Combination of Low-Temperature Electrosurgical Unit and Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Molecular Profiling and Classification of Tissues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
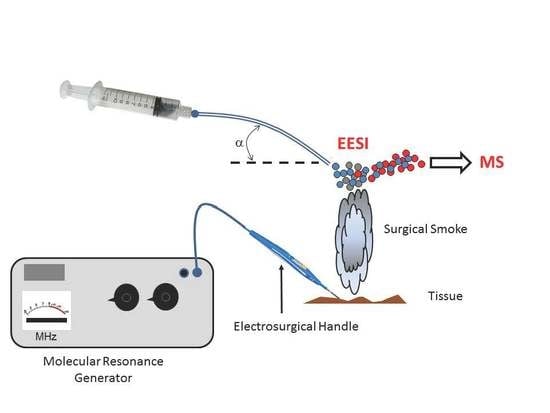
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirnezami:, R.; Spagou, K.; Vorkas, P.A.; Lewis, M.R.; Kinross, J.; Want, E.; Shion, H.; Goldin, R.D.; Darzi, A.; Takats, Z.; et al. Chemical mapping of the colorectal cancer microenvironment via MALDI imaging mass spectrometry (MALDI-MSI) reveals novel cancer-associated field effects. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Mandal, R.; Catherman, A.; Thomas, P.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; Ikonomidou, C.; Li, L. Top-down proteomics with mass spectrometry imaging: A pilot study towards discovery of biomarkers for neurodevelopmental disorders. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, K.C.; Szaniszló, T.; Günther, S.; Balog, J.; Dénes, J.; Keserü, M.; Dezsö, B.; Tóth, M.; Spengler, B.; Takáts, Z. In situ, real-time identification of biological tissues by ultraviolet and infrared laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolman, M.; Ferry, I.; Kuzan-Fischer, C.M.; Wu, M.; Zou, J.; Kiyota, T.; Isik, S.; Dara, D.; Aman, A.; Das, S.; et al. Rapid determination of medulloblastoma subgroup affiliation with mass spectrometry using a handheld picosecond infrared laser desorption probe. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6508–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woolman, M.; Gribble, A.; Bluemke, E.; Zou, J.; Ventura, M.; Bernards, N.; Wu, M.; Ginsberg, H.J.; Das, S.; Vitkin, A.; et al. Optimized Mass Spectrometry Analysis Workflow with Polarimetric Guidance for ex vivo and in situ Sampling of Biological Tissues. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takats, Z.; Wiseman, J.M.; Gologan, B. Mass Spectrometry Sampling Under Ambient Conditions with Desorption Electrospray Ionization. Science 2004, 306, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarmusch, A.K.; Alfaro, C.M.; Pirro, V.; Hattab, E.M.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A.; Cooks, R.G. Differential Lipid profiles of normal human brain matter and gliomas by positive and negative mode desorption electrospray ionization—Mass spectrometry imaging. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, M.; Gharpure, K.; Tibshirani, R.; Zhang, J.; Liang, L.; Liu, J.; Young, J.H.; Dood, R.L.; Sood, A.K.; Eberlin, L.S. Metabolic markers and statistical prediction of serous ovarian cancer aggressiveness by ambient ionization mass spectrometry imaging. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2903–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Lai, Y.-H.; So, P.-K.; Chen, H.; Yao, Z.-P. Direct ionization of biological tissue for mass spectrometric analysis. Analyst 2012, 137, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerian, K.S.; Jarmusch, A.K.; Pirro, V.; Koch, M.O.; Masterson, T.A.; Cheng, L.; Cooks, R.G. Differentiation of prostate cancer from normal tissue in radical prostatectomy specimens by desorption electrospray ionization and touch spray ionization mass spectrometry. Analyst 2015, 140, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, W.; Chingin, K.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wen, H.; Ding, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, H. Tissue spray ionization mass spectrometry for rapid recognition of human lung squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirro, V.; Seró, R.; Jarmusch, A.K.; Alfaro, C.M.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A.; Hattab, E.M.; Cooks, R.G. Analysis of human gliomas by swab touch spray—Mass spectrometry: Applications to intraoperative assessment of surgical margins and presence of oncometabolites. Analyst 2017, 142, 4058–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kertesz, V.; Van Berkel, G.J. Fully automated liquid extraction-based surface sampling and ionization using a chip-based robotic nanoelectrospray platform. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Rector, J.; Lin, J.Q.; Young, J.H.; Sans, M.; Katta, N.; Giese, N.; Yu, W.; Nagi, C.; Suliburk, J.; et al. Nondestructive tissue analysis for ex vivo and in vivo cancer diagnosis using a handheld mass spectrometry system. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sans, M.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.Q.; Feider, C.L.; Giese, N.; Breen, M.T.; Sebastian, K.; Liu, J.; Sood, A.K.; Eberlin, L.S. Performance of the MasSpec Pen for Rapid Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balog, J.; Szaniszló, T.; Schaefer, K.-C.; Denes, J.; Lopata, A.; Godorhazy, L.; Szalay, D.; Balogh, L.; Sasi-Szabó, L.; Toth, M.; et al. Identification of biological tissues by rapid evaporative ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7343–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St John, E.R.; Balog, J.; McKenzie, J.S.; Rossi, M.; Covington, A.; Muirhead, L.; Bodai, Z.; Rosini, F.; Speller, A.V.M.; Shousha, S.; et al. Rapid evaporative ionisation mass spectrometry of electrosurgical vapours for the identification of breast pathology: Towards an intelligent knife for breast cancer surgery. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.; Gildea, L.; Balog, J.; Speller, A.; McKenzie, J.; Muirhead, L.; Scott, A.; Kontovounisios, C.; Rasheed, S.; Teare, J.; et al. A novel methodology for in vivo endoscopic phenotyping of colorectal cancer based on real-time analysis of the mucosal lipidome: A prospective observational study of the iKnife. Surg. Endosc. Other Interv. Tech. 2017, 31, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, A.; Mansoori, P.; Sandoval, L.F.; Feldman, S.R.; Pearce, D.; Williford, P.M. Electrosurgery: Part I. Basics and principles. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 591.e1–591.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr-Locke, D.L.; Day, J. Principles of electrosurgery. In Successful Training in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Helmut, W.; Jurgen, L.; Hans-Jurgen, W.; Rainer, M.; Hans-Dieter, L. Characterization of tissue interaction by analyzation of electrosurgial smoke. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–23 September 1995; pp. 643–644. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, W.L.; Garber, S.M. Surgical smoke—A review of the literature. Is this just a lot of hot air? Surg. Endosc. Other Interv. Tech. 2003, 17, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensman, C.; Baty, D.; Willis, R.G.; Cuschieri, A. Chemical composition of smoke produced by high-frequency electrosurgery in a closed gaseous environment An in vitro study. Surg. Endosc. Other Interv. Tech. 1998, 12, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanker, D.; Vankov, A.; Jayaraman, P. On mechanisms of interaction in electrosurgery. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 123022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balog, J.; Sasi-Szabo, L.; Kinross, J.; Lewis, M.R.; Muirhead, L.J.; Veselkov, K.; Mirnezami, R.; Dezso, B.; Damjanovich, L.; Darzi, A.; et al. Intraoperative Tissue Identification Using Rapid Evaporative Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 194ra93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, S.; Schäfer, K.C.; Balog, J.; Dénes, J.; Majoros, T.; Albrecht, K.; Tóth, M.; Spengler, B.; Takáts, Z. Electrospray post-ionization mass spectrometry of electrosurgical aerosols. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 22, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavon, M.; Calabrese, F.; Nicotra, S.; Marulli, G.; Pozzato, G.; Giacometti, C.; Valente, M.; Rea, F. Favorable tissue effects of quantum molecular resonance device (Vesalius) compared with standard electrocautery: A novel paradigm in lung surgery. Eur. Surg. Res. 2007, 39, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirhan, E.; Çukurova, İ.; Arslan, İ.B.; Ozkan, E.T.; Mengi, E.; Yigitbasi, O.G. Quantum Molecular Resonance–Assisted Phonomicrosurgery: Preliminary Experience. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, K.C.; Dénes, J.; Albrecht, K.; Szaniszló, T.; Balogh, J.; Skoumal, R.; Katona, M.; Tóth, M.; Balogh, L.; Takáts, Z. In vivo, in situ tissue analysis using rapid evaporative ionization mass spectrometry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8240–8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Venter, A.; Cooks, R.G. Extractive electrospray ionization for direct analysis of undiluted urine, milk and other complex mixtures without sample preparation. Chem. Commun. 2006, 2042–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, W.S.; Wang, R.; Hu, B.; Berchtold, C.; Meier, L.; Chen, H.; Zenobi, R. On the Mechanism of Extractive Electrospray Ionization. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4494–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, E.; Sud, M.; Cotter, D.; Subramaniam, S. LIPID MAPS online tools for lipid research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebisch, G.; Vizcaíno, J.A.; Köfeler, H.; Trötzmüller, M.; Griffiths, W.J.; Schmitz, G.; Spener, F.; Wakelam, M.J.O. Shorthand notation for lipid structures derived from mass spectrometry. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, H.; Xu, N.; Chen, H. Direct analysis of biological samples using extractive electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (EESI-MS). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2145–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, B.O.; Sui, J.; Young, A.B.; Whittal, R.M. Interferences and contaminants encountered in modern mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 627, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sukhikh, G.; Chagovets, V.; Wang, X.; Rodionov, V.; Kometova, V.; Tokareva, A.; Kononikhin, A.; Starodubtseva, N.; Chingin, K.; Chen, H.; et al. Combination of Low-Temperature Electrosurgical Unit and Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Molecular Profiling and Classification of Tissues. Molecules 2019, 24, 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162957
Sukhikh G, Chagovets V, Wang X, Rodionov V, Kometova V, Tokareva A, Kononikhin A, Starodubtseva N, Chingin K, Chen H, et al. Combination of Low-Temperature Electrosurgical Unit and Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Molecular Profiling and Classification of Tissues. Molecules. 2019; 24(16):2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162957
Chicago/Turabian StyleSukhikh, Gennady, Vitaliy Chagovets, Xinchen Wang, Valeriy Rodionov, Vlada Kometova, Alisa Tokareva, Alexey Kononikhin, Natalia Starodubtseva, Konstantin Chingin, Huanwen Chen, and et al. 2019. "Combination of Low-Temperature Electrosurgical Unit and Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Molecular Profiling and Classification of Tissues" Molecules 24, no. 16: 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162957
APA StyleSukhikh, G., Chagovets, V., Wang, X., Rodionov, V., Kometova, V., Tokareva, A., Kononikhin, A., Starodubtseva, N., Chingin, K., Chen, H., & Frankevich, V. (2019). Combination of Low-Temperature Electrosurgical Unit and Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Molecular Profiling and Classification of Tissues. Molecules, 24(16), 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162957