Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy on the Performance Degradation of LiFePO4/Graphite Lithium-Ion Battery Due to Charge-Discharge Cycling under Different C-Rates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
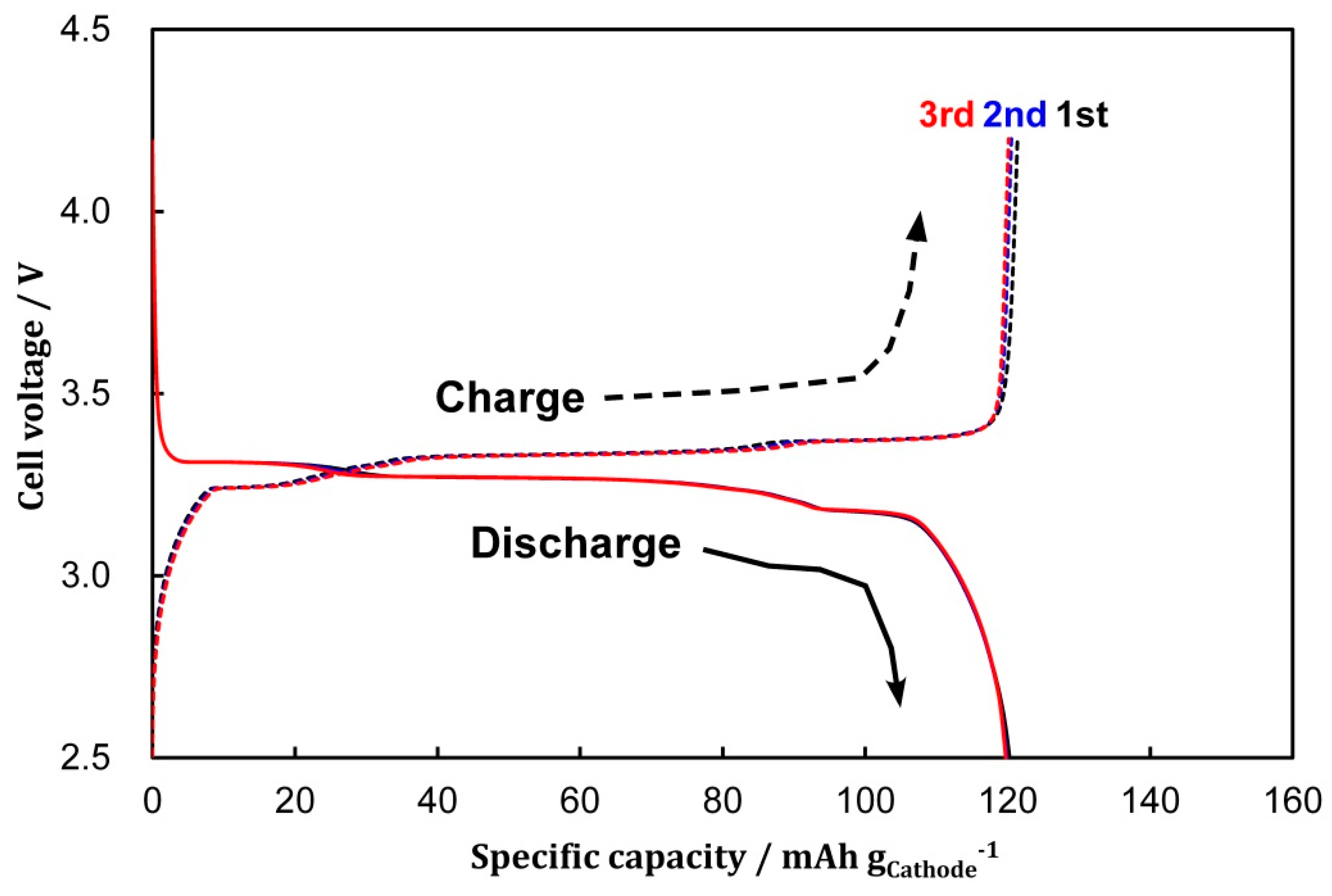
3.1. Cell Formation via CV
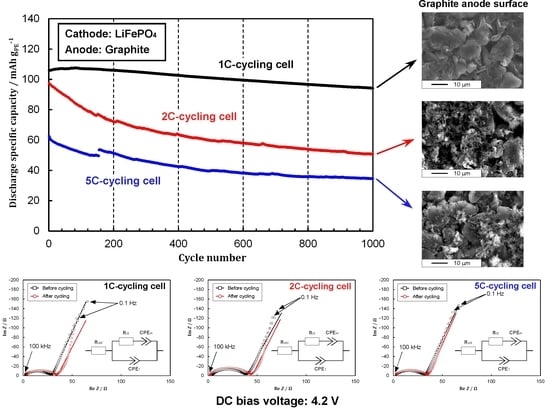
3.2. Cycling Performances under Different C-Rates
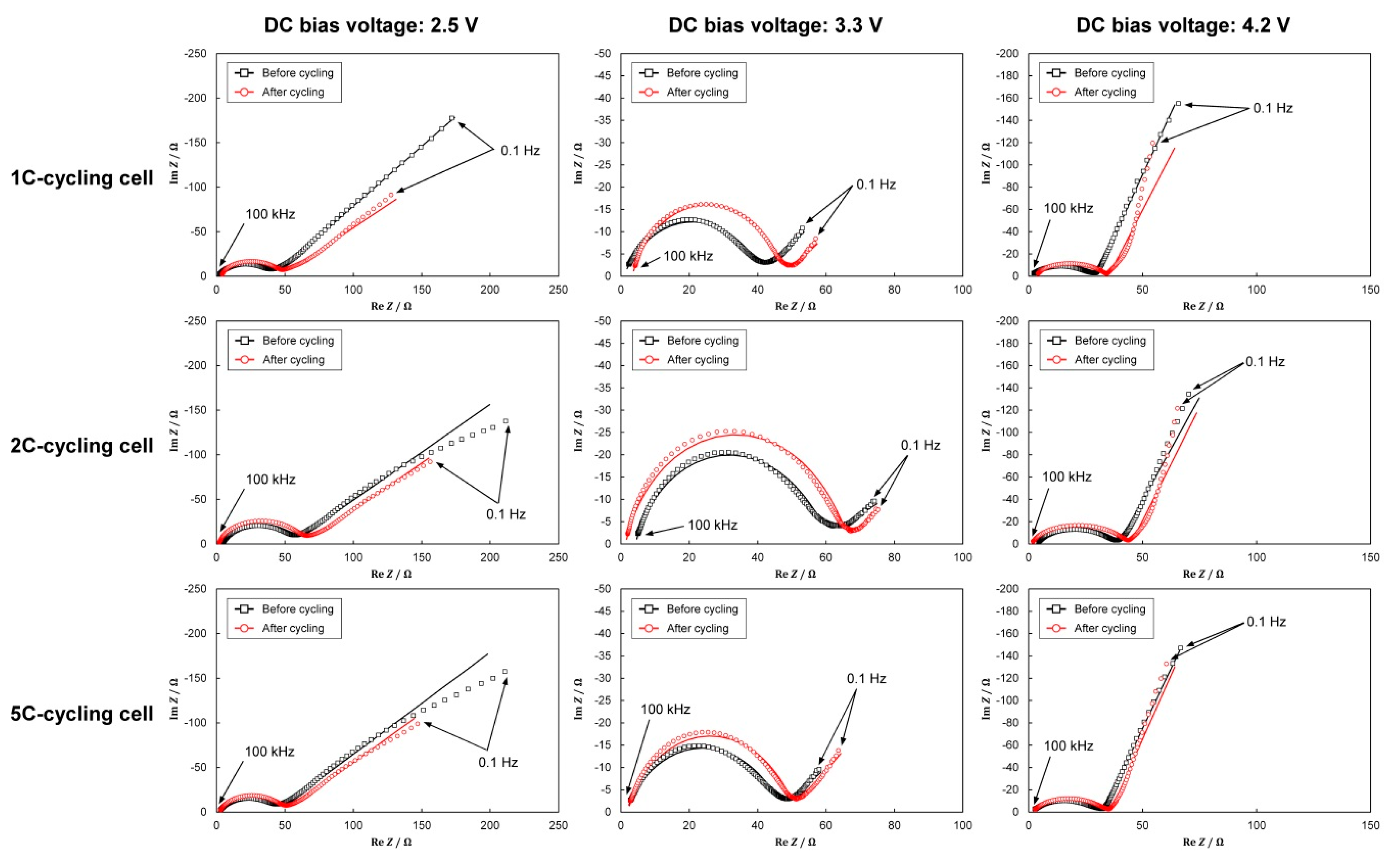
3.3. Impedance Analysis
3.4. Morphology Observation by SEM
3.5. Performance Degradation under Different C-Rates
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bresser, D.; Hosoi, K.; Howell, D.; Li, H.; Zeisel, H.; Amine, K.; Passerini, S. Perspectives of automotive battery R&D in China, Germany, Japan, and the USA. J. Power Sources 2018, 382, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubi, G.; Dufo-López, R.; Carvalho, M.; Pasapglu, G. The lithium-ion battery: State of the art and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placke, T.; Kloepsch, R.; Dühnen, S.; Winter, M. Lithium ion, lithium metal, and alternative rechargeable battery technologies: The odyssey for high energy density. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 1939–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, D.; Hain, H.; Lamp, P.; Maglia, F.; Stiaszny, B. Future high-energy density anode materials from an automotive application perspective. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 17174–17198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, D.; Kim, S.J.; Lamp, P.; Lux, S.F.; Maglia, F.; Paschos, O.; Stiaszny, B. Future generations of cathode materials: An automotive industry perspective. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 6709–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Mitra, S. Carbon coated submicron sized-LiFePO4: Improved high rate performance lithium battery cathode. Energy Procedia 2014, 54, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Bu, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C. A novel LiFePO4/graphene/carbon composite as a performance-improved cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 64, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zeng, T.; Qu, C.; Lu, H.; Jia, M.; Lai, Y.; Li, J. Cycle performance improvement of LiFePO4 cathode with polyacrylic acid as binder. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 80, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobukawa, H.; Alvarado, J.