Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and Its Metabolites from Environmental Water Samples Using Ionic Liquid Modified Magnetic Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 as Sorbent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
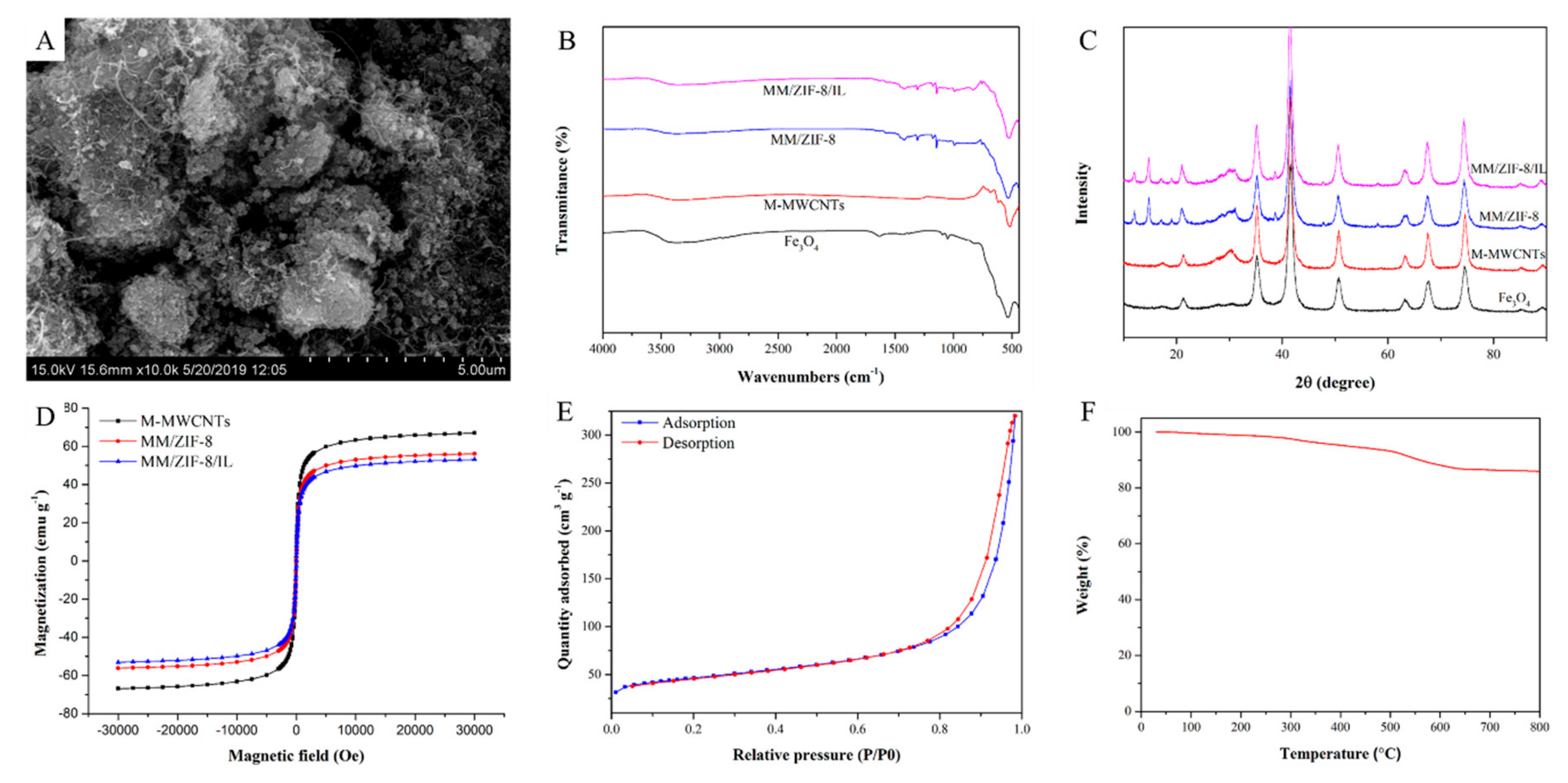
2.1. Characterization of MM/ZIF-8/IL
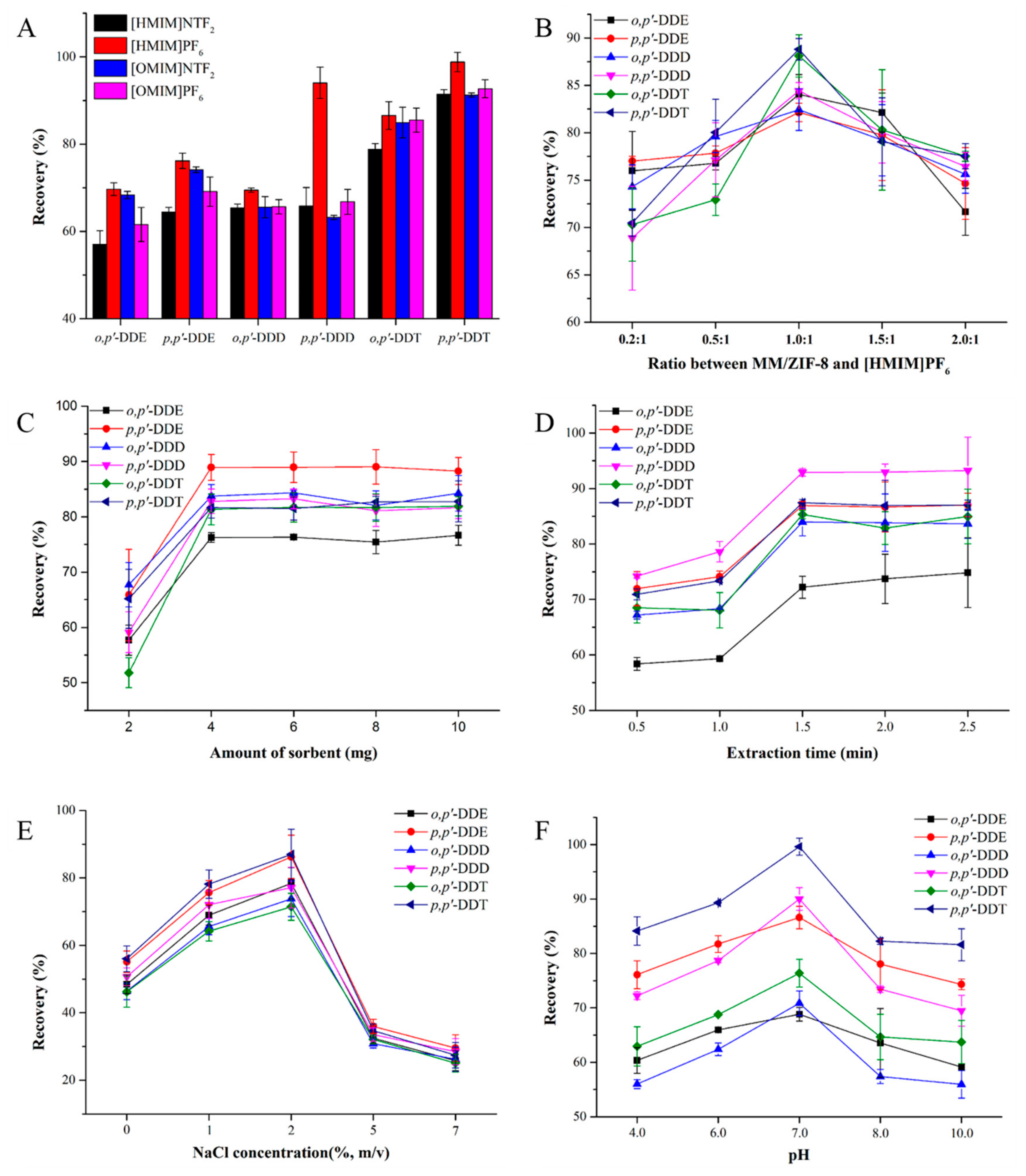
2.2. Optimization of the Extraction Conditions
2.3. Optimization of the Desorption Conditions
2.4. Method Validation
2.5. Comparison of the MM/ZIF-8/IL-Based Method with other Reported Methods
2.6. Real Sample Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.4. Preparation of MM/ZIF-8/IL
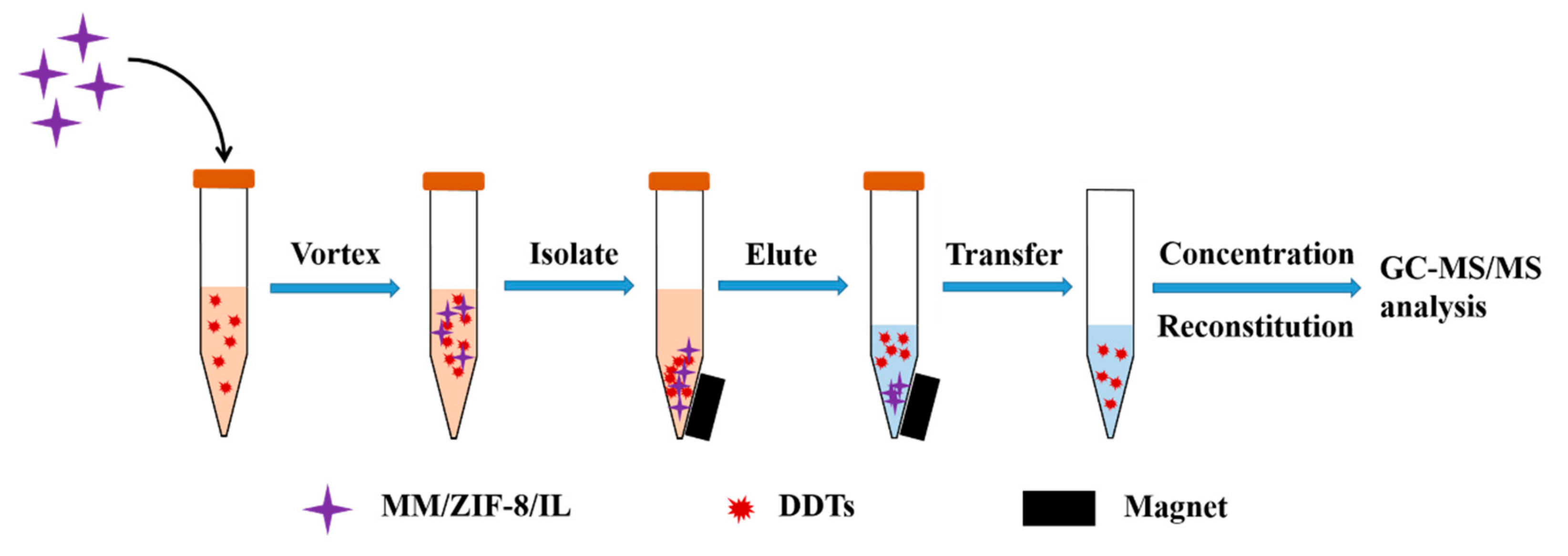
3.5. Extraction Procedure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rani, M.; Shanker, U.; Jassal, V. Recent strategies for removal and degradation of persistent & toxic organochlorine pesticides using nanoparticles: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Han, S.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, G.; Liu, W.; Ma, L.; Luo, M.; Xu, D. Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in surface water around Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24824–24833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadnejad, M.; Farhadpour, M.; Mahdavi, V.; Tabrizchi, M. Rapid monitoring and sensitive determination of DDT and its metabolites in water sample using solid-phase extraction followed by ion mobility spectrometry. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spectrom. 2017, 20, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo, S.N.; Merib, J.; Dias, A.N.; Stolberg, J.; Budziak, D.; Carasek, E. A low-cost biosorbent-based coating for the highly sensitive determination of organochlorine pesticides by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-electron capture detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1525, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferronato, G.; Viera, M.S.; Prestes, O.D.; Adaime, M.B.; Zanella, R. Determination of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in breast milk from Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, using a modified QuEChERS method and gas chromatography-negative chemical ionisation-mass spectrometry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahpishanian, S.; Sereshti, H. One-step green synthesis of β-cyclodextrin/iron