Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) on Bilirubin Concentrations in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome: Sex-Specific GWAS Analysis and Gene-Diet Interactions in a Mediterranean Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Baseline Anthropometric, Biochemical, and Lifestyle Variables
2.3. Genome-Wide Genotyping
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. GWAS Results for Total Serum Bilirubin Concentrations in the Whole Population
3.2. Sex-Specific GWAS Results for Total Serum Bilirubin Concentrations in Men and Women
3.3. Gene-Diet Interactions at the GWAS Level in the Whole Population and Sex-Specific Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atanasovska, B.; Kumar, V.; Fu, J.; Wijmenga, C.; Hofker, M.H. GWAS as a Driver of Gene Discovery in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.J. The genetics of adiposity. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2018, 50, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de los Campos, G.; Vazquez, A.I.; Hsu, S.; Lello, L. Complex-Trait Prediction in the Era of Big Data. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofker, M.H.; Fu, J.; Wijmenga, C. The genome revolution and its role in understanding complex diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1889–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munroe, P.B.; Tinker, A. Genome-wide association studies and contribution to cardiovascular physiology. Physiol. Genom. 2015, 47, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearden, L.; Bouret, S.G.; Ozanne, S.E. Sex and gender differences in developmental programming of metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2018, 15, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Nie, C.; Min, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Ye, R.; Chen, Z.; Bai, C.; Xie, E.; Yin, Z.; et al. Sex Differences in Genetic Associations With Longevity. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e181670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Langefeld, C.D.; Ziegler, J.T.; Taylor, K.D.; Norris, J.M.; Chen, Y.-D.I.; Hellwege, J.N.; Guo, X.; Allison, M.A.; Speliotes, E.K.; et al. Genome-Wide Study of Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue Reveals Novel Sex-Specific Adiposity Loci in Mexican Americans: Genetics of Adipose Deposition. Obesity 2018, 26, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartiala, J.A.; Wilson Tang, W.H.; Wang, Z.; Crow, A.L.; Stewart, A.F.R.; Roberts, R.; McPherson, R.; Erdmann, J.; Willenborg, C.; Hazen, S.L.; et al. Genome-wide association study and targeted metabolomics identifies sex-specific association of CPS1 with coronary artery disease. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byars, S.G.; Inouye, M. Genome-Wide Association Studies and Risk Scores for Coronary Artery Disease: Sex Biases. In Sex-Specific Analysis of Cardiovascular Function; Kerkhof, P.L.M., Miller, V.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1065, pp. 627–642. ISBN 9783319779317. [Google Scholar]
- Schiebinger, L.; Stefanick, M.L. Gender Matters in Biological Research and Medical Practice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, F.S.; Tabak, L.A. Policy: NIH plans to enhance reproducibility. Nature 2014, 505, 612–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clayton, J.A. Studying both sexes: A guiding principle for biomedicine. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordovas, J.M.; Ferguson, L.R.; Tai, E.S.; Mathers, J.C. Personalised nutrition and health. BMJ 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauderman, W.J.; Zhang, P.; Morrison, J.L.; Lewinger, J.P. Finding Novel Genes by Testing G × E Interactions in a Genome-Wide Association Study: Scanning for G × E Interaction to Find New Genes. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Lewinger, J.P.; Conti, D.; Morrison, J.L.; Gauderman, W.J. Detecting Gene-Environment Interactions for a Quantitative Trait in a Genome-Wide Association Study: Detecting Gene-Environment Interactions for a Quantitative. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, J.C.; Hsu, L.; Hutter, C.M.; Lin, Y.; Campbell, P.T.; Baron, J.A.; Berndt, S.I.; Jiao, S.; Casey, G.; Fortini, B.; et al. Genome-Wide Diet-Gene Interaction Analyses for Risk of Colorectal Cancer. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, J.; Dashti, H.S.; Li, S.X.; Sarnowski, C.; Justice, A.E.; Graff, M.; Papoutsakis, C.; Smith, C.E.; Dedoussis, G.V.; Lemaitre, R.N.