Harnessing the Effects of BTKi on T Cells for Effective Immunotherapy against CLL
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Improved Antitumor T-Cell Responses during Treatment with Ibrutinib
2.1. Absolute Number of T Cells
2.2. T-Cell Receptor Repertoire
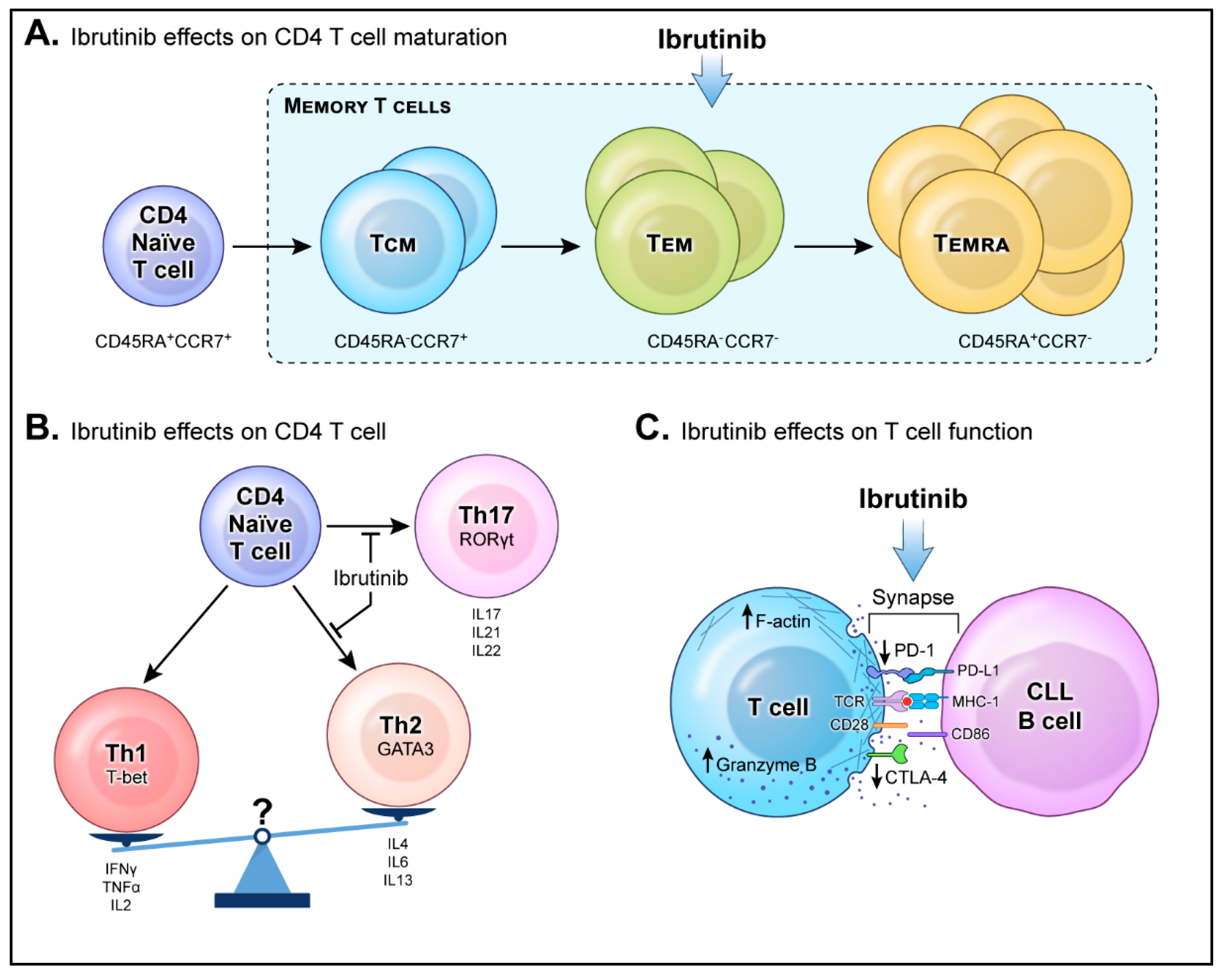
2.3. Memory T Cells
2.4. Th1 and Th2 Polarization
2.5. Th17 and Tregs Balance
2.6. T-Cell Function
2.7. Second Generation BTKi
3. Improved Efficacy with Combinations of BTKi and T-Cell Directed Immunotherapy
3.1. Combining BTK Inhibition with Autologous T-Cell Therapies
3.1.1. BTKi + Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cells
3.1.2. BTKi + Bispecific Antibodies (BsAbs)
3.2. Combining BTK Inhibitors with Immunomodulatory Drugs
3.3. Combining BTK Inhibitors with Checkpoint Inhibitors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herishanu, Y.; Pérez-Galán, P.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Vire, B.; Gibellini, F.; Njuguna, N.; Lee, E.; Stennett, L.; et al. The lymph node microenvironment promotes B-cell receptor signaling, NF-kappaB activation, and tumor proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Flinn, I.W.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Grant, B.; Sharman, J.P.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, I.E.; Underbayev, C.; Albitar, A.; Herman, S.E.; Tian, X.; Maric, I.; Arthur, D.C.; Wake, L.; Pittaluga, S.; Yuan, C.M.; et al. Clonal evolution leading to ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiestner, A. Emerging role of kinase-targeted strategies in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2012, 2012, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschle, M.; Campana, D.; Carding, S.R.; Richard, C.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Brenner, M.K. Interferon gamma inhibits apoptotic cell death in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dancescu, M.; Rubio-Trujillo, M.; Biron, G.; Bron, D.; Delespesse, G.; Sarfati, M. Interleukin 4 protects chronic lymphocytic leukemic B cells from death by apoptosis and upregulates Bcl-2 expression. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schattner, E.J.; Mascarenhas, J.; Reyfman, I.; Koshy, M.; Woo, C.; Friedman, S.M.; Crow, M.K. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia B Cells Can Express CD40 Ligand and Demonstrate T-Cell Type Costimulatory Capacity. Blood 1998, 91, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnara, D.; Kaufman, M.S.; Calissano, C.; Marsilio, S.; Patten, P.E.; Simone, R.; Chum, P.; Yan, X.J.; Allen, S.L.; Kolitz, J.E.; et al. A novel adoptive transfer model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia suggests a key role for T lymphocytes in the disease. Blood 2011, 117, 5463–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riches, J.C.; Davies, J.K.; McClanahan, F.; Fatah, R.; Iqbal, S.; Agrawal, S.; Ramsay, A.G.; Gribben, J.G. T cells from CLL patients exhibit features of T-cell exhaustion but retain capacity for cytokine production. Blood 2013, 121, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovsky, J.A.; Beckwith, K.A.; Natarajan, G.; Woyach, J.A.; Jaglowski, S.; Zhong, Y.; Hessler, J.D.; Liu, T.M.; Chang, B.Y.; Larkin, K.M.; et al. Ibrutinib is an irreversible molecular inhibitor of ITK driving a Th1-selective pressure in T lymphocytes. Blood 2013, 122, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiestner, A. The role of B-cell receptor inhibitors in the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2015, 100, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Catovsky, D.; Miliani, E.; Okos, A.; Galton, D.A. Clinical significance of T-cells in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 1974, 2, 751–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, N.E.; Johnson, J.D.; Stanek, R.; Douglas, S.D. T-cell subpopulations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Abnormalities in distribtuion and in in vitro receptor maturation. Blood 1979, 54, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herrmann, F.; Lochner, A.; Philippen, H.; Jauer, B.; Ruhl, H. Imbalance of T cell subpopulations in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia of the B cell type. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1982, 49, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nunes, C.; Wong, R.; Mason, M.; Fegan, C.; Man, S.; Pepper, C. Expansion of a CD8(+)PD-1(+) replicative senescence phenotype in early stage CLL patients is associated with inverted CD4:CD8 ratios and disease progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niemann, C.U.; Herman, S.E.; Maric, I.; Gomez-Rodriguez, J.; Biancotto, A.; Chang, B.Y.; Martyr, S.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Yuan, C.M.; Calvo, K.R.; et al. Disruption of in vivo Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Tumor-Microenvironment Interactions by Ibrutinib—Findings from an Investigator-Initiated Phase II Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1572–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Q.; Sivina, M.; Robins, H.; Yusko, E.; Vignali, M.; O’Brien, S.; Keating, M.J.; Ferrajoli, A.; Estrov, Z.; Jain, N.; et al. Ibrutinib Therapy Increases T Cell Repertoire Diversity in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burger, J.A.; Sivina, M.; Jain, N.; Kim, E.; Kadia, T.; Estrov, Z.; Nogueras-Gonzalez, G.M.; Huang, X.; Jorgensen, J.; Li, J.; et al. Randomized trial of ibrutinib vs. ibrutinib plus rituximab in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2019, 133, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, M.; Beckwith, K.; Do, P.; Mundy, B.L.; Gordon, A.; Lehman, A.M.; Maddocks, K.J.; Cheney, C.; Jones, J.A.; Flynn, J.M.; et al. Ibrutinib treatment improves T cell number and function in CLL patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3052–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Mellstedt, H.; Jondal, M. Presence of clonal T cell populations in chronic B lymphocytic leukemia and smoldering myeloma. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 171, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farace, F.; Orlanducci, F.; Dietrich, P.Y.; Gaudin, C.; Angevin, E.; Courtier, M.H.; Bayle, C.; Hercend, T.; Triebel, F. T cell repertoire in patients with B chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Evidence for multiple in vivo T cell clonal expansions. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goolsby, C.L.; Kuchnio, M.; Finn, W.G.; Peterson, L. Expansions of clonal and oligoclonal T cells in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia are primarily restricted to the CD3(+)CD8(+) T-cell population. Cytometry 2000, 42, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Villamor, N.; Colomer, D.; Rozman, M.; Raffeld, M.; Montserrat, E.; Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S. Clonal T-cell populations and increased risk for cytotoxic T-cell lymphomas in B-CLL patients: Clinicopathologic observations and molecular analysis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2004, 28, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, G.; Vardi, A.; Puiggros, A.; Gomez-Llonin, A.; Muro, M.; Rodriguez-Rivera, M.; Stalika, E.; Abella, E.; Gimeno, E.; Lopez-Sanchez, M.; et al. Restricted T cell receptor repertoire in CLL-like monoclonal B cell lymphocytosis and early stage CLL. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1432328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardi, A.; Agathangelidis, A.; Stalika, E.; Karypidou, M.; Siorenta, A.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Rosenquist, R.; Hadzidimitriou, A.; Ghia, P.; Sutton, L.A.; et al. Antigen Selection Shapes the T-cell Repertoire in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vardi, A.; Vlachonikola, E.; Karypidou, M.; Stalika, E.; Bikos, V.; Gemenetzi, K.; Maramis, C.; Siorenta, A.