New Curved Reflectors for Significantly Enhanced Solar Power Generation in Four Seasons †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
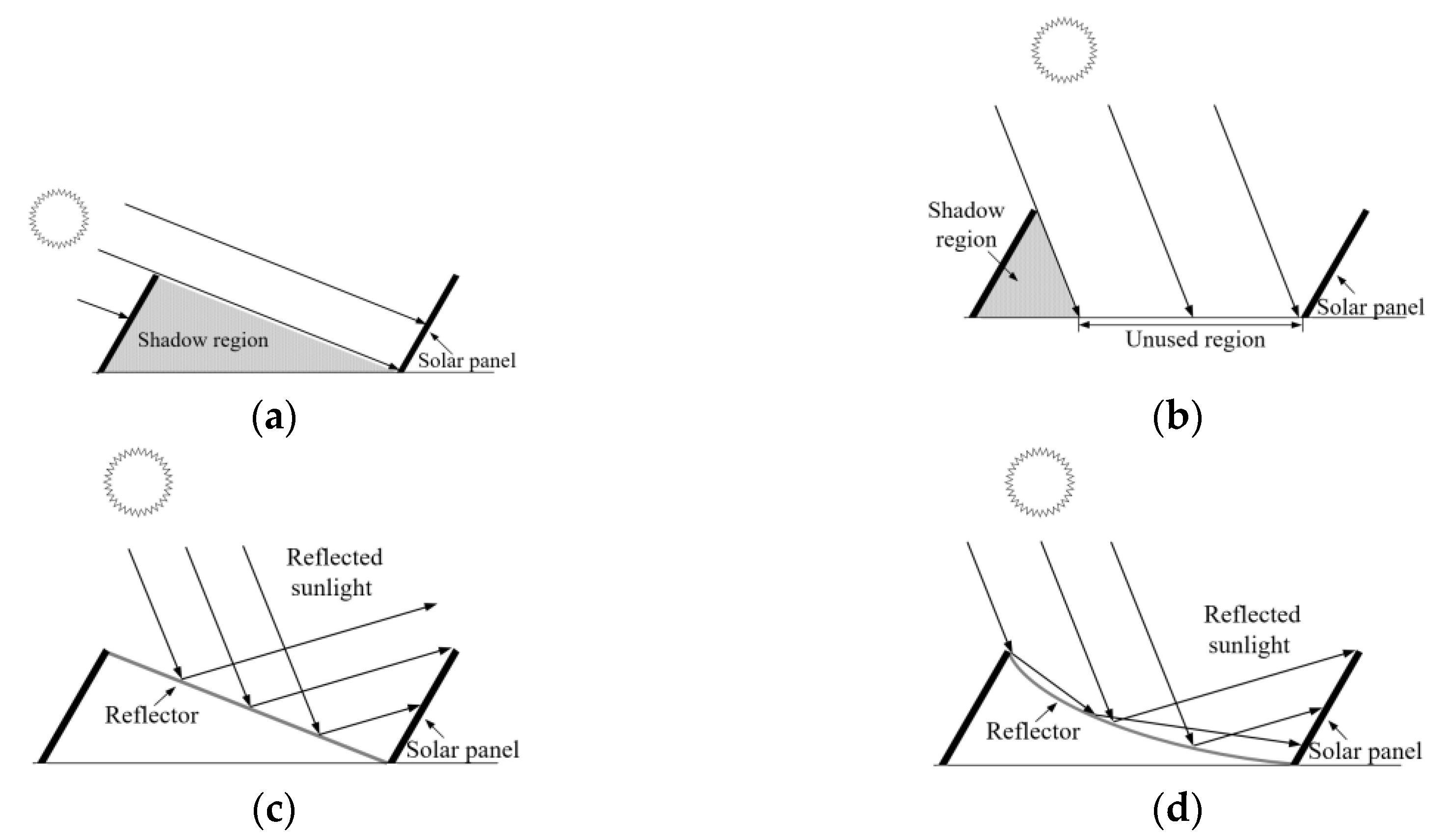
2. Analysis of the Incidence Power for Different Reflector Types
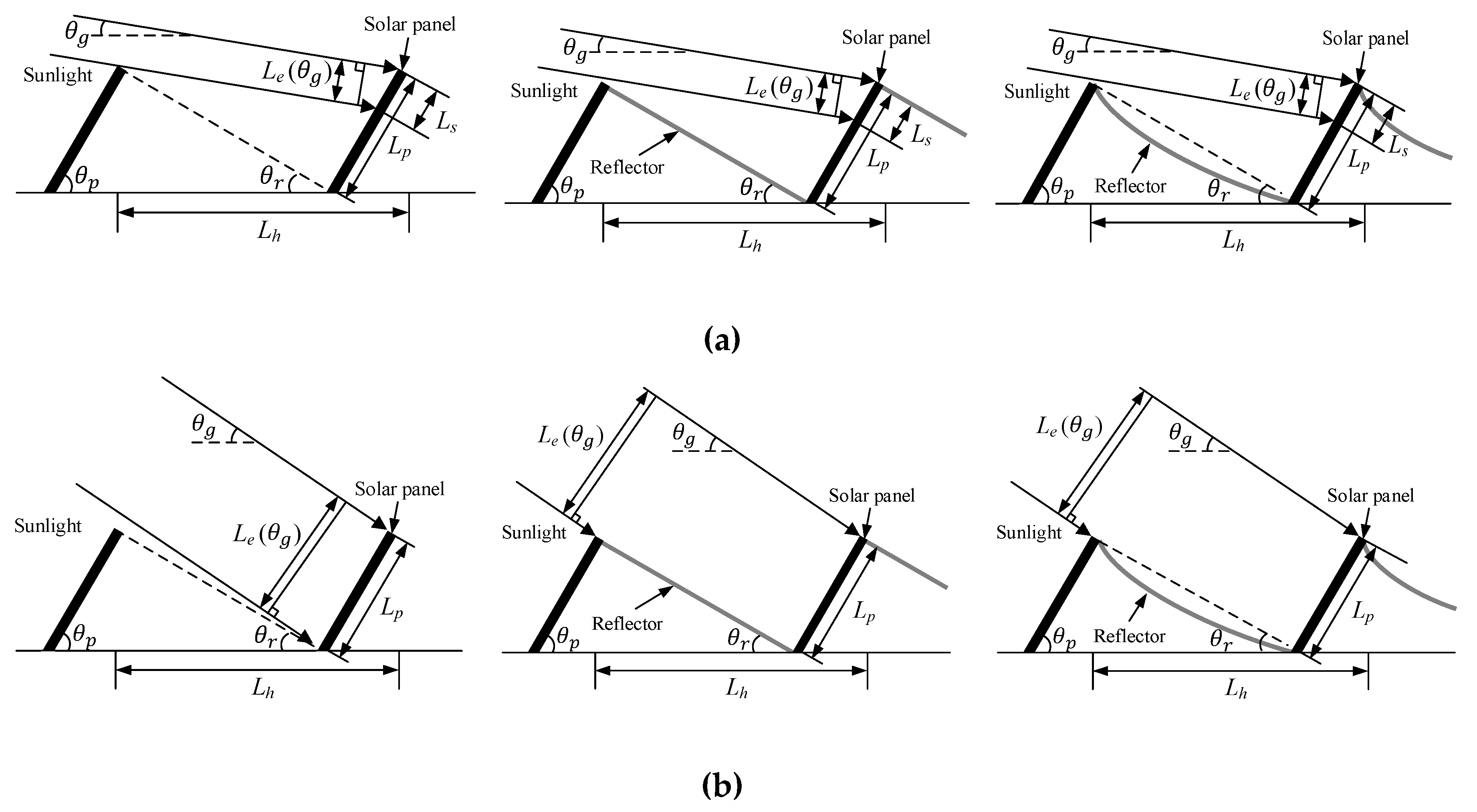
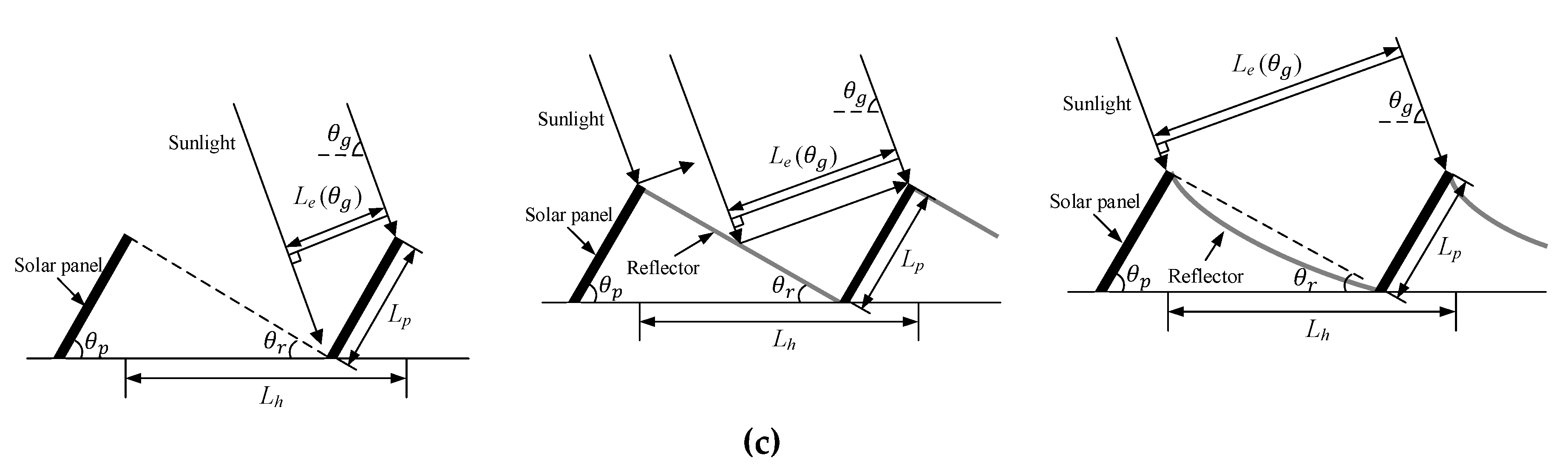
2.1. Effective Amount of Sunlight Normal to a Panel
2.2. Effective Panel Length for the Elevation Angle of the Sun
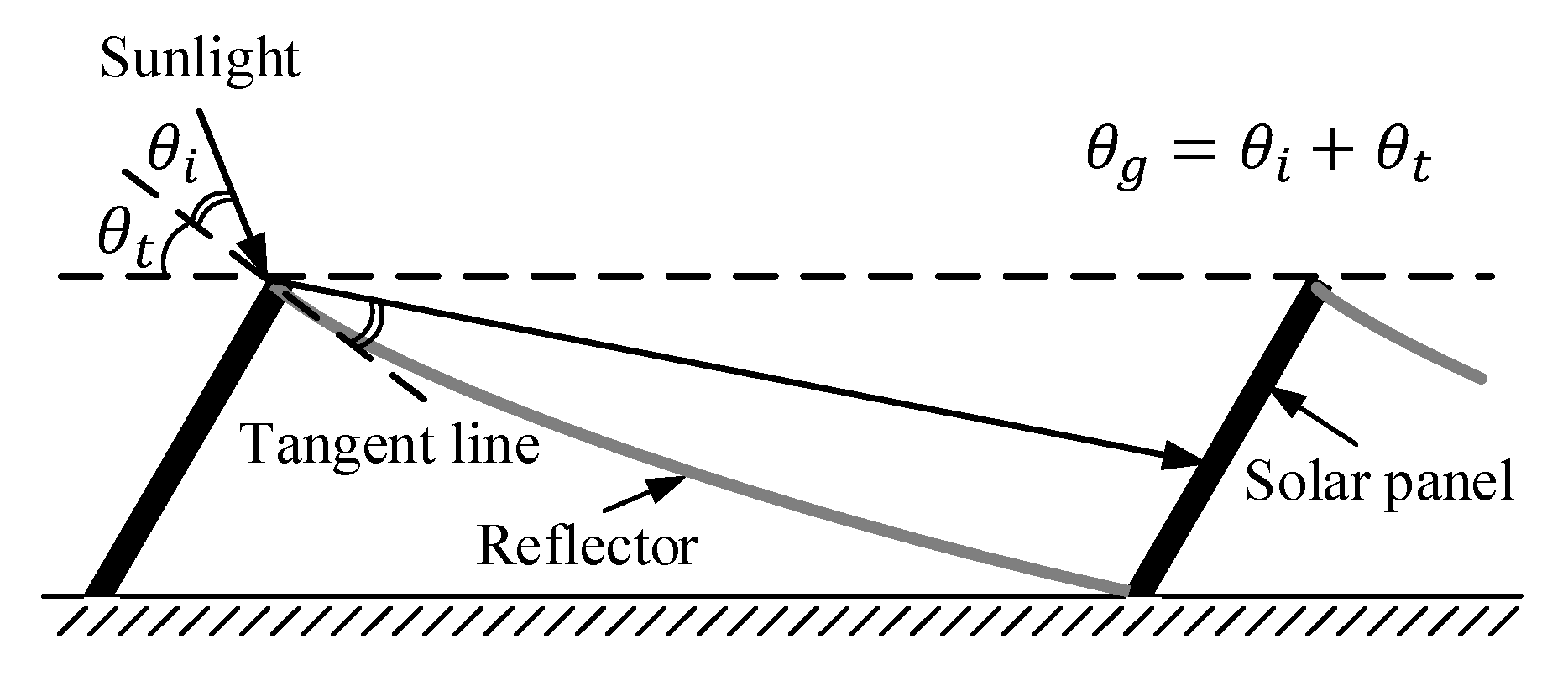
2.3. Design of the Curved Reflector
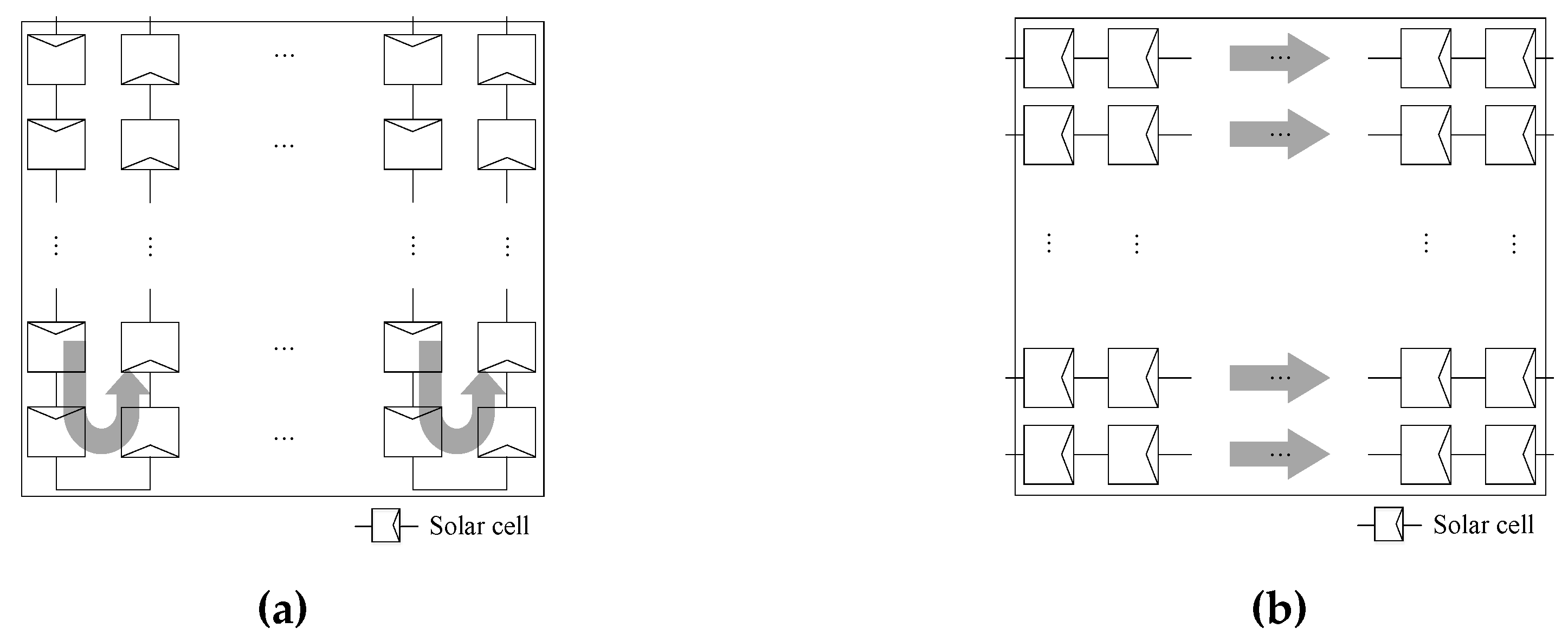
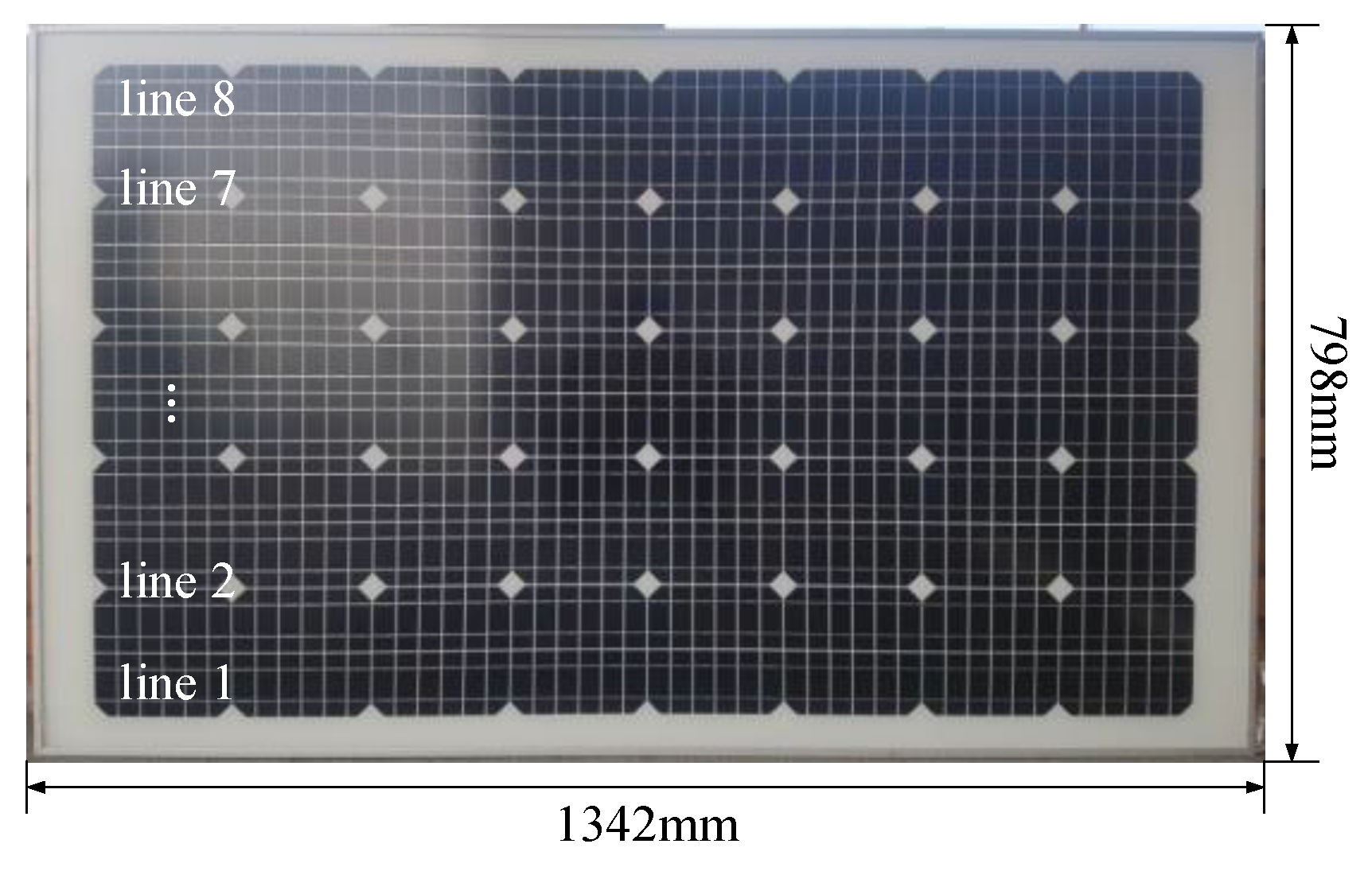
2.4. Design of the Solar Cell Configuration of the Solar Panel
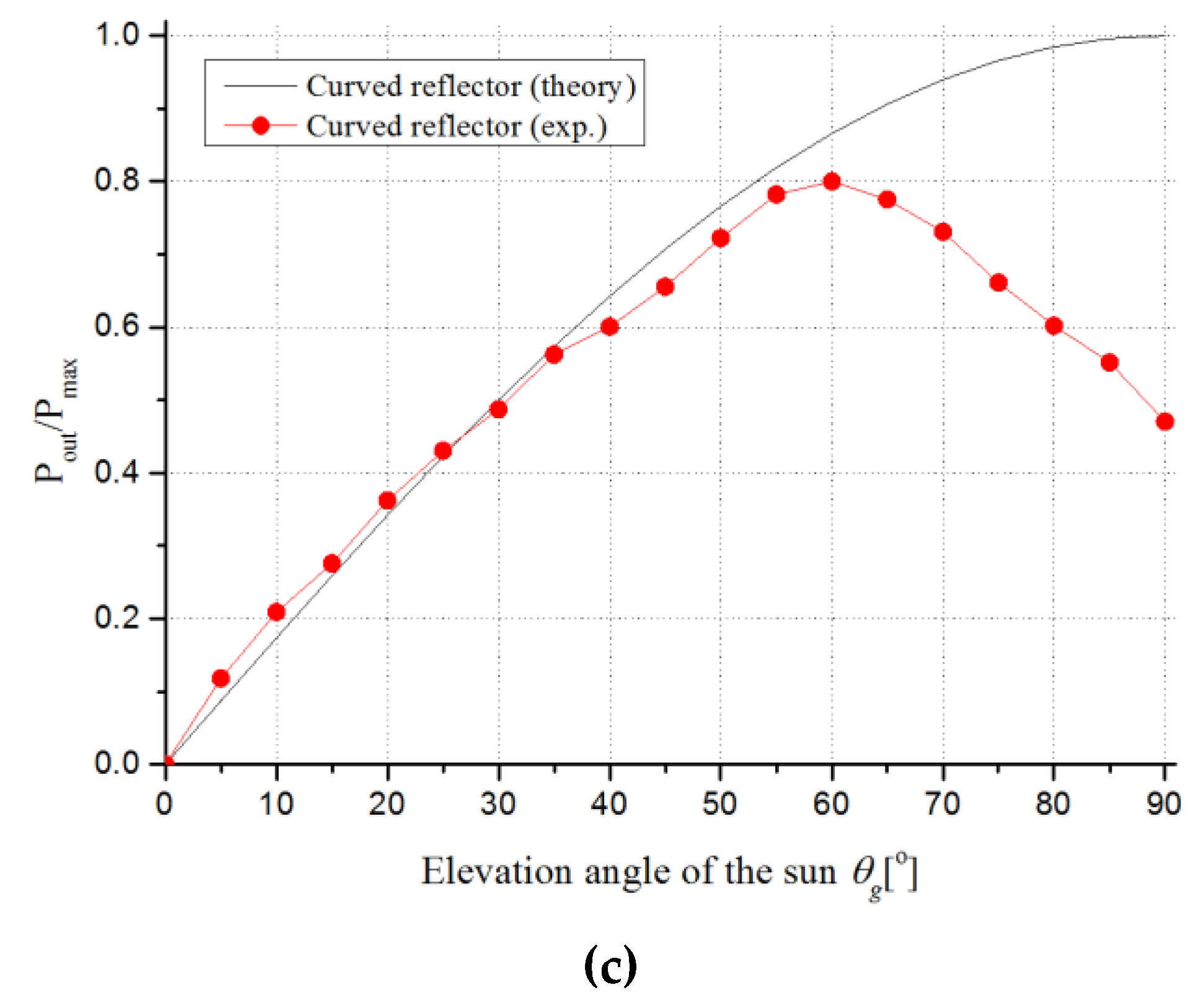
