Improved Detection of Plasmon Waveguide Resonance Using Diverging Beam, Liquid Crystal Retarder, and Application to Lipid Orientation Determination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Results
3. Anisotropic Molecules Orientation Determination
4. Discussion
5. Potential Applications of the Proposed Methodology
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozhevolnyi, S.I. Dynamic components utilizing long-range surface plasmon polaritons. In Nanophotonics with Surface Plasmons, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science: London, UK, 2007; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, W.; Gillespie, D.E.; Lausted, C.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhu, J. Plain silver surface plasmon resonance for Microarray application. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homola, J.; Piliarik, M. Surface plasmon resonance sensor. In Surface Plasmon Resonance Based Sensors; Series on Chemical Sensors and Biosensors; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 45–69. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.; Linman, M.J.; Cheng, Q. New trends in instrumental design for surface plasmon resonance—Based biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 1815–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekgasit, S.; Thammacharoen, C.; Knoll, W. Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy based on evanescent field treatment. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalabney, A.; Abdulhalim, I. Sensitivity methods for surface plasmon sensors. Laser Photon. Rev. 2011, 5, 571–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashunsky, V.; Lirtsman, V.; Golosovsky, M.; Davidov, D. Real-time monitoring of epithelial cell-cell and cell-substrate interactions by infrared surface plasmon spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 4028–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nenninger, G.; TobisÏka, P.; Homola, J.; Yee, S.S. Long-range surface plasmons for high-resolution surface plasmon resonance sensors. Sens. Actuators B 2001, 74, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Keathley, P.D.; Hastings, J.T. Dual—Mode surface plasmon resonance sensor using angular interrogation. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacs, S.; Abdulhalim, I. Long range surface plasmon resonance with ultra-high penetration depth for self-referenced sensing and ultra—low detection limit using diverging beam approach. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 193701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, Z.; Brown, M.F.; Tollin, G. Plasmon resonance spectroscopy: Probing molecular interaction within membranes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999, 24, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harte, E.; Maalouli, N.; Shalabney, A.; Texier, E.; Berthelot, K.; Lecomte, S.; Alves, I.D. Probing the kinetics of lipid membrane formation and interaction of a nontoxic and a toxic amyloid with plasmon waveguide resonance. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 4168–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamon, Z.; Macleod, H.A.; Tollin, G. Coupled plasmon-waveguide resonators: A new spectroscopic tool for probing proteolipid film structure and properties. Biophys. J. 1997, 73, 2791–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zourob, M.; Mohr, S.; Brown, B.J.T.; Fielden, P.R.; McDonnell, M.; Goddard, N.J. The development of a metal clad leaky waveguide sensor for the detection of particles. Sens. Actuators B. 2003, 90, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skivesen, N.; Horvath, R.; Thinggaard, S.; Larsen, N.B.; Pedersen, H.C. Deep-probe metal-clad waveguide biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyama, S.; Doumae, N.; Shoji, A.; Ikariyama, Y. Design and fabrication of waveguide coupled prism device for surface plasmon resonance sensor. Sens. Actuators B 2000, 65, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, V.J.; Tollin, G. Techniques: Plasmon waveguide resonance (PWR) spectroscopy as a tool to study ligand—GPCR interactions. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skivesen, N.; Horvath, R.; Pedersen, H.C. Optimization of metal—Cald waveguide sensors. Sens. Actuators B. 2005, 106, 668–676. [Google Scholar]
- Mahajna, S.; Neumann, M.; Eyal, O.; Shalabney, A. Plasmon waveguide resonance with enhanced Figureure of Merit and their potential for anisotropic biosensing in the near infrared region. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 1898315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Linman, M.J.; Cheng, Q. Sensitivity comparison of surface plasmon resonance and plasmon-waveguide resonance biosensors. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 156, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szunerits, S.; Castel, X.; Boukherroub, R. Surface plasmon resonance investigation of silver and gold films coated with thin indium tin oxide layers: Influence on stability and sensitivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15813–15817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, S.H.; Choi, M.; Kim, Y.L.; Byun, K.M. Dispersion curve engineering of TiO2/silver hybrid substrates for enhanced surface plasmon resonance detection. Sensors 2016, 16, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahav, A.; Shalabaney, A.; Abdulhalim, I. Surface plasmon sensor with enhanced sensitivity using top nano dielectric layer. J. Nanophoton. 2009, 3, 031501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabchevsky, A.; Karabchevsky, S.; Abdulhalim, I. Fast surface plasmon resonance imaging sensor using radon transform. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 155, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.B.; Christy, R.W. Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 6, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitson, I.H. Interspecimen comparison of the refractive index of fused silica. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1965, 55, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimhult, E.; Hook, F.; Kasemo, B. Intact Vesicle Adsorption and Supported Biomembrane Formation from Vesicles in Solution: Influence of Surface Chemistry, Vesicle Size, Temperature, and Osmotic Pressure. Langmuir 2003, 19, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, Z.; Tollin, G. Optical anisotropy in lipids bilayer membranes: Coupled plasmon waveguide resonsnce measurement of molecular orientation, polarizability and shape. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhalim, I. Analytic propagation matrix method for linear optics of arbitrary biaxial layered media. J. Opt. A 1999, 1, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, I.D.; Kurylo, I.; Coffinier, Y.; Siriwardena, A.; Zaitsev, V.; Harte, E.