Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Reduces Visceral Adiposity Partly through the Regulation of Beclin1-Dependent Autophagy in White Adipose Tissues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Quantitative PCR and Immunoblot Analysis
2.3. Histology
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
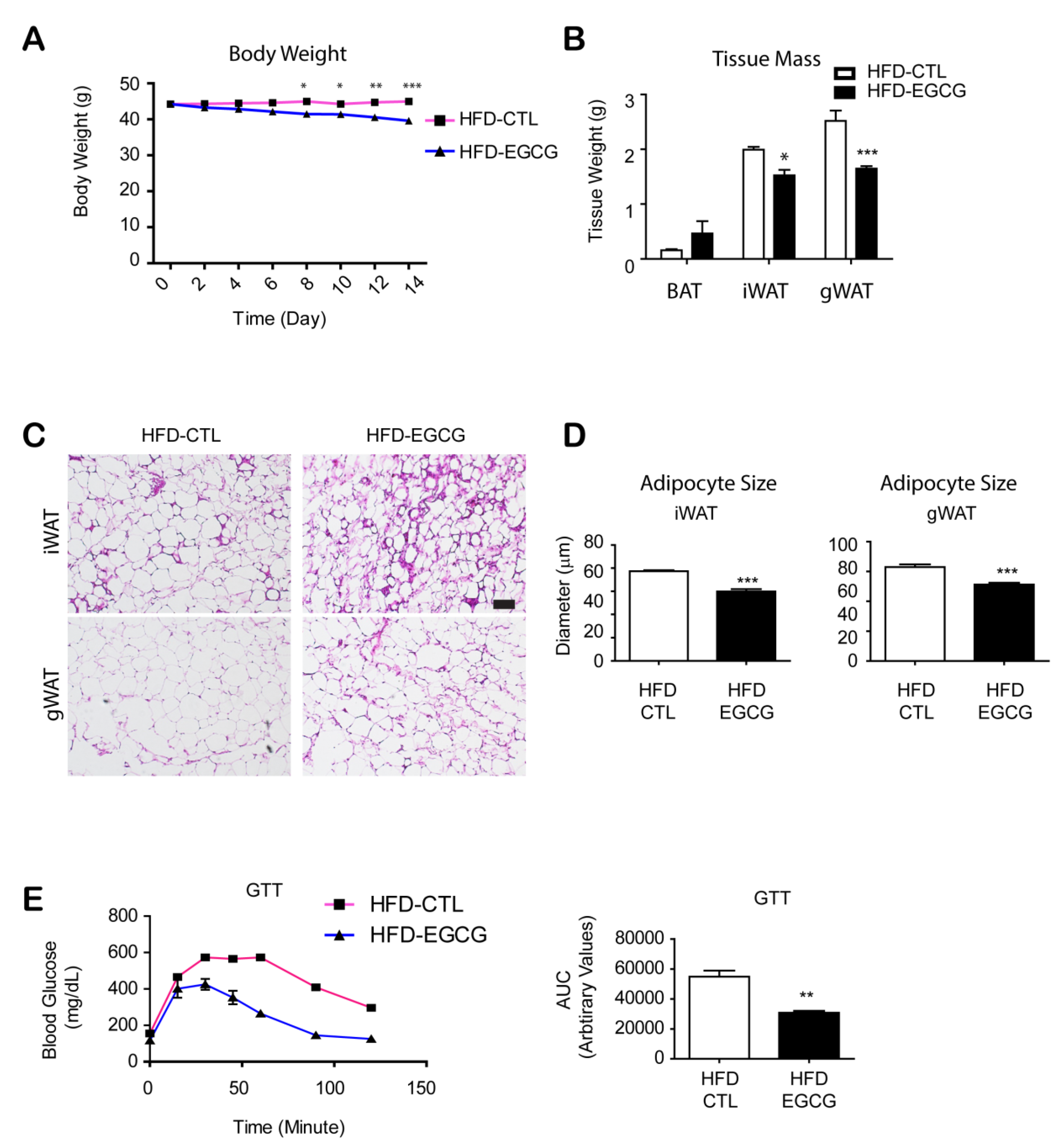
3.1. Two Weeks of EGCG Treatment Reduced Body Weight and Improved Glucose Tolerance in HFD-Fed Mice
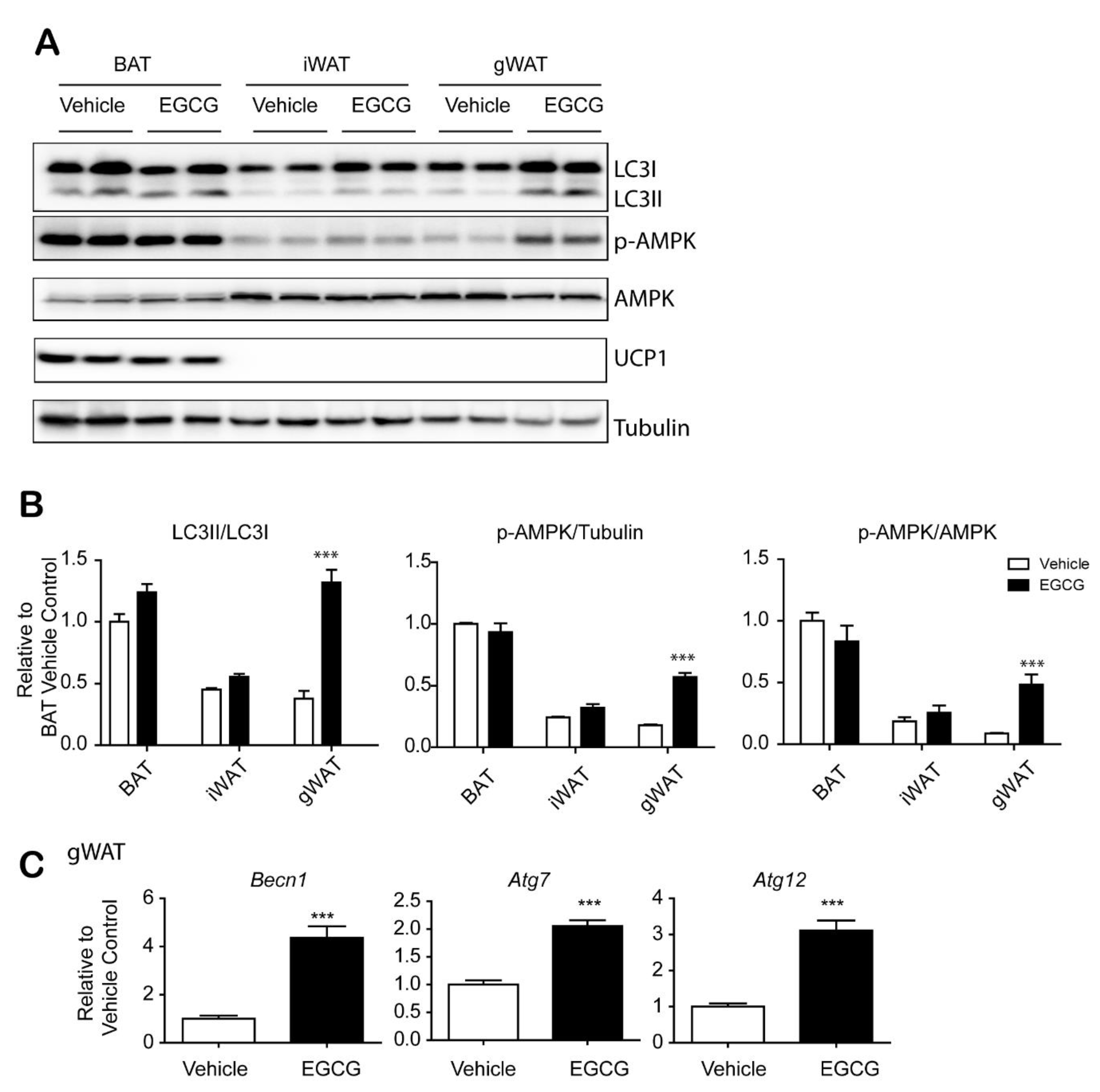
3.2. EGCG Increased Autophagy in Gonadal WAT
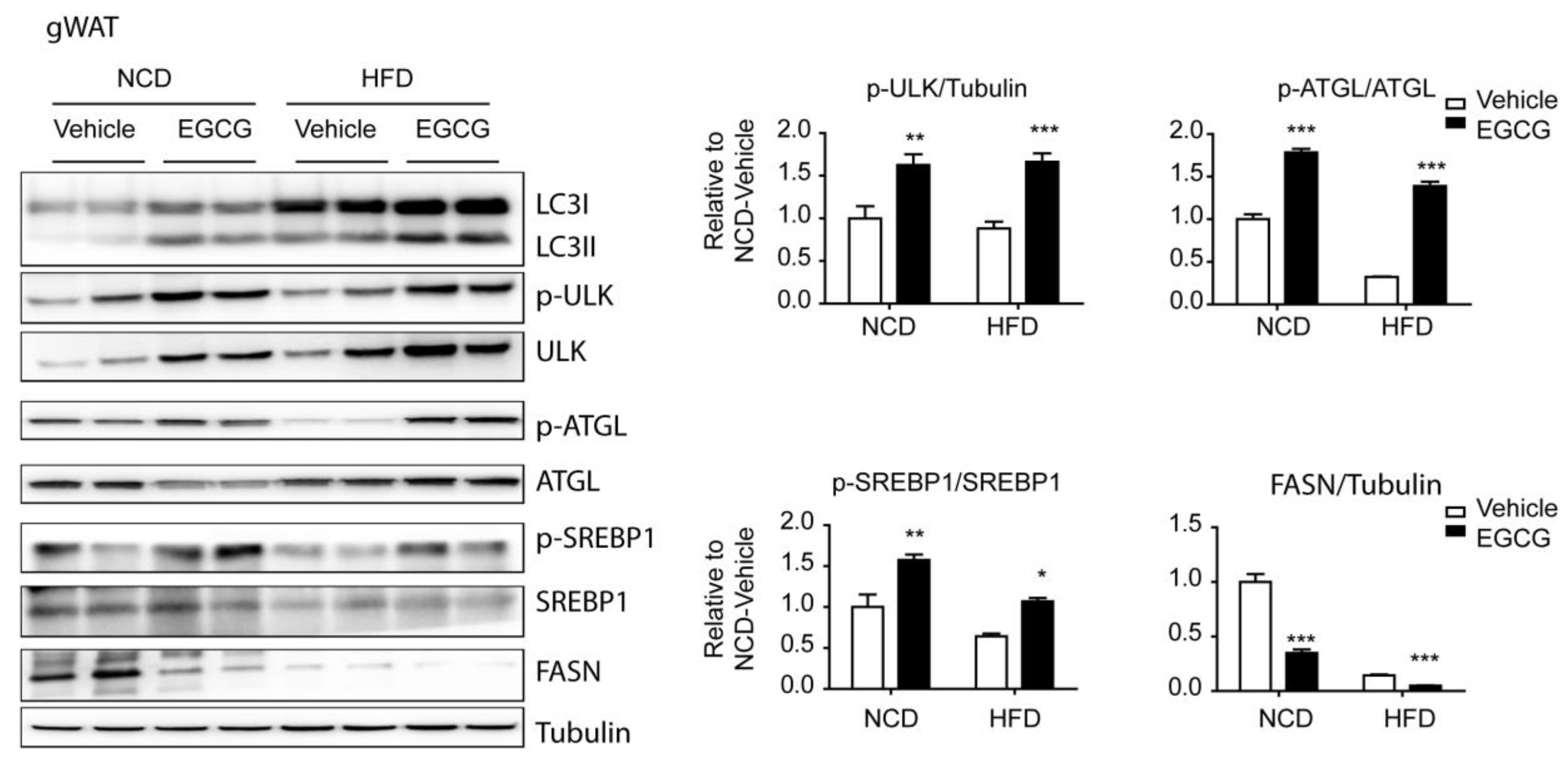
3.3. EGCG Regulated the AMPK Downstream Targets, ATGL and SREBP1-c, in WATs
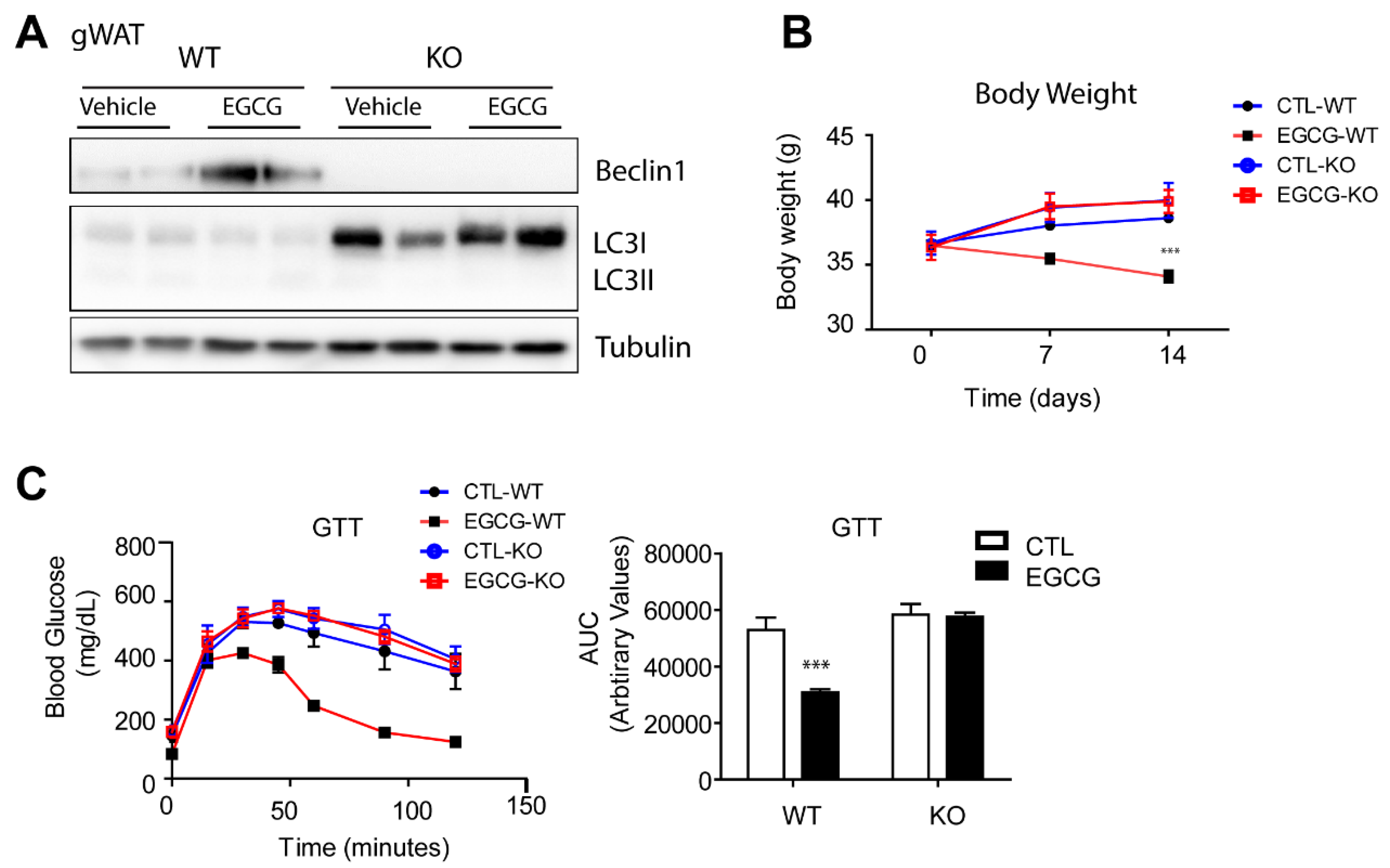
3.4. The Anti-Obesity Effects of EGCG Required Beclin1 Expression in Adipose Tissue
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, Y.-H.; Mottillo, E.P.; Granneman, J.G. Adipose tissue plasticity from wat to bat and in between. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeomans, M.R. Adverse effects of consuming high fat–sugar diets on cognition: Implications for understanding obesity. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartz, A.J.; Rupley, D.C.; Kalkhoff, R.D.; Rimm, A.A. Relationship of obesity to diabetes: Influence of obesity level and body fat distribution. Prev. Med. 1983, 12, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reto, M.; Figueira, M.E.; Filipe, H.M.; Almeida, C.M.M. Chemical composition of green tea (camellia sinensis) infusions commercialized in portugal. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2007, 62, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueoka, N.; Suganuma, M.; Sueoka, E.; Okabe, S.; Matsuyama, S.; Imai, K.; Nakachi, K.; Fujiki, H. A new function of green tea: Prevention of lifestyle-related diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 928, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.S.; Chung, C.S.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, T.G.; Choi, Y.J.; Cho, C.S. Inhibitory effect of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on lipid accumulation of 3t3-l1 cells. Obesity 2007, 15, 2571–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Gao, C.; Yan, P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J. Egcg reduces obesity and white adipose tissue gain partly through ampk activation in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.-S.; Shin, Y.; Jung, S.; Kim, Y. Effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on thermogenesis and mitochondrial biogenesis in brown adipose tissues of diet-induced obese mice. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1325307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechner, R.; Madeo, F.; Kratky, D. Cytosolic lipolysis and lipophagy: Two sides of the same coin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Tang, T.; Abbott, M.; Viscarra, J.A.; Wang, Y.; Sul, H.S. Ampk phosphorylates desnutrin/atgl and hormone-sensitive lipase to regulate lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation within adipose tissue. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadian, M.; Abbott, M.J.; Tang, T.; Hudak, C.S.; Kim, Y.; Bruss, M.; Hellerstein, M.K.; Lee, H.Y.; Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Desnutrin/atgl is regulated by ampk and is required for a brown adipose phenotype. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Mihaylova, M.M.; Zheng, B.; Hou, X.; Jiang, B.; Park, O.; Luo, Z.; Lefai, E.; Shyy, J.Y.J.; et al. Ampk phosphorylates and inhibits srebp activity to attenuate hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Kundu, M.; Viollet, B.; Guan, K.-L. Ampk and mtor regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of ulk1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donà, M.; Dell’Aica, I.; Calabrese, F.; Benelli, R.; Morini, M.; Albini, A.; Garbisa, S. Neutrophil restraint by green tea: Inhibition of inflammation, associated angiogenesis, and pulmonary fibrosis. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-N.; Kwon, H.-J.; Akindehin, S.; Jeong, H.W.; Lee, Y.-H. Effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on autophagic lipolysis in adipocytes. Nutrients 2017, 9, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Son, Y.; Cho, Y.K.; Saha, A.; Kwon, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, M.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, S.N.; Choi, C.; Seong, J.K.; et al. Adipocyte-specific beclin1 deletion impairs lipolysis and mitochondrial integrity in adipose tissue. Mol. Metab. 2020, 39, 101005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.; Koyama, N.; Tan, J.; Segawa, T.; Maeda, M.; Town, T. Combined treatment with the phenolics (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and ferulic acid improves cognition and reduces alzheimer-like pathology in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 2714–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Gordon, M.; Tan, J.; Morgan, D. Oral