Synthesis and Reactions of α-Hydroxyphosphonates
Abstract
:1. Synthetic Routes towards α-Hydroxyphosphonates
1.1. Synthesis of α-Hydroxyphosphonates by the Reaction of Aldehydes/Ketones and Dialkyl Phosphites
1.2. Synthesis of α-Hydroxyphosphonates by the Reaction of Aldehydes/Ketones and Trialkyl Phosphites
1.3. The “Greenest” Protocol for the Synthesis of α-Hydroxyphosphonates
2. Reactions of α-Hydroxyphosphonates
2.1. Alkylations
2.2. Acylations
2.3. Oxidations
2.4. Nucleophilic Substitutions
2.5. Rearrangements
2.6. Hydrolysis
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olszewski, T.K. Environmentally benign syntheses of α-substituted phosphonates: Preparation of α-amino- and α-hydroxyphosphonates in water, in ionic liquids, and under solvent-free conditions. Synthesis 2014, 46, 403–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failla, S.; Finocchiaro, P.; Consiglio, G.A. Syntheses, characterization, stereochemistry and complexing properties of acyclic and macrocyclic compounds possessing α-amino- or α-hydroxyphosphonate units: A review article. Heteroatom. Chem. 2000, 11, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rádai, Z.; Kiss, N.Z.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis of α-Hydroxyphosphonates, an Important Class of Bioactive Compounds; György, K., Ed.; Organophosphorus Chemistry: Novel Developments; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 91–107. 315p. [Google Scholar]
- Gröger, H.; Hammer, B. Catalytic concepts for the enantioselective synthesis of α-amino and α-hydroxy phosphonates. Chem. Eur. J. 2000, 6, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodiazhnyi, O.I. Chiral hydroxyl phosphonates: Synthesis, configuration and biological properties. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2006, 75, 227–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, P.; Marqués-López, E.; Herrera, R.P. Catalytic enantioselective hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes and imines. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilling, C.D.; Malla, R.K. Synthesis of non-racemic α-hydroxyphosphonates via asymmetric phosphor-aldol reaction. Top. Curr. Chem. 2015, 361, 83–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Phillips, A.M.F. Organocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of chiral phosphonates. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2014, 11, 164–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudovik, A.N.; Konovalova, I.V. Addition reactions of esters of phosphorus(III) acids with unsaturated systems. Synthesis 1979, 2, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, V.S.; Kiryukhina, L.I.; Kudryavtseva, N. Reaction of dialkyl esters of phosphorus acids with aldehydes and ketones. XXV. Esters of α-hydroxy-β-(2,2,3-trimethyl3-cyclopentenyl)ethylphosphonic and α-hydroxynitrobenzylphosphonic acids. Zh. Obshch. Khim. 1964, 34, 2235–2238. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, H.; Takahashi, K.; Ohmori, H. Reactions of acyl tributylphosphonium chlorides and dialkyl acylphosphonates with Grignard and organolithium reagents. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 12233–12242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seven, O.; Polat-Cakir, S.; Hossain, M.S.; Emrullahoglu, M.; Demir, A.S. Reactions of acyl phosphonates with organoaluminum reagents: A new method for the synthesis of secondary and tertiary α-hydroxy phosphonates. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 3464–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Jin, C.; Zhang, H. The catalytic aerobic synthesis of quaternary α-hydroxy phosphonates via direct hydroxylation of phosphonate compounds. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, C.; Gu, L. C–H hydroxylation of phosphonates with oxygen in [bmIm]OH to produce quaternary α-hydroxy phosphonates. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 2443–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pudovik, A.N.; Zametaeva, G.A. New synthesis of esters of phosphonic and thiophosphonic acids. XIII. Addition of diethyl thiophosphite to ketones and aldehydes. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Ser. Khim. 1952, 1952, 932–939. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Wu, Z.; Rong, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, G.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L. Highly efficient hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes and unactivated ketones catalyzed by methylene-linked pyrrolyl rare earth metal amido complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 2653–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Ding, H.; Zhao, B.; Lu, C.; Yao, Y. Synthesis and characterization of amidate rare-earth metal amides and their catalytic activities toward hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes and unactivated ketones. Polyhedron 2014, 83, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, S.; Feng, Z.; Wei, Y.; Miao, H.; Guo, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; et al. Synthesis, structure, and catalytic activity of novel trinuclear rare-earth metal amido complexes incorporating μ–η5:η1 bonding indolyl and μ3-oxo groups. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 2521–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Zhou, S.L.; Wang, S.W.; Zhang, L.J.; Wei, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, F.H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Q.B. Rare-earth metal amido complexes supported by bridged bis(β-diketiminato) ligand as efficient catalysts for hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes and ketones. Sci. China Chem. 2013, 56, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Carpentier, J.F.; Sarazin, Y. Highly effective alkaline earth catalysts for the sterically governed hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes and nonactivated ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 13259–13264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, M.A.; Lad, U.P.; Desai, U.V.; Mitragotri, S.D.; Wadgaonkar, P.P. Mechanistic approach for expeditious and solvent-free synthesis of α-hydroxy phosphonates using potassium phosphate as catalyst. C. R. Chim. 2013, 16, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandre, K.P.; Nandre, J.P.; Patil, V.S.; Bhosale, S.V. Barium hydroxide catalyzed greener protocol for the highly efficient and rapid synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates under solvent free conditions. Chem. Biol. Interface 2012, 2, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Pandi, M.; Chanani, P.K.; Govindasamy, S. An efficient synthesis of α-hydroxy phosphonates and 2-nitroalkanols using Ba(OH)2 as catalyst. Appl. Catal. A 2012, 441–442, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardarian, A.R.; Kaboudin, B. Surface-mediated solid phase reactions: Preparation of diethyl 1-hydroxyarylmethylphosphonates on the surface of magnesia. Synth. Commun. 1997, 27, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouani, I.; Lahbib, K.; Touil, S. Green synthesis and antioxidant activity of novel γ-cyano-α-hydroxyphosphonate derivatives. Med. Chem. 2015, 11, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, H.R.; Yusuf, R.O.; Matthews, R.W. The preparation of dimethyl α-hydroxyphosphonates and the chemical shift non-equivalence of their diastereotopic methyl ester groups. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2008, 183, 1527–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; He, H. Synthesis and herbicidal activity of novel dialkoxyphosphoryl aryl methyl 2-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yloxy) benzoate derivatives. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2011, 186, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Lv, X.; Wen, J.; He, H. Solvent-free synthesis of tertiary α-hydroxyphosphates by the triethylamine-catalyzed hydrophosphonylation of ketones. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2013, 188, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajbakhsh, M.; Samad, K.; Zahra, T.; Ahmadreza, B. MgCl2/Et3N base system as a new catalyst for the synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonate. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Shekhar, A.; Pathak, D.D. A new catalyst and solvent-free green synthesis of α-hydroxy phosphonates and α-aminophosphonates. Chem. Sci. Trans. 2014, 3, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Keglevich, G.; Tóth, V.R.; Drahos, L. Microwave-assisted synthesis of α-hydroxy-benzylphosphonates and –benzylphosphine oxides. Heteroatom Chem. 2011, 22, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.L.; Liu, R.D.; Li, G.Z.; Zhang, P.W.; Wu, M.S. A rapid, convenient, solventless green approach for the synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates by grinding. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 1246–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.S.; Reddy, C.B.; Reddy, M.V.N.; Rani, C.R.; Reddy, C.S. Green chemical synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates. Org. Commun. 2012, 5, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Kalla, R.M.N.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, I. Highly efficient green synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates using a recyclable choline hydroxide catalyst. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 5373–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramananarivo, H.R.; Solhy, A.; Sebti, J.; Smahi, A.; Zahouily, M.; Clark, J.; Sebti, S. An eco-friendly paradigm for the synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates using sodium-modified fluorapatite under solventless conditions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.U.M.; Sundar, C.S.; Prasad, S.S.; Rani, C.R.; Reddy, C.S. Neat synthesis and anti-oxidant activity of α-hydroxyphosphonates. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 3343–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhisudha, S.; Sreelakshimi, P.; Jayaprakash, S.H.; Kumar, B.V.; Reddy, C.S. Silica-supported tungstic acid catalyzed synthesis and antioxidant activity of α-hydroxyphosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2015, 190, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Q.; Yuan, D.; Yao, Y. n-BuLi as a highly efficient precatalyst for hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes and unactivated ketones. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 6172–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Chang, L.; Zhao, J.; Shang, D.; Liu, X.; Lin, L.; Feng, X. Highly efficient synthesis of quaternary α-hydroxy phosphonates via Lewis acid-catalyzed hydrophosphonylation of ketones. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 2567–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Noronha, R.G.; Costa, P.J.; Romão, C.C.; Calhorda, M.J.; Fernandes, A.C. MoO2Cl2 as a novel catalyst for C–P bond formation and for hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes. Organometallics 2009, 28, 6206–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzina, A.; Aouf, N.E.; Berredjem, M. Ultrasound assisted green synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates under solvent-free conditions. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 5993–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandhane, P.G.; Joshi, R.S.; Nagargoje, D.R.; Gill, C.H. Ultrasound-promoted greener approach to synthesize α-hydroxy phosphonates catalyzed by potassium dihydrogen phosphate under solvent-free condition. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 1490–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaphal, A.S.; Sonar, S.S.; Pokalwar, R.U.; Shitole, N.V.; Shingare, M.S. Sulphamic acid: An efficient catalyst for the synthesis of α-hydroxy phosphonates using ultrasound irradiation. J. Korean Chem. Soc. 2009, 53, 536–541. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, P.V.; Kategaonkar, A.H.; Shingate, B.B.; Shingare, M.S. An organocatalyzed facile and rapid access to α-hydroxy and α-amino phosphonates under conventional/ultrasound technique. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 2889–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdat, S.M.; Baharfar, R.; Tajbakhsh, M.; Heydari, A.; Baghbanian, S.M.; Khaksar, S. Organocatalytic synthesis of α-hydroxy and α-aminophosphonates. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 6501–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangala, V.B.; Pati, H.N. Efficient synthesis of β-lactam containing α-hydroxy phosphonates using tartaric acid and fumaric acid as mild catalysts. Synth. Commun. 2016, 46, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahani, F.; Zamenian, B.; Khaksar, S.; Tajbakhsh, M. Pyridine 2,6-dicarboxylic acid as a bifunctional organocatalyst for hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes and ketones in water. Synthesis 2010, 19, 3315–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, A.; Arefi, A.; Khaksar, S.; Tajbakhsh, M. Hydrophosphonylation of aldehydes catalyzed by guanidine hydrochloride in water. Catal. Commun. 2006, 7, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.S.; Zeng, J.E. Iodine-catalyzed, efficient synthesis of α-hydroxy phosphonates in water. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2010, 185, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.; Madhav, B.; Murthy, S.N.; Nageswar, Y.V.D. Aqueous-phase synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates catalyzed by β-cyclodextrin. Synth. Commun. 2012, 42, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonar, S.S.; Kategaonkar, A.H.; Ware, M.N.; Gill, C.H.; Shingate, B.B.; Shingare, M.S. Ammonium metavanadate: An effective catalyst for synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates. Arkivoc 2009, 2, 138–148. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, P.; Rajeshwaran, G.G.; Nandakumar, M.; Mohanakrishnan, A.K. Unusual reactivity of aryl aldehydes with triethyl phosphite and zinc bromide: A facile preparation of epoxides, benzisoxazoles, and α-hydroxy phosphonate esters. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 2015, 3513–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jamwal, S.; Khan, S.; Singh, N.; Rai, V.K. Bi(NO3)3·5H2O catalyzed phosphonylation of aldehydes: An efficient route to α-hydroxyphosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2016, 192, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thottempudi, V.; Chung, K.H. Niobium(V) chloride catalyzed Abramov reaction: An efficient protocol for the preparation of α-hydroxy phosphonates. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2008, 29, 1781–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keglevich, G.; Rádai, Z.; Kiss, N.Z. To date the greenest method for the preparation of α-hydroxyphosphonates from substituted benzaldehydes and dialkyl phosphites. Green Process Synth. 2017, 6, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, N.Z.; Rádai, Z.; Mucsi, Z.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis of α-aminophosphonates from α-hydroxyphosphonates; a theoretical study. Heteroat. Chem. 2016, 27, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, W.; Henglein, A.; Schrader, G. The new insecticide O,O-dimethyl 2,2,2-trichloro-1-hydroxyethylphosphonate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 2554–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Mao, H.; Shi, D. Synthesis and herbicidal activity of α-hydroxy phosphonate derivatives containing pyrimidine moiety. Chin. J. Chem. 2010, 28, 2020–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokalwar, R.U.; Hangarge, R.V.; Maske, P.V.; Shingare, M.S. Synthesis and antibacterial activities of α-hydroxyphosphonates and α-acetyloxyphosphonates derived from 2-chloroquinoline-3-carbaldehyde. Arkivoc 2006, 11, 196–204. [Google Scholar]
- Kategaonkar, A.H.; Pokalwar, R.U.; Sonar, S.S.; Gawali, V.U.; Shingate, B.B.; Shingare, M.S. Synthesis, in vitro antibacterial and antifungal evaluations of new α-hydroxyphosphonate and new α-acetoxyphosphonate derivatives of tetrazolo [1, 5-a] quinolone. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhani, S.; Tashrifi, Z. Synthesis of α-functionalized phosphonates from α-hydroxyphosphonates. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brücher, K.; Illarionov, B.; Held, J.; Tschan, S.; Kunfermann, A.; Pein, M.K.; Bacher, A.; Gräwert, T.; Maes, L.; Mordmüller, B.; et al. α-Substituted β-oxa isosteres of fosmidomycin: Synthesis and biological evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6566–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.; Yang, F.; Guo, D.; Xu, J.; Jiang, M.; Liu, C.; Bao, K.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 3,4-diaryl-1,2,5-selenadiazol analogues of combretastatin A-4. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, M.; Nakajima, M.; Kume, A.; Hashizume, A.; Hata, T. Silyl phosphites. XVIII. Versatile utility of α-(trimethylsilyloxy)-alkylphosphonates as key intermediates for transformation of aldehydes into several carbonyl derivatives. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1982, 55, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Sobhani, S. A high yielding preparation of α-trimethylsilyloxyphosphonates by silylation of α-hydroxyphosphonates with HMDS catalyzed by iodine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 3653–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Sobhani, S.; Ghassamipour, S.; Amoozgar, Z. Copper triflate [Cu(OTf)2] is an efficient and mild catalyst for the silylation of α-hydroxyphosphonates to α-trimethylsilyloxyphosphonates with HMDS at room temperature. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Jafari, A.A.; Jafari, M.R. Iron(III) trifluoroacetate [Fe(F3CCO2)3] as an easily available, non-hygroscopic, non-corrosive, highly stable and a reusable Lewis acis catalyst: Efficient O-silylation of α-hydroxyphosphonates, alcohols and phenols by hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS) under solvent-free conditions. J. Organomet. Chem. 2008, 693, 2711–2714. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Miao, Z.; Chen, R. Efficient syntheses of phosphonylated isochromenes by regioselective 6-endo-dig addition to carbon-carbon triple bond catalyzed by Pd(OAc)2. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 2848–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.B.; Shi, D.Q. Synthesis and biological activity of novel phosphonate derivatives containing of pyridyl and 1,2,3-triazole rings. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2008, 183, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shen, P.; Li, Y.; He, H. Synthesis and herbicidal activity of O,O-dialkyl phenoxyacetoxyalkylphosphonates containing fluorine. J. Fluorine Chem. 2006, 127, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, T.; Xie, P.; Chen, T.; He, H.W.; Wan, J. Molecular docking and three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship studied on the binding modes of herbicidal 1-(substituted phenoxyacetoxy)alkylphosphonates to the E1 component of pyruvate dehydrogenase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.P.; Ning, B.K.; Mao, M.Z.; Xue, C.; Wang, H.Y. Synthesis and insecticidal activities of O,O-dialkyl-2-[3-bromo-1-(3-chloropyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carbonyloxy] (aryl) methylphosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2016, 191, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, M. Synthesis, crystal structure and fragmentation pathway of arylcarboxy ester of α-hydroxyphosphonate. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 30, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, H.R.; Jászay, Z.M.; Pianka, M. The preparation and properties of some α-acyloxy- and α-carbamoyloxy-phosphonothionates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2003, 178, 1571–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.Q.; Li, X.J.; Wei, J. 5-Fluorouracil derivatives containing α-hydroxy phosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2007, 182, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Long, Q.; Deng, X.; He, H. Synthesis and herbicidal activities of lithium or potassium hydrogen 1-(substituted phenoxyacetoxy)alkylphosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2013, 188, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Deng, X.; Gao, Y.; Xie, H.; Peng, H.; He, H. Synthesis and herbicidal activities of sodium hydrogen 1-(substituted phenoxyacetoxy)alkylphosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2013, 188, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.W.; Yuan, J.L.; Peng, H.; Chen, T.; Shen, P.; Wan, S.Q.; Li, Y.; Tan, H.L.; He, Y.H.; He, J.B.; et al. Studies of O,O-dimethyl α-(2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetoxy)-ethylphosphonate (HW02) as a new herbicide. 1. Synthesis and herbicidal activity of HW02 and analogues as novel inhibitors of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4801–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Joshi, R.; Li, M.; He, H. Synthesis and biological activity of novel 1-(substituted phenoxyacetoxy) alkyl phosphonates and phosphinates. J. Nepal Chem. Soc. 2009, 23, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Soung, M.G.; Hwang, T.Y.; Sung, N.D. Synthesis and 3D-QSARs analyses of herbicidal O,O-dialkyl-1-phenoxy-1-acetoxy-1-methylphosphonate analogues as a new class of potent inhibitors of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, H.W. An efficient synthesis of α-(2,4-dichloro-phenoxyacetoxy)aryl methyl phosphonate monosodium salts. Synth. Commun. 2004, 34, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, H.W. Simple and improved preparation of α-oxophosphonate monolithium salts. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2004, 179, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, H.W.; Zuo, N.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.S.; Chen, W.; Peng, H. Synthesis and herbicidal activity of 2-(substituted phenoxyacetoxy)alkyl-5,5-dimethyl-1,3,2-dioxaphosphinan-2-one containing fluorine. J. Fluorine Chem. 2012, 142, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, H.W.; Zuo, N.; He, H.F.; Peng, H.; Tan, X.S. Synthesis and herbicidal activity of 2-(substituted phenoxyacetoxy)alkyl-5,5-dimethyl-1,3,2-dioxaphosphinan-2-one. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7581–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Lei, D.Y.; Huang, Y.; Ao, L.H. Synthesis and biological activity of O,O-dimethyl-2,6-pyridinyl diformyloxy alkyl phosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2009, 184, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Sobhani, S.; Amoozgar, Z. Copper triflate as a useful catalyst for the high-yielding preparation of α-acetyloxyphosphonates under solvent-free conditions. Synthesis 2004, 2, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Farahi, S. Solid trichlorotitanium(IV) trifluoromethanesulfonate TiCl3(OTf) catalyzed efficient acylation of –OH and –SH: Direct esterification of alcohols with carboxylic acids and transesterification of alcohols with esters under neat conditions. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2008, 289, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Sobhani, S.; Amoozgar, Z. Facile and high-yielding preparation of α-hydroxyphosphonates assisted by microwave irradiation. Synthesis 2004, 11, 1771–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Atashkar, B.; Moradi, D. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties of magnetic nanoparticle supported guanidine in base catalyzed synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates and α-acetoxyphosphonates. Appl. Catal. A 2013, 467, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.; Elgendy, S.; Patel, G.; Skordalakes, E.; Goodwin, C.A.; Scully, M.F.; Kakkar, V.V.; Deadman, J.J. Substrate related O,O-dialkyldipeptidyly ψ carboxybenzylphosphonates, a new type of thrombin inhibitor. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2000, 156, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ma, J.; Che, W.; Li, M.; Li, G.; Song, B. Microwave-assisted synthesis and antitumor activity of salicyl acyloxy phosphonate derivatives. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 34, 2566–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranpoor, N.; Firouzabadi, H.; Khalili, D. The first Mitsunobu protocol for efficient synthesis of α-acyloxyphosphonates using 4,4′-azopyridine. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2011, 186, 2166–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; You, G.; Peng, H.; He, H. Synthesis and biological activities of O,O-dialkyl 1-((4,6-dichloropyrimidin-2-yl)carbamyloxy) alkylphosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2014, 189, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Zhu, J.G.; Liu, R.J.; Cui, F.L.; Liu, P.; Liu, G.S. Straightforward synthesis of a new series of α-(arylamino thiocarbonyloxy) hydrocarbylphosphonates. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2008, 61, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.G.; Sun, H.K.; Wang, Q.M.; Huang, R.Q. An α-hydrazinoalkylphosphonate as building block for novel N-phosphonoalkylheterocycles. Heteroatom Chem. 2003, 14, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creary, X.; Geiger, C.C.; Hilton, K. Mesylate derivatives of α-hydroxy phosphonates. Formation of carbocations adjacent to the diethyl phosphonate group. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.L.; Li, G.Z.; Liu, R.D. Synthesis and crystal structure of diethyl tosyloxybenzylphosphonate. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 2138–2140. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, R.S.; Sheldon, R.A.; Trippett, S. The reaction of tetraphenyldiphosphine with aromatic carboxylic acids. J. Chem. Soc. 1967, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rádai, Z.; Hodula, V.; Kiss, N.Z.; Kegelevich, G. Unpublished results.
