Medicinal Use of Testosterone and Related Steroids Revisited
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Available Testosterone Analogues
2.1. Analogues of Testosterone with Agonistic Activity
2.2. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs)
2.3. Testosterone and Nandrolone Prodrugs (Prohormones)
2.4. Testosterone Boosters
2.5. Antiandrogens
3. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTH | adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| AIDS | acquired immune deficiency syndrome |
| CYP17 | 17α-hydroxylase-17:20-lyase |
| DHEA | dehydroepiandrosterone |
| DHT | 5α-dihydrotestosterone |
| DMT | desoxymethyltestosterone |
| FSH | follicle-stimulating hormone |
| GnRH | gonadotropin-releasing hormone |
| HDL | high density lipoprotein |
| LDL | low density lipoprotein |
| LH | luteinizing hormone |
| mCRPC | metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer |
| mCSPC | metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer |
| PSA | prostate-specific antigen |
| SARM | selective androgen receptor modulator |
| SERM/SORM | selective (o)estrogen receptor modulator |
| SHBG | sex hormone-binding globulin |
| TRT | testosterone replacement therapy |
| T | testosterone |
| THG | tetrahydrogestrinone |
| WADA | World Anti-Doping Agency |
References
- Dewick, P.M. Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach, 3rd ed.; Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Bohl, C.E.; Dalton, J.T. Chemistry and structural biology of androgen receptor. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3352–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, M.D.; Belakovskiy, A.; McGrath, R.; Yarrow, J.F. Testosterone deficiency, weakness, and multimorbidity in men. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barceloux, D.G.; Palmer, R.B. Anabolic-androgenic steroids. Dis. Mon. 2013, 59, 226–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, A.B.; Evans, N.A. Anabolic androgenic steroids: A survey of 500 users. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ronde, W.; Smit, D.L. Anabolic androgenic steroid abuse in young males. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, R102–R111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, M.I.; Riche, D.M.; Koch, C.A. Transdermal testosterone replacement therapy in men. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2014, 8, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Efros, M.; Carrara, D.; Neijber, A. The efficacy, bioavailability and safety of a novel hydroalcoholic testosterone gel 2% in hypogonadal men: Results from phase ii open-label studies. Andrologia 2016, 48, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinsmore, W.W.; Wyllie, M.G. The long-term efficacy and safety of a testosterone mucoadhesive buccal tablet in testosterone-deficient men. BJU Int. 2012, 110, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemers, J.; van Rooij, K.; de Leede, L.; Frijlink, H.W.; Koppeschaar, H.P.F.; Olivier, B.; Tuiten, A. Single dose sublingual testosterone and oral sildenafil vs. a dual route/dual release fixed dose combination tablet: A pharmacokinetic comparison. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banks, W.A.; Morley, J.E.; Niehoff, M.L.; Mattern, C. Delivery of testosterone to the brain by intranasal administration: Comparison to intravenous testosterone. J. Drug Target. 2009, 17, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, F.; Caliber, M.; Doros, G.; Haider, K.S.; Haider, A. Long-term treatment with testosterone undecanoate injections in men with hypogonadism alleviates erectile dysfunction and reduces risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, prostate cancer, and mortality. Aging Male 2020, 23, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, R.A. Androgens in postmenopausal women: Production, possible role, and replacement options. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2001, 56, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruzicka, L.; Goldberg, M.W.; Rosenberg, H.R. Sexualhormone x. herstellung des 17-methyl-testosterons und anderer androsten- und androstanderivate. zusammenhänge zwischen chemischer konstitution und männlicher hormonwirkung. Helv. Chim. Acta 1935, 18, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschet, U.; Laschet, L.; Paarmann, H.F. Gonadotropin and steroid hormone excretion during treatment with 1-alpha-methyl-5-alpha-androstan-17-beta-ol-3-one (mesterolone). Arzneim.