Abstract
Traditional wastewater treatment methods have become aged and inefficient, meaning alternative methods are essential to protect the environment and ensure water and energy security worldwide. The use of microbial electrolysis cells (MEC) for wastewater treatment provides an innovative alternative, working towards circular wastewater treatment for energy production. This study evaluates the factors hindering industrial adoption of this technology and proposes the next steps for further research and development. Existing pilot-scale investigations are studied to critically assess the main limitations, focusing on the electrode material, feedstock, system design and inoculation and what steps need to be taken for industrial adoption of the technology. It was found that high strength influents lead to an increase in energy production, improving economic viability; however, large variations in waste streams indicated that a homogenous solution to wastewater treatment is unlikely with changes to the MEC system specific to different waste streams. The current capital cost of implementing MECs is high and reducing the cost of the electrodes should be a priority. Previous pilot-scale studies have predominantly used carbon-based materials. Significant reductions in relative performance are observed when electrodes increase in size. Inoculation time was found to be a significant barrier to quick operational performance. Economic analysis of the technology indicated that MECs offer an attractive option for wastewater treatment, namely greater energy production and improved treatment efficiency. However, a significant reduction in capital cost is necessary to make this economically viable. MEC based systems should offer improvements in system reliability, reduced downtime, improved treatment rates and improved energy return. Discussion of the merits of H2 or CH4 production indicates that an initial focus on methane production could provide a stepping-stone in the adoption of this technology while the hydrogen market matures.
1. Introduction
Growing populations and expanding infrastructure have led to a rapidly changing climate and the depletion of global resources. The water crisis is listed in the top five risks to humanity by the World Economic Forum with the global demand for water set to rise by 55% from 2000 to 2050 [1]. On average, 80% of global wastewater is expelled into the environment untreated; this includes industrial, agricultural and municipal waste [2]. The large volumes of untreated waste and the increase in demand for water dramatically increases the strain on the environment and existing ageing infrastructure. New approaches to wastewater treatment are required to treat at the source of generation rather than relying on vast sewerage networks to transport wastewater to a central treatment site. A key shift is necessary whereby wastewater is viewed not as a toxic burden, but rather, a valuable raw material. The transition would see wastewater become a sustainable source of water, bioenergy and nutrients, providing security for generations to come.
Microbial Electrolysis Cells (MECs) can be used in a circular approach to wastewater treatment, enabling the recovery of valuable resources (hydrogen, methane and other value-added chemicals). They offer the promise of creating a closed circular loop of water reuse and nutrient recovery. MECs provide a high yield method of wastewater treatment producing Hydrogen (H2) and Methane (CH4) from biomass [3,4]. MECs can potentially be a crucial step towards fully utilising the potential of wastewater as well as becoming a source of renewable energy that can offer collaboration between industry and research organisations. For progress in the field, there needs to be additional integration between research, industry and governments [5]. Despite a growing body of research regarding the use of MECs for wastewater treatment, adoption by industry has remained slow. This study will evaluate key aspects of the technology to assess the most considerable barriers to adoption and identify the next steps towards the use of MECs for industrial wastewater treatment.
1.1. Current Wastewater Treatment Methods and Limitations
Conventional wastewater treatment relies on sewerage to transport wastewater to a centralised wastewater treatment plant and uses end of pipe technologies to treat the waste in a linear fashion. Transition to a closed-loop model is required [6], in which water is treated while simultaneously recovering energy and nutrients. Compared to centralised solutions, decentralised wastewater treatment plants can demonstrate reduction in operation and capital expenditure (OPEX). Even though decentralised solutions are in their infancy in terms of deployment and optimisation compared to centralised solutions [7], the benefits of decentralisation are showing and trends in wastewater treatment plants are making a transition towards decentralisation with resource recovery [7].
Centralised water systems are not applicable in many parts of the world where there is rapid population growth and a swing towards urbanisation [8]. The shift from rural to urban living has put wastewater infrastructure under pressure and in many cases has meant that well designed and effective wastewater treatment systems have not been implemented. Creating centralised wastewater treatment systems retrospectively is difficult and expensive. Shifting towards distributed and non-networked technologies creates a decentralised wastewater treatment infrastructure that can provide greater resilience and a lower economic and environmental cost compared to conventional systems [9].
1.2. Mechanism of Microbial Electrolysis Cells for Wastewater Treatment
MECs offer an alternative to centralised wastewater treatment methods. The embodied chemical energy potential of wastewater, generated from its organic components, is approximately 9.3 times greater than the energy needed to treat it [10]. Harnessing energy from biomass using biological anaerobic wastewater treatment methods are already popular due to their relative simplicity and robustness [11]. Today, Anaerobic Digestion (AD) is widely used to produce biogas from sludge. AD generates energy via the digestion of acetate to form CH4 and CO2 [12]. However, the process is relatively slow and produces biogas with high levels of CO2, reducing its energy density. The high CO2 content makes the biogas difficult to store and requires extensive chemical treatment, including cryogenic separation, to remove CO2 before use [13]. MECs offer an alternative approach to produce both CH4 and H2.
MECs contain electrodes poised at a set potential and utilise microorganisms as biocatalysts to reduce activation overpotential of a given redox event, increasing the MECs’ voltage efficiency and product yield [14]. Microorganisms form a biofilm on the surface of the anode that can convert chemical energy, present in organic substances, into electrical energy, which is then used to create other valuable products such as H2 and CH4 at the cathode [15]. These microorganisms are electrochemically active and, therefore, can exchange electrons with the electrode in order to maintain cellular function and growth [16]. MECs can be configured for many different outputs, including H2 and CH4 production, through different reactor architecture designs which may include the use of multiple chambers and membranes.
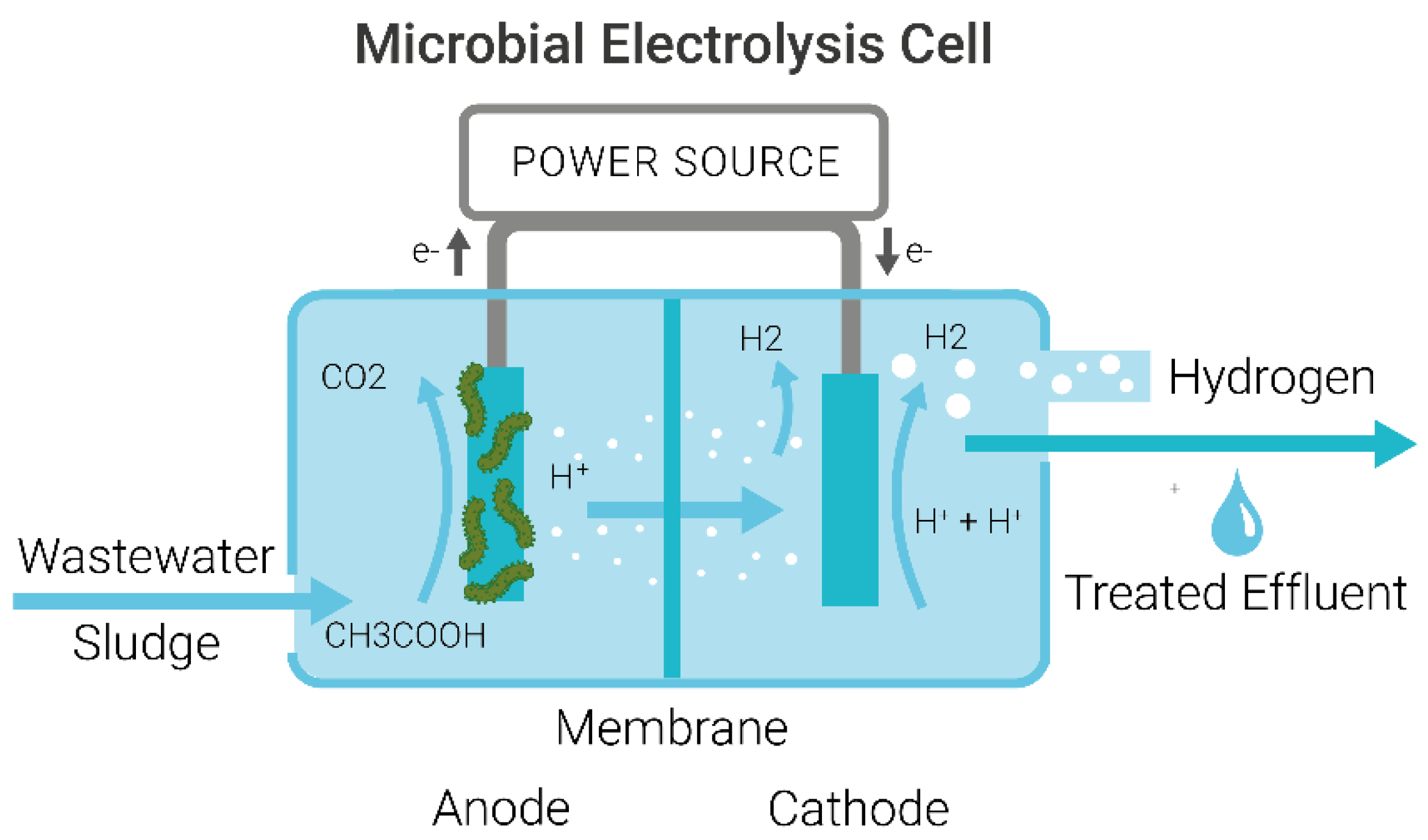
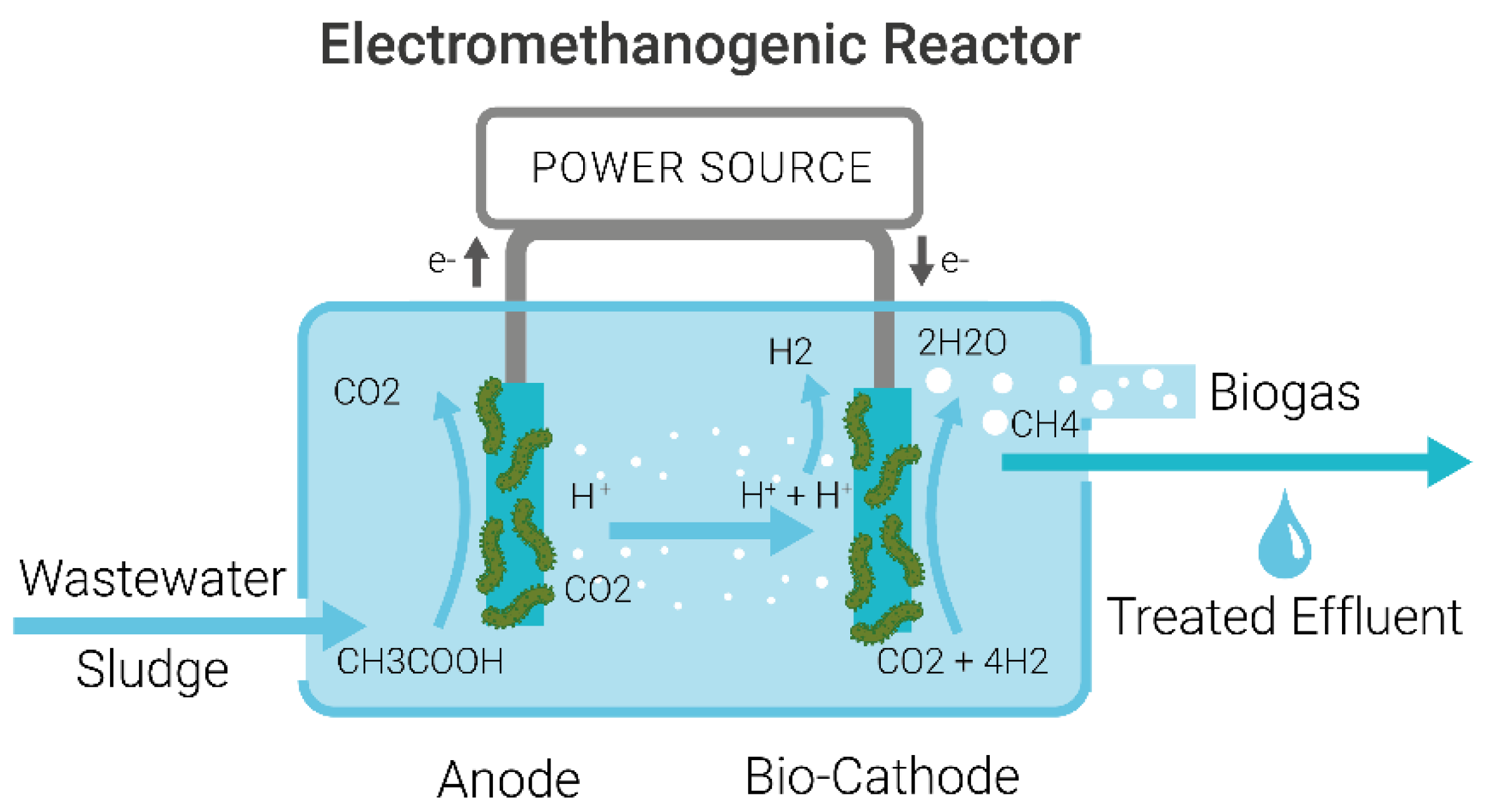
MECs designed for H2 production often require a separator between the bioanode and cathode to stop H2 evolution to CH4, with microorganisms only adhering to the anode, as shown in Figure 1. MECs for CH4 production have a biocathode where methanogenic microorganisms are used to generate CH4 from H2 and CO2 at the cathode, as shown in Figure 2. These systems are called MEC-ADs [17] or methanogenic microbial electrolysis cells (MMEC) [18] and use the process of electro-methanogenesis to produce CH4.