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Y.S. Electrochemical performance and interfacial investigation on Si composite anode for lithium ion batteries in full cell. J. Power Sources 2017, 359, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jung, M.J.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, Y.S. Electrochemical performances of lithium and sodium ion batteries based on carbon materials. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 61, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, A. Low voltage anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 7, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Xu, K.; Jow, T.R. EIS study on the formation of solid electrolyte interface in Li-ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 1636–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, Z. High-temperature capacity fading mechanism for LiFePO4/graphite soft-packed cell without Fe dissolution. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 754, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Guan, T.; Shen, B.; Leng, K.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yin, G. Changes of degradation mechanisms of LiFePO4/graphite batteries cycled at different ambient temperatures. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 237, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Xu, K.; Jow, T.R. The low temperature performance of Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2003, 115, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Sun, S.; Yu, F.; Gao, Y.; Fan, P.; Zuo, P.; Du, C.; Yin, G. The degradation of LiCoO2/graphite batteries at different rates. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 279, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; He, Y.B.; Qian, K.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Chiang, S.W.; Miao, C.; Kang, F.; Zhang, J. Deterioration of lithium iron phosphate/graphite power batteries under high-rate discharge cycling. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 176, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryden, T.S.; Holland, A.; Hilton, G.; Dimitrov, B.; Ponce de León Albarrán, C.; Cruden, A. Lithium-ion degradation at varying discharge rates. Energy Procedia 2018, 151, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Lin, Z.; Ju, Q.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, C.; Wang, Z. Electrochemical impedance spectra for lithium-ion battery ageing considering the rate of discharge ability. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, S. Impedance Analysis and Modeling of Lithium-Ion Batteries; LAMBERT Academic Publishing: Saarbrucken, Germany, 2016; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Orazem, M.E.; Tribollet, B. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; Chapter 13. [Google Scholar]
