Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in NRF2- and Sirtuin-Dependent Maintenance of Cellular Redox Balance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Effects of Hydrogen Sulfide
2.1. H2S and Repairing Antioxidant Defenses
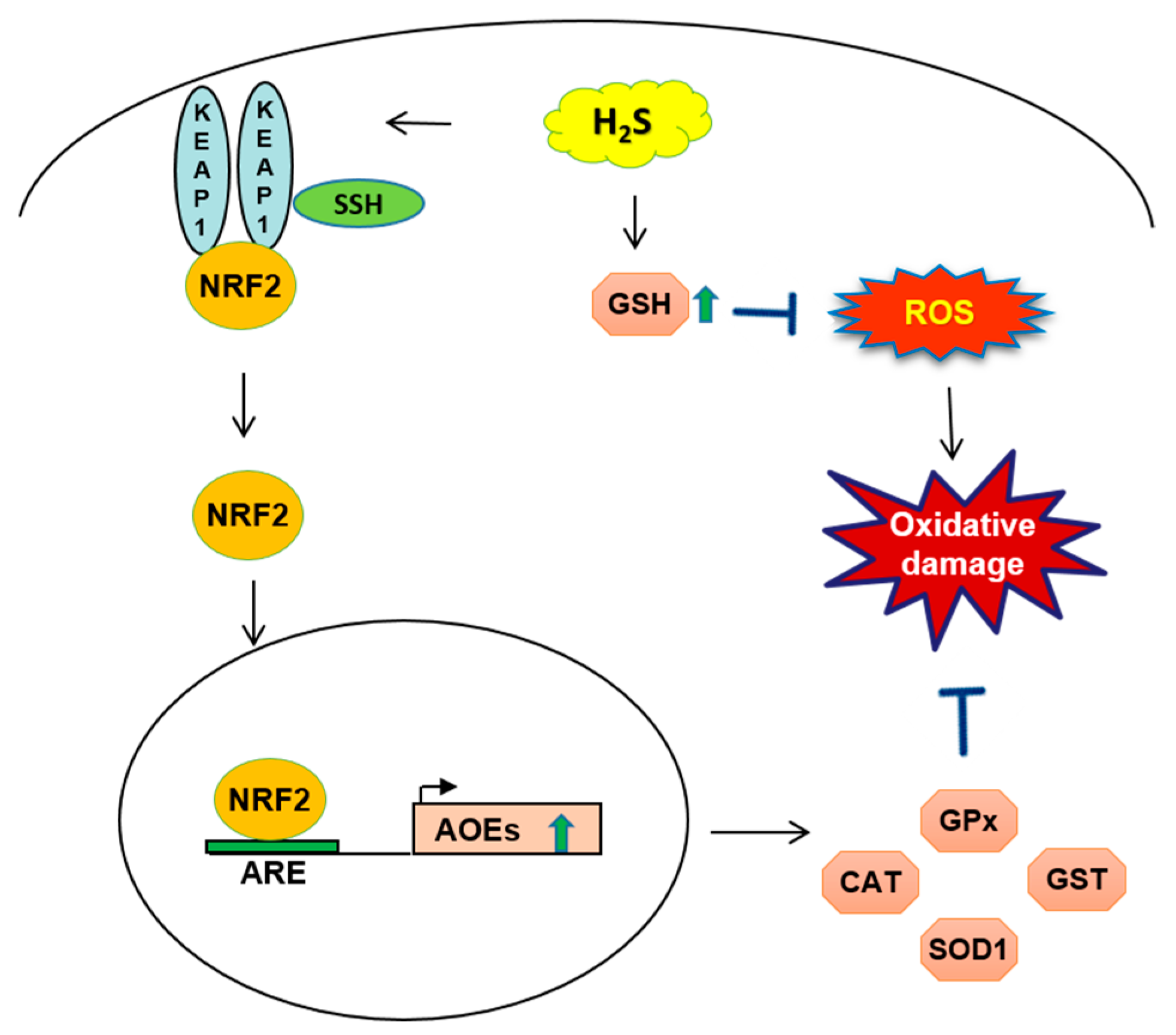
2.2. H2S-Mediated NRF2 Activation
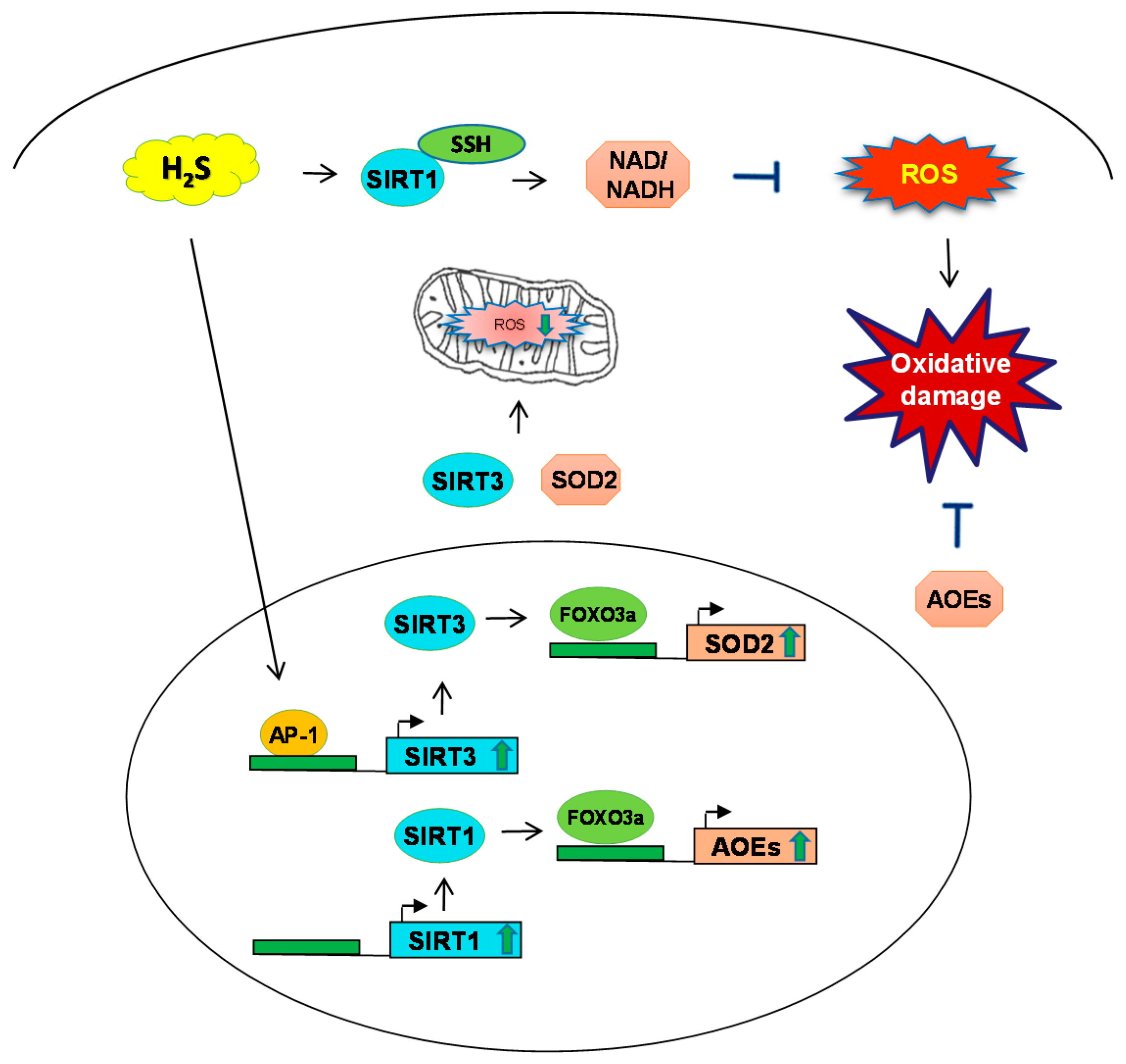
3. H2S and Sirtuin Interaction during Oxidative Stress
4. H2S Treatment in Animal Models of Diseases Associated with Oxidative Damage
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mancardi, D.; Penna, C.; Merlino, A.; Del, S.P.; Wink, D.A.; Pagliaro, P. Physiological and pharmacological features of the novel gasotransmitter: Hydrogen sulfide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1787, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, A.F.; Luciano, M.G.; Ingrosso, D.; Raiola, I.; Pulzella, P.; Sepe, I.; Lanza, D.; Violetti, E.; Capasso, R.; Lombardi, C.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide, the third gaseous signaling molecule with cardiovascular properties, is decreased in hemodialysis patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2010, 20, S11–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H. Production and physiological effects of hydrogen sulfide. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olas, B. Hydrogen sulfide in signaling pathways. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 439, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.H.; Wong, P.T.; Bian, J.S. Hydrogen sulfide: A novel signaling molecule in the central nervous system. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpure, B.V.; Bian, J.S. Interaction of Hydrogen Sulfide with Nitric Oxide in the Cardiovascular System. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 6904327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bearden, S.E.; Beard, R.S.; Pfau, J.C., Jr. Extracellular transsulfuration generates hydrogen sulfide from homocysteine and protects endothelium from redox stress. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H1568–H1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowicka, E.; Beltowski, J. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S)—The third gas of interest for pharmacologists. Pharmacol. Rep. 2007, 59, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giuffre, A.; Vicente, J.B. Hydrogen Sulfide Biochemistry and Interplay with Other Gaseous Mediators in Mammalian Physiology. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 6290931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ida, T.; Sawa, T.; Ihara, H.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Kumagai, Y.; Suematsu, M.; Motohashi, H.; Fujii, S.; Matsunaga, T.; et al. Reactive cysteine persulfides and S-polythiolation regulate oxidative stress and redox signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7606–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, T.; Ida, T.; Wei, F.Y.; Nishida, M.; Kumagai, Y.; Alam, M.M.; Ihara, H.; Sawa, T.; Matsunaga, T.; Kasamatsu, S.; et al. Cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase governs cysteine polysulfidation and mitochondrial bioenergetics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, KR. H2S and polysulfide metabolism: Conventional and unconventional pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 149, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, L.; Bianco, C.L.; Toscano, J.P.; Lin, J.; Akaike, T.; Fukuto, J.M. Chemical Biology of Hydropersulfides and Related Species: Possible Roles in Cellular Protection and Redox Signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazhanov, N.; Ansar, M.; Ivanciuc, T.; Garofal, R.P.; Casola, A. Hydrogen sulfide: A novel player in airway development, pathophysiology of respiratory diseases, and antiviral defenses. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominko, K.; Dikic, D. Glutathionylation: A regulatory role of glutathione in physiological processes. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2018, 69, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. The thioredoxin antioxidant system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordberg, J.; Arner, E.S. Reactive oxygen species, antioxidants, and the mammalian thioredoxin system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 1287–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predmore, B.L.; Lefer, D.J.; Gojon, G. Hydrogen sulfide in biochemistry and medicine. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, P.; Winterbourn, C.C. Rapid reaction of hydrogen sulfide with the neutrophil oxidant hypochlorous acid to generate polysulfides. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 1541–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Goto, Y.; Kimura, H. Hydrogen sulfide increases glutathione production and suppresses oxidative stress in mitochondria. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, C.K.; Lambert, J.P.; Molkentin, J.D.; Sadoshima, J.; Calvert, J.W. Thioredoxin 1 is essential for sodium sulfide-mediated cardioprotection in the setting of heart failure. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvert, J.W.; Jha, S.; Gundewar, S.; Elrod, J.W.; Ramachandran, A.; Pattillo, C.B.; Kevil, C.G.; Lefer, D.J. Hydrogen sulfide mediates cardioprotection through Nrf2 signaling. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kong, A.N. Molecular mechanisms of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, B.D.; Snyder, S.H. H2S: A Novel Gasotransmitter that Signals by Sulfhydration. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Du, J.; Tang, C.; Huang, Y.; Jin, H. H2S-Induced Sulfhydration: Biological Function and Detection Methodology. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Zhao, K.; Ju, Y.; Mani, S.; Cao, Q.; Puukila, S.; Khaper, N.; Wu, L.; Wang, R. Hydrogen sulfide protects against cellular senescence via S-sulfhydration of Keap1 and activation of Nrf2. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1906–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hourihan, J.M.; Kenna, J.G.; Hayes, J.D. The Gasotransmitter Hydrogen Sulfide Induces Nrf2-Target Genes by Inactivating the Keap1 Ubiquitin Ligase Substrate Adaptor Through Formation of a Disulfide Bond between Cys-226 and Cys-613. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buler, M.; Andersson, U.; Hakkola, J. Who watches the watchmen? Regulation of the expression and activity of sirtuins. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 3942–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.; Escande, C.; Denicola, A. Potential Modulation of Sirtuins by Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9831825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Lin, X.; Xu, W.; Zheng, F.; Cai, J.; Yang, J.; Cui, Q.; Tang, C.; Cai, J.; Xu, G.; et al. Sulfhydrated sirtuin-1 increasing its deacetylation activity is an essential epigenetics mechanism of anti-atherogenesis by hydrogen sulfide. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Hu, Q.; Liu, X.; Pan, L.; Xiong, Q.; Zhu, Y.Z. Hydrogen sulfide protects against apoptosis under oxidative stress through SIRT1 pathway in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Nitric Oxide 2015, 46, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, R.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Tang, Z.H.; Ren, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.S.; Wang, Z.; Tang, C.K.; Wei, D.H.; Jiang, Z.S. Hydrogen sulfide prevents H2O2-induced senescence in human umbilical vein endothelial cells through SIRT1 activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Huang, G.X.; Bonkowski, M.S.; Longchamp, A.; Li, C.; Schultz, M.B.; Kim, L.J.; Osborne, B.; Joshi, S.; Lu, Y.; et al. Impairment of an endothelial NAD(+)-H2S signaling network is a reversible cause of vascular aging. Cell 2018, 173, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Li, S.; Tang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xue, X.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Diallyl trisulfide ameliorates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in type 1 diabetic rats: Role of SIRT1 activation. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Feng, H.; Li, S.; Meng, G.; Liu, S.; Tang, X.; Ma, Y.; Han, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Gu, Y.; et al. SIRT3 mediates the antioxidant effect of hydrogen sulfide in endothelial cells. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Song, Q.; Liu, L.; Xie, L.; Han, Y.; Ji, Y. Hydrogen sulfide pretreatment improves mitochondrial function in myocardial hypertrophy via a SIRT3-dependent manner. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 1126–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, G.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Bai, W.; Xie, L.; Shan, L.; Moore, P.K.; Ji, Y. GYY4137 protects against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by attenuating oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats. J. Biomed. Res. 2015, 29, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.L.; Liu, X.H.; Shen, Y.Q.; Wang, N.Z.; Xu, J.; Wu, D.; Xiong, Q.H.; Deng, H.Y.; Huang, G.Y.; Zhu, Y.Z. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase 4-related signaling by sodium hydrosulfide attenuates myocardial fibrotic response. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3770–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testai, L.; Marino, A.; Piano, I.; Brancaleone, V.; Tomita, K.; Di Cesare, M.L.; Martelli, A.; Citi, V.; Breschi, M.C.; Levi, R.; et al. The novel H2S-donor 4-carboxyphenyl isothiocyanate promotes cardioprotective effects against ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of mitoKATP channels and reduction of oxidative stress. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Jin, S.; Teng, X.; Duan, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates cardiac injury in takotsubo cardiomyopathy by alleviating oxidative stress. Nitric Oxide 2017, 67, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polhemus, D.; Kondo, K.; Bhushan, S.; Bir, S.C.; Kevil, C.G.; Murohara, T.; Lefer, D.J.; Calvert, J.W. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates cardiac dysfunction after heart failure via induction of angiogenesis. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Magableh, M.R.; Kemp-Harper, B.K.; Hart, J.L. Hydrogen sulfide treatment reduces blood pressure and oxidative stress in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive mice. Hypertens. Res. 2015, 38, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.F.; Lu, M.; Tiong, C.X.; Dawe, G.S.; Hu, G.; Bian, J.S. Neuroprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide on Parkinson’s disease rat models. Aging Cell 2010, 9, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, H.; Yin, C.; Li, X.; Gong, Q. Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates learning memory impairment in APP/PS1 transgenic mice: A novel mechanism mediated by the activation of Nrf2. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2016, 150–151, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, B.D.; Sbodio, J.I.; Xu, R.; Vandiver, M.S.; Cha, J.Y.; Snowman, A.M.; Snyder, S.H. Cystathionine gamma-lyase deficiency mediates neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease. Nature 2014, 509, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magierowski, M.; Magierowska, K.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Sliwowski, Z.; Pajdo, R.; Ginter, G.; Kwiecien, S.; Brzozowski, T. Exogenous and endogenous hydrogen sulfide protects gastric mucosa against the formation and time-dependent development of ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lesions progressing into deeper ulcerations. Molecules 2017, 22, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Liu, L.; Zou, J.; Qiao, W.; Liu, H.; Qi, Y.; Yan, C. Protective effect of endogenous hydrogen sulfide against oxidative stress in gastric ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Liu, X.; Geng, B.; Fang, L.; Tang, C. Hydrogen sulfide protects rat lung from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Life Sci. 2008, 82, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; An, G.; Chen, J. Inhibitory effects of hydrogen sulphide on pulmonary fibrosis in smoking rats via attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, S.; Calvert, J.W.; Duranski, M.R.; Ramachandran, A.; Lefer, D.J. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury: Role of antioxidant and antiapoptotic signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 295, H801–H806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, H.; Tan, G.; Pan, S.; Sun, X. Role of hydrogen sulfide in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury in rats. Liver Transpl. 2009, 15, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhao, T.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, N.; Tang, X. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) attenuates uranium-induced acute nephrotoxicity through oxidative stress and inflammatory response via Nrf2-NF-kappaB pathways. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 242, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, J. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates diabetic nephropathy in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 28827–28834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, E.M.; Wang, R.; Snijder, P.M.; Boersema, M.; Damman, J.; Fu, M.; Moser, J.