Pharmacological Applications of Nrf2 Inhibitors as Potential Antineoplastic Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nrf2 Domains and Their Functions
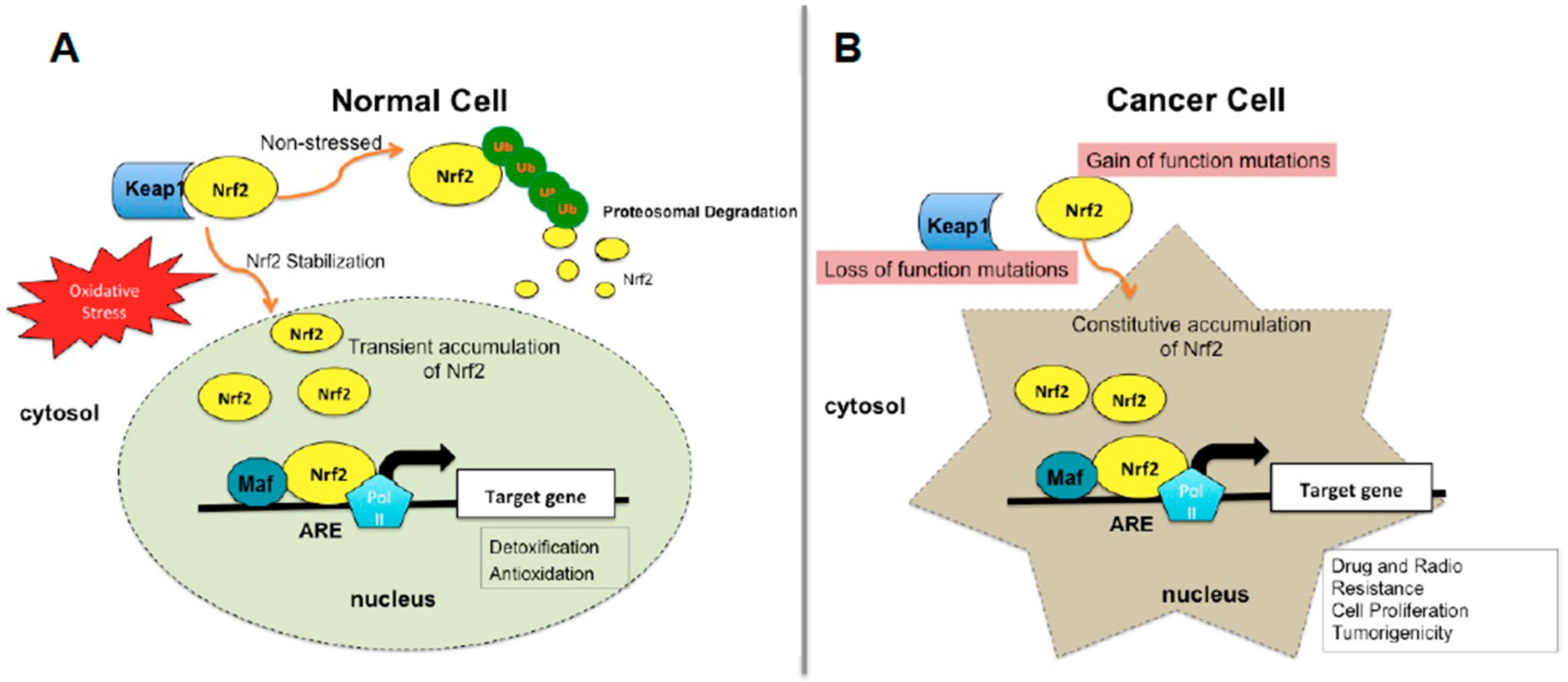
3. Regulation of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway
4. Nrf2 Function in Oxidative Stress and Toxicity
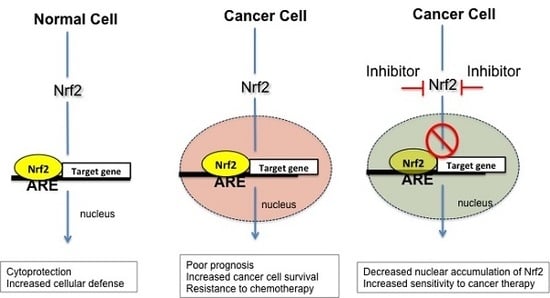
5. Nrf2 in Cancer
5.1. Molecular Basis of Nrf2 Activation in Cancer Cells
5.1.1. Somatic Mutations in Nrf2-Signaling Pathway
5.1.2. Epigenetic Modifications in Nrf2-Signaling Pathway
5.1.3. Cooperation between Nrf2 and Other Proteins
6. Nrf2 Inhibitors as Potential Antineoplastic Drugs
7. Challenges in Nrf2 Inhibitor Drug Development
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APAP | N-acetyl-4-aminophenol |
| ARE | Antioxidant response element |
| CREB | cAMP Response element binding protein |
| CHD6 | Chromo-ATPase/helicase DNA binding protein 6 |
| CNC-bZip | Cap’n’collar type of basic region leucine zipper factor family |
| DME | Drug metabolizing enzymes |
| ER | Estrogen receptors |
| GCL | Glutamate-cysteine ligase |
| GSK-3β | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 |
| GSTs | Glutathione S-transferases |
| HMOX1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase |
| Keap1 | Kelch like ECH associated protein |
| NQO-1 | NADPH quinone oxidoreductase |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor-erythroid 2 p45-related factor 2 |
| OS | Oxidative stress |
| PPAR-α | Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α |
| RAC | Receptor-associated co-activator |
| RAR-α | Retinoic acid receptor |
| RXR | Retinoid X receptor alpha |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SFERR | Short-form estrogen-related receptor |
| β-TrCP | β-Transducin repeat-containing protein |
| Treg | Regulatory T cells |
References
- Global Cancer Observatory. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr (accessed on 16 April 2019).
