Diagnostic Test Accuracy of the 4AT for Delirium Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aims and Design
2.2. Search Methods and Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Data Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Search Outcome
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Assessment of Risk of Bias
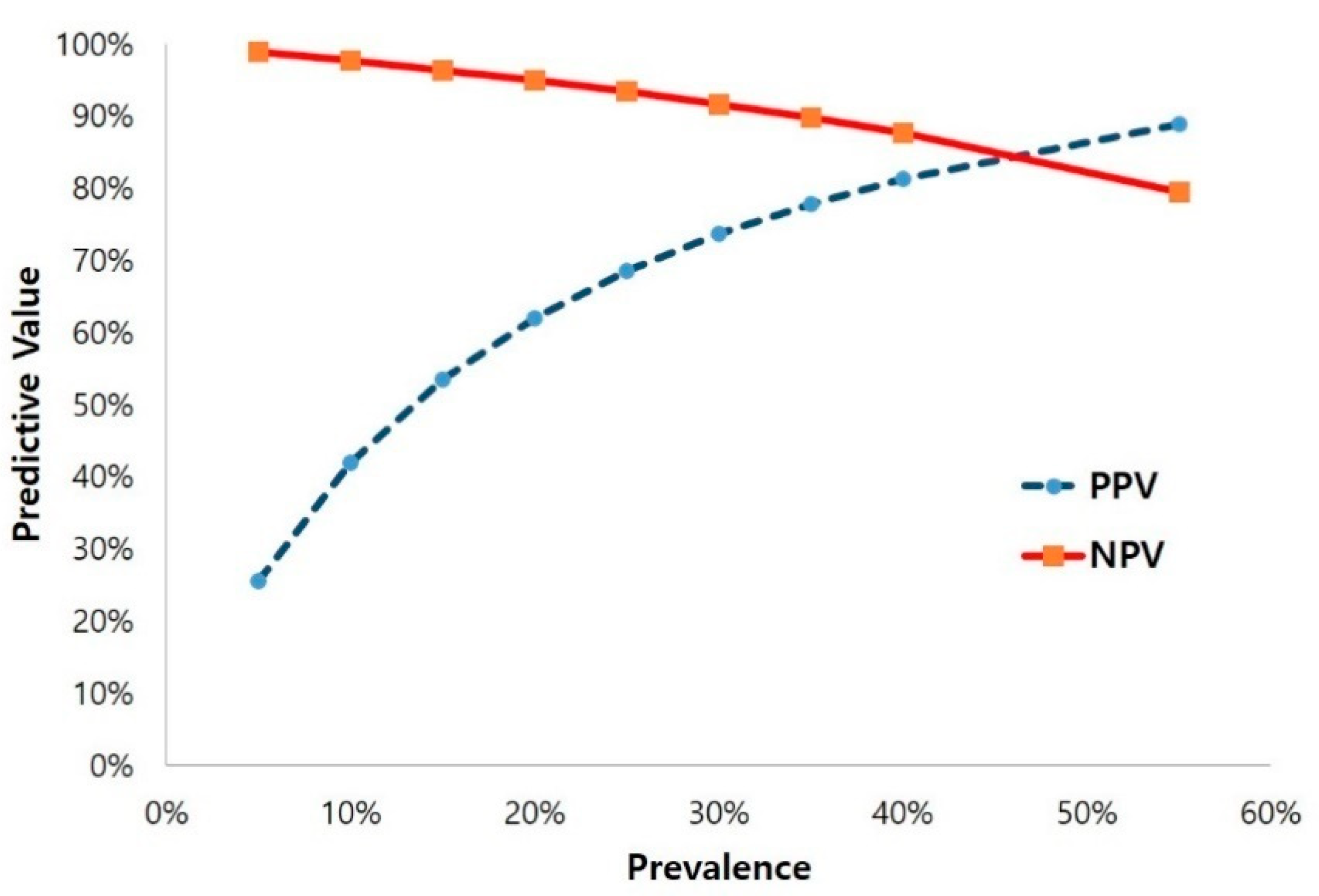
3.4. Diagnostic Test Accuracy of the 4AT
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: Dsm-5, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De Lange, E.; Verhaak, P.F.; van der Meer, K. Prevalence, presentation and prognosis of delirium in older people in the population, at home and in long term care: A review. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatr. 2013, 28, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persico, I.; Cesari, M.; Morandi, A.; Haas, J.; Mazzola, P.; Zambon, A.; Annoni, G.; Bellelli, G. Frailty and delirium in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2018, 66, 2022–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynish, E.L.; Hapca, S.M.; De Souza, N.; Cvoro, V.; Donnan, P.T.; Guthrie, B. Epidemiology and outcomes of people with dementia, delirium, and unspecified cognitive impairment in the general hospital: Prospective cohort study of 10,014 admissions. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatgi, N.; Weng, Y.; Bentley, J.; Lansberg, M.G.; Shepard, J.; Mazur, D.; Ahuja, N.; Hopkins, J. Initiative for prevention and early identification of delirium in medical-surgical units: Lessons learned in the past five years. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, E.A.; Holmes, J. Delirium within the emergency care setting, occurrence and detection: A systematic review. Emerg. Med. J. 2013, 30, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, P.W.; Lamanna, M.; Watson, R.; Maier, A.B. Undiagnosed delirium is frequent and difficult to predict: Results from a prevalence survey of a tertiary hospital. J. Clin. Nurs. 2019, 28, 2537–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario. Delirium, Dementia, and Depression in Older Adults: Assessment and Care; Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario: Tononto, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). Risk Reduction and Management of Delirium (Sign CPG 157); SIGN: Edinburgh, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Asadollahi, A.; Saberi, M.; Entezari, M.; Hoseini, Z.; Hasani, S.A.; Saberi, L.F.; Hoseini, S.M.; Ismaeli, A. Iranian version of 4at, an instrument for rapid delirium screening for later life. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2016, 3, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bellelli, G.; Morandi, A.; Davis, D.H.; Mazzola, P.; Turco, R.; Gentile, S.; Ryan, T.; Cash, H.; Guerini, F.; Torpilliesi, T.; et al. Validation of the 4at, a new instrument for rapid delirium screening: A study in 234 hospitalised older people. Age Ageing 2014, 43, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, P.; Cross, W.; Mart, M.W.S.; Baldwin, C.; Riddell, K.; Dārziņš, P. Hospital discharge data under-reports delirium occurrence: Results from a point prevalence survey of delirium in a major Australian health service. Intern. Med. J. 2019, 49, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macaskill, P.; Gatsonis, C.; Deeks, J.J.; Harbord, R.M.; Takwoingi, Y. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 0.9; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, M.D.F.; Moher, D.; Thombs, B.D.; McGrath, T.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Clifford, T.; Cohen, J.F.; Deeks, J.J.; Gatsonis, C.; Hooft, L.; et al. Preferred reporting items for a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies: The prisma-dta statement. JAMA 2018, 319, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.H.; Huh, J.; Park, S.H. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies evaluating diagnostic test accuracy: A practical review for clinical researchers-part I. General guidance and tips. Korean J. Radiol. 2015, 16, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M. Quadas-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.W.; Choi, S.H.; Huh, J.; Park, S.H. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies evaluating diagnostic test accuracy: A practical review for clinical researchers-part ii. Statistical methods of meta-analysis. Korean J. Radiol. 2015, 16, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H. Overview of the process of conducting meta-analyses of the diagnostic test accuracy. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 25, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuladee, S.; Prachason, T. Development and validation of the thai version of the 4 ‘a’s test for delirium screening in hospitalized elderly patients with acute medical illnesses. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLullich, A.M.; Shenkin, S.D.; Goodacre, S.; Godfrey, M.; Hanley, J.; Stíobhairt, A.; Lavender, E.; Boyd, J.; Stephen, J.; Weir, C.; et al. The 4 ‘a’s test for detecting delirium in acute medical patients: A diagnostic accuracy study. Health Technol. Assess. 2019, 23, 1–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebler, P.; Holling, H. Meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy with mada. R Packag. 2015, 1, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Saller, T.; MacLullich, A.M.J.; Perneczky, R. The 4at—An instrument for delirium detection for older patients in the post-anaesthesia care unit. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 409–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkin, S.D.; Fox, C.; Godfrey, M.; Siddiqi, N.; Goodacre, S.; Young, J.; Anand, A.; Gray, A.; Hanley, J.; MacRaild, A.; et al. Delirium detection in older acute medical inpatients: A multicentre prospective comparative diagnostic test accuracy study of the 4at and the confusion assessment method. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, J.; Wand, A.P.F.; Smerdely, P.I.; Hunt, G.E. Validating the 4a’s test in screening for delirium in a culturally diverse geriatric inpatient population. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatr. 2017, 32, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagné, A.J.; Voyer, P.; Boucher, V.; Nadeau, A.; Carmichael, P.H.; Pelletier, M.; Gouin, E.; Berthelot, S.; Daoust, R.; Wilchesky, M.; et al. Performance of the french version of the 4at for screening the elderly for delirium in the emergency department. CJEM 2018, 20, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendry, K.; Quinn, T.J.; Evans, J.; Scortichini, V.; Miller, H.; Burns, J.; Cunnington, A.; Stott, D.J. Evaluation of delirium screening tools in geriatric medical inpatients: A diagnostic test accuracy study. Age Ageing 2016, 45, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, M.T.; Pardini, M.; Balestrino, M.; Finocchi, C.; Malfatto, L.; Bellelli, G.; Mancardi, G.L.; Gandolfo, C.; Serrati, C. Delirium in the acute phase after stroke: Comparison between methods of detection. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, R.; Corbet, S.; Johnston, C.; Moffitt, E.; Shaw, G.; Quinn, T.J. Test accuracy of short screening tests for diagnosis of delirium or cognitive impairment in an acute stroke unit setting. Stroke 2013, 44, 3078–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myrstad, M.; Watne, L.O.; Johnsen, N.T.; Børs-Lind, E.; Neerland, B.E. Delirium screening in an acute geriatric ward by nurses using 4at: Results from a quality improvement project. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 10, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, D.; Brady, N.; Manning, E.; O’Shea, E.; O’Grady, S.; O’Regan, N.; Timmons, S. Validation of the 6-item cognitive impairment test and the 4at test for combined delirium and dementia screening in older emergency department attendees. Age Ageing 2018, 47, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saller, T.; MacLullich, A.M.J.; Schäfer, S.T.; Crispin, A.; Neitzert, R.; Schüle, C.; von Dossow, V.; Hofmann-Kiefer, K.F. Screening for delirium after surgery: Validation of the 4 a’s test (4at) in the post-anaesthesia care unit. Anaesthesia 2019, 74, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsma, J.B.; Glas, A.S.; Rutjes, A.W.; Scholten, R.J.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Zwinderman, A.H. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2005, 58, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devillé, W.L.; Buntinx, F.; Bouter, L.M.; Montori, V.M.; de Vet, H.C.; van der Windt, D.A.; Bezemer, P.D. Conducting systematic reviews of diagnostic studies: Didactic guidelines. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2002, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glas, A.S.; Lijmer, J.G.; Prins, M.H.; Bonsel, G.J.; Bossuyt, P.M. The diagnostic odds ratio: A single indicator of test performance. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2003, 56, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimundić, A.M. Measures of diagnostic accuracy: Basic definitions. EJIFCC 2009, 19, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Delirium: Prevention, Diagnosis and Management. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg103 (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Mansutti, I.; Saiani, L.; Palese, A. Detecting delirium in patients with acute stroke: A systematic review of test accuracy. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.A.; Fearing, M.A.; Sternberg, E.J.; Inouye, S.K. The confusion assessment method: A systematic review of current usage. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, J.G.; Beth Harrington, M.; Rudolph, J.L. Serial administration of a modified richmond agitation and sedation scale for delirium screening. J. Hosp. Med. 2012, 7, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.J.; Davis, D.H.J.; Bellelli, G.; Hasemann, W.; Meagher, D.; Kreisel, S.H.; MacLullich, A.M.J.; Cerejeira, J.; Morandi, A. Detecting delirium superimposed on dementia: Diagnostic accuracy of a simple combined arousal and attention testing procedure. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2017, 29, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, E.W.; Shintani, A.; Truman, B.; Gordon, S.M.; Harrell, F.E.; Inouye, S.K.; Bernard, G.R.; Dittus, R.S. Delirium as apredictor of mortality in mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit. JAMA 2004, 291, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, T.D.; Jackson, J.C.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Pun, B.T.; Thompson, J.L.; Shintani, A.K.; Gordon, S.M.; Canonico, A.E.; Dittus, R.S.; Bernard, G.R.; et al. Delirium as a predictor of long-term cognitive impairment in survivors of critical illness. Crit Care Med. 2010, 38, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafim, R.B.; Soares, M.; Bozza, F.A.; Silva, J.R.L.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Paulino, M.C.; Povoa, P.; Salluh, J.I.F. Outcomes of subsyndromal delirium in ICU: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2017, 21, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.G.; Ciampi, A.; Belzile, E.; Dubuc-Sarrasin, M. Subsyndromal delirium in older people: A systematic review of frequency, risk factors, course and outcomes. FOCUS 2013, 11, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| First Author | Year | Country | Setting | n | Age (M ± SD or Median [Range]) | Reference Standard | Cut-off Score | TP | FP | TN | FN | Item Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asadollahi | 2016 | Iran | Nursing homes and daily caring centers | 293 | 69.3 ± 1.47 | DSM-V | >3 | 57 | 4 | 125 | 107 | Not done |