administration of green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (egcg) reduces amyloid beta deposition in transgenic mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 198, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.N.; Ahn, S.Y.; Song, H.D.; Kwon, H.J.; Saha, A.; Son, Y.; Cho, Y.K.; Jung, Y.S.; Jeong, H.W.; Lee, Y.H. Antiobesity effects of coumestrol through expansion and activation of brown adipose tissue metabolism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 76, 108300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, K.T.; Hafer, L.J.; Kim, D.W.; Mann, K.K.; Sherr, D.H.; Rogers, A.E.; Sonenshein, G.E. Green tea extracts decrease carcinogen-induced mammary tumor burden in rats and rate of breast cancer cell proliferation in culture. J. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 82, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T.; Tang, D. The beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, Q.F.; Liu, H.Y.; Pi, J.; Liu, Z.; Quon, M.J.; Cao, W. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (egcg), a green tea polyphenol, suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis through 5’-amp-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 30143–30149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.T.; Ha, J.; Park, I.J.; Lee, S.K.; Baik, H.W.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, O.J. Apoptotic effect of egcg in ht-29 colon cancer cells via ampk signal pathway. Cancer Lett. 2007, 247, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.Y.; Hong, C.G.; Suh, Y.S.; Cho, H.C.; Park, J.H.; Bae, J.H.; Park, W.K.; Han, J.; Song, D.K. Role