Effect of Phaseolus Vulgaris on Urinary Biochemical Parameters among Patients with Kidney Stones in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
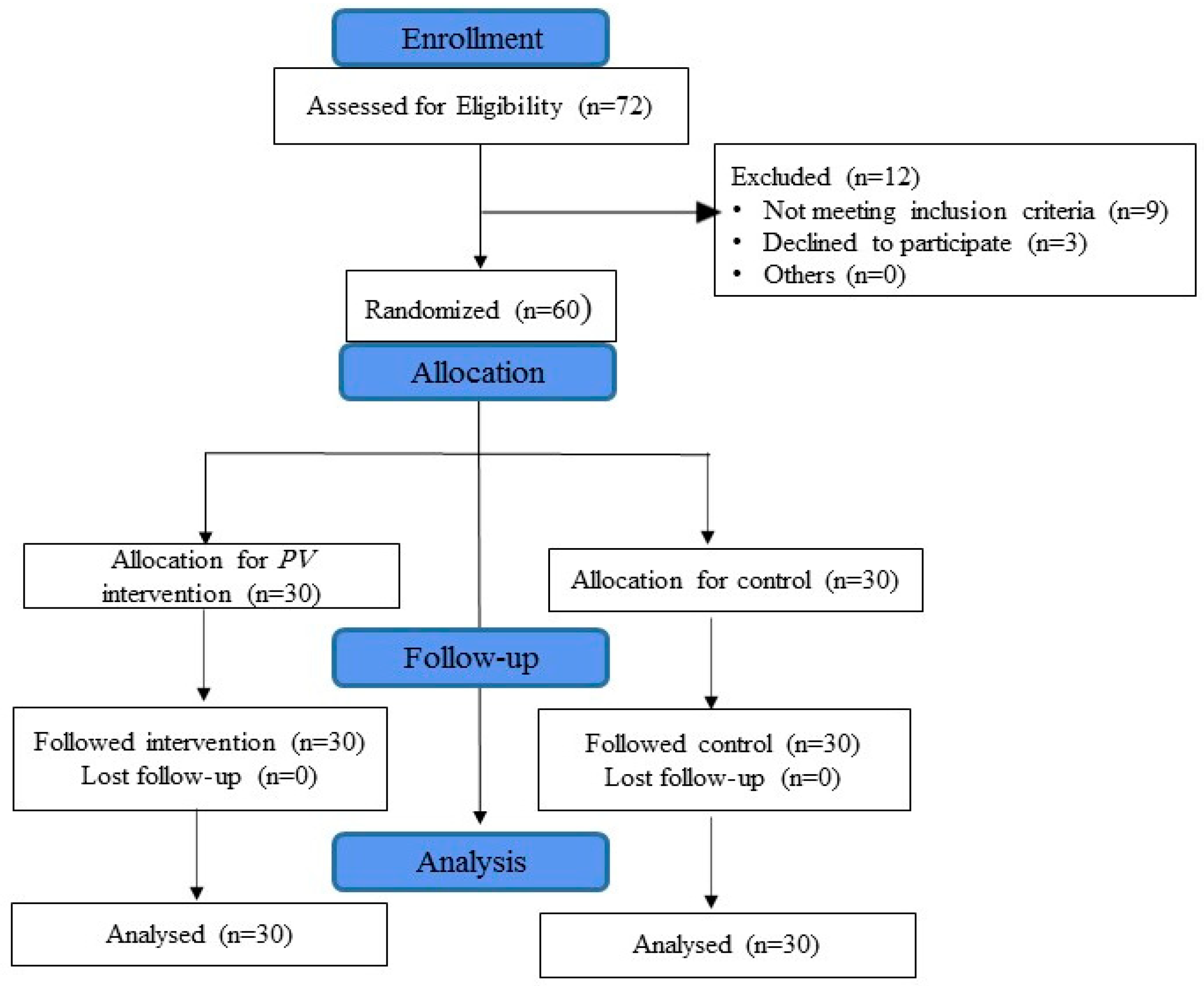
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Sample Size
2.4. Experimental Methods
Climate
2.5. Data Collection Tools
2.5.1. Sociodemographic Measures
2.5.2. Clinical Assessment
2.5.3. Anthropometric Index
2.5.4. Urinary Biochemical Parameters
2.5.5. Renal Ultrasound Scan
2.6. Dietary Intervention
2.6.1. Nutrients of PV
2.6.2. Compliance
2.7. Outcome Measures
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect on Symptoms of Kidney Stones
4.2. Effect on BMI
4.3. Effect on Urinary Biochemicals Parameters
4.4. Effect on Ultrasound Findings of Kidney
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CaOx | calcium oxalate (CaOx) |
| COVID-19 | Corona virus disease-19 |
| NS | Non-Significant |
| pH | Power of Hydrogen |
| PV | Phaseolus Vulgaris |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| USA | United States of America |
| USDA | United States Department of Agriculture |
References
- Sigurjonsdottir, V.K.; Runolfsdottir, H.L.; Indridason, O.S.; Palsson, R.; Edvardsson, V.O. Impact of nephrolithiasis on kidney function. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, V.; Akpinar, H.; Assimos, D.G. Kidney stones: A global picture of prevalence, incidence, and associated risk factors. Rev. Urol. 2010, 12, e86–e96. [Google Scholar]
- Evan, A.P. Physiopathology and etiology of stone formation in the kidney and the urinary tract. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2010, 25, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drewnowski, A. The Nutrient Rich Foods Index helps to identify healthy, affordable foods. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1095S–1101S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassir, A.M. Prevalence and characterization of urolithiasis in the Western region of Saudi Arabia. Urol. Ann. 2019, 11, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.; Hoppe, B. History, epidemiology and regional diversities of urolithiasis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alkhunaizi, A.M. Urinary stones in Eastern Saudi Arabia. Urol. Ann. 2016, 8, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, T. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and pathophysiology of urolithiasis. Eur. Urol. 2010, 9, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Segal, A.M.; Seifter, J.L.; Dwyer, J.T. Nutritional Management of Kidney Stones (Nephrolithiasis). Clin. Nutr. Res. 2015, 4, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuvanc, E.; Yilmaz, E.; Tuglu, D.; Batislam, E. Medical and alternative therapies in urinary tract stone disease. World J. Nephrol. 2015, 6, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Mendoza, C.; Sanchez, E. Bioactive Compounds from Mexican Varieties of the Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): Implications for Health. Molecules 2017, 17, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, C.J. Functional Foods. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khare, C.P. Indian Medicinal Plants: An Illustrated Dictionary; Springer Science and Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 268–269. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, K.V. Antiurolithiatic activity of Phaseolus vulgaris seeds against ethylene glycol-induced renal calculi in Wistar rats. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2018, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varoni, E.M.; Iriti, M. Odontonutraceuticals: Pleiotropic Phytotherapeutic Agents for Oral Health. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abcar, A.C.; Chan, L.; Yeoh, H. What to do for the patient with minimally elevated creatinine level? Perm J. 2004, 8, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Haefeli, M.; Elfering, A. Pain assessment. Eur. Spine J. 2006, 15, S17–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, I.S.K.; Jensen, M.P.; Miro, J.; Tan, G. The validity of pain intensity measures: What do the NRS, VAS, VRS, and FPS-R measure? Scand J. Pain 2018, 26, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutebi, A.; Slack, M.; Warholak, T.L.; Hudgens, S.; Coons, S.J. Interpretation of verbal descriptors for response options commonly used in verbal rating scales in patient-reported outcome instruments. Qual. Life Res. 2016, 25, 3181–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanussen, M.; Stec, K.; ABmann, C.; Meigen, C.; Van Buuren, S. Synthetic growth reference charts. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2016, 28, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, K.; Xu, B. Polyphenol-rich dry common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and their health benefits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geraghty, R.M.; Proietti, S.; Traxer, O.; Archer, M.; Somani, B.K. Worldwide impact of warmer seasons on the incidence of renal colic and kidney stone disease: Evidence from a systematic review of literature. J. Endourol. 