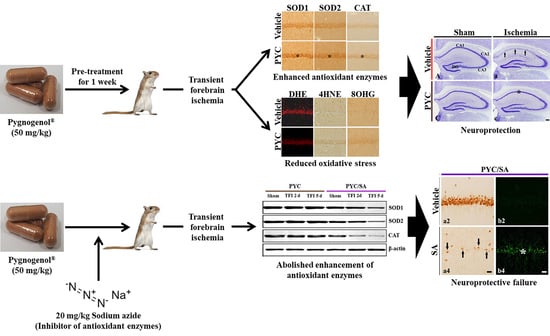
Pycnogenol® Supplementation Attenuates Memory Deficits and Protects Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Neurons via Antioxidative Role in a Gerbil Model of Transient Forebrain Ischemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. PYC Preparation and Characteristics
2.3. Experimental Groups and PYC Supplementation
2.4. TFI Induction
2.5. Tests of Learning and Memory
2.5.1. Passive Avoidance Test (PAT)
2.5.2. 8-Arm Radial Maze Test
2.6. Preparation of Tissue Sections
2.7. Histochemistry with Cresyl Violet (CV)
2.8. Histofluorescence with Fluoro-Jade B (F-J B)
2.9. Immunohistochemical Stainings
2.10. Dihydroethidium (DHE) Histofluorescence
2.11. Treatment of Sodium Azide
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Attenuation of Learning and Memory Deficits
3.1.1. PAT
3.1.2. 8-Arm Radial Maze Test
3.2. Protection of CA1 Pyramidal Cells
3.2.1. CV+ Cells
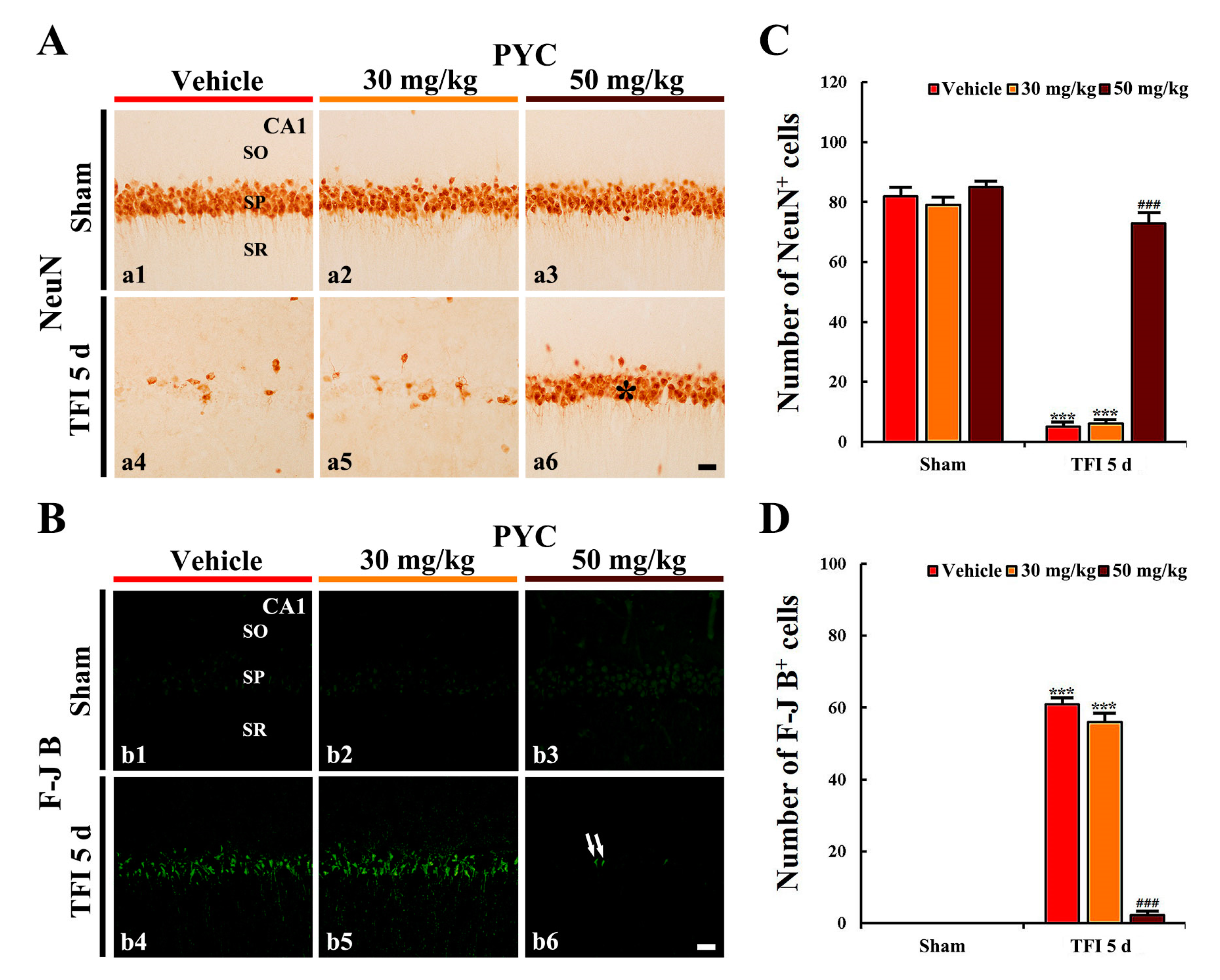
3.2.2. NeuN+ Cells
3.2.3. F-J B+ Cells
3.3. Attenuated Oxidative Stress
3.3.1. DHE Fluorescence
3.3.2. 8-OHG and 4HNE Immunoreactivities
3.4. Increased Antioxidant Enzyme Immunoreactivities
3.4.1. SODs Immunoreactivity
3.4.2. CAT Immunoreactivity
3.5. SA Effect on Oxidative Stress
3.6. Disappearance of Neuroprotection by SA
3.6.1. NeuN+ Cells
3.6.2. F-J B+ Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.C.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Cho, J.H.; Choi, J.H.; Yoo, K.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, I.K.; Kwon, Y.G.; et al. New gabaergic neurogenesis in the hippocampal CA1 region of a gerbil model of long-term survival after transient cerebral ischemic injury. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Nakamura, T.; Toyoshima, T.; Liu, Y.; Hirooka, K.; Kawai, N.; Okabe, N.; Shiraga, F.; Tamiya, T.; Miyamoto, O.; et al. Edaravone, a free radical scavenger, attenuates behavioral deficits following transient forebrain ischemia by inhibiting oxidative damage in gerbils. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 506, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.L.; Bayraktutan, U. Oxidative stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke. Int. J. Stroke J. Int. Stroke Soc. 2009, 4, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yang, S. Targeting oxidative stress for the treatment of ischemic stroke: Upstream and downstream therapeutic strategies. Brain Circ. 2016, 2, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Xie, W.; Xu, Q.; Liang, T.; Xu, X.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Neuroprotective effects of radix scrophulariae on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via mapk pathways. Molecules 2018, 23, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, T.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H.; Tian, M. Effect of chinese herbal medicine on molecular imaging of neurological disorders. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2017, 135, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.C.; Yuan, Y.L.; Chai, F.R.; Ji, F.J. Effect of melilotus officinalis extract on the apoptosis of brain tissues by altering cerebral thrombosis and inflammatory mediators in acute cerebral ischemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Cui, Y.Y. Pine bark extracts: Nutraceutical, pharmacological, and toxicological evaluation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 353, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verlaet, A.A.J.; Maasakkers, C.M.; Hermans, N.; Savelkoul, H.F.J. Rationale for dietary antioxidant treatment of ADHD. Nutrients 2018, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drehsen, G. From ancient pine bark uses to pycnogenol. In Antioxidant Food Supplements in Human Health; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Furumura, M.; Sato, N.; Kusaba, N.; Takagaki, K.; Nakayama, J. Oral administration of french maritime pine bark extract (flavangenol®) improves clinical symptoms in photoaged facial skin. Clin. Interv. Aging 2012, 7, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Packer, L.; Rimbach, G.; Virgili, F. Antioxidant activity and biologic properties of a procyanidin-rich extract from pine (pinus maritima) bark, pycnogenol. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 704–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.L.; Buz’Zard, A.R.; Lau, B.H. Pycnogenol protects neurons from amyloid-beta peptide-induced apoptosis. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2002, 104, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Zaheer, A. Protection of MPTP-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration by pycnogenol. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paarmann, K.; Prakash, S.R.; Krohn, M.; Mohle, L.; Brackhan, M.; Bruning, T.; Eiriz, I.; Pahnke, J. French maritime pine bark treatment decelerates plaque development and improves spatial memory in alzheimer’s disease mice. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2019, 57, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozoner, B.; Yuceli, S.; Aydin, S.; Yazici, G.N.; Sunar, M.; Arslan, Y.K.; Coban, T.A.; Suleyman, H. Effects of pycnogenol on ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammatory and oxidative brain injury in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 704, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.K.; Kim, H.; Song, M.; Lee, J.C.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Yang, G.E.; Ohk, T.G.; Shin, M.C.; Cho, J.H.; et al. Time-course pattern of neuronal loss and gliosis in gerbil hippocampi following mild, severe, or lethal transient global cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J.H.; Choi, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, J.C.; Koo, H.M.; Hwangbo, G.; Yoo, K.Y.; Lee, C.H.; et al. Long-term exercise improves memory deficits via restoration of myelin and microvessel damage, and enhancement of neurogenesis in the aged gerbil hippocampus after ischemic stroke. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2016, 30, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Park, J.; Shin, M.C.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Lee, T.K.; Lee, J.C.; Shin, B.N.; Kim, Y.M.; et al. Long-term treadmill exercise improves memory impairment through restoration of decreased synaptic adhesion molecule 1/2/3 induced by transient cerebral ischemia in the aged gerbil hippocampus. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 103, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, T.K.; Park, C.W.; Park, Y.E.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, H.A.; Won, M.H.; Lee, C.H. Improved hcn channels in pyramidal neurons and their new expression levels in pericytes and astrocytes in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 subfield following transient ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council, N.R. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mulek, M.; Seefried, L.; Genest, F.; Hogger, P. Distribution of constituents and metabolites of maritime pine bark extract (pycnogenol®) into serum, blood cells, and synovial fluid of patients with severe osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2017, 9, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verlaet, A.; van der Bolt, N.; Meijer, B.; Breynaert, A.; Naessens, T.; Konstanti, P.; Smidt, H.; Hermans, N.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; Teodorowicz, M. Toll-like receptor-dependent immunomodulatory activity of pycnogenol®. Nutrients 2019, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rohdewald, P. A review of the french maritime pine bark extract (pycnogenol), a herbal medication with a diverse clinical pharmacology. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 40, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.H.; Shin, M.C.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, H.; Song, M.; Lee, T.K.; Lee, J.C.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.D.; et al. Antioxidant properties of fucoidan alleviate acceleration and exacerbation of hippocampal neuronal death following transient global cerebral ischemia in high-fat diet-induced obese gerbils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, Y.L.; Kang, I.J.; Kim, D.W.; Hwang, I.K.; Lee, C.H.; Yan, B.C.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, T.K.; et al. Melatonin improves vascular cognitive impairment induced by ischemic stroke by remyelination via activation of ERK1/2 signaling and restoration of glutamatergic synapses in the gerbil hippocampus. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Toyoshima, T.; Lu, F.; Sumitani, K.; Shinomiya, A.; Keep, R.F.; Yamamoto, T.; Tamiya, T.; Itano, T. Ameliorative effects of yokukansan on behavioral deficits in a gerbil model of global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2014, 1543, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Ahn, J.H.; Song, M.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, T.K.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.D.; Cho, J.H.; Hwang, I.K.; et al. Pretreated fucoidan confers neuroprotection against transient global cerebral ischemic injury in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 area via reducing of glial cell activation and oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke-Schuller, S.; Schuller, G.; Angenstein, F.; Grosser, O.S.; Goldschmidt, J.; Budinger, E. Brain atlas of the mongolian gerbil (meriones unguiculatus) in CT/MRI-aided stereotaxic coordinates. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 1–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.C.; Park, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Cho, G.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Tae, H.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Kwon, Y.G.L.; et al. Neuroprotection of ischemic preconditioning is mediated by thioredoxin 2 in the hippocampal CA1 region following a subsequent transient cerebral ischemia. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, T.K.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, I.K.; Yan, B.C.; et al. Chronic high-fat diet-induced obesity in gerbils increases pro-inflammatory cytokines and mTOR activation, and elicits neuronal death in the striatum following brief transient ischemia. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 121, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Deng, D.; Chen, W. Inhibitors and activators of sod, GSH-Px, and cat. Enzym. Inhib. Act. 2017, 29, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Somade, O.T.; Olorode, S.K.; Olaniyan, T.O.; Faokunla, O. Quercetin, a polyphenolic phytochemical prevents sodium azide-induced extra-hepatic oxidative stress in rats. Cogent Biol. 2016, 2, 1200798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, M.I.; Cavero, R.Y. Medicinal plants used for neurological and mental disorders in navarra and their validation from official sources. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 169, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.R.; Zhou, S.D.; Shao, Y.J.; Zhang, M.H.; Dong, L.M.; Lv, J.W.; Zhang, H.X.; Tang, Y.H.; Jiang, D.J.; Liu, X.M. Effect of ginkgo biloba extract-761 on motor functions in permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2018, 48, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.J.; Xu, L.; Song, W.T.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wang, L.C.; Zhao, M.B.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, L.Y.; Zeng, K.W.; Tu, P.F. The ethanolic extract of caesalpinia sappan heartwood inhibits cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model through a multi-targeted pharmacological mechanism. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.W.; Im, S.; Jeong, H.R.; Jung, Y.S.; Lee, I.; Kim, K.J.; Park, S.K.; Kim, D.O. Neuroprotective effects of korean red pine (pinus densiflora) bark extract and its phenolics. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, G.L.; Taft, W.C.; Blair, R.E.; Choi, S.C.; DeLorenzo, R.J. Conditions for pharmacologic evaluation in the gerbil model of forebrain ischemia. Stroke 1989, 20, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colbourne, F.; Li, H.; Buchan, A.M.; Clemens, J.A. Continuing postischemic neuronal death in CA1: Influence of ischemia duration and cytoprotective doses of NBQX and SNX-111 in rats. Stroke 1999, 30, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, D.K.; Yoo, K.Y.; Shin, B.N.; Kim, I.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, J.H.; Cho, Y.J.; Kang, I.J.; Kim, Y.M.; et al. Neuronal damage in hippocampal subregions induced by various durations of transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils using Fluoro-Jade B histofluorescence. Brain Res. 2012, 1437, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweatt, J.D. Hippocampal function in cognition. Psychopharmacology 2004, 174, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, C.M.; Burgess, N. The hippocampus and memory: Insights from spatial processing. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preedy, V.R. Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse Volume 1: Foundations of Understanding, Tobacco, Alcohol, Cannabinoids and Opioids; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Penley, S.C.; Gaudet, C.M.; Threlkeld, S.W. Use of an eight-arm radial water maze to assess working and reference memory following neonatal brain injury. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2013, 50940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Song, M.; Kim, H.; Lee, T.K.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, Y.M.; Hwang, I.K.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Rufinamide, an antiepileptic drug, improves cognition and increases neurogenesis in the aged gerbil hippocampal dentate gyrus via increasing expressions of IGF-1, Igf-1r and p-creb. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 286, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yoshioka, H.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.E.; Okami, N.; Sakata, H.; Maier, C.M.; Narasimhan, P.; Goeders, C.E.; Chan, P.H. Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: Mechanisms of cell death and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.; Krishan, P.; Shri, R. Antioxidant-mediated neuroprotection by allium schoenoprasum l. Leaf extract against ischemia reperfusion-induced cerebral injury in mice. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 29, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armogida, M.; Spalloni, A.; Amantea, D.; Nutini, M.; Petrelli, F.; Longone, P.; Bagetta, G.; Nistico, R.; Mercuri, N.B. The protective role of catalase against cerebral ischemia in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2011, 24, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.N.; Kindy, M.S.; Holtsberg, F.W.; St Clair, D.K.; Yen, H.C.; Germeyer, A.; Steiner, S.M.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Hutchins, J.B.; Mattson, M.P. Mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase prevents neural apoptosis and reduces ischemic brain injury: Suppression of peroxynitrite production, lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugawara, T.; Noshita, N.; Lewen, A.; Gasche, Y.; Ferrand-Drake, M.; Fujimura, M.; Morita-Fujimura, Y.; Chan, P.H. Overexpression of copper/zinc superoxide dismutase in transgenic rats protects vulnerable neurons against ischemic damage by blocking the mitochondrial pathway of caspase activation. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, J.C.; Chen, B.H.; Shin, B.N.; Tae, H.J.; Yoo, K.Y.; Hong, S.; et al. Oenanthe javanica extract protects against experimentally induced ischemic neuronal damage via its antioxidant effects. Chin. Med. J. 2015, 128, 2932–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbishegi, M.; Heidari, Z.; Mahmoudzadeh-Sagheb, H.; Valizadeh, M.; Doostkami, M. Neuroprotective effects of withania coagulans root extract on CA1 hippocampus following cerebral ischemia in rats. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2016, 6, 399–409. [Google Scholar]
- Shalavadi, M.H.; Chandrashekhar, V.M.; Ramkishan, A.; Nidavani, R.B.; Biradar, B.S. Neuroprotective activity of stereospermum suaveolens against global cerebral ischemia rat model. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartvelishvili, T.; Abuladze, M.; Asatiani, N.; Akhvlediani, J.; Kiziria, E.; Asanishvili, L.; Lejava, L.; Holman, H.Y.; Sapojnikova, N. Estimation of the cellular antioxidant response to chromium action using esr method. Sci. World J. 2004, 4, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watson, R.R.; Preedy, V.R.; Zibadi, S. Polyphenols: Prevention and Treatment of Human Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Chang, P.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Shan, H.; Zhang, M.; Tao, L. Neuroprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide on sodium azide-induced oxidative stress in PC12 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Phenolic Compounds | Phenolic acids | Benzoic acid | p-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
| protocatechic acid | |||
| Vanilic acid | |||
| Gallic acid | |||
| Cinnamic acid | |||
| p-Cumaric acid | |||
| Caffeic acid | |||
| Ferulic acid | |||
| Catechin | Procyanidin | Major component (70 ± 5% of standardized procyanidins) | |
| Epicatechin | |||
| Taxifolin | Taxifolin glucoside | ||
| Inorganic Ions | calcium, potassium, iron, manganese, zinc, copper, selenium | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, B.; Lee, T.-K.; Park, C.W.; Kim, D.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Sim, H.; Lee, J.-C.; Yang, G.E.; Kim, J.D.; Shin, M.C.; et al. Pycnogenol® Supplementation Attenuates Memory Deficits and Protects Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Neurons via Antioxidative Role in a Gerbil Model of Transient Forebrain Ischemia. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082477
Kim B, Lee T-K, Park CW, Kim DW, Ahn JH, Sim H, Lee J-C, Yang GE, Kim JD, Shin MC, et al. Pycnogenol® Supplementation Attenuates Memory Deficits and Protects Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Neurons via Antioxidative Role in a Gerbil Model of Transient Forebrain Ischemia. Nutrients. 2020; 12(8):2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082477
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Bora, Tae-Kyeong Lee, Cheol Woo Park, Dae Won Kim, Ji Hyeon Ahn, Hyejin Sim, Jae-Chul Lee, Go Eun Yang, Jong Dai Kim, Myoung Cheol Shin, and et al. 2020. "Pycnogenol® Supplementation Attenuates Memory Deficits and Protects Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Neurons via Antioxidative Role in a Gerbil Model of Transient Forebrain Ischemia" Nutrients 12, no. 8: 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082477
APA StyleKim, B., Lee, T.-K., Park, C. W., Kim, D. W., Ahn, J. H., Sim, H., Lee, J.-C., Yang, G. E., Kim, J. D., Shin, M. C., Cho, J. H., Ryoo, S., Kim, Y.-M., Won, M.-H., & Park, J. H. (2020). Pycnogenol® Supplementation Attenuates Memory Deficits and Protects Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Neurons via Antioxidative Role in a Gerbil Model of Transient Forebrain Ischemia. Nutrients, 12(8), 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082477