of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in cell viability, lipogenesis, and retinol-binding protein 4 expression in adipocytes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2010, 382, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Chen, L.; Mo, H.; Shastri, A.; Su, R.; Bapat, P.; Kwun, I.; Shen, C.L. Novel insights of dietary polyphenols and obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remely, M.; Ferk, F.; Sterneder, S.; Setayesh, T.; Roth, S.; Kepcija, T.; Noorizadeh, R.; Rebhan, I.; Greunz, M.; Beckmann, J.; et al. Egcg prevents high fat diet-induced changes in gut microbiota, decreases of DNA strand breaks, and changes in expression and DNA methylation of dnmt1 and mlh1 in c57bl/6j male mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3079148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pervin, M.; Unno, K.; Takagaki, A.; Isemura, M.; Nakamura, Y. Function of green tea catechins in the brain: Epigallocatechin gallate and its metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legeay, S.; Rodier, M.; Fillon, L.; Faure, S.; Clere, N. Epigallocatechin gallate: A review of its beneficial properties to prevent metabolic syndrome. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5443–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takagaki, A.; Yoshioka, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Nagano, T.; Ikeda, M.; Hara-Terawaki, A.; Seto, R.; Ashida, H. Effects of microbial metabolites of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate on glucose uptake in l6 skeletal muscle cell and glucose tolerance in icr mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forester, S.C.; Gu, Y.; Lambert, J.D. Inhibition of starch digestion by the green tea polyphenol, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, C.; Song, H.