oxide-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite with high supramolecular recognition capability: Application for vortex-assisted magnetic solid phase extraction of organochlorine pesticides residue from honey samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1485, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hemmati, M.; Rajabi, M.; Asghari, A. Magnetic nanoparticle based solid-phase extraction of heavy metal ions: A review on recent advances. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Guo, Q.; Chen, X.; Xue, T.; Wang, H.; Yao, P. Rapid and effective sample clean-up based on magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes for the determination of pesticide residues in tea by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wu, R.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Chan, T.W.D. Magnetic porous carbon derived from a bimetallic metal–organic framework for magnetic solid-phase extraction of organochlorine pesticides from drinking and environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1479, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.T.; Zheng, X.; Li, H.F.; Lin, J.M. Application of carbon-based nanomaterials in sample preparation: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 784, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ding, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Q.; Hou, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, H.; Ding, L.; Ren, N. Fast determination of sulfonamides from egg samples using magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes as adsorbents followed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Gao, Q.; Li, X.-S.; Huang, W.; Shi, Z.-G.; Feng, Y.-Q. Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on magnetic carbon nanotube for the determination of estrogens in milk. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, V.; Zougagh, M.; Ríos, Á. Hybrid nanoparticles based on magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotube-nanoC18SiO2 composites for solid phase extraction of mycotoxins prior to their determination by LC-MS. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Vortex assisted magnetic solid phase extraction of lead (II) and cobalt (II) on silica coated magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes impregnated with 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 224, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wei, F.; Luo, Y.B.; Ding, J.; Xiao, N.; Feng, Y.Q. Rapid magnetic solid-phase extraction based on magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in edible oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12794–12800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Jiang, L.; Wu, G.; Xia, Y.; Lu, W.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Determination of six sulfonylurea herbicides in environmental water samples by magnetic solid-phase extraction using multi-walled carbon nanotubes as adsorbents coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1466, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Xu, D.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Zheng, S.; Lin, H.; Gao, H. Novel zeolitic imidazolate frameworks based on magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes for magnetic solid-phase extraction of organochlorine pesticides from agricultural irrigation water samples. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, L.; Huang, X.; Zheng, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, H.; Xu, D. Adsorption and removal of organophosphorus pesticides from environmental water and soil samples by using magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes @ organic framework ZIF-8. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 10772–10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobday, C.L.; Bennett, T.D.; Fairen-Jimenez, D.; Graham, A.J.; Morrison, C.A.; Allan, D.R.; Düren, T.; Moggach, S.A. Tuning the swing effect by chemical functionalization of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhu, L.; Xia, X.; Tang, H. The water–resistant zeolite imidazolate framework 67 is a viable solid phase sorbent for fluoroquinolones while efficiently excluding macromolecules. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.B.; Liu, Q.; Trickett, C.A.; Gutiérrez-Puebla, E.; Monge, M.Á.; Cong, H.; Aldossary, A.; Deng, H.; Yaghi, O.M. Principles of designing extra-large pore openings and cages in zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6448–6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Feng, G.; Song, Z.; Zhou, Y.P.; Chao, H.Y.; Yuan, D.; Tan, T.T.Y.