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of macronutrient intake of 91,114 European ancestry participants from the cohorts for heart and aging research in genomic epidemiology consortium. Mol. Psychiatry 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.E.; Follis, J.L.; Dashti, H.S.; Tanaka, T.; Graff, M.; Fretts, A.M.; Kilpeläinen, T.O.; Wojczynski, M.K.; Richardson, K.; Nalls, M.A.; et al. Genome-Wide Interactions with Dairy Intake for Body Mass Index in Adults of European Descent. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, V.C.; Duncan, M.S.; So-Armah, K.; Re, V.L.; Lim, J.K.; Butt, A.A.; Goetz, M.B.; Rodriguez-Barradas, M.C.; Alcorn, C.W.; Lennox, J.; et al. Bilirubin Is Inversely Associated With Cardiovascular Disease Among HIV-Positive and HIV-Negative Individuals in VACS (Veterans Aging Cohort Study). J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-C.; Lin, C.-P.; Hsu, H.-C.; Shu, J.-H.; Liang, Y.; Hsu, P.-F.; Wang, Y.-J.; Ding, Y.-Z.; Liou, T.-L.; Wang, Y.-W.; et al. Serum bilirubin improves the risk predictions of cardiovascular and total death in diabetic patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 488, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulmer, A.C.; Bakrania, B.; Du Toit, E.F.; Boon, A.-C.; Clark, P.J.; Powell, L.W.; Wagner, K.-H.; Headrick, J.P. Bilirubin acts as a multipotent guardian of cardiovascular integrity: More than just a radical idea. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H429–H447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djoussé, L.; Levy, D.; Cupples, L.A.; Evans, J.C.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Ellison, R.C. Total serum bilirubin and risk of cardiovascular disease in the Framingham offspring study. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 87, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathum, L.; Petersen, H.C.; Rosholm, J.U.; Hyltoft Petersen, P.; Vaupel, J.; Christensen, K. Evidence for a substantial genetic influence on biochemical liver function tests: Results from a population-based Danish twin study. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, B.; Gibbs, P.E.M.; Brookes, P.S.; Maines, M.D. The coordinated increased expression of biliverdin reductase and heme oxygenase-2 promotes cardiomyocyte survival: A reductase-based peptide counters β-adrenergic receptor ligand-mediated cardiac dysfunction. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fretzayas, A.; Moustaki, M.; Liapi, O.; Karpathios, T. Eponym: Gilbert syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, R.; Rinaldi, C.; Donato, L.; Nicocia, G.; Sidoti, A. The combination of new missense mutation with (A(TA)7TAA) dinucleotide repeat in UGT1A1 gene promoter causes Gilbert’s syndrome. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 45, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Lala, V.; Minter, D.A. Liver Function Tests. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-L.; Wu, S.-H.; Hsu, S.-H.; Liou, B.-Y.; Chen, H.-L.; Chang, M.-H. Jaundice revisited: Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of inherited cholestatic liver diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusanya, B.O.; Kaplan, M.; Hansen, T.W.R. Neonatal hyperbilirubinaemia: A global perspective. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzin, S.; Vitek, L.; Watchko, J.; Shapiro, S.M.; Tiribelli, C. A Novel Perspective on the Biology of Bilirubin in Health and Disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziberna, L.; Martelanc, M.; Franko, M.; Passamonti, S. Bilirubin is an Endogenous Antioxidant in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, R.; Haag, M.; Schaeffeler, E.; Nies, A.T.; Zanger, U.M.; Schwab, M. Systemic regulation of bilirubin homeostasis: Potential benefits of hyperbilirubinemia. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, J.; He, Y. The U-Shaped Association between Bilirubin and Diabetic Retinopathy Risk: A Five-Year Cohort Based on 5323 Male Diabetic Patients. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Li, J.; Lv, X.; He, Y. Bilirubin and its changes were negatively associated with diabetic kidney disease incidence and progression: A five-year’s cohort study based on 5323 Chinese male diabetic patients. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2018, 32, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Fang, Q.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Guo, W.; Liu, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; et al. Direct, indirect and total bilirubin and risk of incident coronary heart disease in the Dongfeng-Tongji cohort. Ann. Med. 2018, 50, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, A.