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Ploeg, R.J.; Yang, G.; et al. Cystathionine gamma-lyase protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion by modulating oxidative stress. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.L.; Wang, M.J.; Sun, C.; Huang, Y.; Jin, S.; Mu, X.P.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.C. Protective Effects of Hydrogen Sulfide in the Ageing Kidney. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7570489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Model | Mechanism | H2S donors | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart | |||
| (Mouse) | |||
| Ischemic heart disease | NRF2 activation and up-regulation of AOE expression | Na2S | [22] |
| Angiogenesis | Up-regulation of AOE | DATS | [41] |
| Hypertension | Decrease of NADPH-dependent superoxide | NaHS | [42] |
| (Rat) | |||
| Fibrosis | Decrease in ROS generation | NaHS | [38] |
| Myocardial ischemia | Decrease of NADPH-dependent superoxide generation | 4CPI and GYY4137 | [37,39] |
| Myocardial dysfunction | Decrease of cellular oxidative stress | NaHS | [40] |
| Nervous system | |||
| (Mouse) | |||
| Alzheimer’s disease | NRF2 activation | NaHS | [44] |
| Huntington’s disease | Decreased oxidative stress | cysteine | [45] |
| (Rat) | |||
| Parkinson’s disease | Inhibition of NADPH oxidase activity and production of ROS | NaHS | [43] |
| Intestine | |||
| (Rat) | |||
| Gastric ischemia-reperfusion | Up-regulation of SOD and GSH-Px activity | NaHS and GYY4137 | [46] |
| Decrease of free radical production | L-cysteine | [47] | |
| Lungs | |||
| (Rat) | |||
| Ischemia–reperfusion injury | Reduction of lipid peroxidation and up-regulation of catalase, SOD activity | H2S | [48] |
| Pulmonary fibrosis | NRF2 activation and up-regulation of Trx-1 | NaHS | [49] |
| Liver | |||
| (Mouse and Rat) | |||
| Ischemia–reperfusion injury | Reduction of lipid peroxidation and up-regulation of | Na2S | [50] |
| GSH and Trx-1 activity | NaHS | [51] | |
| Aging | |||
| (Mouse) | NRF2 activation, enhanced SIRT1 and decreased ROS | NaHS | [26,55] |
| Kidney | |||
| (Mouse) | |||
| Renal Ischemia | Reduction of ROS, modulation of oxidative stress via NRF2 | NaHS | [54] |
| (Rat) | |||
| Uranium-induced toxicity | NRF2 activation | NaHS | [52] |
| Diabetic nephropathy | [53] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corsello, T.; Komaravelli, N.; Casola, A. Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in NRF2- and Sirtuin-Dependent Maintenance of Cellular Redox Balance. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7100129
Corsello T, Komaravelli N, Casola A. Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in NRF2- and Sirtuin-Dependent Maintenance of Cellular Redox Balance. Antioxidants. 2018; 7(10):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7100129
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorsello, Tiziana, Narayana Komaravelli, and Antonella Casola. 2018. "Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in NRF2- and Sirtuin-Dependent Maintenance of Cellular Redox Balance" Antioxidants 7, no. 10: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7100129
APA StyleCorsello, T., Komaravelli, N., & Casola, A. (2018). Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in NRF2- and Sirtuin-Dependent Maintenance of Cellular Redox Balance. Antioxidants, 7(10), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7100129