- Ovejas, V.J.; Cuadras, A. Impedance characterization of an LCO-NMC/graphite cell: Ohmic conduction, SEI transport and charge-transfer phenomenon. Batteries 2018, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyroubal, P.; Kazda, T. Equivalent circuit model parameters extraction for lithium ion batteries using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Energy Storage 2018, 15, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habte, B.T.; Jiang, F. Microstructure reconstruction and impedance spectroscopy study of LiCoO2, LiMn2O4 and LiFePO4 Li-ion battery cathodes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 268, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, T.; Mukoyama, D.; Nara, H.; Takami, N.; Momma, T.; Osaka, T. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis for lithium-ion battery using Li4Ti5O12 anode. J. Power Sources 2013, 222, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaka, T.; Momma, T.; Mukoyama, D.; Nara, H. Proposal of novel equivalent circuit for electrochemical impedance analysis of commercially available lithium ion battery. J. Power Sources 2012, 205, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.S.; Chiang, P.C.J.; Lin, J.C. Electrochemical investigations on advanced lithium-ion batteries by three-electrode measurements. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A47–A52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Haran, B.S.; Durairajan, A.; White, R.E.; Podrazhansly, Y.; Popov, B.N. Studies on capacity fade of lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2000, 91, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Kumagai, S. Effect of negative/positive capacity ratio on the rate and cycling performances of LiFePO4/graphite lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2018, 19, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Dedryvère, R.; Ledeuil, J.B.; Bréger, J.; Tessier, C.; Gonbeau, D. Aging mechanisms of LiFePO4 // graphite cells studied by XPS: Redox reaction and electrode/electrolyte interfaces. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A357–A363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| 1st Cycle | 2nd Cycle | 3rd Cycle | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Type | 1C-cycling | 2C-cycling | 5C-cycling | 1C-cycling | 2C-cycling | 5C-cycling | 1C-cycling | 2C-cycling | 5C-cycling |