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Pospisilova, S.; et al. Restrictions in the T-cell repertoire of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: High-throughput immunoprofiling supports selection by shared antigenic elements. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, M.J.; Basumallik, N.; Herman, S.E.M.; Cook, E.M.; Ahn, I.E.; Wiestner, A.; Sun, C.C. Ibrutinib Increases the Clonality of TCR Repertoire in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2018, 132, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallusto, F.; Lenig, D.; Forster, R.; Lipp, M.; Lanzavecchia, A. Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature 1999, 401, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Larbi, A.; Derhovanessian, E.; Ozcelik, D.; Naumova, E.; Pawelec, G. Multiparameter flow cytometric analysis of CD4 and CD8 T cell subsets in young and old people. Immun. Ageing 2008, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pepper, M.; Jenkins, M.K. Origins of CD4(+) effector and central memory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palma, M.; Gentilcore, G.; Heimersson, K.; Mozaffari, F.; Nasman-Glaser, B.; Young, E.; Rosenquist, R.; Hansson, L.; Osterborg, A.; Mellstedt, H. T cells in chronic lymphocytic leukemia display dysregulated expression of immune checkpoints and activation markers. Haematologica 2017, 102, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, T.; Nakui, M.; Sato, M.; Iwakabe, K.; Kitamura, H.; Sekimoto, M.; Ohta, A.; Koda, T.; Nishimura, S. The critical role of Th1-dominant immunity in tumor immunology. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2000, 46 (Suppl. S1), S52–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podhorecka, M.; Dmoszynska, A.; Rolinski, J.; Wasik, E. T type 1/type 2 subsets balance in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia--the three-color flow cytometry analysis. Leuk. Res. 2002, 26, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiyan, P.; Zheng, L.; Ishihara, S.; Reed, J.; Lenardo, M.J. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce cytokine deprivation-mediated apoptosis of effector CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.E.; Sahaf, B.; Logan, A.C.; O’Brien, S.; Byrd, J.C.; Hillmen, P.; Brown, J.R.; Dyer, M.J.; Mato, A.R.; Keating, M.J.; et al. Ibrutinib efficacy and tolerability in patients with relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia following allogeneic HCT. Blood 2016, 128, 2899–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herman, S.E.; Gordon, A.L.; Hertlein, E.; Ramanunni, A.; Zhang, X.; Jaglowski, S.; Flynn, J.; Jones, J.; Blum, K.A.; Buggy, J.J.; et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase represents a promising therapeutic target for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is effectively targeted by PCI-32765. Blood 2011, 117, 6287–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podhorecka, M.; Goracy, A.; Szymczyk, A.; Kowal, M.; Ibanez, B.; Jankowska-Lecka, O.; Macheta, A.; Nowaczynska, A.; Drab-Urbanek, E.; Chocholska, S.; et al. Changes in T-cell subpopulations and cytokine network during early period of ibrutinib therapy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients: The significant decrease in T regulatory cells number. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 34661–34669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perry, C.; Herishanu, Y.; Hazan-Halevy, I.; Kay, S.; Bdolach, N.; Naparstek, E.; Polliack, A.; Grisaru, D. Reciprocal changes in regulatory T cells and Th17 helper cells induced by exercise in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 53, 1807–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Memarian, A.; Asgarian-Omran, H.; Razavi, S.M.; Sarrafnejad, A.; Shokri, F. Downregulation of IL-17-producing T cells is associated with regulatory T cell expansion and disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Tumour Biol. 2013, 34, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lad, D.P.; Varma, S.; Varma, N.; Sachdeva, M.U.; Bose, P.; Malhotra, P. Regulatory T-cell and T-helper 17 balance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression and autoimmune cytopenias. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.M.; Lonergan, R.; Costelloe, L.; Kinsella, K.; Moran, B.; O’Farrelly, C.; Tubridy, N.; Mills, K.H. CD39+Foxp3+ regulatory T Cells suppress pathogenic Th17 cells and are impaired in multiple sclerosis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7602–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pulte, D.; Furman, R.R.; Broekman, M.J.; Drosopoulos, J.H.; Ballard, H.S.; Olson, K.E.; Kizer, J.R.; Marcus, A.J. CD39 expression on T lymphocytes correlates with severity of disease in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011, 11, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.Z.; Grote, D.M.; Ziesmer, S.C.; Xiu, B.; Yates, N.R.; Secreto, F.J.; Hodge, L.S.; Witzig, T.E.; Novak, A.J.; Ansell, S.M. Soluble and membrane-bound TGF-beta-mediated regulation of intratumoral T cell differentiation and function in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, K.W.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Coffman, R.L.; O’Garra, A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 683–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Rodriguez, J.; Wohlfert, E.A.; Handon, R.; Meylan, F.; Wu, J.Z.; Anderson, S.M.; Kirby, M.R.; Belkaid, Y.; Schwartzberg, P.L. Itk-mediated integration of T cell receptor and cytokine signaling regulates the balance between Th17 and regulatory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eken, A.; Cansever, M.; Somekh, I.; Mizoguchi, Y.; Zietara, N.; Okus, F.Z.; Erdem, S.; Canatan, H.; Akyol, S.; Ozcan, A.; et al. Genetic Deficiency and Biochemical Inhibition of ITK Affect Human Th17, Treg, and Innate Lymphoid Cells. J. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 39, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J.; Ha, S.J.; Kaech, S.M.; Haining, W.N.; Sarkar, S.; Kalia, V.; Subramaniam, S.; Blattman, J.N.; Barber, D.L.; Ahmed, R. Molecular signature of CD8+ T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection. Immunity 2007, 27, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wherry, E.J.; Kurachi, M. Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, B.S.; Roessner, P.M.; Yazdanparast, H.; Colomer, D.; Campo, E.; Kugler, S.; Yosifov, D.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Schmidt, M.; Gabriel, R.; et al. Control of chronic lymphocytic leukemia development by clonally-expanded CD8(+) T-cells that undergo functional exhaustion in secondary lymphoid tissues. Leukemia 2019, 33, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgun, G.; Holderried, T.A.; Zahrieh, D.; Neuberg, D.; Gribben, J.G. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induce changes in gene expression of CD4 and CD8 T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, A.G.; Johnson, A.J.; Lee, A.M.; Gorgun, G.; Le Dieu, R.; Blum, W.; Byrd, J.C.; Gribben, J.G. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia T cells show impaired immunological synapse formation that can be reversed with an immunomodulating drug. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.Z.; Grote, D.M.; Ziesmer, S.C.; Xiu, B.; Novak, A.J.; Ansell, S.M. PD-1 expression defines two distinct T-cell sub-populations in follicular lymphoma that differentially impact patient survival. Blood Cancer J. 2015, 5, e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, W.; LaPlant, B.R.; Call, T.G.; Parikh, S.A.; Leis, J.F.; He, R.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Sinha, S.; Le-Rademacher, J.; Feldman, A.L.