-C.; Bulmer, A.C.; Coombes, J.S.; Fassett, R.G. Circulating bilirubin and defense against kidney disease and cardiovascular mortality: Mechanisms contributing to protection in clinical investigations. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2014, 307, F123–F136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheriyath, P.; Gorrepati, V.S.; Peters, I.; Nookala, V.; Murphy, M.E.; Srouji, N.; Fischman, D. High Total Bilirubin as a Protective Factor for Diabetes Mellitus: An Analysis of NHANES Data from 1999–2006. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2010, 2, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, M.C.; Lea, R.A.; Macartney-Coxson, D.; Bellis, C.; Carless, M.A.; Curran, J.E.; Hanna, M.; Eccles, D.; Chambers, G.K.; Blangero, J.; et al. Serum bilirubin concentration is modified by UGT1A1 Haplotypes and influences risk of Type-2 diabetes in the Norfolk Island genetic isolate. BMC Genet. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Huang, C.; Feng, Y. Serum total bilirubin concentration is associated with carotid atherosclerosis in patients with prehypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2018, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, A.J.; Ortega, E.; Perea, V.; Cofán, M.; Sala-Vila, A.; Nuñez, I.; Gilabert, R.; Ros, E. Relationship Between Total Serum Bilirubin Levels and Carotid and Femoral Atherosclerosis in Familial DyslipidemiaHighlights. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 2356–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararaghavan, V.L.; Binepal, S.; Stec, D.E.; Sindhwani, P.; Hinds, T.D. Bilirubin, a new therapeutic for kidney transplant? Transplant. Rev. 2018, 32, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag, K.; Oguzhan, N.; Arıkan, T.; Boz, G. Serum bilirubin level and its impact on the progression of chronic kidney disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-P.; Vitek, L.; Schwertner, H.A. Serum Bilirubin and Genes Controlling Bilirubin Concentrations as Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stec, D.E.; John, K.; Trabbic, C.J.; Luniwal, A.; Hankins, M.W.; Baum, J.; Hinds, T.D. Bilirubin Binding to PPARα Inhibits Lipid Accumulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinds, T.D.; Stec, D.E. Bilirubin, a Cardiometabolic Signaling Molecule. Hypertension 2018, 72, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Meng, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Ren, X.; Zhu, M.; He, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Song, K.; Jia, Q.; et al. The association between total bilirubin and serum triglyceride in both sexes in Chinese. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.C.; Kronenberg, F.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Hopkins, P.N.; Myers, R.H.; Heiss, G. Association of plasma bilirubin with coronary heart disease and segregation of bilirubin as a major gene trait: The NHLBI family heart study. Atherosclerosis 2001, 154, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, S.D.; Horn, P.S.; Sherman, K.E. Serum bilirubin levels in the U.S. population: Gender effect and inverse correlation with colorectal cancer. Hepatology 2004, 40, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.D.; Kavousi, M.; Smith, A.V.; Chen, M.-H.; Dehghan, A.; Aspelund, T.; Lin, J.-P.; van Duijn, C.M.; Harris, T.B.; Cupples, L.A.; et al. Genome-wide association meta-analysis for total serum bilirubin levels. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 2700–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, T.-W.; Kim, H.-J.; Ju, H.; Kim, J.-H.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-C.; Kim, K.-K.; Kim, J.-W.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.Y.; et al. Genome-wide association of serum bilirubin levels in Korean population. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 3672–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Namjou, B.; Marsolo, K.; Lingren, T.; Ritchie, M.D.; Verma, S.S.; Cobb, B.L.; Perry, C.; Kitchner, T.E.; Brilliant, M.H.; Peissig, P.L.; et al. A GWAS Study on Liver Function Test Using eMERGE Network Participants. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wu, C.; He, Y.; Gui, L.; Zhou, L.; Guo, H.; Yuan, J.; Yang, B.; Li, J.; Deng, Q.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study for Serum Bilirubin Levels and Gene-Environment Interaction in a Chinese Population. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielinski, S.J.; Chai, H.S.; Pathak, J.; Talwalkar, J.A.; Limburg, P.J.; Gullerud, R.E.; Sicotte, H.; Klee, E.W.; Ross, J.L.; Kocher, J.-P.A.; et al. Mayo Genome Consortia: A Genotype-Phenotype Resource for Genome-Wide Association Studies with an Application to the Analysis of Circulating Bilirubin Levels. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, S.; Busonero, F.; Maschio, A.; McArdle, P.F.; Usala, G.; Dei, M.; Lai, S.; Mulas, A.; Piras, M.G.; Perseu, L.; et al. Common variants in the SLCO1B3 locus are associated with bilirubin levels and unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 2711–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Ramos, E.; Adeyemo, A.; Shriner, D.; Zhou, J.; Doumatey, A.P.; Huang, H.; Erdos, M.R.; Gerry, N.P.; Herbert, A.; et al. UGT1A1 is a major locus influencing bilirubin levels in African Americans. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 20, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.; Yoshida, E.M.; Paulson, M.S.; Hengen, P.N.; Ge, D.; Kanwar, B.; McNally, J.; Pang, P.S.; Subramanian, G.M.; McHutchison, J.G.; et al. Genome-wide association study to characterize serum bilirubin elevations in patients with HCV treated with GS-9256, an HCV NS3 serine protease inhibitor. Antivir. Ther. 2014, 19, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Corella, D.; Bulló, M.; Fitó, M.; Vioque, J.; Romaguera, D.; Martínez, J.A.; Wärnberg, J.; López-Miranda, J.; et al. Cohort Profile: Design and methods of the PREDIMED-Plus randomized trial. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosique-Esteban, N.; Díaz-López, A.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Goday, A.; Martínez, J.A.; Romaguera, D.; Vioque, J.; Arós, F.; Garcia-Rios, A.; et al. Leisure-time physical activity, sedentary behaviors, sleep, and cardiometabolic risk factors at baseline in the PREDIMED-PLUS intervention trial: A cross-sectional analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On Behalf of the PREDIMED-Plus Investigators; Schröder, H.; Cárdenas-Fuentes, G.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Vioque, J.; Romaguera, D.; Alfredo Martínez, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; Miranda, J.L.; et al. Effectiveness of the physical activity intervention program in the PREDIMED-Plus study: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, L.; Sarmiento, M.; Peñafiel, J.; Donaire, D.; Garcia-Aymerich, J.; Gomez, M.; Ble, M.; Ruiz, S.; Frances, A.; Schröder, H.; et al. Validation of the Regicor Short Physical Activity Questionnaire for the Adult Population. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galilea-Zabalza, I.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Toledo, E.; Ortega-Azorín, C.; Díez-Espino, J.; Vázquez-Ruiz, Z.; Zomeño, M.D.; Vioque, J.; Martínez, J.A.; et al. Mediterranean diet and quality of life: Baseline cross-sectional analysis of the PREDIMED-PLUS trial. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. GigaScience 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, A.P.; Hong, E.L.; Hariharan, M.; Cheng, Y.; Schaub, M.A.; Kasowski, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Park, J.; Hitz, B.C.; Weng, S.; et al. Annotation of functional variation in personal genomes using RegulomeDB. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turner, S.D. qqman: An R package for visualizing GWAS results using Q-Q and manhattan plots. BioRxiv 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cai, L.; Huang, H.; Liu, B.; Wu, Q. Genetic Variations and Haplotype Diversity of the UGT1 Gene Cluster in the Chinese Population. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seigneur, E.; Polepalli, J.S.; Südhof, T.C. Cbln2 and Cbln4 are expressed in distinct medial habenula-interpeduncular projections and contribute to different behavioral outputs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E10235–E10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, M.; Eyries, M.; Montani, D.; Poirier, O.; Girerd, B.; Dorfmüller, P.; Coulet, F.; Nadaud, S.; Maugenre, S.; Guignabert, C.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies a susceptibility locus for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, L.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Krystal, J.; Tabakoff, B.; Zhong, C.; Luo, X. A New Genomewide Association Meta-Analysis of Alcohol Dependence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuura, K.; Sawai, H.; Ikeo, K.; Ogawa, S.; Iio, E.; Isogawa, M.; Shimada, N.; Komori, A.; Toyoda, H.; Kumada, T.