Discovery of a Potent PLK1-PBD Small-Molecule Inhibitor as an Anticancer Drug Candidate through Structure-Based Design
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
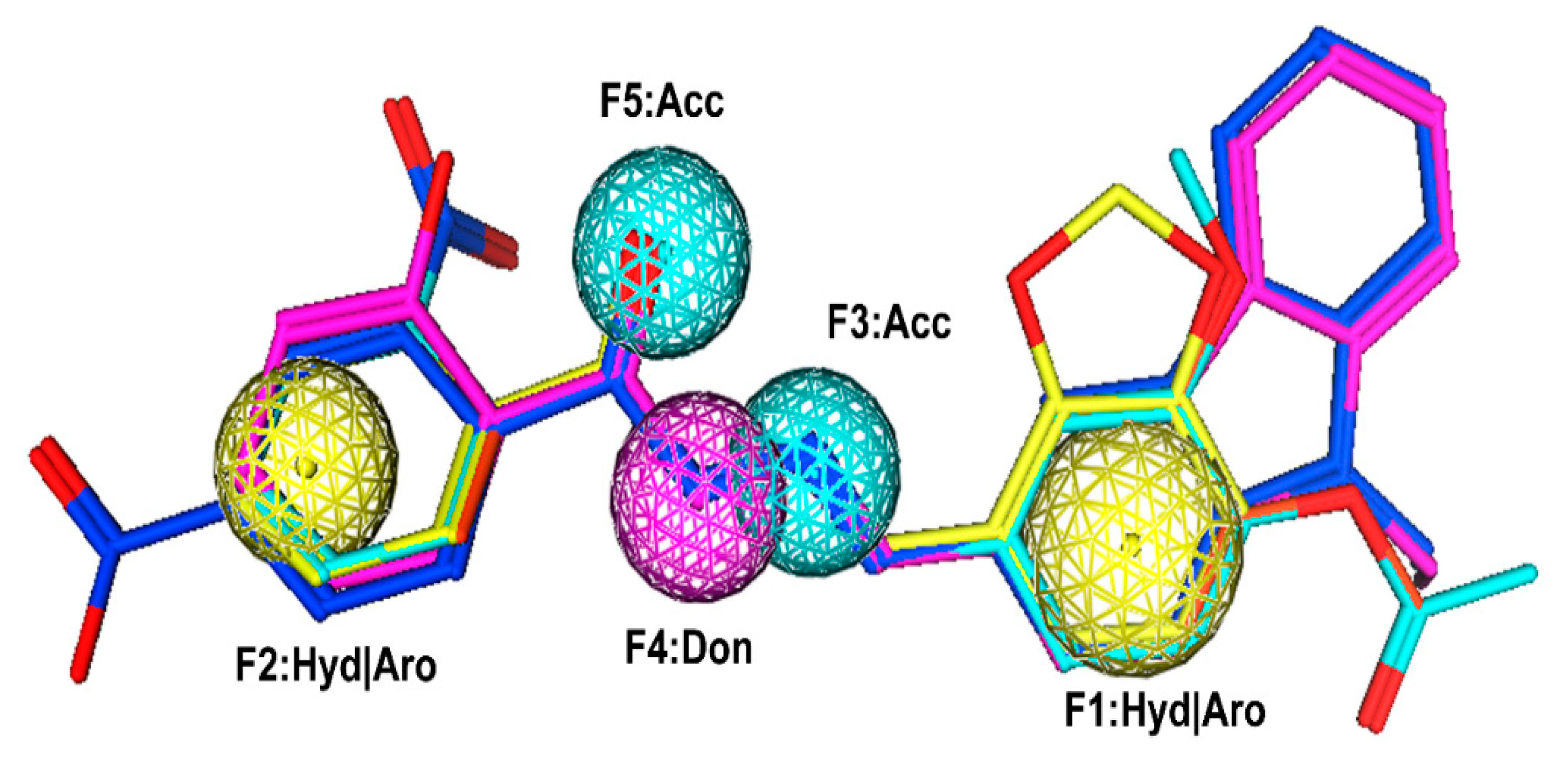
2.1. Pharmacophore Modeling
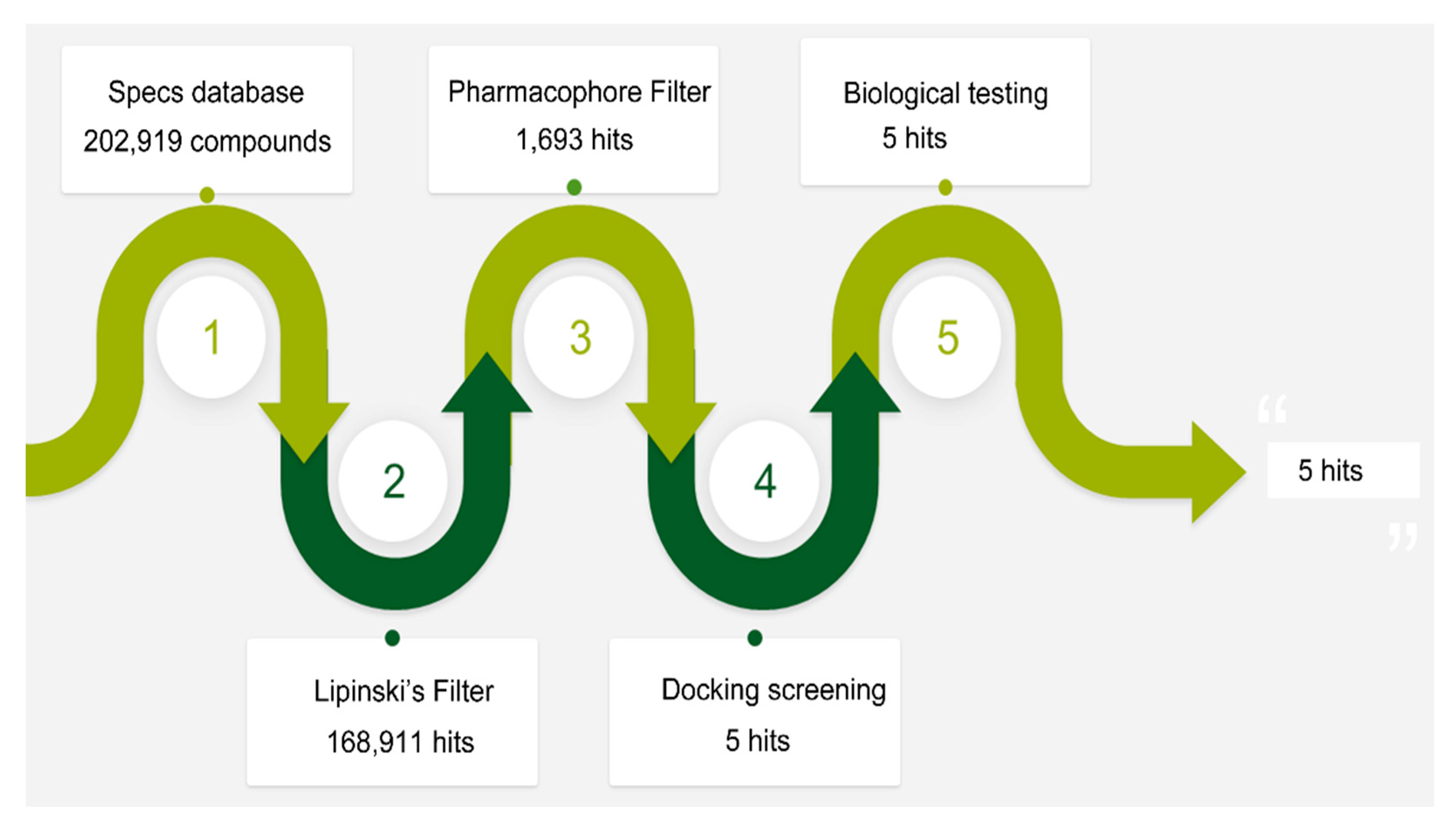
2.2. Validation and Database Screening
2.3. In Vitro Biological Testing
2.4. In Vivo Tumor Inhibition Ability of Hit-5
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Pharmacophore Model Generation and Validation
3.2. Virtual Screening
3.3. Molecular Docking
3.4. Microscale Thermophoresis (MST) Analysis
3.5. MTT Cell Proliferation Assay, Transfection of PLK1 shRNA and Western Blot Assay
3.6. In Vivo Anticancer Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Park, J.E.; Liu, F.; Lee, K.S.; Burke, T.R., Jr. Effects on polo-like kinase 1 polo-box domain binding affinities of peptides incurred by structural variation at the phosphoamino acid position. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3996–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitouni, S.; Nabais, C.; Jana, S.C.; Guerrero, A.; Bettencourt-Dias, M. Polo-like kinases: Structural variations lead to multiple functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 15, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollen, M.; Gerlich, D.W.; Lesage, B. Mitotic phosphatases: From entry guards to exit guides. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strebhardt, K.; Ullrich, A. Targeting polo-like kinase 1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.Y.; Lowe, E.D.; Sinclair, J.; Nigg, E.A.; Johnson, L.N. The crystal structure of the human polo-like kinase-1 polo box domain and its phospho-peptide complex. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5757–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.M.; Moulaei, T.; Lim, D.; Bang, J.K.; Park, J.E.; Shenoy, S.R.; Liu, F.; Kang, Y.H.; Liao, C.; Soung, N.K.; et al. Structural and functional analyses of minimal phosphopeptides targeting the polo-box domain of polo-like kinase 1. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Rhodes, C.A.; McCroskey, L.C.; Wen, J.; Appiah-Kubi, G.; Wang, D.J.; Guttridge, D.C.; Pei, D. Enhancing the cell permeability and metabolic stability of peptidyl drugs by reversible bicyclization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Song, Y.; Rehse, P.H. Thymoquinone blocks pSer/pThr recognition by Plk1 Polo-box domain as a phosphate mimic. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Sanhaji, M.; Kramer, A.; Reindl, W.; Hofmann, M.; Kreis, N.N.; Zimmer, B.; Berg, T.; Strebhardt, K. Polo-box domain inhibitor poloxin activates the spindle assembly checkpoint and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reindl, W.; Yuan, J.; Kramer, A.; Strebhardt, K.; Berg, T. A pan-specific inhibitor of the polo-box domains of polo-like kinases arrests cancer cells in mitosis. ChemBioChem 2009, 10, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfatah, S.; Berg, A.; Huang, Q.; Yang, L.J.; Hamdoun, S.; Klinger, A.; Greten, H.J.; Fleischer, E.; Berg, T.; Wong, V.K.W.; et al. MCC1019, a selective inhibitor of the Polo-box domain of Polo-like kinase 1 as novel, potent anticancer candidate. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ENicola, G.; Smith, C.A.; Lucumi, E.; Kuo, M.R.; Karagyozov, L.; Fidock, D.A.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Abagyan, R. Discovery of novel inhibitors targeting enoyl–acyl carrier protein reductase in Plasmodium falciparum by structure-based virtual screening. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfatah, S.; Berg, A.; Böckers, M.; Efferth, T. A selective inhibitor of the Polo-box domain of Polo-like kinase 1 identified by virtual screening. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 16, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; Cao, Z.X.; Li, L.L.; Jiang, P.D.; Zhao, Y.L.; Luo, S.D.; Yang, S.Y. Pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening for designing potential PLK1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4972–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafique, S.; Bibi, N.; Rashid, S. In silico identification of putative bifunctional Plk1 inhibitors by integrative virtual screening and structural dynamics approach. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 388, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivelan, S.; Sinha, B.N.; Rambabu, G.; Boppana, K.; Jagarlapudi, S.A. Pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening studies to design some potential histone deacetylase inhibitors as new leads. J. Mol. Graphics Modell. 2008, 26, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talele, T.T.; Khedkar, S.A.; Rigby, A.C. Successful applications of computer aided drug discovery: Moving drugs from concept to the clinic. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śledź, P.; Stubbs, C.J.; Lang, S.; Yang, Y.Q.; McKenzie, G.J.; Venkitaraman, A.R.; Hyvönen, M.; Abell, C. From Crystal Packing to Molecular Recognition: Prediction and Discovery of a Binding Site on the Surface of Polo-Like Kinase 1. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4003–4006. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.S.; Śledź, P.; Lang, S.; Stubbs, C.J.; Spring, D.R.; Abell, C.; Best, R.B. Using ligand-mapping simulations to design a ligand selectively targeting a cryptic surface pocket of polo-like kinase 1. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10078–10081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baell, J.B.; Holloway, G.A. New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A. Merck molecular force field. I. Basis, form, scope, parameterization, and performance of MMFF94. J. Comput. Chem. 1996, 17, 490–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Wang, F.; Li, F.; Dong, Y.; Gu, Y. Establishment of a screening protocol for identification of aminopeptidase N inhibitors. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 49, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, H.Y.; Xu, R.F.; Zhu, H.L. Identification of nitroimidazole-oxime derivatives targeting the polo-box domain of polo-like kinase 1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 6581–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasrao, G.; Park, J.E.; Kim, S.; Ahn, M.; Cheong, C.; Nam, K.Y.; Lee, K.S. Design and synthesis of a cell-permeable, drug-like small molecule inhibitor targeting the polo-box domain of polo-like kinase 1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lv, P.C.; Guo, F.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, G.H.; Qian, S.S.; Zhu, H.L. Aromatic diacylhydrazine derivatives as a new class of polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) inhibitor. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 81, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.; Qin, T.; Liu, Y.; Lai, L. Identification of acylthiourea derivatives as potent Plk1 PBD inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manual of Molecular Operating Environment (MOE); Version 2007.09; Chemical Computing Group Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2007.
