Recent Advances in Probiotic Application in Animal Health and Nutrition: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modes of Action of Probiotics
- Probiotics might be effective in modifying both the innate and acquired immune system of the host. This will be effective in preventing infectious diseases and ameliorate the inflammation of the host’s digestive tract;
- The action of probiotics directly on other microorganisms will prevent and serve to control infections and restore the microbial equilibrium in the gut;
- Microbial products such as toxins, antimicrobials and host metabolites may be the key components for probiotic actions. The probiotics help to inactivate the toxins and bile salts detoxification and enhance digestion of food ingredients and absorption of nutrients in the gut.
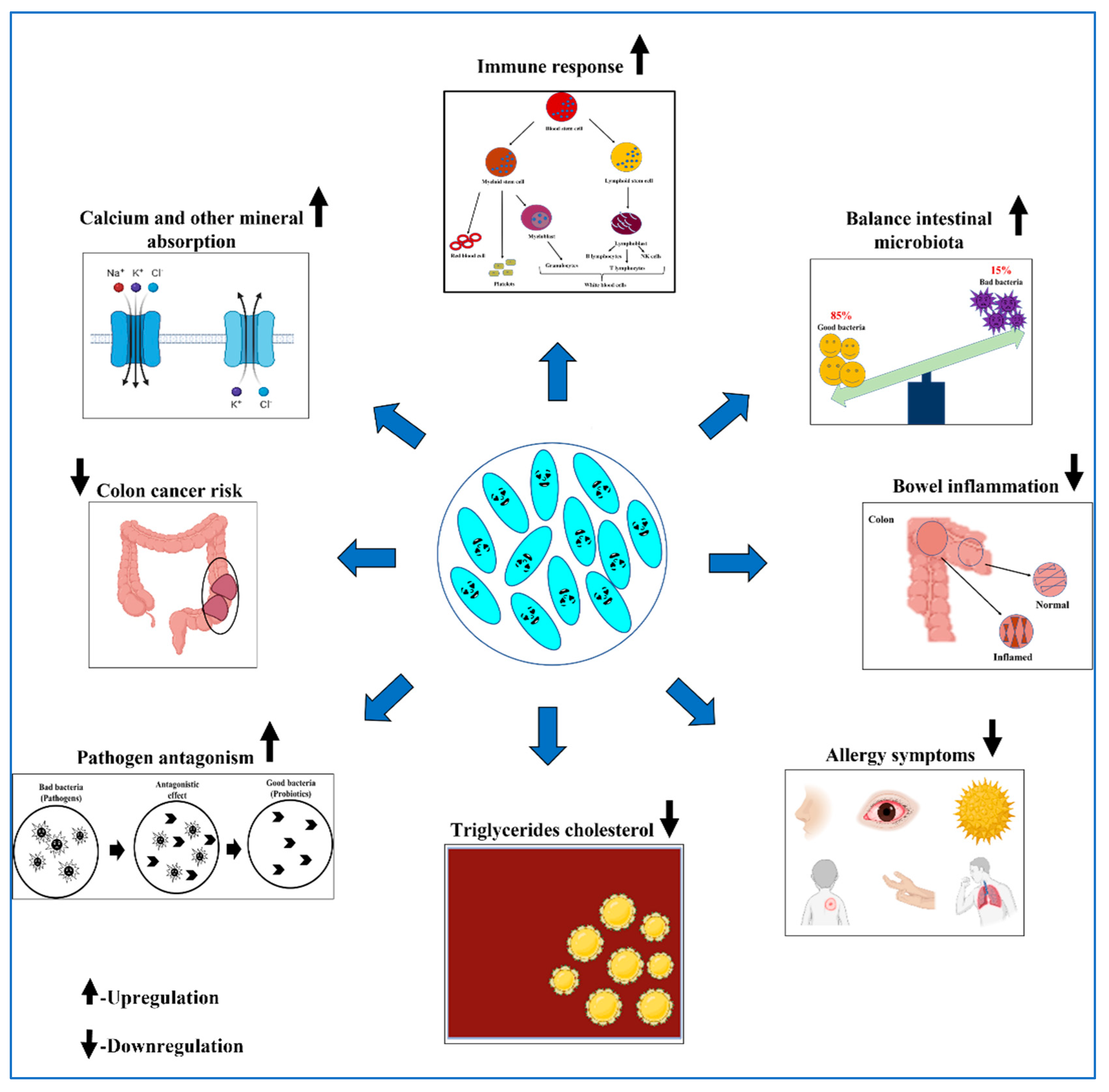
