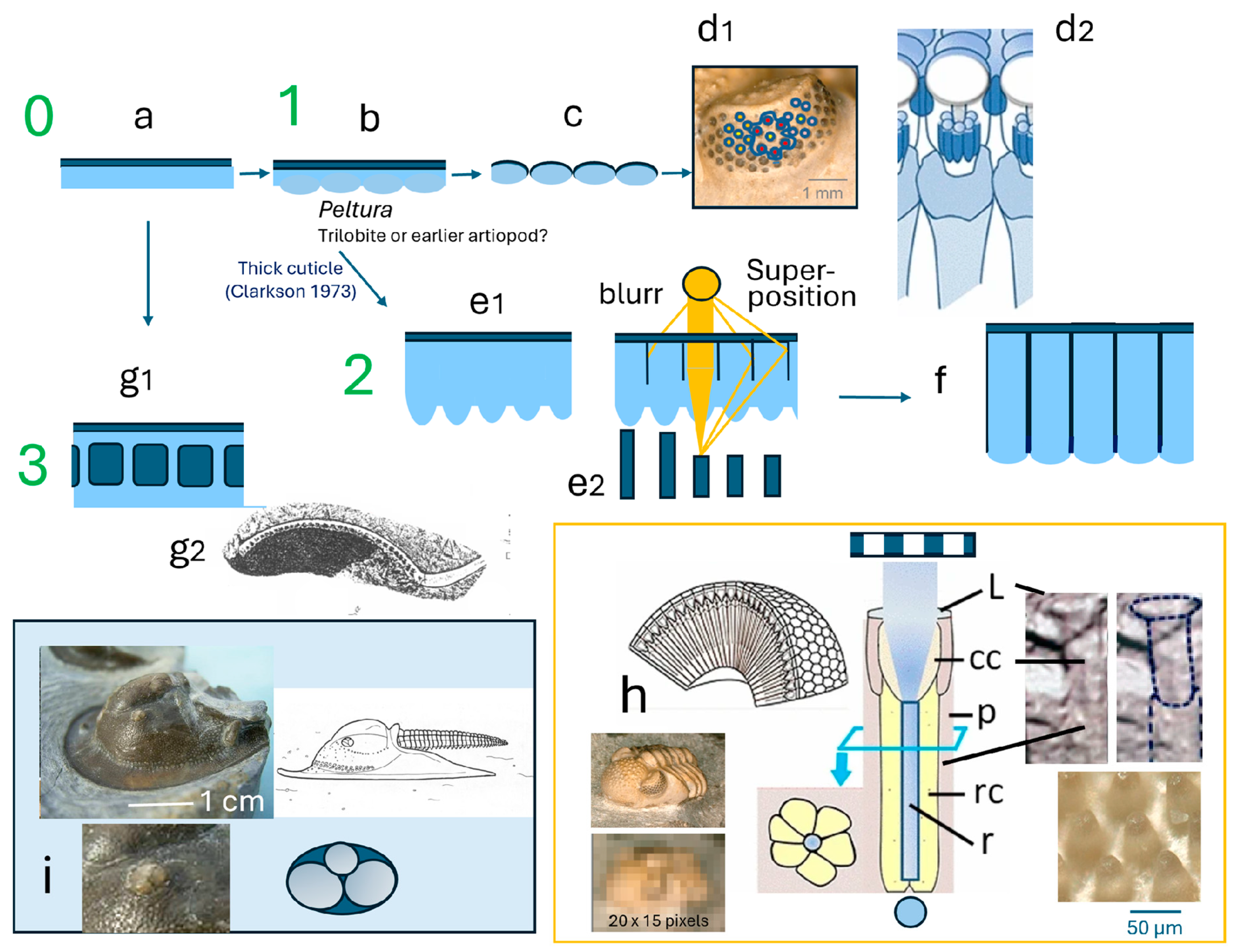
2. Trilobite Eyes and Lindström’s First Descriptions