- ul Qamar, T.; Mumtaz, A.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Azhar, S.; Fatima, T.; Hassan, M.; Hussain, S.S.; Akram, W.; Idrees, S. Computer aided screening of phytochemicals from Garcinia against the dengue NS2B/NS3 protease. Bioinformation 2014, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |




| PDB_ID | Resolution (Å) | Ligand_Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 5NN2 | 1.81 | Z24 |
| 5NEI | 2.68 | 8VB |
| Serial No. | Parameter | Pharmacophore Model |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Total molecules in database (D) | 1000 |
| 2 | Total number of actives in database (A) | 30 |
| 3 | Total hits (Ht) | 34 |
| 4 | Active hits (Ha) | 25 |
| 5 | % Yield of actives [(Ha/Ht) × 100] | 74 |
| 6 | % Ratio of actives [(Ha/A) × 100] | 83 |
| 7 | Enrichment factor (E) [(Ha × D)/(Ht × A)] | 25 |
| 8 | False negatives [A − Ha] | 5 |
| 9 | False positives [Ht − Ha] | 9 |
| 10 | Goodness of hit score (GH) a | 0.77 |
| Hits | ID Number | Structure | RMSD [Å] (a) | Docking Score [kcal/mol] (b) | Pharmacophore/Docking Ranking (c) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AN-329/40093808 | 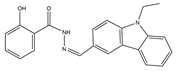 | 0.3152 | –7.6527 | 6/2 |
| 2 | AG-205/07764017 | 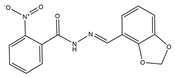 | 0.3668 | –7.2534 | 13/4 |
| 3 | AN-329/10002015 |  | 0.3609 | –7.2088 | 16/5 |
| 4 | AN-329/10080005 |  | 0.3401 | –7.4651 | 11/3 |
| 5 | AN-329/10077003 |  | 0.3128 | –8.0127 | 5/1 |
| Compounds | PLK1-PBD [μM] (a) | PLK2-PBD [μM] (a) | PLK3-PBD [μM] (a) | PLK2-PBD/PLK1-PBD | PLK3-PBD/PLK1-PBD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hit-5 | 26 ± 5 | >400 | >400 | >15 | >15 |
| Poloxin | 34 ± 7 | 152 ± 11 | 284 ± 17 | 4.5 | 8.4 |
| Thymoquinone | 39 ± 6 | 46 ± 5 | 55 ± 10 | 1.2 | 1.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Yan, F.; Huo, X.; Niu, M.-M. Discovery of a Potent PLK1-PBD Small-Molecule Inhibitor as an Anticancer Drug Candidate through Structure-Based Design. Molecules 2019, 24, 4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234351
Zhou Y, Yan F, Huo X, Niu M-M. Discovery of a Potent PLK1-PBD Small-Molecule Inhibitor as an Anticancer Drug Candidate through Structure-Based Design. Molecules. 2019; 24(23):4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234351
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yunjiang, Fang Yan, Xiangyun Huo, and Miao-Miao Niu. 2019. "Discovery of a Potent PLK1-PBD Small-Molecule Inhibitor as an Anticancer Drug Candidate through Structure-Based Design" Molecules 24, no. 23: 4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234351
APA StyleZhou, Y., Yan, F., Huo, X., & Niu, M.-M. (2019). Discovery of a Potent PLK1-PBD Small-Molecule Inhibitor as an Anticancer Drug Candidate through Structure-Based Design. Molecules, 24(23), 4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234351