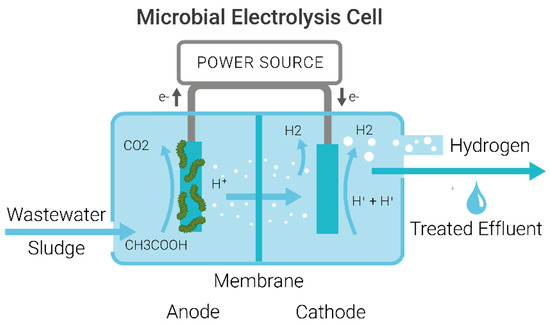
Figure 1.
Schematic of a Microbial Electrolysis Cell for treating wastewater to produce H2, showing the wastewater influent and effluent and an anode and cathode separated by a membrane and connected to a power source.
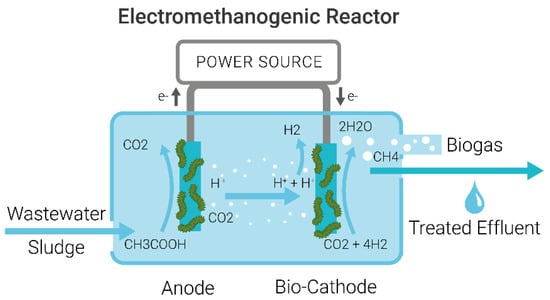
Figure 2.
Schematic of a Microbial Electrolysis Cell-Anaerobic Digestion (MEC-AD) or Electro-Methanogenic Reactor for treating wastewater to produce CH4 showing the wastewater influent and effluent and an anode and cathode connected to a power source.
The anode and cathode are connected to a power source, under anaerobic conditions. Wastewater enters the reactor, and electricity is supplied to the electrodes at precisely controlled potential differences. Biogas is produced, and wastewater is treated, meaning effluent water has significantly lower levels of organic contaminants, as shown in Figure 2.
At the anode, electro-active Bacteria (EAB) (s) grow to form a biofilm which uses electrical energy to oxidise organic matter to CO2 (Equation (1)) [19].
Anode: C2H4O2 + 2H2O → 2CO2 + 8H+ + 8e−
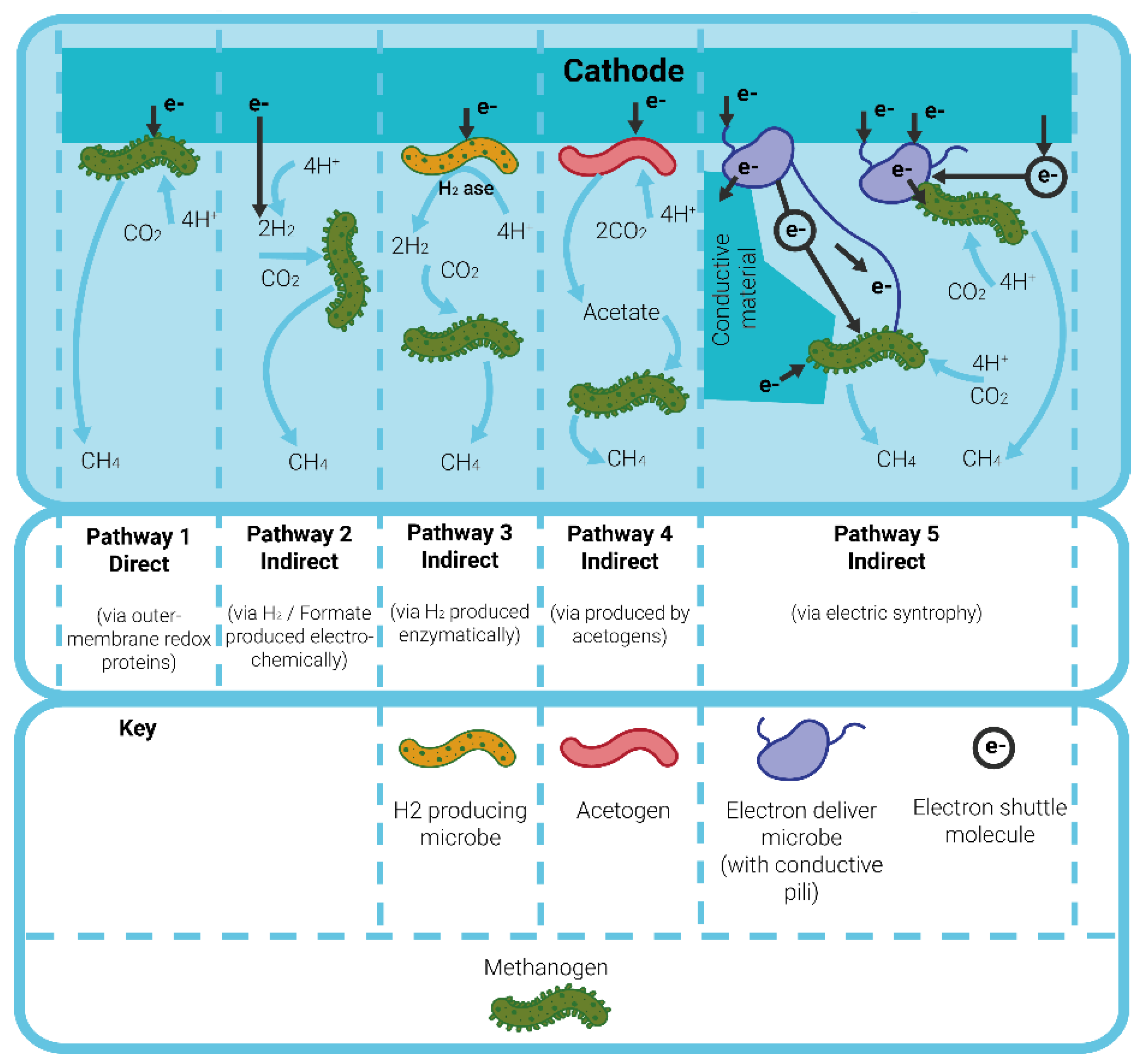
At the cathode, CH4 production takes place. There are several different pathways to CH4 production through direct or indirect electron transfer [19].
Pathway 1, highlighted in Figure 3, illustrates direct methanogenesis where CH4 is directly produced from CO2 via outer membrane redox proteins that are in direct contact with the electrode [20]. Alternatively, indirect electron transfer methanogenesis proceeds via the production of an intermediate. Indirect methanogenesis takes place either via Pathway 2, 3 or 4, as shown in Figure 3.
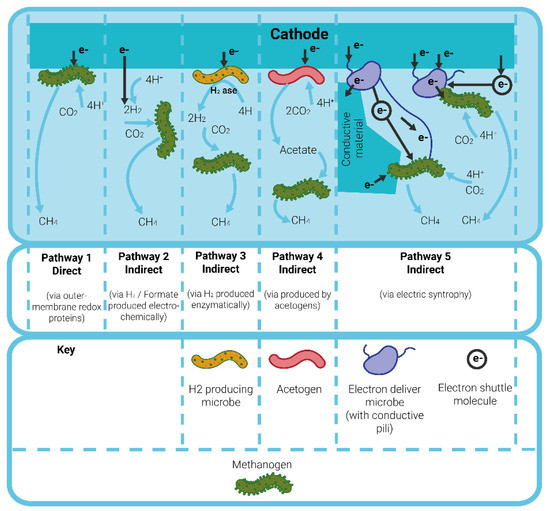
Figure 3.
Schematic outlining the possible routes of methanogenesis for CH4 production. Pathway 1: direct electron transfer, Pathway 2: indirect electron transfer via electrochemically produced H2, Pathway 3: indirect electron transfer via enzymatically produced H2, Pathway 4: indirect electron transfer via biologically produced acetate, and Pathway 5: indirect electron transfer via electric syntrophy. Schematic adapted from [20].
Pathway 2 involves the intermediate production of H2, either electrochemically or bio-electrochemically, used to produce CH4 by hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis [21].
Pathway 3 and 4 involve biologically produced formate or acetate producing CH4 via acetogenic methanogenesis [22] and Pathway 5 involves interspecies electron transfer by electron carriers or nanowires [20].