3. Health Benefits of Probiotics in Animal Growth Performance
3.1. Probiotics in Ruminant Nutrition and Health
3.2. Probiotics in Monogastric Animals Feeding
3.3. Significance of Probiotics in Poultry Feeding and Health
3.4. Probiotics in Poultry Production
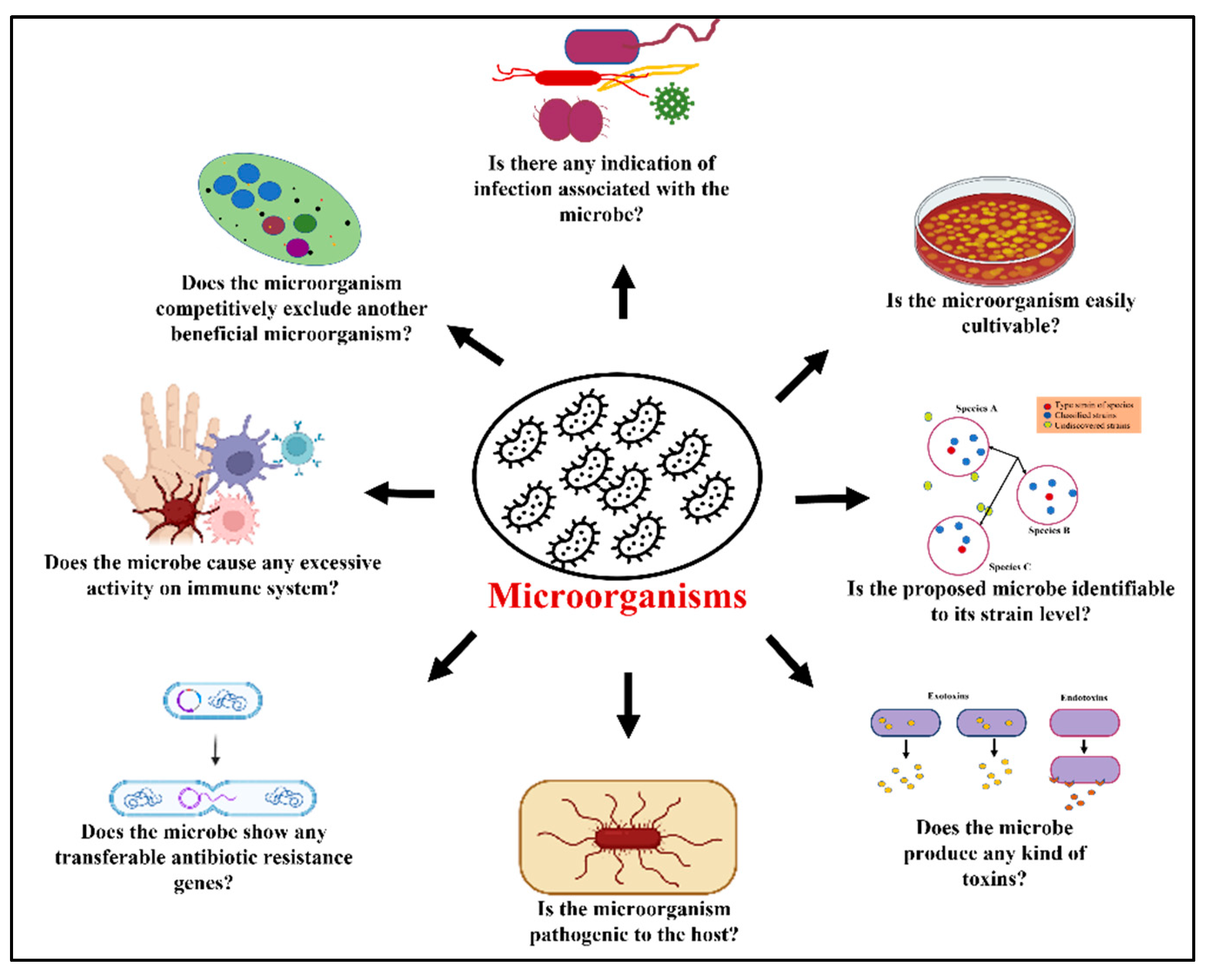
4. Challenges to the Application of Probiotics in Animal Feeding
- GIT infection of the animal that nourished the probiotic;
- GIT infection of the consumers who had animal products that are produced by probiotic fed animals;
- From probiotics, antibiotic resistance transmission to other pathogenic microbes;
- Infections in the animal and animal food handlers;
- Sensitization/irritation of skin or eye in the administrators of probiotics;
- Production of toxins by probiotics causing harmful metabolic or toxic effects in the host;
- Susceptible hosts hyper-stimulation of the immune system.