- Samanta, S.; Zhao, C.G. Organocatalyzed nitroaldol reaction of α-ketophosphonates and nitromethane revisited. Arkivoc 2007, 8, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Guang, J.; Zhao, C.G. Organocatalyzed asymmetric Michael reaction of β-aryl-α-ketophosphonates and nitroalkenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 5703–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Telan, L.A.; Poon, C.D.; Evans, S.A. Diastereoselectivity in the Mukaiyama–Michael reaction employing α-acyl β,γ-unsaturated phosphonates. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 7455–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaboudin, B. Surface-mediated solid-phase reactions: The preparation of acyl phosphonates by oxidation of 1-hydroxyphosphonates on the solid surface. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 3169–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Sobhani, S.; Sardarian, A.R. High yields preparation of α-ketophosphonates by oxidation of α-hydroxyphosphonates with zinc dichromate trihydrate (ZnCr2O7·3H2O) under solvent-free conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 4369–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guliaiko, I.; Nesterov, V.; Sheiko, S.; Kolodiazhnyi, O.I.; Freytag, M.; Jones, P.G.; Schmutzler, R. Synthesis of optically active hydroxyphosphonates. Heteroatom Chem. 2008, 19, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Sobhani, S. Preparation of α-ketophosphonates by oxidation of α-hydroxyphosphonates with pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC). Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2004, 179, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Sobhani, S. Preparation of α-ketophosphonates by oxidation of α-hydroxyphosphonates with neutral alumina supported potassium permanganate (NASPP) under solvent-free conditions and potassium permanganate in dry benzene. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
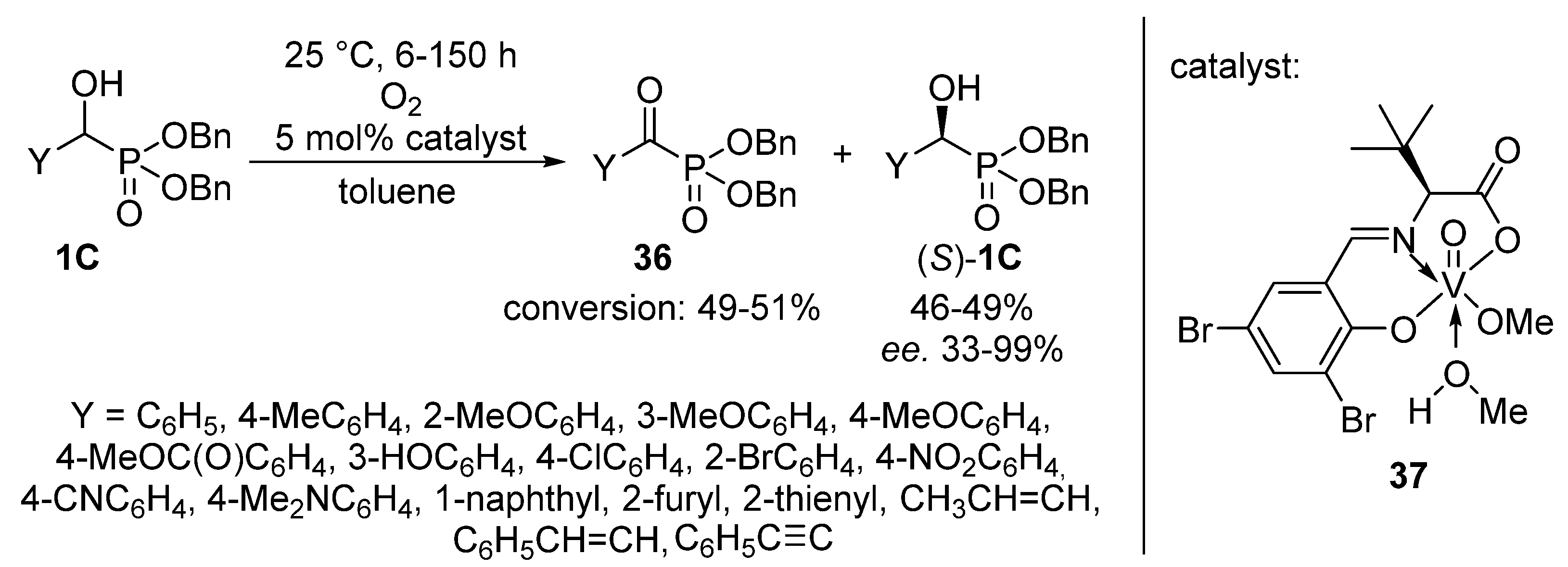
- Pawar, V.D.; Bettigeri, S.; Weng, S.S.; Kao, J.Q.; Chen, C.T. Highly enantioselective aerobic oxidation of α-hydroxyphosphonates catalyzed by chiral vanadyl(V) methoxides bearing N-salicylidene-α-aminocarboxylates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6308–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, W.P.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Widlanski, T.S. Quiescent affinity inactivators of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1996, 4, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulsi, N.S.; Downey, A.M.; Cairo, C.W. A protected l-bromophosphonomethylphenylalanine amino acid derivative (BrPmp) for synthesis of irreversible protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 8679–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, N.A.; Pogson, C.I.; Hayes, D.J.; Blackburn, G.M. The synthesis of novel bisphosphonates as inhibitors of phosphoglycerate kinase (3-PGK). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 2000, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajda, T. Preparation of diethyl 1-bromoalkylphosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1990, 53, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Wu, D.; Fu, J.P.; He, Y.H. A facile and efficient synthesis of diethyl α,α-chlorofluoroalkanephosphonates. Heteroatom Chem. 2010, 21, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; He, Y.; Tang, R.; Guan, Z. The first synthesis of diethyl α,α-chlorofluorobenzylphosphonates. Synlett 2009, 13, 2180–2182. [Google Scholar]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Sobhani, S. PPh3/DDQ as a neutral system for the facile preparation of diethyl α-bromo, α-iodo and α-azidophosphonates from diethyl α-hydroxyphosphonates. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.P.; He, Y.H.; Zhong, J.; Yang, Y.; Deng, X.; Guan, Z. An efficient and general route to the synthesis of diethyl α,α-bromofluorophosphonates. J. Fluorine Chem. 2011, 132, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranpoor, N.; Firouzabadi, H.; Gholinejad, M. 4-Aminophenyldiphenylphosphinite (APDPP), a new heterogeneous and acid scavenger phosphinite—Conversion of alcohols, trimethylsilyl, and tetrahydropyranyl ethers to alkyl halides with halogens or N-halosuccinimides. Can. J. Chem. 2006, 84, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allmendinger, T.; Fujimoto, R.; Gasparini, F.; Schilling, W.; Satoh, Y. α-Fluoro-benzylphosphonates as reagents for the preparation of 1-fluoro-1-aryl alkenes and α-fluorostilbenes. Chimia 2004, 58, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, G.M.; Kent, D.E. A novel synthesis of α- and γ-fluoroalkylphosphonates. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1981, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, G.M.; Kent, D.E. Synthesis of α- and γ-fluoroalkylphosphonates. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1986, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokomatsu, T.; Yamagishi, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Shibuya, S. Stereocontrolled synthesis of hydroxymethylene phosphonate analogues of phosphorylated tyrosine and their conversion to monofluoromethylene phosphonate analogues. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 11725–11738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzyr, O.I.; Zasukha, S.V.; Vlasenko, Y.G.; Chernega, A.N.; Rozhenko, A.B.; Shermolovich, Y.G. Simple route to adducts of (amino)(aryl)carbene with phosphorus pentafluoride. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 4154–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psurski, M.; Błażewska, K.; Gajda, A.; Gajda, T.; Wietrzyk, J.; Oleksyszyn, J. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of novel α- and β-dialkoxyphosphoryl isothiocyanates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4572–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keglevich, G.; Bálint, E. The Kabachnik–Fields reaction: Mechanism and synthetic use. Molecules 2012, 17, 12821–12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bálint, E.; Fazekas, E.; Tripolszky, A.; Tajti, Á.; Kangyal, R.; Milen, M.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis of aminophosphonate derivatives by microwave-assisted Kabachnik–Fields reaction. Organomet. Chem. 2012, 717, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zefirov, N.S.; Matveeva, E.D. Catalytic Kabachnik–Fields reaction: New horizons for old reaction. Arkivoc 2008, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kafarski, P.; Gorny vel Gorniak, M.; Andrasiak, I. Kabachnik–Fields reaction under green conditions—A critical overview. Curr. Green Chem. 2015, 2, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboudin, B. A convenient synthesis of 1-aminophosphonates from 1-hydroxyphosphonates. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, N.Z.; Kaszás, A.; Drahos, L.; Mucsi, Z.; Keglevich, G. A neighbouring group effect leading to enhanced nucleophilic substitution of amines at the hindered α-carbon atom of an α-hydroxyphosphonate. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallikonda, G.; Chakravarty, M. Triflic acid mediated functionalization of α-hydroxyphosphonates: Route for sulfonamide phosphates. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 20503–20511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Singh, A.; Pallikonda, G.; Chakravarty, M.; Quraishi, M.A.; Bahadur, I.; Ebenso, E.E. Aryl sulfonamidomethylphosphonates as new class of green corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 1 M HCl: Electrochemical, surface and quantum chemical investigation. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zou, Y.X.; Fang, X.Y.; Yin, X. Convenient synthesis of α-diarylmethylphosphonates by HOTf catalyzed Friedel–Crafts arylation of α-aryl α-hydroxyphosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2018, 193, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.B.Z.; Pallikonda, G.; Tulichala, R.N.P.; Chakravarty, M. Oxy-Wittig reactions of 1-naphthyl(aryl)methylphosphonates: A new approach to naphthylarylketones. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallikonda, G.; Chakravarty, M. FeCl3-mediated arylation of α-hydroxyphosphonates with unactivated arenes: Pseudo-umpolung in allylic phosphonates. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2013, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallikonda, G.; Chakravarty, M.; Sahoo, M. An easy access to α-aryl substituted γ-ketophosphonates: Lewis acid mediated reactions of 1,3-diketones with α-hydroxyphosphonates and tandem regioselective C–C bond cleavage. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 7140–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, L.A.R.; Stephens, C.W.; Drysdale, J.J. A rearrangement to from diethyl 1-cyanoethyl phosphate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 1768–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K.; Kohno, T.; Morita, T.; Tsukamoto, G. Organic phosphorus compounds. 2. Synthesis and coronary vasodilator activity of (benzothiazolylbenzyl)phosphonate derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 1528–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeary, R.P.; Vella, P.; Mak, J.Y.W.; Guddat, L.W.; Schenk, G. Inhibition of purple acid phosphatase with α-alkoxynaphthylmethylphosphonic acids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumaraswamy, S.; Selvi, R.S.; Swamy, K.C.K. Synthesis of new α-hydroxy-, α-halogeno- and vinylphosphonates derived from 5,5-dimethyl-1,3,2-dioxaphosphinan-2-one. Synthesis 1997, 1997, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, S.; Marczak, J.; Olczak, A.; Główka, M.L. Stereochemistry of 1-hydroxyphosphonate–phosphate rearrangement. Retention of configuration at the phosphorus atom. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 3341–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallitsch, K.; Roller, A.; Hammerschmidt, F. The stereochemical course of the α-hydroxyphosphonate–phosphate rearrangement. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 10200–10206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallikonda, G.; Santosh, R.; Ghosal, S.; Chakravarty, M. BuLi-triggered phospha-Brook rearrangement: Efficient synthesis of organophosphates from ketones and aldehydes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 3796–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kaïm, L.; Gaultier, L.; Grimaud, L.; Santos, A.D. Formation of new phosphates from aldehydes by a DBU-catalysed phospha-brook rearrangement in a polar solvent. Synlett 2005, 15, 2335–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeta, J.; Potáček, M. Applications of caged-designed proton sponges in base-catalyzed transformations. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2014, 395, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rádai, Z.; Szabó, R.; Kiss, N.Z.; Keglevich, G. Unpublished results.