Investigations have been conducted to determine the most favourable route of methanogenesis. Theoretically, CH4 can be produced by direct electron transfer at relatively low voltages [23]. However, in practice, this is very energy-intensive as an electrocatalyst is required to lower the overpotentials. Therefore, a lack of an appropriate catalyst to reduce overpotentials, means that to high electrode potentials are needed to drive the reaction [24]. CH4 generated in ADs mainly originates from acetate (~70%) via acetotrophic methanogenesis where acetate is produced as an intermediate. However, analysis of the microbial consortium present at the cathode in an MEC-AD indicated that intermediate hydrogen production was favoured [25]. Villano et al. demonstrated that only a fraction of CH4 produced was via direct electron transfer, with the majority from H2-mediated methanogenesis via hydrogenotrophic methanogens. This is an important factor to consider when evaluating cathode materials [21]. If H2-mediated methanogenesis is favoured, then the hydrogen evolution ability of the cathode material must be considered. Cathode materials, therefore, can be seen as acting as biocatalysts, by enhancing electrode-microbe electron transfer that improves the rate of formation of products [26].
The review aims to analyse the critical aspects of the treatment process, namely the electrode materials, feedstock, and inoculum, to determine the most efficient parameters for the treatment of wastewater using MEC, then to situate this with economic analysis to evaluate each parameter in the context of what is economically viable to facilitate industrial adoption of this technology. This study seeks to act as a bridge between research and industry analysing the future steps towards commercialisation of the technology.
2. Parameters Affecting the Design of MEC Systems for Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Accelerating the commercialisation of this technology will increase its impact within the sector while increasing funding and research for continuous improvements. There are multiple variables to consider when analysing and comparing MECs for wastewater treatment and energy production. This review identifies the strength and type of feedstock, the anode and cathode materials, the size and electrode surface area to reactor volume, the system architecture, the outputs, and the costs as the most significant parameters affecting the system design. These parameters affect the system performance and the economic viability of commercialising the technology. To make MECs commercially viable, a balance must be struck between system optimising performance and economic efficiency of all components. Future MEC design needs to incorporate anode cost reduction, improvements in organic loading rates, understanding of maintenance requirements and electrode lifetime expectancy [27]. The study will evaluate the parameters in the context of industrial use, where cost and the ease of manufacturing at all stages are considered, in order to identify the next steps, researchers should look towards accelerating the adoption of this technology by industry.
2.1. Feedstock
The identity of the feedstock has a large impact on the performance of MECs. The strength of the wastewater refers to the level of contamination of the water and dictates the treatment time, size of the reactor and the energy requirement and production. High strength wastewater has a higher organic load; therefore, more energy can be recovered by treatment methods. However, high strength wastewater usually takes longer to treat, leading to greater hydraulic retention times (HRT). Research should look at optimising the HRT to help reduce the reactor size and affect energy production/consumption. The organic loading drastically changes depending on the wastewater sources, which in turn effects the organic loading rate (OLR). Table 1 shows the chemical oxygen demand (COD) values of wastewaters that have been treated using bio-electrochemical systems in previous studies.

Table 1.
Industrial Wastewater COD Range adapted from [28] with the required hydraulic retention times (HRT) calculated using OLR = COD (mg/L) × Flow Rate (m3/d) to compare each waste stream.
With improvements in the cost of MECs, a viable organic loading rate (OLR) for a system ranges between 800–1400 mg/L [27]. Urban wastewater is low strength with a COD value of 300–500 mg/L [28], therefore, requiring a shorter HRT of 5–9 h, whereas swine waste, with a higher COD of 18,300 mg/L, requires a very longer HRT of 314 hrs. Longer HRTs act as a significant barrier to industrial adoption, reducing the amount of waste that can be treated per day as well as increasing the size of reactors needed. However, high strength wastewaters produce more energy, therefore can be more economically viable in terms of energy production, as higher organic loads contain higher energy potential. A normalised net energy production of 76.2 kWh/m3/day was achieved for pig slurry, a high strength wastewater, at a volume of 16 L and an anodic and cathodic surface area of 11.25 m2/m3 [39]. However, as for low strength wastewater, (<250 mg/L COD), even though it has a low HRT, it is still difficult to make treatment economically viable due to the very low energy production associated with its lower organics content. When there is even a slight increase in wastewater strength (360–400 mg/L COD) treatment could be considered economically viable due to increased energy production [11].
Table 1 also highlights that waste streams have varying characteristics, and therefore the wastewater treatment method must vary. It is unlikely that there will be a homogenous solution for all organic waste streams. Furthermore, some organic waste streams cannot be treated using MECs. Treatment of cheese whey, for example, using MECs produced no gas; this suggests that the microorganisms present are not able to breakdown the organic waste, potentially due to feedstock inhibiting methanogens [45]. Further research into the performance of MECs for the treatment of different wastewater streams will provide insights in evaluating industry suitability.
Gil-Carrera et al. found that a MEC, optimised for hydrogen production with an OLR greater than 1000–2000 mg COD/L/day, can be competitive with activated sludge treatment [27]. For OLRs of >2000 mg COD/L/day, the theoretical HRT for the different waste streams has been calculated, as shown in Table 1. Table 1 also indicates that it is possible to increase the HRT and still be competitive against activated sludge treatment. MECs also have a significantly lower HRT than AD due to more efficient treatment. The HRT of AD systems is typically between 20–30 days. The long treatment time of AD suggests that using MEC-ADs instead would allow for reduced facilities size, as a higher OLR can be used. MEC-ADs provide multiple further benefits over AD including increased biological stability, higher energy production and an increase in substrate removal, especially of complex compounds that are difficult to remove [17]. The improvement in performance stems from both the presence of electrodes, greater surface area for bacterial attachment, and the applied voltage. Arvin et al. found that with electrodes present but with no voltage applied, COD removal was 49% compared to 58.4%, 64.7% and 72.6% for 0.6 V. 0.8 V and 1.0 V, respectively [46]. Both crude glycerol and cheese whey have very high HRT based on an OLR of 1400 mg COD/L/day, as shown in Table 1. For example, cheese whey would require an OLR of 42,000 mg COD/L/day to have an HRT of 30 days, similar to AD. In these cases, the reactor design would be crucial to lower HRT but increase the solid retention to reduce the size of the reactor.
The energy demands for traditional wastewater treatment are high, especially for activated sludge treatment, equating to 60% of the total energy needed. Using MEC-ADs for wastewater treatment has resulted in a 1.7 times higher energy production [47] and an accelerated substrate removal [17] compared to AD, indicating the potential of highly efficient treatment for any commercial waste streams already used for AD. Furthermore, reducing the need for post-treatment would significantly reduce the energy requirements within the treatment process [48]. Using MECs to reduce the energy consumption of wastewater treatment would have significant impacts throughout the world. Research into the performance of MECs in treating different waste streams is increasing and is helping to generate an understanding of how different microbial communities perform with the substrates. If MECs and MEC-ADs are to become commercially viable, they will compete with other technologies in the field: AD systems that focus on energy generation or activated sludge systems that focus on nutrient and COD removal. Multiple studies have investigated the treatment of urban wastewater; however, from studies in Table 1, the HRT ranges from 8-48 h instead of the suggested 5–9 h.
Going forward, researchers should assess the economic viability of treatment of particular wastes and compare MEC and MEC-AD performance to the state-of-the-art technology used by industry.
2.2. Inoculation
System inoculation constitutes the introduction of microorganisms into the MEC where they will grow and reproduce, forming a biofilm on the electrodes in the case of MECs. Microorganisms are cultivated in the system via inoculation, and therefore the choice of inoculum is critical to the degradation of organic matter [49].
Inoculation also has a direct effect on the start-up time of a MEC system as the microorganism present dictates the reaction. The start-up period for a system is the time taken for the system to start generating hydrogen or biogas. Long start-up times reduce the efficiency of the system as they take longer to start producing energy; therefore, using the right inoculum source is important to maximise the efficiency of the system.
Methods to improve the start-up time of BESs have been explored. Commault et al. found that anodes, initially poised at −0.25 V vs. Ag/AgC and then increased to −0.5 V vs. Ag/AgCl, had a quicker start-up time and a higher concentration of Geobacter than those poised at −0.36 and −0.42 V vs. Ag/AgCl [50]. The study found that after the electrode potentials were all increased to −0.5 V vs. Ag/AgCl, the maximum power density was similar at 270 mW/m2 (−0.25 V) and 250 mW/m2 (−0.36 V) [51]. Activation and biofilm formation has been found to be quicker at the anode than the cathode (days vs. weeks), and incremental increases can support biofilm growth starting at 0.3 and increasing to 1.0 V [50]. The slow cathode biofilm growth indicates that it is important to ensure methanogens are present in the bulk liquid initially. In this case, following a flow rate similar to AD systems will be crucial to reduce bacterial washout.
The choice of inoculum can also be used to reduce the start-up time and increase performance. Mixed inoculum sources combining 1:4 activated sludge and municipal sewage was found to increase biogas production by 18.5% compared to mono-inoculated treatment, indicating that a diverse inoculation supports strong nutrient enrichment, crucial to the digestion process [49]. In addition to the benefit of having a mixed inoculum, having an inoculum that derived from the same source of the substrate to be treated provided an improved performance, as this ensures that an active microbial community is present that is suited to the substrate [52]. Methane production was also higher, indicating that this mixed bacteria consortium is also beneficial in improving the production of hydrogenotrophic methanogens for methane production. The strength of the inoculum also dictates the start-up. Escapa et al. found that when low strength domestic wastewater (230 mg COD L−1) was used as the source of inoculum the reactor failed to start up [52]. Research suggests that larger pilot systems take longer to start-up with gas generation taking between 50–90 days [28,53]. A relatively easy way to reduce start up time for large scale systems is by pre-acclimatization of electrodes with desirable microorganisms as a way of pre-inoculating the system. Xu et al. found that pre-inoculation of carbon electrodes with hydrogenotrophic bacteria derived from natural bog sediment improved start-up times and methane production [54].
Long start-up times can become problematic as payback takes longer. To address start-up time, pre-inoculation of electrodes could offer a low-cost way of reducing them without costly modifications. More research into the most favourable start-up conditions will increase the attractiveness of the technology for industrial use, working towards commercialisation of MECs for global wastewater treatment.
2.3. Anode Material
The performance of the anode is essential to the performance of bio-electrochemical systems, with the anode being transferable from MFCs, MECs and MEC-ADs. Research suggests that the action at the anode is a limiting factor to the performance of the entire system [55]. At the bioanode, electro-active microorganisms (EAB) adhere to the surface, forming a biofilm. Organic species are oxidised to CO2 by EAB, with the activity of the EAB being the most important factor in CO2 production. The efficiency of the anode and biofilm can be measured by the current density, Coulombic Efficiency (CE) and COD reduction [56]. Carbon materials are at present the most commonly used electrode material due to their strong anchorage of EAB, high surface area and availability [57]. Carbon materials have been shown to promote interfacial microbial colonisation and therefore accelerate biofilm formation. Carbon materials, however, have a relatively low conductivity compared to metals. Metallic current collectors are used as electron acceptors, to overcome low conductivity. Titanium wire is frequently used due to its resistance to corrosion [11,30]. Furthermore, it can be argued that the ability to promote interfacial microbial colonies can actually enhance current density by providing a conducive micro-environment for electron transfer compensating for the reduced conductivity [58].