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Z.; Tang, B.Z.; et al. Two-dimensional metal–organic framework with wide channels and responsive turn-on fluorescence for the chemical sensing of volatile organic compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7241–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, K.; Zhang, T.; Lin, W. Postsynthetic metalation of bipyridyl-containing metal–organic frameworks for highly efficient catalytic organic transformations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6566–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, Y. Zeolitic imidazolate framework materials: Recent progress in synthesis and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16811–16831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bux, H.; Liang, F.; Li, Y.; Cravillon, J.; Wiebcke, M.; Caro, J. Zeolitic imidazolate framework membrane with molecular sieving properties by microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16000–16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, B.; Zohrabi, P.; Raza, N.; Kim, K.H. Metal-organic frameworks as advanced sorbents for the extraction and determination of pollutants from environmental, biological, and food media. TrAC-Trend. Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; González-Hernández, P.; Pino, V.; Pasán, J.; Afonso, A.M. Metal-organic frameworks as novel sorbents in dispersive-based microextraction approaches. TrAC-Trend. Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Chen, B.; Koo, Y.-M.; MacFarlane, D.R. Introduction: Ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6633–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Qu, J. Ionic liquids as lubricant additives: A review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3209–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, A.; Ruiz-Ángel, M.J.; Carda-Broch, S. Recent advances on ionic liquid uses in separation techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1559, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; e Silva, F.A.; Quental, M.V.; Mondal, D.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic-liquid-mediated extraction and separation processes for bioactive compounds: Past, present, and future trends. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6984–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumes, B.H.; Silva, M.R.; Andrade, F.N.; Nazario, C.E.D.; Lanças, F.M. Recent advances and future trends in new materials for sample preparation. TrAC-Trend. Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, P.; Zhou, Y. Preparation of ionic liquid modified magnetic metal‒organic frameworks composites for the solid-phase extraction of α–chymotrypsin. Talanta 2018, 182, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, L.; Xu, X.; Zheng, S.; Xu, D.; Gao, H. Preparation of a magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotube@polydopamine/zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 composite for magnetic solid-phase extraction of triazole fungicides from environmental water samples. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 25351–25360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davudabadi Farahani, M.; Shemirani, F. Supported hydrophobic ionic liquid on magnetic nanoparticles as a new sorbent for separation and preconcentration of lead and cadmium in milk and water samples. Microchim. Acta 2012, 179, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Ding, J. A core-shell magnetic metal organic framework of type Fe3O4@ZIF-8 for the extraction of tetracycline antibiotics from water samples followed by ultra-HPLC-MS analysis. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4091–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wu, X.; Xi, X.; Zhang, P.; Yang, X.; Lu, R.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Li, J. Using β-cyclodextrin/attapulgite-immobilized ionic liquid as sorbent in dispersive solid-phase microextraction to detect the benzoylurea insecticide contents of honey and tea beverages. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Li, Z.; Zang, X.; Wang, Z. Metal-organic framework derived magnetic nanoporous carbon: Novel adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 12199–12205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, G.; Xiao, J. Enrichment and sensitive determination of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and its metabolites with temperature controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid phase microextraction prior to high performance liquid phase chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 651, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qu, B.; Liu, H.; Ding, J.; Ren, N. Analysis of organochlorine pesticides in surface water of the Songhua River using magnetoliposomes as adsorbents coupled with GC-MS/MS detection. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Lee, H.K. Micro-solid-phase extraction of organochlorine pesticides using porous metal‒organic framework MIL-101 as sorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1401, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |

