Isolation of Novel ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Peptides from Quinoa Bran Albumin Assisted with an In Silico Approach: Characterization, In Vivo Antihypertension, and Molecular Docking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction and Isolation of Quinoa Bran Albumin
2.3. Preparation of Quinoa Bran Albumin Hydrolysates (QBAH)
2.4. Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Activity and Inhibition Kinetics
2.5. Scavenging Activity of Hydroxyl Radical
2.6. Purification by Gel Chromatography and Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
2.7. Identification of Peptide Sequences
2.8. Screening for ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Peptides by in Silico Approach and Peptide Synthesis
2.9. Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion of Synthesized Peptides
2.10. Molecular Modeling
2.11. Antihypertensive Effect in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats (SHRs)
2.12. Antioxidant Activity of the Peptides
2.12.1. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
2.12.2. Metal Chelating Capacity
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Activity of QBAH
3.2. Isolation of the ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Peptides
3.3. Characterization of Pooled Peptide Fraction by Mass Spectrometry and Screening of ACE-Inhibitory Peptides
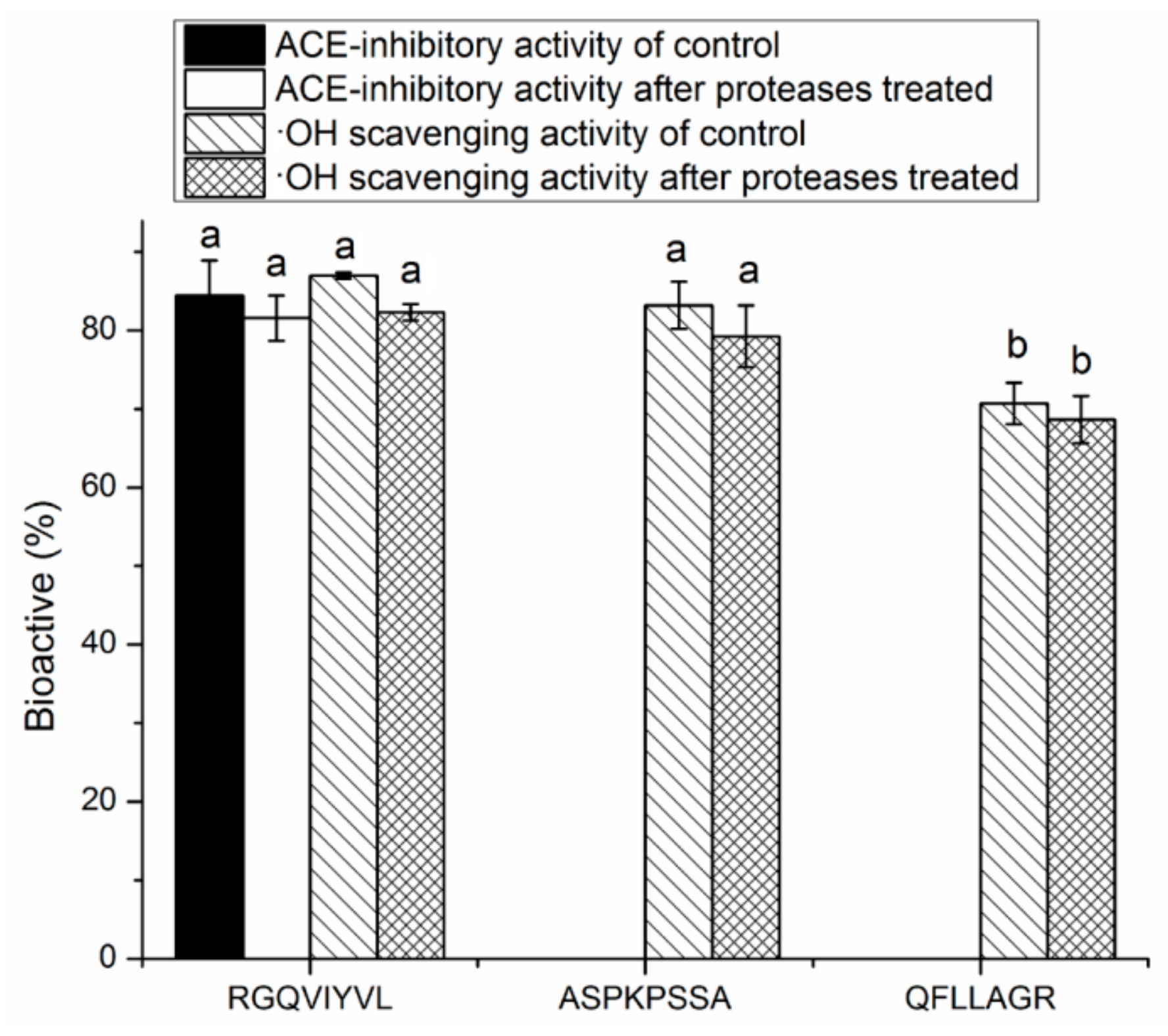
3.4. Stability Against in Vitro Digestion of Synthetic Peptides
3.5. Inhibition Kinetics of Synthetic Peptides
3.6. Molecular Docking Simulation between the Peptides and ACE
3.7. Antihypertensive Effect of Peptides on SHRs
3.8. Antioxidant Activity of the Synthetic Peptides
3.8.1. Radical Scavenging Activity
3.8.2. Fe2+ Chelating Ability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambigaipalan, P.; Shahidi, F. Bioactive peptides from shrimp shell processing discards: Antioxidant and biological activities. J. Funct. Foods. 2017, 34, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. A global brief on hypertension: Silent killer, global public health crisis. 2013. Available online: http://ish-world.com/data/uploads/global_brief_hypertension.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2015).
- Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Contreras, M.M.; Recio, I. Antihypertensive peptides: Production, bioavailability and incorporation into foods. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 165, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shazly, A.B.; He, Z.; EI-Aziz, M.A.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, S.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Fractionation and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from buffalo and bovine casein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuyan, B.J.; Mugesh, G. Synthesis, characterization and antioxidant activity of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himaya, S.W.A.; Ngo, D.H.; Ryu, B.; Kim, S.K. An active peptide purified from gastrointestinal enzyme hydrolysate of Pacific cod skin gelatin attenuates angiotensin-1 converting enzyme (ACE) activity and cellular oxidative stress. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1872–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intarasirisawat, R.; Benjakul, S.; Wu, J.; Visessanguan, W. Isolation of antioxidative and ACE inhibitory peptides from protein hydrolysate of skipjack (Katsuwanapelamis) roe. J. Funct. Foods. 2013, 5, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirinos, R.; Ochoa, K.; Aguilar-Galvez, A.; Carpentier, S.; Pedreschi, R.; Campos, D. Obtaining of peptides with in vitro antioxidant and angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory activities from cañihua protein (Chenopodium pallidicaule Aellen). J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 83, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, A.; Mora, L.; Aristoy, M.C.; Safari, M.; Hashemi, M.; Toldrá, F. Peptidomic analysis of antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory peptides obtained from tomato waste proteins fermented using Bacillus subtilis. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, J.P.; Brayden, D.J.; Ryan, S.M. Evaluation of Pep T1 transport of food-derived antihypertensive peptides, Ile-Pro-Pro and Leu-Lys-Pro using in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo, transport models. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopha. 2017, 115, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abugoch, L.E.; Romero, N.; Tapia, C.A.; Silva, J.; Rivera, M. Study of some physicochemical and functional properties of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) protein isolates. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4745–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakhili, S.; Abdolalizadeh, L.; Hosseini, S.M.; Shojaee-Aliabadi, S.; Mirmoghtadaie, L. Quinoa protein: Composition, structure and functional properties. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Lisboa, R.; Herrera, C.; Zúňiga, R.N.; Enrione, J.; Guzmán, F.; Matiacevich, S.; Astudillo-Castro, C. Quinoa proteins (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) fractionated by ultrafiltration using ceramic membranes: The role of pH on physicochemical and conformational properties. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 102, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.; Johnson, S.K.; Liu, S.Q.; Mesmari, N.; Dahmani, S.; Dhaheri, A.S.A.; Kizhakkayil, J. In vitro investigation of bioactivities of solid-state fermented lupin, quinoa and wheat using Lactobacillus spp. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, B.; Maux, S.L.; Dubrulle, C.; Barre, C.; FitzGerald, R.J. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) protein hydrolysates with in vitro dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory and antioxidant properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 65, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcacundo, R.; Martínez-Villaluenga, C.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Release of dipeptidyl peptidase IV, α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) during in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion. J. Funct. Foods. 2017, 35, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Wilckens, R.; Jara, J.; Aranda, M.; Valdivia, W.; Bustamante, L.; Graf, F.; Obal, I. Protein and antioxidant composition of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) sprout from seeds submitted to water stress, salinity and light conditions. Ind. Crops Prouducts 2017, 107, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiroghene, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Pang, X.Y.; Lv, J.P. α-Glucosidase and ACE dual inhibitory protein hydrolysates and peptide fractions of sprouted quinoa yoghurt beverages inoculated with Lactobacillus casei. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 124985. [Google Scholar]
- Nwachukwu, I.D.; Aluko, R.E. Physicochemical and emulsification properties of flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum) albumin and globulin fractions. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler-Nissen, J. Determination of the degree of hydrolysis of food protein hydrolysates by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1979, 27, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimsheena, V.K.; Gowda, L.R. Colorimetric, high-throughput assay for screening angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9388–9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Zhao, M.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, C.; Kakuda, Y.; Xue, S.J. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from grass carp muscle hydrolysates by consecutive chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Bai, J.; Wu, W.; Lin, Q.; Wu, J. Spent hen-derived ACE inhibitory peptide IWHHT shows antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities in endothelial cells. J. Funct. Foods. 