- Pitot, H.C.; Goldsworthy, T.; Moran, S. The natural history of carcinogenesis: Implications of experimental carcinogenesis in the genesis of human cancer. J. Supramol. Struct. Cell. Biochem. Suppl. 1981, 17, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Vega Rojo, M.; Chapman, E.; Zhang, D.D. NRF2 and the hallmarks of cancer. Cancer Cell. 2018, 34, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.L.; Sieow, J.L.; Wong, S.C. Targeting immune cells for cancer therapy. Redox Biol. 2019, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Tang, Y.; Hua, S. Immunological Approaches Towards Cancer and Inflammation: A Cross Talk. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, F.J.; Hubbard-Lucey, V.M.; Tang, J.; Pusztai, L. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy combinations in metastatic breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Bivona, T.G. Polytherapy and Targeted Cancer Drug Resistance. Trends Cancer. 2019, 5, 70–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewski, W.; Dobrzyński, M.; Szymonowicz, M.; Rybak, Z. Stem cells: Past, present, and future. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, C.M.; Paczesny, S. Biomarkers for Early Complications after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Clin. Lab. Med. 2019, 39, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomans-Kropp, H.A.; Umar, A. Cancer prevention and screening: The next step in the era of precision medicine. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, M. Biomarkers for personalized oncology: Recent advances and future challenges. Metabolism 2015, 64 (Suppl. 1), 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vomund, S.; Schäfer, A.; Parnham, M.J.; Brüne, B.; von Knethen, A. Nrf2, the master regulator of anti-oxidative responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajadimajd, S.; Khazaei, M. Oxidative Stress and Cancer: The Role of Nrf2. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2018, 18, 538–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moi, P.; Chan, K.; Asunis, I.; Cao, A.; Kan, W. Isolation of nf-e2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a nf-e2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9926–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. The nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Igarashi, K.; Hayashi, N.; Nishizawa, M.; Yamamoto, M. Cloning and characterization of a novel erythroid cell-derived CNC family transcription factor heterodimerizing with the small Maf family proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 4184–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motohashi, H.; O’Connor, T.; Katsuoka, F.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. Integration and diversity of the regulatory network composed of Maf and CNC families of transcription factors. Gene 2002, 294, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nioi, P.; Nguyen, T.; Sherratt, P.J.; Pickett, C.B. The carboxy-terminal neh3 domain of Nrf2 is required for transcriptional activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 10895–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Yu, S.; Chen, J.D.; Kong, A.N. The nuclear cofactor RAC3/AIB1/SRC-3 enhances Nrf2 signaling by interacting with transactivation domains. Oncogene 2013, 32, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, M.; Thomas, N.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayes, J.D. Redox-regulated turnover of Nrf2 is determined by at least two separate protein domains, the redox-sensitive neh2 degron and the redox-insensitive neh6 degron. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31556–31567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, K.; Geng, M.; Gao, P.; Wu, X.; Hai, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Hayes, J.D.; Wang, X.J.; et al. RXRα inhibits the NRF2-ARE signaling pathway through a direct interaction with the neh7 domain of NRF2. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3097–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, Y.; Iida, K.; Kang, M.I.; Kobayashi, A.; Mizukami, M.; Tong, K.I.; McMahon, M.; Hayes, J.D.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M. Evolutionary conserved n-terminal domain of Nrf2 is essential for the keap1-mediated degradation of the protein by proteasome. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 433, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebay, L.E.; Robertson, H.; Durant, S.T.; Vitale, S.R.; Penning, T.M.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Hayes, J.D. Mechanisms of activation of the transcription factor Nrf2 by redox stressors, nutrient cues, and energy status and the pathways through which it attenuates degenerative disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 108–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kensler, T.W.; Wakabayashi, N. Nrf2: Friend or foe for chemoprevention? Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; McMahon, M.; Chowdhry, S.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. Cancer chemoprevention mechanisms mediated through the keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1713–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, P.; Rojo, A.I.; Chowdhry, S.; McMahon, M.; Hayes, J.D.; Cuadrado, A. SCF/{beta}-trcp promotes glycogen synthase kinase 3-dependent degradation of the Nrf2 transcription factor in a keap1-independent manner. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhao, F.; Gao, B.; Tan, C.; Yagishita, N.; Nakajima, T.; Wong, P.K.; Chapman, E.; Fang, D.; Zhang, D.D. Hrd1 suppresses Nrf2-mediated cellular protection during liver cirrhosis. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, S.; Wang, S.; Moghaddam, S.J.; Ooi, A.; Chapman, E.; Wong, P.K.; Zhang, D.D. Oncogenic KRAS confers chemoresistance by upregulating NRF2. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7430–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeNicola, G.M.; Karreth, F.A.; Humpton, T.J.; Gopinathan, A.; Wei, C.; Frese, K.; Mangal, D.; Yu, K.H.; Yeo, C.J.; Calhoun, E.S.; et al. Oncogene-induced Nrf2 transcription promotes ROS detoxification and tumorigenesis. Nature 2011, 475, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanderson, L.M.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Desvergne, B.; Müller, M.; Kersten, S. Transcriptional profiling reveals divergent roles of pparalpha and pparbeta/delta in regulation of gene expression in mouse liver. Physiol. Genom. 2010, 41, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisek, K.; Campaner, E.; Ciani, Y.; Walerych, D.; Del Sal, G. Mutant p53 tunes the NRF2-dependent antioxidant response to support survival of cancer cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20508–20523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Li, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, F.; Tang, L.; Li, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Nuclear factor p65 interacts with Keap1 to repress the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Cell Signal. 2011, 23, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, S.; Jain, A.K.; Bloom, D.A.; Jaiswal, A.K. Bach1 competes with Nrf2 leading to negative regulation of the antioxidant response element (ARE)-mediated NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 gene expression and induction in response to antioxidants. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16891–16900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Jeong, J.Y.; Surh, Y.J.; Kim, K.W. Expression of stress-response ATF3 is mediated by Nrf2 in astrocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Brodie, A.M.; Davidson, N.E.; Kensler, T.W.; Zhou, Q. Inhibition of estrogen signaling activates the NRF2 pathway in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010, 124, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polvani, S.; Tarocchi, M.; Galli, A. PPARγ and Oxidative Stress: Con(β) Catenating NRF2 and FOXO. PPAR Res. 2012, 2012, 641087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigawa, S.; Lee, C.H.; Lin, C.S.; Ku, C.C.; Hasegawa, H.; Qin, S.; Kawahara, A.; Korenori, Y.; Miyamori, K.; Noguchi, M.; et al. Jun dimerization protein 2 is a critical component of the Nrf2/MafK complex regulating the response to ROS homeostasis. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namani, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Modulation of NRF2 signaling pathway by nuclear receptors: Implications for cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X.J.; Jiang, T.; Huang, Z.; Fang, D.; Zhang, D.D. Direct interaction between Nrf2 and p21(Cip1/WAF1) upregulates the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Mol. Cell 2009, 34, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Bodas, M.; Wakabayashi, N.; Bunz, F.; Biswal, S. Gain of Nrf2 function in non-small-cell lung cancer cells confers radioresistance. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurer-Orhan, H.; Ince, E.; Konyar, D.; Saso, L.; Suzen, S. The Role of Oxidative Stress Modulators In Breast Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 4084–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S. Transcriptional responses to oxidative stress: Pathological and toxicological implication. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 125, 376–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekiner-Gulbas, B.; Westwell, A.D.; Suzen, S. Oxidative stress in carcinogenesis: New synthetic compounds with dual effects upon free radicals and cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 4451–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q. Role of Nrf2 in Oxidative Stress and Toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.; Sherratt, P.J.; Pickett, C.B. Regulatory mechanisms controlling gene expression mediated by the antioxidant response element. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 43, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talalay, P.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Holtzclaw, W.D. Importance of phase 2 gene regulation in protection against electrophile and reactive oxygen toxicity and carcinogenesis. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 2003, 43, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J. The role of Nrf2 in oxidative stress-induced endothelial injuries. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 225, R83–R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niture, S.K.; Khatri, R.; Jaiswal, A.K. Regulation of Nrf2—An update. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Nioi, P.; Pickett, C.B. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13291–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kong, A.N. Molecular mechanisms of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, J.; Stewart, D.; Touchard, C.; Boinapally, S.; Choi, A.M.; Cook, J.L. Nrf2, a Cap’n’Collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 26071–26078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, M.; Piras, S.; Marinari, U.M.; Moretta, L.; Pronzato, M.A.; Furfaro, A.L. HO-1 Induction in Cancer Progression: A Matter of Cell Adaptation. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Johnson, J.A. The Nrf2-ARE pathway: A valuable therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saso, L.; Firuzi, O. Pharmacological Applications of Antioxidants: Lights and Shadows. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 1177–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutten, A.; Goven, D.; Artaud-Macari, E.; Boczkowski, J.; Bonay, M. NRF2 targeting: A promising therapeutic strategy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Chanas, S.A.; Henderson, C.J.; McLellan, L.I.; Wolf, C.R.; Cavin, C.; Hayes, J.D. The Cap’n’Collar basic leucine zipper transcription factor Nrf2 (NF-E2 p45-related factor 2) controls both constitutive and inducible expression of intestinal detoxification and glutathione biosynthetic enzymes. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3299–3307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.C.; Vargas, M.R.; Pani, A.K.; Smeyne, R.J.; Johnson, D.A.; Kan, Y.W.; Johnson, J.A. Nrf2-mediated neuroprotection in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: Critical role for the astrocyte. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2933–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöblom, T.; Jones, S.; Wood, L.D.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.; Barber, T.D.; Mandelker, D.; Leary, R.J.; Ptak, J.; Silliman, N.; et al. The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science 2006, 314, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Yoshizato, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Maekawa, S.; Okuno, Y.; Kamura, T.; Shimamura, T.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Nagae, G.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Integrated molecular analysis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Fountzilas, E.; Pillay, K.; Zerbini, L.F.; Libermann, T.A.; Cannistra, S.A.; Spentzos, D. Carboplatin-induced gene expression changes in vitro are prognostic of survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. BMC Med. Genom. 2008, 1, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.F.; Yoshinaga, K.; Monma, Y.; Ito, K.; Niikura, H.; Nagase, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Yaegashi, N. Association of keap1 and Nrf2 genetic mutations and polymorphisms with endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma survival. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2011, 21, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lister, A.; Nedjadi, T.; Kitteringham, N.R.; Campbell, F.; Costello, E.; Lloyd, B.; Copple, I.M.; Williams, S.; Owen, A.; Neoptolemos, J.P. Nrf2 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer: Implications for cell proliferation and therapy. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, B.; Hong, B.; Yan, W.; Zhang, J. Impact of nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2–like 2 and p62/sequestosome expression on prognosis of patients with gliomas. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, A.; Douglas, J.; Sommerlad, M.; Andrews, L.; Gould, K.; Hussain, S.; Thomas, G.J.; Packham, G.; Crabb, S.J. The NRF2 transcription factor contributes to resistance to cisplatin in bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, Y.; Motohashi, H.; Takagi, K.; Miki, Y.; Shibahara, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Ishida, T.; Hirakawa, H.; Sasano, H.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. NRF2 immunolocalization in human breast cancer patients as a prognostic factor. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Q.; Tuersun, H.; Jiao, S.J.; Zheng, J.H.; Xiao, J.B.; Hasim, A. Functional Role of NRF2 in Cervical Carcinogenesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. Correlation of NRF2, NQO1, MRP1, cmyc and p53 in colorectal cancer and their relationships to clinicopathologic features and survival. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, T.; Saito, S.; Kokubu, A.; Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Hirohashi, S. Global downstream pathway analysis reveals a dependence of oncogenic NF-E2-related factor 2 mutation on the mTOR growth signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9095–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Ishigami, S.; Arigami, T.; Uenosono, Y.; Yanagita, S.; Uchikado, Y.; Kita, Y.; Nishizono, Y.; Okumura, H.; Nakajo, A.; et al. Clinicopathological significance of nuclear factor (erythroid-2)-related factor 2 (NRF2) expression in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.D.; Vucic, E.A.; Thu, K.L.; Pikor, L.A.; Lam, S.; Lam, W.L. Disruption of KEAP1/CUL3/RBX1 E3-ubiquitin ligase complex components by multiple genetic mechanisms: Association with poor prognosis in head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2015, 37, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, S.