Ginseng Berry Prevents Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage by Improving the Anti-Inflammatory System Damage in Mice and Quality Control of Active Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Standard Compounds in EGB
2.2. Quantitative Analysis of EGB by UPLC-QTOF/MS
2.3. Protective Effect of EGB on Serum AST and ALT in AILD
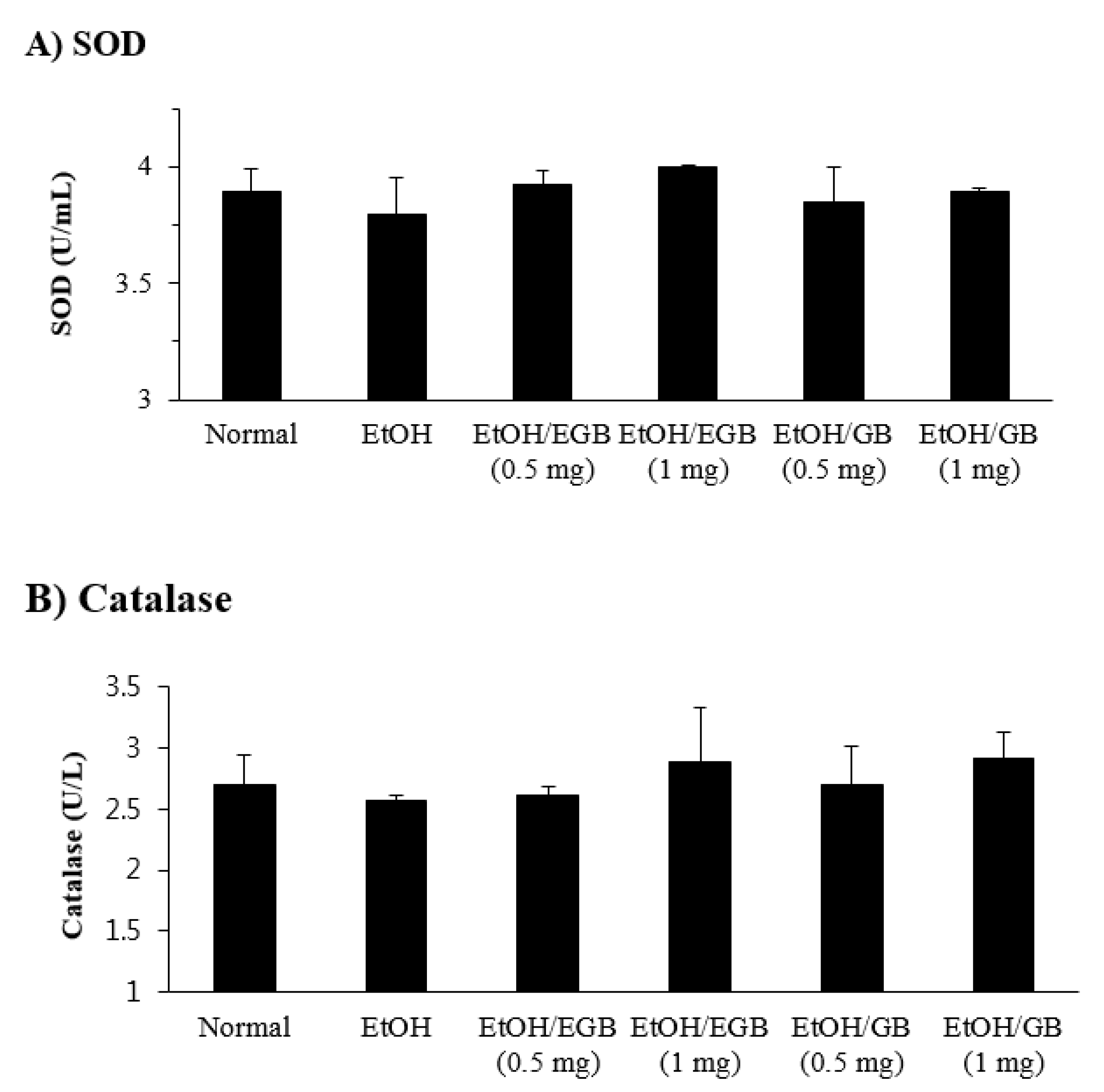
2.4. Antioxidant Effect of EGB in EtOH-Fed Mice
2.5. Changes in Organ Weight by EGB in EtOH-Fed Mice
2.6. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of EGB on LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages
3. Materials and Methods
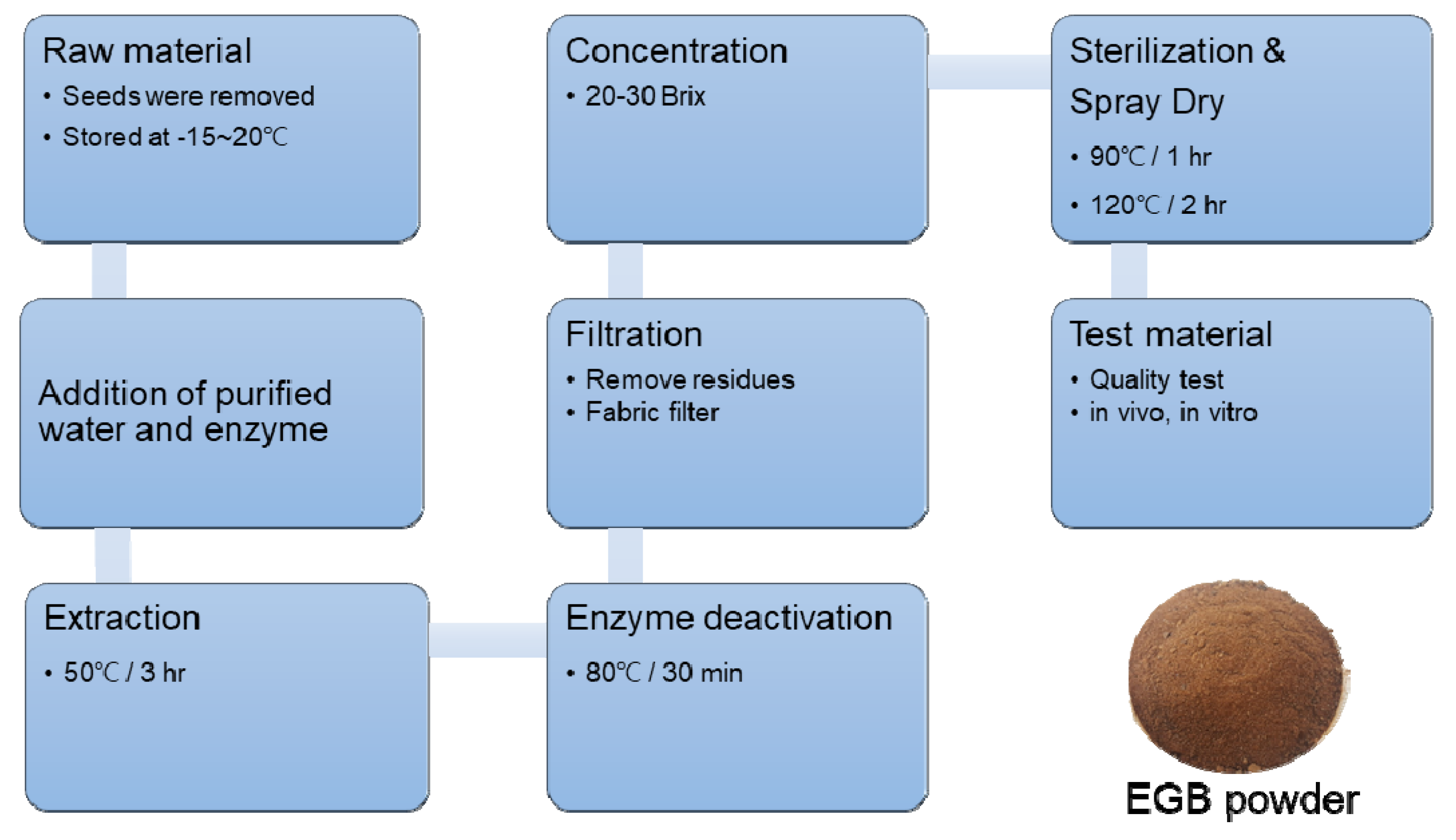
3.1. Preparation of Ginseng Berry Extract by Enzyme Treatment
3.2. Preparation of Sample and Standard Solutions
3.3. Analysis of Ginsenosides Using UPLC-QTOF/MS
3.4. Animals
3.5. Induction of AILD and Measurement of Biochemical Parameters
3.6. Cell Culture
3.7. Cell Viability
3.8. Nitric Oxide, PGE2, and Cytokine Assays
3.9. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frazier, T.H.; Stocker, A.M.; Kershner, N.A.; Marsano, L.S.; McClain, C.J. Treatment of alcoholic liver disease. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2011, 4, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramenzi, A.; Caputo, F.; Biselli, M.; Kuria, F.; Loggi, E.; Andreone, P.; Bernardi, M. Review article: Alcoholic liver diseased pathophysiological aspects and risk factors. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, H.; Nakanishi, K. Proof of the mysterious efficacy of ginseng: Basic and clinical trials: Clinical effects of medical ginseng, Korean red ginseng: Specifically, its anti-stress action for prevention of disease. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 95, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, K.; Alexander, G. Alcoholic liver disease. Postgrad. Med. J. 2000, 76, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lieber, C.S. Biochemical and molecular basis of alcohol-induced injury to liver and other tissues. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Purohit, V.; Gao, B.; Song, B.J. Molecular mechanisms of alcoholic fatty liver. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.K.; Nayak, P.; Vasudevan, D.M. Biochemical markers for alcohol consumption. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2003, 18, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, K.T. Botanical characteristics, pharmacological effects and medicinal components of Korean Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.H. A review on the medicinal potentials of ginseng and ginsenosides on cardiovascular diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, K.K.; Gong, X.J. A review on the medicinal potentials of Panax ginseng saponins in diabetes mellitus. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 47353–47366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.D.; Rhee, D.K.; Lee, Y.H. Biological activities and chemistry of saponins from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Phytochem. Rev. 2005, 4, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Yoo, D.S.; Xu, H.; Park, N.I.; Kim, H.H. Ginsenoside content of berries and roots of three typical Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng) cultivars. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Wu, J.A.; Mcentee, E.; Yuan, C.S. Saponins composition in American ginseng leaf and berry assayed by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2261–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.W.; Wang, C.Z.; Yuan, C.S. Isolation and analysis of ginseng: Advances and challenges. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 467–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, L.; Xiao, E.L.; Li, S.J.; Chen, J.J.; Gao, B.; Min, G.N.; Wang, J.P.; Wu, Y.J. Ginsenoside-Rd exhibits anti-inflammatory activities through elevation of antioxidant enzyme activities and inhibition of JNK and ERK activation in vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Morikawa, T.; Kashima, Y.; Ninomiya, K.; Matsuda, H. Structures of New Dammarane-Type Triterpene Saponins from the Flower Buds of Panax notoginseng and Hepatoprotective Effects of Principal Ginseng Saponins. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lia, P.; Lva, B.; Jianga, X.; Wanga, T.; Ma, X.; Chang, N.; Wang, X.; Gao, X. Identification of NF-κB inhibitors following Shenfu injection and bioactivity-integrated UPLC/Q-TOF-MS and screening for related anti-inflammatory targets in vitro and in silico. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, N.H.; Song, G.Y.; Woo, S.H.; Hyun, J.W.; Koh, Y.S.; Kang, H.K.; Shoyama, Y.; Kim, Y.H. Ginsenosides from the Leaves and Flower Buds of Panax ginseng and their Pharmacological Effects. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2012, 8, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, K.M.; Lee, J.H.; Jeon, H.Y.; Park, C.W.; Hong, D.K. Pharmacokinetic study of ginsenoside Re with pure ginsenoside Re and ginseng berry extracts in mouse using ultra performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometric method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Suh, H.J.; Lee, H.S. A study on the utilization of enzyme treated ginseng leaf for cosmeceutical ingredient. Asian J. Beauty Cosmetol. 2010, 8, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.C.; Cho, J.W.; Lee, Y.K.; Yoo, K.M.; Rho, J.H. Antioxidant Activity of Ginseng Extracts Prepared by Enzyme and Heat Treatment. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 36, 1482–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, M.R.