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with CLL and Richter transformation or with relapsed CLL. Blood 2017, 129, 3419–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Zhou, J.; Young, K.H. PD-1 expression and clinical PD-1 blockade in B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2018, 131, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Josefsson, S.E.; Beiske, K.; Blaker, Y.N.; Forsund, M.S.; Holte, H.; Ostenstad, B.; Kimby, E.; Koksal, H.; Walchli, S.; Bai, B.; et al. TIGIT and PD-1 Mark Intratumoral T Cells with Reduced Effector Function in B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiloo, S.; Allahmoradi, E.; Tehrani, M.; Hossein-Nataj, H.; Shekarriz, R.; Janbabaei, G.; Abediankenari, S.; Asgarian-Omran, H. Frequency and functional characterization of exhausted CD8(+) T cells in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2017, 98, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Shaim, H.; Thompson, P.A.; Burger, J.A.; Keating, M.; Estrov, Z.; Harris, D.; Kim, E.; Ferrajoli, A.; Daher, M.; et al. Ibrutinib modulates the immunosuppressive CLL microenvironment through STAT3-mediated suppression of regulatory B-cell function and inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. Leukemia 2018, 32, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazoglou, D.; Lesnick, C.E.; Wang, V.; Kay, N.E.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Ramsay, A.G. Ibrutinib-Based Therapy Improves Anti-Tumor T Cell Killing Function Allowing Effective Pairing with Anti-PD-L1 Immunotherapy Compared to Traditional FCR Chemoimmunotherapy; Implications for Therapy and Correlative Immune Functional Data from the Phase III E1912 Trial. Blood 2018, 132, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Harrington, B.; O’Brien, S.; Jones, J.A.; Schuh, A.; Devereux, S.; Chaves, J.; Wierda, W.G.; Awan, F.T.; Brown, J.R.; et al. Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, V.; Balakrishnan, K.; Bibikova, E.; Ayres, M.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; Gandhi, V. Comparison of Acalabrutinib, A Selective Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, with Ibrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3734–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pleyer, C.; Sun, C.C.; Niermann, P.; Tian, X.; Ahn, I.E.; Valdez, J.; Lotter, J.; Izumi, R.; Hamdy, A.; Wiestner, A. Partial Reconstitution of Humoral and Cellular Immunity in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Treated with Acalabrutinib. Blood 2018, 132, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.X.; Zhu, H.Y.; Li, X.T.; Xia, Y.; Miao, K.R.; Zhao, S.S.; Wu, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Xu, W.; Li, J.Y. The impacts of zanubrutinib on immune cells in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Liu, X.; Cao, X.; Xu, S. T-cell expression of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase promotes autoreactive T-cell activation and exacerbates aplastic anemia. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porter, D.L.; Levine, B.L.; Kalos, M.; Bagg, A.; June, C.H. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in chronic lymphoid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porter, D.L.; Hwang, W.T.; Frey, N.V.; Lacey, S.F.; Shaw, P.A.; Loren, A.W.; Bagg, A.; Marcucci, K.T.; Shen, A.; Gonzalez, V.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells persist and induce sustained remissions in relapsed refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 303ra139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.X.; Gao, W.J.; You, J.; Wu, L.H.; Liu, J.L.; Wang, Z.X. The efficacy of anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cells for B-cell malignancies. Cytotherapy 2019, 21, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraietta, J.A.; Beckwith, K.A.; Patel, P.R.; Ruella, M.; Zheng, Z.; Barrett, D.M.; Lacey, S.F.; Melenhorst, J.J.; McGettigan, S.E.; Cook, D.R.; et al. Ibrutinib enhances chimeric antigen receptor T-cell engraftment and efficacy in leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruella, M.; Kenderian, S.S.; Shestova, O.; Fraietta, J.A.; Qayyum, S.; Zhang, Q.; Maus, M.V.; Liu, X.; Nunez-Cruz, S.; Klichinsky, M.; et al. The Addition of the BTK Inhibitor Ibrutinib to Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells (CART19) Improves Responses against Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2684–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turtle, C.J.; Hay, K.A.; Hanafi, L.A.; Li, D.; Cherian, S.; Chen, X.; Wood, B.; Lozanski, A.; Byrd, J.C.; Heimfeld, S.; et al. Durable Molecular Remissions in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Treated With CD19-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells After Failure of Ibrutinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3010–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.I.; Vides, V.; Frey, N.V.; Metzger, S.; O’Brien, M.; Hexner, E.; Mato, A.R.; Lacey, S.F.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Pequignot, E.; et al. Prospective Clinical Trial of Anti-CD19 CAR T Cells in Combination with Ibrutinib for the Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Shows a High Response Rate. Blood 2018, 132, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, J.; Hirayama, A.V.; Hay, K.A.; Li, D.; Lymp, J.; Sheih, A.; Purushe, J.; Pender, B.S.; Hawkins, R.M.; Vakil, A.; et al. Comparison of Efficacy and Toxicity of CD19-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cells Alone or in Combination with Ibrutinib for Relapsed and/or Refractory CLL. Blood 2018, 132, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontermann, R.E.; Brinkmann, U. Bispecific antibodies. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Labrijn, A.F.; Janmaat, M.L.; Reichert, J.M.; Parren, P. Bispecific antibodies: A mechanistic review of the pipeline. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 585–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarian, A.A.; Archibeque, I.L.; Nguyen, Y.H.; Wang, P.; Sinclair, A.M.; Powers, D.A. Characterization of bispecific T-cell Engager (BiTE) antibodies with a high-capacity T-cell dependent cellular cytotoxicity (TDCC) assay. J. Biomol. Screen. 2015, 20, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, R.; Pepper, C.; Brennan, P.; Nagorsen, D.; Man, S.; Fegan, C. Blinatumomab induces autologous T-cell killing of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goebeler, M.E.; Knop, S.; Viardot, A.; Kufer, P.; Topp, M.S.; Einsele, H.; Noppeney, R.; Hess, G.; Kallert, S.; Mackensen, A.; et al. Bispecific T-Cell Engager (BiTE) Antibody Construct Blinatumomab for the Treatment of Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Final Results From a Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, H.R.; Qi, J.; Cook, E.M.; Nichols, C.; Dadashian, E.L.; Underbayev, C.; Herman, S.E.M.; Saba, N.S.; Keyvanfar, K.; Sun, C.; et al. A CD19/CD3 bispecific antibody for effective immunotherapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the ibrutinib era. Blood 2018, 132, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, S.H.; Evans, R.; Harasser, M.; El-Kholy, M.; Paredes-Moscosso, S.R.; Della Peruta, M.; Nathwani, A.C. Ibrutinib enhances the efficacy of ROR1 bispecific T cell engager mediated cytotoxicity in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanan-Khan, A.; Miller, K.C.; Musial, L.; Lawrence, D.; Padmanabhan, S.; Takeshita, K.; Porter, C.W.; Goodrich, D.W.; Bernstein, Z.P.; Wallace, P.; et al. Clinical efficacy of lenalidomide in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Results of a phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5343–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kater, A.P.; Tonino, S.H.; Egle, A.; Ramsay, A.G. How does lenalidomide target the chronic lymphocytic leukemia microenvironment? Blood 2014, 124, 2184–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, A.G.; Clear, A.J.; Fatah, R.; Gribben, J.G. Multiple