2017, 31, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadafranca, A.; Rinelli, S.; Riva, A.; Morazzoni, P.; Magni, P.; Bertoli, S.; Battezzati, A. Phaseolus vulgaris extract affects glycometabolic and appetite control in healthy human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salma, S.; Baig, S.G.; Hasan, M.M.; Ahmed, S.; Fatima, S.A. Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Fixed Oil in Rodents. J. Bas. App. Sci. 2018, 14, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo, F.; Gonzalez, D.R.; Moore-Carrasco, R. Effects of Phaseolus vulgaris extract on lipolytic activity and differentiation of 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes into mature adipocytes: A strategy to prevent obesity. J. Nutr. Metab. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, H.; Gu, J.; Wang, J.; Ren, F. Regular intake of white kidney beans extract (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) induces weight loss compared to placebo in obese human subjects. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nolan, R.; Shannon, O.M.; Robinson, N.; Joel, A.; Houghton, D.; Malcomson, F.C. It’s no has bean: A review of the effects of white kidney bean extract on body composition and metabolic health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Risi, R.; Masi, D.; Caputi, A.; Balena, A.; Rossini, G.; Tuccinardi, D.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Manfrini, S.; et al. Current Evidence to Propose Different Food Supplements for Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, P.; Pal, D.K.; Das, M. Does quality of drinking water matter in kidney stone disease: A study in West Bengal, India. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2018, 59, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basiri, A.; Shakhssalim, N.; Khoshdel, A.R.; Pakmanesh, H.; Radfar, M.H. Drinking water composition and incidence of urinary calculus: Introducing a new index. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 5, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Jimenez, A.K.; Reynoso-Camacho, R.; Tejero, M.E.; Leon-Galvan, F.; Loarca-Pina, G. Potential role of bioactive compounds of Phaseolus vulgaris L. on lipid-lowering mechanisms. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestares, T.; Barrionuevo, M.; Lopez-Frias, M.; Vidal, C.; Urbano, G. Effect of different soaking solutions on nutritive utilization of minerals (calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium) from cooked beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in growing rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, N.D.; Marchini, G.S.; Mazzucchi, E.; Reis, S.T.; Srougi, M.; Evazian, D.; Nahas, W.C. Effect of phyllanthus niruri on metabolic parameters of patients with kidney stone: A perspective for disease prevention. Int. braz. J. Urol. 2018, 44, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramsout, R.; Rodgers, A.; Webber, D. Investigation of the effects of Phyllanthus niruri L. on in vitro calcium oxalate crystallization. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 2011, 10, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, A.L.; Benegal, A.; Prusty, V.; Kumar, M.S.; Bhat, V.; Rathnakar, U.P. Diuretic activity of Phyllanthus niruri (Linn) in rats. J. Health 2010, 2, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, F.; Askarpour, M.R.; Eslahi, A.; Nikbakht, H.A.; Jafari, S.H.; Hassanpour, A.; Makarem, A.; Salama, H.; Ayoub, A. The role of ultrasonography in detecting urinary tract calculi compared to CT scan. Res. Rep. Urol. 2018, 15, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Demographic Characteristics | PV Group | Control Group | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 30) | (n = 30) | |||
| N (%) | N (%) | |||
| Age | 20–30 years | 3 (10) | 4 (13.3) | p = 0.957 |
| 31–40 years | 8 (26.7) | 7 (23.3) | ||
| 41–50 years | 11 (36.6) | 10 (33.4) | ||
| 51–60 years | 8 (26.7) | 9 (30) | ||
| Gender | Male | 18 (60) | 21 (70) | p = 0.417 |
| Female | 12 (40) | 9 (30) | ||
| Educational level | Primary school | 7 (23.3) | 12 (40) | p = 0.188 |
| High school and diploma | 17 (56.7) | 16 (53.3) | ||
| University | 6 (20) | 2 (6.7) | ||
| Employment status | Employed | 24 (80) | 22 (73.3) | p = 0.542 |
| Unemployed | 6 (20) | 8 (26.7) | ||
| Marital status | Unmarried | 2 (6.7) | 3 (10) | p = 0.640 |
| Married | 28 (93.3) | 27 (90) | ||
| Physical activity | Sedentary | 17 (56.7) | 16 (53.3) | p = 0.795 |
| Moderate | 13 (43.3) | 14 (46.7) | ||
| Diet pattern | Vegetarian | 1 (3.3) | 1 (3.3) | p = 0.472 |
| Non-vegetarian | 29 (96.7) | 29 (96.7) | ||
| Presence of comorbidities | Diabetes Mellitus | 3 (10%) | 5 (16.7) | p = 0.653 |
| Hypertension | 2 (6.7) | 1 (3.3) | ||
| None | 25 (83.3) | 24 (80) | ||
| Family history of kidney stone | Yes | 4 (13.3) | 2 (6.7) | p = 0.389 |