5. Application of Prebiotics to Complement the Effects of Probiotics in Poultry
6. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lilly, D.M.; Stillwell, R.H. Probiotics: Growth-Promoting Factors Produced by Microorganisms. Science 1965, 147, 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, A.; Walter, J.; Segal, E.; Spector, T.D. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ 2018, 361, k2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dankowiakowska, A.; Bednarczyk, M.; Kozłowska, I. Probiotics, prebiotics and snybiotics in poultry—Mode of action, limitation, and achievements. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2013, 14, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Yan, W.; Ma, Y.; Fang, J. The impact of probiotics on gut health via alternation of immune status of monogastric animals. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on Human Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanon, J.I.R. History of the Use of Antibiotic as Growth Promoters in European Poultry Feeds. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestinaci, F.; Pezzotti, P.; Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial resistance: A global multifaceted phenomenon. Pathog. Glob. Health 2015, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heredia, N.; García, S. Animals as sources of food-borne pathogens: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, P.S.; Slutsker, L.; Dietz, V.; McCaig, L.F.; Bresee, J.S.; Shapiro, C.; Griffin, P.M.; Tauxe, R.V. Food-Related Illness and Death in the United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bywater, R.J. Veterinary Use of Antimicrobials and Emergence of Resistance in Zoonotic and Sentinel Bacteria in the EU. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2004, 51, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, S.; Malik, K.; Kang, S.A.; Kim, H.-Y. Probiotics and their fermented food products are beneficial for health. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogoju, S.; Nahashon, S.; Wang, X.; Darris, C.; Kilonzo-Nthenge, A. A comparative analysis of microbial profile of Guinea fowl and chicken using metagenomic approach. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Ward, L.R.; Burke, C. Screening of marine Streptomyces spp. for potential use as probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2010, 305, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, D.; Jacob, J.C.; Philip, R. Exclusion of Vibrio spp. by an antagonistic marine actinomycete Streptomyces ru-brolavendulae M56. Aquac. Res. 2015, 47, 2951–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelschlaeger, T.A. Mechanisms of probiotic actions—A review. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 300, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado Galdeano, C.; Cazorla, S.I.; Lemme Dumit, J.M.; Vélez, E.; Perdigón, G. Beneficial Effects of Probiotic Consumption on the Immune System. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-B. Effect of probiotics on growth performance and digestive enzyme activity of the shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2007, 269, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S49–S66, Correction in Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, A.B.; Mao, S. Influence of yeast on rumen fermentation, growth performance and quality of products in ruminants: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqué, N.; Berlanga, M.; Miñana-Galbis, D. Health Benefits of Heat-Killed (Tyndallized) Probiotics: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Havenaar, R.; Brink, B.T.; Veld, J.H.J.H.I. Selection of strains for probiotic use. In Probiotics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V.N.; Dargenio, C.; Miniello, V.L.; Barone, M.; Francavilla, R. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics in Gut Inflammation: A Door to the Body. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 578386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnini, C.; Saeed, R.; Bamias, G.; Arseneau, K.O.; Pizarro, T.T.; Cominelli, F. Probiotics promote gut health through stimulation of epithelial innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieco-Saiz, N.; Belguesmia, Y.; Raspoet, R.; Auclair, E.; Gancel, F.; Kempf, I.; Drider, D. Benefits and Inputs from Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Bacteriocins as Alternatives to Antibiotic Growth Promoters During Food-Animal Production. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaee, P.; Kermanshahi, R.K.; Falsafi, T. Antibacterial activity of lactobacilli probiotics on clinical strains of Helicobacter pylori. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 22, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Dai, C.; Zhao, D.-H. VSL#3 probiotics regulate the intestinal epithelial barrier in vivo and in vitro via the p38 and ERK signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 29, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtoranta, L.; Latvala, S.; Lehtinen, M.J. Role of Probiotics in Stimulating the Immune System in Viral Respiratory Tract Infections: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahashon, S.N.; Nakaue, H.S.; Mirosh, L.W. Phytase Activity, Phosphorus and Calcium Retention, and Performance of Single Comb White Leghorn Layers Fed Diets Containing Two Levels of Available Phosphorus and Supplemented with Direct-Fed Microbials. Poult. Sci. 1994, 73, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Song, D.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W.; Miao, H.; Wang, L.; Li, A. Effects of microencapsulated probiotics and prebiotics on growth performance, antioxidative abilities, immune functions, and caecal microflora in broiler chickens. Food Agric. Immunol. 2018, 29, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.H.; Lillehoj, H.S. Immunity, immunomodulation, and antibiotic alternatives to maximize the genetic potential of poultry for growth and disease response. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 250, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment improves intestinal permeability and modulates microbiota dysbiosis in an experimental model of sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanfar, S. Understanding the Mechanism of Action of Indigenous Target Probiotic Yeast: Linking the Manipulation of Gut Microbiota and Performance in Animals. In Saccharomyces; InTech: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nocek, J.; Kautz, W. Direct-fed microbial supplementation on ruminal digestion, health, and performance of pre- and postpartum dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 260–266, Erratum in J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apás, A.L.; Dupraz, J.; Ross, R.; González, S.N.; Arena, M.E. Probiotic administration effect on fecal mutagenicity and microflora in the goat’s gut. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanfar, S.; Anjum, M.I.; Azim, A.; Ahmed, I. Effects of dietary supplementation of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) culture on growth performance, blood parameters, nutrient digestibility and fecal flora of dairy heifers. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2015, 25, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Raheem, A.; Liang, L.; Zhang, G.; Cui, S. Modulatory Effects of Probiotics During Pathogenic Infections with Emphasis on Immune Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 616713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Ge, J.; Shi, H.; Kou, J. Positive effects of dietary supplementation of three probiotics on milk yield, milk composition and intestinal flora in Sannan dairy goats varied in kind of probiotics. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 104, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W. Bifidobacterium bifidum TMC3115 ameliorates milk protein allergy in by affecting gut microbiota: A randomized double-blind control trial. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Jiao, S.; Dai, Y.; An, J.; Lv, J.; Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Han, B. Probiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens C-1 Improves Growth Performance, Stimulates GH/IGF-1, and Regulates the Gut Microbiota of Growth-Retarded Beef Calves. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alawneh, J.I.; James, A.S.; Phillips, N.; Fraser, B.; Jury, K.; Soust, M.; Olchowy, T.W.J. Efficacy of a Lactobacillus-Based Teat Spray on Udder Health in Lactating Dairy Cows. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 584436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Peng, M.; Tong, W.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Z. The Quorum Quenching Bacterium Bacillus licheniformis T-1 Protects Zebrafish against Aeromonas hydrophila Infection. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 12, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Si, X.; Cao, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, H. Beneficial effect of Rhodopseudomonas palustris on in vitro rumen digestion and fermentation. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Sadeq, S.A.; Wu, S.; Swick, R.; Choct, M. Towards the control of necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens with in-feed antibiotics phasing-out worldwide. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Reddy, M.; Rao, S.R.; Praharaj, N. Production Performance, Serum/Yolk Cholesterol and Immune Competence of White Leghorn Layers as Influenced by Dietary Supplementation with Probiotic. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2003, 35, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effect of Probiotic Thepax® and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Supplementation on Performance and Egg Quality of Laying Hens. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2006, 6, 52–54. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, D.; Lu, W.; Piao, X.; Chen, X. Screening of Bacillus strains as potential probiotics and subsequent confirmation of the in vivo effectiveness of Bacillus subtilis MA139 in pigs. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2006, 90, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohmer, B.M.; Kramer, W.; Roth-Maier, D.A. Dietary probiotic supplementation and resulting effects on performance, health status, and microbial characteristics of primiparous sows. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2006, 90, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bon, M.; Davies, H.E.; Glynn, C.; Thompson, C.; Madden, M.; Wiseman, J.; Dodd, C.E.; Hurdidge, L.; Payne, G.; Le Treut, Y.; et al. Influence of probiotics on gut health in the weaned pig. Livest. Sci. 2010, 133, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agazzi, A.; Ferroni, M.; Fanelli, A.; Maroccolo, S.; Invernizzi, G.; Dell’Orto, V.; Savoini, G. Evaluation of the Effects of Live Yeast Supplementation on Apparent Digestibility of High-Fiber Diet in Mature Horses Using the Acid Insoluble Ash Marker Modified Method. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2011, 31, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessi, T.; Sütas, Y.; Hurme, M.; Isolauri, E. Interleukin-10 generation in atopic children following oral Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzese, E.; Callegari, M.L.; Raia, V.; Viscovo, S.; Scotto, R.; Ferrari, S.; Morelli, L.; Buccigrossi, V.; Vecchio, A.L.; Ruberto, E.; et al. Disrupted Intestinal Microbiota and Intestinal Inflammation in Children with Cystic Fibrosis and Its Restoration with Lactobacillus GG: A Randomised Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drago, L. Probiotics and Colon Cancer. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jha, R.; Das, R.; Oak, S.; Mishra, P. Probiotics (Direct-Fed Microbials) in Poultry Nutrition and Their Effects on Nutrient Utilization, Growth and Laying Performance, and Gut Health: A Systematic Review. Animals 2020, 10, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.G.D.L.; Storch, O.; Gil-Turnes, C. Bacillus cereus var. toyoii and Saccharomyces boulardii increased feed efficiency in broilers infected with Salmonella enteritidis. Br. Poult. Sci. 2005, 46, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrc, R.F. Probiotics in man and animals. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1989, 66, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrezenmeir, J.; De Vrese, M. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics—Approaching a definition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 361s–364s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mead, G. Prospects for ‘Competitive Exclusion’ Treatment to Control Salmonellas and Other Foodborne Pathogens in Poultry. Vet. J. 2000, 159, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W.A. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, S87–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celi, P.; Cowieson, A.; Fru-Nji, F.; Steinert, R.; Kluenter, A.-M.; Verlhac, V. Gastrointestinal functionality in animal nutrition and health: New opportunities for sustainable animal production. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 234, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Qi, Z.; Jiang, W.; Quan, S.; Sheng, T.; Tu, J.; Shao, Y.; Qi, K. Effects of probiotics on cecal microbiome profile altered by duck Escherichia coli 17 infection in Cherry Valley ducks. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 138, 103849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-L.; Kho, W.-L.; You, S.-H.; Yeh, R.-H.; Tang, S.-W.; Hsieh, C.-W. Effects of Bacillus subtilis var. natto and Saccharomyces cerevisiae mixed fermented feed on the enhanced growth performance of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manafi, M.; Khalaji, S.; Hedayati, M.; Pirany, N. Efficacy of Bacillus subtilis and bacitracin methylene disalicylate on growth performance, digestibility, blood metabolites, immunity, and intestinal microbiota after intramuscular inoculation with Escherichia coli in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazi, V.; Foroozandeh, A.; Toghyani, M.; Dastar, B.; Koochaksaraie, R.R. Effects of Pediococcus acidilactici, mannan-oligosaccharide, butyric acid and their combination on growth performance and intestinal health in young broiler chickens challenged with Salmonella Typhimurium. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2034–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.Z.; Ho, Y.W.; Abdullah, N.; Jalaludin, S. Digestive and Bacterial Enzyme Activities in Broilers Fed Diets Supplemented with Lactobacillus Cultures. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhogoju, S.; Khwatenge, C.; Taylor-Bowden, T.; Akerele, G.; Kimathi, B.; Donkor, J.; Nahashon, S. Effects of Lactobacillus reuteri and Streptomyces coelicolor on Growth Performance of Broiler Chickens. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaghari, M.; Sarani, P.; Hajati, H. Comparison of two probiotic preparations on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, nutrient digestibility and cytokine gene expression in broiler chickens. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2020, 48, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, W.; Shao, Y.; Gong, X.; Wu, Y.; Geng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y. Effect of dietary Bacillus coagulans supplementation on growth performance and immune responses of broiler chickens challenged by Salmonella enteritidis. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2654–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoluzzi, C.; Vieira, B.S.; Dorigam, J.C.D.P.; Menconi, A.; Sokale, A.; Doranalli, K.; Applegate, T.J. Bacillus subtilis DSM 32315 Supplementation Attenuates the Effects of Clostridium perfringens Challenge on the Growth Performance and Intestinal Microbiota of Broiler Chickens. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whelan, R.A.; Doranalli, K.; Rinttilä, T.; Vienola, K.; Jurgens, G.; Apajalahti, J. The impact of Bacillus subtilis DSM 32315 on the pathology, performance, and intestinal microbiome of broiler chickens in a necrotic enteritis challenge. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 3450–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilina, L.A.; Yildirim, E.A.; Nikonov, I.; Filippova, V.A.; Laptev, G.Y.; Novikova, N.I.; Grozina, A.; Lenkova, T.N.; Manukyan, V.A.; Egorov, I.A.; et al. Metagenomic bacterial community profiles of chicken embryo gastrointestinal tract by using T-RFLP analysis. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 466, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Ragione, R. Bacillus subtilis spores competitively exclude Escherichia coli O78:K80 in poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 79, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, J.T.; Bauer, S.; Young, V.; Pauling, G.; Wilson, J. An Economic Analysis of the Impact of Subclinical (Mild) Necrotic Enteritis in Broiler Chickens. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, H.R.; Abdul-Careem, M.F.; Dara, R.A.; Chambers, J.R.; Sharif, S. Cytokine gene expression in chicken cecal tonsils following treatment with probiotics and Salmonella infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 126, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biloni, A.; Quintana, C.; Menconi, A.; Kallapura, G.; Latorre, J.D.; Pixley, C.; Layton, S.; Dalmagro, M.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Wolfenden, A.; et al. Evaluation of effects of EarlyBird associated with FloraMax-B11 on Salmonella Enteritidis, intestinal morphology, and performance of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannenas, I.; Papadopoulos, E.; Tsalie, E.; Triantafillou, E.; Henikl, S.; Teichmann, K.; Tontis, D. Assessment of dietary supplementation with probiotics on performance, intestinal morphology and microflora of chickens infected with Eimeria tenella. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 188, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggìa, F.; Mattarelli, P.; Biavati, B. Probiotics and prebiotics in animal feeding for safe food production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, S15–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adugna, W.; Belete, Y. Review on Effects of Probiotic in Chicken Feed. Adv. Biotechnol. Microbiol. 