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies TLL1 Variant Associated With Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Eradication of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, S.; Riedmayr, L.M.; Nguyen, O.N.P.; Gießl, A.; Liebscher, T.; Butz, E.S.; Schön, C.; Michalakis, S.; Wahl-Schott, C.; Biel, M.; et al. Peripherin-2 and Rom-1 have opposing effects on rod outer segment targeting of retinitis pigmentosa-linked peripherin-2 mutants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanzo, R.J.; Twede, H.; Ho, K.S.; Prasad, A.; Martin, M.M.; South, S.T.; Wassman, E.R. Clinical significance of copy number variants involving KANK1 in patients with neurodevelopmental disorders. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.E.; Oltman, S.P.; Baer, R.J.; Ryckman, K.K.; Rogers, E.E.; Steurer-Muller, M.A.; Witte, J.S.; Jelliffe-Pawlowski, L.L. Newborn Metabolic Profile Associated with Hyperbilirubinemia With and Without Kernicterus. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-P.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Schwaiger, J.P.; Cupples, L.A.; Lingenhel, A.; Hunt, S.C.; Yang, S.; Kronenberg, F. Association Between the UGT1A1*28 Allele, Bilirubin Levels, and Coronary Heart Disease in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2006, 114, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCarty, M.F. ‘“Iatrogenic Gilbert syndrome”’—A strategy for reducing vascular and cancer risk by increasing plasma unconjugated bilirubin. Med. Hypotheses 2007, 69, 974–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yueh, M.-F.; Chen, S.; Nguyen, N.; Tukey, R.H. Developmental, Genetic, Dietary, and Xenobiotic Influences on Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 91, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maruo, Y.; Morioka, Y.; Fujito, H.; Nakahara, S.; Yanagi, T.; Matsui, K.; Mori, A.; Sato, H.; Tukey, R.H.; Takeuchi, Y. Bilirubin Uridine Diphosphate-Glucuronosyltransferase Variation Is a Genetic Basis of Breast Milk Jaundice. J. Pediatr. 2014, 165, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKiernan, P. Metabolic liver disease. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2012, 36, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, J.M.; Lee, Y.-H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Angkasekwinai, P.; Nallaparaju, K.C.; Flaherty, S.; Chang, S.H.; Watarai, H.; Dong, C. Interleukin-17B Antagonizes Interleukin-25-Mediated Mucosal Inflammation. Immunity 2015, 42, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Total (n = 430) | Men (n = 188) | Women (n = 242) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65.1 ± 0.2 | 63.9 ± 0.4 | 66.1 ± 0.3 | <0.001 |
| Weight (Kg) | 84.5 ± 0.7 | 92.8 ± 1.0 | 78.0 ± 0.6 | <0.001 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 32.4 ± 0.2 | 32.3 ± 0.2 | 32.5 ± 0.2 | 0.629 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 106.1 ± 0.5 | 111.2 ± 0.6 | 102.0 ± 0.6 | <0.001 |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 141.6 ± 0.9 | 143.8 ± 1.3 | 139.9 ± 1.2 | 0.026 |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 81.0 ± 0.5 | 82.6 ± 0.7 | 79.7 ± 0.6 | 0.002 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 196.4 ± 1.8 | 188.3 ± 2.8 | 202.6 ± 2.3 | <0.001 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 125.0 ± 1.5 | 121.6 ± 2.4 | 127.7 ± 1.9 | 0.044 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 51.5 ± 0.5 | 47.5 ± 0.8 | 54.7 ± 0.7 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 141.6 ± 2.9 | 138.2 ± 3.8 | 144.3 ± 4.2 | 0.296 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 112.5 ± 1.3 | 112.8 ± 2.0 | 112.3 ± 1.7 | 0.862 |
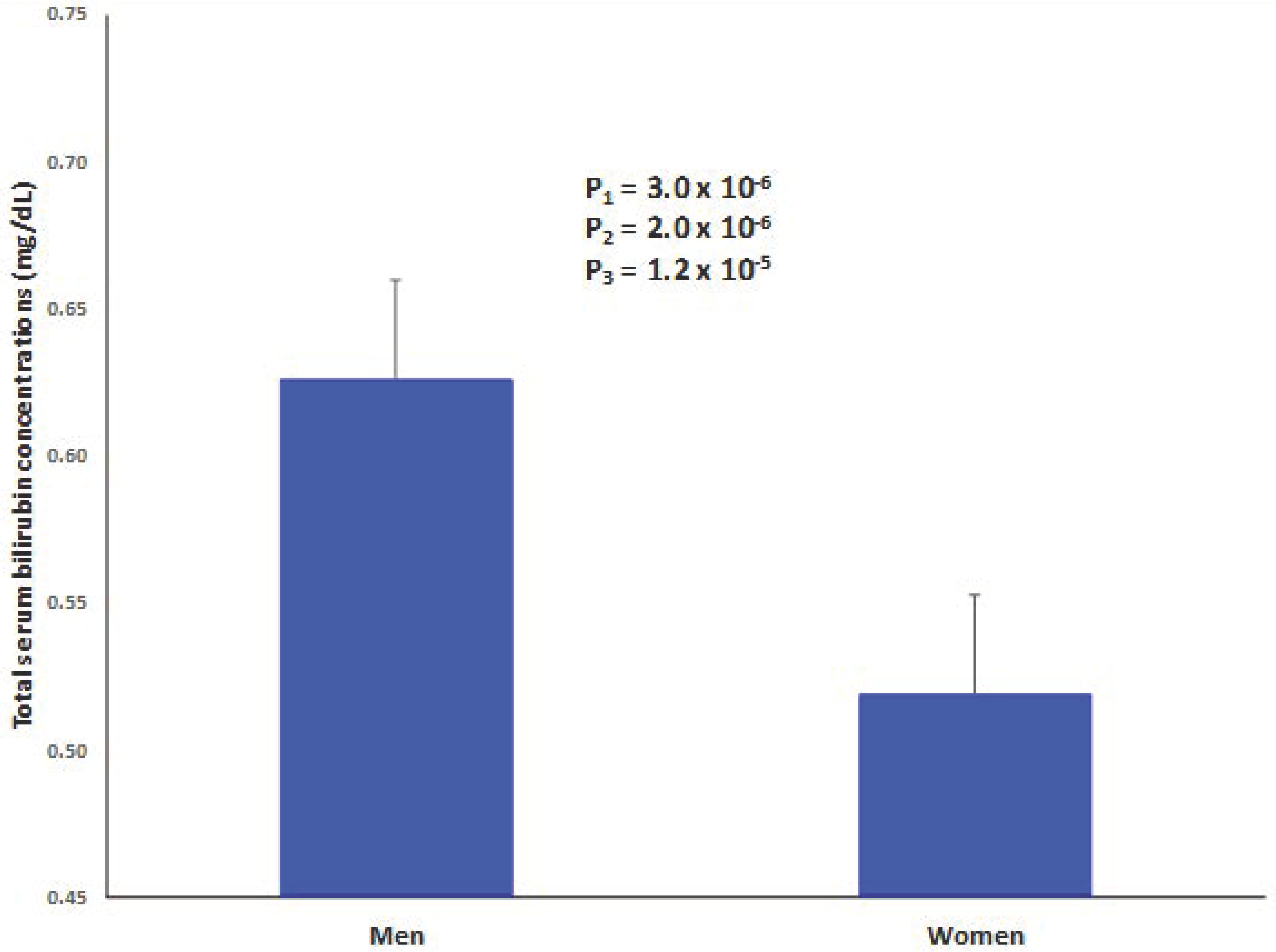
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 0.64 ± 0.02 | 0.53 ± 0.01 | <0.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 26.4 ± 0.4 | 27.7 ± 0.7 | 25.4 ± 0.5 | 0.005 |
| ALT (U/L) | 28.4 ± 0.8 | 30.8 ± 1.2 | 26.6 ± 1.0 | 0.008 |
| Type 2 diabetes: n, % | 169 (39.3) | 74 (39.4) | 95 (39.3) | 0.982 |
| Current smokers: n, % | 49 (11.4) | 30 (16.0) | 19 (7.9) | <0.001 |
| Medications: n, % | ||||
| Antihypertensive drugs | 339 (78.8) | 148 (78.7) | 191 (78.9) | 0.959 |
| Hypolipidemic drugs | 278 (64.7) | 125 (66.5) | 153 (63.2) | 0.482 |
| Insulin | 22 (5.1) | 11 (5.9) | 11 (4.5) | 0.542 |
| Physical Activity (MET.min/week) | 1715 ± 77 | 1940 ± 134 | 1539 ± 89 | 0.227 |
| Adherence to MedDiet (P17) 1 | 7.97 ± 0.13 | 7.79 ± 0.20 | 8.12 ± 0.18 | 0.010 |