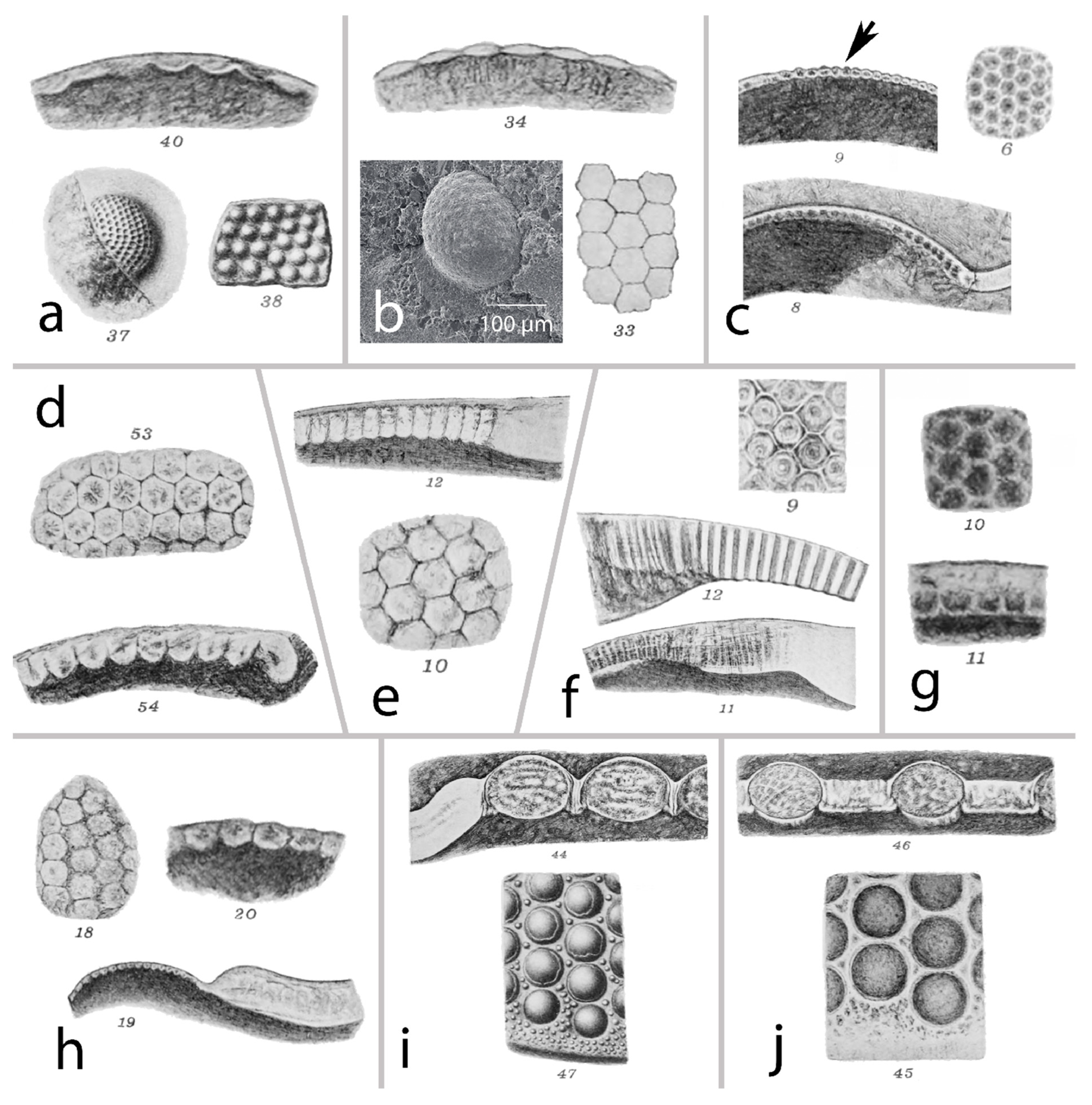
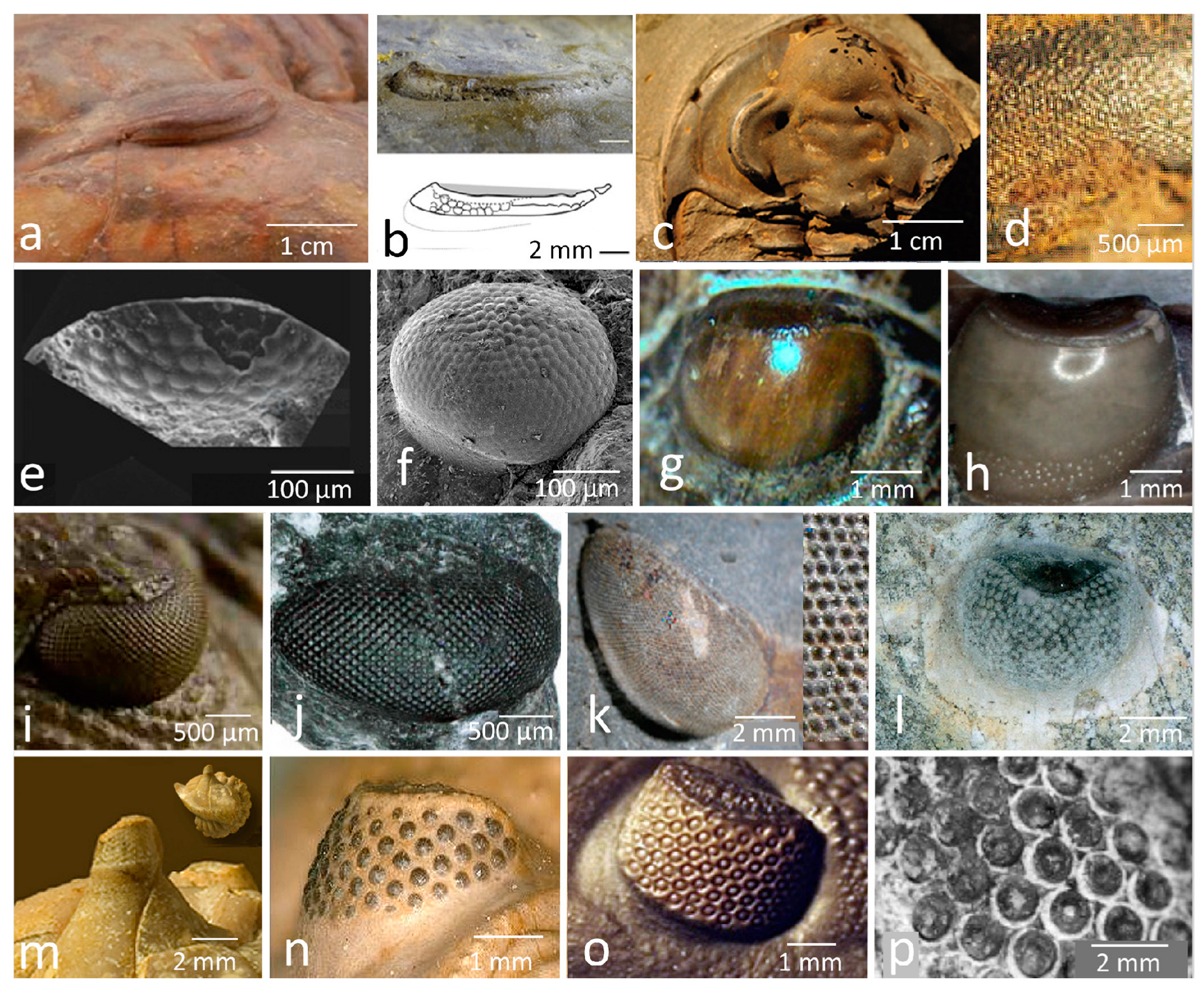
2.1. The Holochroal Eyes
