Atomic-Scale Insights into the Effects of the Foaming Degree on the Glass–Ceramic Matrix Derived from Waste Glass and Incineration Bottom Ash
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
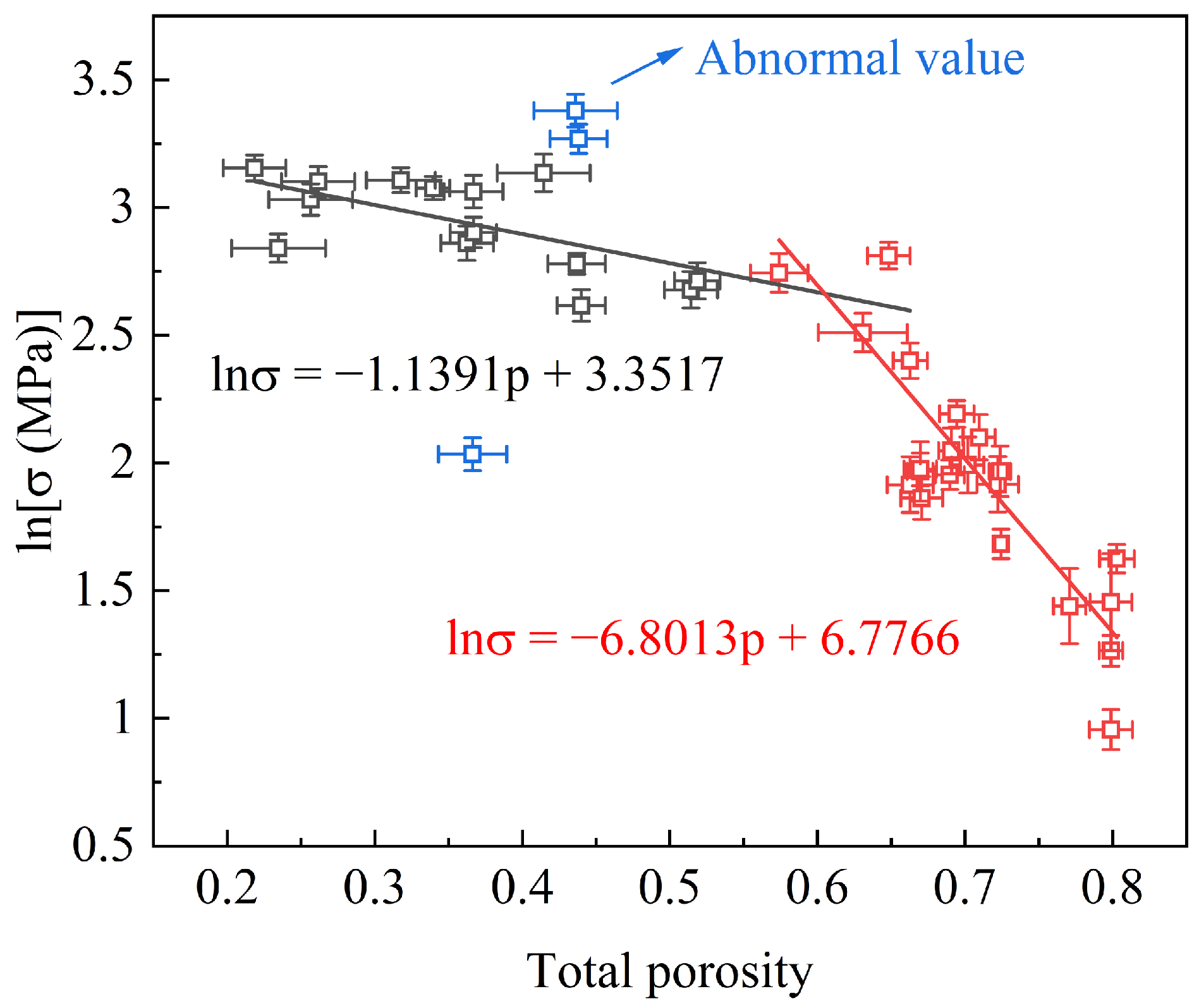
2.1. Experimental Design
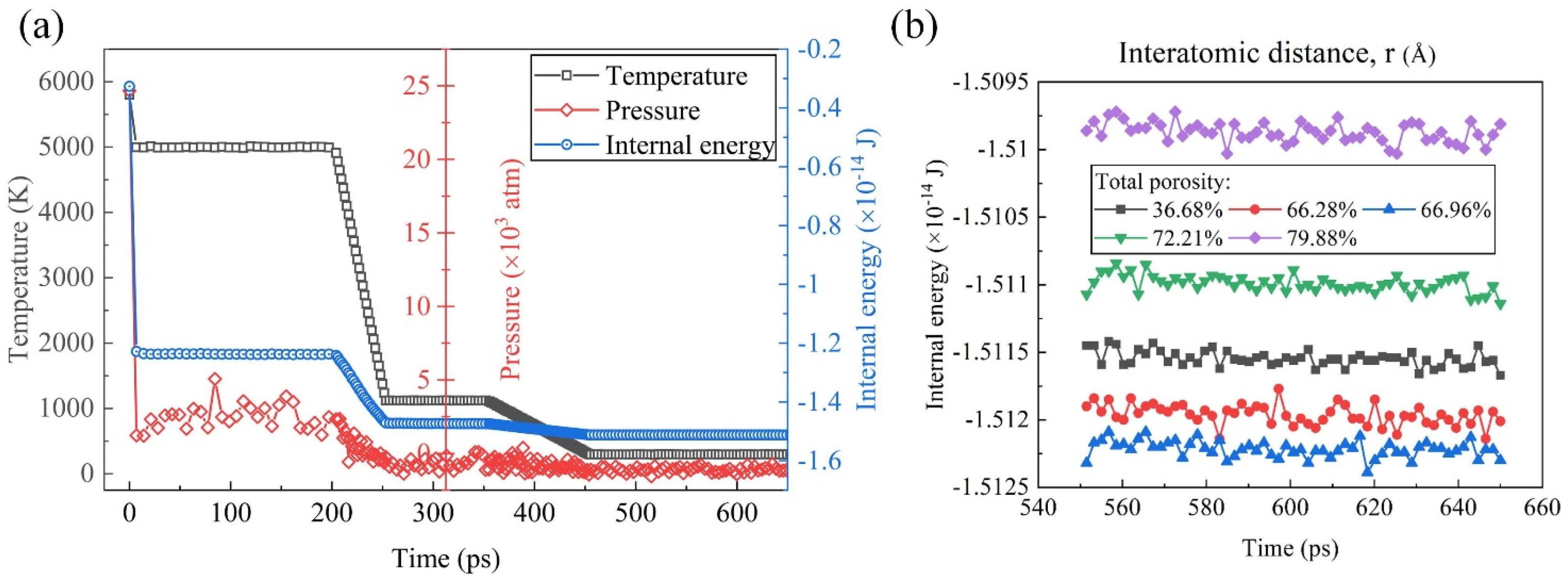
2.2. All-Atomistic Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.3. Analysis Methods
3. Results
3.1. Internal Energy
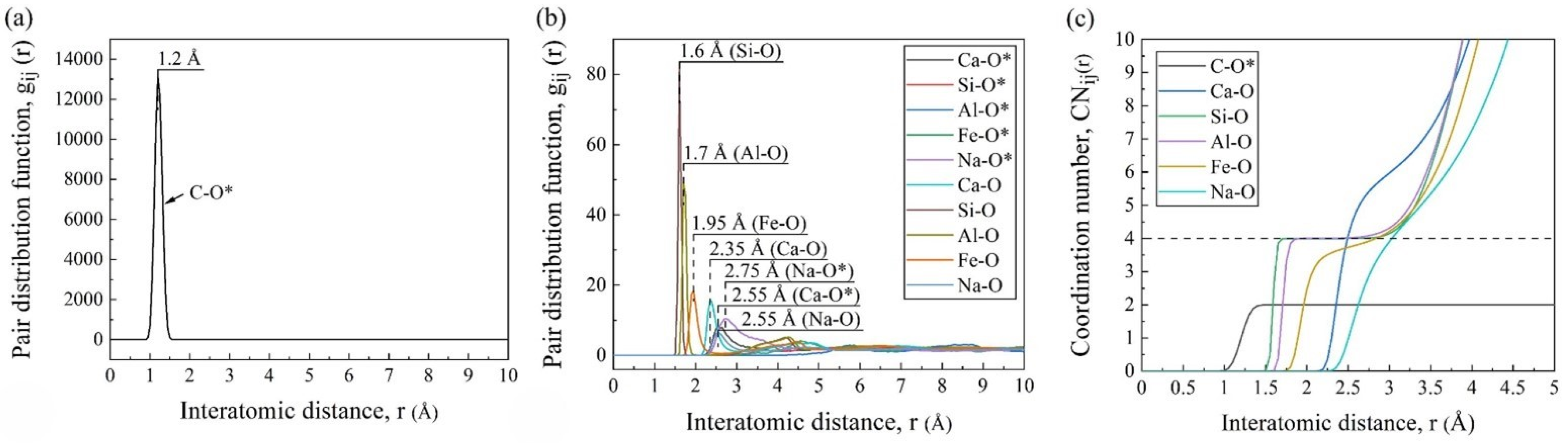
3.2. PDF, CN, and SEM
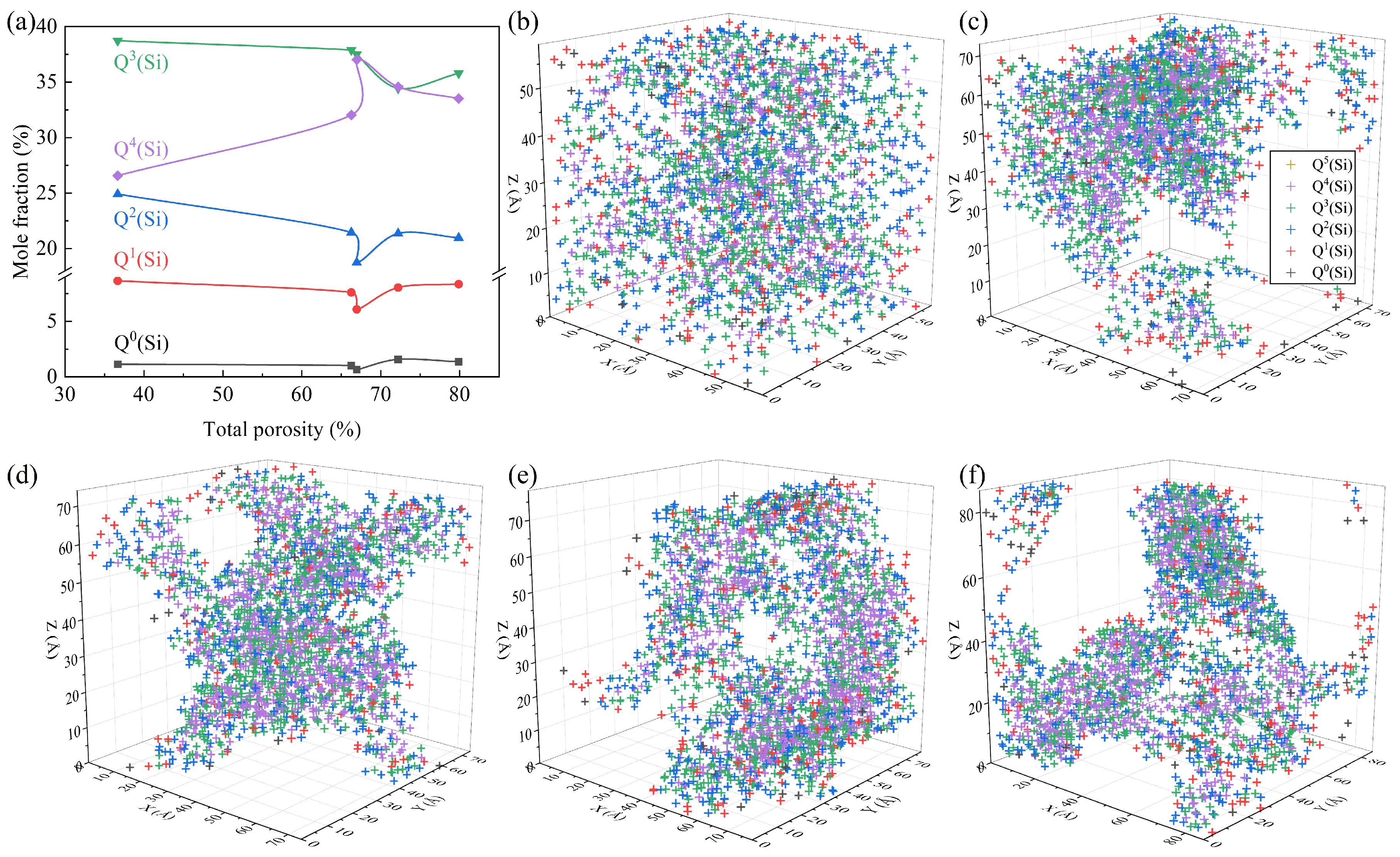
3.3. Effects of Foaming Degree on Si-Related Structure
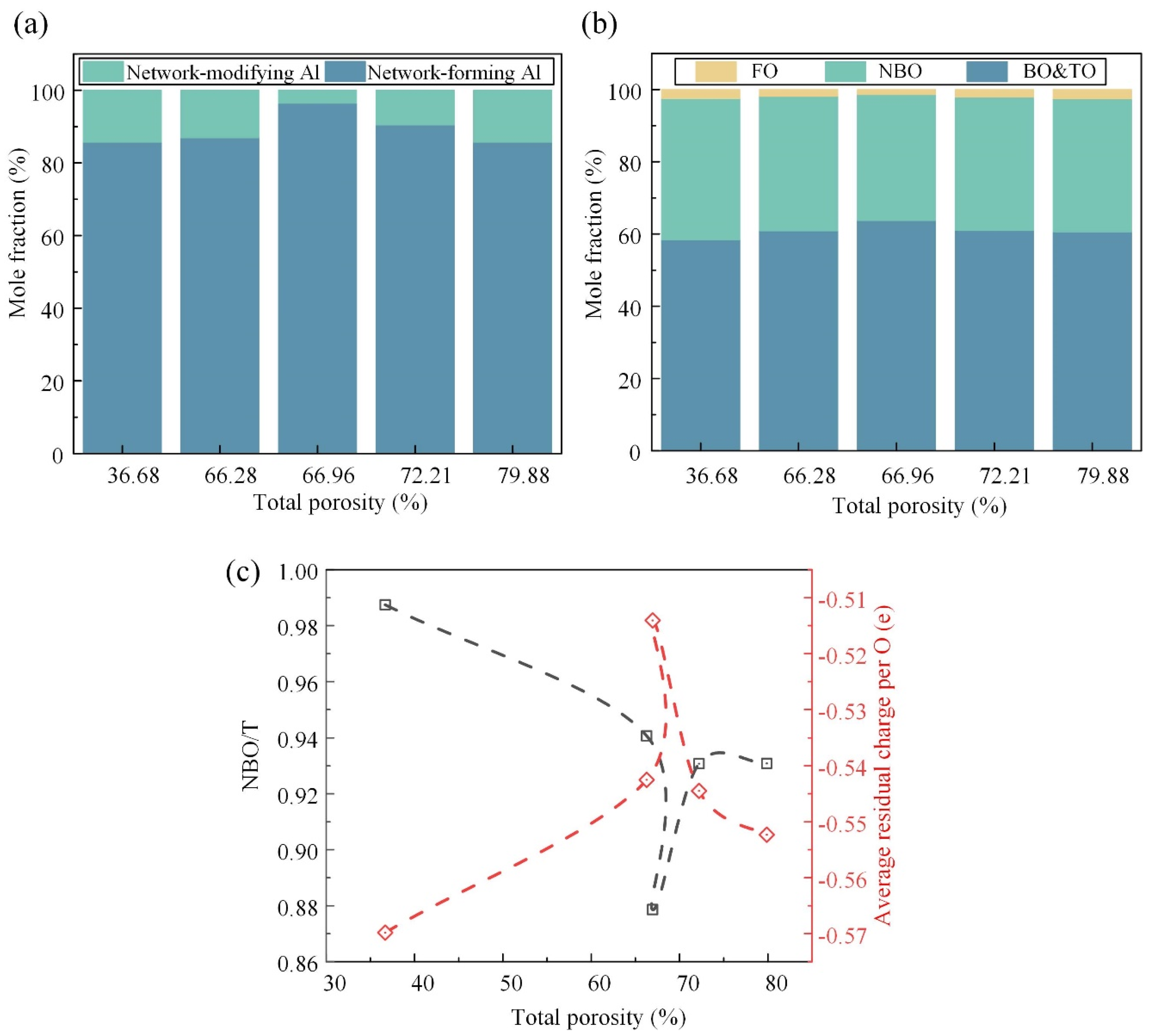
3.4. Effects of Foaming Degree on Al-Related Structure and Oxygen Species
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Na cations were observed to migrate towards the surface of the pore walls due to the attraction by CO2. The Na content on the surface of pore wall (21.3%) surpassed that within the matrix (10.0%), thereby impacting the polymerization degree.
- (2)
- The quantity of bridging oxygen exhibited an initial rise followed by a decline as the total porosity increased, peaking at 66.96%. The matrix of the pore wall was predominantly occupied by high bridging oxygen, fostering the establishment of a cohesive cross-linked network of chemical bonds, and thereby augmenting the matrix polymerization.
- (3)
- As the total porosity increased, the neutron structure analysis revealed an initial augmentation followed by a subsequent diminution in both the overall ring size and average size of the tetrahedral building blocks. This trend aligned with the observed variation in polymerization degree.
- (4)