-ForschungDrug Res. 1966, 16, 469–471. [Google Scholar]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Vignozzi, L.; Maggi, M. Emerging medication for the treatment of male hypogonadism. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2012, 17, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihiko, S.; Shigeo, B. Stable isotope methodology in the pharmacokinetic studies of androgenic steroids in humans. Steroids 1990, 55, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicman, A.T. Pharmacology of anabolic steroids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 502–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasdon, S.C.; Fishman, W.H.; Dart, R.M.; Bonner, C.D.; Homburger, F. Methylandrostenediol in palliative treatment of breast cancer. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1952, 148, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homburger, F.; Kasdon, S.C.; Fishman, W.H. Methylandrostenediol: A non-virilizing derivative of testosterone in metastatic cancer of the breast. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1950, 74, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holma, P.K. Effects of an anabolic steroid (metandienone) on spermatogenesis. Contraception 1977, 15, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaria, S.; Wahlstrom, J.T.; Dobs, A.S. Anabolic-androgenic steroid therapy in the treatment of chronic diseases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5108–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, A.L. Long-term results of treatment with low-dose fluoxymesterone in constitutional delay of growth and puberty and in genetic short stature. Pediatrics 1993, 91, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ingle, J.N. Additive hormonal therapy in women with advanced breast cancer. Cancer 1984, 53, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, T.E.N.; Andal, Z.C.; Lantion-Ang, F.L. Fluoxymesterone-induced gynaecomastia in a patient with childhood aplastic anaemia. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2014207474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fürstenberger, C.; Vuorinen, A.; Da Cunha, T.; Kratschmar, D.V.; Saugy, M.; Schuster, D.; Odermatt, A. The anabolic androgenic steroid fluoxymesterone inhibits 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2-dependent glucocorticoid inactivation. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 126, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, M.B.; Helman, P.; Palmer, P. Hormonal therapy of breast cancer with special reference to masteril therapy. S. Afr. Med. J. 1975, 49, 2036–2040. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krug, K. Contribution to the pathophysiology of the aplastic anaemia and its treatment with metenolone enanthate. Z. Gesamte Inn. Med. 1980, 35, 809–812. [Google Scholar]
- Orr, R.; Fiatarone Singh, M. The anabolic androgenic steroid oxandrolone in the treatment of wasting and catabolic disorders: Review of efficacy and safety. Drugs 2004, 64, 725–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.A. Oxandrolone treatment of childhood hereditary angioedema. Ann. Allergy. Asthma. Immunol. 2004, 92, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.T.; Herndon, D.N.; Tanksley, J.D.; Jennings, K.; Klein, G.L.; Mlcak, R.P.; Clayton, R.P.; Crites, N.N.; Hays, J.P.; Andersen, C.; et al. Five-year outcomes after long-term oxandrolone administration in severely burned children: A randomized clinical trial. Shock Augusta Ga 2016, 45, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, R.G.; France, J.; Attie, K.M.; Brasel, J.A.; Burstein, S.; Cara, J.F.; Chernausek, S.; Gotlin, R.W.; Kuntze, J.; Lippe, B.M.; et al. Six-year results of a randomized, prospective trial of human growth hormone and oxandrolone in turner syndrome. J. Pediatr. 1992, 121, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keele, D.K.; Vose, G.P. A study of bone density: Comparison of the effects of sodium fluoride, inorganic phosphates, and an anabolic steroid (oxymetholone) on demineralized bone. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1969, 118, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengge, U.R.; Stocks, K.; Faulkner, S.; Wiehler, H.; Lorenz, C.; Jentzen, W.; Hengge, D.; Ringham, G. Oxymetholone for the treatment of hiv-wasting: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase iii trial in eugonadal men and women. HIV Clin. Trials 2003, 4, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlatos, A.M.; Fultz, O.; Monberg, M.J.; Vootkur, A. Review of oxymetholone: A 17α-alkylated anabolic-androgenic steroid. Clin. Ther. 2001, 23, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnut III, C.H.; Ivey, J.L.; Gruber, H.E.; Matthews, M.; Nelp, W.B.; Sisom, K.; Baylink, D.J. Stanozolol in postmenopausal osteoporosis: Therapeutic efficacy and possible mechanisms of action. Metabolism 1983, 32, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, K. Current management options for hereditary angioedema. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012, 12, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloane, D.E.; Lee, C.W.; Sheffer, A.L. Hereditary angioedema: Safety of long-term stanozolol therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, I.K.M.; Hall, J.M. Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, S.; Onken, D.; Schubert, A. The steroid story of jenapharm: From the late 1940s to the early 1970s. Steroids 1999, 64, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, J.; Batterham, M.J.; Rekers, H.; Harms, M.K.; Geurts, T.B.P.; Helmyr, P.M.E.; Silva de Mendonça, J.; Carvalho, L.H.F.; Panos, G.; Pinchera, A.; et al. Effects of nandrolone decanoate compared with placebo or testosterone on hiv-associated wasting. HIV Med. 2006, 7, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geusens, P. Nandrolone decanoate: Pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in osteoporosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 1995, 14, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, E.; Alanko, A.; Gröhn, P.; Rissanen, P. Nandrolone decanoate added to tamoxifen in the treatment of advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1985, 5, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elks, J. The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Furuhjelm, U.; Eklund, J. Treatment of aplastic anemia with anabolic steroids and corticosteroids. Ann. Paediatr. Fenn. 1966, 12, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.A. Drugs, Athletes, and Physical Performance; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ebadi, M. Desk Reference of Clinical Pharmacology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe, W.J.; Menon, I.S. Treatment of behcet’s syndrome with phenformin and ethyloestrenol. Lancet 1969, 1, 1239–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, B.; Nilsson, I.M.; Hedner, U. Δ4-Ethylestrenol in recurrent deep venous thrombosis. Acta Med. Scand. 1981, 209, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnley, G.R.; Chakrabarti, R. Phenformin and ethyloestrenol for raynaud’s disease. Lancet 1969, 2, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L. The Encyclopedia of Addictive Drugs; Greenwood Publishing Group: Westport, CT, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R.N.; Bradley, M.H.; Callahan, R.; Peters, B.J.; Kory, R.C. A six-month evaluation of an anabolic drug, norethandrolone, in underweight persons. i. weight gain. Am. J. Med. 1959, 26, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroulik, W.J. Norethandrolone (nilevar) in the treatment of severely burned victims of the chicago school fire. J. Int. Coll. Surg. 1959, 32, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najean, Y.; Pecking, A.; Danvic, M.L.; The Cooperative Group for the Study of Aplastic and Refractory Anaemias Secretaries. Androgen therapy of aplastic anaemia -a prospective study of 352 cases. Scand. J. Haematol. 1979, 22, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, B.; Daxenberger, A.; Meyer, K.; Meyer, H.H. The fate of trenbolone acetate and melengestrol acetate after application as growth promoters in cattle: Environmental studies. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarrow, J.F.; McCoy, S.C.; Borst, S.E. Tissue selectivity and potential clinical applications of trenbolone (17β-hydroxyestra-4,9,11-trien-3-one): A potent anabolic steroid with reduced androgenic and estrogenic activity. Steroids 2010, 75, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieschlag, E.; Kumar, N.; Sitruk-Ware, R. 7α-methyl-19-nortestosterone (mentr): The population council’s contribution to research on male contraception and treatment of hypogonadism. Contraception 2013, 87, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attardi, B.J.; Engbring, J.A.; Gropp, D.; Hild, S.A. Development of dimethandrolone 17β-undecanoate (dmau) as an oral male hormonal contraceptive: Induction of infertility and recovery of fertility in adult male rabbits. J. Androl. 2011, 32, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedel, A.; Geyer, H.; Kamber, M.; Laudenbach-Leschowsky, U.; Schänzer, W.; Thevis, M.; Vollmer, G.; Zierau, O.; Diel, P. 17β-hydroxy-5alpha-androst-1-en-3-one (1-testosterone) is a potent androgen with anabolic properties. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 165, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasiurkowski, B.; Raj, J.; Wisinger, D.; Carlson, R.; Zou, L.; Nadir, A. Cholestatic jaundice and iga nephropathy induced by otc muscle building agent superdrol. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2659–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diel, P.; Friedel, A.; Geyer, H.; Kamber, M.; Laudenbach-Leschowsky, U.; Schänzer, W.; Thevis, M.; Vollmer, G.; Zierau, O. Characterisation of the pharmacological profile of desoxymethyltestosterone (madol), a steroid misused for doping. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 169, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catlin, D.H.; Sekera, M.H.; Ahrens, B.D.; Starcevic, B.; Chang, Y.-C.; Hatton, C.K. Tetrahydrogestrinone: Discovery, synthesis, and detection in urine. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catlin, D.H.; Ahrens, B.D.; Kucherova, Y. Detection of norbolethone, an anabolic steroid never marketed, in athletes’ urine. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 16, 1273–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, A.-N.; Pinon, G.M.; Bens, M.; Fagart, J.; Rafestin-Oblin, M.-E.; Vandewalle, A. The synthetic androgen methyltrienolone (r1881) acts as a potent antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joseph, J.F.; Parr, M.K. Synthetic androgens as designer supplements. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piper, T.; Fusshöller, G.; Schänzer, W.; Lagojda, A.; Kuehne, D.; Thevis, M. Studies on the in vivo metabolism of methylstenbolone and detection of novel long term metabolites for doping control analysis. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohler, M.L.; Bohl, C.E.; Jones, A.; Coss, C.C.; Narayanan, R.; He, Y.; Dong, J.H.; Dalton, J.T.; Miller, D.D. Nonsteroidal selective androgen receptor modulators (sarms): Dissociating the anabolic and androgenic activities of the androgen receptor for therapeutic benefit. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 3597–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L. FDA In Brief: FDA Warns against Using SARMs in Body-Building Products. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/fda-brief/fda-brief-fda-warns-against-using-sarms-body-building-products (accessed on 6 February 2020).
- Dalton, J.T.; Barnette, K.G.; Bohl, C.E.; Hancock, M.L.; Rodriguez, D.; Dodson, S.T.; Morton, R.A.; Steiner, M.S. The selective androgen receptor modulator gtx-024 (enobosarm) improves lean body mass and physical function in healthy elderly men and postmenopausal women: Results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase ii trial. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2011, 2, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dobs, A.S.; Boccia, R.V.; Croot, C.C.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Dalton, J.T.; Hancock, M.L.; Johnston, M.A.; Steiner, M.S. Effects of enobosarm on muscle wasting and physical function in patients with cancer: A double-blind, randomised controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinath, R.; Dobs, A. Enobosarm (gtx-024, s-22): A potential treatment for cachexia. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.; Prado, C.M.M.; Johnston, M.A.; Gralla, R.J.; Taylor, R.P.; Hancock, M.L.; Dalton, J.T. Study design and rationale for the phase 3 clinical development program of enobosarm, a selective androgen receptor modulator, for the prevention and treatment of muscle wasting in cancer patients (power trials). Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narayanan, R.; Coss, C.C.; Dalton, J.T. Development of selective androgen receptor modulators (sarms). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 465, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basaria, S.; Collins, L.; Dillon, E.L.; Orwoll, K.; Storer, T.W.; Miciek, R.; Ulloor, J.; Zhang, A.; Eder, R.; Zientek, H.; et al. The safety, pharmacokinetics, and effects of lgd-4033, a novel nonsteroidal oral, selective androgen receptor modulator, in healthy young men. J. Gerontol.-Ser. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fragkaki, A.G.; Sakellariou, P.; Kiousi, P.; Kioukia-Fougia, N.; Tsivou, M.; Petrou, M.; Angelis, Y. Human in vivo metabolism study of lgd-4033. Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 10, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, J.; Kuhns, J.E.; Lupisella, J.A.; Manfredi, M.C.; Beehler, B.C.; Krystek, S.R., Jr.; Bi, Y.; Sun, C.; Seethala, R.; Golla, R.; et al. Pharmacological and x-ray structural characterization of a novel selective androgen receptor modulator: Potent hyperanabolic stimulation of skeletal muscle with hypostimulation of prostate in rats. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mealy, N.E.; Bás, M. BMS-564929. Drugs Future 2004, 29, 1132. [Google Scholar]
- Piu, F.; Gardell, L.R.; Son, T.; Schlienger, N.; Lund, B.W.; Schiffer, H.H.; Vanover, K.E.; Davis, R.E.; Olsson, R.; Bradley, S.R. Pharmacological characterization of ac-262536, a novel selective androgen receptor modulator. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 109, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oeveren, A.; Motamedi, M.; Mani, N.S.; Marschke, K.B.; López, F.J.; Schrader, W.T.; Negro-Vilar, A.; Zhi, L. Discovery of 6-n,n-bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)amino-4- trifluoromethylquinolin-2(1h)-one as a novel selective androgen receptor modulator. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6143–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajda, E.G.; López, F.J.; Rix, P.; Hill, R.; Chen, Y.; Lee, K.-J.; O’Brien, Z.; Chang, W.Y.; Meglasson, M.D.; Lee, Y.-H. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lgd-3303 [9-chloro-2-ethyl-1- methyl-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-3h-pyrrolo-[3,2-f]quinolin-7(6h)-one], an orally available nonsteroidal-selective androgen receptor modulator. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 328, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanada, K.; Furuya, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Nejishima, H.; Ichikawa, K.; Nakamura, T.; Miyakawa, M.; Amano, S.; Sumita, Y.; Oguro, N. Bone anabolic effects of s-40503, a novel nonsteroidal selective androgen receptor modulator (sarm), in rat models of osteoporosis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.; Chen, J.; Hwang, D.J.; Miller, D.D.; Dalton, J.T. Preclinical characterization of a (s)-n-(4-cyano-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)- 3-(3-fluoro, 4-chlorophenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-propanamide: A selective androgen receptor modulator for hormonal male contraception. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansson, A.; Knych, H.; Stanley, S.; Thevis, M.; Bondesson, U.; Hedeland, M. Investigation of the selective androgen receptor modulators s1, s4 and s22 and their metabolites in equine plasma using high-resolution mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 30, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Dong, J.H.; Bohl, C.E.; Miller, D.D.; Dalton, J.T. A selective androgen receptor modulator for hormonal male contraception. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.P.; Shomali, M.; Lyttle, C.R.; O’dea, L.S.L.; Herendeen, H.; Gallacher, K.; Paquin, D.; Compton, D.R.; Sahoo, B.; Kerrigan, S.A.; et al. Design, synthesis, and preclinical characterization of the selective androgen receptor modulator (sarm) rad140. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, W.; Dalton, J.T. Expanding the therapeutic use of androgens via selective androgen receptor modulators (sarms). Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, D.; Xu, H.; He, Y.; Kirkovsky, L.I.; Miller, D.D.; Dalton, J.T. Pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and metabolism of acetothiolutamide, a novel nonsteroidal agonist for the androgen receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 304, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thevis, M. Detection of the arylpropionamide-derived selective androgen receptor modulator (sarm) s-4 (andarine) in a black-market product. Drug Test. Anal. 2009, 1, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamann, L.G.; Mani, N.S.; Davis, R.L.; Wang, X.-N.; Marschke, K.B.; Jones, T.K. Discovery of a potent, orally active, nonsteroidal androgen receptor agonist: 4-ethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-(trifluoromethyl)-8-pyridono[5,6-g]- quinoline (lg121071) [3]. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 210–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Harada, S.-I.; Kimmel, D.B.; Bai, C.; Chen, F.; Rutledge, S.J.; Vogel, R.L.; Scafonas, A.; Gentile, M.A.; Nantermet, P.V.; et al. Identification of anabolic selective androgen receptor modulators with reduced activities in reproductive tissues and sebaceous glands. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 36367–36376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, A.; Kimmel, D.B.; Bai, C.; Scafonas, A.; Rutledge, S.; Vogel, R.L.; McElwee-Witmer, S.; Chen, F.; Nantermet, P.V.; Kasparcova, V.; et al. Discovery of the selective androgen receptor modulator mk-0773 using a rational development strategy based on differential transcriptional requirements for androgenic anabolism versus reproductive physiology. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17054–17064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, W.; Kim, J.; Dalton, J.T. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nonsteroidal androgen receptor ligands. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1641–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yatsu, T.; Kusakabe, T.; Kato, K.; Inouye, Y.; Nemoto, K.; Kanno, Y. Selective androgen receptor modulator, yk11, up-regulates osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation in mc3t3-e1 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, G.A.; Vukovich, M.; King, D.S. Testosterone prohormone supplements. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, S.S.C. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and longevity: New clues for an old friend. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8167–8169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Gammeren, D.; Falk, D.; Antonio, J. Effects of norandrostenedione and norandrostenediol in resistance-trained men. Nutrition 2002, 18, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.P.; Constantini, N.W. Sports Endocrinology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pokrywka, A.; Obmiński, Z.; Malczewska-Lenczowska, J.; Fijałek, Z.; Turek-Lepa, E.; Grucza, R. Insights into supplements with tribulus terrestris used by athletes. J. Hum. Kinet. 2014, 41, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
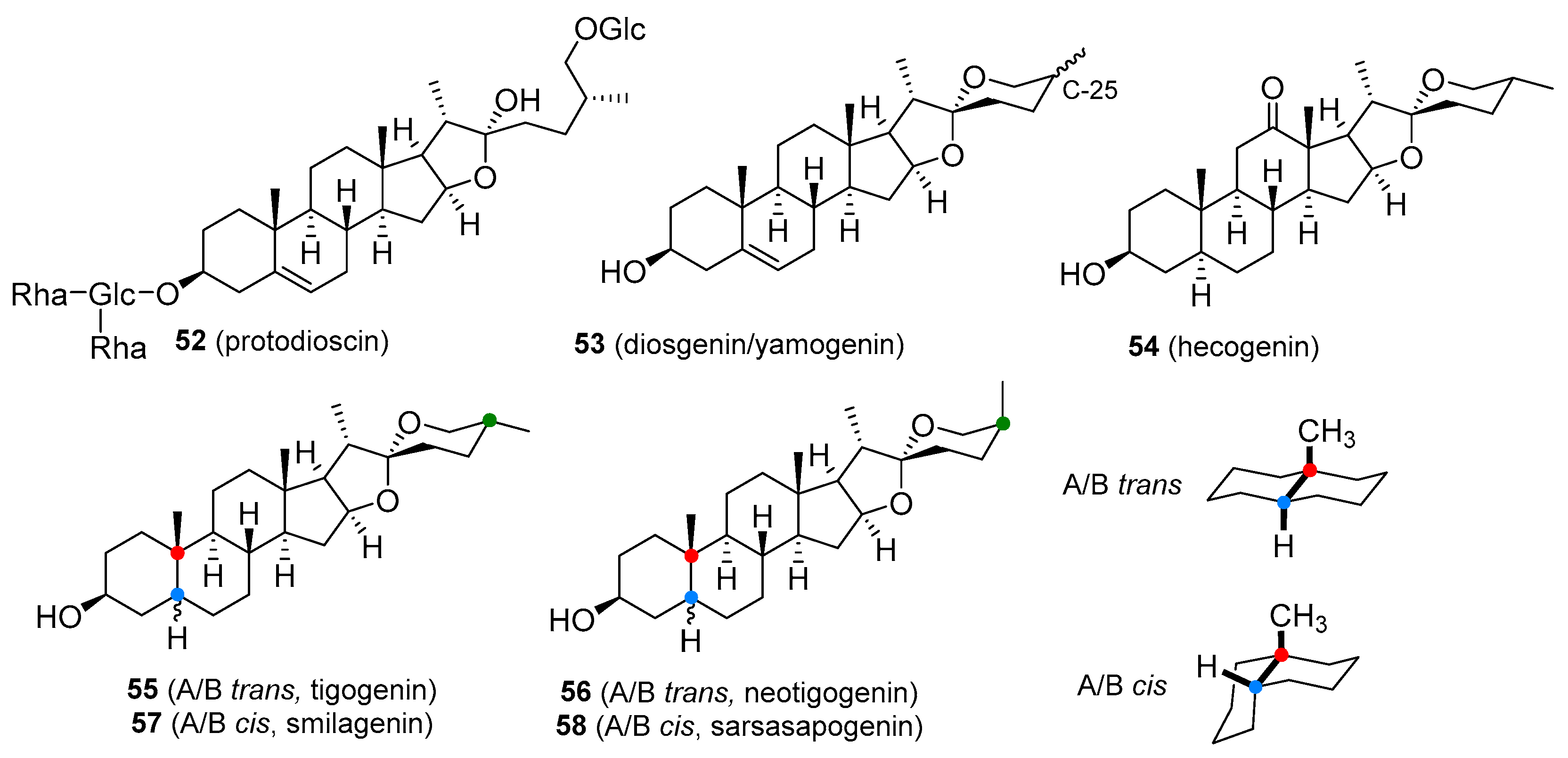