| Myrstad | 2019 | Norway | Acute geriatric ward | 49 | 87 (68–99) | DSM-V | >3 | 10 | 4 | 25 | 10 | Not done |
| Casey | 2019 | Australia | Inpatient wards | 559 | 73 ± 16.4 | 3D-CAM | >3 | 59 | 48 | 420 | 32 | Not done |
| MacLullich | 2019 | United Kingdom | ED, medical admission units, MOE units | 392 | 81.4 ± 6.4 | DSM-IV | >3 | 37 | 19 | 324 | 12 | Done |
| Kuladee | 2016 | Thailand | General medical wards | 97 | 73.6 ± 8.17 | DSM-IV, TDRS | >3 | 20 | 10 | 63 | 4 | Done |
| Hendry | 2016 | United Kingdom | Geriatric medical assessment unit | 434 | 83.1 ± 6.7 | DSM-V | >3 | 72 | 107 | 244 | 11 | Not done |
| De | 2017 | Australia | Geriatric and orthogeriatric services | 257 | 86.0 ± 7.3 | DSM-V, CAM | >3 | 138 | 20 | 78 | 21 | Not done |
| Bellelli | 2014 | Italy | Acute geriatrics ward and department of rehabilitation | 236 | 83.9 ± 6.1 | DSM-IV | >3 | 26 | 33 | 174 | 3 | Done |
| Gagne | 2018 | Canada | ED | 319 | 76.84 ± 7.4 | CAM | >3 | 44 | 108 | 162 | 5 | Not done |
| O’Sullivan | 2018 | Ireland | ED | 350 | 77 a | DSM-V | >3 | 54 | 25 | 267 | 4 | Not done |
| Saller | 2019 | Germany | PACU | 543 | 52 ± 18 | DSM-V, CAM-ICU | >3 | 21 | 4 | 517 | 1 | Not done |
| Infante | 2017 | Italy | Stroke unit | 100 | 79 (19–93) | DSM-V | >3 | 48 | 12 | 38 | 2 | Not done |
| Lees | 2013 | United Kingdom | Acute stroke unit | 100 | 74 (64–85) b | CAM | >3 | 12 | 16 | 72 | 0 | Not done |
| First Author (Year) | Risk of Bias | Applicability Concerns | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Selection | Index Test | Reference Standards | Flow, Timing | Patient Selection | Index Test | Reference Standard | |
| Asadollahi (2016) | unclear | low | low | unclear | low | low | low |
| Myrstad (2019) | low | low | low | low | low | low | low |
| Casey (2019) | high | low | high | unclear | low | low | low |
| MacLullich (2019) | low | low | low | low | low | low | low |
| Kuladee (2016) | low | low | low | low | low | low | low |
| Hendry (2016) | low | low | low | low | low | low | low |
| De (2017) | low | low | low | low | low | low | low |
| Bellelli (2014) | low | low | low | low | low | low | low |
| Gagne (2018) | low | high | high | low | low | low | low |
| O’Sullivan (2018) | low | low | low | low | low | low | low |
| Saller (2019) | low | low | low | low | low | low | low |
| Infante (2017) | low | high | high | low | low | low | low |
| Lees (2013) | low | low | low | low | low | low | low |
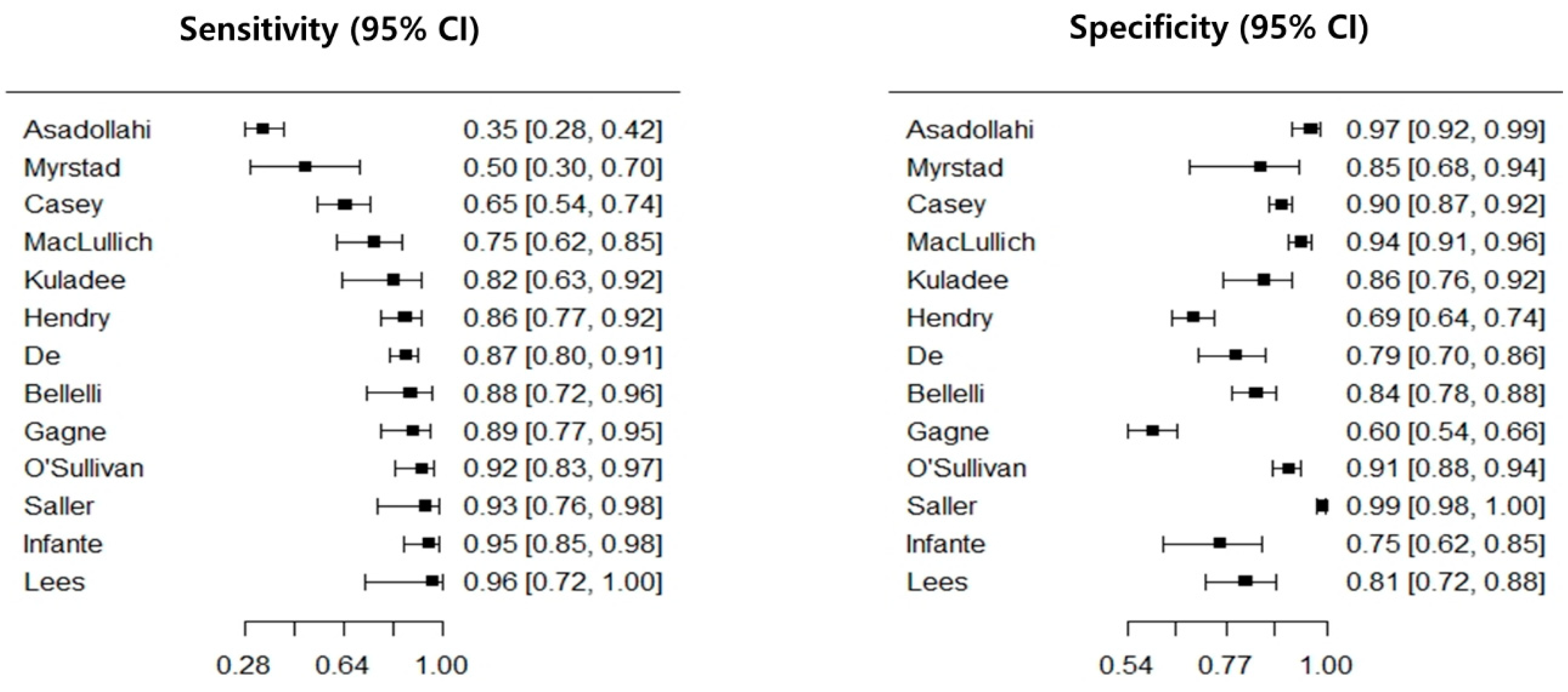
| Author | Year | n | Sn (95% CI) | Sp (95% CI) | DOR (95% CI) * | PLR (95% CI) * | NLR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asadollahi | 2016 | 293 | 0.35 (0.28–0.42) | 0.97 (0.92–0.99) | 14.92 (5.52–40.28) | 10.07 (3.97–25.55) | 0.68 (0.60–0.76) | |
