Potential Use of Extracellular Vesicles Generated by Microbubble-Assisted Ultrasound as Drug Nanocarriers for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
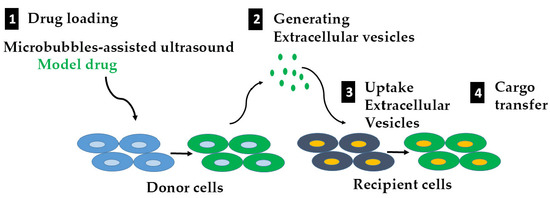
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Loading Model Drugs into Cells
2.2. Triggering EV Release Containing Model Drug Cargo
2.3. Uptake of EVs Carrying CTG and BSA FITC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Preparation for USMB
4.3. Loading Model Drug Using USMB
4.4. Flow Cytometry Measurement
4.5. Immunogold Electron Microscopy
4.6. EV Isolation and Concentration
4.7. Uptake Assay
4.8. RT-PCR
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balachandran, B.; Yuana, Y. Extracellular vesicles-based drug delivery system for cancer treatment. Cogent Med. 2019, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, F.; Xiong, F.; Gu, N. The Smart Drug Delivery System and Its Clinical Potential. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1306–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuana, Y.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Extracellular vesicles in physiological and pathological conditions. Blood Rev. 2013, 27, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, S.; Busatto, S.; Pham, A.; Tian, M.; Suh, A.; Carson, K.; Quintero, A.; Lafrence, M.; Malik, H.; Santana, M.X.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Theranostics 2019, 9, 8001–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, P.; Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Lv, M.; Li, D.; Katirai, F.; Shen, G.X.; et al. Delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs in tumour cell-derived microparticles. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Meel, R.; Fens, M.H.; Vader, P.; van Solinge, W.W.; Eniola-Adefeso, O.; Schiffelers, R.M. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: Lessons from the liposome field. J. Control Release 2014, 195, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fais, S.; O’Driscoll, L.; Borras, F.E.; Buzas, E.; Camussi, G.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; Cordeiro da Silva, A.; Del Portillo, H.; El Andaloussi, S.; et al. Evidence-Based Clinical Use of Nanoscale Extracellular Vesicles in Nanomedicine. ACS Nano. 2016, 10, 3886–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitragotri, S. Healing sound: The use of ultrasound in drug delivery and other therapeutic applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennoga, C.A.; Kanbar, E.; Auboire, L.; Dujardin, P.A.; Fouan, D.; Escoffre, J.M.; Bouakaz, A. Microbubble-mediated ultrasound drug-delivery and therapeutic monitoring. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouakaz, A.; Zeghimi, A.; Doinikov, A.A. Sonoporation: Concept and Mechanisms. In Therapeutic Ultrasound; Escoffre, J.-M., Bouakaz, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 175–189. ISBN 978-3-319-22536-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lentacker, I.; De Cock, I.; Deckers, R.; De Smedt, S.C.; Moonen, C.T. Understanding ultrasound induced sonoporation: Definitions and underlying mechanisms. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 72, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, R.; Klibanov, A.L. Co-administration of Microbubbles and Drugs in Ultrasound-Assisted Drug Delivery: Comparison with Drug-Carrying Particles. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 880, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.Z.; Du, L.N.; Lu, C.T.; Jin, Y.G.; Ge, S.P. Potential and problems in ultrasound-responsive drug delivery systems. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1621–1633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuana, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lammertink, B.H.A.; Vader, P.; Deckers, R.; Bos, C.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Moonen, C.T. Microbubbles-Assisted Ultrasound Triggers the Release of Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zomer, A.; Maynard, C.; Verweij, F.J.; Kamermans, A.; Schafer, R.; Beerling, E.; Schiffelers, R.M.; de Wit, E.; Berenguer, J.; Ellenbroek, S.I.; et al. In Vivo imaging reveals extracellular vesicle-mediated phenocopying of metastatic behavior. Cell 2015, 161, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lammertink, B.; Deckers, R.; Storm, G.; Moonen, C.; Bos, C. Duration of ultrasound-mediated enhanced plasma membrane permeability. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 482, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donahue, N.D.; Acar, H.; Wilhelm, S. Concepts of nanoparticle cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and kinetics in nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 143, 68–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega, F.G.; Roefs, M.T.; de Miguel Perez, D.; Kooijmans, S.A.; de Jong, O.G.; Sluijter, J.P.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Vader, P. Interfering with endolysosomal trafficking enhances release of bioactive exosomes. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, R.; Larson, B.J.; Cheng, T.C.; Gibson, M.A.; Otani, S.; Naerdemann, W.; Howell, S.B. Abnormal lysosomal trafficking and enhanced exosomal export of cisplatin in drug-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro-Ibáñez, E.; Neuvonen, M.; Takatalo, M.; Thanigai Arasu, U.; Capasso, C.; Cerullo, V.; Rhim, J.S.; Rilla, K.; Yliperttula, M.; Siljander, P.R.M. Metastatic state of parent cells influences the uptake and functionality of prostate cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, M. Characteristics of SonoVuetrade mark. Echocardiography 1999, 16, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwaha, R.; Sharma, M. DQ-Red BSA Trafficking Assay in Cultured Cells to Assess Cargo Delivery to Lysosomes. Bio-Protocol 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lammertink, B.H.A.; Bos, C.; van der Wurff-Jacobs, K.M.; Storm, G.; Moonen, C.T.; Deckers, R. Increase of intracellular cisplatin levels and radiosensitization by ultrasound in combination with microbubbles. J. Control. Release 2016, 238, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Pol, E.; Coumans, F.A.; Grootemaat, A.E.; Gardiner, C.; Sargent, I.L.; Harrison, P.; Sturk, A.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; Nieuwland, R. Particle size distribution of exosomes and microvesicles determined by transmission electron microscopy, flow cytometry, nanoparticle tracking analysis, and resistive pulse sensing. J. Thromb. Haemost 2014, 12, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cizmar, P.; Yuana, Y. Detection and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles by Transmission and Cryo-Transmission Electron Microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1660, 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Pol, E.; Coumans, F.; Varga, Z.; Krumrey, M.; Nieuwland, R. Innovation in detection of microparticles and exosomes. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuana, Y.; Balachandran, B.; van der Wurff-Jacobs, K.M.G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Moonen, C.T. Potential Use of Extracellular Vesicles Generated by Microbubble-Assisted Ultrasound as Drug Nanocarriers for Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3024. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21083024
Yuana Y, Balachandran B, van der Wurff-Jacobs KMG, Schiffelers RM, Moonen CT. Potential Use of Extracellular Vesicles Generated by Microbubble-Assisted Ultrasound as Drug Nanocarriers for Cancer Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(8):3024. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21083024
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuana, Yuana, Banuja Balachandran, Kim M. G. van der Wurff-Jacobs, Raymond M. Schiffelers, and Chrit T. Moonen. 2020. "Potential Use of Extracellular Vesicles Generated by Microbubble-Assisted Ultrasound as Drug Nanocarriers for Cancer Treatment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 8: 3024. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21083024
APA StyleYuana, Y., Balachandran, B., van der Wurff-Jacobs, K. M. G., Schiffelers, R. M., & Moonen, C. T. (2020). Potential Use of Extracellular Vesicles Generated by Microbubble-Assisted Ultrasound as Drug Nanocarriers for Cancer Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(8), 3024. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21083024