SERSNet: Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Based Biomolecule Detection Using Deep Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
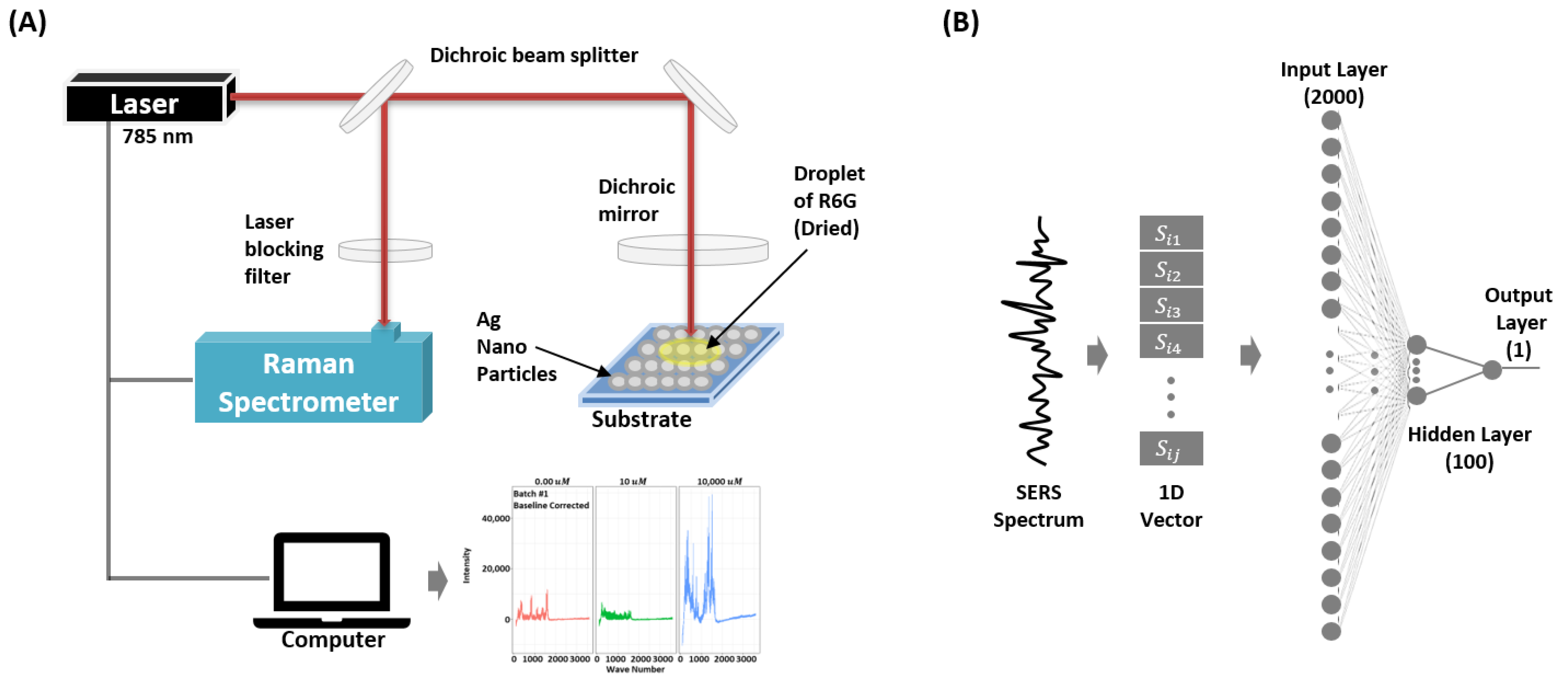
2.1. SERS Measurements
2.2. Preprocessing
2.3. Model Configurations
2.4. Model Training
2.5. Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Exploratory Data Analysis
3.2. Performance Evaluation of SERSNet
3.3. Comparative Analysis
3.3.1. Inter-Batch Prediction Performance
3.3.2. Intra-Batch Prediction Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langer, J.; Jimenez de Aberasturi, D.; Aizpurua, J.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Auguié, B.; Baumberg, J.J.; Bazan, G.C.; Bell, S.E.; Boisen, A.; Brolo, A.G.; et al. Present and future of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Nano 2019, 14, 28–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Xu, Z. Detection of foodborne pathogens by surface enhanced raman spectroscopy. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodelón, G.; Pastoriza-Santos, I. Recent progress in surface-enhanced Raman scattering for the detection of chemical contaminants in water. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaban, M.; Galaly, A. Highly sensitive and selective in-situ SERS detection of Pb 2+, Hg 2+, and Cd 2+ using nanoporous membrane functionalized with CNTs. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, G.; Bian, J.; Tian, X.; Cheng, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, H. Multiplexed SERS barcodes for anti-counterfeiting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 28532–28538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, N.; Janot, J.M.; Lepoitevin, M.; Smietana, M.; Vasseur, J.J.; Torrent, J.; Balme, S. Machine learning to improve the sensing of biomolecules by conical track-etched nanopore. Biosensors 2020, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, M.; Rüger, J.; Kirchberger-Tolstik, T.; Schie, I.W.; Henkel, T.; Weber, K.; Cialla-May, D.; Krafft, C.; Popp, J. A droplet-based microfluidic chip as a platform for leukemia cell lysate identification using surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A.; Ahmed, A.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Furukawa, H.; Arya, S.; Khosla, A. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors: Applications, Challenges, and Future Scope. Biosensors 2021, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Lin, C.; Long, L.; Masaki, T.; Tang, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Luo, X.; et al. Charge-transfer resonance and electromagnetic enhancement synergistically enabling MXenes with excellent SERS sensitivity for SARS-CoV-2 S protein detection. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lin, C.; Long, L.; Hu, J.; He, J.; Zeng, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.Y.; Tanemura, M.; et al. Human ACE2-Functionalized Gold “Virus-Trap” Nanostructures for Accurate Capture of SARS-CoV-2 and Single-Virus SERS Detection. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, A.; Ullah, R.; Khan, S.; Bilal, M.; Khan, A. Raman spectroscopy based analysis of milk using random forest classification. Vib. Spectrosc. 2018, 99, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.J.; Liang, P.; Wu, Y.X.; Dong, Q.M.; Li, J.B.; Bai, Y.; Xu, B.J.; Yu, Z.; Ni, D. Rapid qualitative and quantitative determination of food colorants by both Raman spectra and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS). Food Chem. 2018, 241, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dies, H.; Raveendran, J.; Escobedo, C.; Docoslis, A. Rapid identification and quantification of illicit drugs on nanodendritic surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, K.C.; Lednev, I.K. Differentiation of human blood from animal blood using Raman spectroscopy: A survey of forensically relevant species. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 282, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Yu, J.S.; Choi, S. Based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for diagnosing prenatal diseases in women. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7100–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrift, W.J.; Cabuslay, A.; Laird, A.B.; Ranjbar, S.; Hochbaum, A.I.; Ragan, R. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based odor compass: Locating multiple chemical sources and pathogens. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Nanou, A.; Rikkert, L.; Coumans, F.A.; Otto, C.; Terstappen, L.W.; Offerhaus, H.L. Label-free prostate cancer detection by characterization of extracellular vesicles using raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11290–11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussier, F.; Thibault, V.; Charron, B.; Wallace, G.Q.; Masson, J.F. Deep learning and artificial intelligence methods for Raman and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, J.; Huang, L. Deep learning networks for the recognition and quantitation of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2020, 145, 4827–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.X.; Lee, Y.H.; Koh, C.S.L.; Phan-Quang, G.C.; Han, X.; Phang, I.Y.; Ling, X.Y. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Taster: A Machine-Learning-Driven Multireceptor Platform for Multiplex Profiling of Wine Flavors. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2642–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciloglu, F.U.; Caliskan, A.; Saridag, A.M.; Kilic, I.H.; Tokmakci, M.; Kahraman, M.; Aydin, O. Drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteria detection by combining surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) and deep learning techniques. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jinadasa, M.W.N.; Kahawalage, A.C.; Halstensen, M.; Skeie, N.O.; Jens, K.J. Deep Learning Approach for Raman Spectroscopy. In Recent Developments in Atomic Force Microscopy and Raman Spectroscopy for Materials Characterization; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/online-first/78632 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Wang, C.; Xiao, L.; Dai, C.; Nguyen, A.H.; Littlepage, L.E.; Schultz, Z.D.; Li, J. A Statistical Approach of Background Removal and Spectrum Identification for SERS Data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cialla, D.; Pollok, S.; Steinbrücker, C.; Weber, K.; Popp, J. SERS-based detection of biomolecules. Nanophotonics 2014, 3, 383–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.Y.; Liu, T.Y.; Wang, K.S.; Tsai, K.T.; Chen, Z.X.; Chang, Y.C.; Tseng, Y.Q.; Wang, C.H.; Wang, J.K.; Wang, Y.L. SERS detection of biomolecules by highly sensitive and reproducible Raman-enhancing nanoparticle array. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Su, H.; Liu, Q.; Gu, J.; Deng, T.; Zhang, D. Highly sensitive, reproducible and uniform SERS substrates with a high density of three-dimensionally distributed hotspots: Gyroid-structured Au periodic metallic materials. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, e462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cong, S.; Wang, Z.; Gong, W.; Chen, Z.; Lu, W.; Lombardi, J.R.; Zhao, Z. Electrochromic semiconductors as colorimetric SERS substrates with high reproducibility and renewability. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.H.; Pan, M.J.; Jargalsaikhan, Z.; Ishdorj, T.O.; Tseng, F.G. Development of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS)-Based Surface-Corrugated Nanopillars for Biomolecular Detection of Colorectal Cancer. Biosensors 2020, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, Y.; Lin, B.Y. Silver SERS adenine sensors with a very low detection limit. Biosensors 2020, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikulina, A.S.; Stetsyura, I.Y.; Onses, M.S.; Yilmaz, E.; Skirtach, A.G.; Volodkin, D. Mesoporous One-Component Gold Microshells as 3D SERS Substrates. Biosensors 2021, 11, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.J.; Chao, S.H.; Hsu, S.C. Rapid Detection of Glucose on Nanostructured Gold Film Biosensor by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Biosensors 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.K.; Davis, B.; Knudsen, G.M.; Gudihal, R.; Ben-Amotz, D.; Davisson, V.J. Detection and relative quantification of proteins by surface enhanced Raman using isotopic labels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9624–9625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.C.; Yu, C.C.; Sheu, S.F. Low concentration rhodamine 6G observed by surface-enhanced Raman scattering on optimally electrochemically roughened silver substrates. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 3546–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselkov, K.A.; Vingara, L.K.; Masson, P.; Robinette, S.L.; Want, E.; Li, J.V.; Barton, R.H.; Boursier-Neyret, C.; Walther, B.; Ebbels, T.M.; et al. Optimized preprocessing of ultra-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry urinary metabolic profiles for improved information recovery. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5864–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Rennie, J.D.; Shih, L.; Teevan, J.; Karger, D.R. Tackling the poor assumptions of naive bayes text classifiers. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-03), Washington, DC, USA, 21–24 August 2003; pp. 616–623. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, J.R. Induction of decision trees. Mach. Learn. 1986, 1, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2011, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.E.; Chang, K.W.; Hsieh, C.J.; Wang, X.R.; Lin, C.J. LIBLINEAR: A library for large linear classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 1871–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y. RBF kernel based support vector machine with universal approximation and its application. In International Symposium on Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 512–517. [Google Scholar]



| Problem | Technique | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Cell type classification | SVM | [7] (2018) |
| Origin of milk classification (from 4 species) | RF | [11] (2018) |
| Blood origin classification | PLSDA | [14] (2018) |
| Illicit drug detection | SVM | [13] (2018) |
| Prenatal disease diagnosis | PCA-SVM | [15] (2018) |
| Food colorants detection | PCA | [12] (2018) |
| Prostate cancer detection | PCA | [17] (2018) |
| Odor source direction identification | SVM, CNN | [16] (2019) |
| DNA sensing | SVM | [6] (2020) |
| Drug recognition in urine | FCNN, CNN | [19] (2020) |
| Wine flavor classification | SVM | [20] (2021) |
| Pathogen detection | DNN | [21] (2021) |
| Negative | Positive | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| concentration (μM) | 0 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 10 | 100 | 10,000 |
| batch1 | 500 | 0 | 0 | 500 | 0 | 500 |