-D.; Son, Y.; Cho, Y.K.; Ahn, S.-Y.; Jung, Y.-S.; Yoon, Y.C.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, Y.-H. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Reduces Visceral Adiposity Partly through the Regulation of Beclin1-Dependent Autophagy in White Adipose Tissues. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103072
Choi C, Song H-D, Son Y, Cho YK, Ahn S-Y, Jung Y-S, Yoon YC, Kwon SW, Lee Y-H. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Reduces Visceral Adiposity Partly through the Regulation of Beclin1-Dependent Autophagy in White Adipose Tissues. Nutrients. 2020; 12(10):3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103072
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Cheoljun, Hyun-Doo Song, Yeonho Son, Yoon Keun Cho, Sang-Yeop Ahn, Young-Suk Jung, Young Cheol Yoon, Sung Won Kwon, and Yun-Hee Lee. 2020. "Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Reduces Visceral Adiposity Partly through the Regulation of Beclin1-Dependent Autophagy in White Adipose Tissues" Nutrients 12, no. 10: 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103072
APA StyleChoi, C., Song, H.-D., Son, Y., Cho, Y. K., Ahn, S.-Y., Jung, Y.-S., Yoon, Y. C., Kwon, S. W., & Lee, Y.-H. (2020). Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Reduces Visceral Adiposity Partly through the Regulation of Beclin1-Dependent Autophagy in White Adipose Tissues. Nutrients, 12(10), 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103072