| CapC * (mAh· gCathode−1) | 121 | 121 | 122 | 121 | 120 | 121 | 120 | 119 | 121 |
| CapD ** (mAh· gCathode−1) | 120 | 119 | 121 | 120 | 119 | 120 | 120 | 118 | 120 |
| CE (%) | 99.1 | 99.0 | 98.9 | 99.5 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.7 | 99.4 | 99.4 |
| Model A | Model B | Model C | Model D | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Cycling | DC Bias Voltage | DC Bias Voltage | DC Bias Voltage | DC Bias Voltage | |||||
| 2.5 V | 4.2 V | 2.5 V | 4.2 V | 2.5 V | 4.2 V | 2.5 V | 4.2 V | |||
| Rsol | Before | 1.26 | 1.04 | * 1.0 × 10−5 | * 1.0 × 10−5 | 1.05 | 0.46 | * 1.0 × 10−5 | * 1.0 × 10−5 | |
| After | 3.39 | 3.50 | 0.02 | * 1.0 × 10−5 | 3.38 | 3.12 | 2.02 | 0.10 | ||
| Rsei | Before | - | - | 3.72 | 2.67 | - | - | 19.6 | 13.8 | |
| After | - | - | 3.78 | 4.32 | - | - | 29.1 | 3.67 | ||
| Rct | Before | 36.2 | 22.8 | 32.1 | 20.5 | 41.2 | 29.5 | 38.7 | 19.9 | |
| After | 43.6 | 26.2 | 42.5 | 24.9 | 44.0 | 32.1 | 38.5 | 30.9 | ||
| Wz | α | Before | 110 | 48.2 | 112 | 49.0 | - | - | - | - |
| After | 67.1 | 41.4 | 67.9 | 42.0 | - | - | - | - | ||
| CPEw | p | Before | - | - | - | - | 0.59 | 0.86 | 0.67 | 0.94 |
| After | - | - | - | - | 0.51 | 0.84 | 0.62 | 0.83 | ||
| T | Before | - | - | - | - | 5.90 × 10−3 | 9.38 × 10−3 | 3.93 × 10−3 | 7.49 × 10−3 | |
| After | - | - | - | - | 1.05 × 10−2 | 1.25 × 10−2 | 6.88 × 10−3 | 1.25 × 10−2 | ||
| CPE1 | p | Before | 0.75 | 0.76 | 0.63 | 1 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 0.95 | 0.89 |
| After | 0.82 | 0.85 | 1 | 1 | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.96 | 1 | ||
| T | Before | 2.59 × 10−5 | 2.44 × 10−5 | 6.79 × 10−5 | 5.58 × 10−7 | 3.96 × 10−5 | 7.16 × 10−5 | 6.88 × 10−6 | 1.21 × 10−5 | |
| After | 1.50 × 10−5 | 1.02 × 10−5 | 1.23 × 10−7 | 1.73 × 10−7 | 1.54 × 10−5 | 2.41 × 10−5 | 5.49 × 10−6 | 1.67 × 10−7 | ||
| CPE2 | p | Before | - | - | 0.85 | 0.87 | - | - | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| After | - | - | 0.85 | 0.93 | - | - | 0.37 | 0.82 | ||
| T | Before | - | - | 1.09 × 10−5 | 9.42 × 10−6 | - | - | 1.87 × 10−3 | 1.96 × 10−3 | |
| After | - | - | 1.07 × 10−5 | 5.48 × 10−6 | - | - | 3.51 × 10−3 | 1.53 × 10−5 | ||
| Cell | 1C-cycling Cell | 2C-cycling Cell | 5C-cycling Cell | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC Bias Voltage | DC Bias Voltage | DC Bias Voltage | ||||||||
| Element | Cycling | ** 2.5 V | 3.3 V | ** 4.2 V | 2.5 V | 3.3 V | 4.2 V | 2.5 V | 3.3 V | 4.2 V |