Ü.; Wen, Q.; Wang, J. Nrf2 is a potential prognostic marker and promotes proliferation and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeNicola, G.M.; Chen, P.H.; Mullarky, E.; Sudderth, J.A.; Hu, Z.; Wu, D.; Tang, H.; Xie, Y.; Asara, J.M.; Huffman, K.E.; et al. NRF2 regulates serine biosynthesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hintsala, H.R.; Jokinen, E.; Haapasaari, K.M.; Moza, M.; Ristimäki, A.; Soini, Y.; Koivunen, J.; Karihtala, P. Nrf2/Keap1 Pathway and Expression of Oxidative Stress Lesions 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine and Nitrotyrosine in Melanoma. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Spentzos, D.; Fountzilas, E.; Francoeur, N.; Sanisetty, S.; Grammatikos, A.P.; Hecht, J.L.; Cannistra, S.A. Keap1 mutations and Nrf2 pathway activation in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5081–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soini, Y.; Eskelinen, M.; Juvonen, P.; Kärjä, V.; Haapasaari, K.M.; Saarela, A.; Karihtala, P. Nuclear Nrf2 expression is related to a poor survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2014, 210, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizio, F.P.; Costantini, M.; Copetti, M.; la Torre, A.; Sparaneo, A.; Fontana, A.; Poeta, L.; Gallucci, M.; Sentinelli, S.; Graziano, P.; et al. 2017. Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in kidney cancer: Frequent methylation of KEAP1 gene promoter in clear renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 11187–11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziros, P.G.; Manolakou, S.D.; Habeos, I.G.; Lilis, I.; Chartoumpekis, D.V.; Koika, V.; Soares, P.; Kyriazopoulou, V.E.; Scopa, C.D.; Papachristou, D.J.; et al. Nrf2 is commonly activated in papillary thyroid carcinoma, and it controls antioxidant transcriptional responses and viability of cancer cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1422–E1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pölönen, P.; Levonen, A.L. Insights into the role of NRF2 in cancer provided by cancer genomics. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2016, 1, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, M.C.; Zhang, D.D. The emerging role of the Nrf2-keap1 signaling pathway in cancer. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 2179–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stępkowski, T.M.; Kruszewski, M.K. Molecular cross-talk between the NRF2/KEAP1 signaling pathway, autophagy, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, B.; Tong, K.I.; Ohta, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Scharlock, M.; Ohtsuji, M.; Yamamoto, M. Structural basis for defects of keap1 activity provoked by its point mutations in lung cancer. Mol. Cell. 2006, 21, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.J.; Yoo, H.S.; Shin, S.; Park, Y.J.; Jeon, S.M. Dysregulation of NRF2 in cancer: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2018, 26, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, L.D.; Lee, J.; Gnad, F.; Klijn, C.; Schaub, A.; Reeder, J.; Daemen, A.; Bakalarski, C.E.; Holcomb, T.; Shames, D.S.; et al. Recurrent loss of NFE2L2 exon 2 is a mechanism for Nrf2 pathway activation in human cancers. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2605–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhofer, M.; Florian, S.; Krauth, M.T.; Aichberger, K.J.; Bilban, M.; Marculescu, R.; Printz, D.; Fritsch, G.; Wagner, O.; Selzer, E.; et al. Identification of heme oxygenase-1 as a novel BCR/abl-dependent survival factor in chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3148–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscarella, L.A.; Parrella, P.; D’Alessandro, V.; la Torre, A.; Barbano, R.; Fontana, A.; Tancredi, A.; Guarnieri, V.; Balsamo, T.; Coco, M.; et al. Frequent epigenetics inactivation of KEAP1 gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Singh, A.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Esopi, D.; Kombairaju, P.; Bodas, M.; Wu, H.; Bova, S.G.; Biswal, S. Loss of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 function in prostate cancer cells causes chemoresistance and radioresistance and promotes tumor growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujambio, A.; Lowe, S.W. The microcosmos of cancer. Nature 2012, 482, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Kim, K.C.; Kang, H.K.; Chang, W.Y.; Park, I.C.; Keum, Y.S.; Surh, Y.J.; Hyun, J.W. Epigenetic modification of Nrf2 in 5-fluorouracil-resistant colon cancer cells: Involvement of TET-dependent DNA demethylation. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangokoya, C.; Telen, M.J.; Chi, J.T. MicroRNA mir-144 modulates oxidative stress tolerance and associates with anemia severity in sickle cell disease. Blood 2016, 116, 4338–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Yao, Y.; Eades, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q. MiR-28 regulates Nrf2 expression through a keap1-independent mechanism. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 129, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eades, G.; Yang, M.