| No | 26 (86.7) | 28 (93.3) | ||
| Quantity of drinking water in liters per day | 1 | 21 (70) | 19 (63.3) | p = 0.584 |
| 2–3 | 9 (30) | 11(36.7) | ||
| Clinical Symptoms | PV Group (n = 30) | Control (n = 30) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Test | Post-Test | Pre-Test | Post-Test | |||||
| Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |
| Pain in the abdomen | 2 (6.7) | 28 (93.3) | 0 (0) | 30 (100) | 3 (10) | 27 (90) | 2 (6.7) | 28 (93.3) |
| Pain in lower back | 4 (13.3) | 26 (86.7) | 1 (3.3) | 29 (96.7) | 3 (10) | 27 (90) | 3 (10) | 27 (90) |
| Pain in urinary tract | 3 (10) | 27 (90) | 0 (0) | 30 (100) | 2 (6.7) | 28 (93.3) | 1 (3.3) | 29 (96.7) |
| Feeling nauseated | 5 (16.7) | 25 (83.3) | 1 (3.3) | 29 (96.7) | 3 (10) | 27 (90) | 3 (10) | 27 (90) |
| Sweating | 5 (16.7) | 25 (83.3) | 3 (10) | 27 (90) | 6 (20) | 24 (80) | 5 (16.7) | 25 (83.3) |
| Chills | 3 (10) | 27 (90) | 0 (0) | 30 (100) | 3 (10) | 27 (90) | 1 (3.3) | 29 (96.7) |
| Fever | 1 (3.3) | 29 (96.7) | 0 (0) | 30 (100) | 2 (6.7) | 28 (93.3) | 0 (0) | 30 (100) |
| Measurements | PV Group (n = 30) | Control (n = 30) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Test | Post-Test | Pre-Test | Post-Test | |||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Paired ‘t’ Test | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Paired ‘t’ Test | |
| Weight (kg) | 71.82 ± 7.35 | 71.59 ± 7.24 | t = 2.7162 | 70.77 ± 7.87 | 70.98 ± 7.97 | t = 1.4196 |
| p = 0.01101 * | p = 0.1664 NS | |||||
| BMI | 26.44 ± 2.7 | 26.36 ± 2.65 | t = 2.75; | 26.28 ± 2.84 | 26.36 ± 2.88 | t = 1.38; |
| p = 0.01017 * | p = 0.17716 NS | |||||
| Urinary Parameters | PV Group (n = 30) | Control (n = 30) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Test | Post-Test | Pre-Test | Post-Test | Paired ‘t’ Test | ||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Paired ‘t’ test | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||
| Urine volume (mL) | 1962 ± 152.8 | 2005 ± 148.8 | t = 3.0328 | 1992 ± 134.2 | 1964.2 ± 122.9 | t = 1.013 |
| p = 0.005 * | p = 0.3194 (NS) | |||||
| Calcium (mg) | 205.4 ± 11.99 | 198.4 ± 12.52 | t = 5.6538 | 201 ± 11.45 | 201.7 ± 12.74 | t = 1.0838 |
| p = 0.000 * | p = 0.2874 (NS) | |||||
| Magnesium (mg) | 70.69 ± 4.37 | 81.28 ± 4.73 | t = 7.55 | 72.82 ± 6.62 | 71.13 ± 4.3 | t = 1.796 |
| p = 14.5385 (NS) | p = 0.08293 (NS) | |||||
| Potassium (mEq) | 44.07 ± 3.66 | 52.15 ± 4.37 | t = 7.42946 | 43.99 ± 4.96 | 45.34 ± 5.44 | t = 1.00713 |