inhibitory ligands induce impaired T-cell immunologic synapse function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia that can be blocked with lenalidomide: Establishing a reversible immune evasion mechanism in human cancer. Blood 2012, 120, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aue, G.; Sun, C.; Liu, D.; Park, J.H.; Pittaluga, S.; Tian, X.; Lee, E.; Soto, S.; Valdez, J.; Maric, I.; et al. Activation of Th1 Immunity within the Tumor Microenvironment Is Associated with Clinical Response to Lenalidomide in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, A.M.; Bahlo, J.; Sandra, R.; Al-Sawaf, O.; Aldaoud, A.; Hebart, H.; Jentsch-Ulrich, K.; Doerfel, S.; Fischer, K.; Wendtner, C.M.; et al. Lenalidomide Maintenance after Front Line Therapy Substantially Prolongs Progression Free Survival in High Risk CLL: Interim Results of a Phase 3 Study (CLL M1 study of the German CLL Study Group). Blood 2016, 128, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Ruppert, A.S.; Heerema, N.A.; Halvorson, A.E.; Hoke, E.; Smith, M.R.; Godwin, J.E.; Couban, S.; Fehniger, T.A.; Thirman, M.J.; et al. Lenalidomide consolidation benefits patients with CLL receiving chemoimmunotherapy: Results for CALGB 10404 (Alliance). Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1705–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujjani, C.; Wang, H.; Skarbnik, A.; Trivedi, N.; Ramzi, P.; Khan, N.; Cheson, B.D. A phase 1 study of lenalidomide and ibrutinib in combination with rituximab in relapsed and refractory CLL. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sagiv-Barfi, I.; Kohrt, H.E.; Czerwinski, D.K.; Ng, P.P.; Chang, B.Y.; Levy, R. Therapeutic antitumor immunity by checkpoint blockade is enhanced by ibrutinib, an inhibitor of both BTK and ITK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E966–E972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Younes, A.; Brody, J.; Carpio, C.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Ben-Yehuda, D.; Ferhanoglu, B.; Nagler, A.; Ozcan, M.; Avivi, I.; Bosch, F.; et al. Safety and activity of ibrutinib in combination with nivolumab in patients with relapsed non-Hodgkin lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A phase 1/2a study. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e67–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masso-Valles, D.; Jauset, T.; Serrano, E.; Sodir, N.M.; Pedersen, K.; Affara, N.I.; Whitfield, J.R.; Beaulieu, M.E.; Evan, G.I.; Elias, L.; et al. Ibrutinib exerts potent antifibrotic and antitumor activities in mouse models of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Kinoshita, T.; Sukbuntherng, J.; Chang, B.Y.; Elias, L. Ibrutinib Inhibits ERBB Receptor Tyrosine Kinases and HER2-Amplified Breast Cancer Cell Growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, W.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Wu, S.; Dai, B.; Ou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Heymach, J.V.; Gold, K.A.; et al. Selective antitumor activity of ibrutinib in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molina-Cerrillo, J.; Alonso-Gordoa, T.; Gajate, P.; Grande, E. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) as a promising target in solid tumors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 58, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mhibik, M.; Wiestner, A.; Sun, C. Harnessing the Effects of BTKi on T Cells for Effective Immunotherapy against CLL. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010068
Mhibik M, Wiestner A, Sun C. Harnessing the Effects of BTKi on T Cells for Effective Immunotherapy against CLL. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010068
Chicago/Turabian StyleMhibik, Maissa, Adrian Wiestner, and Clare Sun. 2020. "Harnessing the Effects of BTKi on T Cells for Effective Immunotherapy against CLL" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010068