- Baguley, T.D.; Xu, H.C.; Chatterjee, M.; Nairn, A.C.; Lombroso, P.J.; Ellman, J.A. Substrate-based fragment identification for the development of selective, nonpeptidic inhibitors of striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 7636–7650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beers, S.A.; Malloy, E.A.; Wu, W.; Wachter, M.P.; Gunnia, U.; Cavender, D.; Harris, C.; Davis, J.; Brosius, R.; Pellegrino-Gensey, J.L.; et al. Nitroarylhydroxymethylphosphonic acids as inhibitors of CD45. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1997, 5, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, R.K.M.; Bearne, S.L. Inhibition of mandelate racemase by the substrate–intermediate–product analogue 1,1-diphenyl-1-hydroxymethylphosphonate. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 15, 4342–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, N.A.; Pogson, C.I.; Hayes, D.J.; Blackburn, G.M. Novel bisphosphonate inhibitors of phosphoglycerate kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlani, G.; Occhipinti, A.; Berlicki, Ł.; Dziedzioła, G.; Wieczorek, A.; Kafarski, P. Tailoring the structure of aminobisphosphonates to target plant P5C reductase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3193–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Occhipinti, A.; Berlicki, Ł.; Giberti, S.; Dziedzioła, G.; Kafarski, P.; Forlani, G. Effectiveness and mode of action of phosphonate inhibitors of plant glutamine synthetase. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desai, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Malwal, S.R.; Oldfield, E. Isoprenoid biosynthesis inhibitors targeting bacterial cell growth. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016, 11, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Madan, D.; Prestwich, G.D. Aromatic phosphonates inhibit the lysophospholipase D activity of autotaxin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 21, 5098–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nesterov, V.V.; Kolodiazhnyi, O.I. Efficient method for the asymmetric reduction of α- and β-ketophosphonates. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 6720–6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colton, I.J.; Yin, D.T.; Grochulski, P.; Kazlauskas, R.J. Molecular basis of chiral acid recognition by candida rugosa lipase: X-ray structure of transition state analog and modeling of the hydrolysis of methyl 2-methoxy-2-phenylacetate. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 2529–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


















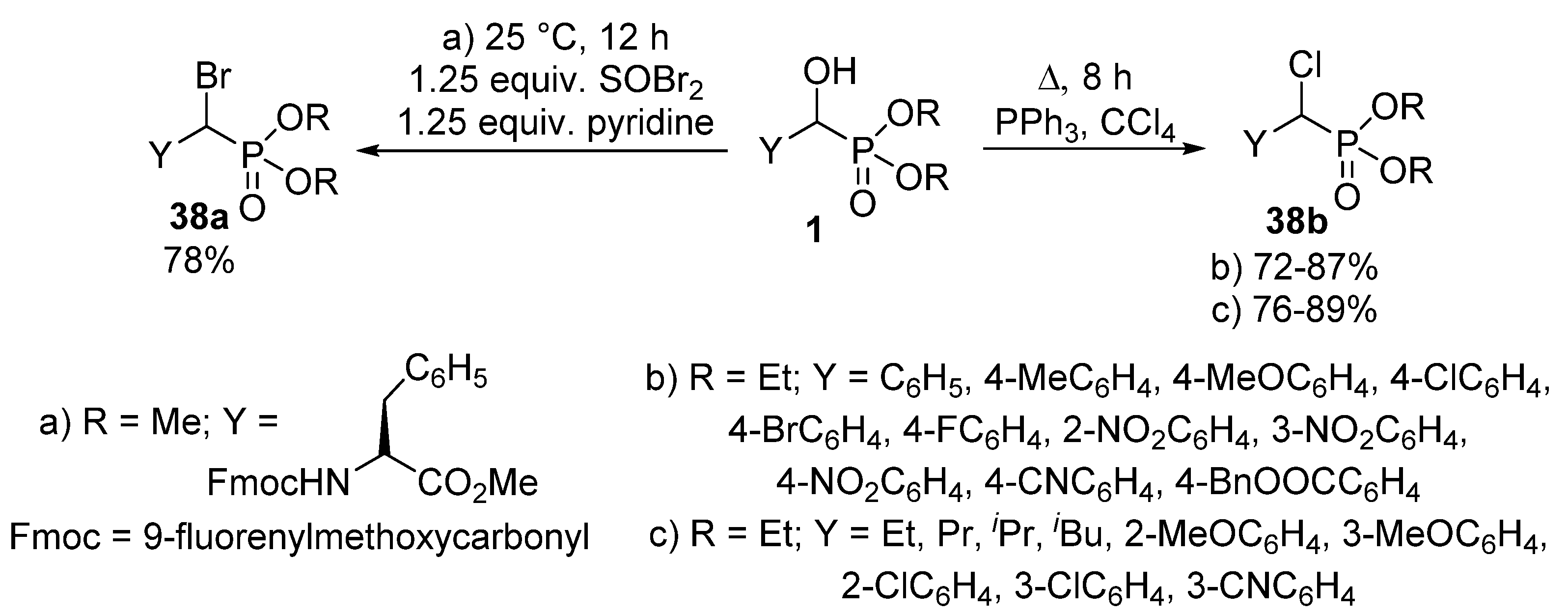










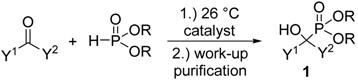
| Entry | Y1 | Y2 | R | Catalyst | Amount of Catalyst | Conditions | Yield (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | iPr, cHex, C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-iPrC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 3,4-diMeOC6H3, 4-ClC6H4, 2-NO2C6H4, 4-CNC6H4, C6H5CH=CH, 3,4-OCH2OC6H3, 4-CH2=CHCH2OC6H4, 4-PhCH2OC6H4, 2-furyl, 2-thienyl | H | Me, Et, iPr | K3PO4 | 5 mol % | 25 °C, 4–8 min for aromatic aldehydes, 24 h for aliphatic aldehydes | 20–98 | [21] |
| 2 | C6H5, 4-MeOC6H4, 3,4-diMeOC6H3, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 2,3-diClC6H3, 2,4-diClC6H3, 2,6-diClC6H3, 2-BrC6H4, 4-BrC6H4, 3-FC6H4, 4-FC6H4, 2-NO2C6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 4-CNC6H4, C6H5CH=CH, 2-thienyl, 4-pyridyl | H | Et | Ba(OH)2 | 10 mol % | 25 °C, 4–10 min | 70–98 | [22] |
| 3 | iBu, C6H5, 2-MeC6H4, 3-MeC6H4, 4-MeC6H4, 4-EtC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 2,3,4-triMeOC6H2, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 2,6-diClC6H3, 3-BrC6H4, 4-BrC6H4, 3-FC6H4, 4-FC6H4, 2-NO2C6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 3-CNC6H4, 4-CNC6H4, 2-furyl, 2-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl, 1-naphthyl, 2-naphthyl, 9-anthryl, C6H5CH=CH | H | Et, Bu, Bn | Ba(OH)2·8H2O | 2–7 mol % | 25 °C, 15 min, THF | 72–99 | [23] |
| 4 | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 3-MeOC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 3-HOC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 2,6-diClC6H3, 2-NO2C6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 4-Me2NC6H4, C6H5CH=CH, 2-furyl, 1-naphthyl, 2-naphthyl | H | Et | MgO | 1 equiv. | 25 °C, 2 min–4 h | 80–100 | [24] |
| 5 * | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4 | (CH2)2CN, MeCHCH2CN | Me, Et | MgO | 2 equiv. | 25 °C, 1–6 h | 70–82 | [25] |