| p = 0.000 * | p = 0.03181 (NS) | |||||
| Oxalate (mg) | 37.12 ± 5.38 | 33.02 ± 5.71 | t = 4.6643 | 38.3 ± 5.57 | 38.65 ± 5.51 | t = 1.6353 |
| p = 0.000 * | p = 0.1128 (NS) | |||||
| Uric acid mg/dL | 6.88 ± 0.7 | 6.31 ± 0.58 | t = 5.8204 | 6.51 ± 0.87 | 6.7 ± 0.8 | t = 1.7278 |
| p = 0.000 * | p = 0.09466 (NS) | |||||
| pH | 6.03 ± 0.27 | 6.59 ± 0.31 | t = 7.4993 | 6.01 ± 0.37 | 6.13 ± 0.37 | t = 1.5137 |
| p = 2.889 (NS) | p = 0.1409(NS) | |||||
| Renal Scan Findings | PV Group (n = 30) | Control (n = 30) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Test | Post-Test | Pre-Test | Post-Test | |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |
| Location of the kidney stone | ||||
| Right | 13 (43.3) | 9 (30) | 10 (33.3) | 9 (30) |
| Left | 11 (36.7) | 6 (20) | 17 (56.7) | 16 (53.3) |
| Both | 6 (20) | 5 (16.7) | 3 (10) | 3 (10) |
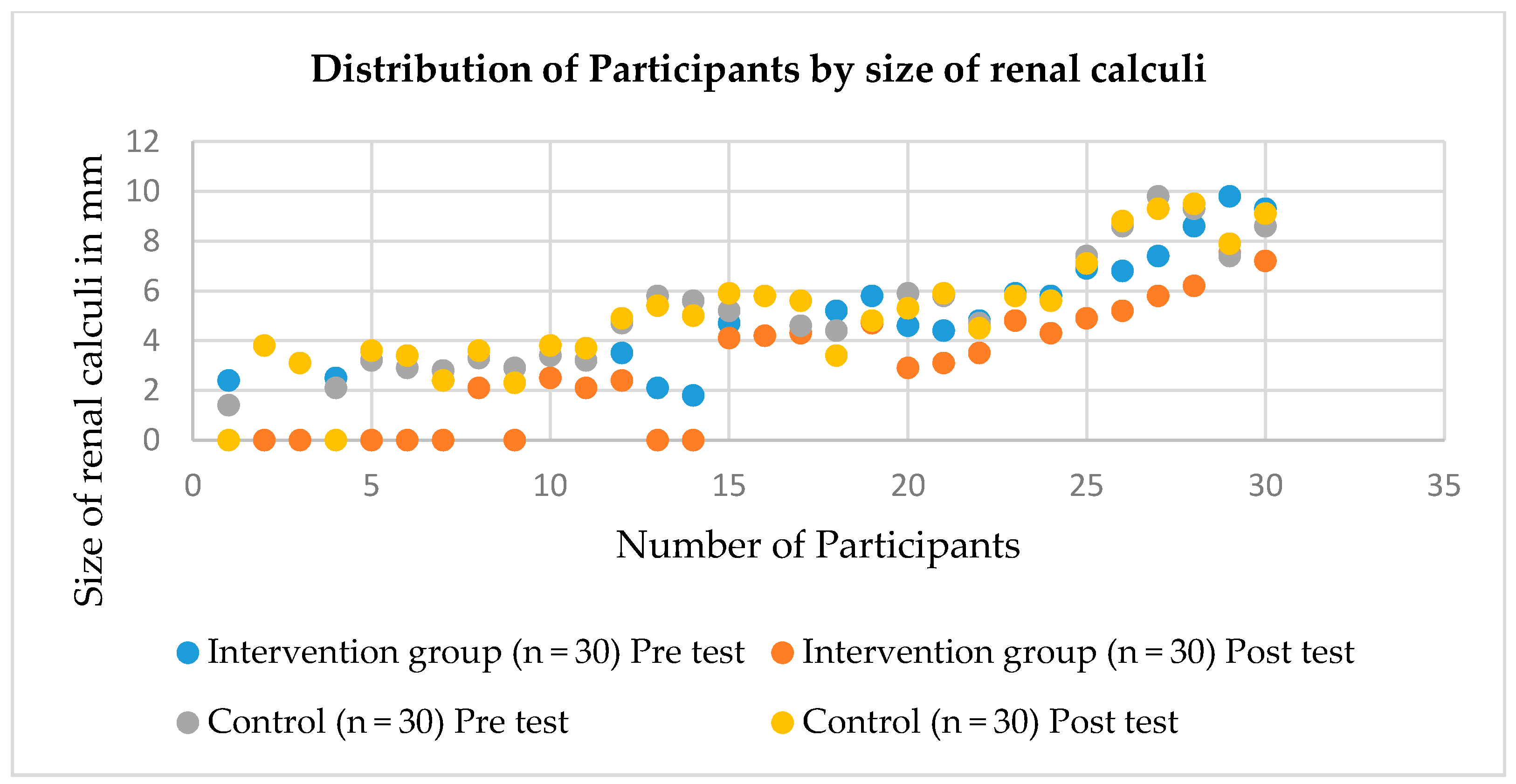
| Size of calculi | ||||
| 1–3.9 mm | 14 (46.7) | 8 (26.7) | 11 (36.7) | 10 (33.3) |
| 4–6.9 mm | 12 (40) | 10 (33.3) | 13 (43.3) | 12 (40) |
| 7–9.9 mm | 4 (13.3) | 2 (6.7) | 6 (20) | 6 (20) |
| Number of calculi | ||||
| Single | 22 (73.3) | 14 (46.7) | 25 (83.3) | 23 (76.7) |
| Multiple | 8 (26.7) | 6 (20) | 5 (16.7) | 5 (16.7) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jalal, S.M.; Alsultan, A.A.; Alotaibi, H.H.; Mary, E.; Alabdullatif, A.A.I. Effect of Phaseolus Vulgaris on Urinary Biochemical Parameters among Patients with Kidney Stones in Saudi Arabia. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3346. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113346
Jalal SM, Alsultan AA, Alotaibi HH, Mary E, Alabdullatif AAI. Effect of Phaseolus Vulgaris on Urinary Biochemical Parameters among Patients with Kidney Stones in Saudi Arabia. Nutrients. 2020; 12(11):3346. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113346
Chicago/Turabian StyleJalal, Sahbanathul Missiriya, Abdulrahman Abdulhadi Alsultan, Hala Hazam Alotaibi, Ester Mary, and Abeer Abbas Ibrahim Alabdullatif. 2020. "Effect of Phaseolus Vulgaris on Urinary Biochemical Parameters among Patients with Kidney Stones in Saudi Arabia" Nutrients 12, no. 11: 3346. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113346
APA StyleJalal, S. M., Alsultan, A. A., Alotaibi, H. H., Mary, E., & Alabdullatif, A. A. I. (2020). Effect of Phaseolus Vulgaris on Urinary Biochemical Parameters among Patients with Kidney Stones in Saudi Arabia. Nutrients, 12(11), 3346. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113346