Graphite is cheap, abundant and conductive and, therefore, has become one of the most widely used electrode materials [59]. Various forms of graphite electrodes have been used, including brushes, granular, rods, felts and foams [58]. However, as the structure and morphology of graphite is planar, it has a relatively low surface porosity for bacterial attachment, when compared to other carbon materials. Recent studies have tended to focus on 3-D porous carbon materials that increase surface area, including carbon foams, meshes, felts and brushes [60]. Carbon fibre (CF) electrodes are functional and have been showed to achieve high performances in previous studies [61]. However, they are more expensive [62]. Mesh CF anodes tend to produce higher current densities than plate shaped anodes due to better mass transfer, surface area and biofilm formation. Despite the fact that carbon fibre brushes produce good lab results, they are not used as often in large-scale BES due to the high cost. Carlotta-Janes et al., however, found that using recycled carbon fiber anodes greatly improved performance compared to graphite felt anodes and greatly reduced cost of materials compared to previous pilots where carbon fibre electrodes were used [29,61,63].
From the pilot-scale studies analysed, carbon-based materials have been used in the form of brushes, felt and fibres; however, biofilm formation observed was relatively low. In 130 L and 45 L pilot systems, it was found that the average biofilm coverage was only 5%, reaching a maximum of 16% on one part of the electrode [64]. With such a significant amount of the anode not containing a biofilm, it is likely that increasing biofilm adhesion and density to the anode will see greater improvements than increasing the surface area of the anode. For commercial viability, reducing the required size of the anode would be beneficial, as the anode material represents a high cost, equating to 69% of the total system [63], which requires an approximate 90% reduction in cost to make it economically viable [27].
Metals are also considered as good electrode materials. Metals are much more conductive than carbon materials [65], though untreated metals are rarely used due to limited biocompatibility [66]. Yamashita et al. conducted extensive screening of 45 metal-based anodes, both treated and untreated. Molybdenum anodes, both treated and untreated, showed the highest maximum power densities compared to all other materials [66]. Molybdenum anodes also displayed good durability, not corroding or reducing in current production over 350 days. The durability of electrode materials is also a key factor to consider, and there is a lack of data regarding the durability of the electrode materials, with most experiments lasting no longer than a year. However, the dissipation of electrode materials is generally not considered, which has significant implications when considering materials to use on a commercial scale.
Stainless steel is suitable as it is cost effective, durable, easy-to-handle and has a large range of possibilities for scaling up the size of the electrodes [67]. Stainless steel has advantages over carbon anodes as it is more conductive and has larger scale-up potential due to low capital costs [68]. However, the biocompatibility of stainless steel is reduced due to a relatively smooth surface. Flame spray oxidation makes stainless steel more biocompatible by generating an iron oxide film on the surface, fostering the attachment of iron-reducing bacteria as well as increasing the surface roughness without compromising the corrosion resistance [68]. It is also a cheap and scalable method of modifying the surface of metal electrodes for optimal performance. Further research into the longevity of stainless steel will need to be explored as it has not been tested on pilot systems.
Cotterill et al. investigated the effect of scale on H2 production comparing a 30 L tank to a 175 L tank. It was found that when the anode surface area was increased from 0.06 m2 to 1 m2, a 16-fold increase, the H2 production relative to the anode surface area was four times larger in the smaller MEC than the larger one [63]. The lower performance in the larger MEC highlights a negative correlation between scale and gas production showing that as scale increases efficiency decreases. It was extrapolated that a further 30% increase in anode size would result in no increase in gas captured [63]. These efficiency decreases highlight the need for a greater transfer of lab-scale to pilot-scale research to evaluate whether an electrode material that is effective in the lab is effective on a larger scale.
Currently, carbon-based anodes are the most economically viable option; however, they still present a high cost. Working towards commercialisation, a cost-benefit analysis needs to be carried out on anode materials that also takes into consideration the availability of material, its corrosion resistance, and the ability to increase the scale.
2.4. Cathode Material
Reactions at the cathode are dictated by the desire to produce either CH4 or H2 and this is dependent on the desire and capability to produce and use CH4 or H2 on site. The rate of consumption of H2 is dependent on methanogenic activity. If the system is operating as a membrane-less single chamber, then it is likely that the hydrogen will be consumed during the reaction, therefore the biogas produced will be CH4 [30]. The operating temperature also has a direct effect on the activity of methanogens, with temperatures above 35 °C greatly improving the activity of methanogens [69]. In MECs where CH4 is produced, research indicates that hydrogenotrophic methanogens are more abundant, producing CH4 via the intermediate production of H2 [21]. The CH4 production pathway indicates that the hydrogen evolution ability of the cathode material is a crucial design consideration. Therefore, the cathode has a dual purpose acting as both a biocatalyst, by enhancing electrode-microbe electron transfer [26], and as an electrocatalyst accelerating the hydrogen evolution reactions (HER). Waste streams contain hydrogen scavenging microorganisms, which is why membranes are required if pure hydrogen is desired. Membrane systems have been successfully tested with multiple studies reaching over 98% hydrogen purity [33,34,35].
Successful cathode materials must have a high specific surface area, good conductivity, strong biocompatibility, good corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties [70]. Additionally, cathode materials must also reduce large overpotentials of hydrogen evolution. For industrial use, cathode construction needs to be low cost using materials that are readily available and use standard manufacturing techniques for large scale deployment to be feasible. Research has focused on metals as they are more conductive than carbon-based materials [71] and have been shown to have good biocompatibility, and cathode potentials protect from corrosion [72]. Platinum is often championed as the best electrode material due to its very low overpotential, biological inactivity and corrosion resistance [31]. Platinum also has the highest HER activity [73], leading to better H2 evolution [31]. However, there are many disadvantages of platinum, namely high cost and large environmental impact associated with mining; this calls for the development of novel metallic electrode materials [72]. In term of non-precious metals, stainless steel and nickel have shown good results [3,39]. From Table S1 (SI), stainless steel is the primary cathodic material used in pilot-scale studies.
Stainless steel is a relatively inexpensive metal and is commonly used for electrodes. Stainless steel with a high specific surface area can perform similarly to a carbon-containing platinum catalyst electrode for H2 production [3]. Stainless steel mesh is reported to have good ohmic resistance and electron transport resistance due to its strong conductivity as a transient metal [74]. The low cost and high performance of stainless steels, particularly mesh and brushes, show promising potential as a non-precious metal cathode for future testing and scaleup. The research correlates with the pilot-scale systems where often meshes [30], and wool, [29] are used to create a low-cost, high surface area cathode.
Amongst the non-platinum metals, nickel also exhibits good corrosion resistance and HER activity [73]. Nickel and stainless steel cathodes can quite easily be interchangeable when they come in similar configurations; however, nickel mesh has been shown to outperform stainless steel mesh, increasing CH4 production by 1.42 times compared to AD [31]. Nickel is also more durable than stainless steel. Durability is an important factor for an economically viable electrode. Hydrogenotrophic methanogens contribute to the improved performance, indicating that the strong HER activity of nickel compared to the other material improved its performance [72]. To maximise the efficiency of cathodes, HER activity needs to be a primary focus of research. Currently, stainless steel is shown through pilot research to be the best suitable cathode material for scaleup due to its availability, cost and machinability. A pilot-scale comparative study using nickel and stainless steel cathodes would be prudent to determine whether the performance of nickel can justify the higher cost.
2.5. Systems Architecture
Reactor design is one of the most crucial aspects of scaling up MECs [19]. The optimisation of reactor design can maximise energy efficiency and output by reducing internal resistance and increase substrate mixing to maximise efficiency. The existence of a membrane separating the anode and the cathode compartments largely dictates the architecture of the system. Dual-chamber MECs are favourable for H2 production as the membrane reduces hydrogen losses to methanogenic microorganisms [19,75]. Over 95% H2 purity has been reported when a membrane was used to separate the anode and the cathode chambers [39] whereas, when a single chamber was used, 0% H2 and 86% CH4 was produced [30]. A successful membrane material must allow the transfer of H+ ions from the anode to the cathode. A variety of membranes have been tested including proton-exchange membranes [76], cation exchange bipolar membranes [77,78], anion-exchange membranes [76], charge mosaic membranes [79,80] and microporous membranes [28,32,33]. Using a dual-chamber reactor separated by a membrane can create a pH gradient across the membrane leading to potential losses due to the ions transferring from one chamber to another [81]. Continuous flow systems can continually increase the pH gradient; however, continually changing the catholyte can equalise the system [82]. Another approach to reduce the pH gradient is by flowing CO2 through the cathode chamber, reducing the pH and improving the system performance [83]. However, recirculated CO2 will then mix with the H2 gas and increase system complexity. Overcoming pH gradients is important in increasing system performance and the problem can be avoided by removing the membrane entirely. Membrane separated systems suffer from reduced power densities and lower coulombic efficiencies [75].
Removing membranes to have a single chamber system increases the simplicity of the system design and maintenance. Internal resistance is lowered by removing the membrane, allowing the easier transfer of H+ ions from the anode to the cathode. However, as discussed previously, removing the membrane will reduce H2 as it is consumed by microorganisms. Membrane-less systems are likely to produce CH4 through hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis and will act as MEC-ADs. Either low cost membranes or membrane-less operation are required to reduce the system cost, which is prohibitive to commercialisation [19]. Going forward, membrane-less systems will reduce operational challenges of pH gradients, membrane fouling and catholyte replenishment. From the pilot-studies explored in this research, only one was membrane-less which yielded the highest energy production. The 1000 L system produced 11.31 MJ/day using graphite fibre brush anodes and stainless steel mesh cathodes at an applied voltage of Vapp = 0.9 V [30]. Further research and demonstration of membrane-less pilot systems should be explored as they show promise as a route to industrial adoption.
The system architecture also includes the size and placement of the electrodes. Rivera et al. found that increasing the size of stainless steel mesh cathodes from 71 cm2 to 142 cm2 increased H2 production by 9%, but when normalised to the surface area, the larger cathode had a H2 production rate (HPR) of 78% compared to the smaller cathodes [84]. This highlights the fact that the electrochemical limitations of increased resistances due to electrode size have implications when scaling up systems. The electrode placement also needs to be taken into consideration, and situating electrodes close together can reduce the internal resistance within the cell, reducing ohmic losses [85]. In membrane-less systems, close electrode spacing can increase hydrogen losses through hydrogenotrophic methanogenic activity. In other studies, decreasing the electrode distance from 4 cm to 1 cm increased coulombic efficiency by 18.2% at an applied voltage of Vapp = 1.0 V [84]. Electrode spacing does play an important role; however, the anode biofilm quality is more significant in MEC performance [86]. Combining several carbon felt layers to increase the anode volume increased the HPR and current in MECs, and using a stainless steel cathode on both sides of the anode saw further increases in HPR; however, the dual cathode leads to higher hydrogenotrophic activity, increasing methane percentages [87]. Further research around the electrode placement in membrane-less systems should be explored to further increase system coulombic efficiency and HPR.