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Plasmon waveguide resonance for sensing glycan-lectin interactions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 873, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamon, Z.; Lindblom, G.; Tollin, G. Plasmon waveguide resonance and impedance spectroscopy studies of the interaction between penetratin and supported lipids bilayer membranes. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, I.; Correia, I.; Jiao, C.Y.; Sachon, E.; Sagan, S.; Lavielle, S.; Tollin, G.; Chassaing, G. The interaction of cell-penetrating peptides with lipid model systems and subsequent lipid reorganization: Thermodynamic and structural characterization. J. Pept. Sci. 2009, 15, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniti, O.; Alves, I.; Trugnan, G.; Ayala-Sanmartin, J. Distinct Behaviour of the Homeodomain Derived Cell Penetrating Peptide Penetratin in Interaction with Different Phospholipid. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, I.D.; Bechara, C.; Walrant, A.; Zaltsman, Y.; Jiao, C.Y.; Sagan, S. Relationships between membrane binding, affinity and cell internalization efficacy of a cell-penetrating peptide: Penetratin as a case study. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24096. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado, G.F.; Vogel, A.; Marquant, R.; Feller, S.E.; Bouaziz, S.; Alves, I.D. The role of Membranes in the organization of HIV-1 Gag p6 and Vpr: p6 shows high affinity for membrane bilayers which substantially increases the interaction between p6 and Vpr. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7157–7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaid, S.; Libersou, S.; Oudali, M.; Morellet, N.; Desbat, B.; Alves, I.D.; Lepault, J.; Bouaziz, S. A Peptide Derived from the Rotavirus Outer Capsid Protein VP7 Permeabilizes Artificial Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.; Vignaud, H.; Bobo, C.; Decossas, M.; Lambert, O.; Harté, E.; Alves, I.D.; Cullin, C.; Lecomte, S. Interaction of aβ1-42 amyloids with lipids promotes “off-pathway” oligomerization and membrane damage. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calmet, P.; De Maria, M.; Harté, E.; Lamb, D.; Serrano-Vega, M.; Jazayeri, A.; Tschammer, N.; Alves, I.D. Real time monitoring of membrane GPCR reconstitution by plasmon waveguide resonance: On the role of lipids. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 36181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, I.D.; Cowell, S.M.; Salamon, Z.; Devanathan, S.; Tollin, G.; Hruby, V.J. Different structural states of the proteolipid membrane are produced by ligand binding to the human delta-opioid receptor as shown by plasmon-waveguide resonance spectroscopy. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, I.D.; Delaroche, D.; Mouillac, B.; Salamon, Z.; Tollin, G.; Hruby, V.J. The two NK-1 binding sites correspond to distinct, independent, and non-interconvertible receptor conformational states as confirmed by plasmon-waveguide resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 5309–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devanathan, S.; Yao, Z.; Salamon, Z.; Kobilka, B.; Tollin, G. Plasmon-waveguide resonance studies of ligand binding to the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 