- The inflection points of the depolymerization degree and the average residual charge per O atom coincided at a total porosity of approximately 66.96%, which corresponded to the optimum sample. The subsequent increase in the total porosity led to the emergence of interconnected pores and breakpoints within the foaming glass–ceramic, which significantly reduced its compressive strength.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, L.; Tian, J.; Feng, K.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Q. Sound Absorption Model of Foam Glass-Ceramics Based on Microstructure. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2023, 604, 122136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Colombo, P. Processing, Properties and Applications of Highly Porous Geopolymers: A Review. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 16103–16118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Li, K.; Dou, M.; Liu, L.; Feng, Y.; Feng, C. Towards Optimized Pore Structure to Balance the Thermal-Mechanical Performance of Foamed Ceramic. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, P.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Lu, A. Preparation, Characterization and Discussion of Glass Ceramic Foam Material: Analysis of Glass Phase, Fractal Dimension and Self-Foaming Mechanism. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 243, 122614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yio, M.H.N.; Xiao, Y.; Ji, R.; Russell, M.; Cheeseman, C. Production of Foamed Glass-Ceramics Using Furnace Bottom Ash and Glass. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 8697–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Qian, D.; Xing, Y. A Novel and Clean Utilization of Multiple Solid Wastes to Produce Foam Glass-Ceramic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 370, 130711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Deng, C.