| batch2 | 0 | 500 | 500 | 0 | 500 | 0 |
| Model | Train | Test | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1-Score | MCC | BACC | Youden’s Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAW | Batch1 | Batch2 | 0.667 ± 0.000 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.800 ± 0.000 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.500 ± 0.000 | 0.000 ± 0.000 |
| Batch2 | Batch1 | 0.651 ± 0.034 | 0.976 ± 0.050 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.788 ± 0.025 | −0.042 ± 0.088 | 0.488 ± 0.025 | −0.024 ± 0.05 | |
| Average | 0.659 ± 0.025 | 0.988 ± 0.037 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.794 ± 0.019 | −0.021 ± 0.064 | 0.494 ± 0.018 | −0.012 ± 0.037 | ||
| PSN | Batch1 | Batch2 | 0.676 ± 0.092 | 0.517 ± 0.141 | 0.995 ± 0.008 | 0.669 ± 0.129 | 0.510 ± 0.103 | 0.756 ± 0.068 | 0.511 ± 0.135 |
| Batch2 | Batch1 | 0.667 ± 0.000 | 0.500 ± 0.000 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.667 ± 0.000 | 0.500 ± 0.000 | 0.750 ± 0.000 | 0.500 ± 0.000 | |
| Average | 0.671 ± 0.064 | 0.508 ± 0.098 | 0.997 ± 0.006 | 0.668 ± 0.089 | 0.505 ± 0.071 | 0.753 ± 0.047 | 0.506 ± 0.093 | ||
| Proposed (BN) | Batch1 | Batch2 | 0.971 ± 0.002 | 0.999 ± 0.002 | 0.916 ± 0.007 | 0.979 ± 0.002 | 0.936 ± 0.005 | 0.957 ± 0.003 | 0.915 ± 0.007 |
| Batch2 | Batch1 | 0.966 ± 0.006 | 0.979 ± 0.009 | 0.940 ± 0.011 | 0.975 ± 0.004 | 0.924 ± 0.013 | 0.960 ± 0.005 | 0.920 ± 0.011 | |
| Average | 0.969 ± 0.005 | 0.989 ± 0.012 | 0.928 ± 0.015 | 0.977 ± 0.004 | 0.930 ± 0.011 | 0.959 ± 0.005 | 0.917 ± 0.009 | ||
| Models | Train/Test | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch1/Batch2 | Batch2/Batch1 | ||
| LR | 0.960 ± 0.000 | 0.446 ± 0.032 | 0.703 ± 0.257 |
| LinSVM | 0.953 ± 0.001 | 0.399 ± 0.010 | 0.676 ± 0.277 |
| NB | 0.749 ± 0.000 | 0.750 ± 0.000 | 0.750 ± 0.001 |
| DT | 0.737 ± 0.198 | 0.633 ± 0.119 | 0.685 ± 0.052 |
| RF | 0.431 ± 0.032 | 0.530 ± 0.007 | 0.481 ± 0.049 |
| RBFSVM | 0.894 ± 0.003 | 0.548 ± 0.004 | 0.721 ± 0.173 |
| Proposed | 0.957 ± 0.003 | 0.960 ± 0.005 | 0.959 ± 0.002 |
| Model | Train/Test | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch1/Batch1 | Batch2/Batch2 | ||
| LR | 0.999 ± 0.003 | 0.996 ± 0.007 | 0.998 ± 0.006 |
| LinSVM | 0.998 ± 0.004 | 0.997 ± 0.006 | 0.997 ± 0.005 |
| NB | 0.789 ± 0.024 | 0.789 ± 0.030 | 0.789 ± 0.026 |
| DT | 0.979 ± 0.020 | 0.946 ± 0.020 | 0.962 ± 0.026 |
| RF | 0.994 ± 0.005 | 0.980 ± 0.012 | 0.987 ± 0.012 |
| RBFSVM | 0.998 ± 0.003 | 0.974 ± 0.017 | 0.986 ± 0.017 |
| Proposed | 0.998 ± 0.003 | 0.995 ± 0.007 | 0.997 ± 0.006 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Lee, J.; Khan, S.; Wahab, A.; Kim, M. SERSNet: Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Based Biomolecule Detection Using Deep Neural Network. Biosensors 2021, 11, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120490
Park S, Lee J, Khan S, Wahab A, Kim M. SERSNet: Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Based Biomolecule Detection Using Deep Neural Network. Biosensors. 2021; 11(12):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120490
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seongyong, Jaeseok Lee, Shujaat Khan, Abdul Wahab, and Minseok Kim. 2021. "SERSNet: Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Based Biomolecule Detection Using Deep Neural Network" Biosensors 11, no. 12: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120490
APA StylePark, S., Lee, J., Khan, S., Wahab, A., & Kim, M. (2021). SERSNet: Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Based Biomolecule Detection Using Deep Neural Network. Biosensors, 11(12), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120490