2.2. The Structure of Holochroal Compound Eyes of Trilobites
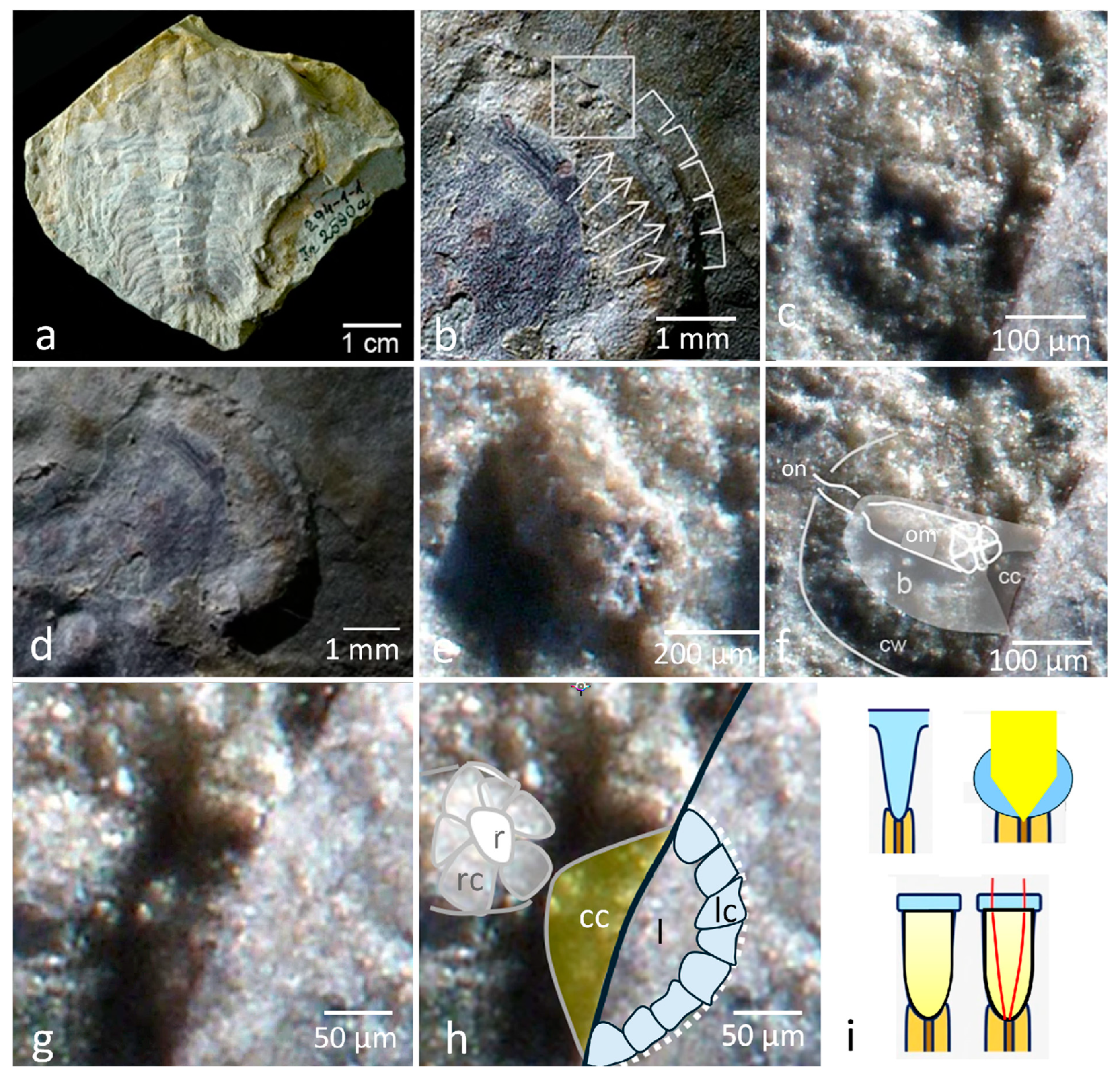