Sludge build-up and extraction is another factor to consider when evaluating system architecture. Carlotta-Jones et al. found that sludge build-up in reactors reduced the COD reduction, suggesting that future designs should consider either sludge recirculation or inline extraction to justify this technology for industrial use [61]. Within wastewater treatment, the solid retention time (SRT) is an important parameter in the system design and operational performance. Simulations into oxidation ponds found that increasing the SRT generated cost savings from the increase in operational performance [88]. Research into SRT is an area that should be explored for optimising the scale-up of MECs, as it is an area of limited research within the field. The end of life of MECs is also important from a cost and environmental perspective. Aiken et al. found that the recovery of materials at the end of life had the largest effect on the Net Present Value (NPV) and systems should be designed to incorporate reusability [27]. An area researcher should consider is the ease of disassembly of the electrodes at their end of life to reduce costs.
The operational mode of the reactors largely affects the performance of the MEC and is considered one of the most important factors [46]. MECs are either operated in batch, continuously or batch with recirculation. When operated in batch the reactor is fed and left for a set amount of time, whereas for continuous operation the reactor is continuously fed; to compare the two modes the HRT has to remain equal. Arvin et al., found that the COD removal was significantly better when a reactor was operated in batch, compared to continuously, when treating petroleum wastewater [46]. This indicates that when operated in batch mode the electro-active bacteria are able to oxidise more substrate, leading to improved breakdown of organics [46]. However, in terms of methane production, this study found that this was 1.6 times higher when the reactor was operated in continuous mode compared to batch mode [46]. This highlights that that the operational mode has a large impact on the performance of the reactor and should therefore be decided based on the desired outcome of the system. Furthermore, the operational mode can also dictate the plant configuration. If operating in batch a larger footprint may be required as a holding tank would be needed to feed from. This may act as a significant barrier to adoption if space is a constraint.
3. Evaluation of the Barriers to Commercialisation of MECs for Wastewater Treatment
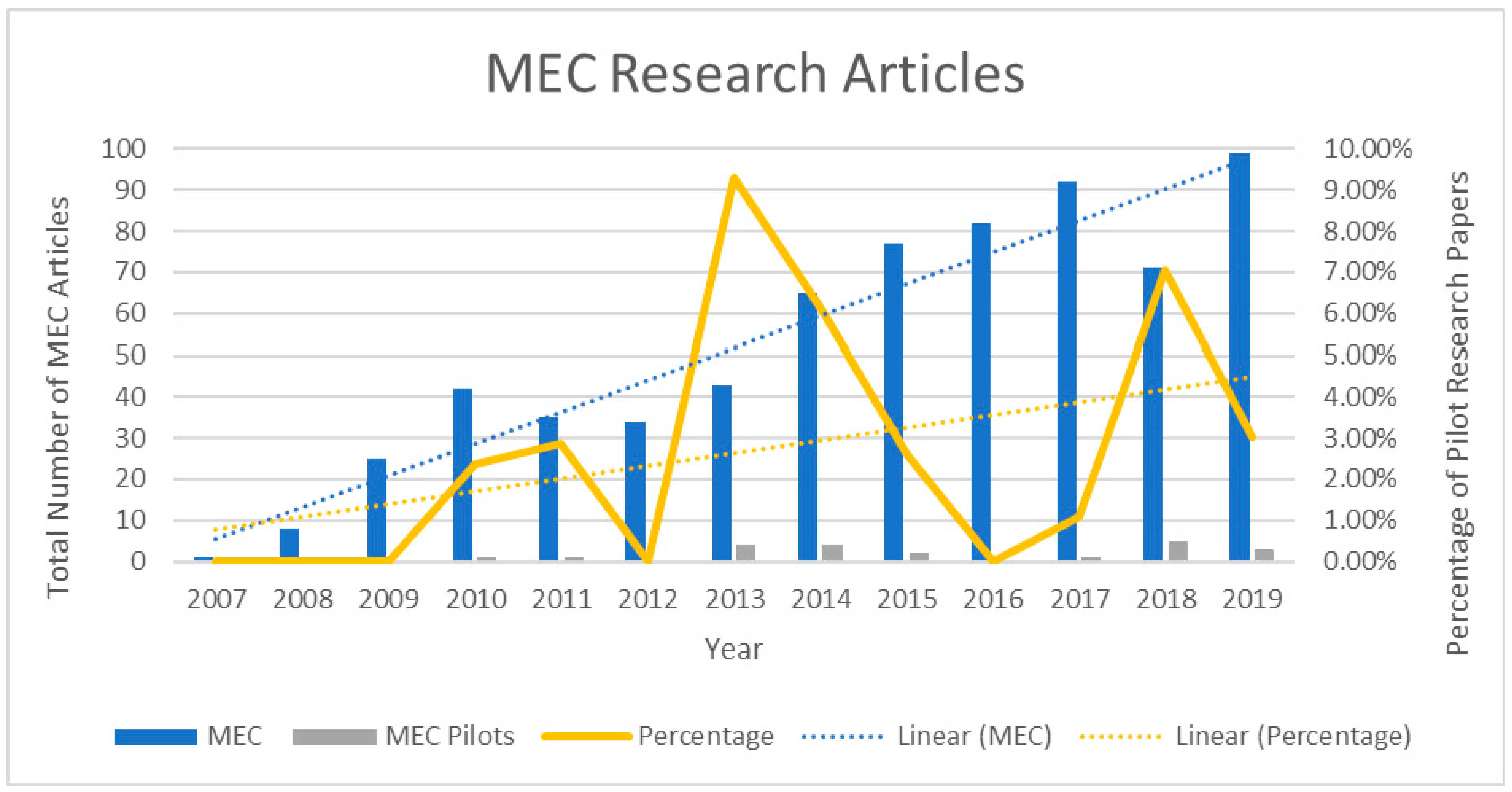
A significant barrier to adoption of MEC wastewater treatment systems is the lack of understanding of the performance of systems on a large scale. There is a very limited number of studies at large benchtop (10–100 L) and pilot-scales (>100 L) present in the literature. As shown in Figure 4, there has been a steady increase in published papers discussing MECs for wastewater treatment since 2007; however, there is a notable disparity between the amount of research at lab-scale and pilot-scale. This disparity means that issues regarding scaling and its effects are generally unknown and have often been extrapolated.
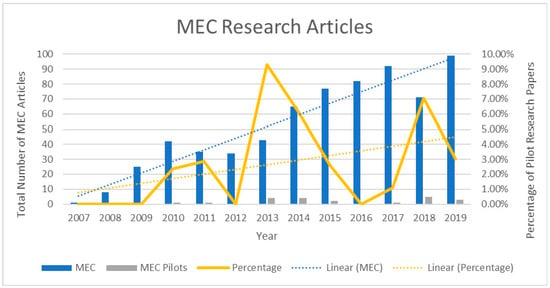
Figure 4.
Representation of the number of previous studies conducted investigating the use of MECs for wastewater treatment at lab-scale (blue) and pilot-scale (yellow). For the number of articles for MECs a Google Scholar Search was carried out to include (allintitle: “Microbial Electrolysis”). For MEC pilot-scale, a second Google Scholar was used (allintitle: Scaleup OR Scale-up OR Scaling OR Pilot “Microbial Electrolysis”).
In general, smaller systems generate higher energy output per volume when normalised compared to larger pilot systems. For urban wastewater the benchtop study generated a normalised net energy production of 25.96 kWh/m3/day, [61] whereas a pilot-scale system generated a normalised net energy production of 0.11 kWh/m3/day [53], indicating that energy production cannot be accurately scaled and that there is a reduction in efficiency when size is increased. The net energy production of a 1000 L pilot-scale system was calculated to be 2.11 kWh/m3/day for winery wastewater with a cathodic surface area of 18.1 m2/m3 [30]. This data shows that there is a reduction in methane production in proportion to the size of the reactor indicating that there is still a lot to learn about scaling up benchtop systems towards pilot and then industrial scale. One barrier to scale-up is the difficulty of accurately comparing the different setups in the research. The reactor size is only one parameter and does not give a true representation of the system scalability. Including details in the research such as organic loading rate and the electrode surface area to reactor volume ratio can help in providing a more comparative context between studies.
3.1. Economic and Cost Analysis
Critical to the progression of a technology from the laboratory to the field is validation that it is cost effective on a large scale and has efficiency comparable or better than other solutions on the market. A Techno-Economic Analysis (TEA) is essential to advance a technology for commercial use. The economic analysis of energy technologies includes a Life-Cycle Cost Analysis (LCCA), to allow the identification and evaluation of operational and capital expenditure (OPEX and CAPEX). Output results include monetary service values (revenue streams), Levelised Cost of Energy targets (expressed as £/kWh, £/m2 and £/kWh/cycle), including indications of where cost can be reduced through operational optimisation of services and collocation synergy (with renewables and energy storage solutions), as well as indications of Net Present Value (NPV) and Return of Investment (ROI). The LCCA assessment should be performed in parallel to the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), making the same assumptions, to evaluate the environmental impact. Using these calculations will help understand future costs, implementation strategies, and risks for MECs. It is also important to compare new technologies like MECs and MEC-ADs with existing wastewater treatment technologies such as AD and activated sludge treatment to evaluate the impact of MECs.
CAPEX refers to the cost of implementation and OPEX refers to the operational cost during operation. Solutions that are cheap to implement have a low CAPEX but may be inefficient and require more maintenance and, therefore, have a higher OPEX. Therefore, it is important to take both the CAPEX and OPEX into consideration when evaluating the full LCCA of new technologies. Furthermore, in a technology like MEC-AD for wastewater treatment where energy is produced, a high CAPEX can be justified when the return on investment from the energy production is considered.
In general, activated sludge wastewater treatment is energy intensive, requiring approximately ~1 kWh to oxidise 1 kg of COD; therefore, treating 1 m3 of wastewater would require ~0.5 kWh (30 kWh per capita per year) [89]. In the current UK market 1 kWh of electricity costs £0.144 therefore, the electricity cost of treating 1 m3 of urban wastewater is approximately £0.072. Activated sludge treatment generates 0.4 kg of sludge per 1 kg of COD treated, resulting in further processing which is commonly AD to recover a portion of the energy [89]. MECs on the other hand have the potential to reduce COD and generate energy. Using MECs to reduce the COD of wastewater more efficiently than activated sludge treatment is an attractive proposition for water utilities to save energy and reduce carbon emissions. Alternatively, MECs could be used to treat the sludge independently or integrated into ADs. However, MECs currently require large CAPEX to implement and are approximately 248 times more expensive than activated sludge systems [27]. The high costs are likely to be a significant barrier for many global utility companies.
Escarpa et al. developed three case studies to assess the economic costs of integrating MEC systems into a wastewater utility to identify the purchase price for the MEC/m3 [79]. In scenarios 2 and 3 the MEC is integrated into an existing wastewater treatment plant as a step between a grit chamber and an aerobic biological treatment chamber [79]. Scenario 2 represents a modest system whereas Scenario 3 represents an optimised set-up. In both cases the MEC was configured to produce hydrogen and have been shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Estimation of Microbial Electrolysis Cell (MEC_ costs integrated into wastewater treatment Parameters—Table adapted from [79].