| 6 * | Pr, Bu, C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-iPrC6H4, 2,4,6-triMeC6H2, 2-OHC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 4-BrC6H4, 3-FC6H4, 4-FC6H4, 4-Br-2-OHC6H3, 3,4-diMeOC6H3, 3,4-OCH2OC6H3, 2-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 2-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl, 1-naphthyl, 2-naphthyl | H, Me | Me | Al2O3 | 3 equiv. | 25 °C, 72 h | 52–98 | [26] |
| 7 | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 4-FC6H4, 4-NO2C6H4 | H | Me, Et | Al2O3 + KF | 1 + 2 equiv. | 25 °C, 30 min | 53–88 | [27] |
| 8 * | Me, ClCH2, C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 3-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 3-BrC6H4, 4-BrC6H4, 2-FC6H4, 4-FC6H4, 2,4-diClC6H3, 2-furyl, 2-thienyl | Me, Pr, Ph | Me | Et3N | 1 equiv. | 40 °C, 2 h | 63–89 | [28] |
| 9 * | Pr, C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 4-CNC6H4, (CH2)2C6H5, C6H5CH=CH, 2-furyl, 2-naphthyl, 9-anthryl | H, Me | Me | Et3N + MgCl2 | 3 + 1 equiv. | 50 °C, 1–2 h | 85–98 | [29] |
| 10 | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-OHC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 4-BrC6H4, 2-NO2C6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4 | H | Et | – | – | MW, 90–100 °C, 10–20 min | 79–95 | [30] |
| 11 | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 4-NO2C6H4 | H | Me, Et | Na2CO3 | 0.75 equiv. | MW, 110 °C, 20 min | 62–88 | [31] |
| 12 | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4 | H | Et | Na2CO3 | 1 equiv. | Grinding, 25 °C, 10 min | 75–83 | [32] |
| 13 | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-iPrC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 3,4-diMeOC6H3, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 2-NO2C6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 4-Me2NC6H4, 4-PhCH2OC6H4, 4-C5H4NC6H4, 9-anthryl | H | Et |  | 1 equiv. | Grinding, 25 °C, 2–10 min | 78–96 | [33] |
| 14 | C6H5, 2-MeC6H4, 4-MeC6H4, 2-iPrC6H4, 3,5-diMeC6H3, 2-MeOC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 3,5-diMeOC6H3, 3,4,5-triMeOC6H2, 4-EtOC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 2-BrC6H4, 3-BrC6H4, 4-BrC6H4, 2-Cl-6-furylC6H3, 2-F-4-BrC6H3, 2-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 9-anthryl, 1-pyrenyl, 2-furyl, 1-C6H5-4-pyrazolyl | H | Et | 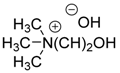 | 10 mol % | 25 °C, 5–10 min | 90–98 | [34] |
| 15 * | C6H5, 3-MeOC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, C6H5CH=CH | H, Me | Me, Et | Na-modified fluoroapatite | 1 g/1.25 mol acetophenone | 20–25 °C, 1–1.5 min | 75–98 | [35] |
| 16 | 4-iPrC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 2,6-diMeOC6H3, 3,5-diMeOC6H3, 4-OHC6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-Me2NC6H4, 2-PhCH2OC6H4, 2-imidazyl, 3-indolyl | H | Et | KHSO4 | 20 mol % | 25 °C, 2–4 h | 82–91 | [36] |
| 17 | 3-FC6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 3,4-OCH2OC6H3, 4-MeSC6H4, C5H10N, 3-MeO-4-OHC6H3, 4-C4H8NC6H4, 2-furyl, 2-thienyl, 4-imidazyl, 2-pyrrolyl, 4-pyridyl | H | Me | silica-supported tungstic acid | 20 mol % | 25 °C, 30 min | 85–96 | [37] |
| 18 * | Me, Pr, iBu, Pent, C6H5, 2-MeC6H4, 4-MeC6H4, 2-MeOC6H4, 3-MeOC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 3-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 2-BrC6H4, 4-BrC6H4, 4-FC6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 1-naphthyl, 2-naphthyl, 2-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-pyridyl | H, Me, Ph, CF3, (CH2)10CH3, C(O)Ph, CH2C(O)Ph | Et, iPr, Ph | BuLi | 0.1 mol % | 10–25 °C, 5 min, hexane | 35–99 | [38] |
| 19 * | Et, cHex, C6H5, 3-MeC6H4, 4-MeC6H4, 3-MeOC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 3,4-diClC6H3, 2,3,4-triClC6H2, 2-FC6H4, 4-FC6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 3-CF3C6H4CH2=CH, 3-CF3C6H4CH(OH)CH2, 2-thienyl, 2-naphthyl, EtOC(O)CHBn | Me, Et, Ph, CH(OEt)2, COOMe, (CH2)2Cl | Me | Ti(OiPr)4 | 5 mol % | 30 °C, 15 min | 74–98 | [39] |
| 20 | C6H5, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-FC6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 4-CF3C6H4, 4-CNC6H4, 4-MeOC(O)C6H4, (CH2)2C6H5, C6H5CH=CH | H | Et | MoO2Cl2 | 5 mol % | 80 °C, 1–24 h | 70–96 | [40] |
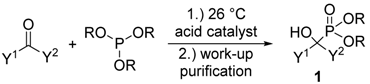
| Entry | Y1 | Y2 | R | Catalyst | Amount of Catalyst | Conditions | Yield (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 * | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-iPrC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 4-BrC6H4, 4-FC6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 4-CF3C6H4, 4-Me2NC6H4, CH2C6H5, (CH2)2C6H5 | H, Me, Et, Ph | Me, Et | – | – | Sonication, 25 °C, 10–35 min | 84–94 | [41] |