2020, 3, 555913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokapirnasari, W.P.; Pribadi, T.B.; Al Arif, A.; Soeharsono, S.; Hidanah, S.; Harijani, N.; Najwan, R.; Huda, K.; Wardhani, H.C.P.; Rahman, N.F.N.; et al. Potency of probiotics Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus casei to improve growth performance and business analysis in organic laying hens. Vet. World 2019, 12, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahashon, S.N.; Nakaue, H.S.; Snyder, S.P.; Mirosh, L.W. Performance of Single Comb White Leghorn Layers Fed Corn-Soybean Meal and Barley-Corn-Soybean Meal Diets Supplemented with a Direct-Fed Microbial. Poult. Sci. 1994, 73, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahashon, S.N.; Nakaue, H.S.; Mirosh, L.W. Performance of Single Comb White Leghorn fed a diet supplemented with a live microbial during the growth and egg laying phases. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1996, 57, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, H.; Tahoun, A.; Rizk, A.M.; Suzuki, T.; Elmonir, W.; Nassef, E.; Shukry, M.; Germoush, M.O.; Farrag, F.; Bin-Jumah, M.; et al. Evaluation of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus Probiotics as Alternative Therapy for Salmonella typhimurium Infection in Broiler Chickens. Animals 2020, 10, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazelnia, K.; Fakhraei, J.; Yarahmadi, H.M.; Amini, K. Dietary Supplementation of Potential Probiotics Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Synbiotic Improves Growth Performance and Immune Responses by Modulation in Intestinal System in Broiler Chicks Challenged with Salmonella Typhimurium. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, D.S.; Zeng, D.; Khalique, A.; Rajput, S.S.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, N.; Ni, X. Pretreatment with probiotics ameliorate gut health and necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens, a substitute to antibiotics. AMB Express 2020, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sawah, A.A.; Aboelhadid, S.M.; El-Nahass, E.N.; Helal, H.E.S.; Korany, A.M.; El-Ashram, S. Efficacy of probiotic Enterococcus faecium in combination with diclazuril against coccidiosis in experimentally infected broilers. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, A.H.; Ullah, K.S.; Naveed, S.; Latif, F.; Pasha, T.N.; Hussain, I.; Qaisrani, S.N. Effects of spray dried yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) on growth performance and carcass characteristics, gut health, cecal microbiota profile and apparent ileal digestibility of protein, amino acids and energy in broilers. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Si, W.; Barbe, F.; Chevaux, E.; Sienkiewicz, O.; Zhao, X. Effects of novel probiotic strains of Bacillus pumilus and Bacillus subtilis on production, gut health, and immunity of broiler chickens raised under suboptimal conditions. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Gao, C.; Du, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Shan, X.; Wang, G. Effects of single or conjoint administration of lactic acid bacteria as potential probiotics on growth, immune response and disease resistance of snakehead fish (Channa argus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 102, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punetha, M.; Roy, A.K.; Ajithakumar, H.M.; Para, I.A.; Gupta, D.; Singh, M.; Bharati, J. Immunomodulatory effects of probiotics and prilled fat supplementation on immune genes expression and lymphocyte proliferation of transition stage Karan Fries cows. Vet. World 2018, 11, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, T.; Nii, T.; Isobe, N.; Yoshimura, Y. Effects of Probiotics Lactobacillus reuteri and Clostridium butyricum on the Expression of Toll-like Receptors, Pro- and Anti-inflammatory Cytokines, and Antimicrobial Peptides in Broiler Chick Intestine. J. Poult. Sci. 2019, 57, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Jia, H.; Zhu, Z.; Li, H.; Ma, Y. Supplementation of probiotics in water beneficial growth performance, carcass traits, immune function, and antioxidant capacity in broiler chickens. Open Life Sci. 2021, 16, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, F. A Commentary on the Safety of Probiotics. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 41, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Akkermans, L.M.; Haller, D.; Hammerman, C.; Heimbach, J.T.; Hörmannsperger, G.; Huys, G. Safety assessment of probiotics for human use. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 164–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortt, C. The probiotic century: Historical and current perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, C.A.; Murray, B.E. The rise of the Enterococcus: Beyond vancomycin resistance. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 10, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibson, G.R.; Probert, H.M.; Van Loo, J.; Rastall, R.A.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Updating the concept of prebiotics. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2004, 17, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.Q.; Gong, L.M.; Ma, Y.X.; He, Y.H.; Li, D.F.; Zhai, H.X. Effect of stachyose supplementation on growth performance, nutrient digestibility and caecal fermentation characteristics in broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2006, 47, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-L.; Deng, Z.-Y.; Yang, C.-B.; Yin, Y.-L.; Xie, M.Y.; Wu, G.-Y.; Li, T.-J.; Li, L.-L.; Tang, Z.-R.; Kang, P.; et al. Dietary oligochitosan supplementation enhances immune status of broilers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 87, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, M.; El-Hack, M.A.; Hassan, F.; El-Saadony, M.; Khafaga, A.; Batiha, G.; Yehia, N.; Elnesr, S.; Alagawany, M.; El-Tarabily, K.; et al. The potential mechanistic insights and future implications for the effect of prebiotics on poultry performance, gut microbiome, and intestinal morphology. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Arif, M.; Sajjad, N.; Al-Ghadi, M.Q.; Alagawany, M.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Alhimaidi, A.R.; Elnesr, S.S.; Almutairi, B.O.; Amran, R.A.; et al. Dietary effect of probiotics and prebiotics on broiler performance, carcass, and immunity. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6946–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajati, H.; Rezaei, M. The Application of Prebiotics in Poultry Production. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2010, 9, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, D.; Yu, Z. Intestinal microbiome of poultry and its interaction with host and diet. Gut Microbes 2013, 5, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Rothrock, M.J., Jr.; Ricke, S.C.; Rothrock, M.J. Applications of Microbiome Analyses in Alternative Poultry Broiler Production Systems. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 00157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricke, S.C. Impact of Prebiotics on Poultry Production and Food Safety. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2018, 91, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ayichew, T.; Belete, A.; Alebachew, T.; Tsehaye, H.; Berhanu, H.; Minwuyelet, A. Bacterial probiotics their importance and lim-itations: A review. J. Nutr. Health Sci. 2017, 4, 202. [Google Scholar]
- Zommiti, M.; Chikindas, M.L.; Ferchichi, M. Probiotics—Live biotherapeutics: A story of success, limitations, and future pro-spects—Not only for humans. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1266–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Microorganisms | Animals | Common Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Pig | ||
| E. faecalis E. faecium Bacillus cereus B. subtilis B. licheniformis L. reuteri L. acidophilus S. cerevisiae | Colostrum quality improvement, increase in milk quality and quantity Size of litter and vitality improvement weight gain in piglets Reduction of diarrhea Feed efficiency improvement, increase in diet digestibility and meat quality Control of constipation and Decrease in stress | |
| Poultry | ||
| L. animalis L. fermentum L. salivarius L. acidophilus S. faecium L. reuteri E. faecium S. cerevisiae Bacillus sps | Body weight gain improvement Mortality reduction Carcass quality improvement and decreasing contamination Increase in bone quality Increase in egg production Increased immune response Increase enzymatic activity in digestion and absorption of nutrients | |
| Horse | ||
| Lactobacillus pentosus L. rhamnosus L. acidophilus L. plantarum L. casei S. boulardii S. cerevisiae | Improvement in diet digestibility, milk quality and quantity Reduction in diarrhea Avoid hindgut disorders (acidosis, colic) Reduce stress (Transportation, race etc.) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhogoju, S.; Nahashon, S. Recent Advances in Probiotic Application in Animal Health and Nutrition: A Review. Agriculture 2022, 12, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12020304
Bhogoju S, Nahashon S. Recent Advances in Probiotic Application in Animal Health and Nutrition: A Review. Agriculture. 2022; 12(2):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12020304
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhogoju, Sarayu, and Samuel Nahashon. 2022. "Recent Advances in Probiotic Application in Animal Health and Nutrition: A Review" Agriculture 12, no. 2: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12020304
APA StyleBhogoju, S., & Nahashon, S. (2022). Recent Advances in Probiotic Application in Animal Health and Nutrition: A Review. Agriculture, 12(2), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12020304