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masters, G.M. Renewable and Efficient, Electric, Power, Systems; John, Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kroposki, B.; Johnson, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gevorgian, V.; Denholm, P.; Hodge, B.; Hannegan, B. Achieving a 100% renewable, grid: Operating, electric, power, systems with, extremely, high, levels of, variable, renewable, energy. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2017, 15, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwongwanich, A.; Blaabjerg, F. Mitigation of interharmonics in, PV systems with maximum power point tracking modification. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 8279–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundareswaran, K.; Sankar, P.; Nayak, P.S.R.; Simon, S.P.; Palani, S. Enhanced energy output from a, PV system under partial shaded conditions through artificial bee colony. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 6, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dein, M.Z.S.; Kazerani, M.; Salama, M.M.A. Optimal photovoltaic array reconfiguration to reduce partial shading losses. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koran, A.; LaBella, T.; Lai, J. High efficiency photovoltaic source simulator with fast response time for solar power conditioning systems evaluation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger-Waldau, A. Snapshot of, Photovoltaics—February 2019. Energies 2019, 12, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Cao, W.; Wu, J.; Ji, B.; Holliday, D. Thermography-based virtual, MPPT scheme for improving, PV energy efficiency under partial shading conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 5667–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xenophontos, A.; Bazzi, A.M. Model-based, maximum, power, curves of, solar, photovoltaic, panels under, partial, shading, conditions. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2018, 8, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taretto, K.; Soldera, M.; Koffman-Frischknecht, A. Material, Parameters and, Perspectives for, Efficiency, Improvements in, Perovskite, Solar, Cells, Obtained by, Analytical, Modeling. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2017, 7, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subudhi, B.; Pradhan, R. A comparative study on maximum power point tracking techniques for photovoltaic power systems. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Rahmani, R.; Mekhilef, S.; Oo, A.M.T.; Stojcevski, A.; Soon, T.K.; Ghandhari, A.S. Simulation and hardware implementation of new maximum power point tracking technique for partially shaded, PV system using hybrid, DEPSO method. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 6, 850–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xiong, C. Passive cooling technology for photovoltaic panels for domestic houses. Int. J. Low Carbon Technol. 2014, 9, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Rahman, S.; Pipattanasomporn, M. Distribution voltage regulation through active power curtailment with, PV inverters and solar generation forecasts. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 8, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strache, S.; Wunderlich, R.; Heinen, S. A comprehensive, quantitative comparison of inverter architectures for various, PV systems, PV cells, and irradiance profiles. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckx, S.; Gonzalez, C.; Driesen, J. Combined central and local active and reactive power control of, PV inverters. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaez, S.A.; Deline, C.; Greenberg, P.; Stein, J.S.; Kostuk, R.K. Model and validation of single-axis tracking with bifacial, PV. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2019, 9, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molin, E.; Stridh, B.; Molin, A.; Wackelgard, E. Experimental yield study of bifacial, PV modules in, Nordic conditions. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2018, 8, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, M.; Migan-Dubois, A.; Bourdin, V.; Pons, M.; Haeffelin, M. Experimental and numerical study of the influence of string mismatch on the yield of, PV modules augmented by static planar reflectors. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2015, 5, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augustin, D.; Chacko, R.; Jacob, J. Canal top solar, PV with reflectors. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International, Conference on Power, Electronics, Drives and, Energy, Systems (PEDES), Trivandrum, India, 14–17 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- TenKsolar, Hopes to, Raise, Funds for, Wave-Like, Solar, System. Available online: https://gigaom.com/2011/04/26/tenksolar-raising-funds-for-wave-like-solar-system/ (accessed on 2 October 2019).