The Eye of Schmidtiellus Reetae Bergström 1973
2.3. The Process of Evolving Proper, Focusing Lenses
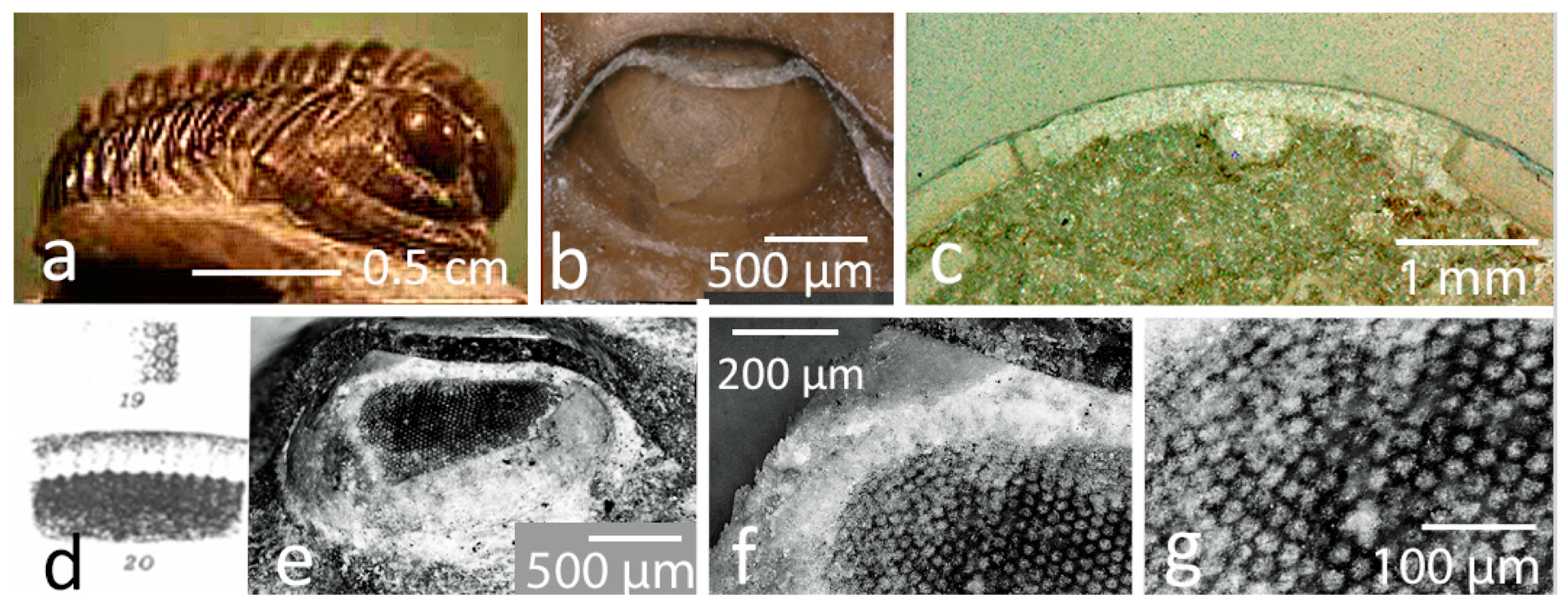