| Myrstad b | 2019 | 49 | 0.50 (0.30–0.70) | 0.85 (0.68–0.94) | 5.67 (1.52–21.16) | 3.33 (1.29–8.65) | 0.59 (0.37–0.93) | |
| Casey | 2019 | 559 | 0.65 (0.55–0.74) | 0.90 (0.87–0.92) | 15.87 (9.43–26.72) | 6.25 (4.60–8.50) | 0.39 (0.30–0.52) | |
| MacLullich b | 2019 | 392 | 0.75 (0.62–0.85) | 0.94 (0.91–0.96) | 49.92 (22.74–109.62) | 13.23 (8.35–20.96) | 0.27 (0.16–0.43) | |
| Kuladee b | 2016 | 97 | 0.82 (0.63–0.92) | 0.86 (0.76–0.92) | 27.55 (8.20–92.52) | 5.78 (3.21–10.42) | 0.21 (0.09–0.49) | |
| Hendry b | 2016 | 434 | 0.86 (0.77–0.92) | 0.70 (0.65–0.74) | 14.34 (7.40–27.80) | 2.83 (2.36–3.38) | 0.20 (0.12–0.34) | |
| De b | 2017 | 257 | 0.87 (0.80–0.91) | 0.79 (0.70–0.86) | 24.67 (12.68–47.98) | 4.18 (2.83–6.18) | 0.17 (0.11–0.25) | |
| Bellelli b | 2014 | 236 | 0.88 (0.72–0.96) | 0.84 (0.78–0.88) | 39.44 (12.19–127.63) | 5.49 (3.92–7.68) | 0.14 (0.05–0.37) | |
| Gagne | 2018 | 319 | 0.89 (0.77–0.95) | 0.60 (0.54–0.66) | 12.12 (4.84–30.36) | 2.22 (1.87–2.65) | 0.18 (0.08–0.41) | |
| O’Sullivan b | 2018 | 350 | 0.92 (0.83–0.97) | 0.91 (0.88–0.94) | 127.05 (44.74–360.75) | 10.61 (7.27–15.49) | 0.08 (0.03–0.20) | |
| Saller b | 2019 | 543 | 0.94 (0.76–0.99) | 0.99 (0.98–1.0) | 1648.33 (247.14–10993.70) | 108.44 (42.94–273.80) | 0.07 (0.01–0.31) | |
| Infante | 2017 | 100 | 0.95 (0.85–0.99) | 0.76 (0.62–0.85) | 59.75 (14.41–247.77) | 3.88 (2.39–6.31) | 0.07 (0.02–0.22) | |
| Lees b | 2013 | 100 | 0.96 (0.72–1.0) | 0.82 (0.72–0.88) | 109.85 (6.19–1950.64) | 5.19 (3.31–8.13) | 0.05 (0.00–0.72) | |
| Pooled estimates a | ||||||||
| All included studies | 3729 | 81.5 (70.7–89.0) | 87.5 (79.5–92.7) | AUC: 0.911 | ||||
| Subgroup analysis b | 2458 | 84.3 (75.4–90.4) | 88.5 (79.0–94.0) | AUC: 0.918 | ||||
| Author | Year | Sample Size | Sn (95% CI) | Sp (95% CI) | DOR (95% CI) * | PLR (95% CI) * | NLR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item 1. Alertness (cut-off point: 4) | |||||||
| MacLullich | 2019 | 392 | 0.31 (0.20–0.45) | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) | 50.0 (13.78–181.41) | 35.0 (10.51–116.54) | 0.70 (0.58–0.84) |
| Kuladee | 2016 | 97 | 0.38 (0.21–0.57) | 0.97 (0.91–0.99) | 21.30 (4.17–108.74) | 13.69 (3.18–59.0) | 0.64 (0.47–0.88) |
| Bellelli | 2014 | 236 | 0.52 (0.34–0.69) | 0.96 (0.93–0.98) | 26.65 (9.66–73.53) | 13.38 (6.23–28.76) | 0.50 (0.34–0.73) |
| Pooled estimates a | 725 | 39.6 (26.5–54.4) | 97.9 (94.6–99.2) | AUC: 0.810 | |||
| Item 2. AMT-4 (cut-off point: 1) | |||||||
| MacLullich | 2019 | 392 | 0.63 (0.49–0.75) | 0.83 (0.78–0.86) | 8.29 (4.35–15.80) | 3.68 (2.68–5.04) | 0.44 (0.31–0.64) |
| Kuladee | 2016 | 97 | 0.96 (0.80–0.99) | 0.67 (0.56–0.77) | 46.96 (5.98–368.73) | 2.92 (2.08–4.09) | 0.06 (0.01–0.43) |
| Bellelli | 2014 | 236 | 0.97 (0.83–0.99) | 0.55 (0.48–0.61) | 33.66 (4.50–252.05) | 2.13 (1.80–2.51) | 0.06 (0.01–0.44) |
| Pooled estimates a | 725 | 90.4 (58.5–98.4) | 69.2 (49.8–83.6) | AUC: 0.832 | |||
| Item 2. AMT-4 (cut-off point: 2) | |||||||