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Suh, H.J. Changes of ginsenoside content by mushroom mycelial fermentation in Red ginseng extract. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Im, K.S.; Chang, E.H.; Je, N.G. A modified alkaline hydrolysis of total ginsenosides yielding genuine aglycones and prosapogenol. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1995, 18, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, R.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; He, Y.; Yang, C. Complete assignments of 1H and 13C NMR data for nine protopanaxatriol glycosides. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2002, 40, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.-K.; Xu, F.; Gong, X.-J. Isolation, purification and quantification of ginsenoside F5 and F3 isomeric compounds from crude extracts of flower buds of Panax ginseng. Molecules 2016, 21, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.G.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, J.W.; Park, H.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Yang, D.C.; Baek, N.I. Physicochemical characterization and NMR assignments of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rc, and Rd isolated from Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2010, 34, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.D.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, T.; Jang, S.A.; Kang, S.C.; Koo, H.J.; Sohn, E.; Bak, J.P.; Namkoong, S.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Protects against Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage by Modulating Inflammatory Mediators in Mice and HepG2 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checha, F.; Kaplowitz, N. Oxidative stress and alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Health Res. World 1997, 21, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Nikam, P.; Nikam, S.; Sontakke, A.; Khanwelkar, C. Biochemical Changes in Alcoholic Hepatitis with Phyllanthus Amarus Therapy: A Study. Biomed. Res. 2009, 20, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, A. Glutathione peroxidise. In Enzymatic Basis of Detoxification; Jokby, W.B., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 333–348. [Google Scholar]
- Bode, C.; Kugler, V.; Bode, J.C. Endotoxemia in patients with alcoholic and non-alcoholic cirrhosis and in subjects with no evidence of chronic liver disease following acute alcohol excess. J. Hepatol. 1987, 4, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R. Endotoxemia and gut barrier dysfunction in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 50, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Bala, S. Alcoholic liver disease and the gut-liver axis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginseng GAP Standard Cultivation Guideline; Rural Development Administration: Suwon, Korea, 2009; pp. 47–117. ISBN 11-1390625-000051-01.