The research assesses an individual cassette MEC design which would require a purchase cost of between £396—£1,149 *1 per m3 [79]. Compared to current pilot-system costs, MECs would require a price reduction. The construction cost of the Cotterill et al. pilot-system was £1308/m3 [63] and for that of Heidrich et al. this was £2344/m3 [90]. With improved manufacturing and economies of scale, MECs are likely to reach the desired cost. The study found that the price of hydrogen was the most significant influence in economic viability [79].
Aiken et al. built on previous work by Escarpa et al. by simulating seven scenarios using real-world conditions, pilot data and varying operational conditions [27]. The baseline cost of the MEC system was £2344/m3 [90] and the MEC was compared to activated sludge. The current MEC CAPEX is double that of activated sludge; however, the energy demand was 10 times less [27]. With MECs’ ability to generate bioenergy, they have the potential to be energy neutral or energy positive, whereas activated sludge is the most energy-intensive part of current wastewater treatment processes [29]. Overall, the costs of MECs need to reduce by 84% to £375/m3, which is in the lower range of Scenario 2 given by Escapa et al. [27,79]. Aiken et al. found that the materials represented the highest cost of MECs [27]. Going forward, researchers should focus on cost reduction to make MECs cost affective compared to activated sludge or alternative solutions. One approach is by using readily available materials, and another is assessing if the system can be easily manufactured at scale.
Currently, only a few economic studies on MECs are presented, which are aimed towards urban wastewater treatment and focus on hydrogen production. Further economic assessments of MECs’ treatment of different waste streams may provide further insights into the economic viability of industrial applications. MEC-ADs have also shown technical improvements over standard AD systems [17]. Techno-economic assessments comparing AD to MEC-AD could also demonstrate further insights into new commercial applications. Creating a standardised TEA and life cycle assessment is crucial to allow comparative and reproducible analysis that can guide researchers, investors and policymakers [80]. More information is required for a detailed examination of the technology, the capital investment required, and market conditions to assess the suitability of MECs for widescale use.
3.2. Scale-up Strategies
Despite the clear potential of MECs and MEC-AD for wastewater treatment, the practical implications of its scale-up remain uncertain [63]. Scale-up of MECs can be approached by multiple avenues. Large tanks can be built to increase treatment capacity with many small modules stacked in a cassette style to scale-up reactor size or alternatively, smaller vessels can be connected in series.
Cusick et al. tested pilot-scale MEC fed winery wastewater using multiple, stacked modules and found that there was equal performance across all 24 modules (a total of 144 electrode pairs in a 1000 L reactor) that was comparable to the small-scale lab test [30]. This highlights a benefit of a modular approach in terms of scale-up performance. It was found that poor electrical connection between modules resulted in appreciable ohmic losses, resulting in different current densities among modules, highlighting the need to use high quality connections between modules [30]. Furthermore, this approach can be more costly than using large tanks as more materials are required to produce the different modules, increasing the CAPEX of the system and acting as a barrier to commercialisation.
When evaluating the effect of scaling, Coterill et al. used cassette style electrodes [63]. The study found that when the scale of the electrodes was increased 16-fold, the start-up time was not affected, which has significant impact in the implementation of MECs [63]. It was found that current density in the scaled-up cassette reactor compared to the small scale control, but hydrogen gas production per litre remained the same. Hydrogen produced per electrode surface area was four times larger in the small MEC (2 L m2 of anode) than in the large MEC (0.5 L m2 of anode). Overall, scale up in this manner did not seem to be detrimental to performance, but these findings demonstrate that further understanding is needed when scaling up to real-world applications as the effects of scale up are not well understood [63]. Forneo et al. identified that when considering a stacked method of scale up of hydrogen producing MECs, the separation membrane between anode and cathode chambers acts as a significant barrier [91]. The study found that high internal resistances within the scaled-up cell are caused by slow movement of electrons over the membrane [91]. Furthermore, as membranes are expensive, having many membranes could make the system very expensive, acting as a significant barrier to commercialisation [91]. This indicates that membraneless systems may be more easily scalable. The method of connecting smaller cells in series is comparably less well documented; many small vessels arranged in series as opposed to one larger tank means that the system can take advantage of improved mixing, solid retention, reduced ohmic losses and improved microbial consortium stratification through the treatment process [92]. Arranging MEC vessels in this way allows a modular approach to scale up, leading to a more flexible and expandible water treatment system. In traditional wastewater treatment systems, large, permanent treatment vessels are often limited in treatment capacity. Arranging reactor vessels in series allows settling of solids throughout the system, improving solid retention time and creating microenvironments within the system in response to the level of organics found [92]. Tanks at the beginning of the series will typically have a higher concentration of larger, undigested organics than tanks towards the end of the series. Microbial communities develop in response to these distinct conditions, as well as to varying dissolved oxygen, pH, volatile solids, and volatile fatty acids. It has been shown that this improves treatment efficiency by allowing an optimal microbial community at each stage in treatment [29,93,94].
3.3. Analysis of Hydrogen or Methane Production and Its Implications for Industrial Implementation
The use of hydrogen as an energy carrier for global use is becoming more economically viable, with the hydrogen market maturing year on year. The need for integrated energy storage is increasing along with the demand to store renewable energy [5]. Most MEC research generally focuses on recovering hydrogen rather than methane. Pure hydrogen can be used as a valuable resource for fuel and manufacturing other chemicals. Hydrogen has a higher energy content than methane, encouraging the development of hydrogen production over methane [95] the high gross heating value of hydrogen is 39.4 kWh/kg whereas for methane it is 13.8–15.4 kWh/kg. However, hydrogen production adds complexity to the system design and operation. MECs for hydrogen production require a dual-chamber reactor with a membrane to stop hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis at the cathode [88] further increasing the cost and complexity of the system. As discussed previously, the material cost makes up the most considerable portion of the CAPEX. In real wastewaters, there is a complex mix of microbes present, making the cathode vulnerable to biofouling which could result in periodic replacement, increasing costs [27].
Furthermore, generating pure hydrogen is rarely achieved, with only one study producing 100% purity but at low volumes (0.015 m3/m3 reactor/day) [90]. Impure hydrogen requires post-processing to remove impurities adding to the process costs. Moreover, hydrogen also requires sophisticated storage facilities and processing equipment. Hydrogen is, however, 1.5–4.5 times more valuable if it is required for the manufacture of other chemicals. In the case of onsite energy generation, the value of both methane and hydrogen will come down to the Levelised Cost of Energy (LCOE) and Levelised Cost of Heat (LCOH) that is generated and utilised onsite. Cusick et al. found that an MEC was able to generate hydrogen at £3470/t-H2 *2 (winery wastewater) and £2310/t-H2 *2 (urban wastewater) [96], which is significantly higher than when produced from natural gas (£462–1386/t_H2 *2). The high cost of MEC produced hydrogen indicates that it is unlikely to compete with H2 derived from natural gas unless other factors including the costs of waste treatment or carbon tax are included.
Taking this into account, in terms of energy production, methane offers an attractive alternative. There are extensive infrastructure and equipment to store and convert methane into electrical and thermal energy. Roland et al. developed a pilot-scale system configured to produce methane and resulting in a large net energy production of 2.11 kWh/m3/day [30]. Comparatively, the normalised net energy production reported for a hydrogen producing MEC is 76.2 kWh/m3/day at 98% purity [39]. The higher energy output of the hydrogen producing MEC indicates it may be possible to produce more energy when producing hydrogen. However, notably, this high hydrogen production was for a 16 L reactor, and the performance has not been demonstrated on a large scale.
Gas storage infrastructure also plays a significant role in the commercial viability of using MECs for energy generation. Reducing the storage complexity, cost and parasitic energy requirements are key for the future of this technology. It has been proposed that MECs can be coupled with renewable power sources [97,98]. The renewable energy will power the MEC, generating gas that can act as energy storage. Methane has a higher energy density than hydrogen at atmospheric pressure. The higher energy density and larger molecule size of methane make it a more viable option for non-compressed energy storage. However, hydrogen is likely to play a significant role in renewable energy storage in the future [99]. AD produces low-grade biogas that is not easily stored, with the energy input of storage equating to 10% of the energy value [100]. MEC-ADs produce higher quality biogas with CH4 concentrations reaching 86 ± 6% [30], highlighting the advantage of MEC-ADs over AD systems in terms of energy storage potential. MEC-ADs configured to produce methane have the potential to compete with AD technology; however, this is relatively unexplored on a large scale in terms of cost. Future work directly comparing AD to MEC-AD for wastewater treatment for methane production would aid the industrial adoption of this technology.
Unlike the production of electricity from hydrogen, there is a range of technologies that can utilise biogas directly including reciprocating engines, microturbines, fuel cells, gas turbines, steam turbines and combined cycle systems. Biogas can also be upgraded to biomethane for injection back into the grid [100]. Ultimately, the maturity of hydrogen storage and conversion technology is less developed compared to methane. Further assessment in the total system cost comparing MEC-AD to MECs will provide insights into the economic viability of the two systems.
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Despite growing research regarding using MECs and MEC-ADs for wastewater treatment, there has not yet been a meaningful adoption within industry. This review aimed at identifying the barriers hindering the progression of MEC use from lab-scale investigations to pilot-scale systems and beyond to inform future research aims. The study identified three main parameters that need to be addressed to make MECs both efficient and cost-effective to enable adoption by industry: the feedstock, the electrode material, and the system architecture.
In terms of electrode materials, untreated carbon anodes and stainless-steel cathodes are currently the most viable option and are used consistently in research. A cost-benefit analysis needs to be carried out on anode and cathode materials that also takes into consideration the availability of the material and its life span. Corrosion resistance is important to the longevity of the electrode, which will directly affect the OPEX. Electrodes should ideally last many years to reduce downtime for maintenance and operational cost for new components. There is little research on longevity beyond a year in the pilots and this will be an area of interest for the industry in determining the commercial viability of MECs for wastewater treatment.
The research also indicates a gap regarding scaling the size and morphology of electrodes. Scalability has considerable implications when discussing the commercialisation of these technologies. Current research shows that electrode materials and designs that are effective in the lab may not show the same performance output when scaled up, with pilot systems showing a lower performance.
When working at a pilot-scale, the cost consideration of electrode materials becomes more important than when working at a lab-scale. Construction cost considerations are vital when considering electrode materials for commercial MEC systems, with CAPEX being one of the crucial factors for adoption and viability. The current pilot-scale research indicates that construction costs are high and will need to be reduced, in some cases considerably.
One of the main factors indicated is the cost-effectiveness of a system, as high manufacturing costs need to be considered. There are many ways to improve system performance; however, this can lead to a considerable increase in complexity and cost. If this technology is going to be adopted for wastewater treatment on a large scale, researchers need to optimise the system using readily available materials and manufacturing techniques, with cost considered at all stages of development.