| CHR | SNP | BETA | SE | R2 | p1 | p2 | MA | MAF | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | rs4148325 | 0.149 | 0.016 | 0.174 | 1.97 × 10−19 | 9.25 × 10−24 | C | 0.354 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs6742078 | 0.148 | 0.016 | 0.173 | 2.84 × 10−19 | 1.29 × 10−23 | T | 0.348 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs887829 | 0.148 | 0.016 | 0.171 | 3.72 × 10−19 | 1.39 × 10−23 | T | 0.354 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs4148324 | 0.147 | 0.016 | 0.170 | 4.62 × 10−19 | 9.48 × 10−24 | G | 0.353 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs17863787 | 0.142 | 0.016 | 0.157 | 1.40 × 10−17 | 4.70 × 10−20 | G | 0.263 | UGT1A6 4 |
| 2 | rs17862875 | 0.146 | 0.017 | 0.152 | 4.46 × 10−17 | 1.68 × 10−20 | A | 0.295 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs3771341 | 0.143 | 0.017 | 0.150 | 8.64 × 10−17 | 2.65 × 10−20 | A | 0.330 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs6744284 | 0.141 | 0.017 | 0.144 | 4.39 × 10−16 | 4.06 × 10−18 | T | 0.390 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs929596 | 0.136 | 0.017 | 0.132 | 8.14 × 10−15 | 1.83 × 10−18 | G | 0.324 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs2070959 | 0.127 | 0.016 | 0.127 | 2.47 × 10−14 | 3.78 × 10−16 | G | 0.278 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs1105879 | 0.121 | 0.016 | 0.123 | 8.14 × 10−14 | 1.84 × 10−15 | C | 0.325 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs1105880 | 0.120 | 0.016 | 0.120 | 1.55 × 10−13 | 3.30 × 10−15 | G | 0.343 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs2741045 | 0.119 | 0.017 | 0.109 | 2.50 × 10−12 | 2.03 × 10−14 | T | 0.159 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs7583278 | 0.111 | 0.016 | 0.105 | 7.21 × 10−12 | 3.87 × 10−13 | T | 0.391 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs2018985 | 0.111 | 0.016 | 0.103 | 1.19 × 10−11 | 3.49 × 10−14 | G | 0.441 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs6725478 | 0.110 | 0.016 | 0.102 | 1.22 × 10−11 | 5.42 × 10−13 | T | 0.388 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs7604115 | 0.106 | 0.016 | 0.088 | 3.28 × 10−10 | 3.09 × 10−12 | T | 0.350 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs3755319 | 0.102 | 0.016 | 0.086 | 7.53 × 10−10 | 7.28 × 10−12 | A | 0.450 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs4148326 | 0.101 | 0.016 | 0.085 | 8.03 × 10−10 | 8.20 × 10−12 | T | 0.480 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs4663965 | 0.101 | 0.016 | 0.084 | 1.00 × 10−09 | 1.10 × 10−11 | T | 0.415 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs4124874 | 0.100 | 0.016 | 0.083 | 1.04 × 10−09 | 9.01 × 10−12 | T | 0.412 | UGT1A6 3 |
| 2 | rs2008595 | 0.101 | 0.016 | 0.083 | 1.08 × 10−09 | 1.67 × 10−11 | C | 0.412 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs1875263 | 0.102 | 0.016 | 0.084 | 1.10 × 10−09 | 1.02 × 10−10 | T | 0.417 | UGT1A6 3 |
| 2 | rs6431628 | 0.100 | 0.016 | 0.083 | 1.29 × 10−09 | 1.30 × 10−11 | A | 0.410 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs2741027 | 0.102 | 0.016 | 0.083 | 1.32 × 10−09 | 9.63 × 10−12 | A | 0.177 | __ |
| 2 | rs10179091 | 0.100 | 0.016 | 0.083 | 1.34 × 10−09 | 1.01 × 10−11 | T | 0.482 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs4663333 | 0.100 | 0.016 | 0.083 | 1.35 × 10−09 | 1.38 × 10−11 | G | 0.411 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs4663963 | 0.100 | 0.016 | 0.083 | 1.35 × 10−09 | 1.35 × 10−11 | T | 0.420 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs871514 | 0.100 | 0.016 | 0.082 | 1.37 × 10−09 | 1.82 × 10−11 | T | 0.428 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs10197460 | 0.099 | 0.016 | 0.083 | 1.42 × 10−09 | 2.32 × 10−10 | T | 0.298 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs2741029 | 0.102 | 0.017 | 0.081 | 1.79 × 10−09 | 1.07 × 10−11 | G | 0.177 | UGT1A8 |
| 2 | rs4399719 | 0.099 | 0.016 | 0.081 | 1.89 × 10−09 | 1.63 × 10−11 | T | 0.415 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs2602373 | 0.102 | 0.017 | 0.080 | 2.16 × 10−09 | 1.51 × 10−11 | C | 0.177 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs2602374 | 0.105 | 0.017 | 0.080 | 2.16 × 10−09 | 2.36 × 10−11 | T | 0.173 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs4294999 | 0.098 | 0.016 | 0.079 | 3.15 × 10−09 | 4.78 × 10−11 | A | 0.426 | UGT1A6 |
| 18 | rs658995 | 0.286 | 0.047 | 0.079 | 3.33 × 10−09 | 2.50 × 10−08 | A | 0.282 | CBLN2 |
| 2 | rs10179094 | 0.096 | 0.016 | 0.078 | 3.75 × 10−09 | 5.34 × 10−10 | A | 0.297 | UGT1A10 3 |