- Energy, Farm, Co. LTD. Photovoltaic Power Generation Device. JP Patent 2012. Available online: http://abpat.kipris.or.kr/abpat/biblioa.do?method=biblioFrame&searchFg=N&publ_key=JP201400103381A0&cntry=JP&start=biblio (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Matsushima, T.; Setaka, T.; Muroyama, S. Concentrating solar module with horizontal reflectors. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2003, 75, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.M.S.; Rahman, A.N.M.M. Performance comparison of mirror reflected solar panel with tracking and cooling. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th IEEE International Conference on the Development in the in Renewable Energy Technology (ICDRET), Dhaka, Bangledash, 7–9 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Joardder, M.U.H.; Halder, P.K.; Rahim, M.A.; Masud, M.H. Solar pyrolysis: converting waste into asset using solar energy. In Clean Energy for Sustainable Development: Comparisons and Contrasts of New Approaches; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Rim, C.T. Incidence solar power analysis of, PV panels with curved reflectors. In Proceedings of the 2017 18th IEEE Workshop on Control and Modeling for Power Electronics (COMPEL), Stanford, CA, USA, 9–12 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Karafil, A.; Ozbay, H.; Kesler, M.; Parmaksiz, H. Calculation of optimum fixed tilt angle of, PV panels depending on solar angles and comparison of the results with experimental study conducted in summer in, Bilecik, Turkey. In Proceedings of the 2015 9th IEEE International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey, 26–28 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bakirci, K. General models for optimum tilt angles of solar panels: Turkey case study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 6149–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubleday, K.; Choi, B.; Maksimovic, D.; Deline, C.; Olalla, C. Recovery of inter-row shading losses using differential power-processing submodule, DC–DC converters. Solar Energy 2016, 135, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narvarte, L.; Lorenzo, E. Tracking and ground cover ratio. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2008, 16, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passias, D.; Källbäck, B. Shading effects in rows of solar cell panels. Solar Cells 1984, 11, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bany, J.; Appelbaum, J. The effect of shading on the design of a field of solar collectors. Solar Cells 1987, 20, 201–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.S.; Alam, M.K. Effect of angle of incidence on the performance of bulk heterojunction organic solar cells: A unified optoelectronic analytical framework. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 065101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| No Reflector | Plane-Type Reflector | Curved-Type Reflector | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low angle () | |||
| Middle angle () | |||
| High angle ( | |||
| High angle ( | |||
| Ground cover ratio (GCR) |
| No Reflector | Plane-Type Reflector | Curved-Type Reflector | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Theory (W/100kLux) | 107.0 ( = 30°) | 185.3 ( = 60°) | 214.0 ( = 90°) |
| Experiment (W/100kLux) | 105.6 ( = 35°) | 161.5 ( = 55°) | 171.2 ( = 60°) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.S.; Choi, B.G.; Kim, J.H.; Ryu, S.-T.; Rim, C.T.; Kim, Y.-S. New Curved Reflectors for Significantly Enhanced Solar Power Generation in Four Seasons. Energies 2019, 12, 4602. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234602
Choi JS, Choi BG, Kim JH, Ryu S-T, Rim CT, Kim Y-S. New Curved Reflectors for Significantly Enhanced Solar Power Generation in Four Seasons. Energies. 2019; 12(23):4602. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234602
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Jin S., Byeong G. Choi, Ji H. Kim, Seung-Tak Ryu, Chun T. Rim, and Yun-Su Kim. 2019. "New Curved Reflectors for Significantly Enhanced Solar Power Generation in Four Seasons" Energies 12, no. 23: 4602. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234602
APA StyleChoi, J. S., Choi, B. G., Kim, J. H., Ryu, S.-T., Rim, C. T., & Kim, Y.-S. (2019). New Curved Reflectors for Significantly Enhanced Solar Power Generation in Four Seasons. Energies, 12(23), 4602. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234602