Assessing the parameters of MECs across studies is important. Research papers need to be more transparent and record a full data set. As shown in the supporting material condensed into Table 1, there is a lack of consistency in data reporting. The gaps in information make it challenging to compare studies and data cohesively, preventing the determination of which parameters improve performance. Researchers should as a minimum record feedstock (type and organics content), inoculum source, system design (batch/flow, architecture, scale, electrode materials and surface area, cost), operational factors (HRT, duration, start-up period, applied voltage, temperature) and outputs (gas production and composition, energy production, cathodic coulombic efficiency, COD input, COD removal (%) and COD output).
Comparing MEC systems to alternative wastewater treatment systems, both in terms of cost and efficiency, is imperative in getting the industry to adopt the new technology. When comparing MECs to AD, further research regarding the start-up period for COD reduction should be explored. The start-up is crucial as it can affect the suitability of the technology; long start-up times may not be applicable in some commercial applications where waste needs to be treated instantly to avoid pollution. Going forward, future research regarding the start-up period for organic removal, along with effective start-up procedures, will increase the attractiveness of the technology.
There are several factors that determine whether hydrogen or methane production is favoured, including the scale and location of the site. Currently, due to the maturity of methane and biogas infrastructure, electro-methanogenesis may be the most feasible initial route to market. Methane infrastructure is mature, and methane can be easily stored. Therefore, bio-electrochemically generated methane can be directly connected to existing gas infrastructure for use in cooking and transportation. However, the hydrogen economy is predicted to become a major part of decarbonising our energy network with extensive research being conducted worldwide to make hydrogen a viable fuel. However, practically there are great challenges in both hydrogen storage and end use. Therefore, methane production can act as a stepping-stone for this technology while the hydrogen production market matures. A technical-economic analysis comparing both systems for producing hydrogen and methane will provide a more precise route to commercialisation that can direct future research.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/13/4/445/s1, Table S1: Collation of data from previous studies of using microbical electrolysis cells to treat different organic influents.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council EP/P504244/1 United Kingdom for the funded Doctoral Training Program. The authors would also like to thank London South Bank University and the European Regional Development Fund for their Low Carbon London Programme. Without their support the research would not have been possible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| BES | Bioelectrochemical System |
| MEC | Microbial Electrolysis Cell |
| MEC-AD | Microbial Electrolysis Cell Anaerobic Digester |
| MMEC | Methanogenic Microbial Electrolysis Cell |
| EMR | Electro-methanogenic Reactor |
| AD | Anaerobic Digestion |
| OLR | Organic Loading Rate |
| CF | Carbon Fibre |
| TRL | Technology Readiness Level |
| EAB | Electro-active Bacteria |
| NPV | Net Present Value |
| SRT | Solid Retention Time |
| CAPEX | Capital Expenditure |
| OPEX | Operational Expenditure |
References
- OECD. Water. In OECD Environmental Outlook to 2050; OECD: Paris, France, 2012; Chapter 5; pp. 207–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWAP (United Nations World Water Assessment Programme). The United Nations World Water Development Report 2017. Wastewater: The Untapped Resource; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2017.
- Zhang, Y.; Merrill, M.D.; Logan, B.E. The use and optimization of stainless steel mesh cathodes in microbial electrolysis cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 2020–12028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, R.; San-Martín, M.I.; Escapa, A.; Morán, A. Domestic wastewater treatment in parallel with methane production in a microbial electrolysis cell. Renew. Energy 2016, 93, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandev, M.; Lucchese, P.; Mansilla, C.; Duigou, A.L.; Abrashev, B.; Vladikova, D. Hydrogen Economy: The future for a sustainable and green society. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 49, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, C.M.; Katuri, K.P.; Hari, A.R.; Chen, W.; Lai, Z.; Logan, B.E.; Amy, G.L.; Saikaly, P.E. Graphene-Coated Hollow Fiber Membrane as the Cathode in Anaerobic Electrochemical Membrane Bioreactors—Effect of Configuration and Applied Voltage on Performance and Membrane Fouling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4439–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Baserba, M.; Vinardell, S.; Molinos-Senante, M.; Rosso, D.; Poch, M. The Economics of Wastewater Treatment Decentralization: A Techno-economic Evaluation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8965–8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. The World ’s Cities in 2018; World’s Cities 2018—Data Booklet; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Starkl, M.; Brunner, N.; Feil, M.; Hauser, A. Ensuring Sustainability of Non-Networked Sanitation Technologies: An Approach to Standardization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6411–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.; Park, Y.H.; In, S.-I. Improved Microbial Electrolysis Cell Hydrogen Production by Hybridization with a TiO2 Nanotube Array Photoanode. Energies 2018, 11, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escapa, A.; Mateos, R.; Martínez, E.J.; Blanes, J. Microbial electrolysis cells: An emerging technology for wastewatertreatment and energy recovery. From laboratory to pilot plantand beyond. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 55, 942–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eerten-Jansen, M.C.A.A.; Ter Heijne, A.; Buisman, C.J.N.; Hamelers, H.V.M. Microbial electrolysis cells for production of methane from CO2: Long-term performance and perspectives. Int. J. Energy Res. 2011, 36, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awe, O.W.; Zhao, Y.; Nzihou, A.; Minh, D.P.; Lyczko, N. A Review of Biogas Utilisation, Purification and Upgrading Technologies. Waste Biomass-Valoriz. 2017, 8, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitching, M.; Butler, R.; Marsili, E. Microbial bioelectrosynthesis of hydrogen: Current challenges and scale-up. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2017, 96, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, D.; Singh, A.; Van Bogaert, G.; Olsen, S.I.; Nigam, P.S.; Diels, L.; Vanbroekhoven, K. Bioelectrochemical systems (BES) for sustainable energy production and product recovery from organic wastes and industrial wastewaters. R. Soc. Chem. Adv. 2011, 2, 1248–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Sleutels, T.H.; Ter Heijne, A.; Buisman, C.J.; Hamelers, H.V. Bioelectrochemical Systems: An Outlook for Practical Applications. ChemSusChem 2012, 6, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Leng, X.; Zhao, S.; Ji, J.; Zhou, T.; Khan, A.; Kakde, A.; Liu, P.; Li, X. A review on the applications of microbial electrolysis cells in anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 255, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegert, M.; Yates, M.D.; Spormann, A.M.; Logan, B.E. Methanobacterium Dominates Biocathodic Archaeal Communities in Methanogenic Microbial Electrolysis Cells. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadier, A.; Simayi, Y.; Abdeshahian, P.; Azman, N.F.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Kalil, M.S. A comprehensive review of microbial electrolysiscells (MEC) reactor designs and configurations for sustainable hydrogen gas production. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco-Gómez, R.; Batlle-Vilanova, P.; Villano, M.; Balaguer, M.D.; Colprim, J.; Puig, S. On the Edge of Research and Technological Application: A Critical Review of Electromethanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villano, M.; Aulenta, F.; Ciucci, C.; Ferri, T.; Giuliano, A.; Majone, M. Bioelectrochemical reduction of CO2 to CH4 via direct and indirect extracellular electron transfer by a hydrogenophilic methanogenic culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3085–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, K.P.; Hensley, S.A.; Franks, A.E.; Summers, Z.M.; Ou, J.; Woodard, T.L.; Snoeyenbos-West, O.L.; Lovley, D.R. Electrosynthesis of Organic Compounds from Carbon Dioxide Is Catalyzed by a Diversity of Acetogenic Microorganisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2882–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelabhotla, A.B.T.; Dinamarca, C. Bioelectrochemical CO2 Reduction to Methane: MES Integration in Biogas Production Processes. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Li, Y. Recent advances in heterogeneous electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14942–14962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheb-Alam, S.; Singh, A.; Hermansson, M.; Persson, F.; Schnürer, A.; Wilén, B.M.; Modin, O. Effect of Start-Up Strategies and Electrode Materials on Carbon Dioxide Reduction on Biocathodes. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Nie, H.; Bain, T.S.; Lu, H.; Cui, M.; Snoeyenbos-West, O.L.; Franks, A.E.; Nevin, K.P.; Russell, T.P.; Lovley, D.R. Improved cathode materials for microbial electrosynthesis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 6, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, D.C.; Curtis, T.P.; Heidrich, E.S. Avenues to the financial viability of microbial electrolysis cells [MEC] for domestic wastewater treatment and hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 2426–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Wastewater Treatment and Discharge. In 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 5, pp. 6.1–6.28. [Google Scholar]
- Heidrich, E.S.; Edwards, S.R.; Dolfing, J.; Cotterill, S.E.; Curtis, T.P. Performance of a pilot scale microbial electrolysis cell fed on domestic wastewater at ambient temperatures for a 12 month period. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 173, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusick, R.D.; Bryan, B.; Parker, D.S.; Merrill, M.D.; Mehanna, M.; Kiely, P.D.; Liu, G.; Logan, B.E. Performance of a pilot-scale continuous flow microbial electrolysis cell fed winery wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, T.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W.; Cui, M.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, A. Cathode material as an influencing factor on beer wastewater treatment and methane production in a novel integrated upflow microbial electrolysis cell (Upflow-MEC). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 2189–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.-Y.; Kim, H.W.; Lim, K.-H.; Shin, H.-S. Effects of organic loading rates on the continuous electricity generation from fermented wastewater using a single-chamber microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, S33–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rago, L.; Baeza, J.A.; Guisasola, A. Bioelectrochemical hydrogen production with cheese whey as sole substrate. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 92, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.J.; Ismail, Z.Z. Slaughterhouse wastewater biotreatment associated with bioelectricity generation and nitrogen recovery in hybrid system of microbial fuel cell with aerobic and anoxic bioreactors. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 125, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christwardana, M.; Prabowo, A.K.; Tiarasukma, A.P.; Ariyanti, D. Microbial Fuel Cells for Simultaneous Electricity Generation and Organic Degradation from Slaughterhouse Wastewater. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2016, 5, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, T.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Mitra, A.; Mukherjee, C. Enhanced Power Generation in Microbial Fuel Cell Using MnO2-Catalyzed Cathode Treating Fish Market Wastewater; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Taiganides, P.E. Pig Waste Management & Recycling—The Singapore Experience; International Development Research Centre: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, R.C.; Regan, J.M.; Oh, S.-E.; Zuo, Y.; Logan, B.E. Hydrogen and methane production from swine wastewater using microbial electrolysis cells. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1480–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San-Martín, M.I.; Sotres, A.; Alonso, R.M.; Díaz-Marcos, J.; Morán, A.; Escapa-González, A. Assessing anodic microbial populations and membrane ageing in a pilot microbial electrolysis cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 17304–17315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.B.; Freitas, A.V.; Leitão, R.C.; Pinto, G.A.; Santaella, S.T. Anaerobic digestion of crude glycerol: A review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2012, 1, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chookaew, T.; Prasertsan, P.; Ren, Z.J. Two-stage conversion of crude glycerol to energy using dark fermentation linked with microbial fuel cell or microbial electrolysis cell. New Biotechnol. 2014, 31, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selembo, P.A.; Perez, J.M.; Lloyd, W.A.; Logan, B.E. High hydrogen production from glycerol or glucose by electrohydrogenesis using microbial electrolysis cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 5373–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escapa-González, A.; Manuel, M.