- Harrison-Findik, D.D.; Schafer, D.; Klein, E.; Timchenko, N.A.; Kulaksiz, H.; Clemens, D.; Fein, E.; Andriopoulos, B.; Pantopoulos, K.; Gollan, J. Alcohol metabolism-mediated oxidative stress down-regulates hepcidin transcription and leads to increased duodenal iron transporter expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22974–22982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Compounds | Rt b (min) | Calibration Curve c | R2 | Line Arrangement (μg/mL) | LOD (ppm) | LOQ (ppm) | Amount (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.69 | y = 1333.7x + 5378.3 | 0.998 | 0.5–60 | 0.010 | 0.034 | 45.9 |
| 2 | 13.52 | y = 1137.3x + 251.22 | 0.998 | 0.01–10 | 0.015 | 0.049 | 3.3 |
| 3 | 13.99 | y = 1137.3x + 251.22 | 0.999 | 1–10 | 0.004 | 0.012 | 4.0 |
| 4 | 19.12 | y = 3295.6x + 10613 | 0.998 | 1–20 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 6.2 |
| Optimal Q-TOF/MS Condition | |
|---|---|
| Ion Source | ESI Negative Mode |
| Source Temp. and Desolvation Temp. | 120 °C/550 °C |
| Cone Gas and Desolvation Gas Flow | 30 L/h/800 L/h |
| Capillary and Cone Volt | 3 kV/40 V |
| Mass Range (m/z) | 100 to 1500 |
| Collision Energy Range | 20 to 45 eV |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Yoon, D.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, G.-S.; Yoo, Y.C. Ginseng Berry Prevents Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage by Improving the Anti-Inflammatory System Damage in Mice and Quality Control of Active Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143522
Lee DY, Kim M-J, Yoon D, Lee Y-S, Kim G-S, Yoo YC. Ginseng Berry Prevents Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage by Improving the Anti-Inflammatory System Damage in Mice and Quality Control of Active Compounds. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(14):3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143522
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dae Young, Min-Jee Kim, Dahye Yoon, Young-Seob Lee, Geum-Soog Kim, and Yung Choon Yoo. 2019. "Ginseng Berry Prevents Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage by Improving the Anti-Inflammatory System Damage in Mice and Quality Control of Active Compounds" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 14: 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143522
APA StyleLee, D. Y., Kim, M.-J., Yoon, D., Lee, Y.-S., Kim, G.-S., & Yoo, Y. C. (2019). Ginseng Berry Prevents Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage by Improving the Anti-Inflammatory System Damage in Mice and Quality Control of Active Compounds. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143522