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q. MiR-200a regulates Nrf2 activation by targeting keap1 mrna in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 40725–40733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, N.; Slocum, S.L.; Skoko, J.J.; Shin, S.; Kensler, T. When NRF2 talks, who’s listening? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraonio, R.; Vergara, P.; Di Marzo, D.; Pierantoni, M.G.; Napolitano, M.; Russo, T.; Cimino, F. P53 suppresses the Nrf2-dependent transcription of antioxidant response genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 39776–39784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, M.; Kurokawa, H.; Waguri, S.; Taguchi, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Ichimura, Y.; Sou, Y.S.; Ueno, I.; Sakamoto, A.; Tong, K.I.; et al. The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of keap1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inami, Y.; Waguri, S.; Sakamoto, A.; Kouno, T.; Nakada, K.; Hino, O.; Watanabe, S.; Ando, J.; Iwadate, M.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. Persistent activation of Nrf2 through p62 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camp, N.D.; James, R.G.; Dawson, D.W.; Yan, F.; Davison, J.M.; Houck, S.A.; Tang, X.; Zheng, N.; Major, M.B.; Moon, R.T. Wilms tumor gene on X chromosome (WTX) inhibits degradation of NRF2 protein through competitive binding to KEAP1 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6539–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Cai, H.; Wu, T.; Sobhian, B.; Huo, Y.; Alcivar, A.; Mehta, M.; Cheung, K.L.; Ganesan, S.; Kong, A.N.; et al. PALB2 interacts with KEAP1 to promote NRF2 nuclear accumulation and function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hast, B.E.; Goldfarb, D.; Mulvaney, K.M.; Hast, M.A.; Siesser, P.F.; Yan, F.; Hayes, D.N.; Major, M.B. Proteomic analysis of ubiquitin ligase KEAP1 reveals associated proteins that inhibit NRF2 ubiquitiniation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, A.; Nishikawa, K.; Kawatani, Y.; Mimura, J.; Hosoya, T.; Harada, N.; Yamamato, M.; Itoh, K. The novel Nrf2-interacting factor KAP1 regulates susceptibility to oxidative stress by promoting the Nrf2-mediated cytoprotective response. Biochem. J. 2011, 436, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, S.; Forman, H.J. C-Myc is a Nrf2-interacting protein that negatively regulates phase II genes through their electrophile responsive elements. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayanju, A.; Copple, I.M.; Bryan, H.K.; Edge, G.T.; Sison, R.L.; Wong, M.W.; Lai, Z.Q.; Lin, Z.X.; Dunn, K.; Sanderson, C.M.; et al. Brusatol provokes a rapid and transient inhibition of Nrf2 signaling and sensitizes mammalian cells to chemical toxicity-implications for therapeutic targeting of Nrf2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 78, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Boldin-Adamsky, S.; Thimmulappa, R.K.; Rath, S.K.; Ashush, H.; Coulter, J.; Blackford, A.; Goodman, S.N.; Bunz, F.; Watson, W.H.; et al. RNAi-mediated silencing of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer inhibits tumor growth and increases efficacy of chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7975–7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigawa, S.; Fujii, M.; Hou, D.X. Action of Nrf2 and Keap1 in ARE-mediated NQO1 expression by quercetin. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Fan, L.; Wu, X.; Xin, A.; Ren, H.; Wang, X.J. Luteolin inhibits Nrf2 leading to negative regulation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway and sensitization of human lung carcinoma A549 cells to therapeutic drugs. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, K.; Tsujita, T.; Hayashi, M.; Ojima, A.; Keleku-Lukwete, N.; Katsuoka, F.; Otsuki, A.; Kikuchi, H.; Oshima, Y.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Halofuginone enhances the chemo-sensitivity of cancer cells by suppressing NRF2 accumulation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 103, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, S.; Lee, I.S.; Kang, B.Y.; Choi, H.J. 4-methoxychalcone enhances cisplatin-induced oxidative stress and cytotoxicity by inhibiting the Nrf2/ARE-mediated defense mechanism in A549 lung cancer cells. Mol. Cells 2013, 36, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.X.; Zhe, H.; He, Z.X.; Zhou, S.F. Bardoxolone methyl (CDDO-Me) as a therapeutic agent: An update on its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2014, 8, 2075–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sova, M.; Saso, L. Design and development of Nrf2 modulators for cancer chemoprevention and therapy: A review. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 3181–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhu, J.; Lin, H.; Gu, K.; Feng, F. Recent progress in the development of small molecule Nrf2 modulators: A patent review (2012–2016). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017, 27, 763–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, R.; Xue, P.; Zhang, Q.; Bud Nelson, M.; Qu, W.; Feng, B.; Pi, J. Camptothecin suppresses NRF2-ARE activity and sensitises hepatocellular carcinoma cells to anticancer drugs. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Misra, V.; Thimmulappa, R.K.; Lee, H.; Ames, S.; Hoque, M.O.; Herman, J.G.; Baylin, S.B.; Sidransky, D.; Gabrielson, E.; et al. Dysfunctional Keap1-Nrf2 interaction in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.R.; Oh, J.E.