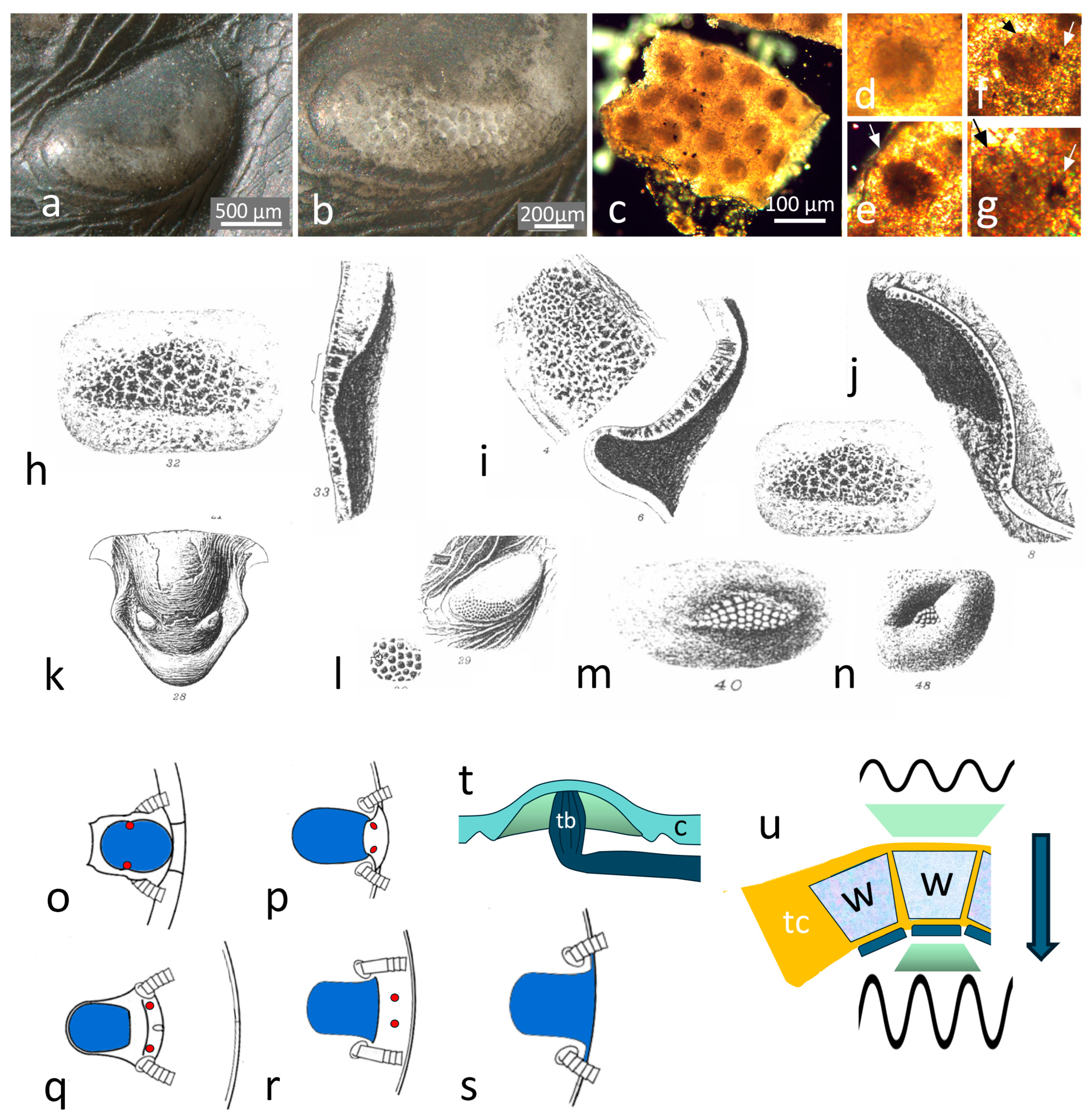
2.4. Schizochroal Eyes
The Third Type of Eye?
3. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clarkson, E.N.K.; Levi-Setti, R.; Horváth, G. The eyes of trilobites: The oldest preserved visual system. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2006, 35, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenemann, B. Evolution of eye reduction and loss in trilobites and some related fossil arthropods. Emerg. Sci. J. 2018, 2, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenemann, B. An overview on trilobite eyes and their functioning. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2021, 61, 101032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Land, M.F. Optics and Vision in Invertebrates. In Handbook of Sensory Physiology; Autrum, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 471–592. [Google Scholar]
- Land, M.F.; Nilsson, D.E. Animal Eyes; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Towe, K.M. Trilobite eyes: Calcified lenses in vivo. Science 1973, 179, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenemann, B.; Clarkson, E.N.K. The median eyes of trilobites. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenacher, H. Untersuchungen über das Arthropoden-Auge; Stiller: Berlin, Germany, 1877; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Grenacher, H. Untersuchungen über das Sehorgan der Arthropoden, Insbesondere der Spinnen, Insecten und Crustaceen; Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht: Göttingen, Germany, 1879. [Google Scholar]
- Exner, S. Die Physiologie der Facettirten Augen von Krebsen und Insecten: Eine Studie; Franz Deuticke: Leipzig, Germany, 1891. [Google Scholar]
- Lindström, G. Researches on the visual organs of the trilobites. Kongliga Sven. Vetenskapsakademiens Handl. 1901, 34, 1–87. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, J.M. The structure and development of the visual area in the trilobite, Phacops rana, Green. J. Morphol. 1898, 2, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clarkson, E.N.K. The eyes of Asaphus raniceps Dalman (Trilobita). Palaeontology 1973, 16, 425–444. [Google Scholar]
- Fortey, R.A.; Wilmot, N.V. Trilobite cuticle thickness in relation to palaeoenvironment. Paläontol. Z. 1991, 65, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöning, H. Ein Fund von Scopelochasmops wrangeli (Schmidt, 1881) aus einem mittelordovizischen Geschiebe. Geschiebekd 1997, 13, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Jell, P.A. The abathochroal eye of Pagetia, a new type of trilobite eye. Foss. Strat. 1975, 4, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-g.; Clarkson, E.N. Phosphatized eodiscoid trilobites from the Cambrian of China. Palaeontogr. Abt. A 2012, 297, 1–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysiuk, J.; Caron, J.B. Burgess Shale fossils shade light on the agnostid problem. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20182314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.J.; Walossek, D. Morphology, ontogeny and life habit of Agnostus pisiformis from the Upper Cambrian of Sweden. Foss. Strat. 1987, 19, 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, T.J.; Fortey, R.A. Comparative morphology and relationships of the Agnostina. In Crustacea and Arthropod Relationships(19); Koenemann, S., Jenner, R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 95–136. [Google Scholar]
- Fortey, R. Trilobite systematics: The last 75 years, J. Paleontol. 2001, 75, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Schoenemann, B.; Hou, X.-G.; Melzer, R.R.; Liu, Y. A unique 1 Lower Cambrian arthropod with two different compound eye systems. Commun. Biol. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, T.; Fortey, R.A. Independent testing of a paleobiological hypothesis: The optical design of two Ordovician pelagic trilobites reveals their relative paleo bathymetry. Paleobiology 1998, 24, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenemann, B.; Clarkson, E.N.K. Eyes and vision in the coeval Furongian trilobites Sphaerophthalmus alatus (Boeck, 1938) and Ctenopyge (Mesoctenopyge) tumida Westergård, 1922, from Bornholm, Denmark. Palaeontology 2015, 58, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, G.; Schoenemann, B.; El Hariri, K.; Ono, T.; Clarkson, E.; Maeda, H. Vision in a Middle Ordovician trilobite eye. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2015, 433, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenemann, B.; Clarkson, E.N.K.; Ahlberg, P.; Alvarez, M.E. A tiny eye indicating a planktonic trilobite. Palaeontology 2010, 53, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenemann, B.; Pärnaste, H.; Clarkson, E.N. Structure and function of a compound eye, more than half a billion years old. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13489–13494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ax, P. Multicellular Animals: The Phylogenetic System of the Metazoa; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg, E.; Nilsson, H.L.; Elofsson, R. Classification of amphipod compound eyes—The fine structure of the ommatidial units (Crustacea, Amphipoda). Zoomorphologie 1980, 94, 279–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrenbach, W.H. The morphology of the eyes of Limulus: II. Ommatidia of the compound eye. Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat. 1968, 93, 451–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, H.F. Eye structure and the monophyly of the arthropod eye. In Arthropod Phylogeny; Gupta, A.P., Ed.; Van Nostrand Reinhold & Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 299–383. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenemann, B.; Poschmann, M.; Clarkson, E.N.K. Insights into the 400 million-year-old eyes of giant sea scorpions (Eurypterida) suggest the structure of Palaeozoic compound eyes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M.F. Structure of the retinae of the principal eyes of jumping spiders (Salticidae: Dendryphantinae) in relation to visual optics. J. Exp. Biol. 1958, 51, 443–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwin, C. On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Races in the Struggle of Life, 1st ed.; John Murray: London, UK, 1859. [Google Scholar]