| Rsol [Ω] | before | 1.05 | 0.87 | 0.46 | 4.30 | 4.27 | 3.46 | 1.79 | 1.55 | 1.18 |
| after | 3.38 | 3.32 | 3.12 | 1.53 | 1.37 | 1.13 | 2.15 | 1.96 | 1.66 | |
| Rct [Ω] | before | 41.2 | 39.6 | 29.5 | 51.0 | 53.1 | 36.1 | 42.6 | 44.3 | 31.8 |
| after | 44.0 | 43.9 | 32.1 | 63.4 | 64.0 | 43.9 | 48.1 | 48.0 | 34.3 | |
| p of CPEw | before | 0.59 | 0.41 | 0.86 | 0.52 | 0.30 | 0.83 | 0.54 | 0.39 | 0.86 |
| after | 0.51 | 0.39 | 0.84 | 0.52 | 0.42 | 0.85 | 0.53 | 0.47 | 0.86 | |
| T of CPEw | before | 5.90 × 10−3 | 73.5 × 10−3 | 9.38 × 10−3 | 5.98 × 10−3 | 58.6 × 10−3 | 10.8 × 10−3 | 5.47 × 10−3 | 77.5 × 10−3 | 9.90 × 10−3 |
| after | 10.5 × 10−3 | 95.7 × 10−3 | 12.5 × 10−3 | 9.64 × 10−3 | 93.2 × 10−3 | 12.2 × 10−3 | 9.08 × 10−3 | 64.0 × 10−3 | 11.2 × 10−3 | |
| p of CPE1 | before | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.69 |
| after | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.75 | |
| T of CPE1 | before | 3.96 × 10−5 | 4.60 × 10−5 | 7.16 × 10−5 | 1.46 × 10−5 | 1.79 × 10−5 | 2.67 × 10−5 | 2.48 × 10−5 | 3.30 × 10−5 | 5.08 × 10−5 |
| after | 1.54 × 10−5 | 1.75 × 10−5 | 2.41 × 10−5 | 1.23 × 10−5 | 1.39 × 10−5 | 1.94 × 10−5 | 1.56 × 10−5 | 1.84 × 10−5 | 2.89 × 10−5 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abe, Y.; Hori, N.; Kumagai, S. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy on the Performance Degradation of LiFePO4/Graphite Lithium-Ion Battery Due to Charge-Discharge Cycling under Different C-Rates. Energies 2019, 12, 4507. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234507
Abe Y, Hori N, Kumagai S. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy on the Performance Degradation of LiFePO4/Graphite Lithium-Ion Battery Due to Charge-Discharge Cycling under Different C-Rates. Energies. 2019; 12(23):4507. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234507
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbe, Yusuke, Natsuki Hori, and Seiji Kumagai. 2019. "Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy on the Performance Degradation of LiFePO4/Graphite Lithium-Ion Battery Due to Charge-Discharge Cycling under Different C-Rates" Energies 12, no. 23: 4507. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234507
APA StyleAbe, Y., Hori, N., & Kumagai, S. (2019). Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy on the Performance Degradation of LiFePO4/Graphite Lithium-Ion Battery Due to Charge-Discharge Cycling under Different C-Rates. Energies, 12(23), 4507. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234507