| 2 | rs2741012 | 0.098 | 0.016 | 0.078 | 4.11 × 10−09 | 3.22 × 10−11 | T | 0.191 | __ |
| 2 | rs6724485 | 0.095 | 0.016 | 0.077 | 4.50 × 10−09 | 1.12 × 10−09 | A | 0.358 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs12988520 | −0.098 | 0.016 | 0.077 | 5.01 × 10−09 | 6.94 × 10−10 | C | 0.470 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs13015720 | 0.096 | 0.016 | 0.077 | 5.06 × 10−09 | 9.86 × 10−10 | A | 0.362 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs7572563 | −0.098 | 0.016 | 0.077 | 5.43 × 10−09 | 1.03 × 10−09 | G | 0.403 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs4261716 | 0.095 | 0.016 | 0.076 | 6.40 × 10−09 | 1.45 × 10−09 | T | 0.358 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs17862866 | −0.097 | 0.016 | 0.076 | 6.86 × 10−09 | 1.12 × 10−09 | A | 0.402 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs6736743 | 0.094 | 0.016 | 0.075 | 7.24 × 10−09 | 1.69 × 10−09 | A | 0.362 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs6736508 | 0.094 | 0.016 | 0.075 | 7.25 × 10−09 | 1.68 × 10−09 | A | 0.362 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs12623271 | 0.094 | 0.016 | 0.075 | 7.65 × 10−09 | 1.75 × 10−09 | G | 0.362 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs10168155 | 0.094 | 0.016 | 0.075 | 7.87 × 10−09 | 1.69 × 10−09 | T | 0.362 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs6753320 | 0.093 | 0.016 | 0.074 | 1.03 × 10−08 | 2.30 × 10−09 | C | 0.363 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs7563561 | 0.093 | 0.016 | 0.074 | 1.03 × 10−08 | 2.30 × 10−09 | G | 0.362 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs4553819 | 0.093 | 0.016 | 0.074 | 1.05 × 10−08 | 2.43 × 10−09 | G | 0.358 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs6753569 | 0.093 | 0.016 | 0.074 | 1.09 × 10−08 | 2.39 × 10−09 | C | 0.362 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs4347832 | 0.093 | 0.016 | 0.074 | 1.13 × 10−08 | 2.52 × 10−09 | C | 0.358 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs11680450 | 0.092 | 0.016 | 0.072 | 1.73 × 10−08 | 3.54 × 10−09 | C | 0.362 | UGT1A10 |
| 2 | rs7556676 | 0.093 | 0.017 | 0.069 | 3.51 × 10−08 | 6.99 × 10−10 | G | 0.497 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs2361502 | 0.096 | 0.017 | 0.069 | 3.69 × 10−08 | 1.17 × 10−08 | C | 0.282 | MROH2A |
| 2 | rs11690786 | 0.096 | 0.017 | 0.067 | 6.38 × 10−08 | 7.05 × 10−09 | T | 0.281 | MROH2A |
| 18 | rs595333 | 0.252 | 0.046 | 0.066 | 7.46 × 10−08 | 5.81 × 10−07 | T | 0.291 | CBLN2 |
| 3 | rs6439106 | 0.409 | 0.077 | 0.062 | 1.79 × 10−07 | 3.14 × 10−08 | T | 0.221 | __ |
| CHR | SNP | Beta | SE | R2 | p1 | p2 | MA | MAF | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | rs4148324 | 0.177 | 0.027 | 0.189 | 4.44 × 10−10 | 4.77 × 10−11 | G | 0.353 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs887829 | 0.176 | 0.027 | 0.188 | 5.89 × 10−10 | 7.04 × 10−11 | T | 0.354 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs3771341 | 0.174 | 0.028 | 0.166 | 6.20 × 10−09 | 1.20 × 10−09 | A | 0.330 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs17862875 | 0.173 | 0.029 | 0.161 | 1.00 × 10−08 | 2.40 × 10−09 | A | 0.295 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs929596 | 0.171 | 0.029 | 0.154 | 2.29 × 10−08 | 3.75 × 10−09 | G | 0.324 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs17863787 | 0.159 | 0.028 | 0.149 | 4.37 × 10−08 | 1.04 × 10−08 | G | 0.263 | UGT1A6 3 |
| 2 | rs1105879 | 0.150 | 0.027 | 0.144 | 8.14 × 10−08 | 1.07 × 10−08 | C | 0.325 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs2070959 | 0.155 | 0.028 | 0.143 | 8.44 × 10−08 | 2.15 × 10−08 | G | 0.278 | UGT1A6 |
| CHR | SNP | Beta | SE | R2 | p1 | p2 | MA | MAF | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | rs4148324 | 0.142 | 0.017 | 0.218 | 1.99 × 10−14 | 2.15 × 10−14 | G | 0.353 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs6742078 | 0.142 | 0.018 | 0.217 | 2.69 × 10−14 | 2.97 × 10−14 | T | 0.348 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs17863787 | 0.135 | 0.017 | 0.202 | 2.14 × 10−13 | 2.40 × 10−13 | G | 0.263 | UGT1A6 3 |
| 2 | rs17862875 | 0.141 | 0.018 | 0.199 | 3.61 × 10−13 | 4.03 × 10−13 | A | 0.295 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs3771341 | 0.136 | 0.018 | 0.189 | 1.52 × 10−12 | 1.67 × 10−12 | A | 0.330 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs6744284 | 0.134 | 0.018 | 0.182 | 5.16 × 10−12 | 5.70 × 10−12 | T | 0.390 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs929596 | 0.128 | 0.019 | 0.166 | 4.48 × 10−11 | 4.65 × 10−11 | G | 0.324 | UGT1A1 |