-F.; Morán, A.; Gómez, X.; Guiot, S.R.; Tartakovsky, B. Hydrogen Production from Glycerol in a Membraneless Microbial Electrolysis Cell. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 4612–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, R.; Escapa-González, A.; Cara, J.; Carracedo, B.; Gómez, X. A two-stage process for hydrogen production from cheese whey: Integration of dark fermentation and biocatalyzed electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montpart, N.; Rago, L.; Baeza, J.A.; Guisasola, A. Hydrogen production in single chamber microbial electrolysis cells with different complex substrates. Water Res. 2015, 68, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvin, A.; Hosseini, M.; Amin, M.-M.; Najafpour-Darzi, G.; Ghasemi, Y. Efficient methane production from petrochemical wastewater in a single membrane-less microbial electrolysis cell: The effect of the operational parameters in batch and continuous mode on bioenergy recovery. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, T.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Tao, Y.; He, X.; Li, D.; Yan, Z. A new upgraded biogas production process: Coupling microbial electrolysis cell and anaerobic digestion in single-chamber, barrel-shape stainless steel reactor. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 45, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, P. Towards energy positive wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achinas, S.; Euverink, G.J.W. Effect of Combined Inoculation on Biogas Production from Hardly Degradable Material. Energies 2019, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.S.; Fontmorin, J.-M.; Izadi, P.; Daud, W.R.W.; Scott, K.; Yu, E.H. Impact of applied cell voltage on the performance of a microbial electrolysis cell fully catalysed by microorganisms. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 2557–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Freguia, S.; Dennis, P.G.; Chen, X.; Donose, B.C.; Keller, J.; Gooding, J.J.; Rabaey, K. Effects of Surface Charge and Hydrophobicity on Anodic Biofilm Formation, Community Composition, and Current Generation in Bioelectrochemical Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7563–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escapa-González, A.; San-Martín, M.; Mateos, R.; Morán, A. Scaling-up of membraneless microbial electrolysis cells (MECs) for domestic wastewater treatment: Bottlenecks and limitations. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 180, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, J.A.; Martínez-Miró, À.; Guerrero, J.; Ruiz, Y.; Guisasola, A. Bioelectrochemical hydrogen production from urban wastewater on a pilot scale. J. Power Sources 2017, 356, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Liu, H. Startup performance of microbial electrolysis cell assisted anaerobic digester (MEC-AD) with pre-acclimated activated carbon. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 5, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.S.; Yu, E.H.; Daud, W.R.W.; Kim, B.H.; Scott, K. Bioanode as a limiting factor to biocathode performance in microbial electrolysis cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, S.G.; Peixoto, L.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Ter Heijne, A.; Kuntke, P.; Alves, M.M.; Pereira, M.A. Influence of carbon anode properties on performance and microbiome of Microbial Electrolysis Cells operated on urine. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 267, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.P.; Pandit, S. Important Factors InfluencingMicrobial Fuel Cell Performance; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Cheng, C.; Thomas, A. Carbon-Based Microbial-Fuel-Cell Electrodes: From Conductive Supports to Active Catalysts. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1602547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Roca-Puigros, M.; Geppert, F.; Caizán-Juanarena, L.; Na Ayudthaya, S.P.; Buisman, C.; Ter Heijne, A. Granular Carbon-Based Electrodes as Cathodes in Methane-Producing Bioelectrochemical Systems. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Prévoteau, A.; Patil, S.A.; Rabaey, K. Engineering electrodes for microbial electrocatalysis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 149–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlotta-Jones, D.I.; Purdy, K.; Kirwan, K.; Stratford, J.; Coles, S.R. Improved hydrogen gas production in microbial electrolysis cells using inexpensive recycled carbon fibre fabrics. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 304, 122983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötschke, L.; Huber, P.; Schriever, S.; Rizzotto, V.; Gries, T.; Blank, L.M.; Rosenbaum, M.A. Rational Selection of Carbon Fiber Properties for High-Performance Textile Electrodes in Bioelectrochemical Systems. Front. Energy Res. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotterill, S.; Dolfing, J.; Jones, C.; Curtis, T.P.; Heidrich, E.S. Low Temperature Domestic Wastewater Treatment in a Microbial Electrolysis Cell with 1 m2Anodes: Towards System Scale-Up. Fuel Cells 2017, 17, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotterill, S.; Dolfing, J.; Curtis, T.P.; Heidrich, E.S. Community Assembly in Wastewater-Fed Pilot-Scale Microbial Electrolysis Cells. Front. Energy Res. 2018, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, C.M.; Babanova, S.; Artyushkova, K.; Cornejo, J.A.; Ista, L.K.; Bretschger, O.; Marsili, E.; Atanassov, P.; Schuler, A.J. Influence of anode surface chemistry on microbial fuel cell operation. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 106, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Yokoyama, H. Molybdenum anode: A novel electrode for enhanced power generation in microbial fuel cells, identified via extensive screening of metal electrodes. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocaznoi, D.; Calmet, A.; Etcheverry, L.; Erable, B.; Bergel, A. Stainless steel is a promising electrode material for anodes of microbial fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9645–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Donose, B.C.; Soeriyadi, A.H.; Prévoteau, A.; Patil, S.A.; Freguia, S.; Gooding, J.J.; Rabaey, K. Flame Oxidation of Stainless Steel Felt Enhances Anodic Biofilm Formation and Current Output in Bioelectrochemical Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7151–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Im, S.; Chung, J.W. Optimizing the operating temperature for microbial electrolysis cell treating sewage sludge. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 27784–27791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, Z.; Guo, Z.; Sangeetha, T.; Yang, C.; Gao, L.; Wang, A.; Liu, W. Microbial community development on different cathode metals in a bioelectrolysis enhanced methane production system. J. Power Sources 2019, 444, 227306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, C.; Arbizzani, C.; Erable, B.; Ieropoulos, I. Microbial fuel cells: From fundamentals to applications. A review. J. Power Sources 2017, 356, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegert, M.; Yates, M.D.; Call, D.F.; Zhu, X.; Spormann, A.; Logan, B.E. Comparison of Nonprecious Metal Cathode Materials for Methane Production by Electromethanogenesis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, A.; Vaszilcsin, N.; Brandl, W.; Duteanu, N. Kinetics of hydrogen evolution reaction on skeleton nickel and nickel–titanium electrodes obtained by thermal arc spraying technique. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 3258–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, A.; Yue, X. Energy recovery from tubular microbial electrolysis cell with stainless steel mesh as cathode. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokabian, B.; Gude, V.G. Role of membranes in bioelectrochemical systems. Membr. Water Treat. 2015, 6, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Grot, S.; Logan, B.E. Electrochemically Assisted Microbial Production of Hydrogen from Acetate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4317–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozendal, R.A.; Hamelers, H.V.; Euverink, G.J.; Metz, S.J.; Buisman, C.J. Principle and perspectives of hydrogen production through biocatalyzed electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2006, 31, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozendal, R.A.; Sleutels, T.H.J.A.; Hamelers, H.V.; Buisman, C.J.N. Effect of the type of ion exchange membrane on performance, ion transport, and pH in biocatalyzed electrolysis of wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escapa, A.; Gómez, X.; Tartakovsky, B.; Morán, A. Estimating microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) investment costs in wastewater treatment plants: Case study. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 18641–18653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.; Murthy, G.S. Techno-economic and life cycle assessments of anaerobic digestion—A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 101207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozendal, R.A.; Hamelers, H.V.; Molenkamp, R.J.; Buisman, C.J.N. Performance of single chamber biocatalyzed electrolysis with different types of ion exchange membranes. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premier, G.; Michie, I.; Boghani, H.C.; Fradler, K.; Kim, J. Reactor design and scale-up. In Microbial Electrochemical and Fuel Cells; Scott, K., Yu, E.H., Eds.; Wood House Publishing: Chippenham, UK, 2016; pp. 215–239. [Google Scholar]
- Ki, D.; Popat, S.C.; Torres, C.I. Reduced overpotentials in microbial electrolysis cells through improved design, operation, and electrochemical characterization. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, I.; Bakonyi, P.; Buitrón, G. H2 production in membraneless bioelectrochemical cells with optimized architecture: The effect of cathode surface area and electrode distance. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Ren, Z.J. Microbial electrolysis cells for waste biorefinery: A state of the art review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Logan, B.E. High hydrogen production rate of microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) with reduced electrode spacing. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 102, 3571–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Carrera, L.; Mehta, P.; Escapa-González, A.; Morán, A.; García, V.; Guiot, S.R.; Tartakovsky, B. Optimizing the electrode size and arrangement in a microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9593–9598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muoio, R.; Palli, L.; Ducci, I.; Coppini, E.; Bettazzi, E.; Daddi, D.; Fibbi, D.; Gori, R. Optimization of a large industrial wastewater treatment plant using a modeling approach: A case study. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaey, K.; Verstraete, W. Microbial fuel cells: Novel biotechnology for energy generation. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, E.S.; Dolfing, J.; Scott, K.; Edwards, S.R.; Jones, C.; Curtis, T.P. Production of hydrogen from domestic wastewater in a pilot-scale microbial electrolysis cell. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 97, 6979–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornero, J.J.; Rosenbaum, M.; Angenent, L.T. Electric Power Generation from Municipal, Food, and Animal Wastewaters Using Microbial Fuel Cells. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Kim, Y. Stacked multi-electrode design of microbial electrolysis cells for rapid and low-sludge treatment of municipal wastewater. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, C.; Zhu, G. Performance, process kinetics and functional microbial community of biocatalyzed electrolysis-assisted anaerobic baffled reactor treating carbohydrate-containing wastewater. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 41150–41162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Carrera, L.; Escapa, A.; Moreno, R.; Morán, A. Reduced energy consumption during low strength domestic wastewater treatment in a semi-pilot tubular microbial electrolysis cell. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 122, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katuri, K.P.; Ali, M.; Saikaly, P.E. The role of microbial electrolysis cell in urban wastewater treatment: Integration options, challenges, and prospects. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusick, R.D.; Kiely, P.D.; Logan, B.E. A monetary comparison of energy recovered from microbial fuel cells and microbial electrolysis cells fed winery or domestic wastewaters. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 8855–8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, K.-J.; Choi, M.-J.; Kim, K.-Y.; Ajayi, F.F.; Chang, I.-S.; Kim, I.S. A Solar-Powered Microbial Electrolysis Cell with a Platinum Catalyst-Free Cathode To Produce Hydrogen. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9525–9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.-L.; Li, X.-J.; Zang, G.-L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhou, Q. A solar assisted microbial electrolysis cell for hydrogen production driven by a microbial fuel cell. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82276–82281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.; Shabani, B. Where does Hydrogen Fit in a Sustainable Energy Economy? Procedia Eng. 2012, 49, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas-Oyanedel, J.R.; Schmidt, J.E. Increasing Profits in Food Waste Biorefinery—A Techno-Economic Analysis. Energies 2018, 11, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).