- Sautour, M.; Mitaine-Offer, A.-C.; Lacaille-Dubois, M.-A. The dioscorea genus: A review of bioactive steroid saponins. J. Nat. Med. 2007, 61, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, E.J.; Wilkin, P.; Sarasan, V.; Fraser, P.D. Metabolite profiling of dioscorea (yam) species reveals underutilised biodiversity and renewable sources for high-value compounds. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, D.; Yan-Yong, C.; De-Zu, W.; Chong-Ren, Y. Steroidal saponins from a cultivated form of agave sisalana. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 2787–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, M.K.; Ambrosio, G.; Wuest, B.; Mazzarino, M.; de la Torre, X.; Sibilia, F.; Joseph, J.F.; Diel, P.; Botrè, F. Targeting the administration of ecdysterone in doping control samples. Forensic Toxicol. 2020, 38, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koduru, S.; Kumar, R.; Srinivasan, S.; Evers, M.B.; Damodaran, C. Notch-1 inhibition by withaferin-a: A therapeutic target against colon carcinogenesis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davydov, M.; Krikorian, A.D. Eleutherococcus senticosus (rupr. and maxim.) maxim. (araliaceae) as an adaptogen: A closer look. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 72, 345–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.D.; Rhee, D.K.; Lee, Y.H. Biological activities and chemistry of saponins from panax ginseng c. a. meyer. Phytochem. Rev. 2005, 4, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, I.C. Food Supplements. In Food Safety: The Science of Keeping Food Safe; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2018; pp. 452–483. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, K.; Tezuka, Y.; Awale, S.; Li, F.; Kadota, S. Quassinoids from eurycoma longifolia. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewczyk, K.; Zidorn, C. Ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and bioactivity of the genus turnera (passifloraceae) with a focus on damiana-turnera diffusa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 424–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarikwu, S.O.; Onuah, C.L.; Singh, S.K. Plants in the management of male infertility. Andrologia 2020, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
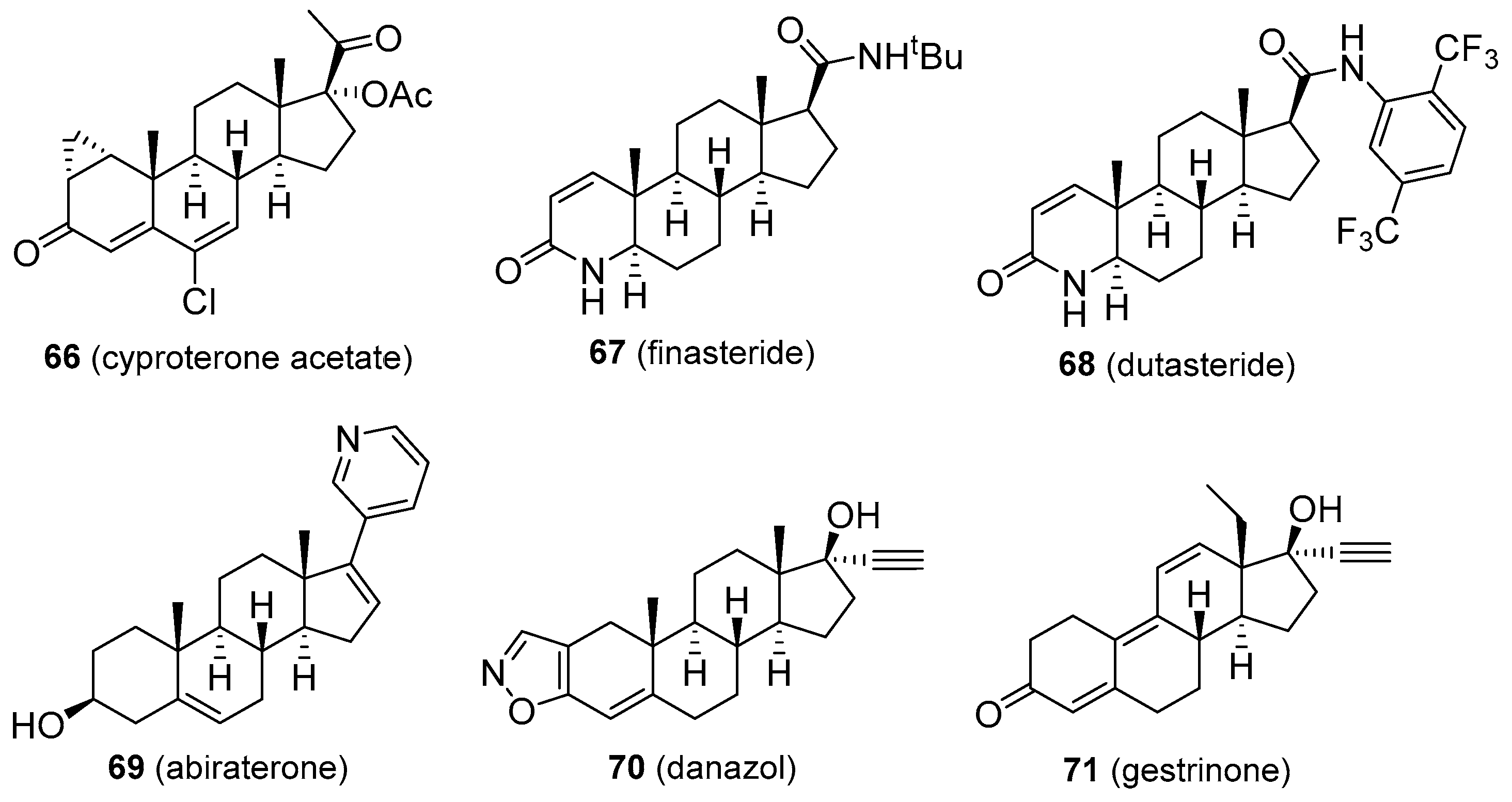
- Neumann, F. The antiandrogen cyproterone acetate: Discovery, chemistry, basic pharmacology, clinical use and tool in basic research. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 1994, 102, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diviccaro, S.; Melcangi, R.C.; Giatti, S. Post-finasteride syndrome: An emerging clinical problem. Neurobiol. Stress 2020, 12, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bono, J.S.; Logothetis, C.J.; Molina, A.; Fizazi, K.; North, S.; Chu, L.; Chi, K.N.; Jones, R.J.; Goodman, O.B., Jr.; Saad, F.; et al. Abiraterone and increased survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromham, D.R.; Booker, M.W.; Rose, G.L.; Wardle, P.G.; Newton, J.R. A multicentre comparative study of gestrinone and danazol in the treatment of endometriosis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1995, 15, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Compound | Main Areas of Medicinal Application | Usual Route of Administration/Available Forms |
|---|---|---|
| AAS | ||
| Testosterone | Male hypogonadism, oestrogen-dependent breast cancer in women, adjunct to hormone replacement therapy in menopausal women (to improve libido), testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) | Transdermal (patch, gel, cream), oral tablets (undecanoate ester), buccal, sublingual, and intranasal formulations, subcutaneous implants, and various esters for intramuscular injection (caproate, cypionate, decanoate, enanthate, isobutyrate, phenylpropionate, propionate, undecanoate) |
| Dihydrotestosterone (DHT; androstanolone) | Hypogonadism, gynecomastia, breast cancer (discontinued in some countries) | Transdermal gel, buccal and sublingual formulations, enanthate, propionate, and valerate esters (intramuscular injection) |
| Methyltestosterone | Delayed puberty, hypogonadism, cryptorchidism, erectile dysfunction, menopausal symptoms (osteoporosis, hot flashes, to improve libido), postpartum breast pain and engorgement, breast cancer in women | Oral tablets, buccal and sublingual formulations |
| Methandriol | Breast cancer in women (now discontinued in most countries) | Oral tablets or propionate and bisenanthoyl acetate esters (intramuscular injection) |
| Boldenone | Wasting syndrome, osteoporosis (now discontinued in most countries) | Undecylenate ester (intramuscular injection) |
| Fluoxymesterone (halotestin) | Hypogonadism, delayed puberty in males, breast cancer in women, some types of anemia | Oral tablets |