| 2 | rs2018985 | 0.115 | 0.018 | 0.147 | 9.23 × 10−10 | 1.00 × 10−09 | G | 0.441 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs2070959 | 0.111 | 0.018 | 0.139 | 2.40 × 10−09 | 2.57 × 10−09 | G | 0.278 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs2741045 | 0.108 | 0.018 | 0.128 | 1.08 × 10−08 | 1.07 × 10−08 | T | 0.159 | UGT1A10 |
| 1 | rs359935 | 0.353 | 0.061 | 0.126 | 1.99 × 10−08 | 2.17 × 10−08 | A | 0.053 | __ |
| 2 | rs6725478 | 0.104 | 0.018 | 0.123 | 2.13 × 10−08 | 2.28 × 10−08 | T | 0.388 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs1105880 | 0.103 | 0.018 | 0.123 | 2.30 × 10−08 | 2.40 × 10−08 | G | 0.343 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs1105879 | 0.103 | 0.018 | 0.123 | 2.30 × 10−08 | 2.40 × 10−08 | C | 0.325 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs7583278 | 0.105 | 0.018 | 0.124 | 2.57 × 10−08 | 2.75 × 10−08 | T | 0.391 | UGT1A6 |
| 2 | rs7604115 | 0.107 | 0.019 | 0.122 | 2.57 × 10−08 | 2.76 × 10−08 | T | 0.350 | UGT1A6 |
| Low Adherence Mediterranean Diet 1 | High Adherence Mediterranean Diet 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHR | SNP | Beta1 3 | SE1 3 | Beta2 4 | SE2 4 | p5 Gene-Diet Interaction | MA | MAF | Gene |
| 5 | rs6887452 | 0.045 | 0.016 | −0.087 | 0.018 | 3.14 × 10−08 | G | 0.397 | IL17B |
| 10 | rs6585514 | −0.061 | 0.016 | 0.063 | 0.019 | 5.89 × 10−07 | A | 0.395 | __ |
| 6 | rs7770270 | −0.046 | 0.024 | 0.140 | 0.030 | 1.52 × 10−06 | A | 0.112 | LAMA2 |
| 17 | rs1242492 | 0.038 | 0.015 | −0.074 | 0.018 | 2.78 × 10−06 | C | 0.249 | __ |
| 4 | rs13108021 | 0.052 | 0.017 | −0.069 | 0.020 | 2.96 × 10−06 | A | 0.228 | __ |
| 10 | rs10886342 | 0.059 | 0.017 | −0.067 | 0.022 | 4.19 × 10−06 | A | 0.277 | __ |
| 18 | rs12964365 | −0.048 | 0.017 | 0.073 | 0.020 | 4.59 × 10−06 | T | 0.150 | LOC107985179 |
| 6 | rs6904763 | −0.046 | 0.024 | 0.128 | 0.030 | 5.32 × 10−06 | C | 0.126 | LAMA2 |
| 5 | rs907195 | 0.054 | 0.017 | −0.070 | 0.021 | 5.91 × 10−06 | C | 0.253 | __ |
| 4 | rs10305895 | 0.061 | 0.020 | −0.076 | 0.023 | 6.04 × 10−06 | G | 0.341 | EDNRA |
| 1 | rs11208512 | 0.037 | 0.016 | −0.075 | 0.019 | 6.35 × 10−06 | T | 0.417 | __ |
| 5 | rs7443165 | −0.046 | 0.019 | 0.089 | 0.024 | 8.62 × 10−06 | A | 0.277 | __ |
| 10 | rs4642993 | −0.060 | 0.015 | 0.043 | 0.018 | 9.19 × 10−06 | A | 0.455 | __ |
| 18 | rs687862 | −0.043 | 0.017 | 0.074 | 0.020 | 9.70 × 10−06 | A | 0.220 | LINC01541 |
| 5 | rs16871933 | 0.111 | 0.027 | −0.072 | 0.031 | 9.70 × 10−06 | G | 0.081 | LINC01331 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coltell, O.; Asensio, E.M.; Sorlí, J.V.; Barragán, R.; Fernández-Carrión, R.; Portolés, O.; Ortega-Azorín, C.; Martínez-LaCruz, R.; González, J.I.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) on Bilirubin Concentrations in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome: Sex-Specific GWAS Analysis and Gene-Diet Interactions in a Mediterranean Population. Nutrients 2019, 11, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010090
Coltell O, Asensio EM, Sorlí JV, Barragán R, Fernández-Carrión R, Portolés O, Ortega-Azorín C, Martínez-LaCruz R, González JI, Zanón-Moreno V, et al. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) on Bilirubin Concentrations in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome: Sex-Specific GWAS Analysis and Gene-Diet Interactions in a Mediterranean Population. Nutrients. 2019; 11(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleColtell, Oscar, Eva M. Asensio, José V. Sorlí, Rocio Barragán, Rebeca Fernández-Carrión, Olga Portolés, Carolina Ortega-Azorín, Raul Martínez-LaCruz, José I. González, Vicente Zanón-Moreno, and et al. 2019. "Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) on Bilirubin Concentrations in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome: Sex-Specific GWAS Analysis and Gene-Diet Interactions in a Mediterranean Population" Nutrients 11, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010090
APA StyleColtell, O., Asensio, E. M., Sorlí, J. V., Barragán, R., Fernández-Carrión, R., Portolés, O., Ortega-Azorín, C., Martínez-LaCruz, R., González, J. I., Zanón-Moreno, V., Gimenez-Alba, I., Fitó, M., Ros, E., Ordovas, J. M., & Corella, D. (2019). Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) on Bilirubin Concentrations in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome: Sex-Specific GWAS Analysis and Gene-Diet Interactions in a Mediterranean Population. Nutrients, 11(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010090