- Paulus, H.F. Phylogeny of the Myriapoda–Crustacea–Insecta: A new attempt using photoreceptor structure. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2000, 38, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitsch, C.; Bitsch, J. Evolution of eye structure and arthropod phylogeny. Crustac. Issues 2005, 16, 185–214. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, D.-E. The evolution of eyes and visually guided behavior. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2833–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, D.-E. Eye evolution and its functional basis. Vis. Neurosci. 2013, 30, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walossek, D. The upper Cambrian Rehbachiella and the phylogeny of Branchiopoda and Crustacea. Foss. Strat. 1993, 32, 1–102. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, A.; Braun, A.; Dong, X.P.; Donoghue, P.C.; Müller, K.J.; Olempska, E.; Repetski, J.E.; Siveter, D.J.; Stein, M.; Waloszek, D. The ‘Orsten’—More than a Cambrian Konservat-Lagerstätte yielding exceptional preservation. Palaeoworld 2006, 15, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenemann, B.; Clarkson, E.N.K. Insights into a 429-million-year-old compound eye. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Jago, J.B.; García-Bellido, D.C.; Edgecombe, G.D.; Gehling, J.G.; Paterson, J.R. Modern optics in exceptionally preserved eyes of Early Cambrian arthropods from Australia. Nature 2011, 474, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, J.R.; García-Bellido, D.C.; Lee, M.S.; Brock, G.A.; Jago, J.B.; Edgecombe, G.D. Acute vision in the giant Cambrian predator Anomalocaris and the origin of compound eyes. Nature 2011, 480, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, J.R.; Edgecombe, G.D.; García-Bellido, D.C. Disparate compound eyes of Cambrian radiodonts reveal their developmental growth mode and diverse visual ecology. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarkson, E.N.K. Invertebrate Palaeontology and Evolution; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- McGhee, G.R., Jr.; Clapham, M.E.; Sheehan, P.M.; Bottjer, D.J.; Droser, M.L. A new ecological-severity ranking of major Phanerozoic biodiversity crises. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2013, 370, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algeo, T.J.; Shen, J. Theory and classification of mass extinction causation. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwad237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, K. The optical system of the crayfish eye. J. Comp. Physiol. 1980, 135, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, K. Optics of the crayfish eye. Z. Naturforschung 1975, 30, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenemann, B.; Clarkson, E.N. Points of view in understanding trilobite eyes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtz, G.; Staude, A.; Dunlop, J.A. Trilobite compound eyes with crystalline cones and rhabdoms show mandibulate affinities. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannier, J.; Schoenemann, B.; Gillot, T.; Charbonnier, S.; Clarkson, E. Exceptional preservation of eye structure in arthropod visual predators from the Middle Jurassic. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenemann, B.; Clarkson, E.N.K.; Bartels, C.; Südkamp, W.; Rössner, G.E.; Ryck, U. A 390 million-year-old hyper-compound eye in Devonian phacopid trilobites. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarkson, E.N.K.; Levi-Setti, R. Trilobite eyes and the optics of Des Cartes and Huygens. Nature 1975, 254, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gál, J.; Horváth, G.; Clarkson, E.N.; Haiman, O. Image formation by bifocal lenses in a trilobite eye? Vis. Res. 2000, 40, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egri, Á.; Horváth, G. Possible optical functions of the central core in lenses of trilobite eyes: Spherically corrected monofocality or bifocality. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2012, 29, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenemann, B.; Hoekstra, H.J.; Horváth, G.; Clarkson, E.N.K. Vision of Trilobites and Polarized Light. In Polarization Vision and Environmental Polarized Light; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 347–403. [Google Scholar]
- Buschbeck, E.K.; Ehmer, B.; Hoy, R.R. The unusual visual system of the Strepsiptera: External eye and neuropils. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2003, 189, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschbeck, E.; Ehmer, B.; Hoy, R. Chunk versus point sampling: Visual imaging in a small insect. Science 1999, 286, 1178–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.S.W. The functional anatomy of phacopid trilobites: Musculature and eyes. J. Proc. R. Soc. New South Wales 1975, 108, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, E.N.K. The eye: Morphology, function and evolution. In Treatise on Invertebrate Palaeontology; Moore, R.C., Ed.; Part O- Arthropoda (Trilobitomorpha); Geological Society of America and University of Kansas Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1997; pp. 14–132. [Google Scholar]