| DDTs | Calibration Equation | Linear Range (µg L−1) | R2 | LOD (µg L−1) | RSDa (%) (n = 6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intraday | Interday | |||||
| o,p′-DDE | y = 4916.2x − 39626 | 0.5–500 | 0.9956 | 0.0016 | 5.5 | 7.1 |
| p,p′-DDE | y = 4303.6x − 28468 | 0.5–500 | 0.9971 | 0.0021 | 2.3 | 4.5 |
| o,p′-DDD | y = 7825.8x − 64397 | 0.5–500 | 0.9955 | 0.0034 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| p,p′-DDD | y = 7345.3x − 73748 | 0.5–500 | 0.9934 | 0.0033 | 6.5 | 8.9 |
| o,p′-DDT | y = 6887.9x − 54005 | 0.5–500 | 0.9953 | 0.0032 | 2.9 | 5.4 |
| p,p′-DDT | y = 5730.4x − 59956 | 0.5–500 | 0.9927 | 0.0072 | 1.9 | 6.3 |
| Method | Sorbent | Sample Amount (mL) | Sorbent Amount (mg) | Extraction Time (min) | Type and Volume of Eluent (mL) | Desorption Time (min) | Linear Range | LOD | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSPE-GC-MS/MS | Magnetoliposome | 400 | 140 | 20 | Acetonitrile, 3.0; acetone, 3.0 | 2 | 1–125 ng L−1 | 0.35 ng L−1 | [40] | ||
| μ-SPE-GC-MS | MIL-101 | 10 | - | 40 | Ethyl acetate, 0.1 | 15 | 0.05–50 μg L−1 | 0.003 µg L−1 | [41] | ||
| MSPE-GC-MS | BMZIF-derived porous carbon a | 10 | 6 | 10 | Dichloromethane, 2 | 10 | 2–500 ng L−1 | 0.39–0.65 ng L−1 | [9] | ||
| MSPE-GC-MS/MS | M-M-ZIF-67 b | 5 | 6 | 20 | Acetonitrile, 4 | 10 | 1–200 µg L−1 | 0.07–1.03 µg L−1 | [17] | ||
| MSPE-GC-MS/MS | MM/ZIF-8/IL | 10 | 4 | 1.5 | Ethyl acetate, 1.6 | 4 | 0.5–500 µg L−1 | 0.0016–0.0072 µg L−1 | This work |
| Matrix | Analyte | Spiked Concentration (µg L−1) (n = 3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 100 | ||||
| Found | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Tap water | o,p′-DDE | ND. a | 87.8 | 2.7 | 93.7 | 1.5 |
| p,p′-DDE | ND. | 95.3 | 2.7 | 95.4 | 2.3 | |
| o,p′-DDD | ND. | 95.0 | 2.5 | 94.3 | 2.2 | |
| p,p′-DDD | ND. | 90.0 | 2.9 | 93.4 | 2.2 | |
| o,p′-DDT | ND. | 81.0 | 4.1 | 85.5 | 3.4 | |
| p,p′-DDT | ND. | 93.1 | 0.6 | 97.5 | 0.5 | |
| River water | o,p′-DDE | ND. | 79.8 | 1.4 | 88.2 | 2.6 |
| p,p′-DDE | ND. | 89.4 | 1.8 | 93.9 | 2.1 | |
| o,p′-DDD | ND. | 81.6 | 1.2 | 85.1 | 1.4 | |
| p,p′-DDD | ND. | 96.6 | 1.8 | 98.5 | 0.7 | |
| o,p′-DDT | ND. | 82.2 | 1.7 | 90.7 | 1.5 | |
| p,p′-DDT | ND. | 84.7 | 1.7 | 91.2 | 1.6 | |
| Underground water | o,p′-DDE | ND. | 87.3 | 0.4 | 89.6 | 1.1 |