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, S.; Han, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Q.; Lu, A. Preparation of Self-Foamed Glass Ceramics Based on the Cooperative Treatment of Various Solid Wastes: Characterization of Structure-Properties and Analysis of Self-Foaming Behavior. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 2570–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ji, W.; Huang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Poon, C.S. Upcycling Municipal Solid Wastes to Self-Foaming Glass-Ceramics by Chemical Additive-Free and Rapid Low-Temperature Sintering. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 444, 141261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Pan, X.; Qi, Y.; Yu, H.; Tu, G. Preparation and Characterization of Ultra-Lightweight Ceramsite Using Non-Expanded Clay and Waste Sawdust. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Mao, H.; Cui, K. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of High Strength Porous Ceramics with High Sewage Sludge Content. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryshkewitch, E. Compression Strength of Porous Sintered Alumina and Zirconia. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1953, 36, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, R.W. Comparison of Stress Concentration versus Minimum Solid Area Based Mechanical Property-Porosity Relations. J. Mater. Sci. 1993, 28, 2187–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, R.W. Comparison of Physical Property-Porosity Behaviour with Minimum Solid Area Models. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 1509–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, H.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Ren, S. Transferability of Interatomic Potentials with Insights into the Structure–Property Relationship of SiO2–CaO–MgO–Al2O3 Melts. Mol. Simul. 2020, 46, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sakamaki, T.; Skinner, L.B.; Jing, Z.; Yu, T.; Kono, Y.; Park, C.; Shen, G.; Rivers, M.L.; Sutton, S.R. Atomistic Insight into Viscosity and Density of Silicate Melts under Pressure. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, X. Investigation of Cooling Processes of Molten Slags to Develop Multilevel Control Method for Cleaner Production in Mineral Wool. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, F.; Sridhar, S. Molecular Dynamics Study of the Structural Properties of Calcium Aluminosilicate Slags with Varying Al2O3/SiO2 Ratios. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, B.; Sator, N. Carbon Dioxide in Silicate Melts: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 1829–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Xiao, P.; Yuan, Z. Effects of BaO on the Viscosity and Structure of a New Fluorine-Free CaO-Al2O3-TiO2-Based Mold Flux for High Titanium Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2020, 51, 2119–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasmy, A.; Ispas, S.; Hehlen, B. Percolation Transitions in Compressed SiO2 Glasses. Nature 2021, 599, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Du, T.; Guo, L.; Smedskjaer, M.M.; Bauchy, M. New Insights into the Structure of Sodium Silicate Glasses by Force-Enhanced Atomic Refinement. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2020, 536, 120006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, S.; Wen, G.; Jiang, W.; Tang, P. Computational Insight into the Thermal Conductivity of CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-MgO-Na2O Melts. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2020, 51, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, X.; Qin, S. The Crystal Chemistry and the Compressibility of Silicate-Carbonate Minerals: Spurrite, Galuskinite and Tilleyite. Geosci. Front. 2015, 6, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Meng, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X. Structural and Viscous Insight into Impact of MoO3 on Molten Slags. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2021, 52, 3730–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Lu, J.X.; Huang, Y.; Xuan, D.; Ou, G.; Sun Poon, C. Recycling of Waste Glass in Lightweight Geopolymer Using Incineration Bottom Ash as a Foaming Agent: Towards Energy Conservation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.E.; Lin, C.M.; Shen, J.M.; Luo, S.F.; Yu, K.W.; Wu, W. The Effect of the Addition of Alumina on the Viscosity, Surface Tension, and Foaming Efficiency of 2.5(CaO/SiO2)-XAl2O3-YFeO-MgO Melts. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 21994–22003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanao, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kawamoto, M.; Takatani, K. Evaluation of Surface Tension of Molten Slag in Multi-Component Systems. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnan, I.; Stebbins, J.F. The Nature of the Glass Transition in a Silica-Rich Oxide Melt. Science 1994, 265, 1206–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; Zhang, Y. Exploration of the Amphoteric Transition of Al2O3 on Melt Structure and Viscosity of Silicate Slag. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 25815–25822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X. Insight into the Relationship Between Viscosity and Structure of CaO-SiO2-MgO-Al2O3 Molten Slags. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2019, 50, 2930–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Neuefeind, J.; Ma, D.; Page, K.; Lamberson, L.A.; Smith, N.J.; Tandia, A.; Song, A.P. Ring Size Distribution in Silicate Glasses Revealed by Neutron Scattering First Sharp Diffraction Peak Analysis. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2019, 516, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Deng, B.; Gulbiten, O.; Bauchy, M.; Zhou, Q.; Neuefeind, J.; Elliott, S.R.; Smith, N.J.; Allan, D.C. Revealing the Relationship between Liquid Fragility and Medium-Range Order in Silicate Glasses. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Raw Materials | SiO2 | Na2O | CaO | Al2O3 | MgO | Fe2O3 | K2O | SO3 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waste glass | 63.2 | 17.7 | 12.0 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| Incineration bottom ash | 34.8 | 6.7 | 10.4 | 3.9 | 12.4 | 24.1 | 3.4 | 4.1 | 0.2 |
| I | Silicate potential | |||
| (eV) | (Å) | (eV/Å6) | (eV/Å12) | |
| Ca0.945-O−0.945 | 155,356.043 | 0.178 | 42.2587 | 0 |
| Si1.89-O−0.945 | 50,186.0509 | 0.161 | 46.2967 | 0 |
| Mg0.945-O−0.945 | 32,587.272 | 0.178 | 27.2803 | 0 |
| Al1.4175-O−0.945 | 28,482.1454 | 0.172 | 34.577 | 0 |
| Fe0.945-O−0.945 | 8034.05 | 0.19 | 0 | |
| Na0.4725-O−0.945 | 145,402.3125 | 0.178 | 18.8075875 | 0 |
| O−0.945-O−0.945 | 6479.68212 | 0.276 | 85.0902 | 0 |
| II | ||||
| III | CO2-CO2 intermolecular potential | |||
| (eV) | (Å) | |||
| C0.5888-C0.5888 | 0.002490 | 2.792 | ||
| C0.5888-O*−0.2944 | 0.004214 | 2.896 | ||