- Fortey, R.A. Ontogeny, hypostome attachment and trilobite classification. Palaeontology 1990, 33, 529–576. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, W.K. The Hypostomic Eyes of Trilobites. Geol. Mag. 1903, 10, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanström, B. Untersuchungen über die Relative Größe der Gehirnzentren Verschiedener Arthropoden unter Berücksichtigung der Lebensweise; Zeitschrift für Mikr.-Anatom. Forschung Bd. 7 Heft 2/3; Akademische verkassgesellschaft: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1926. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, P.E. The appendages, anatomy, and relationships of the trilobites. Mem. Conn. Acad. Arts Sci. 1920, 7, 1–169. [Google Scholar]
- Hupé, P. Sur les affinités des trilobites. Bull. de la Société Géologique de Fr. 1951, 6, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Størmer, L. Studies on trilobite morphology, part I, the thoracic appendages and their phylogenetic significance. Nor. Geol. Tidsskr. 1939, 19, 143–273. [Google Scholar]
- Størmer, L. Studies on trilobite morphology, part II, the larval development, the segmentation and the sutures, and their bearing on trilobite classification. Nor. Geol. Tidsskr. 1942, 21, 49–163. [Google Scholar]
- Størmer, L. Studies on trilobite morphology, part III, the ventral cephalic structures with remarks on the zoological position of trilobites. Nor. Geol. Tidsskr. 1951, 29, 108–158. [Google Scholar]
- Whittington, H.B.; Evitt, W.R. Silicified Middle Ordovician Trilobites; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1953; Volume 59, pp. 1–137. [Google Scholar]
- Vinther, J.; Briggs, D.E.; Prum, R.O.; Saranathan, V. The colour of fossil feathers. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindgren, J.; Uvdal, P.; Sjövall, P.; Nilsson, D.E.; Engdahl, A.; Schultz, B.P.; Thiel, V. Molecular preservation of the pigment melanin in fossil melanosomes. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.W.; Millecchia, R.; Mauro, A. The ventral photoreceptor cells of Limulus: I. The microanatomy. J. Gen. Physiol. 1969, 54, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, E.D.; Barlow, R.B. The Limulus-eye view of the world. Vis. Neurosci. 1992, 9, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, G. Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Morphologie und Entwicklung des Gehirns von Limulus polyphemus. Acta Zool. 1933, 14, 1–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrenbach, W.H. The visual system of the horseshoe crab Limulus polyphemus. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1975, 41, 285–349. [Google Scholar]
- Bruton, D.L.; Haas, W. The puzzling eye of Phacops. Spec. Pap. Palaeontol. 2003, 70, 349–362. [Google Scholar]
- Seilacher, A.; Gishlick, A.D. Sensory Organs II: Trilobite Eyes. In Morphodynamics; Seilacher, A., Gishlick, A.D., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2015; pp. 370–379. [Google Scholar]
- Zill, S.N.; Chaudhry, S.; Büschges, A.; Schmitz, J. Directional specificity and encoding of muscle forces and loads by stick insect tibial campaniform sensilla, including receptors with round cuticular caps. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2013, 42, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.R.; Torney, C.; Owen, A.W. Magnesium-rich intralensar structures in schizochroal trilobite eyes. Palaeontology 2007, 50, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.R.; Torney, C.; Owen, A.W. Biomineralization in the Palaeozoic oceans: Evidence for simultaneous crystallization of high and low magnesium calcite by phacopine trilobites. Chem. Geol. 2012, 314, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, T.J. The Phylogeny and Morphological Evolution of Cambrian Trilobites and Their Relatives. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK, 2002. Available online: https://research-information.bris.ac.uk/ws/portalfiles/portal/34498254/393951.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Cotton, T.J.; Braddy, S.J. The phylogeny of arachnomorph arthropods and the origin of the Chelicerata. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. Earth Sci. 2004, 94, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teigler, D.J.; Towe, K.M. Microstructure and composition of the trilobite exoskeleton. Foss. Strat. 1975, 4, 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren, J.; Nilsson, D.E.; Sjövall, P.; Jarenmark, M.; Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Kear, B.P.; Schultz, B.P.; Sylvestersen, R.L.; Madsen, H.; et al. Fossil insect eyes shed light on trilobite optics and the arthropod pigment screen. Nature 2019, 573, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klug, C.; Schulz, H.; De Baets, K. Red Devonian trilobites with green eyes from Morocco and the silicification of the trilobite exoskeleton. Acta Palaeontl. Polon. 2009, 54, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torney, C.; Lee, M.R.; Owen, A.W. An Electron Backscatter Diffraction Study of Geesops: A Broader View of Trilobite Vision? Cuadernos del Museo Geominero, n°9 Advances in Trilobite Research; Instituto Geológico y Minéro de España: Madird, Spain, 2008; pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Torney, C.; Lee, M.R.; Owen, A.W. Microstructure and growth of the lenses of schizochroal trilobite eyes. Palaeontology 2014, 57, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaten, E. Optics and phylogeny: Is there an insight? The evolution of superposition eyes in the Decapoda (Crustacea). Contrib. Zool. 1998, 67, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schoenemann, B. Trilobite Eyes and Their Evolution. Arthropoda 2025, 3, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda3010003
Schoenemann B. Trilobite Eyes and Their Evolution. Arthropoda. 2025; 3(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda3010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchoenemann, Brigitte. 2025. "Trilobite Eyes and Their Evolution" Arthropoda 3, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda3010003
APA StyleSchoenemann, B. (2025). Trilobite Eyes and Their Evolution. Arthropoda, 3(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda3010003