| Metandienone (dianabol®) | Hypogonadism (now discontinued in most countries) | |
| Drostanolone | Breast cancer (now discontinued in most countries) | Propionate ester (intramuscular injection) |
| Methenolone | Bone marrow failure-associated anemia, wasting syndromes, osteoporosis, sarcopenia | Acetate (orally active) and enanthate esters (intramuscular injection) |
| Oxandrolone | Osteoporosis-derived pain, weight loss, protein catabolism, AIDS-induced wasting, alcoholic hepatitis, severe burns, anemia, hereditary angioedema, Turner syndrome, hypogonadism, idiopathic short stature | Oral tablets |
| Oxymetholone | Anemia, osteoporosis (largely discontinued for these conditions), muscle wasting, AIDS wasting syndrome | |
| Stanozolol | Anemia, osteoporosis, burns, skeletal muscle injury (largely discontinued for these conditions), hereditary angioedema | Aqueous suspensions (intramuscular injection) or oral tablets |
| Turinabol | Osteoporosis (now discontinued in most countries) | Acetate ester (intramuscular injection) or oral tablets |
| Nandrolone | Burns, breast cancer, anemia, osteoporosis, HIV-induced wasting (now discontinued in most countries) | Decanoate and phenylpropionate esters (intramuscular or subcutaneous injections) or sulfate (eye drop formulation) |
| Ethylestrenol | Wasting syndromes, osteoporosis-associated pain, burns, severe injuries, various types of anemias, conditions of veins and arteries, arthritis, short stature (now discontinued in most countries) | Oral tablets |
| Norethandrolone | Wasting syndromes, burns, severe injuries, various types of anemias (now discontinued in most countries) | |
| Trenbolone | Wasting syndromes (now discontinued in most countries) | Acetate and hexahydrobenzylcarbonate esters (intramuscular injection) |
| T and Nandrolone Prodrugs | ||
| Androstenediol | To raise T levels (never marketed for medicinal use) | Oral tablets |
| Androstenedione | ||
| 19-nor-5-androstenediol | ||
| 19-nor-4-androstenediol | ||
| 19-nor-5-androstenedione | ||
| 19-nor-4-androstenedione | ||
| Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) | To raise T levels (never marketed for medicinal use; though it is available as a dietary supplement) | |
| Experimental AAS | ||
| Trestolone | Under development as a male contraceptive, for TRT, and hypogonadism | Subcutaneous implants, intramuscular injection (acetate ester) |
| Dimethandrolone | Under development as a male contraceptive and for TRT | Oral tablets |
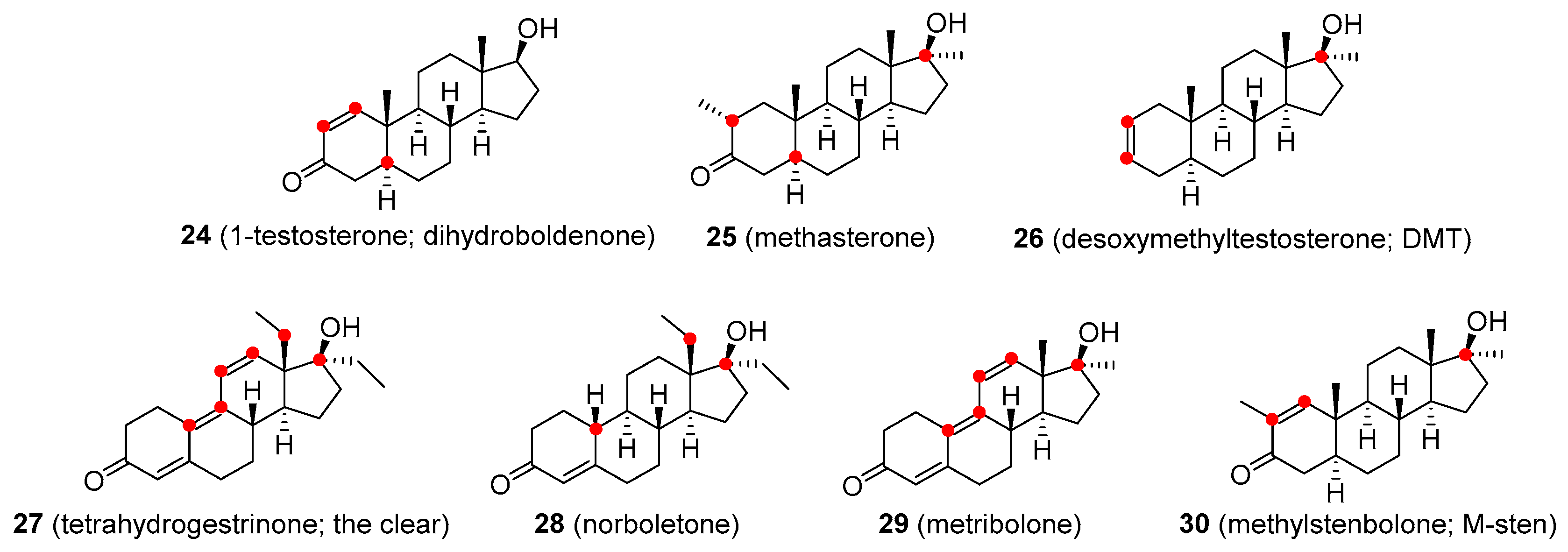
| Designer Steroids | ||
| 1-testosterone | Never marketed for medicinal use | Intramuscular injections |
| Methasterone | Oral tablets | |
| Desoxymethyltestosterone | ||
| Tetrahydrogestrinone | Oral tablets, intramuscular injection | |
| Norboletone | ||
| Metribolone | ||
| Methylstenbolone | ||
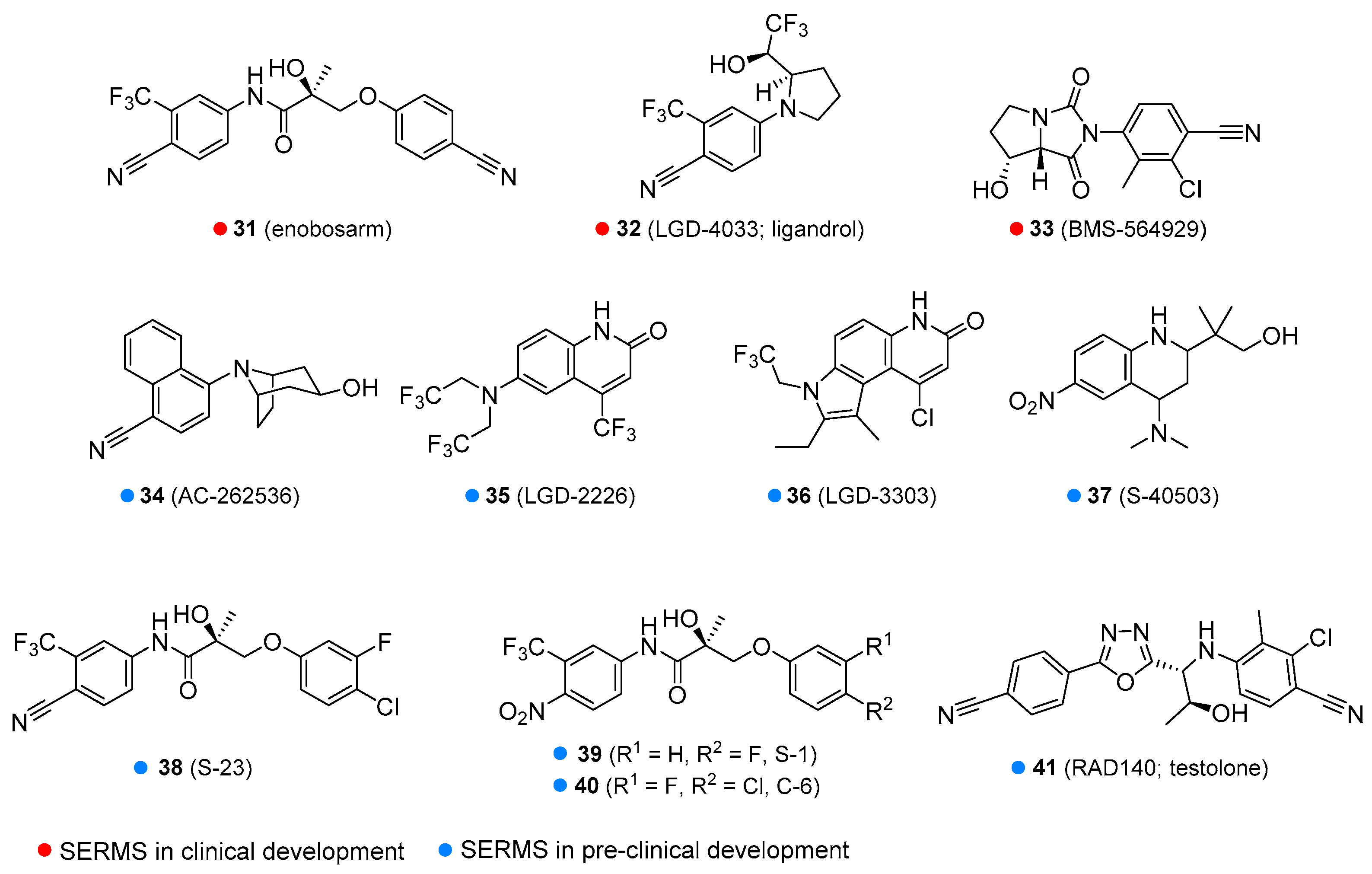
| SARMs | ||
| Enobosarm | Under development for cancer-related wasting, sarcopenia, breast cancer, osteoporosis, and stress urinary incontinence in menopausal women | Oral tablets |
| Ligandrol | Under development for wasting syndrome and osteoporosis | |
| BMS 564929 | Under development for wasting syndrome, osteoporosis, diabetes, hypertension, reduced libido, depression | |
| AC-262356 | In pre-clinical development | |
| LGD-2226 | ||
| LGD-3303 | ||
| S-40503 | ||
| S-23 | ||
| S-1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tauchen, J.; Jurášek, M.; Huml, L.; Rimpelová, S. Medicinal Use of Testosterone and Related Steroids Revisited. Molecules 2021, 26, 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041032
Tauchen J, Jurášek M, Huml L, Rimpelová S. Medicinal Use of Testosterone and Related Steroids Revisited. Molecules. 2021; 26(4):1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041032
Chicago/Turabian StyleTauchen, Jan, Michal Jurášek, Lukáš Huml, and Silvie Rimpelová. 2021. "Medicinal Use of Testosterone and Related Steroids Revisited" Molecules 26, no. 4: 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041032
APA StyleTauchen, J., Jurášek, M., Huml, L., & Rimpelová, S. (2021). Medicinal Use of Testosterone and Related Steroids Revisited. Molecules, 26(4), 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041032