| 2 | Pr, iBu, C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 3-OHC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, C6H5CH=CH, 3-chromonyl, 6-Cl-7-Me-3-chromonyl, 2-Cl-3-quinolinyl | H | Et | KH2PO4 | 5 mol % | Sonication, 25 °C, 5–45 min | 48–92 | [42] |
| 3 | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 3-pyridyl, 3-chromonyl, 6,8-diMe-3-chromonyl, 2-Cl-3-quinolinyl, 6-Cl-3-chromonyl, 6,7-diCl-3-chromonyl, 6,8-diCl-3-chromonyl, 6-Br-3-chromonyl, 6-Cl-7-Me-3-chromonyl, 2-Cl-6-Me-3-quinolinyl, 2-Cl-7-Me-3-quinolinyl, 2-Cl-8-Me-3-quinolinyl, 2-Cl-6-MeO-3-quinolinyl, 2-Cl-6-EtO-3-quinolinyl, 2-Cl-8-Et-3-quinolinyl | H | Me, Et |  | 25 mol % | Sonication, 25 °C, 1–60 min | 78–98 | [43] |
| 4 | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-OHC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 3,4-OCH2OC6H3, C6H5CH=CH, 2-furyl, 2-thienyl, 2-Cl-3-quinolinyl, 4-tetrazolo[1,5-a]quinolinyl | H | Et | 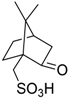 | 10 mol % | Sonication, 25 °C, 8–20 min | 85–93 | [44] |
| 5 | Pr, iPr, Pent, cHex, C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-OHC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 4-CNC6H4, C6H5CH=CH, 2-furyl | H | Me | (COOH)2 | 10 mol % | 80 °C, 3 h | 83–98 | [45] |
| 6 | 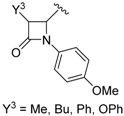 | H | Me, Et | 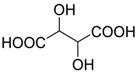 | 10 mol % | ∆, 30 min, acetonitrile | 41–69 | [46] |
| 7 * | Pr, C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 4-CNC6H4, (CH2)2C6H5, C6H5CH=CH, 2-furyl | H, Me | Me | 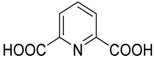 | 10 mol % | 50 °C, 1.3–3 h, H2O | 60–95 | [47] |
| 8 | Pr, iPr, Bu, tBu, Hex, cHex, C6H5, 4-ClC6H4, 2-furyl, 2-pyridyl | H | Me | 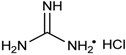 | 0.5 mol % | 50 °C, 2 h, H2O | 60–95 | [48] |
| 9 | Me, Et, iPr, C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 2,4-diClC6H3, 2-NO2C6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, C6H5CH=CH, 2-furyl, 2-thienyl | H | Et | I2 | 10 mol % | 80 °C, 15–120 min, H2O | 83–97 | [49] |
| 10 | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 2-OHC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 4-BrC6H4, 4-FC6H4, 3-NO2C6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 2-pyridyl, 2-naphthyl, 2-furyl, 2-thienyl | H | Et | β-cyclodextrin | 1 equiv. | 60–70 °C, 8–12 h, H2O | 80–93 | [50] |
| 11 | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 3-OHC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, C6H5CH=CH, 3-chromonyl, 6-Cl-3-chromonyl, 6,7-diCl-3-chromonyl, 6,8-diCl-3-chromonyl, 6-Cl-7-Me-3-chromonyl, 2-Cl-3-quinolinyl, 2-Cl-6-Me-3-quinolinyl, 2-Cl-7-MeO-3-quinolinyl, 2-Cl-8-Et-3-quinolinyl, 2-Cl-6-EtO-3-quinolinyl | H | Et | NH4VO3 | 10 mol % | 25 °C, 5–40 min | 80–94 | [51] |
| 12 | 4-ClC6H4, 2,4-diClC6H3, 4-BrC6H4, 4-MeOC(O)C6H4, 4-CF3C6H4, 2-NO2-3,6-diMeOC6H2, 1-naphthyl | H | Et | ZnBr2 | 10 mol % | 25 °C, 10–30 min | 68–91 | [52] |
| 13 | C6H5, 4-MeC6H4, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-HOC6H4, 2-ClC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, 4-NO2C6H4, 4-Me2NC6H4, C6H5CH=CH, 2-Cl-3-quinolinyl, 2-Cl-6-Me-3-quinolinyl | H | Et | Bi(NO3)3·5H2O | 10 mol % | MW, 70 °C, 10–15 min | 88–95 | [53] |
| 14 * | Et, Pr, iPr, tBu, cHex, CH3CH=CH, C6H5, 4-MeOC6H4, 4-ClC6H4, (CH2)2C6H5, C6H5CH=CH | H, Me | Me, Et | NbCl5, TMSCl | 0.05 mol % | 25 °C, 20–90 min | 44–96 | [54] |
| Entry | Y1 | Y2 | Reaction Time (min) | Yield (%) | Product | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | nPr | 10 | 78 | 44a | [129] |
| 2 | H | nBu | 15 | 86 | 45a | [129] |
| 3 | H | cHex | 10 | 84 | 46a | [129] |
| 4 | Cl | nPr | 15 | 60 | 44b | [50] |
| 5 | Cl | nBu | 20 | 50 | 45b | [56] |
| 6 | Cl | cHex | 30 | 54 | 46b | [56] |
| 7 | Me | nPr | 15 | 58 | 44c | [56] |
| 8 | Me | nBu | 15 | 79 | 45c | [56] |
| 9 | Me | cHex | 30 | 73 | 46c | [56] |
| 10 | OMe | nPr | 15 | 72 | 44g | [56] |
| 11 | OMe | nBu | 30 | 66 | 45g | [56] |
| 12 | OMe | cHex | 30 | 70 | 46g | [56] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rádai, Z.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis and Reactions of α-Hydroxyphosphonates. Molecules 2018, 23, 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061493
Rádai Z, Keglevich G. Synthesis and Reactions of α-Hydroxyphosphonates. Molecules. 2018; 23(6):1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061493
Chicago/Turabian StyleRádai, Zita, and György Keglevich. 2018. "Synthesis and Reactions of α-Hydroxyphosphonates" Molecules 23, no. 6: 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061493
APA StyleRádai, Z., & Keglevich, G. (2018). Synthesis and Reactions of α-Hydroxyphosphonates. Molecules, 23(6), 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061493