| MacLullich | 2019 | 392 | 0.41 (0.28–0.55) | 0.96 (0.94–0.98) | 17.51 (7.91–38.76) | 10.77 (5.73–20.24) | 0.62 (0.49–0.78) |
| Kuladee | 2016 | 97 | 0.88 (0.69–0.96) | 0.81 (0.70–0.88) | 29.50 (7.70–112.97) | 4.56 (2.78–7.48) | 0.16 (0.05–0.45) |
| Bellelli | 2014 | 236 | 0.90 (0.74–0.96) | 0.80 (0.74–0.85) | 35.09 (10.12–121.62) | 4.53 (3.35–6.11) | 0.13 (0.04–0.38) |
| Pooled estimates a | 725 | 77.2 (39.2–94.7) | 88.3 (69.7–96.1) | AUC: 0.908 | |||
| Item 3. Attention (cut-off point: 1) | |||||||
| MacLullich | 2019 | 392 | 0.71 (0.58–0.82) | 0.79 (0.74–0.83) | 9.41 (4.81–18.43) | 3.40 (2.60–4.46) | 0.36 (0.23–0.57) |
| Kuladee | 2016 | 97 | 0.96 (0.8–0.99) | 0.41 (0.31–0.53) | 16.05 (2.05–125.36) | 1.63 (1.32–2.01) | 0.10 (0.02–0.70) |
| Bellelli | 2014 | 236 | 0.93 (0.78–0.98) | 0.50 (0.43–0.57) | 13.37 (3.10–57.68) | 1.85 (1.57–2.19) | 0.14 (0.04–0.53) |
| Pooled estimates a | 725 | 89.9 (68.5–97.3) | 58.1 (33.6–79.2) | AUC: 0.821 | |||
| Item 3. Attention (cut-off point: 2) | |||||||
| MacLullich | 2019 | 392 | 0.31 (0.20–0.45) | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) | 50.0 (13.78–181.41) | 35.0 (10.51–116.54) | 0.70 (0.58–0.84) |
| Kuladee | 2016 | 97 | 0.50 (0.31–0.69) | 0.95 (0.87–0.98) | 17.25 (4.76–62.48) | 9.13 (3.25–25.65) | 0.53 (0.35–0.79) |
| Bellelli | 2014 | 236 | 0.86 (0.69–0.95) | 0.83 (0.77–0.87) | 29.69 (9.74–90.53) | 4.96 (3.56–6.90) | 0.17 (0.07–0.42) |
| Pooled estimates a | 725 | 57.6 (23.8–85.6) | 95.4 (78.8–99.1) | AUC: 0.892 | |||
| Item 4. Acute change or fluctuating course (cut-off point: 4) | |||||||
| MacLullich | 2019 | 392 | 0.63 (0.49–0.75) | 0.83 (0.78–0.86) | 8.29 (4.35–15.80) | 3.68 (2.68–5.04) | 0.44 (0.31–0.64) |
| Kuladee | 2016 | 97 | 0.75 (0.55–0.88) | 0.88 (0.78–0.93) | 21.33 (6.70–67.90) | 6.08 (3.16–11.70) | 0.29 (0.14–0.57) |
| Bellelli | 2014 | 236 | 0.69 (0.51–0.83) | 0.94 (0.90–0.97) | 36.11 (13.57–96.13) | 11.90 (6.52–21.70) | 0.33 (0.19–0.57) |
| Pooled estimates a | 725 | 68.0 (57.7–76.8) | 89.0 (79.7–94.3) | AUC: 0.760 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, E.; Park, J.; Lee, J. Diagnostic Test Accuracy of the 4AT for Delirium Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207515
Jeong E, Park J, Lee J. Diagnostic Test Accuracy of the 4AT for Delirium Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(20):7515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207515
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Eunhye, Jinkyung Park, and Juneyoung Lee. 2020. "Diagnostic Test Accuracy of the 4AT for Delirium Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 20: 7515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207515
APA StyleJeong, E., Park, J., & Lee, J. (2020). Diagnostic Test Accuracy of the 4AT for Delirium Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(20), 7515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207515