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, M.R.; Park, S.W.; Han, J.Y.; Eom, H.S.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, S.H. Oncogenic Nrf2 mutations in squamous cell carcinomas of oesophagus and skin. J. Pathol. 2010, 220, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.K.; Hill, T.; Alexander, C.M. The involvement of Nrf2 in lung cancer. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 746432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Chiba, T.; Takahashi, S.; Ishii, T.; Igarashi, K.; Katoh, Y.; Oyake, T.; Hayashi, N.; Satoh, K.; Hatayama, I.; et al. An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporn, M.B.; Liby, K.T. NRF2 and cancer: The good, the bad and the importance of context. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanzaro, E.; Calcabrini, C.; Turrini, E.; Sestili, P.; Fimognari, C. Nrf2: A potential therapeutic target for naturally occurring anticancer drugs? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, P.L.; Hsu, C.S.; Liu, W.M.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, C.L. Prognostic and predictive values of Nrf2, Keap1, p16 and E-cadherin expression in ovarian epithelial carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5642–5649. [Google Scholar]
- Cescon, D.W.; She, D.; Sakashita, S.; Zhu, C.Q.; Pintilie, M.; Shepherd, F.A.; Tsao, M.S. NRF2 pathway activation and adjuvant chemotherapy benefit in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Zhou, T.; Gurguis, C.I.; Xu, X.; Wen, Q.; Lv, J.; Fang, F.; Hecker, L.; Cress, A.E.; Natarajan, V.; et al. Nuclear factor, erythroid 2-like 2-associated molecular signature predicts lung cancer survival. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16889–16899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikaw, T. Genetic polymorphism in the NRF2 gene as a prognosis marker for cancer chemotherapy. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfadda, A.A.; Sallam, R.M. Reactive oxygen species in health and disease. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 936486–936500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copple, I.M. The keap1-Nrf2 cell defense pathway-a promising therapeutic target? Adv. Pharmacol. 2012, 63, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.Y.; Kwak, M.K.; Pi, J. Nrf2 in host defense: Over the rainbow. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 975839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, F.; Fu, J.; Xu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Kou, H.H.; Zhai, C.; Nelson, M.B.; Zhang, Q.; et al. An overview of chemical inhibitors of the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway and their potential applications in cancer therapy. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2016, 99, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Reddy, N.M.; Higbee, E.M.; Potteti, H.R.; Noel, S.; Racusen, L.; Kensler, T.W.; Sporn, M.B.; Reddy, S.P.; Rabb, H. The Nrf2 triterpenoid activator, CDDO-imidazolide, protects kidneys from ischemia–reperfusion injury in mice. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, A.; Itoh, K.; Nagayoshi, E.; Haruta, J.; Kimura, T.; O’Connor, T.; Harada, T.; Yamamoto, M. High sensitivity of Nrf2 knockout mice to acetaminophen hepatotoxicity associated with decreased expression of ARE-regulated drug metabolizing enzymes and antioxidant genes. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 59, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Ishii, Y.; Itoh, K.; Kiwamoto, T.; Kimura, T.; Matsuno, Y.; Morishima, Y.; Hegab, A.E.; Homma, S.; Nomura, A. Nrf2-deficient mice are highly susceptible to cigarette smoke-induced emphysema. Genes Cells 2005, 10, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becks, L.; Prince, M.; Burson, H.; Christophe, C.; Broadway, M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Mathis, M.; Orchard, E.; Shi, R. Aggressive mammary carcinoma progression in Nrf2 knockout mice treated with 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 540–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzkowitz, S.H.; Yio, X. Inflammation and cancer IV. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: The role of inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 287, G7–G17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, T.O.; Huang, M.T.; Kwon, K.H.; Chan, J.Y.; Reddy, B.S.; Kong, A.N. Nrf2-deficient mice have an increased susceptibility to dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11580–11584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, T.O.; Huang, M.T.; Prawan, A.; Liu, Y.; Hao, X.; Yu, S.; Cheung, W.K.; Chan, J.Y.; Reddy, B.S.; Yang, C.S. Increased Susceptibility of Nrf2 Knockout Mice to Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2008, 1, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okawa, H.; Motohashi, H.; Kobayashi, A.; Aburatani, H.; Kensler, T.W.; Yamamoto, M. Hepatocyte-specific deletion of the keap1 gene activates NRF2 and confers potent resistance against acute drug toxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 339, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramoto, K.; Satoh, H.; Suzuki, T.; Moriguchi, T.; Pi, J.; Shimosegawa, T.; Yamamoto, M. Myeloid lineage-specific deletion of antioxidant system enhances tumor metastasis. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maj, T.; Wang, W.; Crespo, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Wei, S.; Zhao, L.; Vatan, L.; Shao, I.; Szeliga, W. Oxidative stress controls regulatory T cell apoptosis and suppressor activity and PD-L1-blockade resistance in tumor. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, R.; Sayin, V.I.; Davidson, S.M.; Bauer, M.R.; Singh, S.X.; LeBoeuf, S.E.; Karakousi, T.R.; Ellis, D.C.; Bhutkar, A.; Sánchez-Rivera, F.J.; et al. Keap1 loss promotes Kras driven lung cancer and results in dependence on glutaminolysis. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, H.; Motohashi, H. NRF2 addiction in cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkovic, L.; Zarkovic, N.; Saso, L. Controversy about pharmacological modulation of Nrf2 for cancer therapy. 2017, Controversy about pharmacological modulation of Nrf2 for cancer therapy. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegon, S.; Columbano, A.; Giordano, S. The Dual Roles of NRF2 in Cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 578–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesh, S.; Chen, Y.; Hu, L. Small molecule modulators of Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as potential preventive and therapeutic agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2012, 32, 687–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.I.; Katoh, Y.; Kusunoki, H.; Itoh, K.; Tanaka, T.; Yamamoto, M. Keap1 recruits Neh2 through binding to ETGE and DLG motifs: Characterization of the two-site molecular recognition model. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 2887–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, A.; Rojo, A.I.; Wells, G.; Hayes, J.D.; Cousin, S.P.; Rumsey, W.L.; Attucks, O.C.; Franklin, S.; Levonen, A.L.; Kensler, T.W.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the NRF2 and KEAP1 partnership in chronic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type of Cancer | Number of Patients | Conclusion | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brain Glioma | 75 | The expression of Nrf2 and p62 was associated with tumor grade and survival in patients with gliomas | [64] |
| Bladder cancer | 44 | Nrf2 expression is associated with short overall survival in bladder cancer patients | [65] |
| Breast cancer | 106 | Nrf2 protein plays important roles in the proliferation and/or progression of breast carcinoma | [66] |
| Cervical cancer | 89 | Strong nuclear expression of NRF2 was significantly associated with reduced cytoplasmic Keap1 expression in cervical cancers due to hypermethylation. | [67] |
| Colorectal cancer | 76 | Nrf2 was highly expressed in CRC tissues compared with adjacent non-tumor tissues | [68] |
| Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | 82 | Oncogenic Nrf2 mutation induces dependence on the mTOR pathway during carcinogenesis | [69] |
| Gastric cancer | 175 | Nrf2 expression is closely associated with clinicopathological factors and the prognosis of gastric cancer patients | [70] |
| Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | 302 | Nrf2 activation is potentially clinically relevant as a prognostic indicator in HNSCC | [71] |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 65 | Nrf2 was up-regulated in HCC, and expression of Nrf2 was correlated with tumor differentiation metastasis, and tumor size | [72] |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | 443 | NRF2 regulates serine biosynthesis in non-small cell lung cancer | [73] |
| Melanoma | 121 | Nrf2 influences prognosis in melanoma | [74] |
| Ovarian cancer | 64 | Nrf2 may serve as an important therapeutic target for novel drugs capable of preventing or reversing resistance to chemotherapy in ovarian cancer | [75] |
| Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | 103 | Nuclear Nrf2 expression is related to a poor survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma | [76] |
| Renal cell cancer | 89 | Keap1/Nrf2 axis deregulation is an important prognostic marker in renal cell carcinoma | [77] |
| Tyroid carcinoma | 42 | Nrf2 pathway has potential diagnostic, prognostic, and/or therapeutic utility in papillary thyroid carcinoma | [78] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Telkoparan-Akillilar, P.; Suzen, S.; Saso, L. Pharmacological Applications of Nrf2 Inhibitors as Potential Antineoplastic Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082025
Telkoparan-Akillilar P, Suzen S, Saso L. Pharmacological Applications of Nrf2 Inhibitors as Potential Antineoplastic Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(8):2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082025
Chicago/Turabian StyleTelkoparan-Akillilar, Pelin, Sibel Suzen, and Luciano Saso. 2019. "Pharmacological Applications of Nrf2 Inhibitors as Potential Antineoplastic Drugs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 8: 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082025
APA StyleTelkoparan-Akillilar, P., Suzen, S., & Saso, L. (2019). Pharmacological Applications of Nrf2 Inhibitors as Potential Antineoplastic Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(8), 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082025