| p,p′-DDE | ND. | 85.4 | 1.7 | 95.4 | 0.8 | |
| o,p′-DDD | ND. | 95.1 | 1.9 | 96.8 | 1.0 | |
| p,p′-DDD | ND. | 84.7 | 3.3 | 85.7 | 1.6 | |
| o,p′-DDT | ND. | 72.6 | 1.9 | 84.7 | 1.8 | |
| p,p′-DDT | ND. | 87.7 | 1.8 | 91.8 | 0.8 | |
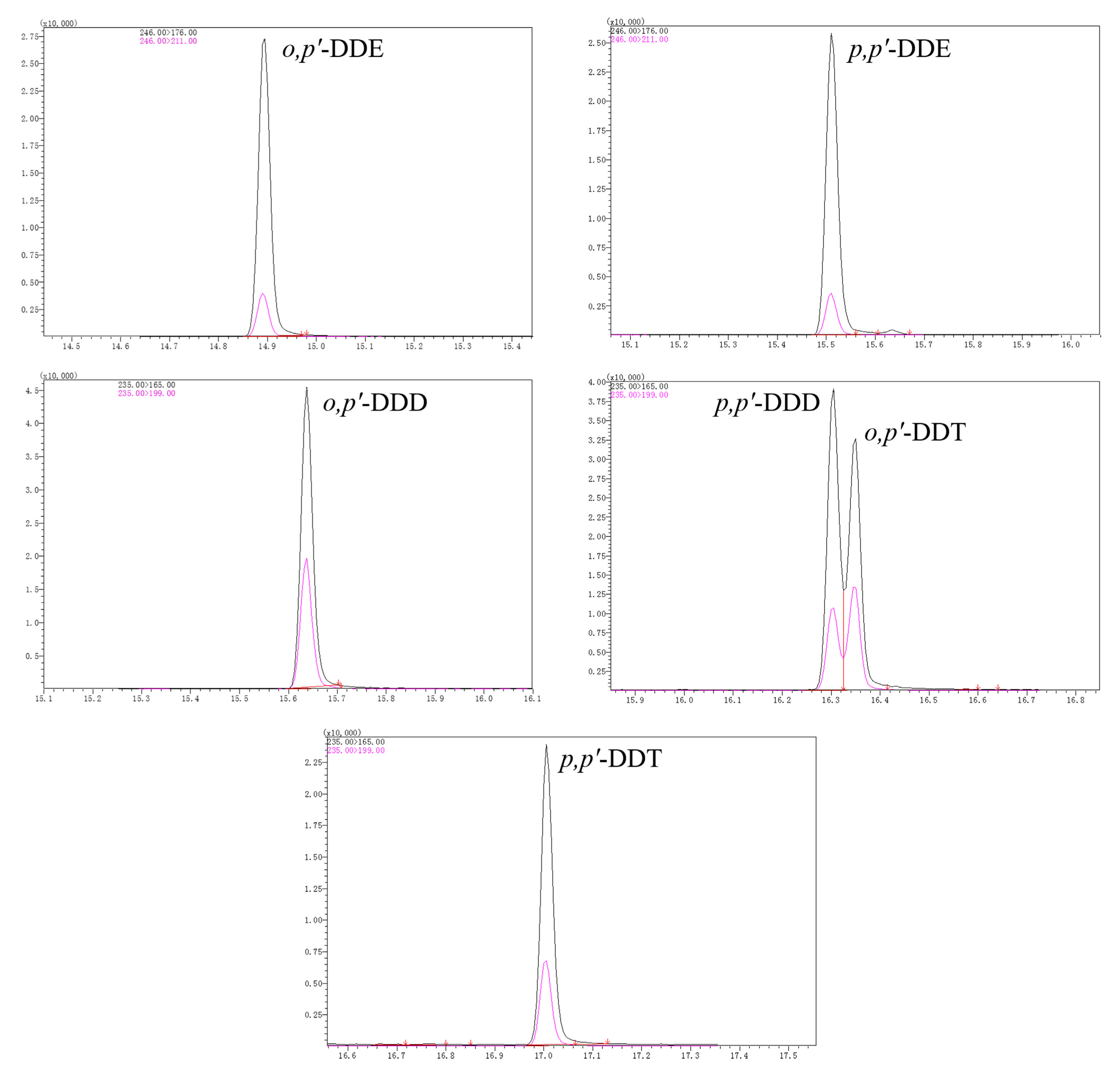
| DDTs | tR (min) | MRM1 (m/z) | CE1 a (eV) | MRM2 (m/z) | CE2 (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| o,p′-DDE | 14.943 | 246.00 > 176.00 | 30 | 246.00 > 211.00 | 22 |
| p,p′-DDE | 15.560 | 246.00 > 176.00 | 30 | 246.00 > 211.00 | 22 |
| o,p′-DDD | 15.600 | 235.00 > 165.00 | 24 | 235.00 > 199.00 | 14 |
| p,p′-DDD | 16.350 | 235.00 > 165.00 | 24 | 235.00 > 199.00 | 14 |
| o,p′-DDT | 16.402 | 235.00 > 165.00 | 24 | 235.00 > 199.00 | 16 |
| p,p′-DDT | 17.058 | 235.00 > 165.00 | 24 | 235.00 > 199.00 | 16 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Lv, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Xu, D. Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and Its Metabolites from Environmental Water Samples Using Ionic Liquid Modified Magnetic Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 as Sorbent. Molecules 2019, 24, 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152758
Huang X, Liu Y, Liu H, Liu G, Xu X, Li L, Lv J, Liu Z, Zhou W, Xu D. Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and Its Metabolites from Environmental Water Samples Using Ionic Liquid Modified Magnetic Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 as Sorbent. Molecules. 2019; 24(15):2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152758
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiaodong, Yanan Liu, Huifang Liu, Guangyang Liu, Xiaomin Xu, Lingyun Li, Jun Lv, Zhongxiao Liu, Wenfeng Zhou, and Donghui Xu. 2019. "Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and Its Metabolites from Environmental Water Samples Using Ionic Liquid Modified Magnetic Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 as Sorbent" Molecules 24, no. 15: 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152758
APA StyleHuang, X., Liu, Y., Liu, H., Liu, G., Xu, X., Li, L., Lv, J., Liu, Z., Zhou, W., & Xu, D. (2019). Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and Its Metabolites from Environmental Water Samples Using Ionic Liquid Modified Magnetic Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 as Sorbent. Molecules, 24(15), 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152758