2019, 53, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Sun, L.P.; Zhuang, Y.L. Preparation and identification of novel inhibitory angiotensin-I-converting enzyme peptides from tilapia skin gelatin hydrolysates: inhibition kinetics and molecular docking. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5251–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Wang, J.L.; He, G.Q.; Wu, J. Purification, identification, and in vivo activity of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide, from ribbon fish (Trichiurus haumela) backbone. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C1–C7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selamassakul, N.; Laohakunjit, O.; Kerdchoechuen, N.; Yang, L.; Maier, C.S. Isolation and characterisation of antioxidative peptides from bromelain hydrolysed brown rice protein by proteomic technique. Process Biochem. 2018, 70, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.B.; De Lumen, B.O.; Jeong, H.J. Lunasin peptide purified from Solanumnigrum L. protects DNA from oxidative damage by suppressing the generation of hydroxyl radical via blocking fenton reaction. Cancer Lett. 2010, 293, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Purification of novel angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from beef myofibrillar proteins and analysis of their effect in spontaneously hypertensive rat model. Biomed Pharmacot. 2019, 116, 109046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskara, B.; Ananthanarayana, L.; Jamdar, S. Purification, identification, and characterization of novel angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from alcalase digested horse gram flour. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 103, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Fu, X.; Li, S.; Wei, J. A novel antioxidant and ACE inhibitory peptide from rice bran protein: Biochemical characterization and molecular docking study. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, S.; Lunow, D.; Kaiser, S.; Henle, T. Identification and quantification of ACE-inhibiting peptides in enzymatic hydrolysates of plant proteins. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Lu, W.; Jiang, L.; Du, M. Identification of a novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from casein and evaluation of the inhibitory mechanisms. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montone, C.M.; Capriotti, A.L.; Cavaliere, C.; Barbera, G.L.; Piovesana, S.; Chiozzi, R.Z.; Laganà, A. Characterization of antioxidant and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from cauliflower by-products by multidimensional liquid chromatography and bioinformatics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3573–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandi, R.; Willmore, W.G.; Tsopmo, A. Peptidomic analysis of hydrolyzed oat bran proteins, and their in vitro antioxidant and metal chelating properties. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 27949–27957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welderufael, F.T.; Gibson, T.; Methven, L.; Jauregi, P. Chemical characterisation and determination of sensory attributes of hydrolysates produced by enzymatic hydrolysis of whey proteins following a novel integrative process. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ruan, X.H.; Zhang, R.G.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhao, S.L. Purification, characterization, synthesis, in vivo ACE inhibition and in vitro antihypertensive activity of bioactive peptides derived from palm kernel expeller glutelin-2 hydrolysates. J. Funct. Foods. 2017, 28, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Mu, T.H.; Sun, M.J. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from sweet potato protein hydrolysates by Alcalase. Food Chem. 2014, 7, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohit, A.C.; Sathisha, K.; Aparna, H.S. A variant peptide of buffalo colostrum β-lactoglobulin inhibits angiotensin I-converting enzyme activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 53, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Nasri, R.; Mora, L.; Jridi, M.; Toldra, F.; Nasri, M. In silico analysis and molecular docking study of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from smooth-hound viscera protein hydrolysates fractionated by ultrafiltration. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babini, E.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Martini, S.; Più, L.D.; Gianotti, A. LC-ESI-QTOF-MS identification of novel antioxidant peptides obtained by enzymatic and microbial hydrolysis of vegetable proteins. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.E.; Ahn, C.B.; Je, J.Y. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptides from enzymatically hydrolyzed ark shell (Scapharca subcrenata). Process Biochem. 2018, 72, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.L.; Sun, L.P. Preparation of reactive oxygen scavenging peptides from tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) skin gelatin: Optimization using response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C483–C489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds (quinoa bran albumin and globulin) are available from the authors. |








| Peptides | Molecular Mass (Da) | Matched Sequence in Chenopodium quinoa Willd. a | Calculated pI | Hydrophobic Residue Content | IC50 (μM) of ACE-Inhibitory Activity | IC50 (μM) of ·OH Scavenging Ability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGGGGGGGSGGAH | 941.4 | G.NGGGGGGGSGGAH.A | 5.67 | 15.38% | ||
| GEHMAGGS | 744.8 | I.GEHMAGGS.S | 6.76 | 22.22% | ||
| RGQVIYVL | 946.6 | R.RGQVIYVL.G | 4.98 | 62.50% | 38.16 | 61.69 |
| LGGGAGGGGGIGGG | 943.5 | R.GREEEEGR.G | 9.06 | 21.43% | ||
| SKIGEHMA | 872.0 | G.SKIGEHMA.G | 6.76 | 37.50% | ||
| ASPKPSSA | 743.8 | T.ASPKPSSA.S | 8.02 | 50.00% | 76.47 | |
| SGGSGAG | 491.4 | P.SGGSGAG.P | 5.33 | 14.29% | ||
| AGGGGGYGAGG | 651.6 | A.GGGGGYGAG.G | 5.90 | 18.18% | ||
| DQGAGYGGG | 780.7 | G.DQGAGYGGG.G | 5.90 | 11.11% | ||
| EAGGGEGGGGGEGG | 1046.9 | Q.EAGGGEGGGGGEGG.G | 5.97 | 7.14% | ||
| QFLLAGR | 803.5 | G.QFLLAGR.G | 8.16 | 30.00% | 117.46 | |
| QGAGYGGGGGSGG | 980.9 | D.QGAGYGGGGGSGG.G | 5.90 | 7.69% |
| Ligand | T-Score | Hydrogen Bond Number | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGQVIYVL | 10.66 | 13 | ASP415: 2.49; Ala356: 1.81,1.99; Ala354: 2.05; His353: 2.89; Tyr 146: 1.64; Lys511: 2.22, 1.89; Tyr520: 2.10; Gln281: 2.04; Thr282: 1.73; Asn277: 2.73; Lys454: 1.90 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tian, H.; Shi, P.; Li, G. Isolation of Novel ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Peptides from Quinoa Bran Albumin Assisted with an In Silico Approach: Characterization, In Vivo Antihypertension, and Molecular Docking. Molecules 2019, 24, 4562. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244562
Zheng Y, Wang X, Zhuang Y, Li Y, Tian H, Shi P, Li G. Isolation of Novel ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Peptides from Quinoa Bran Albumin Assisted with an In Silico Approach: Characterization, In Vivo Antihypertension, and Molecular Docking. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4562. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244562
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yajun, Xian Wang, Yongliang Zhuang, Yan Li, Hailong Tian, Panqi Shi, and Guifeng Li. 2019. "Isolation of Novel ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Peptides from Quinoa Bran Albumin Assisted with an In Silico Approach: Characterization, In Vivo Antihypertension, and Molecular Docking" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4562. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244562
APA StyleZheng, Y., Wang, X., Zhuang, Y., Li, Y., Tian, H., Shi, P., & Li, G. (2019). Isolation of Novel ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Peptides from Quinoa Bran Albumin Assisted with an In Silico Approach: Characterization, In Vivo Antihypertension, and Molecular Docking. Molecules, 24(24), 4562. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244562