| O*−0.2944-O*−0.2944 | 0.007135 | 3.000 | ||
| IV | More potential between C of CO2 and O of silicate | |||
| (eV) | (Å) | (Å) | ||
| C-O | 5.0249 | 1.162 | 0.2 | |
| V | CO2-silicate potential | |||
| (eV) | (Å) | (eV/Å6) | (eV/Å12) | |
| O−0.945-O*−0.2944 | 3239.84106 | 0.276 | 42.5451 | 0 |
| Ca0.945-O*−0.2944 | 155,356.043 | 0.178 | 42.2587 | 0 |
| Si1.89-O*−0.2944 | 50,186.0509 | 0.161 | 46.2967 | 0 |
| Mg0.945-O*−0.2944 | 32,587.272 | 0.178 | 27.2803 | 0 |
| Al1.4175-O*−0.2944 | 28,482.1454 | 0.172 | 34.577 | 0 |
| Fe0.945-O*−0.2944 | 8034.05 | 0.19 | 0 | |
| Na0.4725-O*−0.2944 | 145,402.3125 | 0.178 | 18.8075875 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H. Atomic-Scale Insights into the Effects of the Foaming Degree on the Glass–Ceramic Matrix Derived from Waste Glass and Incineration Bottom Ash. Materials 2024, 17, 2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17122820
Wei Y, Chen Z, Wang H. Atomic-Scale Insights into the Effects of the Foaming Degree on the Glass–Ceramic Matrix Derived from Waste Glass and Incineration Bottom Ash. Materials. 2024; 17(12):2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17122820
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Ying, Ziwei Chen, and Hao Wang. 2024. "Atomic-Scale Insights into the Effects of the Foaming Degree on the Glass–Ceramic Matrix Derived from Waste Glass and Incineration Bottom Ash" Materials 17, no. 12: 2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17122820
APA StyleWei, Y., Chen, Z., & Wang, H. (2024). Atomic-Scale Insights into the Effects of the Foaming Degree on the Glass–Ceramic Matrix Derived from Waste Glass and Incineration Bottom Ash. Materials, 17(12), 2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17122820