3280–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, T.; Devanathan, S.; Stropova, D.; Park, C.K.; Salamon, Z.; Tollin, G.; Hruby, V.J.; Roeske, W.R.; Yamamura, H.I.; Verga, E. Unique agonist-bound cannabinoid CB1 receptor conformations indicate agonist specificity in signaling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 581, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, K.; Billottet, C.; Pujol, N.; Alves, I.D.; Bikfalvi, A. Ligand activation induces different conformational changes in CXCR3 receptor isoforms as evidenced by plasmon waveguide resonance (PWR). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, I.D.; Salamon, Z.; Verga, E.; Yamamura, H.I.; Tollin, G.; Hruby, V.J. Direct observation of G-protein binding to the human delta-opioid receptor using plasmon-waveguide resonance. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48890–48897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, I.D.; Ciano, K.; Boguslavski, V.; Verga, E.; Salamon, Z.; Yamamura, H.I.; Hruby, V.J.; Tollin, G. Selectivity, cooperativity and reciprocity in the interactions between the delta opioid receptor, its ligands and G-proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44673–44682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, I.D.; Salgado, G.F.J.; Salamon, Z.; Brown, M.F.; Tollin, G.; Hruby, V.J. Phosphatidylethanolamine enhances rhodopsin photoactivation and transducin binding in a solid supported lipid bilayer as determined using plasmon-waveguide resonance spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, I.D.; Salamon, Z.; Hruby, V.J.; Tollin, G. Ligand Modulation of Lateral Segregation of a G-Protein-Coupled Receptor into Lipid Microdomains in Sphingomyelin/Phosphatidylcholine Solid-Supported Bilayers. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 9168–9178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
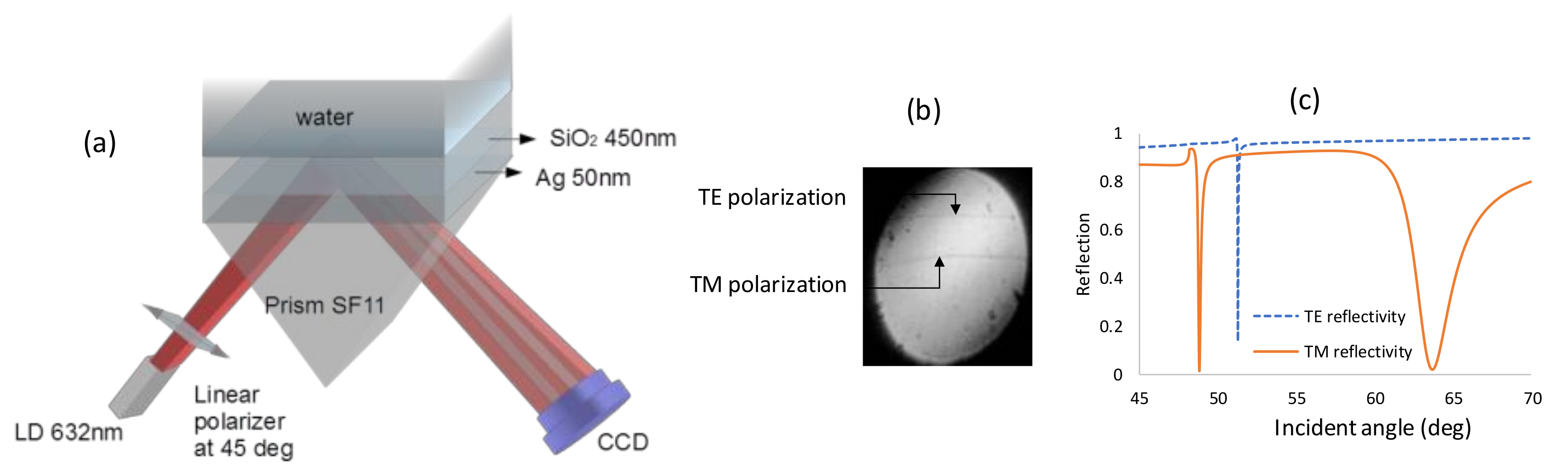







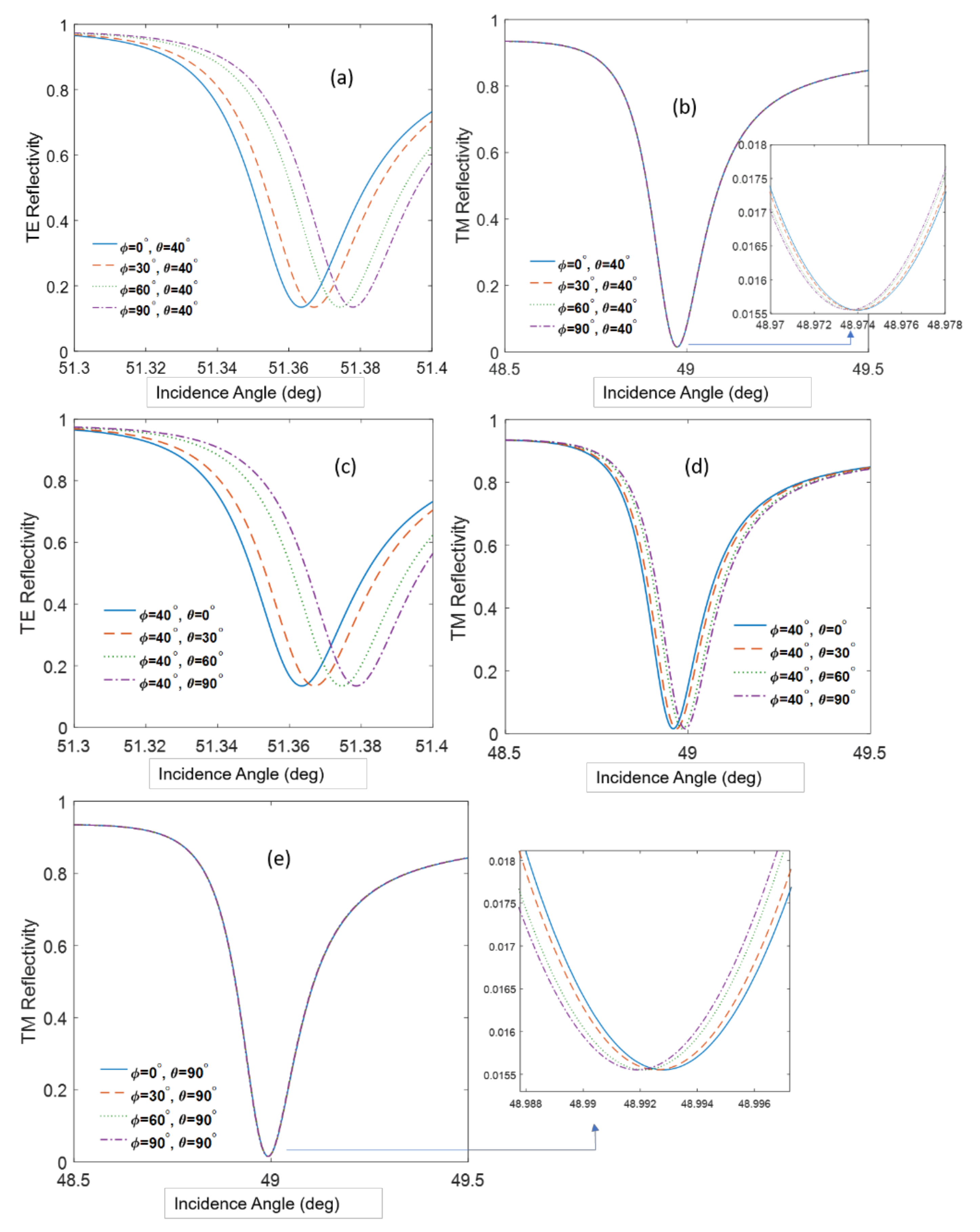
| (θ = 40°) Incidence Angle (deg) | (θ = 90°) Incidence Angle (deg) | |
|---|---|---|
| Φ = 0° | 48.9741 | 48.9928 |
| Φ = 30° | 48.9739 | 48.9925 |
| Φ = 60° | 48.9737 | 48.9921 |
| Φ = 90° | 48.9736 | 48.9918 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Isaacs, S.; Harté, E.; D. Alves, I.; Abdulhalim, I. Improved Detection of Plasmon Waveguide Resonance Using Diverging Beam, Liquid Crystal Retarder, and Application to Lipid Orientation Determination. Sensors 2019, 19, 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061402
Isaacs S, Harté E, D. Alves I, Abdulhalim I. Improved Detection of Plasmon Waveguide Resonance Using Diverging Beam, Liquid Crystal Retarder, and Application to Lipid Orientation Determination. Sensors. 2019; 19(6):1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061402
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsaacs, Sivan, Etienne Harté, Isabel D. Alves, and Ibrahim Abdulhalim. 2019. "Improved Detection of Plasmon Waveguide Resonance Using Diverging Beam, Liquid Crystal Retarder, and Application to Lipid Orientation Determination" Sensors 19, no. 6: 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061402
APA StyleIsaacs, S., Harté, E., D. Alves, I., & Abdulhalim, I. (2019). Improved Detection of Plasmon Waveguide Resonance Using Diverging Beam, Liquid Crystal Retarder, and Application to Lipid Orientation Determination. Sensors, 19(6), 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061402







